A plant such as salvia (Salvia) is also called sage, and it belongs to the genus of perennial shrubs and herbaceous plants that are part of the labiate or lamb family. In the wild, they can be found in temperate as well as tropical areas in any part of the world with the exception of Australia. The name of such a plant comes from the Latin word "salvus" in translation "to be healthy." The thing is that there are types of salvia, the medicinal properties of which have been known for a very long time. For example, a broth of sage is able to get rid of the flux in the shortest possible time if it is systematically rinsed with it. There are almost 900 species of such a plant, while all of them are photophilous. It is customary to call salvia those species that are used for decorative purposes. And the species used for medicinal purposes and in the form of a spicy herb are called sage. But at the same time, do not forget that salvia is the same sage, only it is grown solely for decorative purposes. They learned about medicinal sage during the Roman Empire, but decorative salvia appeared in European countries only in the 18th century during the era of the horticultural boom. Separately, there is such a plant as salvia divinorum, which is called narcotic sage or "sage of the diviner". Its leaf plates contain salvinorin, which is a psychoactive hallucinogen. However, below we will talk about salvia, which is a beautiful shrub plant.
Features of salvia
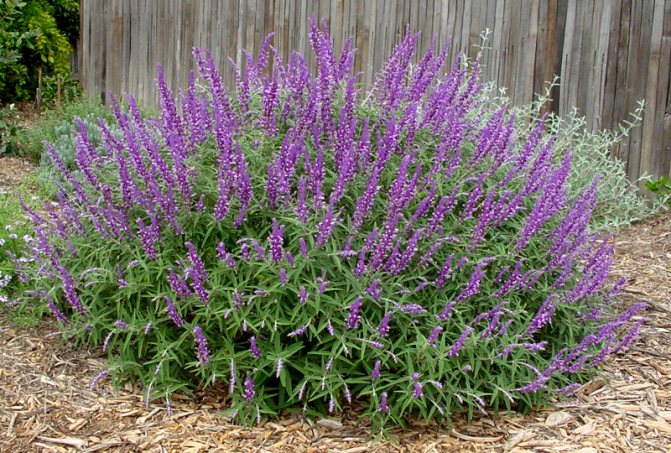

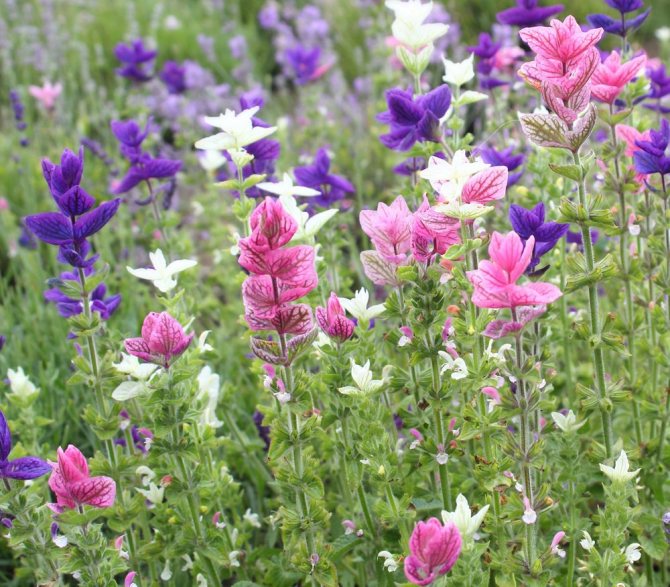
Such a rhizome plant is essentially a perennial. However, in mid-latitudes it is cultivated as one-year or two-year. There are species that can quite successfully overwinter in the open field, but if the winter is too frosty, and the snow cover is scarce, the flower will freeze. Ascending or erect tetrahedral shoots can be up to 1.2 meters high. Most often, the leaf plates are solid, but sometimes they are pinnately dissected. They are petiolate and oppositely located, their front side is dark green in color, and the back side is whitish. At the ends of the shoots are complex whorled inflorescences, spike-shaped or paniculate, and the length of which can reach from 15 to 20 centimeters. They are made up of small flowers. The bracts, which have a bright color (white, purple, pink or lilac), look especially impressive. The fruit of this plant contains 4 nuts. The seeds ripen 4 weeks after the plant blooms. They retain good germination for 5 years.
Varieties
Divinorum - This sage variety is often called the herb of diviners. This perennial does not tolerate frost.
Also, recently, it has been included in the list of prohibited plants, as it has a strong hallucinogenic effect. The cultivation of Salvia Divinorum in the country is prohibited by law.


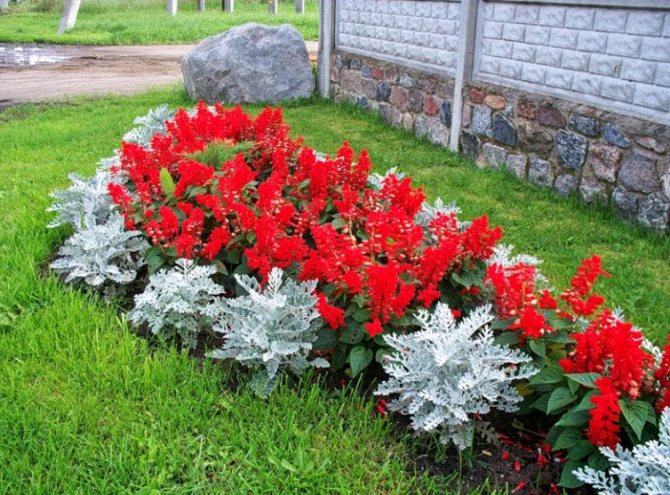
Salvia brilliant (or sparkling) are bright red, fairly common annuals that will decorate any flower bed.
The height of the flowers is up to 50 cm, in warm countries it grows like a perennial, in our country it is grown as an annual plant. There are varieties of Salvia with pink, white, purple flowers.
Growing salvia from seeds


What time are the seeds sown
Salvia, which is an annual or biennial, is grown from seeds. If the plant is perennial, then it can be propagated both by seeds and cuttings or by dividing the rhizome. Seed can be grown both in seedling and non-seedling ways. If you decide to resort to a seedless growing method, then sowing can be done in open ground in the spring or before winter. However, it should be borne in mind that the type of brilliant Salvia, or brilliant Salvia (Salvia splendens) can be grown exclusively by seedlings. It must be remembered that in a specialty store you can buy simple seeds, as well as granules. In addition to seeds, the granules contain substances that make the seedlings more resistant and strong, however, the germination of granules takes longer than a simple seed. It is recommended to sow seeds for seedlings from the second half of February to the first days of March.
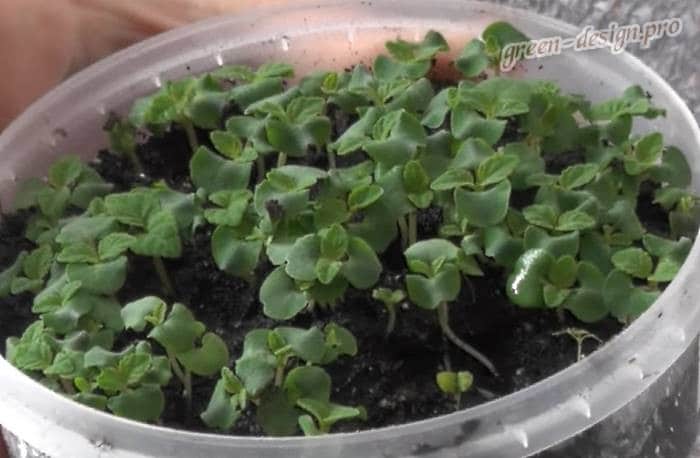
Salvia seedlings
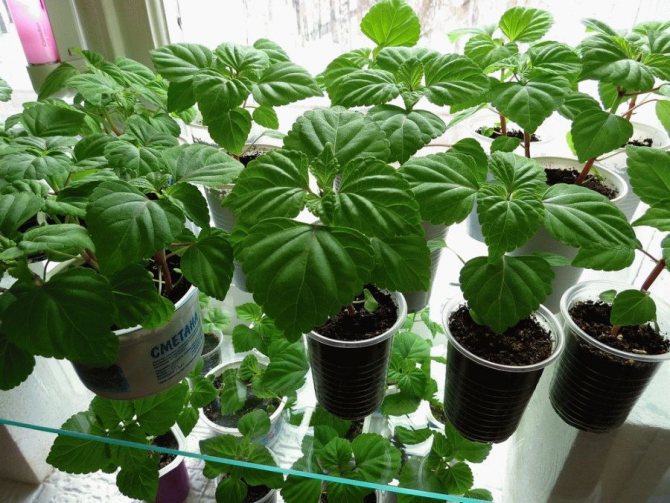


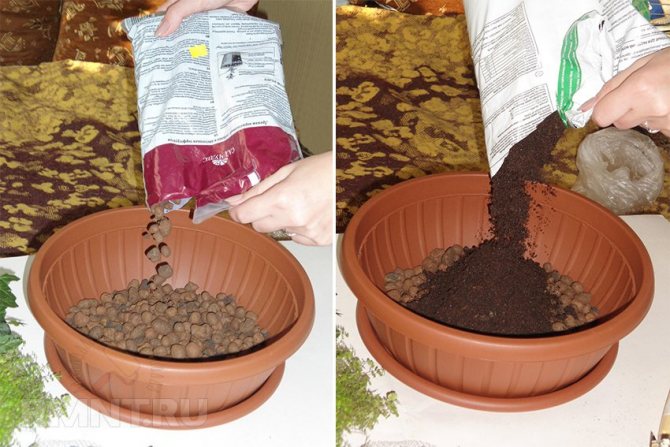
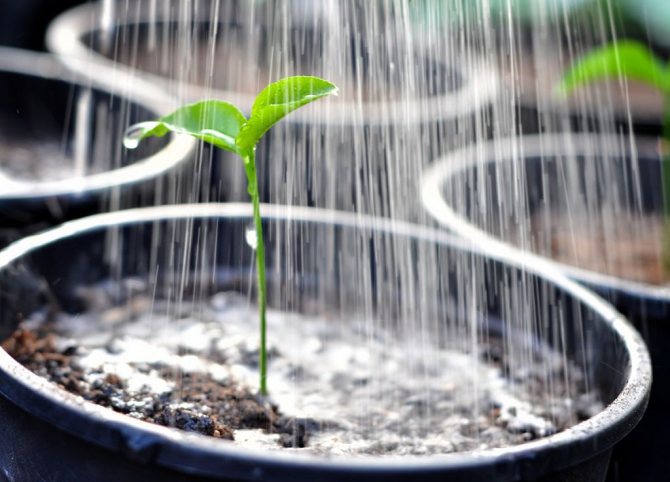
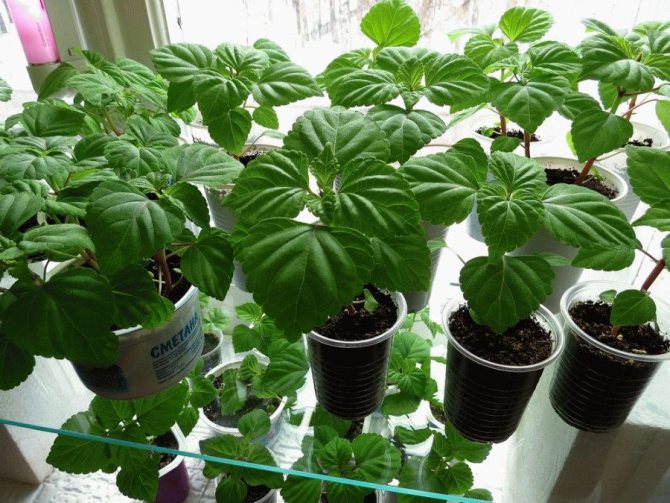
Fill the container with moist, loose soil. It is necessary to distribute seeds or granules on its surface. They can be left like this or sprinkled with a two-millimeter layer of soil. Transfer the container to a warm (approximately 25 degrees) place. Watering can be done through a pallet or using a spray bottle. In order to keep the substrate moist for a long time, cover the container with a paper sheet. The first seedlings can be seen in 2-4 weeks. In order for the planted plants to take root quickly, they need a powerful root system. In this regard, the senses must be dived 2 times. The first pick is made when the plants grow 2 or 3 true leaf plates. They are transplanted into a new box, while the distance between the seedlings should be 5 centimeters, they need to be buried in the ground by a cotyledon leaf. 20 days after the picking, the plant should be transplanted a second time into individual pots, the diameter of which should be about 10-12 centimeters. After the appearance of 3 or 4 real leaves, it is necessary to pinch so that the salvia is more bushy. The hardening of plants can begin with the onset of April. To do this, at night it is necessary to maintain an air temperature of about 10 degrees.
Planting sage
The choice of a place for planting plants should be approached responsibly: some of them love shade and coolness, others require a lot of light. In an improperly designed environment, sage can die.
Depending on the preferred growing conditions, varieties of this herb can be divided into 2 groups:
- Cold-hardy salvias can be planted both in the sun and in partial shade. Some species grow better in the shade.
- Heat-loving flowers should be grown only in sufficiently lighted areas. They do not require frequent watering and do not die in drought.
For planting all types of sage, it is better to choose sandy soils, because there is not much humus in them. Plants of different varieties must be placed on different sides of the garden or suburban area, because they can cross. For this reason, they can multiply using seeds.
Planting salvia in open ground


When do you land in open ground?
For such a plant, a sandy light soil is suitable, which should pass water well, be enriched with humus and lime. Choose a well-lit area as it is a light-loving plant. However, salvia sticky is suitable for growing in a shaded area. Planting in open soil can be done after no frost at night. This time most often falls on the first days of June.
Landing rules
Planting salvia is very easy, especially if the seedlings are strong and seasoned. Planting holes should be prepared at a distance of 25-30 centimeters from each other. In each of them, you need to pour a handful of humus, and then transfer the plants from the pots into them.
Origin and cultivation of Salvia
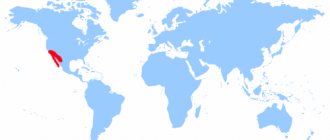
A photo of a plant may surprise you, because it is unfamiliar to ordinary summer residents.However, experts are well aware of its features.
Salvia is close relative of sage, which represent the family of luciferous. If you try to translate the name of the plant, you will understand its purpose - to be healthy. Sage belongs to a group of traditional plants, the beneficial properties of which people learned many centuries ago. Even in the days of Ancient Egypt, it was used to combat various ailments. Salvia is one of the decorative forms that, like sage, originated from common ancestors. However, in European countries it has long been customary to equate salvia and sage.
Starting from the moment when a person first learned about the existence of a plant, they began to actively cultivate it in a variety of species. The largest representation of wild salvia is in America and Europe. The genus Salvia is quite numerous and includes more than 900 different varieties... There are some pretty interesting species on this list, like the hallucinogenic variety. It is a very light-loving plant that grows best on light soils.
Care features
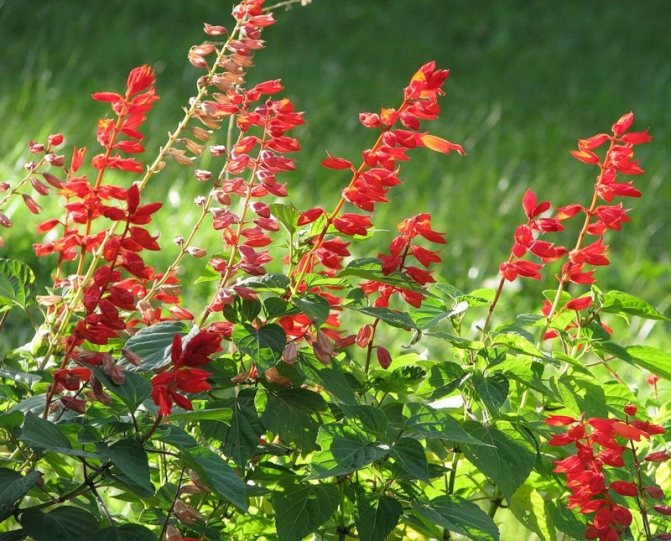


Growing
It is necessary to take care of this flower in the same way as for most of the others. It needs to be weeded, watered, fed in a timely manner, and also loosened the soil surface. Watering should be done only when the soil is completely dry and always in the evening. Remember that a large amount of water should not be poured, because if the liquid stagnates in the soil, the root system of the salvia can easily rot. After the water is absorbed into the soil, its surface must be loosened, at the same time it is necessary to remove the weeds. During the season, this plant must be fed with complex mineral fertilizer at least 2 times. It is necessary to feed the plants with a weak nutrient solution while they are still in the house in the boxes. The second time this procedure is carried out during budding.
It is somewhat more difficult to care for a perennial salvia than for a one or biennial, which are sown with seeds before winter. The point is that these plants need formative pruning. It will protect the shoots from stretching and exposing, and the plant will become more bushy, as young stems will actively begin to grow. At the end of flowering, do not forget to remove all wilted flowers from the salvia. Before wintering or at the beginning of the next period of intensive growth, the bush will need to be trimmed. To do this, you need to remove the old stems, which are lignified, so that only a few centimeters of them with buds, as well as young greens, remain.
Diseases and pests
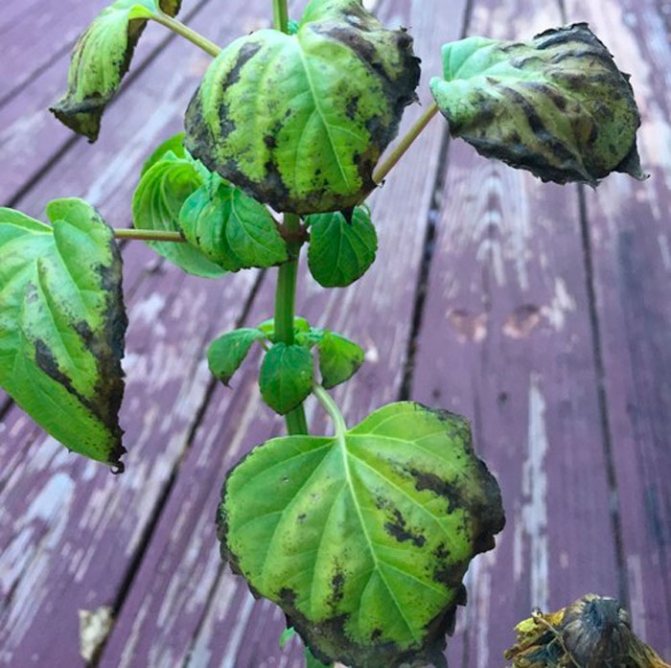


This plant has resistance to almost all types of diseases. However, such harmful insects as thrips, ticks, whiteflies, aphids, as well as snails and slugs that eat salvia leaves can settle on it.
You can get rid of slugs and snails by picking them up with your hands. To do this, you can spread pieces of slate or rags between the plants, and then systematically collect the pests hiding under cover in the daytime. You can also make traps. To do this, on the site you need to put several saucers filled with fruit juice or beer. Slugs, like snails, love these drinks and slide down, drawn by their aroma, you just have to collect them. Make special umbrellas that can protect the saucers from rain and debris.
To kill other harmful insects, you will need an appropriate insecticide.
Salvia after flowering


The beginning of flowering of such a plant occurs in June, and when it ends, it directly depends on the species (sometimes only with the onset of the first frost). There are species that bloom twice a year.For example, when the flowering of forest salvia is over, it is recommended to cut off its shoots completely, in which case at the end of the summer period the bush will bloom again, especially if fertilizers are applied to the soil. After such a perennial plant has finished blooming completely, it must be cut off, and then sprinkled with a layer of mulch (garden compost) on the surface of the soil, pay special attention to the growth points. In this case, the salvia will be prepared even for severe winter frosts. For greater reliability, it is still recommended to cover young bushes with dried leaves or spruce branches.
Planting salvia on a flower bed
Salvia seedlings are planted on flower beds quite late - not earlier than June 10. The flower spends almost half of the growing season in a pot.
Culture prefers sunny, unshaded places. There should also be no stagnation of water. A place for salvia is usually not planned in advance, so the seedlings are planted in the place of bulbs that are dug out at this time (tulips, daffodils, etc.) or that have already lost their charm, for example, pansies.
Salvia is not particularly demanding on the composition of the soil, but it is still recommended to loosen heavy soils with sand.
Advice. The area where salvia will be planted is not recommended to be heavily fertilized with humus. In this case, the root system will develop well, and there will be few flowers.
Since the plants are already planted quite large, holes of a suitable size should be prepared for planting. The required interval is 20-30 cm. The dug holes are well filled with water, salvia is transferred into the resulting mud along with a lump of soil from the pot. With this method of planting, the plant is not injured, it grows quickly and begins to bloom.
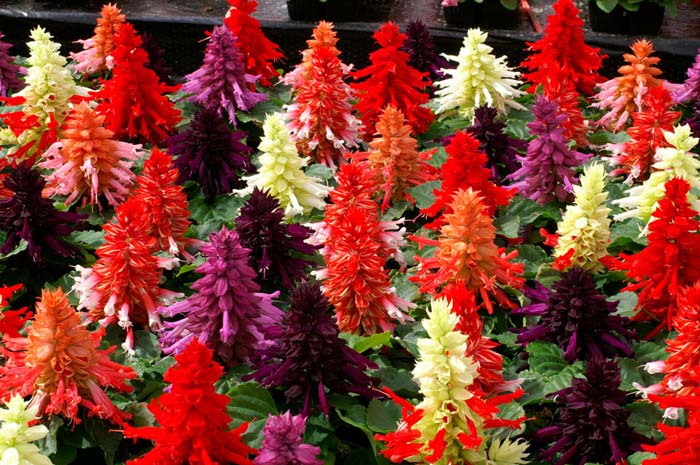


Salvia flowers of different shades
Caring for sparkling salvia is quite standard:
- watering as needed;
- regular loosening of the soil, removal of weeds;
- feeding several times during the season with complex mineral fertilizer.
Salvia practically does not bloom in shade. Therefore, it should be planted away from tall plants.
Advice. A flower bed will look very beautiful, consisting only of salvias of brilliant one or more flowers. Also, this plant looks great in the background in border plantings next to undersized marigolds and annual phlox.
Main types and varieties with photos and names
All types of salvia are divided into 3 groups according to biological characteristics, as well as agrotechnical characteristics.
First group
The first group includes species belonging to the subtropics of America. In mid-latitudes, they are grown as annuals. They need a constantly moist soil and warmth. Even a slight frost can kill the plant.
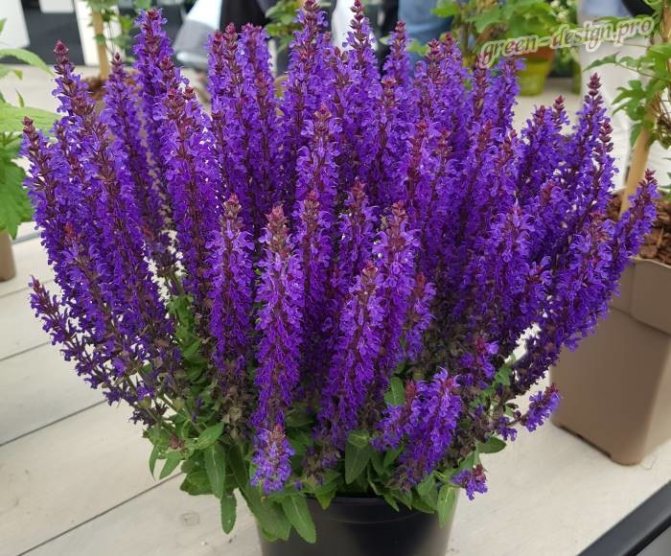
Salvia sparkling, or brilliant (Salvia splendens)
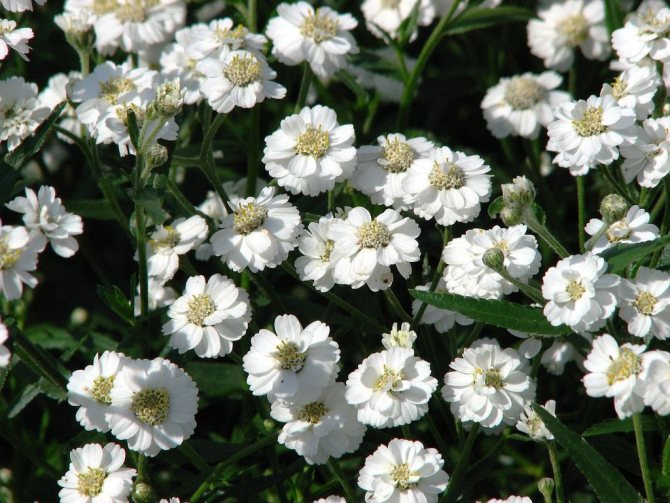


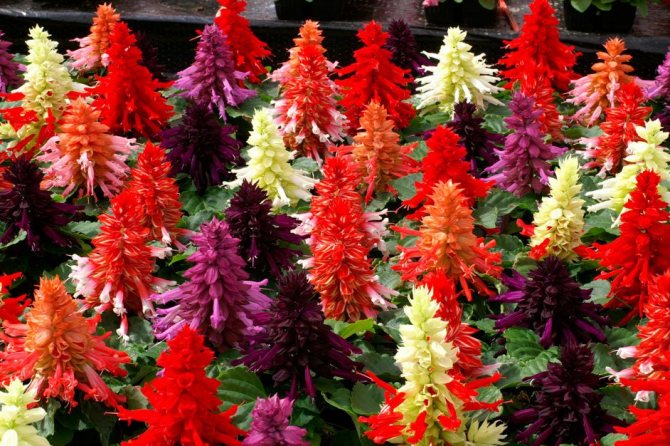
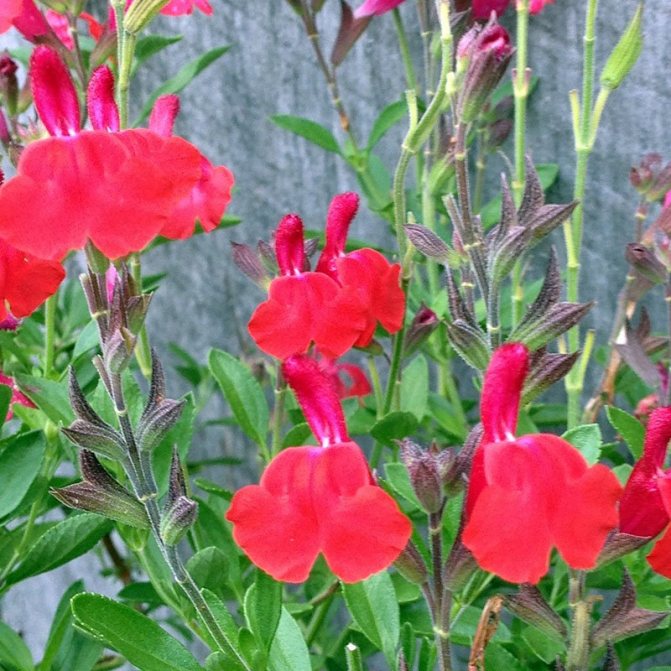
The height of a compact bush can vary from 20 to 80 centimeters. It has very dense foliage. Opposite petioled whole leaf plates are ovoid. Their front side is colored dark green, and the back side is pale green. Large flowers have an irregular shape and a double perianth. They are whorly collected from 2 to 6 flowers in inflorescences in the form of a brush, 14 to 25 centimeters long. As a rule, the corolla and calyx are colored deep red, but purple, white and pink can be found. Flowering is observed from the beginning of the summer period until the first frost.
Salvia sparkling white is a species of this plant. Its difference from rich red is that its inflorescences are more liquid and the calyx looks creamy against the background of a snow-white bracts.
And in salvia, pink inflorescences are not so long in comparison with red ones. The calyx and corolla have the same pink color, but the corolla has a velvety surface.
Sparkling Salvia Violet is a very showy plant. The fact is that the rich purple color is greatly enhanced by dense pubescence.
The most popular varieties: Red Arrows, Fiery Star, Sahara, Salvator.
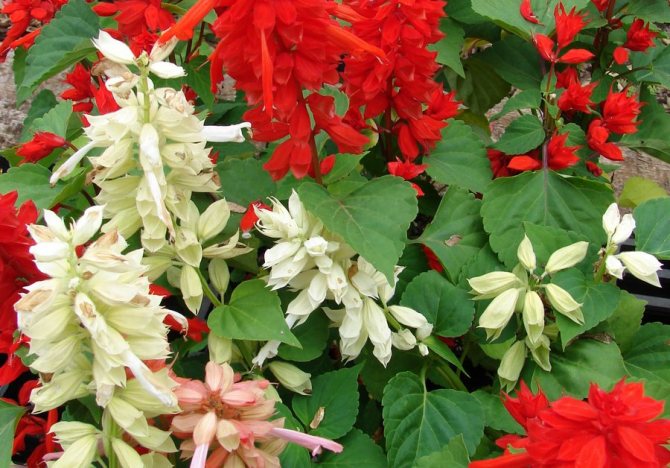
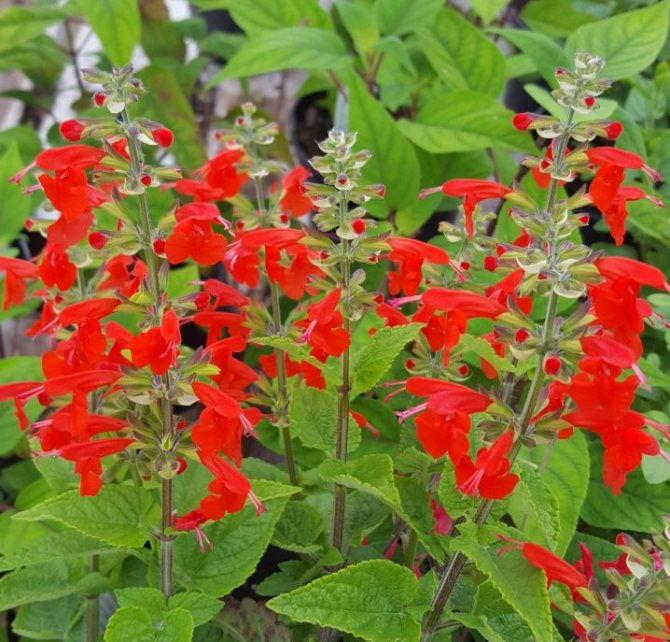
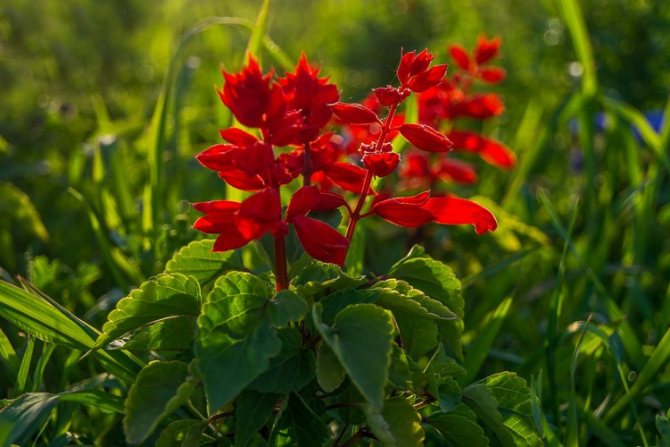
Salvia bright red (Salvia coccinea)
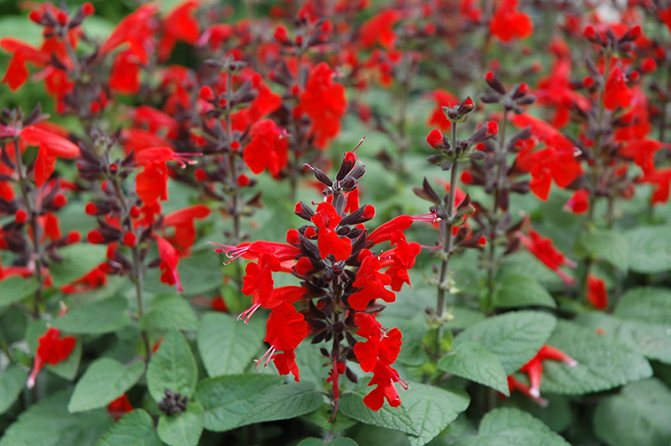


A branching bush with straight shoots in height can reach from 50 to 70 centimeters. There is dense pubescence on the surface. Egg-shaped petiolate leaf plates are finely serrated along the edge. Their front side is naked, and on the surface of the seamy there is pubescence. The length of the loose inflorescence varies from 15 to 30 centimeters. On them are whorled flowers with a long tube and a scarlet-red corolla. Flowering begins in July and ends with the onset of the first frost. Popular varieties: "Lady in Red" - the bush reaches a height of 40 centimeters, the color of the flowers is deep red; "Sherry Blossom" - a bush of this early variety has a height of about 40 centimeters, and the flowers are pink.
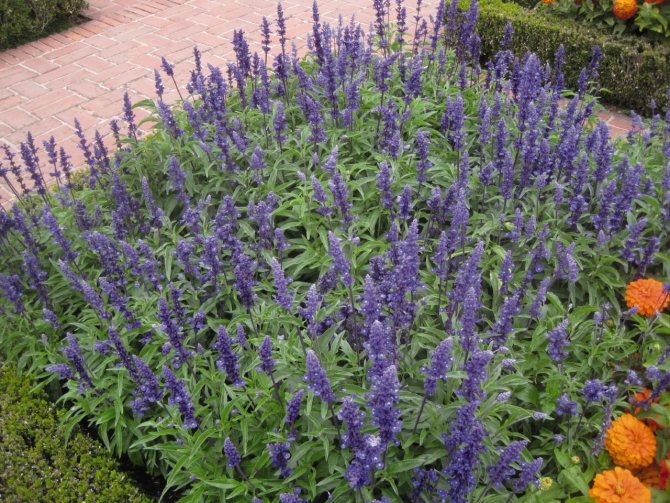
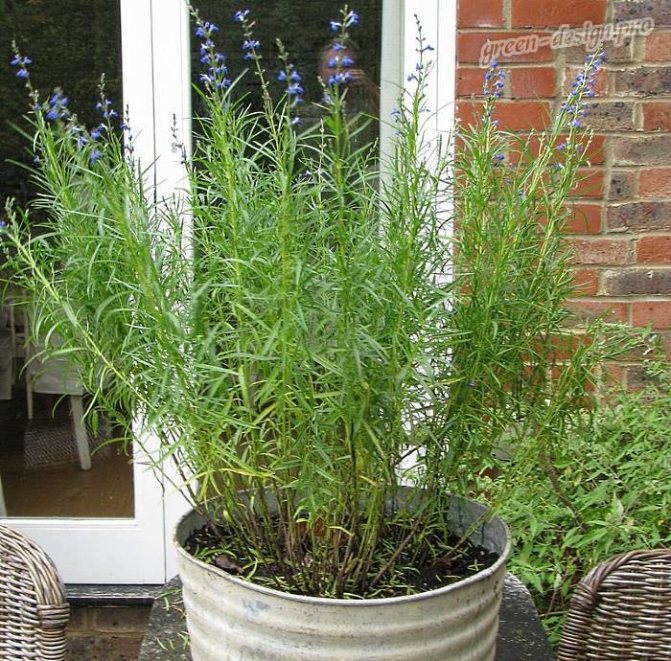
Mealy salvia (Salvia farinacea)
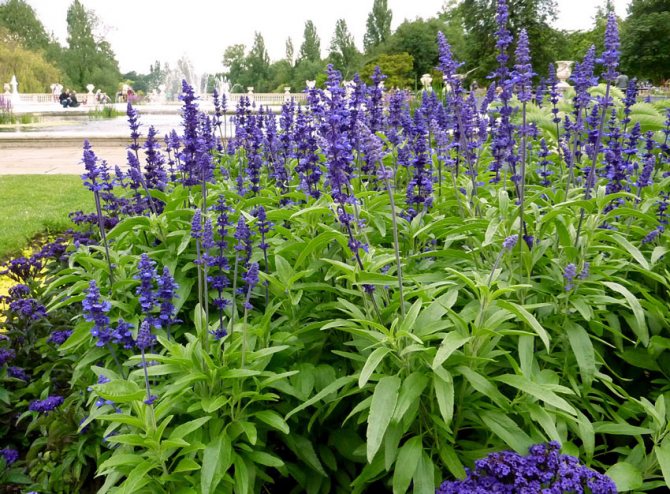


Such an unpretentious plant is long-flowering. The bush has a pyramidal appearance and reaches a height of 60 to 90 centimeters. Petiolate, whole-edged ovate-oblong leaf plates have pubescent veins. Quite long inflorescences (15–20 centimeters) are located on rather high peduncles. They include from 5 to 28 flowers of two centimeters in length. Most often the corolla is dark blue, but white is also found. Flowering begins in the second half of August and ends in late autumn. Popular varieties: "Anshuld" - flowers have a whitish-silver color; "Strata" - there are blue flowers on a compact bush; "Victoria" - the variety blooms very profusely, the flowers are dark blue.
Second group
The second group includes Mediterranean species. They are not afraid of drought and they are more frost-resistant. Loose soil is ideal for them, they need mineral fertilizers.
Salvia green, or variegated (Salvia viridis)
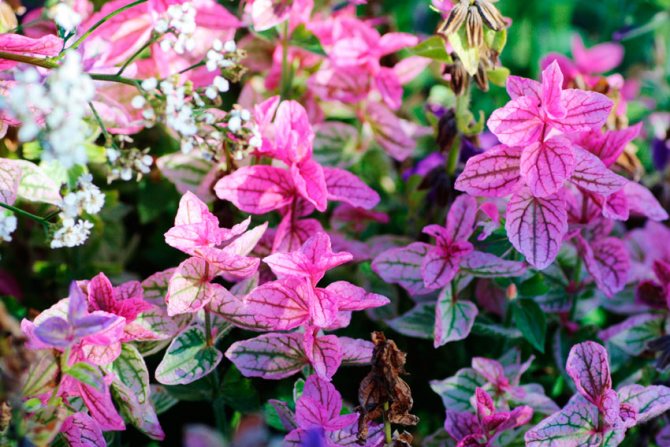


Among the representatives of this species, only the Horminum variety is decorative. Her bracts are painted in a rich color. The bush of this annual reaches a height of 40-60 centimeters. There are a large number of straight branching shoots, on the surface of which there is a glandular fluff. There is pubescence on the surface of the elliptical-oblong petiole leaf plates. The length of simple inflorescences varies from 18 to 30 centimeters. They include false whorls with 4–6 flowers, the corolla of which is pink. But the bracts, which have a rich purple or pink color, are striking. Popular varieties: "White Swan" - white flowers, and bracts - purple or pink; "Oxford Blue" - violet-blue bracts; "Pink Sandy" - pink bracts.
Salvia verticillata (Salvia verticillata)
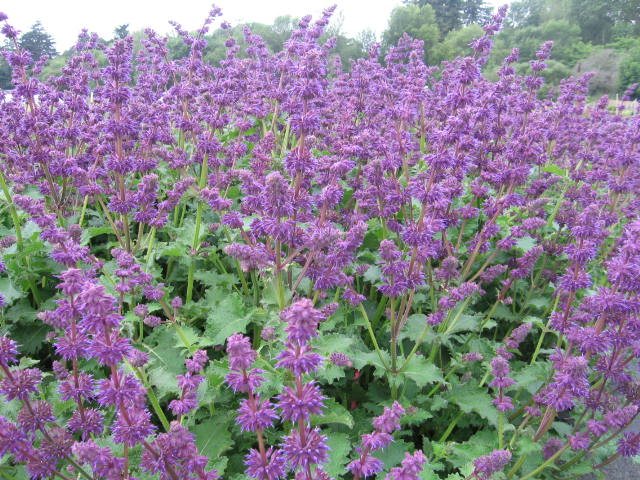


The bush has ascending or straight shoots with dense pubescence and a height of 35 to 40 centimeters. Unusually shaped leaf plates are long-petiolate and pubescent. Flowers are collected in dense whorls of 5-30 pieces and have a corolla of blue-lilac color. Variety "Purple Rain" is distinguished by flowers with purple cups and a corolla of dark purple color.
Dandelion-leaved Salvia (Salvia taraxacifolia)
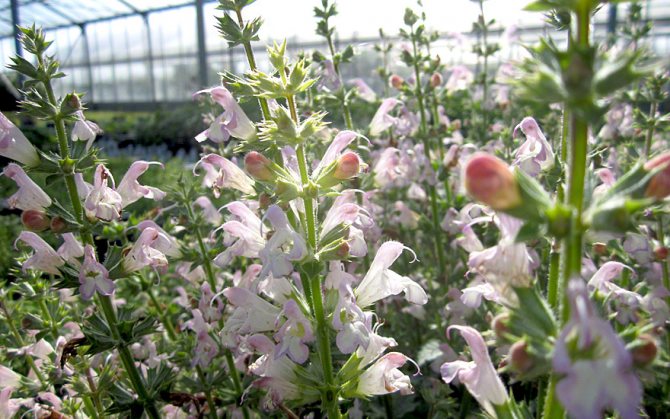


Such a herbaceous plant has a root leaf rosette. Slightly branching straight shoots. Any part of this plant has a pleasant smell. Cirro-dissected leaf blades have an irregularly serrated edge. Their front side is naked, and the seamy side is pubescent. The length of simple inflorescences can reach 28 centimeters. They include whorls with several flowers, the corolla of which is colored light pink, and the throat is light green with purple dots.
Salvia jurisicii
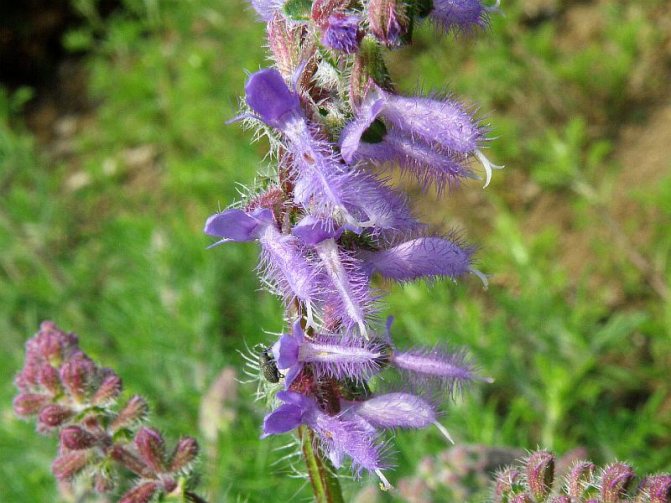


It also belongs to this group, but gardeners rarely grow it.
Third group
The composition includes frost-resistant species. These are the species that grow in the temperate climate of the Old World, and also include the Ethiopian Salvia. These plants are distinguished by the fact that they bloom very luxuriantly from the second year of life. They are not capricious, shade-tolerant and frost-resistant. They need to be sheltered only when there is a meager snow cover in winter.
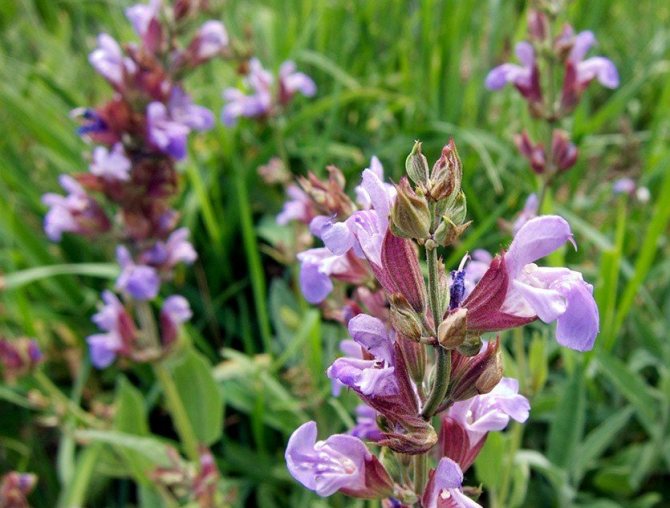
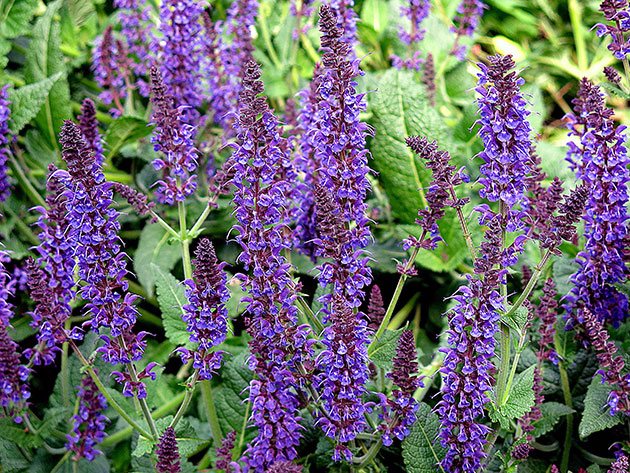
Salvia oak, or forest (Salvia nemorosa, Salvia sylvestris)
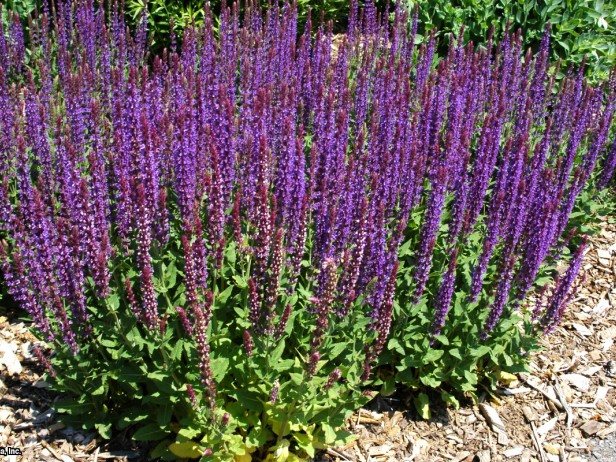


The height of the bushes reaches 60 centimeters, there is pubescence on the surface of the branchy shoots. Sessile leaf plates located in the upper part are smaller than the lower petiolar ones. The inflorescences have several pairs of lateral branches. They include false whorls, and each has 2 to 6 small flowers. Corolla color is violet-blue. There are quite large purple bracts that are conspicuous. Flowering begins in the last days of June and lasts until the beginning of the autumn period. Popular varieties: dark lavender "Plumosa", blue-violet "Mainht", violet-pink "Amethyst".
Salvia glutinosa
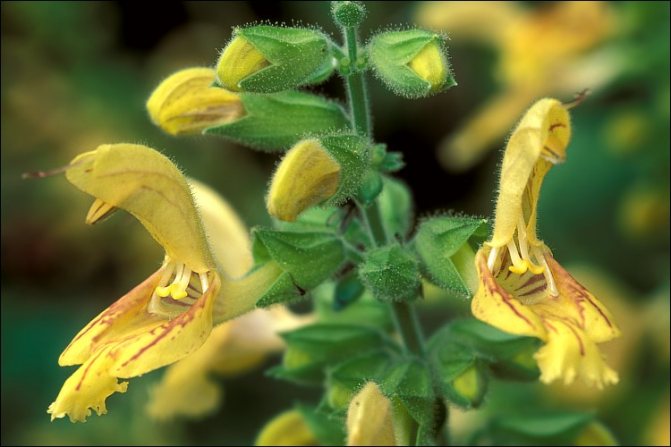


Feels good in mid-latitudes. The height of a large bush can reach 0.9 meters. There are many straight pubescent-glandular shoots. Long-petiolate large serrated leaf plates have a triangular-ovoid shape and are colored greenish-yellow. Loose inflorescences consist of flowers in whorls. Corolla is pale yellow. Flowering lasts from late summer to late autumn.
Planting and caring for salvia
In recent years in cities Salvia is often used for street decoration, which can be explained by a number of reasons:
- salvia is one of those rare plants that are distinguished by continuous flowering, decorating the earth until the first frost;
- this attractive plant has a tendency to grow, therefore, the composition created on its basis will not lose its original form;
- salvia feels good even in conditions of air pollution, which does not prevent it from maintaining its decorative appeal;
- compositions based on salvia look especially impressive if varieties of different shades are used.
For a long time around the world, gardeners have been practicing growing salvia at home. In this perennial plant, they are attracted not only by the bright scarlet color of the panicles, but also by the rich color palette. If you wish, you can arrange a tiered landingif you use species of salvia of a certain height. However, in order for this plant to retain its beautiful flowers as long as possible, it is necessary to approach the process of growing seedlings correctly.
Diseases and pests
Snails and slugs can damage leaves and stems, affecting growth and appearance. These creatures do not carry great danger. Getting rid of parasites is very simple: they need to be detected and removed manually.
The aphid, spoiling the shape and appearance of the flower, sucks out elements rich in carbohydrates and amino acids from the leaves and stems. Fall (thick, sweet mucus), formed as a result of the vital activity of this insect, attracts other pests to plant. In addition, aphids, being one of the most parasitic creatures, carry viral infections, which are called galls. These bacteria weaken the plant and lead to its death.
Salvia suffer from downy mildew, which is provoked by the activity of oomycete fungi. White bloom forms on the bottom of the leaves, and golden and brown spots appear on the upper side. The organs of the plant begin to lose moisture and finally dry out. To treat this pathology that occurs on excessively moist soils, copper-based solutions are used.
Thrips are tiny pests that prefer to find food in ornamental plants.These insects, by their activity, provoke shedding of pollen, which reduces the flowering time of the salvia. In order to get rid of the pest, a ten-day course of spraying with special insecticides is required.
The roots of Salvia (sparkling, red, mealy) often undergo rotting and pathology called "black leg". The causative agents of these diseases are fungi growing on the ground. The flower can die within several days, if the spread of infection is not prevented, since the development of organs stops, and the root acquires a brown tint and brown plaque. The whole problem lies in the infected soil, so it must be completely replaced and fertilized with trace elements and active biological products. A solution of potassium permanganate can serve as an alternative to chemicals.