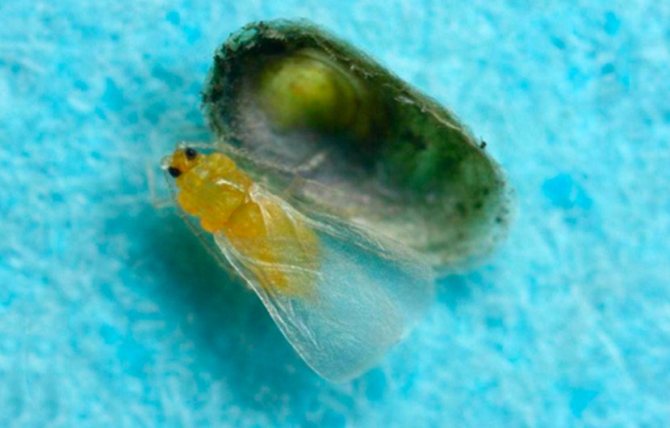
False shield (coccidus) is a harmful insect, a close relative of the shield insect. Belongs to the Hemiptera family.
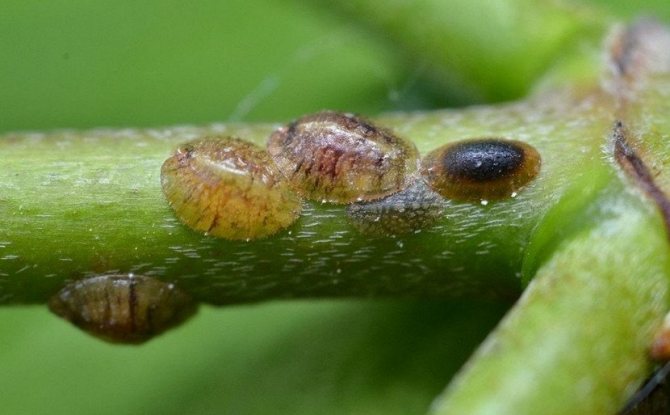
It is distinguished from scale insects by the absence of a wax shield, but it is sufficiently protected by a shield, which is a secretory zone and larval skins. The larvae and eggs are covered by the drying skin of a dying female.
Males live very little, but they are able to quickly move and fly, moving from place to place, in contrast to females, which are practically motionless.
Plants are harmed by larvae and females, which stick to a leaf or stem and feed on sap, inhibiting growth and development.
False shields or coccids (Coccidae)
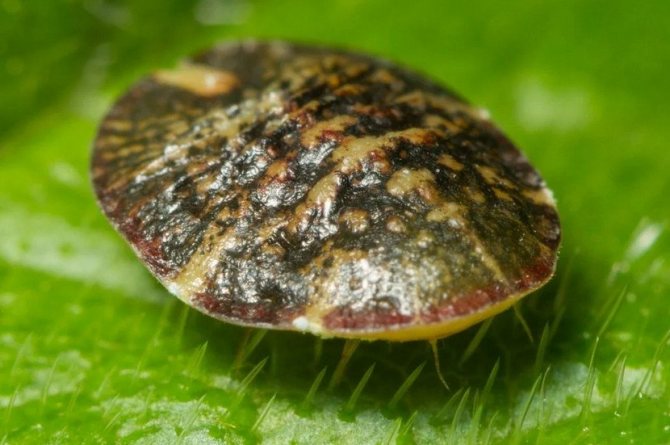
This is a harmful insect that is very difficult to kill. It got its name from the wax shell that covers the top of the body. Belongs to the order of hemiptera, like the family of scale insects. They have common features: they belong to the same class - parasites, have a similar appearance. They feed on plant sap with nutrients. The shape of the body is rounded. Females lack legs and wings, so they lead an immobile lifestyle. Small insects in size. Scabbards are larger than coccids.
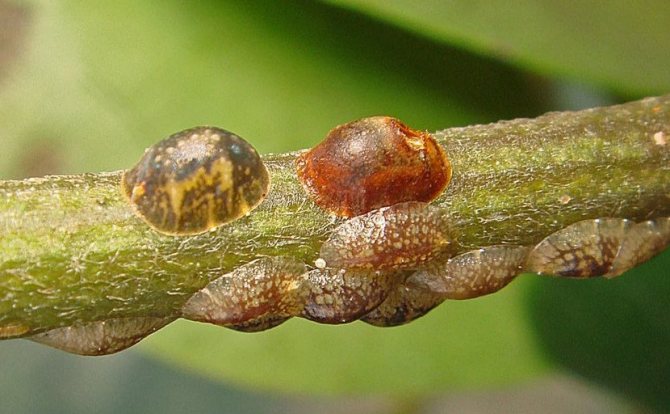
The differences between the families are in the shield. In a false shield or cushion, it is a skin that dies off after molting. It is more convex than that of a related insect. Rising above the body, it keeps it warm and the eggs laid. It can be detached if you pry it with something. In the case of the shield, this is impossible, because it is firmly connected to the body. A sticky liquid is isolated - a pad, on which a fungus settles, which worsens the condition of the plant.
These species are examples of sexual dimorphism. Individuals have quite large differences. Males are smaller than females, more mobile, equipped with wings. Their life cycle is short - only a few days. They are of no interest to study. Their presence is not required during reproduction. The purpose of existence is to travel long distances.
In poor conditions, there will be more males, this will help to find a new breeding place.
Fusarium
The disease is treatable if detected early.
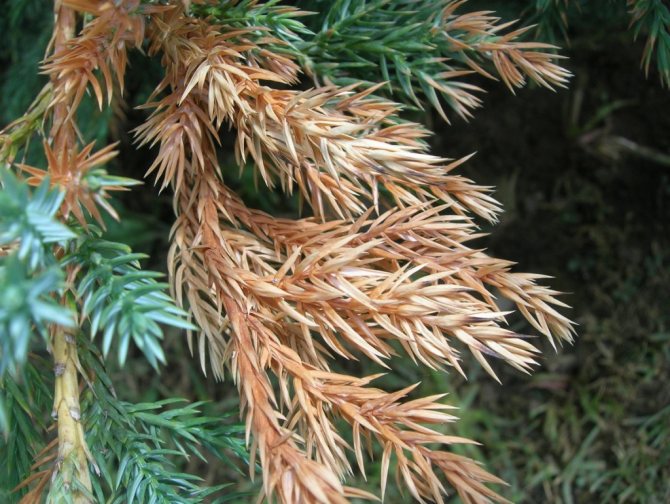
Tracheomycotic wilting also begins with the defeat of the roots, which gradually rot and acquire a brown color.
The mycelium grows at this time, the number of spores increases, preventing the penetration of nutrients to the ground parts of the plant.
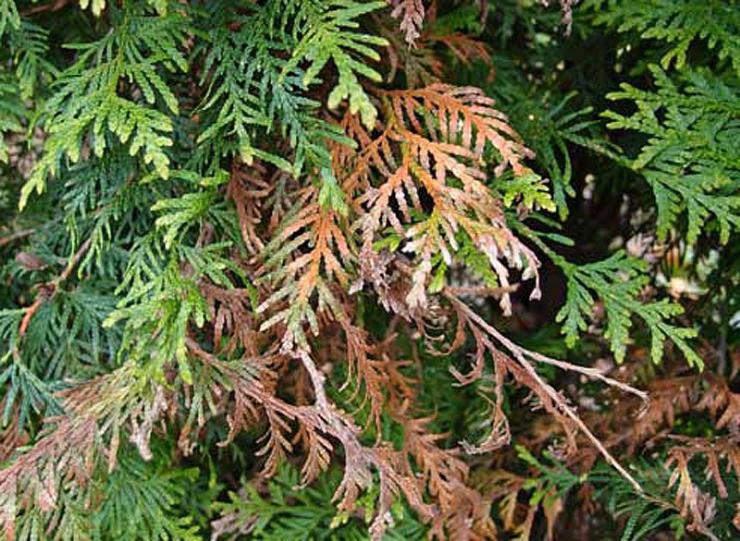
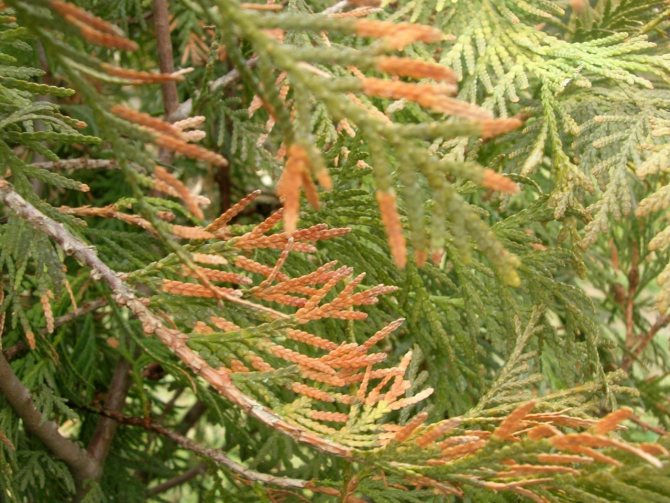
Shoots suspend their development, begin to dry out from below. The needles lose their natural green color, first turn yellow, then red, and subsequently die off.
The development of fusarium is facilitated by the lack of natural light, waterlogging of the soil due to excessive watering, planting in heavy clay areas or on slopes or in lowlands.
For prevention, the soil should be fed with mixtures that contain copper and iron, and all parts of the plant (including underground) should be watered with fungicide preparations (HOM, 0.2% Fundazol solution).
If thuja has a fungal disease, treatment is considered useless: the plant must be dug up, burned, and the earth must be disinfected.
Types of false shields
There are several of the most common types.
| View | Description | Affected plants |
| Soft | Length 4-5 mm.Body shape - egg, sometimes asymmetrical. Color: yellowish green to brown. Has a pattern: longitudinal and 2 transverse stripes. Fertility: up to 600 eggs. The larvae hibernate in the open field. Per year: 6-7 generations in the greenhouse, 3-4 in the garden. They spoil the appearance of the plant, cause curvature of the trunk, drying of the leaves. | Indoor: orchids, citrus and palm, calla, ficus. |
| Acacia | The female is painted in different colors depending on her age: young - light brown with an oval body; adult - red-brown round-oval. 1 fold is located along and 2 across. Male: long slender body, 3 pairs of eyes, mustache and legs are yellow, everything else is reddish brown. The larvae differ in shape: oval - female, oblong - male. Lay 500-1500 eggs. The female dies after laying eggs. 1 generation grows up. | Fruit: peach, plum, acacia, sweet cherry, apple tree. Berries: currants, gooseberries. Forest and decorative deciduous species. Grapes. |
| Spruce | Males are rare. Females with a round brown or chestnut carapace. Fertility: 3000 eggs. Allocate a mass that attracts ants, bees and wasps. | Coniferous forests: natural and cultivated. Especially dangerous for young plants - up to 10 years. |
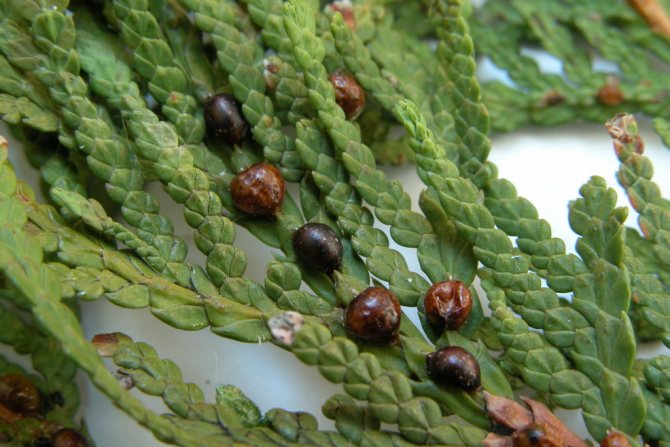
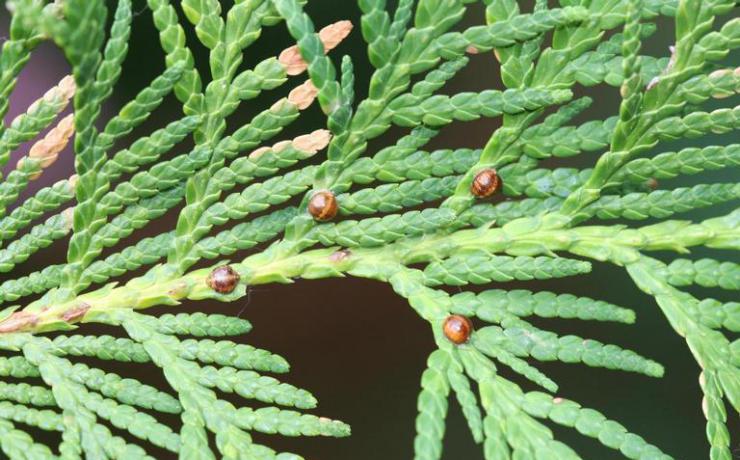
| Tuevaya | Spherical shape. Yellow-brown color. Relatively large insect (up to 3 mm). The larvae hibernate under the bark. | Thuja, spruce. |
| Hawthorn or bicornate | Body shape: hemisphere or wide oval. Has 4 pcs. shiny tubercles, 2 pcs. of them are more visible. On the side there are 7-8 ribs located across. Color: light gray to brown. Fertility: up to 1100 eggs. They excrete sticky excrement on which sooty mushrooms grow. The male is inconspicuous. | Plants of the Rosaceae family: apple, medlar, quince, hazel, apricot, blackthorn, cherry plum. |
| Hemispherical or plum | The female has a dark brown scutellum. The male is dull red. Eggs are yellowish pink. Lay up to 1200 eggs. The second generation of larvae appears at the end of summer and hibernates in the soil. | Flower and decorative crops. |
| Japanese wax | The surface of the body is covered with a thick layer of wax. Has 8 records. Color: cherry red. Fertility: up to 2500 eggs. | Citrus and other subtropical crops. |
Phytophthora
Photo:
It is considered the most famous and dangerous fungal disease of thuja. It is a root disease that destroys the top layer.
This is reflected in the appearance of the thuja as follows: it withers, turns gray, the lower part of the trunk becomes soft to the touch.
The tissue under the bark changes color to brown, and plaque appears below. The root becomes brittle, with a rotten smell.
Basically, late blight affects thuja growing on soil that is poorly drained, the water is often stagnant here.
Treatment
For the prevention of phytophthora, it is often necessary to water it with fungicides.
If the disease nevertheless reached it, and the roots fester, it is best to destroy the tree, and replace the earth, since this fungus can live for a long time.
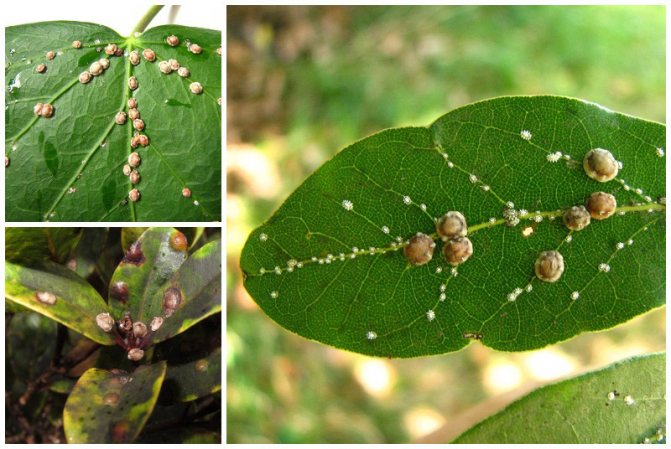
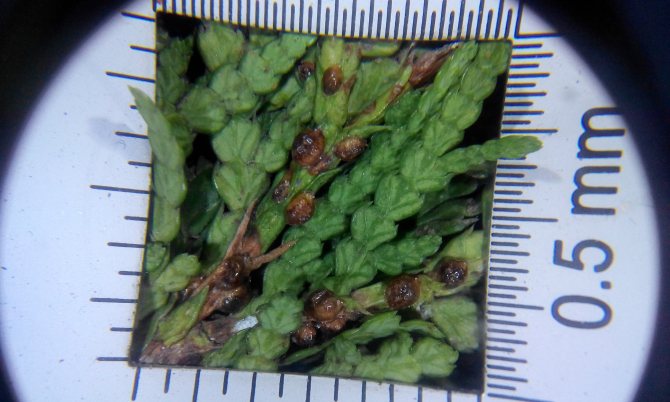
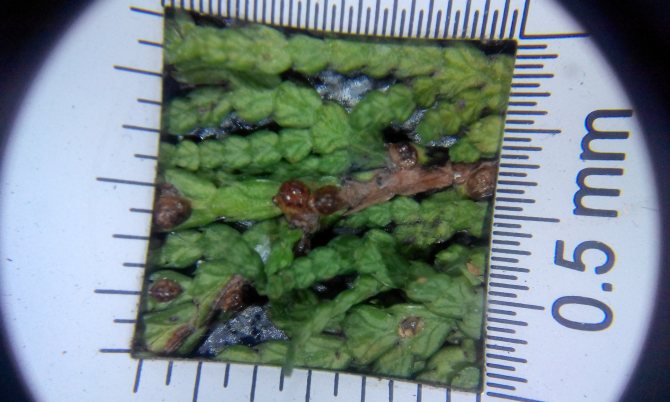
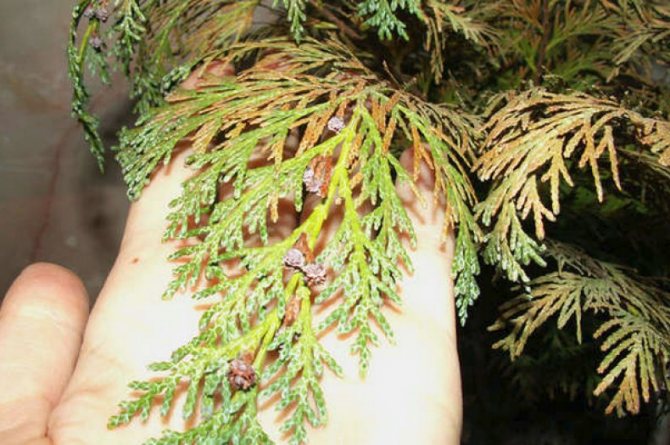
External signs of plant damage by false shields
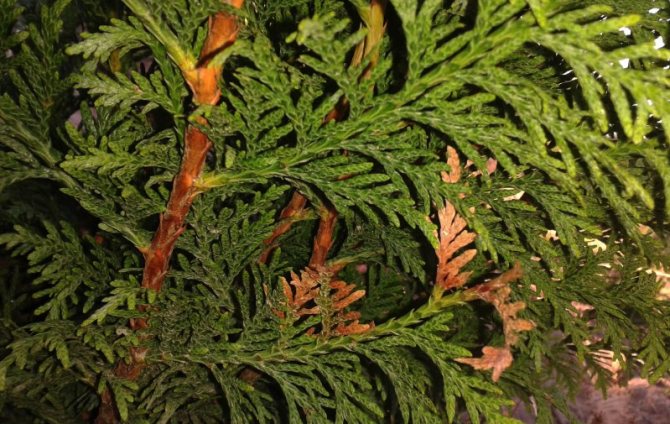
The coccid feeds on juices with nutrients, which leads to the depletion of the plant. Therefore, growth slows down, buds are formed extremely rarely or are completely absent. A sticky bloom is clearly visible on the leaves, which then turns black. The reason for the color change is the growth of a sooty fungus, for the development of which favorable conditions have been created.

In a favorable climate, the false shield multiplies constantly.
How to recognize the presence of scale insects
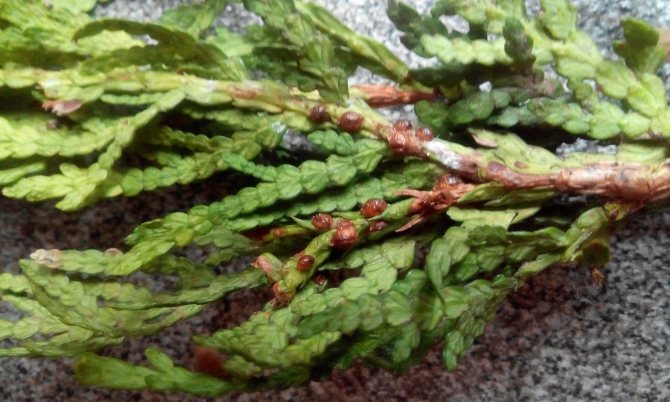
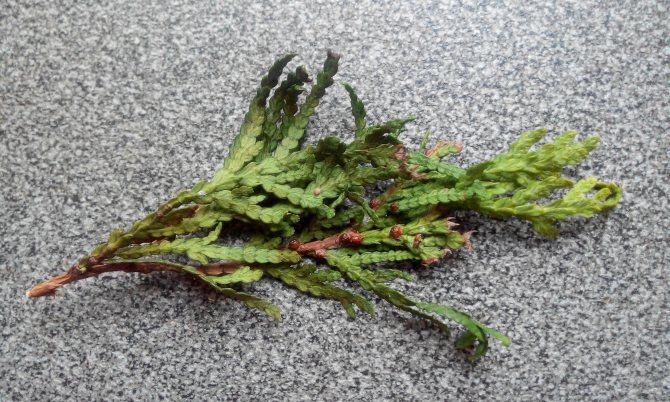
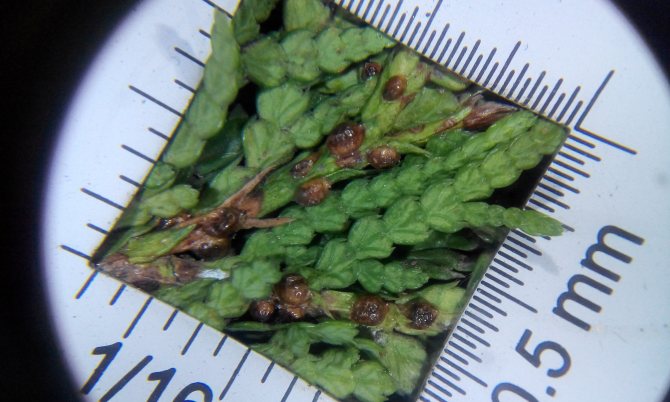
Signs of the presence of coccidus on thuja are:
- brown needles;
- its premature fall.
Find out why the thuja turns black.
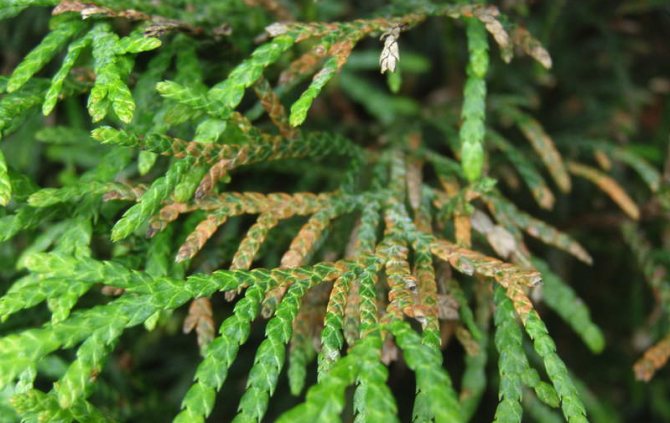
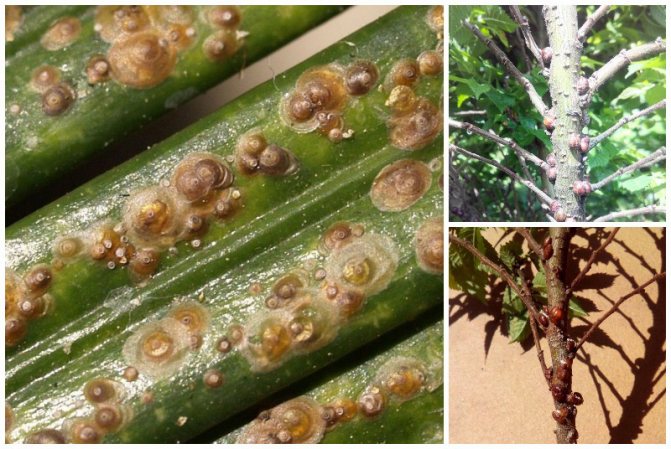
They recognize the presence of a false shield on the thuja by a brown sticky coating on the needles and branches. It arises as a result of females' secretions, which have the consistency of a sweet mass.A saprophytic fungus, Apiosporium piniphilum, develops in the plaque, and stains the sticky substance black.


Females and coccid larvae suck juices from needles, branches, young growths, bark, immature green cones. Yellow-brown spots appear on the damaged areas, then these parts of the plant die off. Damaged shoots are clearly visible, they are characterized by insignificant growth. As a result of the vital activity of a large number of coccids, the bark begins to die off and the growth of thuja slows down.
The formation of brown, rounded scales, which are difficult to separate, indicates the presence of adult scale insects. The appearance of coccidic plaques is difficult to notice right away, and when there are already a lot of them, it becomes more difficult to fight. Large clusters of insects can be confused with growths on the trunk. Thuja seedlings are the most vulnerable, so they often die.


Anti-false shield measures
Fighting this parasite is difficult, but possible. There are several ways to do this.
Mechanical
It consists in removing pests by a natural method. They can be brushed off with a soft toothbrush or cotton swab, damp sponge or rag. For delicate leaves, a more gentle option is chosen so as not to damage them. For indoor flowers, a fairly effective measure. Scrape off the tree with a knife. They are trying to wash off large plants with a jet of water under high pressure.
Folk remedies
An effective method of treatment with a small area of infection and a low number of pests.
| Ingredients | Preparation of the solution | Application |
| Denatured alcohol, soap. | 10 ml and 15 g per 1 liter of water. | Check on 1 sheet. And then use it on the whole plant. Thin leaves can burn. |
| Garlic (onion). | 5 medium chopped cloves (1 medium onion) per 250 ml. Insist in the dark for several hours. | Sprayed. |
| Pepper. | 50 g per 0.5 l. Boiled, filtered, kept for a day. | |
| Pepper tincture, soap. | 10 g of tincture and 5 g of soap per liter of water. |
Chemical
If simple methods do not help, then they resort to the use of chemicals. Sometimes it is necessary to carry out several treatments. Usually 2 times are enough, but sometimes there can be up to 4 of them with an interval of 1.5-2 weeks. This is necessary for the complete destruction of all pests. The plant itself and the immediate environment are processed. It is advisable to replace the soil to eliminate eggs and larvae that are not visible.
Effective drugs:
- Aktara: intestinal action. Water, spray in accordance with the instructions. If necessary, apply during the growing season.


- BI-58, Confidor. They have contact and systemic effects. They are distributed evenly over the plant and get inside the pest. Poison his intestinal tract. Dangerous for bees and fish, can be toxic to humans (if it gets on the mucous membranes).


- Actellic: a non-systemic drug. Sprayed. Not recommended for residential use. Toxic.
- Karbofos. Organophosphorus preparation. Provides nervous excitement, thus poisoning the entire body of the insect.


- Arrivo, Calypso, Fitoverm. They have a contact and intestinal effect.


- Admiral: hormonal insecticide. Use a solution: 6 ml per 10 l.
- Aploud: an inhibitor of chitin synthesis. Spray, diluting in the proportion: 10 g per 10 l.


- Bankcol. Applied in a ratio of 0.5-0.7 g per 1 liter.


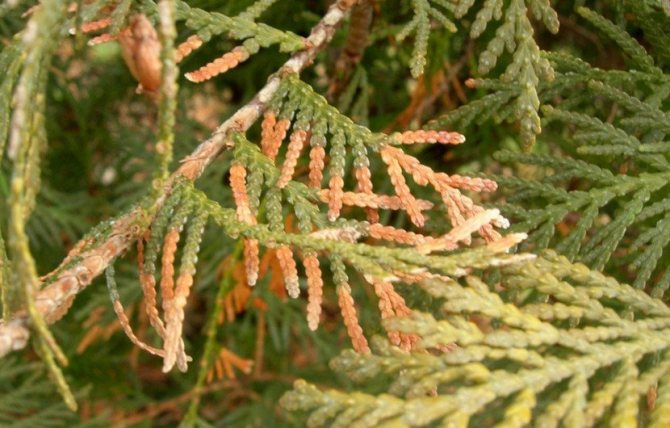
Brown shoots


This is a fungal disease that appears in early spring. You can notice it by the yellowed scales. In a late stage of development, the disease affects the entire shoot, and it dies off.
How to overcome?
To protect the thuja from this disease, it is constantly fed, and also the roots are covered with limestone.
In the period July-October until October, every 2 weeks it is advisable to spray the thuja with Fundazol (2% solution).
If you see at least one affected shoot, it should be cut out immediately, and then the disease will not spread further.
Mr. Dachnik advises: preventive measures to prevent damage to false shields
To prevent plants from being attacked by a pest, a number of preventive measures must be followed:
- Inspect regularly and thoroughly. Preferably with a magnifying glass.
- Water in a timely manner.
- Spray.
- Provide fresh air for indoor plants.
- Apply fertilizers to improve stability.
- Remove damaged branches, dried leaves, dead bark.
- Do not plant densely to avoid crowding.
- Place in a sufficiently lit place.
Gray mold


If gardeners do not take enough care of the plants and violate the rules of agricultural technology, thuja can become covered with gray mold.
This is a fungal disease, while a characteristic spot with a grayish tint appears on the tree, which subsequently acquires a brown color.
Affected shoots die off. If the thuja dries, experts explain what to do in a similar situation.
We need such measures as thinning the thickened crown, removing diseased branches, followed by burning.
Next, you need to treat the tree with a fungicide solution. For prophylaxis, spray with Biosept 33 SL, Teldor 500 SC.
Signs of pests and diseases in thuja
Thuja is universally considered an unpretentious plant, the care of which does not require excessive effort, and this is indeed the case. However, a careless attitude towards this shrub quickly makes itself felt. Violations committed during cultivation affect both the decorative qualities of the thuja and the state of its growth. This is also true in the case of a disease or pest attack. Often the following signs help to understand that something is wrong with the plant.
- slowing down the growth of shrubs;
- changing the color of the needles to black, brown or yellow;
- drying out of the tips of young shoots of thuja;
- increased falling of needles;
- delamination of the bark of the trunk and branches;
- deformation of thuja shoots;
- the appearance of light or dark spots on scaly leaves;
- softening of the trunk or changes in its pigmentation;
- the appearance of neoplasms or unusual plaque on the branches and crown;
- an increase in the number of tracks on the thuja.
If a plant has 2 or more symptoms, it is worth monitoring its condition for 5 - 7 days, paying especially a lot of recommendations for caring for thuja. If within the allotted time the negative changes do not subside, most likely, the thuja's health has been attacked by fungal organisms or insects. In this case, you should try to determine the cause of the deterioration in the health of the bush. Below are descriptions of the most common diseases and pests of thuja with a photo.
Important! Thuja can change the color of the needles, in particular, turn black if pets urinate on it regularly. The situation can be corrected by the construction of special fences around the bushes.
Methods for killing parasites
How to deal with the scabbard on thujas, spruces, pines, and other conifers depends on the degree of infestation, personal preferences. Professional drugs and folk remedies are used to destroy scale insects.
You should not try to get rid of the false scale insects on conifers in a physical way. When trying to remove a bug, the shell remains in the hands, and the insects themselves hide in needles, it is difficult to catch it there. In this way, it is possible only to facilitate the process of leaving the larvae from the scutellum; the parasites will also remain grateful for such assistance.
On a note!
If the bark of coniferous trees is heavily infected, it is allowed to remove the top layer with a special spatula or knife. After the procedure, spray the tree with soapy water.
Fighting the scabbard on spruce trees with the help of insecticides is also not so easy.A strong shell protects insects from the effects of poison; it is problematic to destroy pests by contact. But do not despair, with the right approach, the choice of an effective remedy, you can save the tree.
Lifestyle
Young larvae (up to 1.5 mm long) overwinter on old branches of damaged plants. In May, when the air temperature rises to 10 ° C, they crawl onto 2-3-year-old branches and stick to them with their long proboscis.
The larvae grow rapidly and in the second half of June turn into females covered with a hemispherical shield. Each female lays up to 2000 eggs and dies.
In July, vagrant larvae hatch from the eggs. They crawl out from under the scutes and stick to the underside of the leaves along the veins, where they feed until autumn, sucking out the cell sap, and with the onset of cold weather they crawl onto the branches, where they remain to winter.