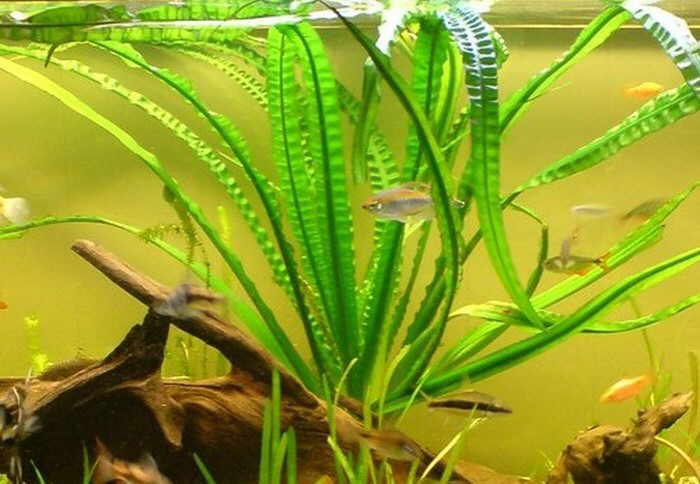
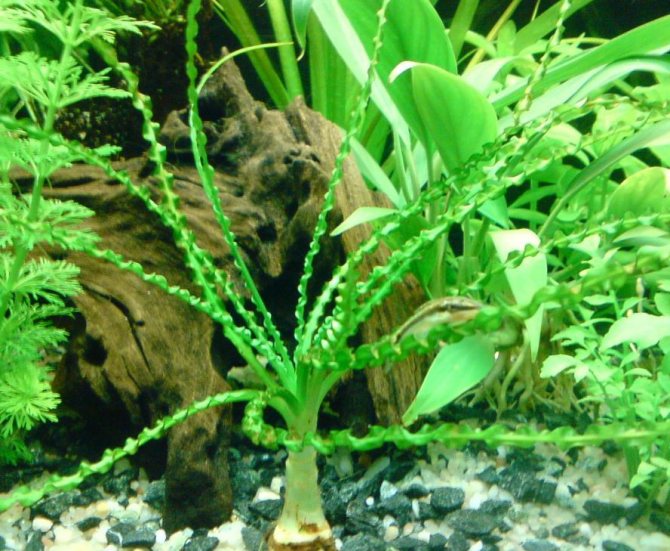
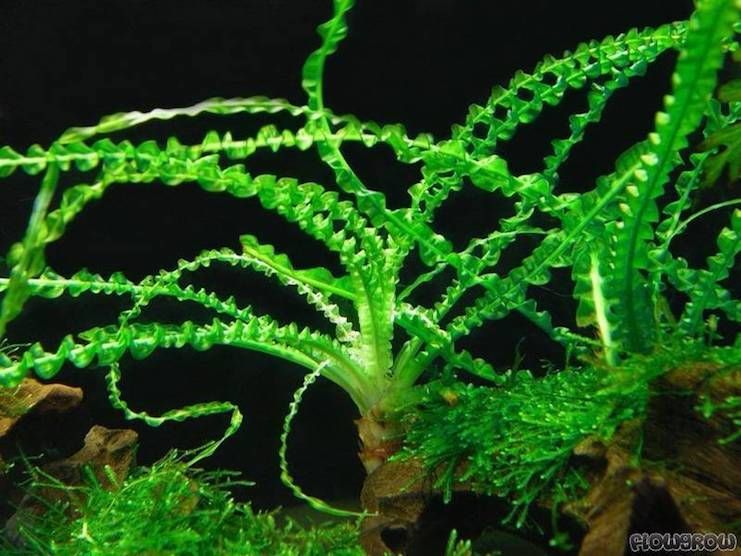
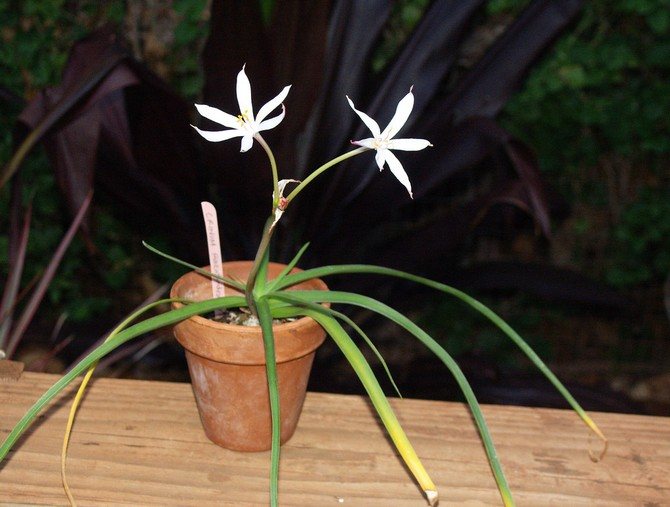
Crinum wavy is a fairly well-known freshwater plant, especially among those who are fond of the aquarium hobby, belongs to the amaryllis family. It was imported from western Africa. This plant in the wild is an inhabitant of periodically drying up reservoirs, so it can be outdoors for some time.
Crinum wavy is a fairly small representative of this species, but even this does not make its size less impressive. The length of the leaves can reach 120 cm, which should not frighten the owners of small aquariums, the krinum tolerates a haircut remarkably.
Description of garden and potting culture
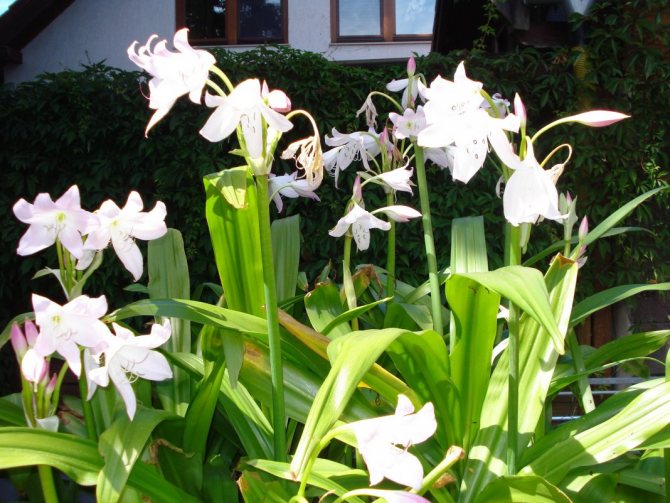
It is worth starting a description of this garden culture with the fact that in Russia it is best to grow krinum plants as a pot culture for landscaping light residential premises, offices, and winter gardens. In summer, they can be used to decorate balconies and verandas. The most suitable for these purposes are Krinum Mura, Krinum red (blooms in late winter and spring), and Krinum Cape.
Family Amaryllis. Homeland - subtropical and tropical regions of the Western and Eastern Hemisphere. There are more than 100 species. Perennial flowering bulbous plant.
The leaves of the krinum are sessile, bright green, long, belt-like (can be up to 1 m in length). The flowers are large, funnel-shaped, fragrant, 10 - 12 cm in diameter, 8 - 12 on small peduncles. The inflorescence is an umbrella.
Coloring from white to pink. Blooms from July to September. The fruit is almost spherical capsule. The seeds are large, green. Bulbs are large, rounded or slightly elongated with whitish scales, up to 15 cm in diameter.
1.Krinum - description
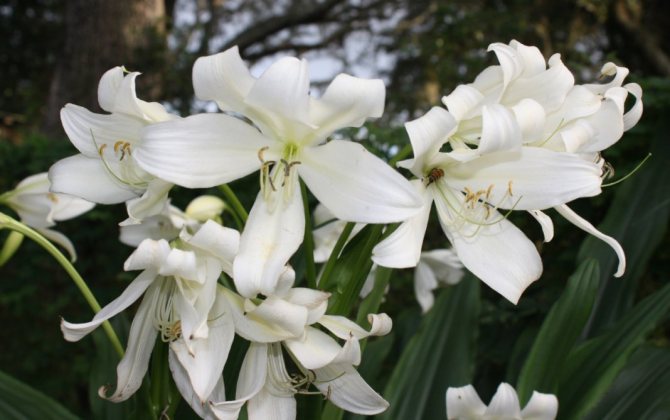
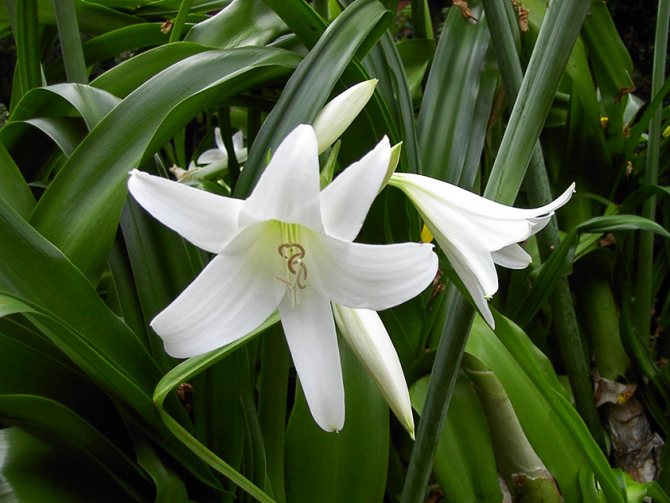
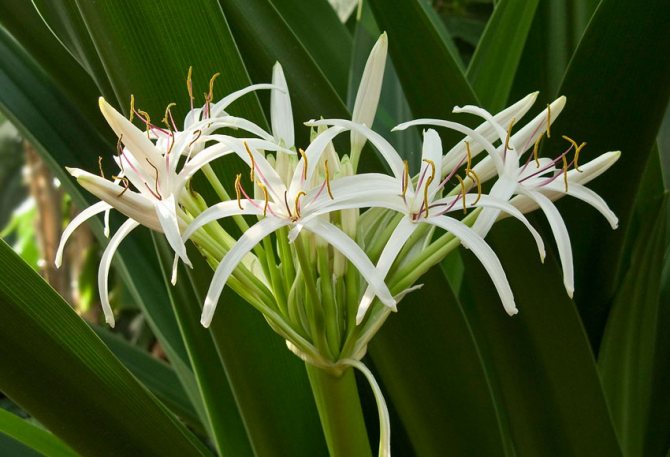
Krinum is an enchantingly beautiful plant, spectacular, graceful, delicate, but at the same time very impressive in size. Its lily-shaped flowers reach a length of 15 cm, grow in a lush inflorescence, which the stem raises to a height of 1.5 m. And the belt-like leaves are noticeable in length - up to 1 m. In addition, it has a strong, but not annoying aroma, reminiscent of caramel essence. Agree, this is a very important advantage, because among modern plants there are so few smelling ones. In many countries, krinum has long been recognized as one of the most beautiful bulbous, blooming at the end of summer.
However, in the amaryllis family, to which he belongs, there are no ugly plants. In nature, there are about 130 species of krinum. They grow in Asia, America and Africa.
- In the greenhouse and indoor culture, about a dozen of its species are grown.
- There are also aquatic species with interesting long leaves and are used for aquariums.
- And for the garden, Powell's crinum is best suited - the most hardy hybrid.
Lighting and temperature
Bright sunlight is important for krinum due to its natural growth potential. In winter, the sun is less, so additional lighting is organized, increasing the day to 16 hours. For krinum, the best place in the house is the south window. On the western and eastern windowsills, the krinum will also develop well. In summer, sunbathing on the balcony is useful for the flower, excluding the possibility of rainfall.
Ventilation of the premises is carried out all year round.
For the winter period, the krinum needs to organize low temperatures up to 10 degrees, which is difficult in an apartment. Heat is destructive for krinum.
There is a caveat: krinums, which were born in tropical regions, require temperatures slightly higher than other species. In summer, they feel good at 25 ° С, and in winter not lower than 14 ° С.
Krinum Mura is a very light-loving plant. It is highly resistant to changing environmental conditions and can even withstand direct sunlight.
For this reason, Krinum Mura can be safely located in the southern or southeastern part of the house or garden.
If necessary, a pink lily can grow in other parts of the room, but you can not wait for flowering.
The temperature for Krinum Moore should be around 24-28 ° C. It is a heat-loving lily. The only time when the plant needs to lower the temperature to 14-16 ° C is the winter rest period. At the same time, they contain a pot with an onion in the most lighted rooms.
Bulbs and peduncles of krinum (with photo)
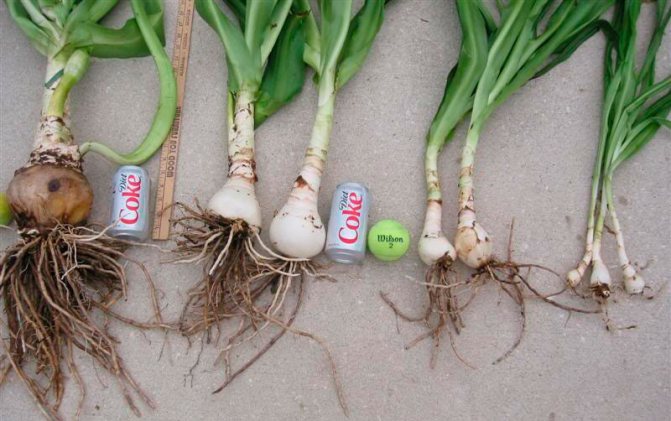
The perennial krinum bulbs (the proposed photo will allow you to examine them more closely) are usually large, 60-90 cm in length, up to 25 cm in diameter, the neck is oblong:
The leaves are evergreen, belt-like, light green in color, up to 1 m long, form a false stem, at the end of which there is a fan - it is created by leaf blades. Young leaves are rolled into a tube. A well-developed plant has more than 20 leaves.
The length of the peduncle sometimes reaches a meter, the evergreen krinum flower is pale pink, sometimes with a raspberry tint, funnel-shaped, with a weak aroma. Removing dead flowers can extend the flowering time of the plant. 9-12 leaves are formed between the inflorescences, the inflorescence itself develops only where the leaf blades have already dried up. They stay on the plant for 4-5 weeks.
Blooms mainly in autumn. Short day plant. In the conditions necessary for well-being, the bulb lives for a long time. The more the krinum grows, the more territory it will capture.
Serves as an excellent decor for large rooms with low temperatures, both in residential buildings and in public places. Lives well in the winter garden. Some species do well in aquariums.
Spectacular host in the garden: landscape tricks (with photo)
The plant needs good lighting, easily tolerates bright sun. After flowering, it is advisable to take the krinum out into the air. In winter, during the dormant period, the plant is placed in a room with a temperature of 14-1b ° C. The bulbs are planted.
Planting a garden krinum: one bulb is planted in small (15 - 17 cm in diameter) pots so that it protrudes 2/3 above the soil surface. Crinum is transplanted when planting in the open ground no more than once every 3-4 years, using a flower substrate or a mixture consisting of leaf and greenhouse soil and sand (2: 1: 1). However, if you see that the plant has formed a lot of children, we recommend separating and planting them.
After the end of flowering, the krinum begins a dormant period, but the plant does not shed its leaves. Therefore, watering is reduced, but the soil in the pot must not be allowed to dry out. The plant must be kept at this time in a cool place (no higher than 8 - 10 ° C).
Reproduction. Baby bulbs and seeds. It is best to separate the babies in the spring, during the transplant (April - May). Separating the babies promotes better plant growth and flowering.
The baby is planted in small pots with a diameter of 11 - 13 cm. During the growing season, young plants are transplanted 1 - 2 times into more spacious dishes. Watering abundantly and regularly during the growing season. Every 12 - 15 days, plants are fed with liquid fertilizer or a solution of mineral fertilizers (NPK), 5 - 7 g per 1 liter of water. Proper planting of a garden krinum will make it easier to care for the plant and speed up the flowering process.
The flowering time of crinums can be adjusted by changing the watering regime or by increasing and decreasing the amount of light. So for winter flowering, the dormant period is moved to summer - early autumn.After which the plant is watered abundantly, the krinum begins to grow intensively and blooms quickly. To speed up flowering, the plant is transferred for a short day, in which in the morning and in the evening the plant is covered with a bag of black opaque film or paper.
The plant goes well with both flowering and other decorative deciduous species, it is effective in single plantings.
If you decide to plant a hosta in the garden, landscape tricks will help make this plant an excellent decoration for your site. Hosts are used in a variety of floral arrangements. Giants become spectacular accents in a mixborder or on a lawn, medium-sized specimens form curbs along the paths, and "little ones" perfectly decorate rocky slides or mini-flower beds.
The main decoration of the hosta is its leaves. They can be plain, with a contrasting border along the edge or a stripe in the center. Often they are decorated with strokes, spots. In some varieties, the color of the foliage changes during the season: from blue it turns into green, the golden-yellow center of the leaves becomes creamy white by the end of summer.
How to care for a garden krinum?
All horticultural crops imply individual care, the garden krinum is a very whimsical and demanding plant, so the following rules must be observed:
- regular and moderate watering, especially with the growth of buds;
- periodic fertilizing with fertilizers;
- after the foliage withers, it is necessary to prepare the flower for winter;
- during the winter, the ground where the bulbs are stored can be slightly moistened;
- it is not allowed to store bulbs in a too warm room, above + 15 ° C.
Caring for garden crinum means timely removal of weeds and loosening of the soil. In addition to periodically fertilizing the soil with organic and mineral products, the flower can be watered with complex fertilizing during the flowering period. The faded buds are cut to reduce the stress on the bulb.
Attention! Do not be afraid of the moment when, after flowering, the leaves of the krinum will gradually fade. This is the natural process of preparing a plant for winter.
The following agents are usually used as top dressing:
- a mixture of superphosphate with potassium salt - to stimulate growth;
- organics for general strengthening, for example, chicken manure or cow dung;
- a thick layer of humus.

The main rule for feeding any flowers is proportionality and moderation. With an excess of fertilizer, excessive greenery will appear without peduncles. For each plant, you need to spend about 0.5 liters of liquid fertilizer. Improper care will lead to rotting of the bulbs.
Humidity and watering
Humidity for Krinum Moore can be around 55%. On particularly hot days, spraying with soft, warm water from a fine spray can be carried out. No spraying is needed in winter.
Regarding watering, Krinum Mura needs it in the summer. During this time, you can water the plant abundantly and regularly. The water should be kept warm.
Stagnation of water in the pot provokes rotting of the bulb. Therefore, they take care of the presence of good drainage in the tank in advance.
During the winter rest period, Krinum Mura is watered to keep the soil slightly moist.
Krinum is not pretentious about the humidity of the surrounding air. Rubbing the leaves with a damp cloth is permissible.
Crinum is watered when it is in bloom, abundantly, but only after the top layer has dried. After flowering, watering is brought closer to a moderate regime, about once every seven days.
During the dormant period, only a moderate moisture content of the earth clod is maintained. Overdrying will destroy the bulb and root system.
Water for water procedures is taken only soft, separated and strictly at room temperature or slightly warmer.
Types for indoor cultivation


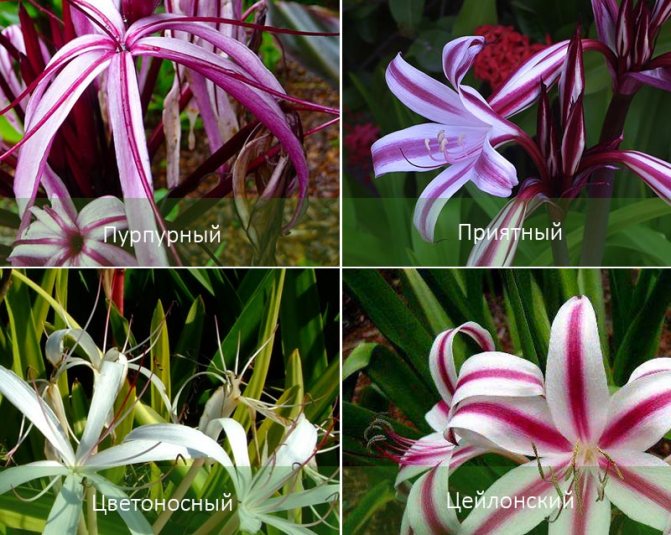
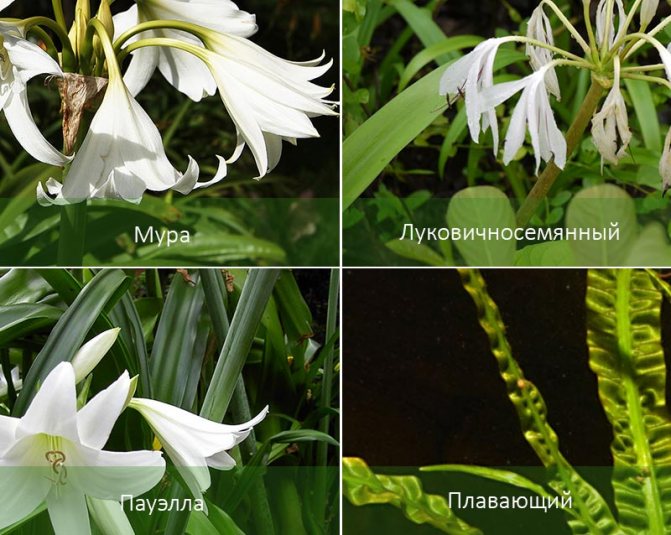
Several types of krinum are intended for breeding at home. The most popular among florists - Crinum Moore (Crinum moorei). In everyday life it was called "pink lily". It has large lily-shaped flowers (6-10 pieces) and belt-like leaves (60-90 cm). Other indoor types of krinum include:
- Krinum Abyssinian;
- Asian crinum;
- Krinum is large;
- Krinum is pleasant;
- Krinum Makovana;
- Krinum is majestic;
- Krinum is reddish;
- Crinum bell-shaped;
- Krinum Ceylon.
All varieties have the same structure, but differ in flowering period, flower size, as well as the length of the leaves and flower arrow.
Diseases and pests
Krinum is susceptible to flower diseases: anthracnose, staganospore. When the water regime is violated, root rot often occurs.
Pests: mealybug, spider mite, marillis bug.
- Amaryllis worm, which will help to cope with a solution of a special insecticide (2 ml per liter of water).
Needless to say, some difficulties await florists who decide to grow krinum at home. However, in all other respects, the krinum is not whimsical at all - if it is possible to adjust the temperature regime, there will be no more problems.
In any case, the majestic handsome krinum is the plant for which it is not a pity to try, and its flowering can conquer any heart.
Krinum Mura is a very hardy plant. He may suffer from noncommunicable diseases if the rules of care are grossly violated.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Pickled cucumbers with aspirin for the winter: the best recipes with photos
You should not grow a plant without sources of bright light, lead to stagnant phenomena of water in the soil, transplant Krinum Moore in pots that are too wide.
These actions will provoke flowering problems and affect the deterioration of the decorative qualities of Krinum Moore. Against the background of this, a scabbard may appear.
The plant can be protected by various preparations of biological or chemical origin.
Fitoverm, Aktara, Decis, soap solution or private tincture - everything will work if you follow the instructions. But remember that the best protection for a plant is early care and maintenance.
And for those who like to know more, we suggest that you read the video about Krinum Moore
The most problematic is Moore's crinum, which we'll talk about. Pests and common diseases that have to be dealt with sometimes affect other plant species. But this happens much less often.
If you find suspicious red spots on the bulb of your plant, then it should be treated with a foundation. These spots, the so-called "burns", are the result of the occurrence of Staganospor. If the plant is very heavily stained, then you need to prepare a mixture of chalk, about 100 g, which must be ground into powder, add 5 g of copper sulfate and 10 g of OP-7 (adhesive). All this must be diluted with water to get a thick mass. Then, it is necessary to completely coat the entire plant, from the bulb to the leaves.
Also, Anthracnose may develop. Its signs are black spots appear on the leaves. Such a disease develops only under conditions of high air temperature. To overcome the disease, you will have to remove all affected leaves. The bulb must be treated with a foundation (2 g per liter of water). After processing, it is necessary to move the plant to a darker and cooler place.
Also, scabbards - sticky secretions can develop on the leaves. This is the most harmless damage to the plant, which can be easily overcome with a solution of water and laundry soap.
Of the parasites, the most common are mealy worms, spider aphids. They appear when the plant was not properly cared for - it was not watered, the leaves were not moistened. You can remove them with special solutions that are sold in stores.


With poor care, the flower is affected by spider mites and mealybugs.
Pests are removed with cotton wool moistened with potassium permanganate, alcohol or laundry soap.
If folk remedies did not help, then the flower is sprayed with Aktellik, Aktar or Bankol.
All children and animals are preliminarily taken out of the room.
After spraying, the plant is placed out of the reach of children and pets. If drugs get on the skin or inside, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Of the diseases in "Krinum" only rotting of the root system was observed. The reason is excessive watering. At the first sign, the flower is transplanted into another pot, new soil is poured and watering is stopped. Severely decayed root areas are removed with garden shears.
"Krinum" is an evergreen flowering plant. It responds well to subcortexes, systematic watering and gentle care. Can withstand direct sunlight.
It grows well in bright rooms at a temperature of 21-26 ° C. During the dormant period, it can actively shed leaves. May be affected by mealybugs and spider mites.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl Enter.
In rooms, the greatest harm to the plant is caused by the red spider mite. It multiplies rapidly in dry and overly warm air. The mite settles on the underside of the leaves, damaging them. Symptoms of a tick lesion - the leaves acquire a whitish bloom, turn yellow and fall off prematurely.
Disease and pest control measures - increasing air humidity, spraying the plant with settled water. Reducing the temperature of the plant. In case of severe infection - treatment with actellik.
Of the diseases, the most common is the rapid shedding of leaves caused by the Septoria fungus.
Control measures. Spraying plants with bayleton, saprole or basezolam.
With an excess of moisture during the dormant period, the roots of the krinum can rot. It is necessary to reduce watering.
Diseases, pests, possible problems
One of the main problems is the appearance of rot on the roots. It occurs due to excessive watering during dormant periods. In addition to decay, the appearance of such parasites is dangerous for krinum:
- Mealybug (hairy lice). They are easy to distinguish with the naked eye, because their length is 3-6 mm, less often 10 mm. Mature individuals stick to young shoots, leaves and flowers. A white cotton-like trail is left behind. Because of them, the growth and development of the plant slows down.To get rid of pests, you need to clean the cinnum from the worms and wipe it with soapy water. Then spray a solution of green soap three times (10 g for 1 liter of water). This procedure is carried out once a week. For prevention, you need to keep the plant clean and periodically wipe it with a damp sponge.
- Spider mite... Appears on all plants except aquatic species. Signs of the appearance of the parasite are white dots on the leaves and the presence of a thin cobweb that braids the organs of the plant. Because of the mite, the plant is weakened and exposed to many infections. To fight the mite, the plant is washed with warm water and laundry soap. In cases of severe damage, chemical preparations will help: insectoacaricides (Akarin, Vertimek, Kleschevit) and acaricides (Floromite, Borneo, Apollo).
Soil and fertilizer
The soil for Krinum Moore should be nutritious, medium-heavy, have good water and air permeability with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. The transplant is carried out once every two to three years in early spring in slightly larger pots, despite the large number of roots.
For this, a soil mixture is prepared from the following components:
- sod land (1 part);
- sheet land (1 part);
- humus earth (1 part);
- sand (1 part);
- expanded clay (part 1).
Fertilize Krinum Moore with ripe cow dung or universal organic fertilizers, which are applied along with irrigation. Concentration for liquid feeding is prepared according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
Given the size of the future plant, a wide and deep container is prepared for planting krinum, up to 35 cm in diameter. Powerful roots are carefully cleaned and placed in a new soil substrate so that the bulb is one third above ground level.
The soil needs to be loose and nutritious. Mix for this in equal parts: turf soil, humus, leafy soil, peat and coarse sand. Ready-made primer can be purchased.
Crinum is rarely transplanted, in the spring every four years, more often by transshipment.
A good drainage layer is laid on the bottom of the pot.


Crinum purple.
Conditions and care
Before growing a plant, you need to familiarize yourself with the rules for caring for crinum at home. For a tropical plant to grow indoors, certain conditions are needed, otherwise it will not grow or simply wither. The main ones are the correct level of illumination and the correct temperature of the content, which is selected depending on the variety.
Lighting and location
In the wild, krinum grows in sunny areas, so you also need to provide intense light in the house. Under the rays of the sun, its growth is activated, so the best place for a flowerpot is the windowsill on the south side. Long leaves should not be allowed to touch the window pane. they can get burned.
In the spring and summer seasons, as well as in warm autumn, the krinum can be taken out into the fresh air: in the garden or on the veranda. Only heavy rainfall should be avoided. The plant definitely needs clean air, so the room should be periodically ventilated, even in the cold season.
If the flower lacks sunlight due to the short daylight hours (in winter), you need to purchase artificial lighting lamps. For normal growth, it is enough to light 16 hours a day. If this is not done, the lower foliage of the krinum will wither and fall off.
Temperature and humidity
The required temperature regime for different varieties will not be the same:
- Tropical krinum is most often grown in greenhouses. During active growth and flowering period (spring-summer), the temperature should be around 24 degrees. If the weather is warm and calm, then the plant can be taken outside. In winter, when the plant is dormant, the temperature is reduced - not less than 14 and not more than 18 degrees.
- Krinum from the arid regions of southern Africa. It is resistant to lower temperatures, so the optimal one in summer is 22-27 degrees, and in winter - 2-6 degrees. In the subtropical zone, the plant can be grown outdoors even in winter, providing easy shelter.
The moisture level does not affect the growth of krinum and its development, therefore, special instructions are not required. The only thing is that the leaves are wiped from time to time with a damp sponge so that dust does not accumulate on their surface.
The soil
The best soil for the growth of krinum is an earthen mixture of the following ingredients:
- leafy ground (1/6);
- clay-sod land (2/6);
- peat (1/6);
- humus (1/6);
- sand (1/6).
You can also add some charcoal to prevent putrefaction.
Landing, transplanting


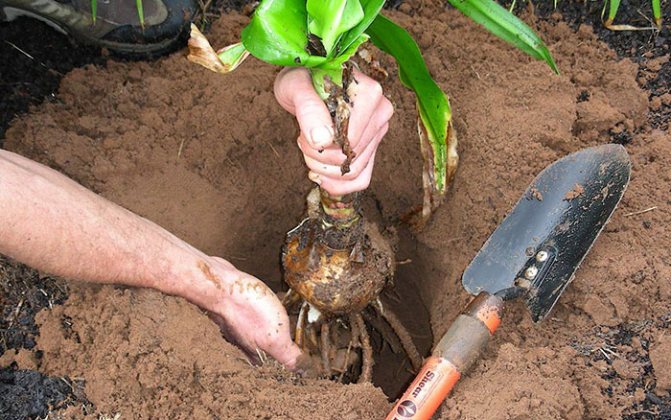
Crinum transplant should be done very carefully and rarely enough (once every 3-4 years). The strong root system reaches 60-90 cm in length, so it can be easily damaged. Before replanting the plant, water it abundantly to make it easier to remove from the pot. Next, the root system is examined, and the dried parts are removed.
The new plant pot should be large and deep. The soil must be drained by pouring river pebbles or expanded clay onto the bottom. Without drainage, the earth is compacted, dries out extremely unevenly, and the abundant moisture in the soil harms the flower. The onion planted in the soil should rise 1/3 above the surface.
Watering
How to water a flower depends on several factors:
- during the period of active growth and flowering (summer), abundant watering with warm water is required. Water regularly - as soon as the topsoil dries up;
- in the fall, the frequency of watering is reduced, but the land should remain moderately moist;
- at rest they rarely watered, trying to prevent drying out. Due to a lack of moisture, the root system withers.
It is worth noting that watering can change the flowering period. If watering is reduced in late summer and early autumn, the peduncle will begin to grow. So the flowering period will change to the winter season.
Top dressing
For feeding, use ready-made liquid fertilizers for flowering ornamental plants. Crinum is fed twice a month. This is done for the first time after the appearance of young leaves, and you need to finish it after the end of flowering. All instructions regarding the dosage of the fertilizer are indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging.
Dormant period
As soon as flowering ends, a dormant period begins. At this time, there is no visible growth of the plant, but the old foliage withers. Krinum definitely needs peace, otherwise it will not bloom again. The temperature at this time drops to 16 degrees.
Variety host: description and photo
Hosta is a perennial herbaceous stemless plant with a thickened rhizome and a large number of filamentous roots. Lanceolate, or cordate, pointed leaves with distinct venation are collected in a basal rosette. The lilac or white flowers of the hosta in a multi-flowered raceme rise above the leaves. The hosts bloom from mid-July to August.
The shape of the host leaves is surprisingly diverse: oval, round, heart-shaped, lanceolate. In some varieties, the surface of the leaves is smooth and shiny, while in others they seem to be covered with pimples.
Hosts can be real giants - up to 90 cm. Huge green leaves with a yellow border cover an area of about 2 m2. Dwarf varieties with small leaves do not exceed 10 cm.
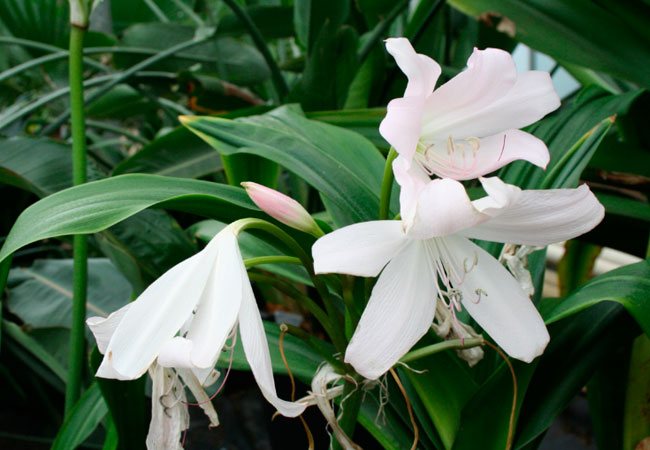
Types of krinum for home breeding
The flower is very sensitive to the environment, it loves fresh, clean air, so not so many varieties of krinum were able to adapt to home cultivation. But even from what breeders have domesticated, there are enough copies to enjoy the splendor of the flower. Consider home types of krinum.
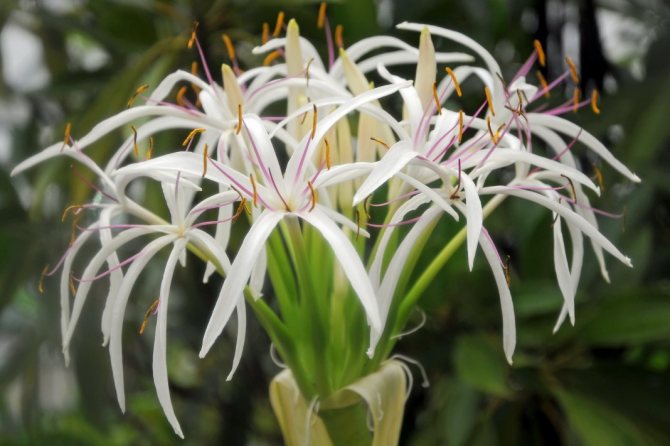
- K. Asian (Crinum asiaticum). The shrub grows up to one and a half meters in height. Its bulb is medium-sized, about 15 cm in diameter and 30 cm in height. The number of ribbon-like leaves in one bush does not exceed 25-30 pcs. But inflorescences can form a lot of flowers - more than 30. The color of the flowers is white. Thin linear petals gracefully bend and hang down like hairs. The culture blooms for a long time - from March to mid-October.
- K. beloved (Crinum amabile). It is a medium-sized bush, the length of the leaves of which reaches 1.5 m. Its leaves are slightly wider than that of other species. During flowering, an umbrella and 20-30 flowers are formed on the peduncle. The flowers of this plant are very beautiful - purple with white tints, thin curving petals and long stamens. The bush can bloom 2 times a year.
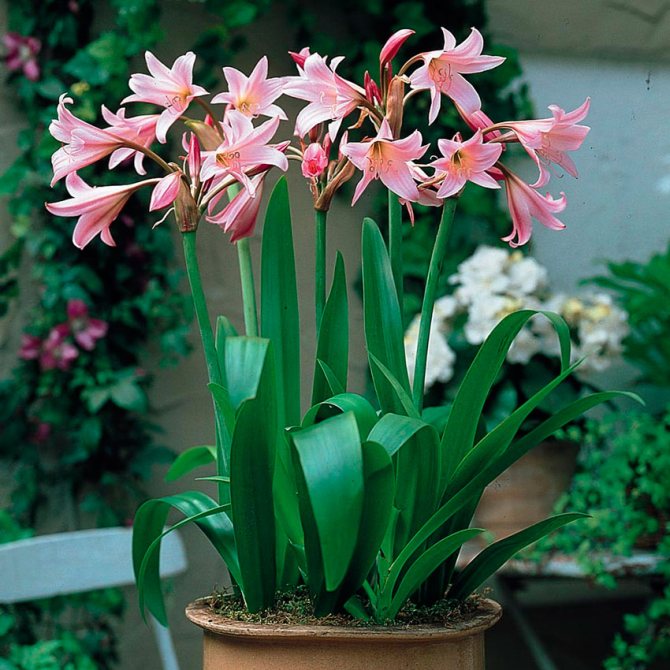
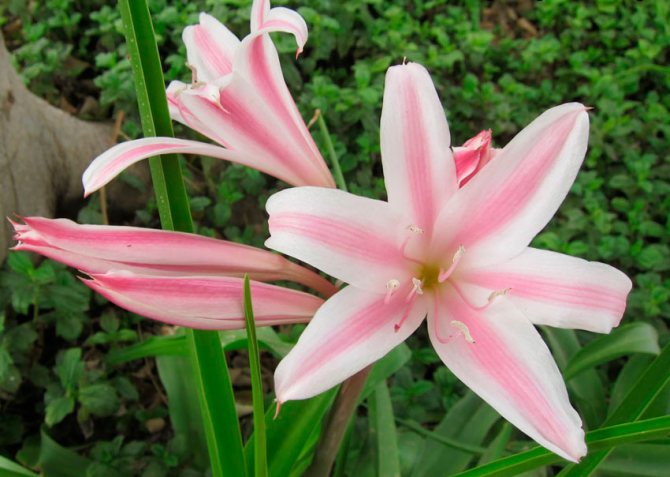
- K. Moore (Crinum moorei). The most common species, popularly called "pink lily". The krinum bulb is large - up to 25 cm in diameter and up to 70 cm in length. Height can reach 3 m. Ribbon leaves are slightly wavy, have a glossy sheen. On a thick rigid peduncle, up to 12 large, beautiful pink flowers are formed.
- K. Yagus (Crinum jagus). The species is also known as the "giant krinum". But he received this name not for the growth, but for the size of the flowers. Their diameter is 18-22 cm. Leaves, up to 90 cm long, are wavy with clearly visible veins. The flowers are white in color, with a yellowish throat and wide petals.
- Crinum abyssinic (Crinum abyssinicum). It is rarely found in culture; it is grown mainly in the open field. The bulb of a medium-sized plant. The bush itself is low - 1-1.5 meters.On the peduncle, about 5-7 white flowers are formed, up to 10 cm in diameter.
- Crinum campanulatum (Crinum campanulatum). This species grows exclusively in water (in swamps, lakes, along river channels). In culture, it is planted either in aquariums, or grown in decorative ponds. The height of the bush is small - up to 1 meter. Leaves are thin, long, emerald green. Funnel-shaped flowers, 5-8 in umbrellas, have a beautiful pink-white color.


Types of krinum for home breeding
The best varieties of phlox with photos and names
Even ten years ago, no more than 2-3 species of these herbaceous short-rhizome perennials were grown in our gardens. In recent years, planting material of modern varieties has begun to come from abroad. Among them, you can choose hosts whose foliage is painted in various shades of green, yellow, cream or blue. Below is an overview of the most popular types of these plants.
The host is swollen - forms a large bush with a height and a diameter of about 80 cm. Its leaves are salad green, with noticeable venation, and the flowers are light purple.
Khosta ornamental - is probably an old Japanese garden form. The bush is medium in size (height 40-45 cm, diameter 50-55 cm), leaves are oblong, dark green, with a white wavy edge, flowers are light purple.
Hosta Siebold - differs in large bluish-green shiny wrinkled leaves. The blueness of the leaves is more evident in the spring and early summer. A large bush reaches a height of 60-70 cm and a diameter of 70-80 cm, flowers are light purple.
Small hosta is a low (up to 15 cm) plant with a long rhizome, dark green leaves and dark purple flowers.


Khosta narrow-leaved - forms a small bush with a height and a diameter of about 40 cm. Leaves are shiny, dark green, narrow, purple flowers. Blooms late, from mid-August.
Hosta Fortchuna (X. white-bordered) - is distinguished by a compact bush 40-50 cm high and 50-60 cm in diameter. Dark green leaves have a white, irregular border. The flowers are dark purple.
There are many hosta varieties, more than 7000 garden forms and about 4000 registered varieties are known. Shared hosts:
- by color (blue, green, variegated (variegated) - white and yellow-bordered, tricolor),
- shape (round, spiral, oval, heart-shaped, linear-lanceolate, etc.),
- leaf texture (smooth and shiny, with a waxy coating, with a "waffle" surface, etc.).
- according to the height of the bush, 6 groups are distinguished — from dwarf ones with a height of less than 8 cm (Blue Mouse Ears, Oze) and to giant ones — exceeding 75 cm (Blue Mammoth, Parasol).
Before planting phlox in the garden, you need to decide on the varieties that are suitable for growing in your area. Perennial phloxes are divided into two main groups. The first is creeping, or carpet, phlox with a height of 5 to 20 cm. In our conditions, creeping phlox, as a rule, bloom twice a year: the first flowering in mid-May, the second in early September.
The second group is phlox with tall erect stems that bloom in summer and autumn. The main representative of this group is phlox paniculata (Ph, paniculata) - the ancestor of most modern hybrids and varieties, one of the longest flowering crops in the garden. Its continuous flowering can be ensured by selecting varieties.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: Garden plants - Schizanthus (schizanthus) on the Your Garden portal!
As a result of long-term culture (about 200 years), about 400 of the best varieties of phlox paniculata were obtained. They all differ in height and shape of the bush, color of flowers and timing of flowering.
With proper planting of phlox and care in the open field - early varieties bloom at the end of June, late ones - from the second decade of August. Flowering lasts 2-3 weeks. By selecting varieties, you can achieve continuous flowering of phlox in the garden for more than two months. Many varieties of phlox obtained by breeders are combined under the name garden phlox.
The strength of the stems matters when choosing plants.If the bush is loose and fragile, then the variety quickly loses some of its decorative value. Therefore, varieties with a compact, durable bush are more popular, since they do not need a garter and are resistant to adverse weather conditions.
There are a number of varieties of phlox paniculata that are highly susceptible to disease, especially during rainy summers. Therefore, when choosing a variety, it is important to be guided not only by the decorative qualities of the plant, but also by its resistance to diseases.
Krinum, basic information about the plant
Crinum Is a perennial bushy bulbous plant belonging to the Amaryllidaceae family.
In translation from Latin "crinum" is translated as "hair". The flower received this name for the similarity of its thin and long petals and leaves with hair.
The plant is native to South Africa. It is also found in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, South America, Mexico. Krinum is hygrophilous, therefore it grows near rivers, lakes, swamps, and sea coasts.
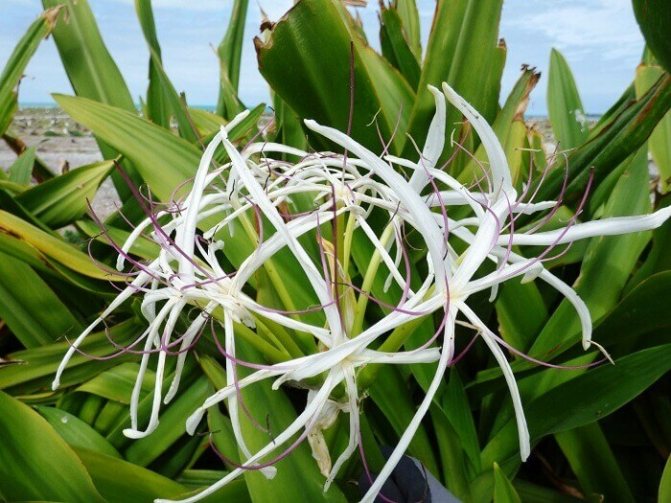
In nature, there are about 150 species of this plant. The flower bulb is large - about 70-90 cm in length and up to 30 cm in diameter. The height of the shrub itself can reach 4-5 m in the wild. Long belt-like (ribbon-like) leaves are light green in color. As they grow, they spread out in different directions and bend. Krinum has one difference from other types of amaryllis plants - its young leaves are twisted into a thin tube and they unfold only when they reach a certain length.
Crinum begins to bloom in spring, and can bear flowers until autumn. The bush produces a long, straight peduncle from the center. At its tip, umbrella-shaped inflorescences of 6-12 flowers are formed.
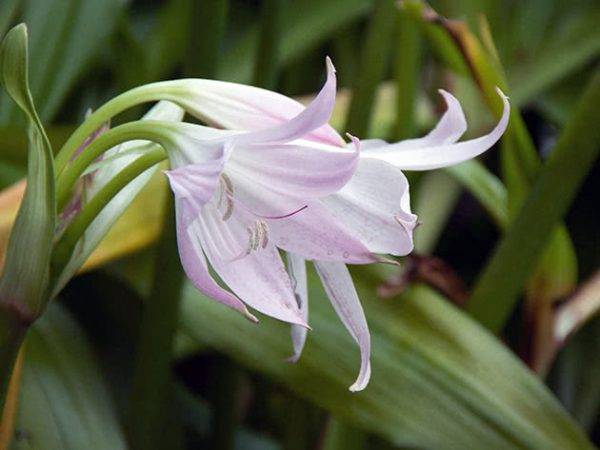
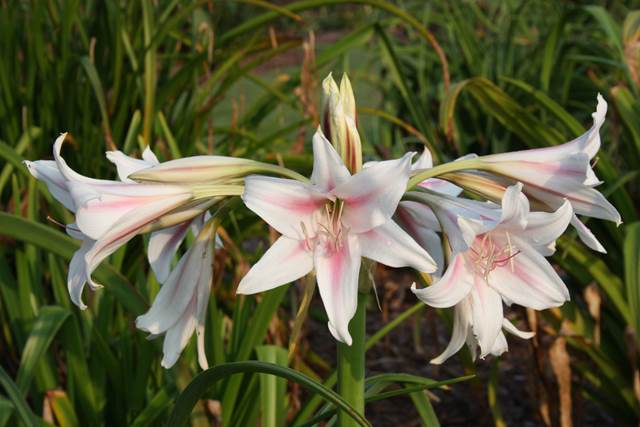
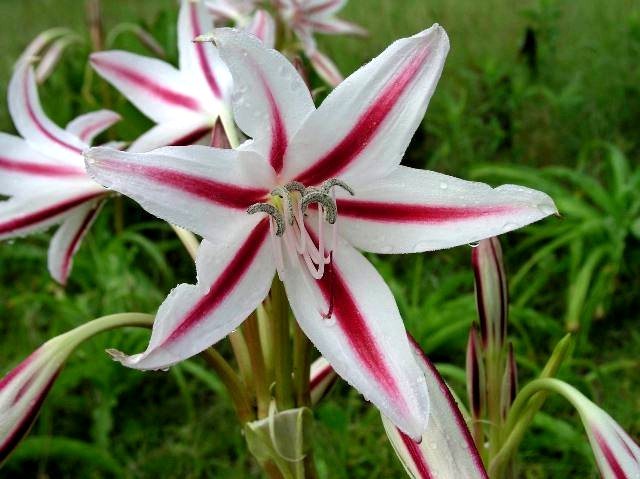
The shape of the flowers in krinum is funnel-shaped, the flowers themselves are very similar to a lily, only much larger (up to 20 cm in diameter), with a pale pink or white color of the petals. There are species in which flowers have very interesting thin petals, beautifully bending to the sides.
The aroma of flowers is pleasant, sweetish, but not intense. The plant is prized among florists, interior and landscape designers for its magnificent decorative appearance.
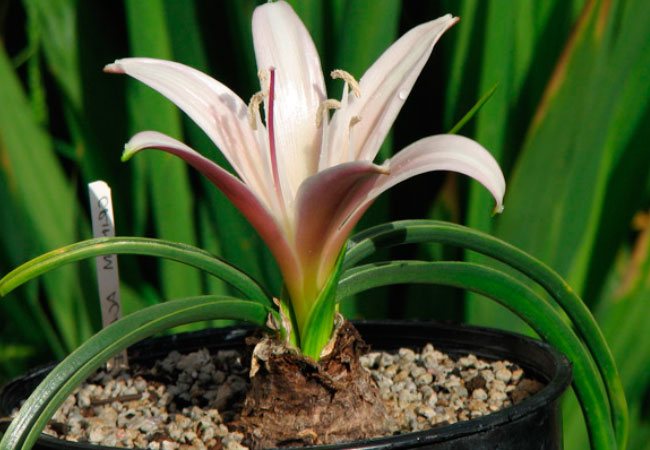


How to care for crinum at home
Hosta growing conditions: shade or sun
Choosing the right landing site is very important. Which place to choose for the hosts: shade or sun? In their homeland, in China, hosts grow where there is always enough moisture in the soil, and the canopy of tall plants protects them from direct sunlight. The most suitable place for a host is a semi-shady area with neutral or slightly acidic, moist, but well-drained soil.
In open sunny places, hosts tend to feel uncomfortable. It is believed that yellow-leaved varieties show their characteristic color only in good light. But even they can suffer from heat and bright light - the leaves fade, the contrasting border burns out, and sunburn occurs.
Hosts with bluish or gray-blue foliage look especially inexpressive in open places. The delicate wax coating melts easily in the sun, the leaves turn green and lose their blueness. If you really want to plant a hosta in a sunny flower garden, then it is better to be shaded by taller perennials.
At the same time, it must be remembered that hosta is not the kind of plant that can be used to decorate completely dark areas. In places with cold soil, where the sun never comes, hosts simply survive. They grow slowly and do not show the typical foliage coloration.
Hosts are durable, grow up to 20-25 years in one place. They prefer moist, but without stagnant water, weakly acidic fertile loamy soils.
Diseases, pests, difficulties in care
It is not easy to create conditions for the flowering of krinum. The main difficulties faced by the gardener are the choice of a planting site and adherence to a certain level of soil moisture.Pests rarely affect flowers, but there is a risk of mealybugs, narcissus flies, spider mites or thrips. Typical signs of a diseased plant:
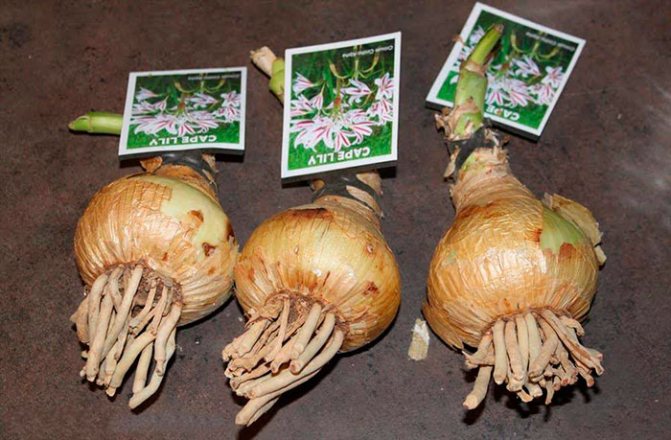


- decay of the bulb;
- the appearance of red longitudinal spots on the leaves;
- long absence of flowering;
- lethargy foliage.
In addition to insects, excessive watering and excessive fertilization of the soil causes great harm to krinums. Also, the plant suffers from a lack of dormancy or lack of sunlight. Insects can be detected by the presence of a translucent thin web or the appearance of suspicious whitish lumps. If you do not take action, the whitish lumps will turn into plaque, which contributes to the appearance of a sooty fungus. Treatment with special preparations will be an effective solution to the problem. Fungicides are applied to rotten areas. Red longitudinal burns on the leaves are characteristic of nutrient deficiencies.
In addition to the listed problems, every gardener should inquire about the selected variety of krinum, since some varieties contain the poisonous substance "krinin". Despite all the difficulties of growing, krinum remains one of the most sought-after garden plants. Flowers can decorate landscape design not only in a single version. The group of krinums looks especially impressive.
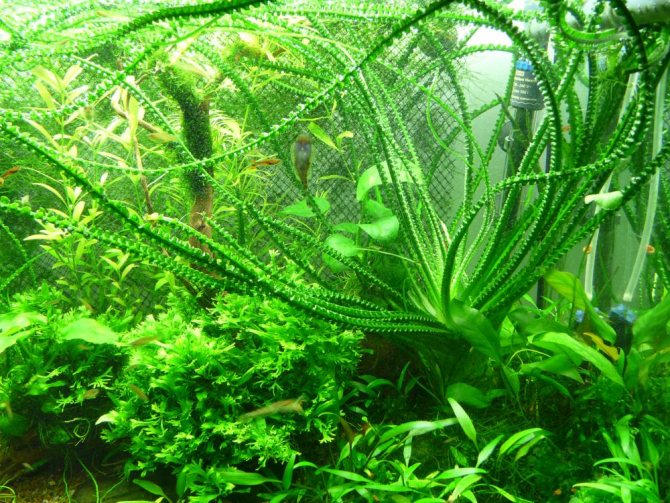
Where can you plant and what will come out in the end
Also, your fish will not damage the aquarium krinums, since they do not eat them. Another plus. If you care for it constantly and with love, you can achieve amazing results.
As for the view of Moore, one thing is clear - it will give you an unprecedented freshness and wonderful aroma. In addition, very beautiful inflorescences that appear in the summer and will delight you until the end of autumn. Having planted several of these at home, you will feel as if you are in the tropics - the birthplace of the plant in South Africa.
growing experience at home ... read
Hosts are not capricious: they forgive the lack of attention and are able to grow in the garden of any, even an inexperienced grower. But they will show their best qualities if you make some effort.
Before planting the host, you should carefully prepare the planting site: remove the weeds, add 1-2 buckets of compost to the soil and dig it to a depth of about 30 cm. Next, make a hole, add fertile soil with humus and complex mineral fertilizers to it. The roots are spread on an earthen mound, covered with soil, compacted and watered abundantly. It is useful to mulch the planting with peat or compost.
Do not plant hosts near trees or shrubs with shallow root systems. With such a neighborhood, plants will suffer from a lack of moisture and nutrients.
After planting, it is advisable to cut off some of the leaves from the seedlings in order to reduce the loss of moisture due to evaporation. Until the hosts take root in a new place, they need to be watered regularly.
Before planting phlox, choose a planting site, it should be open or slightly shaded. The soil is prepared in advance: 2-3 weeks before planting, 1 bucket of humus or compost, a half-liter can of ash and 60 g of complex mineral fertilizer per 1 m2 are introduced. Fertilizers are scattered, the soil is dug to a depth of about 15 cm. On heavy soils, plants develop poorly and bloom poorly.
Phlox can be planted in spring and autumn. You should not delay the spring planting, the best time is mid-May. Autumn planting is best done from mid-August to mid-September, so that young bushes have time to take root before the onset of frost.
Depending on the size of the bush, small planting holes are dug, approximately to the depth of a shovel bayonet (20-25 cm). For one bush for 3-4 years, it is enough to provide a feeding area of 60 × 60 cm. Carefully spread the roots of the seedling in the hole and cover it with earth. The root collar should be 3-5 cm deep.
Seedlings with closed roots can be planted throughout the season, but after planting, shading in hot weather and abundant watering will be required.
Winter storage of krinum
In winter, the flower requires special care. Even before the onset of frost, a shelter of straw or peat is organized for the bulbs. After the end of frost, the shelter is removed to prevent rotting of the root sections. In regions with harsh winters, the bulbs are dug up, dried and pruned. They can be stored in a refrigerator or cool room.
At rest, krinums are not watered, irrigation with water is allowed only if there is a risk of overdrying the earth layer. Violation of the storage temperature, as well as excessive humidity, will inevitably lead to damage to root cuttings. Improper wintering can negatively affect the flowering of plants.
If the bulbs are stored indoors, it must be dry. It is advisable to disinfect the cellar and equip it with ventilation. In the spring, you can see that the krinum has woken up - it starts up an escape as soon as it comes out of a state of rest. If there is no dormant period, the plant is unlikely to bloom in summer.
Agrotechnics
The question of how to feed the host is asked by all lovers of this flower. Experts advise against sprinkling compost on the bushes of miniature hosts. They are too small to rip out under a thick layer of mulch. The host responds well to spring feeding with full mineral fertilizer.
Caring for mature plants is simple: watering in drought conditions and mulching the soil with compost in the fall.
Most host varieties bloom in July. Small bells of lilac or white flowers appear on tall peduncles. If the hosts are grown as ornamental deciduous plants, it is better to cut the flower arrows - this helps to keep the compact shape of the bush.
Every year the bushes increase in size, the color of the foliage becomes brighter, the patterns on the leaves become clearer. You can see all the characteristic varietal characteristics only 3-4 years after planting, and at the age of 8-10 years, the plants will appear in full splendor. For example, white-bordered hosts do not fully show their color at a young age.
Botanical description of krinum
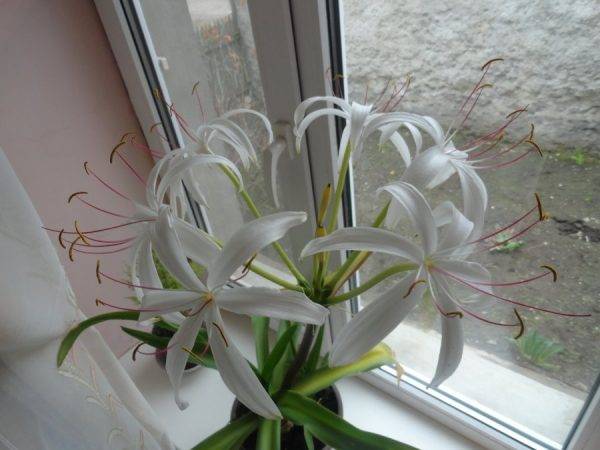


The perennial plant "crinis" means "hair" in Latin. It got this name due to the unusual shape of the numerous foliage. It is long (up to 150 cm), linear or xiphoid, so each leaf resembles a curl. The leaves of a young plant are somewhat different from an adult: initially they are rolled into a tube, and over time they straighten and become flat.
Umbrella-shaped inflorescences are located on the flower stem (up to 1 m). On them - flowers of pink or white with a raspberry tint. The diameter of each of them reaches 20 cm. The fruit of the krinum resembles a box in shape, in which there are seeds with thick pulp. Their shell is filled with a large amount of liquid necessary for the growth of the bulb of a young krinum flower.
The main distinguishing features of the krinum from other members of this family are its relatively large size. Almost all Amaryllidaceae have a small flower diameter and do not grow more than 50 cm.
Reproduction: when to divide and how to plant the host


Before planting a host, you need to know a few important points about this process. Hosts are propagated mainly by dividing the bush. The bushes are transplanted and divided in early spring before the leaves begin to unfold. The plant is dug up entirely, shaken off or washed from the ground and cut off by dividing with 2-3 buds. Slices are recommended to be sprinkled with crushed coal.
When to share a hosta - this question is often worried about novice growers. Do not rush and divide the young bushes - let them grow properly. The old bushes of the host are divided at the end of August. The delenki planted at this time will have time to give new roots and prepare for the arrival of winter.
With whom can you be kept?
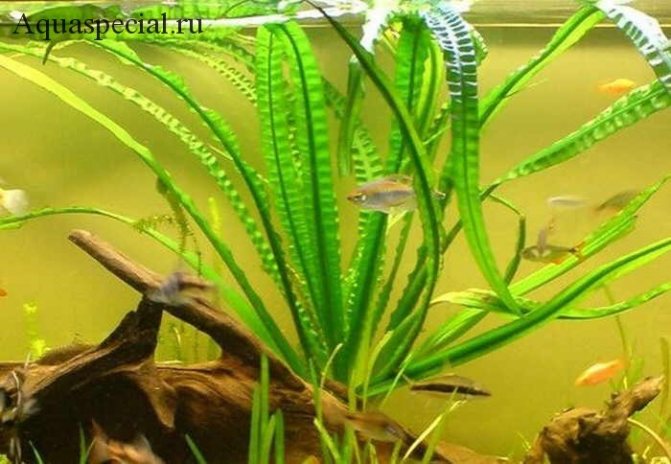
Even the largest and most active pets, who like to dig soil and dig up plants, will not be able to damage the crinum. Its bulbs are firmly rooted, and the leaves are so dense that they are completely unattractive even for herbivorous fish. As for neighboring plants, you should choose unpretentious species. Aquarium krinum grows very large and creates a large amount of shadow, blocking the light of the rest of the vegetation.


Why hosta leaves turn yellow and what to do about it
There can be several reasons why hosta leaves turn yellow, one of them is a dangerous virus. In recent years, a dangerous infection caused by the host X virus has spread rapidly around the world. Symptoms of the disease are usually most noticeable in yellow-leaved hosts. Gray or green spots appear along the veins of the leaves. Sometimes the leaves curl up and become wrinkled.
Virus X is transmitted through the sap of infected plants. This can happen when digging and dividing, pruning leaves and peduncles. Experienced amateur flower growers, in order not to spread the disease, be sure to disinfect their hands and tools after working with each, especially recently acquired, instance of the hosta.
What to do if the leaves of the hosta turn yellow - this question is asked by many concerned lovers of this plant. Unfortunately, the disease cannot be cured. Infected plants need to be dug up, trying to capture all the roots, and burned. The virus lives only in plant tissues and quickly dies in the soil, therefore, about a year after digging, when all the fragments of roots remaining in the soil rot, a new hosta can be planted in the vacant space.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Diseases of goslings: description, how to treat, symptoms
Reproduction of krinum at home
Propagates krinum using bulbs. They appear next to the mother's trunk, and gradually grow. When the time comes, the bulbs can be detached from the main plant and planted around the aquarium.
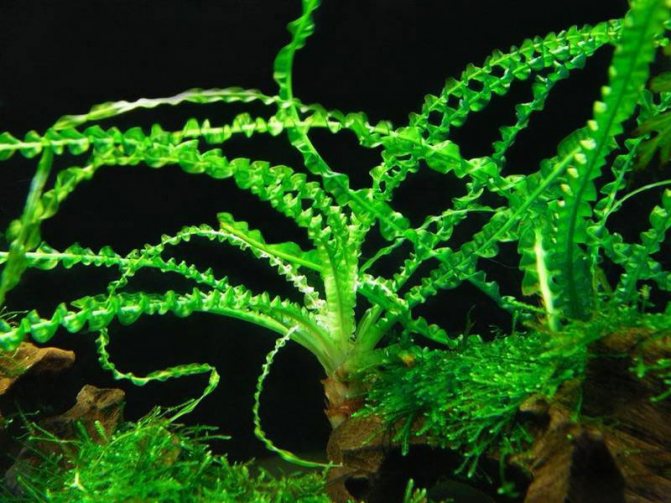


Increased circulation of water in the aquarium favors plant reproduction. If you turn on the water filters to the maximum, or install a pump, then the growth of baby bulbs should increase. However, in general, we can say that the new plant will grow rather slowly, and you will have to be patient before you have new large specimens. The larger your tank, and the more spacious the plant is in it, the more likely it is to produce more offspring. This will allow new bulbs to grow faster and more confidently in a large, spacious aquarium.
Spectacular host in the garden: landscape tricks (with photo)
Phlox in landscape design are good both on their own and in combination with other perennials: astilbe, tall bells, nivyans, daylilies. They are planted in massifs, groups, on bed-beds, flower beds, in mixborders. Phlox organically look in flower beds on the edges, along the banks of natural and man-made reservoirs, along streams. The path to the house looks beautiful if it is decorated with phlox on both sides.
Drummond's annual phlox is an integral part of the low, variegated country-style flower garden.
Low-growing varieties of phlox (up to 60 cm high) are most often used for borders, tall ones (up to 180 cm) can be planted as a backdrop.
Perennial phloxes have been widely used in cutting in recent years. They are effective in combination with gypsophila and asparagus. To keep them decorative for a longer time and not crumble, add half a tablet of aspirin or 2-3 drops of vinegar essence to the water. Half-fill the vases of water, change the water and cut the stems daily, making an oblique cut.
Output
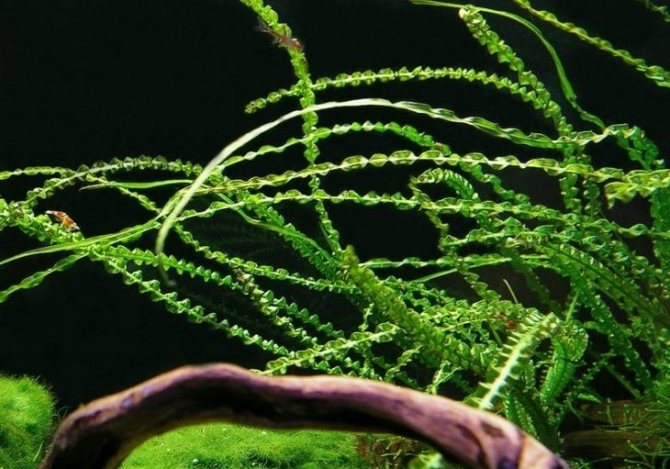
Krinum wavy - although a fragile plant, it has a number of advantages over other algae:
- Attractive and aesthetic appearance of the socket;
- The ability to bloom;
- Not eaten by fish;
- If the conditions are met, it is able to reproduce by budding, which means that, having bought one plant, you can multiply it over time, which is very beneficial.
- Can grow in slightly salted water.
The conditions that this aquarium algae requires are not so harsh. Almost every 3rd type of domestic fish requires the same.
Powdery mildew on phlox: how to process a flower
What phlox looks like: a perennial plant with erect, branchy shoots, lignified in the lower part. An important characteristic of the varieties of phlox paniculata is the shape of the bush and its height, which determine the nature of the use of plants when planting in flower beds. Plant height ranges from 40 to 180 cm.
Phlox inflorescences are multi-flowered (up to 80-100 flowers), paniculate, 15-30 cm in diameter, are very large. The size of the corolla in varietal phlox varies from 1 to 5.5 cm, while the size of the flower does not have a decisive effect on the decorativeness of the variety. Large flowers are more susceptible to adverse weather conditions (wind, rain), while plants with small flowers are more resistant to the vagaries of the weather.
The garden phlox lacks only blue and yellow coloration. Many varieties are bicolor with a dark or light spot in the center. Flowers are predominantly bright colors. The main tone of the corolla can change under the influence of some environmental factors (soil composition, light intensity, precipitation).
Powdery mildew on phlox is the main scourge of this flower. First, a white bloom appears on the lower leaves, then on the upper, younger ones. The diseased leaves gradually dry out. The bushes suffer especially strongly during a thickened planting, when there is no ventilation, therefore, it must be borne in mind that phlox bushes grow strongly, and plant them at a distance of 70-80 cm from each other.
All gardeners need to know how to treat phlox from powdery mildew. There are several effective solutions.
Sick plants are treated with a copper-soap solution once every 10 days (25 g of copper sulfate and 100 g of laundry soap per bucket of water).
Can be treated with a 0.5% solution of Bordeaux liquid or another approved copper-containing preparation. For prevention in early spring, when phloxes are just beginning to grow, it is advisable to dust the plants with colloidal sulfur. Colloidal sulfur powder is poured into a gauze bag and carefully, through gauze, each growing stem is powdered. After 10 days, when the plants reach a height of 15-20 cm, re-dusting is carried out.
Types of indoor krinum
Scientists have described more than 150 species of evergreen krinum. In room culture, the following types are most popular.
Asian crinum (C. asiaticum), a bulb up to 10-15 cm in diameter. Wide leaves of a curved shape, with a whole edge, about 120 cm. Inflorescence of 20-50 fragrant snow-white flowers, with elongated narrowed petals. Researchers believe it comes from water bodies in West Africa.
Krinum beloved (C. amabile), medium-sized bulb. Leaves are on average 25-30, a meter and a half long. The inflorescence umbrella contains about 30 flowers. Red flowers shimmer with purple and white shades, very fragrant. Straight petals, their inner side is white, 10-15 cm long. Decorated with purple stamens. Flowering usually occurs in March, sometimes blooms again. The homeland is the distant forests of Sumatra.
Crinum Moore (C. moorie), leaves of a light green hue, they have a special pattern of thin veins of about 90 cm.The bulb is about 20 cm in size. The flower of such a krinum can be seen in the photo: snow-white, sometimes pinkish flowers, in the form of bells, placed in 6-12 pieces.
Crinum bulbous: grows up to 80 cm in height. With wide curved leaves, with a wavy edge, flowers on elongated cuttings, the color is light pink or white. The petals are decorated with a wide red stripe.
Crinum Powell: is a hybrid obtained from crossing Moore's krinum and bulbous krinum. The bulb is spherical, up to 15 cm in diameter. Belt-like leaves up to 100 cm in length.It blooms with an inflorescence of 8-12 bright pink or white bells.
Crinum Abyssinian (C. abyssinicum). Grows in the mountainous regions of Ethiopia. The bulb is oval, 7 cm thick, with a short neck. Leaves tapering upward, usually in the amount of 6 pieces, rough edges, length 30-45 cm, width 1.5 cm.
Big krinum (C. giganteum). A large bulb, veins create a pronounced pattern on the leaf, the leaves themselves fall in waves downwards, 60-90 cm long. The flowers are white, with a distinct odor, 20 cm long. The peri-colored tube is gracefully curved, 10-15 cm. It blooms best in summer.
Crinum American (C. americanum). In room conditions, it is quite rare - because of its size. More suitable for a conservatory or a large room.
How to grow phlox: growing conditions
Before growing phlox, you need to study the requirements for soil and lighting. Phlox paniculata is undemanding to lighting. Grows well both in the sun and in partial shade. It is better to plant varieties with red and raspberry color in partial shade so that the flowers do not fade. Phlox are moisture-loving and need watering during the season. In arid conditions, flowers and inflorescences become smaller, leaves fall.
Plants thrive on any cultivated, neutral (pH 6.5-7) garden soil. Heavy clayey soils with poor permeability and stagnant water are undesirable. They prefer dry areas, grow well and bloom on sandy and rocky soils.
Grow best in sunny areas that are shaded at noon. The soils should be well moistened, but with a low groundwater table.
Content
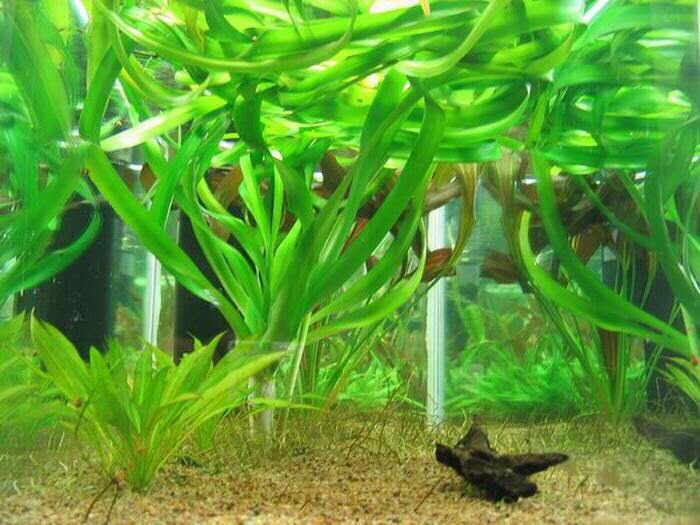
Due to its size, keeping krinum in an aquarium will require a lot of storage. The optimal water level will be about 1 meter.
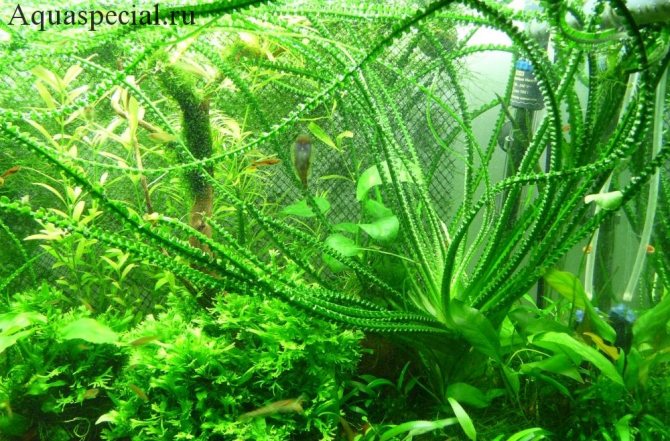


To create a comfortable environment for krinum, several rules must be considered:
- Carefully consider the planting site of the plant, since it does not respond well to transplants from place to place;
- Provide flora with adequate and high-quality lighting;
- Plant roots in fine soil - sand, small pebbles;
- Install a filter to purify water and create a small current;
- Adhere to a temperature range of 20-27 degrees and a hardness of 6-8 dGH;
- Siphon the soil regularly and carry out weekly water changes;
- Thinning the plant periodically, removing old and damaged leaves;
- In order for the krinum to bloom, it will be necessary to soften the water and increase the supply of oxygen.
Krinum needs good lighting, but this can cause harmful algae to grow in the aquarium. To avoid this problem, it is recommended to add a small flock of Labeos, algae eaters, or a couple of Ancistrus. They will scrape off algae from the surface of the leaves, thereby providing them with access to vital light.
How to feed phlox and other agricultural practices (with video)
The question of how to feed phlox for their healthy growth and lush flowering is asked by many amateur gardeners. Care during the season provides for 2-3 top dressing: in early spring, phloxes are fed with a solution of ammonium nitrate or urea at the rate of 20-30 g per adult bush with the addition of superphosphate and ash, in the second half of May and in mid-June - with a solution of nitrogen fertilizers only, and in In July, superphosphate is added to them again (15 - 20 g per bush). The introduction of micronutrients (iron, boron, magnesium, manganese) during the period of plant regrowth has a beneficial effect on flowering.
Caring for phlox during the season involves pinching the shoots. As a result, the plant branches and blooms longer. Phlox is a moisture-loving culture; in dry summers, they need frequent and abundant watering. In dry hot weather, phlox are watered 2-3 times a week (10 liters of water per bush) and loosen the soil.
Another important agricultural practice will tell you how to care for phlox in the fall.Closer to autumn, some bushes bulge out of the soil, their root system is exposed, so each adult bush must be spud with a bucket of humus or nutrient mixture. Adding soil to the roots is also protection from freezing in harsh winters. In autumn, the stems with leaves must be cut off at soil level, and the remaining plants and the soil around them should be sprayed with 1-2% Bordeaux liquid.
In the fall, after freezing, the soil, the shoots of phlox are cut off. Phloxes usually hibernate well, but some varieties are less resistant. It is recommended to cover such plants for the winter with peat, fallen leaves or spruce branches.
Crinum transplant and substrate
You should not change the containers for krinum too often. These plants can be replanted once every 2-3 years. The transplant is carried out just before the beginning of growth, but before the first signs of growth appear, at the end of the resting phase.
It is believed that krinum can be grown in any soil mixture, as long as it is sufficiently loose. Crinums can even be grown in ordinary garden or vegetable garden soil, they thrive in any universal substrate or special soil for amaryllis. But the better the soil mixture is, the higher its air and water permeability (and the less the risk of compaction), the better. If you are mixing the substrate yourself, take equal parts of sand, deciduous soil and humus and 2 parts of turf soil, or mix equal amounts of greenhouse soil, leaf soil, and sand.
The krinum bulb is removed carefully, all roots are freed and examined. Damaged or dry roots must be removed, as well as dry films from the bulbs. In a new container, the bulbs are placed so that about 1/3 rise above the ground. A thick layer of drainage must be laid on the bottom of the pots (expanded clay is preferred).
Containers for krinum should be selected from among the spacious ones. Crinum is not picky about materials, but very much about width. Since a large bulb grows in breadth and produces superficial roots, low, wide containers are chosen for krinum, rather than standard high ones.
Reproduction of phlox - cuttings, division and root shoots
In one place, phlox grows for 5-6 years, then its flowers and leaves become smaller, and division and transplantation are necessary for rejuvenation. Propagation of this culture by cuttings, root shoots, dividing the bushes.
Reproduction of phlox by cuttings is the most popular and uncomplicated method. The best time for cuttings in the middle lane is the first half of May. 1/3 of the shoots can be cut off without harm to the plant. 2-3 cuttings are obtained from each shoot. The lower cut is made under the sheet, and the upper cut is 0.5 cm above the sheet. The leaf blades are removed by half to reduce evaporation. Cuttings taken with part of the rhizome take root well.
Cuttings are planted in film or glass greenhouses. First, a good nutritious soil is poured into them with a layer of 5-7 cm, then a layer of sand 2-3 cm. The cuttings are planted obliquely at a distance of 10 cm from each other, 15-20 cm between rows so that the leaves of the cuttings do not touch.
In the first 2-3 weeks after planting, the cuttings are sprayed with water 4-5 times a day. After about 3 weeks, white juicy roots are formed, and by autumn a strong planting material is ready, which can be planted in flower beds.
Reproduction of phlox by dividing overgrown bushes is another simple way. It is necessary to divide them into small parts, be sure to remove dead diseased pieces of the old rhizome. The bushes are divided in early spring before bud break or in autumn in early September. Each division should have 2-3 shoots and a root segment at least 10 cm long.
Some varieties of phlox easily form adventitious buds on the roots and give abundant root growth. The shoots are separated from the mother plant and grown on ridges with light fertile soil.
Tags: disease, pest, crinum
About
«Previous post
Reproduction
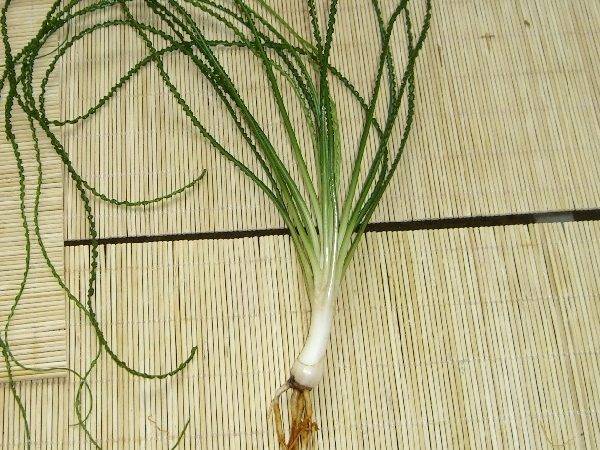


Crinum propagates by bulbs or seeds.
- The seed method is almost never used. There is a risk that the seeds will not sprout.
- The bulbous method is much easier. The daughter bulb is planted in a small pot (up to 20 cm in diameter). The capacity is not changed during the year. With an increase in the root system, a larger pot is chosen. Watering and proper fertilization are important for normal growth and development. The first flowering occurs in the 3-4th year after planting the bulb.
Important! There is no need to rush to cut the daughter bulbs from the mother. Their number directly affects the nature of flowering. It is abundant if there are many bulbs.
General information
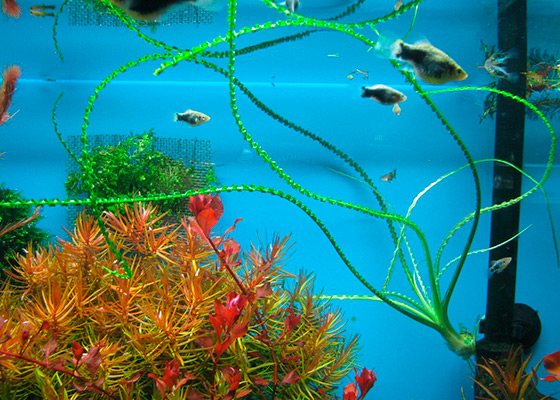


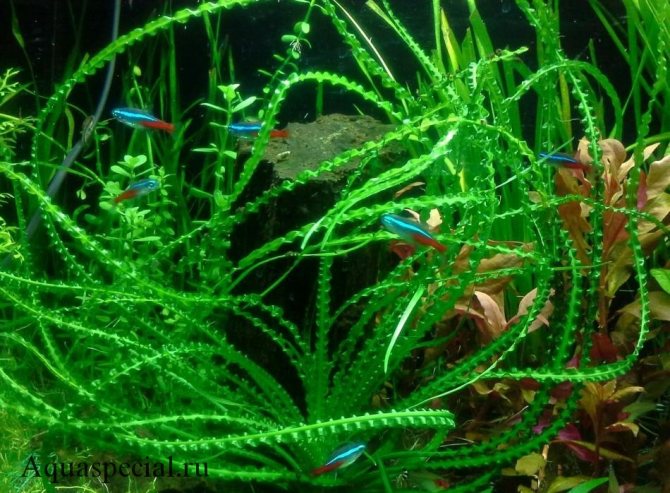
The peculiarity of keeping all types of aquarium krinum is that they love running water. If your aquarium does not have a circulation pump, then you should not start Crinum.
This grass significantly suspends the silting of the bottom, actively absorbs carbon dioxide that is formed in the water.
Aquarium species are considered unpretentious. However, of course, there are comfortable conditions for them. In particular, the water temperature is considered the best in the range from 19 to 26 degrees. The water should be neutral or slightly alkaline. Water hardness should be between 6.5 and 7.5 units. Be sure to install a circulation pump and an air compressor. Under such conditions, the grass will develop successfully and please with a wonderful view.
What have we learned
If you are an experienced florist, you can try to grow krinum in your backyard. This venture is difficult and risky, but at the same time, interesting. Just imagine how the look of your flower bed will change if such a resident appears on them. It is important to pay attention to the competent care of the krinum flower, and to create all the conditions so that even in northern Russia it feels at home.
Now read:
- Do-it-yourself correct cultivation of Adenium succulent
- How to create hanging gardens in an apartment with indoor vines
- Variety of shapes and colors of Calathea from the Marantov family
- Care, feeding at home of a predatory Dionea
About
Leading Researcher of the Laboratory of Vegetable and Berry Crops, Yakutsk Research Institute of Agriculture, Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Main types
Crinum abyssinicum
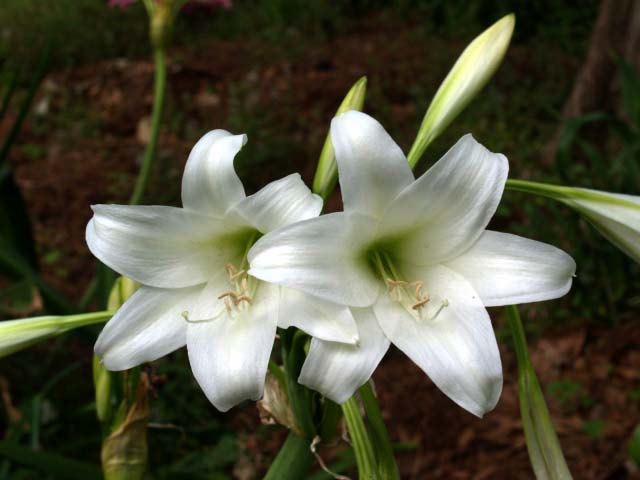


With a short neck, the bulb has a rounded-elongated shape, and its thickness is 7 centimeters. 6 leaves of a linear shape gradually taper towards the apex. Such leaves with a rough edge can be 30 to 45 centimeters long and 1.5 centimeters wide. The length of the peduncle is 30–40 centimeters, while it bears an umbrella-shaped inflorescence with 4 to 6 flowers. White sessile flowers have short stalks. The thin tube of the perianth reaches a length of 5 centimeters. The elongated petals are 2 centimeters wide and 7 centimeters long. Homeland are the mountains in Ethiopia.
Asian Crinum (Crinum asiaticum)
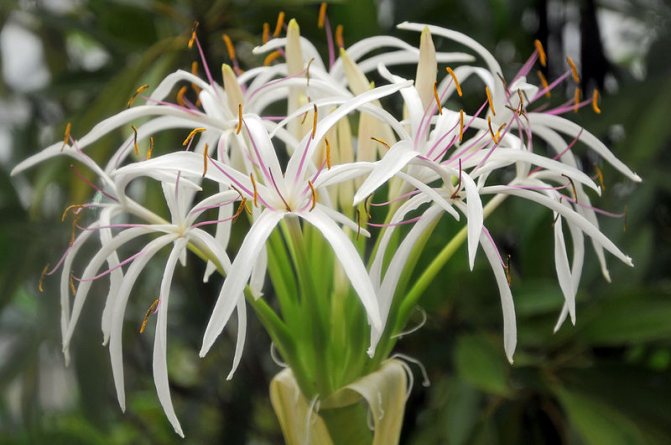


The width of the bulb is 10-15 centimeters, and the length of its neck can vary from 15 to 35 centimeters. There are from 20 to 30 thin, whole-edged, belt-shaped leaves, the length of which is 90–125 centimeters, and the width is from 7 to 10 centimeters. The umbrella-shaped inflorescence bears from 20 to 50 non-fragrant flowers, which are perched on three-centimeter legs. A straight perianth tube 10 centimeters long has a light green pattern on the surface. Length of linear white petals 5-10 centimeters, reddish stamens diverge in different directions. Long bloom from March to October. The homeland is the stagnant reservoirs of Western Tropical Africa.
Big Crinum (Crinum giganteum)
The bulb, which has a short neck, is quite large. So, its width is 10-15 centimeters. Veins are distinctly protruding on the surface of the wavy green leaves. The length of the leaf is 60–90 centimeters, and its width is 10 centimeters. The length of a rather strong peduncle is from 50 to 100 centimeters.It bears an umbellate inflorescence, usually consisting of 4-6 flowers, but there are also 3-12 flowers. The length of the fragrant seated flowers is 20 centimeters. The curved, elongated, light green perianth tube has a length of 10 to 15 centimeters, while its pharynx has the shape of a bell and is 7–10 centimeters long. The width of the white petals is 3 centimeters, and the length is 5–7 centimeters, while the stamens of the same color are somewhat shorter. As a rule, flowering occurs in summer.
Crinum augustum
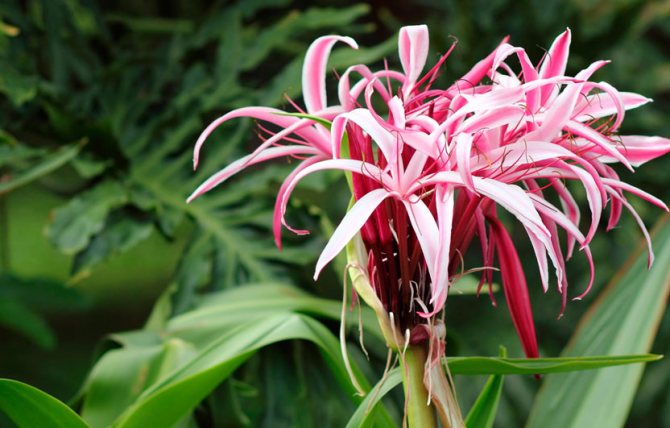


The bulb is 15 centimeters wide and its neck is 35 centimeters long. There are many dense belt-shaped leaves, the length of which is from 60 to 90 centimeters, and the width is from 7 to 10 centimeters. The upper part of the flattened peduncle is colored dark red. The inflorescence is in the shape of an umbrella and bears, as a rule, more than 20 pleasantly smelling flowers, which sit on short pedicels. The reddish strong perianth tube is slightly curved or straight in length reaches 7-10 centimeters. The outer surface of erect lanceolate petals has a deep red color. Their length is 10-15 centimeters, and their width is from 1.5 to 2 centimeters. Expanded stamens are colored red. Flowering is observed in spring and summer. Homeland are the rocky mountain slopes of the Seychelles and Mauritius. Grown in warm greenhouses.
Crinum maiden, or virginian (Crinum virgineum, or virginicum)


It has a large brownish bulb. Thin belt-shaped leaflets taper both to the apex and to the base, on their surface transverse veins clearly protrude. The leaves are 7-10 centimeters wide and 60 to 90 centimeters long. The peduncle bears an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, consisting of 6 flowers, which are sessile or have short pedicels. The length of the curved light green perianth tube is 7 to 10 centimeters. In this case, the white petals have the same length. As a rule, flowering is observed in the fall. Originally from South Brazil. Grown in warm greenhouses.
Crinum campanulatum
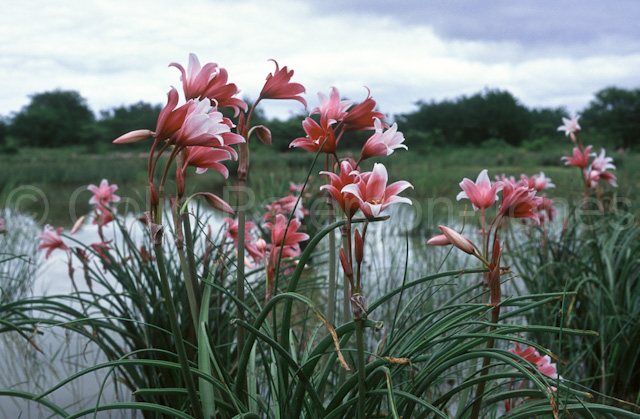


The small onion is oval in shape. Grooved, linear leaves with a sharp edge in length reach 90-120 centimeters. A narrow green peduncle bears an umbellate inflorescence, consisting of 4-8 flowers, located on short pedicels about 2 centimeters long. An elongated, sinuous, cylindrical perianth tube reaches a length of 4-6 centimeters, and there is also a campanulate pharynx. There are greenish stripes on its red surface. The petals are very close to each other. At the base, they are white with reddish stripes, and then the color becomes pink-green-red. Flowering is observed during the summer months. Originally from the Cape Province in South Africa, where it prefers to grow in ponds.
Crinum amabile
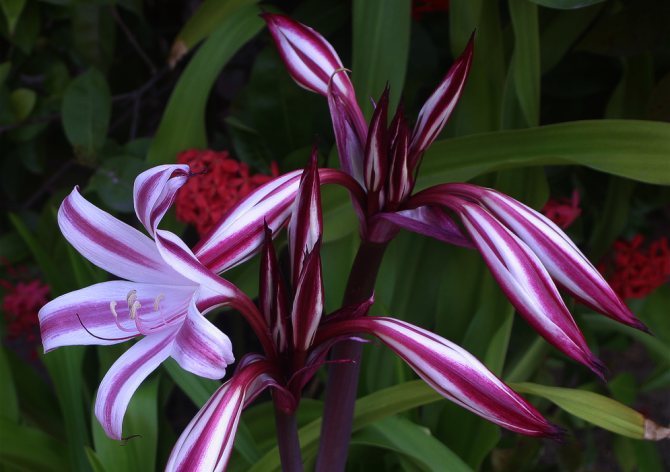


A not very large bulb has a neck 20 to 35 centimeters long. 25–30 entire belt-shaped leaflets are 100–150 centimeters long and 7–10 centimeters wide. The umbrella-shaped inflorescence consists of 20-30 flowers, they sit on pedicels, the length of which is 2-3 centimeters. Fragrant deep red flowers have a whitish or purple hue. The length of the dark purple straight perianth tube is 8 to 10 centimeters. The inner part of linear petals is white, their length is 10–15 centimeters, and their width is 1–1.5 centimeters. The wide stamens are purple in color. Flowering is observed in winter, but most of all in March. There may be repeated flowering. It can be found in wetlands, as well as in the mountainous regions of Sumatra.
Crinum reddish (Crinum erubescens Aiton)


The oval-shaped bulb is up to 10 centimeters wide. Many belt-like leaves reach 60 to 90 centimeters in length and 5 to 8 centimeters in width. The edges of the seamy side of the leaves are slightly rough.The peduncle is very long (60 to 90 centimeters). It bears 4-6 large fragrant flowers, which can be either sessile or have short pedicels. The outer part of the flower is red and the inner part is white. The erect, light-red perianth tube reaches a length of 10-15 centimeters. Petals are lanceolate, reversed. Flowering is observed during the summer months. Originally from tropical America.
Crinum pratense
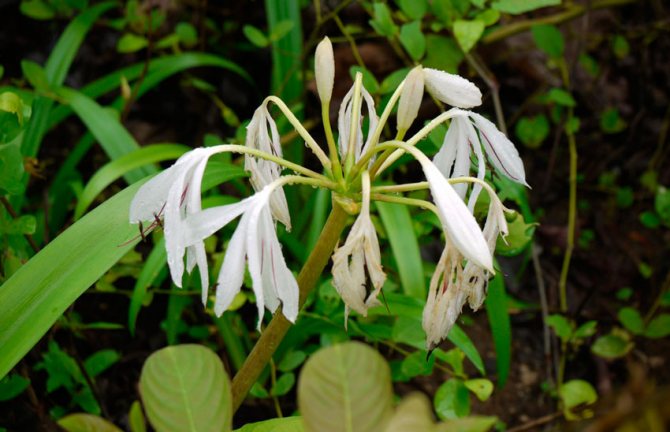


The egg-shaped bulb has a short neck and reaches a diameter of 10 to 15 centimeters. As a rule, there are 6-8 linear leaflets, which reach 45-65 centimeters in length. The peduncle is 30 centimeters long and 1.5 centimeters wide. Umbellate inflorescence bears from 6 to 12 white sessile or on short stalks of flowers, which reach 7-10 centimeters in length. The width of the lanceolate petals is 1.5 centimeters, and their length is the same as that of the tube. The red stamens are widened. Flowering is observed during the summer months. Originally from East India.
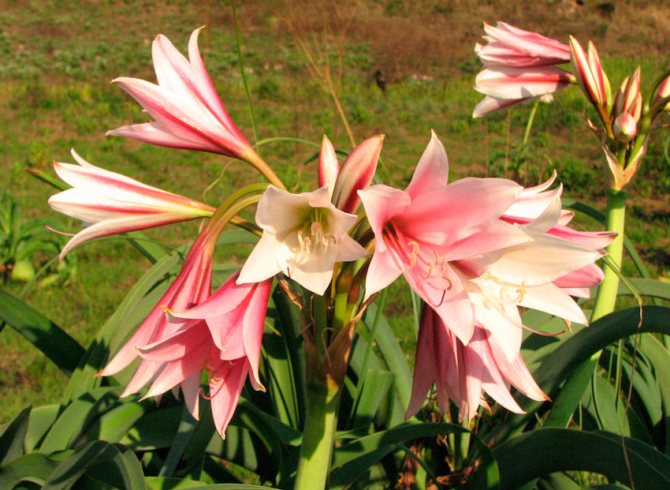
Crinum bulbispermum or Crinum capense


The onion has the shape of a bottle, while it has a narrow and long neck. Greenish-gray narrow-linear, grooved leaves reach 60–90 centimeters in length. They are directed upwards and have a rough edge. The almost round peduncle can be over 40 centimeters long and bears 4 to 12 flowers. Large fragrant flowers are white (sometimes with a purple tint). They are located on pedicels, the length of which is from 3 to 5 centimeters. The slightly curved cylindrical tube of the perianth is 7 to 10 centimeters long and has a whitish funnel-shaped edge. The outer surface of the 3 outer petals is colored pinkish-purple (sometimes white). Their length is 7-10 centimeters. Flowering is observed in July and August. Originally from South Africa, where it prefers to grow in shady areas with sandy soil. Grow in cold greenhouses.
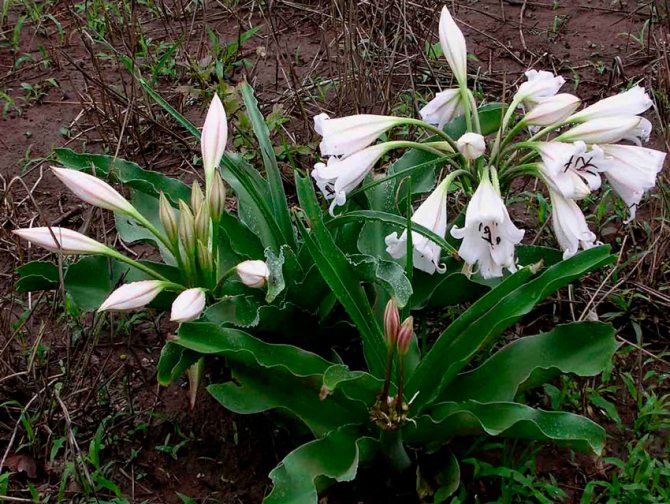
Crinum macowanii


A large round bulb in diameter reaches 25 centimeters, the length of its neck is also 25 centimeters. The width of the leaves is 10 centimeters, and their length is from 60 to 90 centimeters. The height of the peduncle is 60–90 centimeters. It bears an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, consisting of 10-15 flowers. The length of the greenish curved perianth tube is 8–10 centimeters. The pink petals are 8 to 10 centimeters long. Bloom in late autumn. Homeland - rocky mountain slopes in Natal (South Africa). Grown in cold greenhouses.
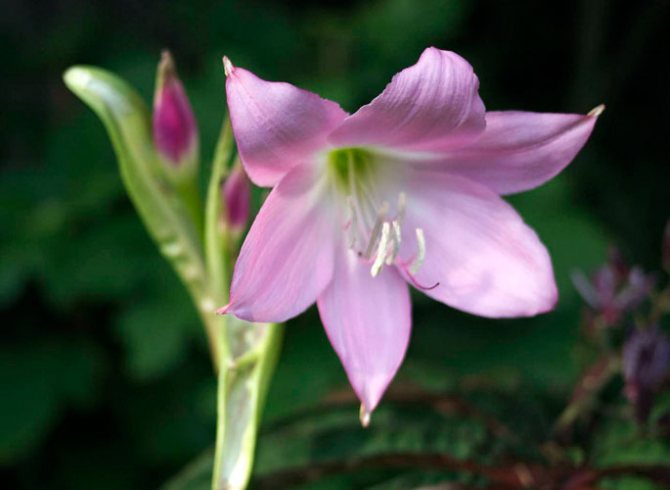
Crinum moorei


A large onion has a diameter of about 20 centimeters, and its neck can be up to 45 centimeters long. Many babies can form. There are from 12 to 15 wavy, belt-shaped leaves, the length of which is 60-90 centimeters, and the width is from 6 to 10 centimeters. On their surface there are embossed veins, and their edges are pale white smooth. The length of a powerful greenish peduncle is from 45 to 60 centimeters. It bears an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, consisting of 6-10 flowers. Pink flowers have pedicels eight centimeters long. The curved perianth tube is 7 to 12 centimeters long and has a funnel-shaped pharynx. The petals are 4 centimeters wide and 7 to 12 centimeters long. The light pink stamens are not as long as the petals. A pistil protrudes above the petals. Flowering is observed in the summer. It is most popular with florists. In nature, it is found on rocky mountain slopes in Natal (South Africa). Grown in cold greenhouses.
Crinum Powell (Crinum x powellii)
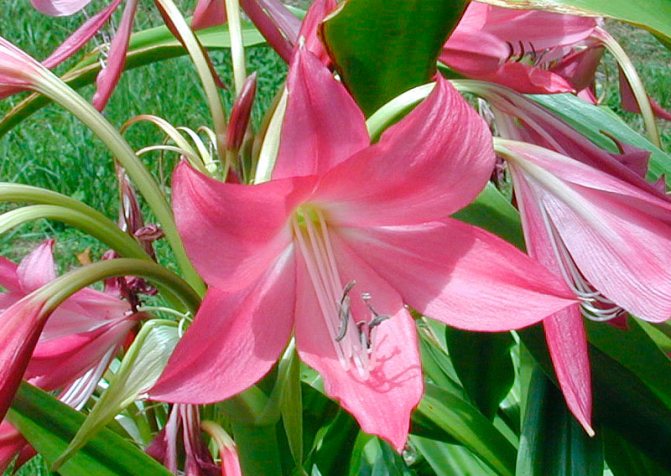


This hybrid is obtained by crossing Moore's krinum and bulbous krinum. The spherical bulb has a diameter of 15 centimeters. The length of the belt-like leaves is up to 100 centimeters. A meter-high, leafless peduncle bears an umbrella-shaped inflorescence, which consists of fragrant flowers with a diameter of 15 centimeters. The color of the perianth is deep pink.
Crinum pedunculatum


The bulb is 10 centimeters thick and its neck is 15 centimeters long. There are from 20 to 30 leaves, the length of which is 90–120 centimeters. Flowers are collected in umbrella-shaped inflorescences, 20-30 pieces each. Fragrant whitish-green flowers have pedicels 2.5-4 centimeters long.The corolla tube is longer than the petals; there are reddish expanded stamens. Flowering is observed during the summer months. Originally from Eastern Australia. Cultivated in cold greenhouses.
Ceylon ceylon (Crinum zeylanicum)


The diameter of a round bulb is from 12 to 15 centimeters, there is a short neck. There are 6–12 thin belt-like leaves that reach 7–10 centimeters in width and 60–90 centimeters long. Their edges are slightly rough. The length of the powerful reddish peduncle is 90 centimeters, it bears an umbellate inflorescence with 10–20 flowers with short pedicels. The length of the drooping green or red perianth tube varies from 7 to 15 centimeters and has a pharynx that is placed horizontally. The width of the lanceolate-elongated petals is 3 centimeters and their upper part is horizontally spread. They are dark purple in color, have a whitish edge, and have stripes on the outside. The stamens are shorter than the pistil. Blooming is observed in spring. Originally from Tropical Asia. Grow in warm greenhouses.
Crinum scabrum


The diameter of the round bulb is 10-15 centimeters, the neck is short. Dense, wavy, grooved, glossy leaves are belt-shaped and green in color. They have a sharp edge and are 60–90 centimeters long and 5 centimeters wide. The powerful peduncle bears an umbellate inflorescence with 4–8 fragrant flowers, which can be sessile or have short pedicels. The length of the bent pale green perianth tube is 8 to 15 centimeters. The diameter of the throat is 6–8 centimeters. The petals range in width from 2.5 to 3.5 centimeters. Their upper part is white, and in the middle there is a wide stripe of bright red color. Blooming is observed in May and June. Originally from Tropical Africa. Grown in warm greenhouses.
Crinum broadleaf (Crinum latifolium)


The width of a round bulb is from 15 to 20 centimeters, there is a short neck. Many thin belt-like leaves are colored green. They are 60–100 centimeters long and 7–10 centimeters wide. The umbrella-shaped inflorescence has 10–20 flowers on short stalks. The length of the green curved perianth tube is 7–10 centimeters. The pharynx is horizontal and has the same length as the tube. The lower surface of the thirty-centimeter elongated-lanceolate petals is light red. Blooms in August and September. Originally from East India. Grown in cold greenhouses.
Growing methods
Seed method
Seed propagation of krinum is laborious and troublesome, and flowering with this method of cultivation does not occur earlier than after 4 years. Large, fleshy seeds do not require any preparation for planting, as they are saturated with sufficient moisture for rapid germination. It is recommended to sow each seed in a prepared hole, one at a time in a small flower container.
The most suitable substrate for planting seeds consists of equal parts of peat and coarse sand. Planting depth is about 1-1.5 cm. When greenhouse conditions are created, small bulbs are formed from seeds, which are later used for planting in open ground.
Growing from bulbs
Planting material
The bulbs can be detached from the root of the mother plant or purchased from flower shops. After separation, it is recommended to sprinkle the places of cuts or breaks with charcoal or activated carbon, which will prevent the appearance of rot.


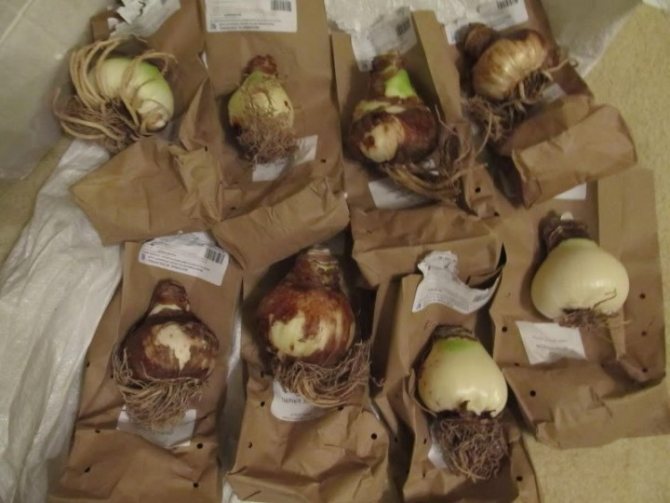
When buying, you should pay attention to the size and external characteristics. Crinum bulbs should be rounded or slightly elongated in shape and covered with light scales. The average diameter is 15-20 cm.
How does a swamp lily behave in winter
For many gardeners, it remains a mystery how the krinum can behave in winter. Krinum is a greenhouse plant that needs moisture and warm temperatures.Is it really capable of withstanding the Russian frosts? Krinum can tolerate wintering well if the gardener has previously completed all the necessary activities. To do this, you need to start preparing in early autumn.
Shelter is being made for the bulbs. It should consist of one small layer of peat, and the next layer consists of straw or other mulch. Such a layer should reach a height of about 50 centimeters. Over time, under the weight of the snow, this slide will settle. In the spring, the entire cover over the bulb is removed, and they already wake up in the sun. It is important here that the bulb does not rot. Therefore, it is good to cleanse it of flowers, leaves, weeds that grow nearby.
If you live in central Russia or the northern part, where winters are quite harsh, and temperatures can drop below 25 degrees, then it is better to dig up the bulbs. They need to be dried well in the shade, then put in the refrigerator.
If the plants are grown in pots and containers, then the krinum is placed in a cold room, where the temperature in winter does not drop below five degrees. If the temperature nevertheless approaches zero degrees, it is better to cover the flowers with special warm materials. Plants are not watered, only occasionally sprayed from a spray bottle.
Some gardeners tend to leave the krinum in the ground for the winter, thus improving its immunity. Others, on the contrary, do not want to take risks, dry the onion and then send it to the refrigerator. This is the most humane means of flower preservation.


How to transplant and propagate crinum
After three to four years of flowering, the bulb does not just die off. She leaves offspring that can be planted in new places and multiplied. It is better to plant babies during the period when the bulb is at rest. This is the moment when the flowering has already passed, and the bulb is preparing for hibernation. But some gardeners take a risk, they do not want to do this procedure until the onset of flowering:
- To carry out such a procedure, it is imperative to dig out the mother bush;
- Branched parts are separated from it, seated in the necessary places or in pots. This procedure must be carried out carefully, because there is a great risk of damaging not only the main bulb, but also small shoots.
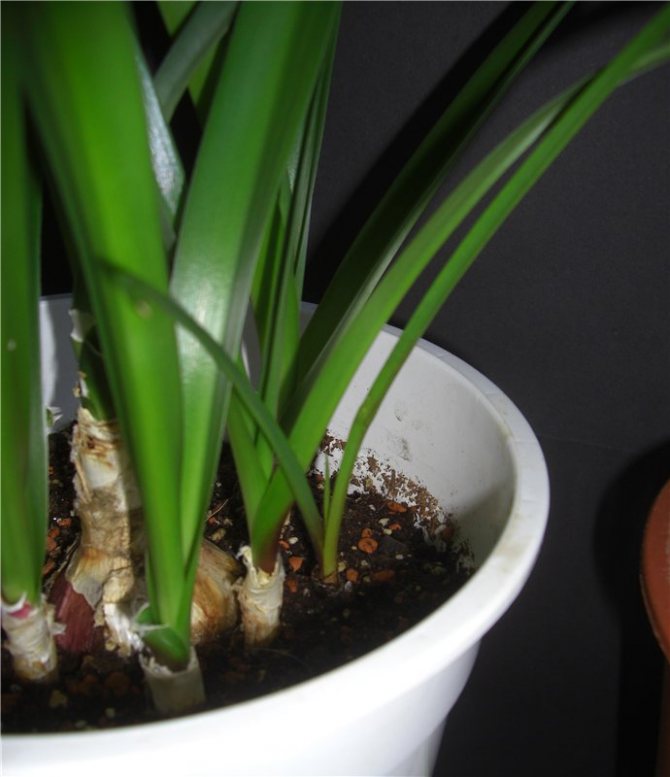


Shoots grow well in the presence of feeding and fertilization and have time to grow well in just one season. By the time winter comes, they are ready, and are unlikely to be able to die from the cold. When branching children from the mother bush, it is important to be careful. One wrong mechanical action, and the main bush can damage, the same goes for small shoots.
Popular: Bright anemone flower (anemone) for growing in the garden
Description and appearance of the plant
The name "krinum" unites a huge number of plant species from the Amaryllis family. They are able to grow not only in water, but also on land, and are sometimes found in mountainous areas above 1000 m above sea level. But only one and a half dozen species have adapted to living in fresh water bodies.
All of these plants have a number of common traits, for example:
- long narrow leaves of dense structure;
- stalk thick at the base, tapering upward;
- powerful roots in the form of scaly bulbs.
Krinum flowers, which are considered one of the most beautiful among such plants, deserve special attention. They rise above the surface of the reservoir, located 2-3 pieces on one shoot. The color of the petals depends on the type of plant, and the flowering period lasts from 1 to 6 weeks.
The length of the krinum stems is determined by the variety, as well as the number of leaves on the bush. Most of the aquarium varieties of culture are characterized by unpretentiousness and a long lifespan, due to which they have gained great popularity.
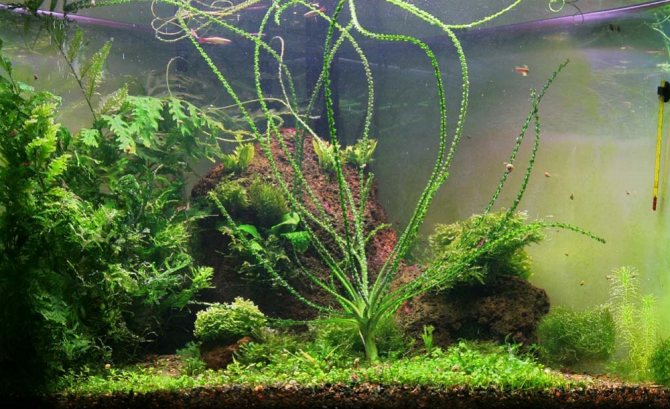


There are several different types of Krinum that can grow in fresh water.
Important! Since the crinum is a bulky plant, it should be placed in large and tall aquariums, the culture normally feels at a depth of at least 1 m.
Planting and caring for crinum
- Landing: planting bulbs in open ground - in April or May.
- Bloom: from spring to autumn.
- Lighting: bright sunlight.
- The soil: loose, rich in humus, well-drained, sandy-loamy.
- Watering: regular: during the period of budding and flowering, the soil should be slightly damp all the time.
- Top dressing: twice a month with mineral and organic solutions alternately.
- Reproduction: seeds and bulbs.
- Diseases: anthracnose and staganosporosis (red burn).
- Pests: mealybugs, scale insects, spider mites.
Read more about the cultivation of krinum below.
Garden crinum in winter
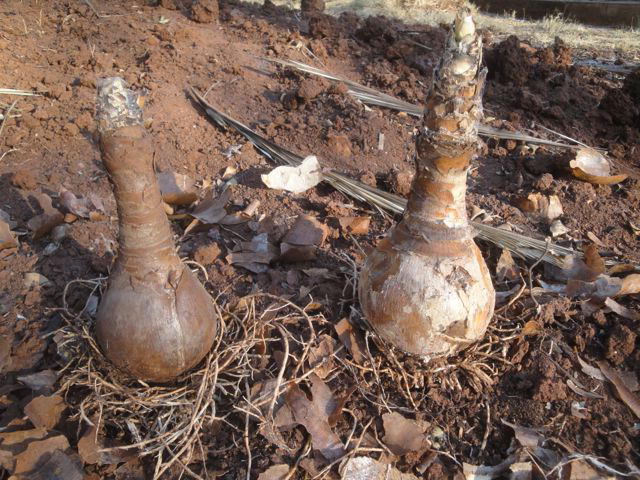


Krinum bulbs ready for wintering photo
Wintering krinum is possible only with the vigilant care of the grower. In autumn, it is necessary to cover the bulbs from a thick layer of peat or replace the mulch with straw up to half a meter thick (then it will settle). In the spring, as soon as the frosts pass and the snow melts, the mulch is removed so that the bulbs quickly wake up and do not rot.
If you have frosty winters, dig up the bulbs, dry them lightly in the shade and store in the refrigerator in the vegetable compartment. Garden krinums can also be simply transplanted into pots and placed in a cool, dark place, and contain plants without watering.
Plants grown in containers are brought into cold rooms, where in winter the temperature will be around 5 ° C. If there is a threat of lowering to zero, it is imperative to cover with warm covering materials.
By the way, some gardeners prefer not to risk it, because after the flowering of the krinum, the rainy season may well begin, which can provoke rotting of the bulbs. Therefore, krinums are dug up, cut off, dried in the shade and sent to storage in a cool dry room (you can sprinkle the bulbs with dry sawdust and store in boxes at + 5 ° C).
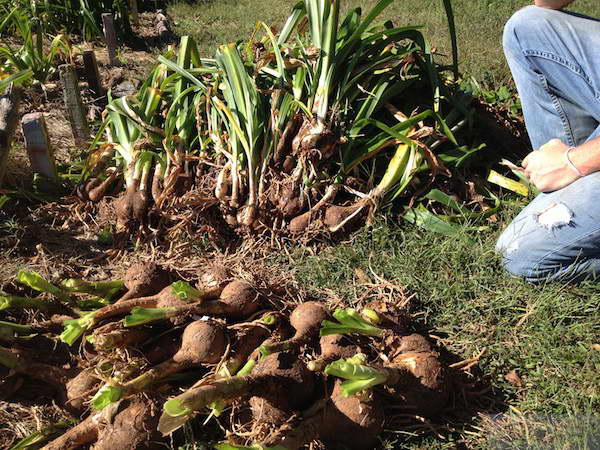


Preparing krinum bulbs for photo storage
How to plant and transplant a potted indoor krinum


The pot and soil for adult specimens should be changed once every 3-4 years. This should only be done during resting time of the plant. Landing is carried out this wayso that the bulb is half above the soil level.
Use only a deep container for krinum. This is due to a well-developed root system. A drainage layer should be laid at the bottom of the flowerpot, which can be used as crushed red brick, pebbles or expanded clay.
This video shows how the Asiatic krinum blooms and how to transplant the plant correctly.
Planting a flower in open ground
Depending on the type of krinum, you need to choose the right place. Drought tolerant plant, - the place is spacious, there is a lot of sun and almost no shade, without wind and drafts.
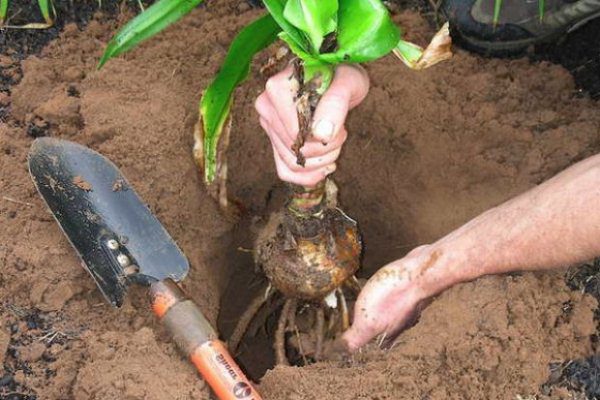


Planting Krinum in open ground.
We try to provide suitable humid conditions for plants of a moisture-loving variety, with warmth and light, but not in the sun itself, without drafts, in a protected area from the wind.
In order to get a strong and powerful plant, it is recommended to plant the bulbs in pots in early spring.
With the onset of warm weather, around the end of April-May, we prepare open ground for transshipment of plants from pots. The soil must be nutritious, light and breathable, therefore mix the garden soil with compost and sand in advance... The swamp lily planted in such a nutritious soil will delight you with luxurious flowering.


The soil for Krinum is a mixture of sand, soil and river silt.
Description


Krinum is an evergreen flower. Refers to bulbous plants. Homeland considered South Africa, Asia.
Grows well in the tropics of the United States. Endowed with spectacular beauty. In the wild, it reaches a height of more than 5-7 meters.
Flower bulbs reach 18-26 cm in diameter. The leaves are narrow, elongated, reaching more than 1.5 meters in length.In indoor conditions, the leaves grow to 65-100 cm in length.
Due to its large size, this representative of the flora is not suitable for growing in small rooms, since it will take up almost all of the space. This giant is great suitable for decorating offices, director's office, schools, kindergartens, sales areas and various store premises.
"Krinum" refers to unpretentious plants and definitely does not require careful maintenance. Due to its spectacular appearance, it can often be found in greenhouses, winter and botanical gardens. Belongs to the family: Amaryllidaceae.
IMPORTANT! The flower is very demanding on the purity of oxygen. Does not tolerate gas pollution, persistent smell of diesel fuel and fuel oil. When grown in open areas, "Krinum" is protected from excessive precipitation and cold winds.
For your attention a photo of "Krinum":
Crinum aquarium plant
There are types of krinum that can be grown in large aquariums (see photo), which enhances their decorative effect. These include:
- Floating crinum, which is a very large and original plant with leaves up to one and a half meters long and one and a half to five centimeters wide. On one bush, they can be counted up to twenty-five pieces, the color is dark green, the form is ribbon-like with compression along the edge. Peduncles up to seventy centimeters in height have an oblong shape. Flowers of white or red color are collected in inflorescences. The bulb reaches four and a half centimeters in diameter;
- Purplesmall in size. The length of its leaves and peduncles reaches no more than thirty centimeters. Umbrella inflorescences contain six to ten flowers with purple petals and reddish stamens. Perianth tubes are narrow, up to fifteen centimeters in height. The bulbs are small up to five centimeters in diameter. Flowering occurs in summer;
- Thai krinum, which is a rather rare species with swirling, soft green ribbon-shaped leaves from one to three meters long and up to two and a half centimeters wide. Small teeth run along the edge of the foliage. Peduncles are erect and up to eighty centimeters high. Inflorescences can contain up to ten flowers of white color with a charming scent. Perianth tubes are straight up to fourteen centimeters long, bulbs have a diameter of about seven centimeters;
- Wavy (kalamistratum, curly) krinum, which has a small elongated bulb and slightly twisted ribbon-shaped foliage up to two meters long and no more than one centimeter wide. It has a dark green color and highly wavy edges. Long and straight stalks reach eighty centimeters in height. The inflorescences usually consist of three white flowers with a pleasant aroma.
What a potted krinum requires
Krinum is a difficult and rather capricious plant. Therefore, in order for the plant to actively grow and bloom, it is necessary to study all the subtleties of caring for it.
Lighting
Krinum needs bright but diffused lighting. It should be placed on the western or eastern side of the room, in the southern part it is recommended to close it from the bright rays of the sun during especially hot weather.
The plant should not be located in the north, as its growth will slow down and flowering may not occur.
Temperature and humidity
Starting in spring, and until the end of flowering, the air temperature in the room where the crinum is contained should be maintained from twenty-two to twenty-seven degrees. In summer, it is recommended to take the plant out into the open air. With the onset of the dormant period, the temperature is reduced to ten degrees.
Krinum is not very sensitive to the level of humidity in the air. But, nevertheless, it requires wiping with a wet cloth to remove dust and give a fresh appearance.
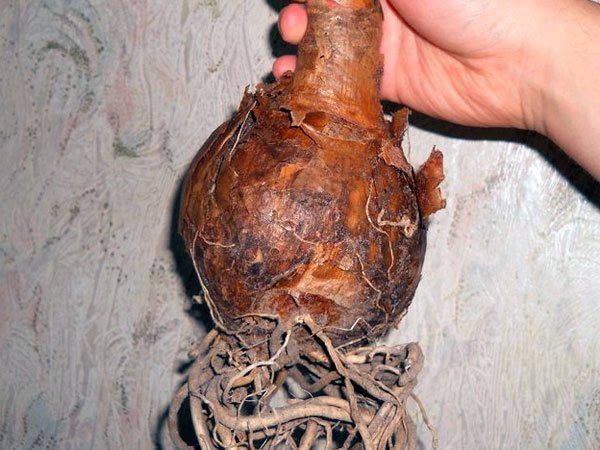

Watering and feeding
With the beginning of the growing season, the krinum is watered with warm, soft water as needed several times a week.With the onset of flowering, watering is carried out so that the soil is always slightly moist, and after it ends, they are reduced, but without bringing the soil to dryness. Same overflows must not be allowed at any time of the year, since the root system of the krinum is very prone to decay.
Since almost all krinums are impressive in size, they quickly consume nutrients contained in the soil. Therefore, after the plant leaves the dormant period, it is necessary to feed it twice a month, using complex mineral and organic fertilizers. Finish it when the last flowers fall.
Soil and pot
The soil for krinum can be made up of two parts of sod land, one part of leafy land, two parts of humus, one part of sawdust or moss. At the same time, to increase the nutritional value of the soil, you need to add phosphorus fertilizer to the resulting mixture at the rate of three tablespoons per ten liters of soil.
Since the bulbs and the plant itself are large enough, the container for adult specimens must be chosen large and deep, at least thirty centimeters in diameter. It is desirable that it be clay and thick-walled; wooden tubs are also often used for planting. Due to its large dimensions, the krinum can turn over ordinary plastic containers.
All common types of Kalanchoe are described in detail in the article at this address:
Here is a detailed story about how to care for Kalanchoe at home.
And what to do if the Kalanchoe does not bloom, read here.
Transfer
Krinum takes the transplant hard, so it is carried out no more than once every three to four years after the end of the dormant period, usually in March. For this, a container of the appropriate size is selected, a large drainage layer is made at its bottom and the substrate is poured.
The bulb should be immersed in the soil by half or two-thirds. In subsequent years, before the next transplant, it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil and replace it with a new one.
Dormant period
After the cinnum has faded, it begins a dormant period, while it does not completely shed its leaves. You don't need to cut them off, you can only remove the dried bottom ones.
At this time, they stop feeding, reduce watering, but do not complete them completely in order to prevent the soil from completely drying out, which can lead to the death of the bulbs. It is advisable to keep the plant at an air temperature within ten degrees.
Crinums that hibernate at high temperatures practically do not enter a dormant period, this is the main reason that the plant does not bloom in the next season.
Potted krinum
The crinum flower, which is grown in pots at home, is an evergreen plant. Its bulbs with a neck that is located above the surface of the ground, and in some varieties can form false trunks, growing from sixty to ninety centimeters in height, are round in shape and light in color. As you can see in the photo of the krinum bulb, it is covered with large brown scales.
Abundant foliage of light green color has, as a rule, a linear-lanceolate or belt-like shape, wavy edges. In adult plants, they hang in the form of arcs, and in young plants they are wrapped in a tube.
Luxurious funnel-shaped krinum flowers can be white, pink or crimson in color, they are characterized by a wide pharynx. They are located on a high, powerful peduncle, on which from three to thirty buds can form at the same time. They gather in umbrella-shaped inflorescences and bloom alternately, emitting delicate aromas. Each flower takes a long time to bloom, usually about five weeks.
Potted types of crinums are fairly large plants, their peduncles can reach more than one meter in height, and the flowers of some species have a diameter of about twenty centimeters.After the plant has finished flowering, fruits are formed on it in the form of decaying capsules, in which there are green bulb seeds. To get them at home, it is necessary to carry out artificial pollination.
Crinum seeds germinate and form bulbs even without moisture entering them, since their shell contains more than thirty-two percent of water.
Potted krinums are distinguished by longevity, with the right content, their life expectancy can be about thirty years.
Basic care
Flower care is not difficult and does not take much time.
Irrigation mode
Excess moisture is the biggest threat to the full development of krinum. Water the flowers in moderation, but regularly. The soil should always remain slightly damp. Watering is especially important during active growth and bud formation.
Fertilization
Organic fertilizers in liquid form (bird droppings, mullein) are recommended to be applied alternately with complex mineral fertilizers (potassium salt, superphosphate) every two weeks. A thick mulch layer of humus also nourishes the soil and protects it from dryness and weeds.


Soil care consists in loosening and timely removal of weeds.
Pruning of krinum peduncles is carried out after the end of flowering.
Krinum


All about krinums in the aquarium
Crinum (Latin Crinum) is a genus of bulbous plants of the Amaryllidaceae family. Perennial herbaceous plants. Krinum differs from other amaryllis primarily in its large size, although there are also small plants among the representatives of the genus.
Crinum bulb with an elongated or short neck. Many species form a false stem from the base of the leaves, ending in a fan of leaf blades.
Leaves are numerous, long - up to 1 m, linear-lanceolate, belt-like. Unlike other amaryllisaceae, the young leaves of crinums are not flat, but curled up into a tube.
The genus of crinums includes more than 10 species. Some of them are suitable for keeping in an aquarium and ponds - these are, first of all:
Crinum wavy or curly (Crinum calamistratum) - leaves up to 2 meters.
- Crinum floating (Crinum natans) with floating leaves up to 1 meter long.
- Purple Crinum (Crinum purpurascens) whose leaves are more modest in size - up to 30 cm.
- Krinum Thai (Crinum thaianum), they are grown at a low water level in a flowerpot with clay soil.
Keeping crinums in the aquarium


Krinum in the aquarium photo
Krinum can only be kept in a large aquarium. Sitting like a serpentine on the surface of the water, krinum leaves can overlap the entire surface of the aquarium, shading other plants. It is usually planted at the back or side walls of the aquarium.
Water parameters for keeping krinum: the plant should be grown in a tropical aquarium at a water temperature of 23 ℃. In colder water, growth slows down significantly, the plant begins to shed old leaves and degrade. The water can be soft and slightly hard. It should be borne in mind that at a stiffness below 4 ℃, growth may be unstable. An active reaction should be neutral or slightly alkaline, pH 6.5-8. In slightly acidic water, the old leaves of the plant are destroyed very quickly. The water should be clean, without excess nitrogenous compounds, 1/4 of its volume should be regularly changed once a week. Lighting can be moderate or strong 50-100 + Lm / L. Long leaves of krinum rise to the surface and are located in close proximity to the light source, so that the plant receives enough light even from a relatively weak source. The duration of daylight hours should be at least 8-12 hours (depending on the intensity of lighting and other conditions).
The substrate for krinum must contain a large amount of organic matter. When planting in new soil, it is advisable to place a substrate or fertilizer tablets, such as Tetra Crypto, under the roots of the krinum.As a substrate, you can use medium fraction soil and sand. The thickness of the soil layer when planting a young plant can be about 5 cm.As the plant develops, the soil can be poured, increasing its layer to 10 cm.
Liquid fertilizers can not be added to the aquarium water, since the plant receives its main nutrition through the soil and roots.
Crinum propagates in an aquarium only vegetatively, forming daughter-bulbs, in the immediate vicinity of the mother plant. This process is quite long. From the moment of planting a young plant to the appearance of its first children, even under the best conditions, at least 3 years pass.
At high temperatures, low water levels and bright sunlight, you can achieve flowering krinum, but it has not yet been possible to obtain full-fledged seeds in aquarium conditions.
Types of crinums that are grown in aquariums
Krinum wavy or curly in an aquarium
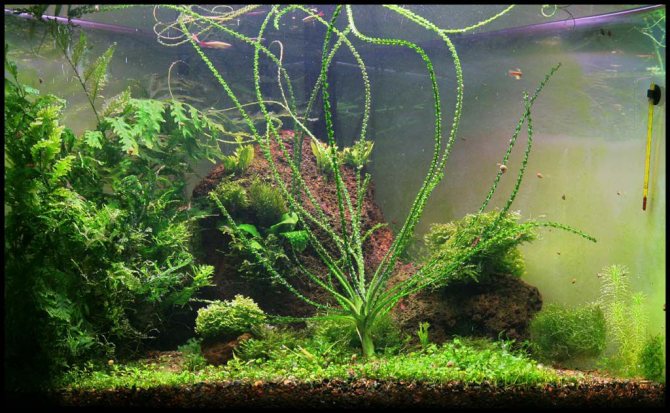


Krinum wavy in the aquarium photo
Crinum calamistratum Is a plant with an elongated bulb, 1-3 cm thick, up to 10 cm long. The leaves are collected in a rosette, ribbon-like, somewhat twisted, 70-200 centimeters long, 0.2-0.7 centimeters wide, dark green, wavy leaf edge. Distinct central vein. Peduncle up to 80 cm long, straight. Inflorescence up to 80 cm long with 1-3 flowers emitting aroma. Bracts about 3.5 cm long. Flowers with a straight green tube near the flower garden, 10–12 cm long, in white, slanting back, 6–7 cm long and 0.5–0.8 cm wide of tepals (lobes) and 6 stamens. The pistil is about 7 cm long.
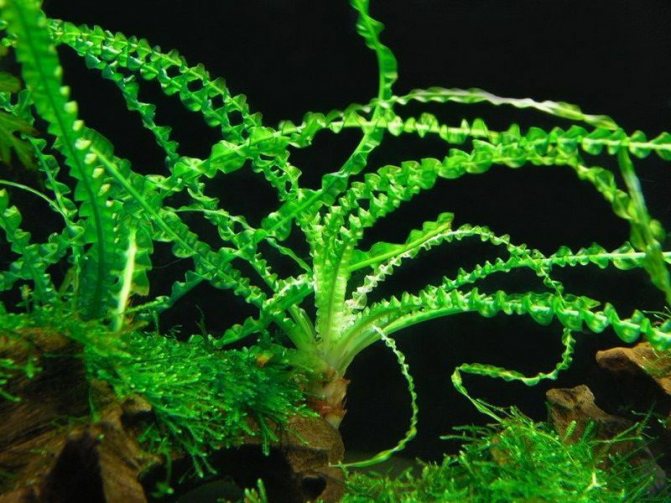


Krinum wavy in the aquarium photo
The wavy crinum with strong is a very attractive bulbous plant. It is not a very demanding plant: a soft to medium hard water with a pH of 7 is recommended. The soil should be nutritious and at least 8 centimeters high. The strong water flow promotes plant growth. Medium intensity lighting is sufficient. Crinum wavy grows much slower than other species, so you have to wait a few months before a good specimen grows out of the sprout.
The wavy transplant has a negative effect on the crinum. The plant is intended for keeping in aquariums with a water column of 50 centimeters or more.
Crinum floating in the aquarium


Krinum floating in the aquarium photo
Crinum natans Baker - habitat in West Africa from Guinea to Cameroon and south to Zaire. The species grows in forest tropical streams and rivers with very fast currents, also in direct sunlight, in pebble and rocky or muddy ground.
A large, strongly plant with an almost round bulb, up to 5 cm thick. Rosette leaves, ribbon-like, dark green, up to 150 cm long and up to 5 cm wide, usually strongly curly, rarely almost flat, the leaf edge is irregularly corrugated.


Krinum floating in the aquarium photo
This is a very large decorative type of krinum. Growing requires large aquariums so that ribbon-like leaves can spread over the surface of the water. In an aquarium, floating crinum develops well from soft to medium hard water and pH 7. The substrate, in accordance with the size of the bulb, should have a height of at least 10 cm and is nutritious. Since plants prefer places with a fast flow, care should be taken to maintain a good water flow in the aquarium. Krinum aquatic sometimes propagates vegetatively by daughter bulbs on large mother plants. With artificial pollination, seeds are tied. The seeds germinate well, and young plants grow quickly, and after about 10 weeks they reach a height of about 15 cm. There are forms with more or less strongly curled leaves.
Crinum purple in the aquarium


Crinum purple in the aquarium photo
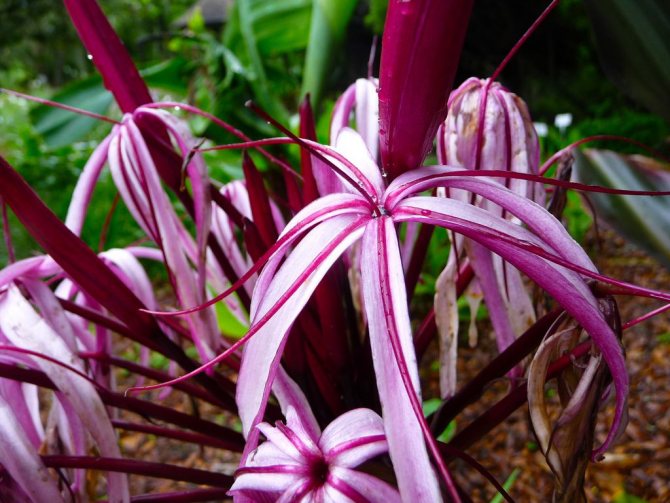


Crinum magenta photo
Crinum purpurascens - grows in nature on the banks of reservoirs and rivers in Guinea. The bulb is ovoid, small, 5 cm in diameter, easily forms babies. Leaves are 30 cm long.Peduncle 30 cm long, with 5-9 flowers in an umbrella, petals 6-7 cm, purple, red. It is cultivated in warm paludarium, planted in ponds, in which it is planted in a semi-submerged state.
Krinum thai in the aquarium
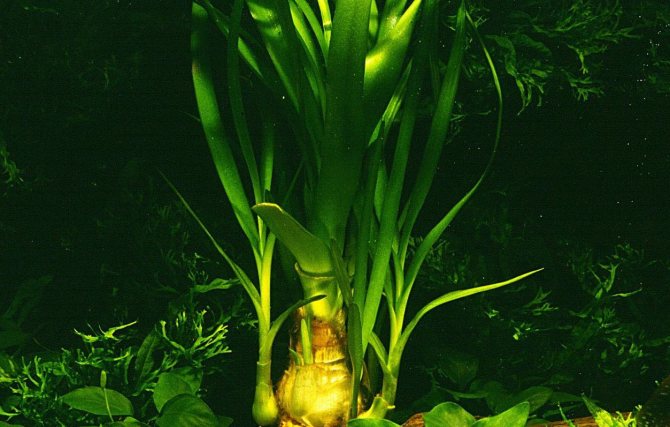


Krinum thai in the aquarium photo
Crinum thaianum - habitat Southeast Asia. An aquatic plant. It is rarely found among aquarists. It is an aquatic plant with a bulb up to 7 cm thick. Rosette leaves, ribbon-like, more or less strongly twisted, soft, torn with difficulty, 1-3 m long, 1.5-2.5 cm wide, green. The edge of the sheet is finely corrugated, not wavy.
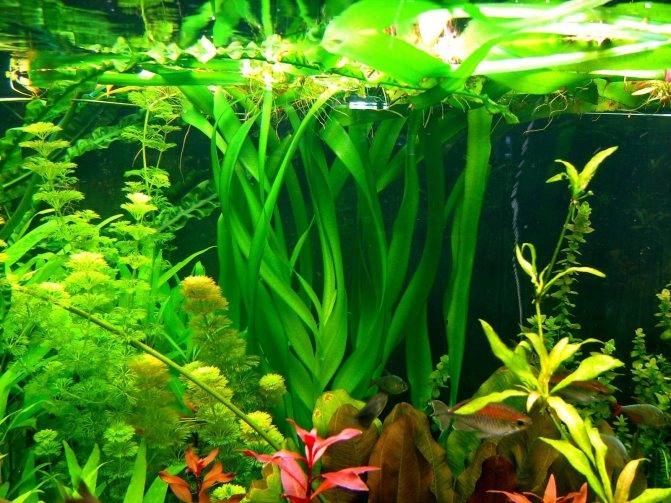


Krinum thai in the aquarium photo
It grows quickly, the leaves, being serpentine on the surface of the water, they can overlap the entire surface of the aquarium, shading other plants. Krinum can only be kept in a large aquarium. It is usually placed at the back or side walls of the aquarium.
Prefers diffused lighting, moderate. It develops well in soft and hard water at temperatures from 23 to 27 ℃, needs a nutritious substrate and soil ~ 10 centimeters, in which a powerful root can grow freely. Reproduction of old plants by daughter bulbs is more frequent than in Crinum natans.
Krinum video review
PRACTICAL NOTE ABOUT GROWING AQUARIUM PLANTS


This post can be found in all FanCheck articles about aquarium plants. This is a cheat sheet with a link that will help you grow any aquarium plant and herbalist of any complexity.
Most of the reference materials are located in the site section Aquascape, we also recommend our brochure: Aquarium Navigator for Beginners: "Semiramis Underwater Gardens".
The success formula for growing plants can be displayed as follows.
First of all, you need a proper level of lighting.
(light intensity - Lumens)
Further, the proper concentration of CO2
Further macro-fertilizers and micro-fertilizers
Water parameters, care and quality water changes
The gradation of this formula is built according to the degree of importance. The intensity of illumination is primary, and then downward. Therefore, if your plants have holes in the leaves, they have sciatica (twisted) or have problems with algae, then please do not read the "bad advice" - this is chlorosis (iron deficiency), this is a lack of potassium ... diarrhea, phimosis and endometriosis )
You always have to tackle the problem of attuning the herbalist from major to minor. Plants will die most quickly from a lack of lighting than from a lack of Fe and K. Moreover, the latter are always present to one degree or another in the aquarium, but it is difficult to measure their clear value.
Below, let's go from major to minor.
Lighting in an aquarium with plants... Remember, the most important thing in the world is this is its intensity (Lumens)! All other lighting characteristics: spectrum, Kelvin, PAR / PAR, Ra ... are important but secondary. There will be no light intensity, there will be nothing. At the same time, the lighting intensity should be balanced - selected specifically for your project (the height of the water column, the number and types of plants, daylight hours).
Based on the above, choose aquarium lighting primarily by the number of Lumens, and then everything else.
Lighting is the most expensive part. The most budgetary solution is to install conventional building-street spotlights above the aquarium... Fortunately, they are now very thin and aesthetic. And believe me, under them everything grows with a bang, of course, subject to the presence of all the other components.
In order not to be unfounded, here are photos of our herbalists who are grown exclusively under LED spotlights or with their presence.


If you want professional lighting or aesthetics. Then you have to fork out. The amounts can vary from 10,000 to 50,000+ rubles for a 100 liter aquarium. It is difficult to advise something, tk. everyone's needs and capabilities are different. In this article, we talk about the products of our partners – Tetra, Laguna, ISTA lighting.
We tried to briefly and objectively tell about them. Then it's up to you to decide. In any case, we do not really recommend that you pay attention to handicraft light assemblies from folk craftsmen. Not all, but as a rule, figs know which diodes are shoved into such an assembly, they collect all this on their knees ... and believe me, more than once on the forum you hear the echoes of the consequences of such a purchase. Still, a firm is a firm. At least you are given warranty and post-warranty service.
If you are a beginner, your first herbalist, then LED spotlights are your choice. Let's go further, but the note is not very short =)
CO2 for aquarium plants... The plant is about 90% water, the remaining 10% is dry matter. Of these 10% - 46% is carbon. This is why CO2 supply is so important in a plant aquarium.
Plants in an aquarium get their carbon "from the water" - from carbon-containing compounds. But the natural concentration of C-carbon in water is small and only sufficient for unpretentious plants, but they, and even more whimsical plants, will be happy with additional carbon feeding. CO2 can be supplied mash or CO2 balloon system, lemon or in other ways.
The best, professional, simple and in the future budget option is the supply of carbon dioxide through a cylinder. One thing, but - a starting purchase of a kit: a cylinder, a MG valve, a diffuser .... hit the budget.
Is it possible to do without CO2, but for a couple of bushes of simple plants (cryptocorynes, echinodorus, most ludwigies etc.).
What balloon systems can you recommend? The most budgetary option is an assembly from craftsmen who sell CO2 systems in VK and on forums. Everything is very high quality.
If you want a branded item, we recommend the cheapest and at the same time high quality CO2 systems from ISTA (Taiwan)... We have been sitting on them for 5 years and we advise you.


On sale you will find two series of ISTA Aluminum CO2 Cylinder cylinders, with horizontal and vertical threads 1 and 3 liters.
Fertilizers for aquarium plants... All fertilizers of any brand can be divided into MACRO FERTILIZERS and MICRO-FERTILIZERS.
Macro fertilizers - this is nitrate NO3 and phosphate PO4 from which plants take N-nitrogen and P-phosphorus. These are the most important elements after CO2 - C-carbon.
Remember - Redfield's proportion rules... Keep it under control at all times and everything will be ok. Right, based on our observations, the Redfield proportion rules only in full N-P-C ratios. Incomplete proportion - without carbon C does not give good results.
Micro fertilizers... These are all the other less important elements that are necessary for plants (see link). It is not worth placing a strong emphasis on them. Firstly, they are all contained in one or another quantity in tap water and, with changes, are restored in the aquarium. Secondly, an overdose of micro very quickly leads to an outbreak of algae.
A common mistake for beginners is not understanding what they are pouring into the aquarium. For example, take such a popular and popular fertilizer as Tetra PlantaMin... Read the product annotation on the link - it strengthens, stimulates, gives a chic habit.
A beginner, without delving into the essence, applies it and gets an outbreak of algae, scribbles on the forums - "Like, fu, what a bad Tetra." And the trouble lies not in the drug, but in misunderstanding nitrogen cycle and balance in the herbalist... The beginner is skewing according to Redfield (let's say generally zero N and P) and instead of making up for the lack of these primary elements, he fills the aquarium with Tetra PlantMin - a micro-fertilizer (iron, potassium, manganese). As a result, busting on micro is only harmful, because plants lack a base - nitrogen and phosphorus.
Thus, you must understand what plants are missing and understand fertilizers.
How to understand what plants lack? It's simple.Now the market is packed with a variety of expensive and not very good aquarium water tests. We recommend from inexpensive domestic - drip tests VladOx, they are sold online and offline.


We also recommend, we will not be afraid of this word - innovative domestic tests UHE... They are currently only sold online.
The minimum set of tests for a herbalist is NO3 and PO4. It is desirable to have the entire nitrogen range: NH4, NO2, NO3. Also kH and pH tests.
Tests help us monitor the situation in the herbalist, but over time it is desirable to learn to see and feel the aquarium for ourselves. With experience, you need to move away from "seizure testing", the best aquarium test and instrument is ourselves.
Let's summarize this part. Macro, it is also macro in Africa. The link above generally contains a recipe for how to make them yourself. If you are not yet ready for samomes, then always and everywhere you will find a line of fertilizers from Tetra: Tetra Planta Macro, Tetra PlantaMicro, substrates, root tablets and more.


Of course, there are tons of other brands that make aquarium fertilizers. There is a possibility, use the products at least ADA. In taste and color, all markers are different. The main thing is to use it with a clear understanding of what you are using it for and what you want to get in the end.
From a professional line of fertilizers, at an adequate price, we can recommend Prodibo (soils, soils, macro, micro, stimulants, etc.).
So, something note turns into the Talmud. Not surprisingly, the topic is very broad. There is one moment left.
Water parameters for aquarium plants. Link1 and Link2, please look at these articles, they explain the essence well enough.
Here we note that the quality of photosynthesis is influenced by the process of caring for the aquarium: water parameters (kH, pH below 7), high-quality filtration and aeration, competent and timely water changes.
Please study
Historical background about krinum
The krinum plant belongs to the amaryllis family. This flower rightfully belongs to the bulbous genus. By their nature, krinums grew in the tropics and subtropics, so they got used to excessive humidity, high temperatures, and fertile soils. Therefore, when planting it, you need to look for the most favorable soils that were previously flooded. Krinum can be found on the coast, along the banks of rivers and swamps.
Most of the krinum species can be found in South Africa, since the temperature and climate are most favorable for this flower. Krinum comes from the Latin name for "hair". This word emphasizes the appearance of the plant.
Krinum has oblong, flowing petals that vaguely resemble long locks of hair. Growing bulbous krinum in the garden is a rare experience, but interesting.
Pests
The flower is rarely attacked by pests. More often in room conditions, you can encounter a false shield or stragonosporosis. A fungicide will help to cope.
In the garden there are spider mites and mealybugs. To kill a tick, you need to choose potent acaricidal or insectoacaricidal agents: Fitoverm, Actellik, Karbofos. There are many methods of dealing with the worm. There are folk and professional remedies. The former include various infusions: garlic, citrus, alcohol, horsetail tincture and others. The second group includes insecticides and insectoacaricides of intestinal action: Inta-vir, Aktellik, Bankol and others. Everyone chooses what they think is effective.
How does it multiply?
On the basal bulb, baby bulbs can form. They consist of several layers of leafy scales and can eject young leaves. When there are at least 4-5 leaves, the bulbs can be carefully separated and fixed separately in the ground. The distance between individuals should be increased, since the root system that grows in the future will experience inconvenience.
Bulbs do not appear immediately. The plant must be mature and healthy.In addition, adequate lighting, adequate water quality and nutrient availability are required.
It is better to take sandy or fine gravel for high-quality growth. It should not be prone to silting, be able to breathe and at the same time be nutritious. To do this, it is additionally fertilized with special fertilizers.
Caring for crinum in the garden
How to care for crinum
Planting krinum and caring for this bulbous plant in the open field does not contain any difficulties. You will need to water and feed the plant during the growth period, loosen the soil around it and weed the weeds, and with the onset of autumn, prepare the krinum for wintering. As soon as the plant enters a dormant period, and the signal for this is the yellowing and falling of the leaves, the bushes are covered with a layer of straw or peat up to half a meter thick. If your winters are harsh, and even snowless, then it is better to dig up the krinum bulbs and store them in the vegetable drawer of the refrigerator until spring. Or, transplant them into a container in the fall and keep them in a cool room without watering.
How to make hippeastrum bloom at home
Watering and feeding krinum
The soil around the krinum should be kept in a slightly moist state, especially during the period of active growth and budding, but the soil should not be moistened abundantly, since the bulbs deteriorate and die in dampness. Water for irrigation should be settled and heated in the sun.
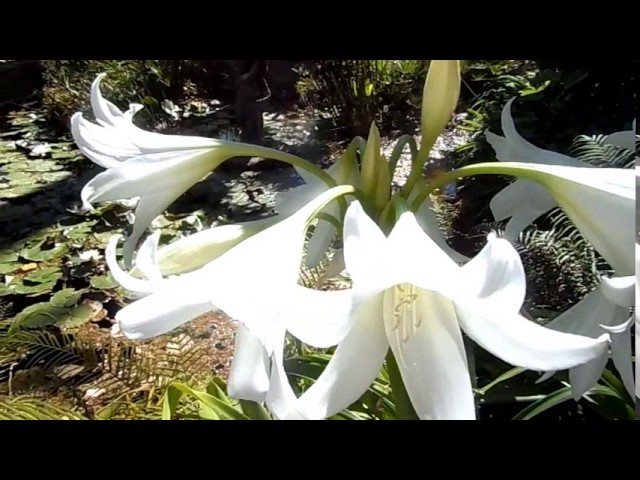


Crinum is fertilized in the open field twice a month with liquid mineral and organic compounds alternately. To prepare the mineral composition, 5 g of complex fertilizer is dissolved in 10 liters of water. For organic solutions, manure, bird droppings are used, or ready-made fertilizers are used, which can be purchased in specialized stores. Before flowering, a solution of potassium salt and superphosphate is introduced into the soil.
Diseases and pests of krinum
Of the pests, spider mites, scale insects and worms pose a danger to krinum.
Amaryllis worms strongly oppress the plant, it begins to lag behind in growth, its leaves turn yellow and fall off, and a sooty mushroom settles on the sticky secretions left by pests. If the bulbs are severely affected by worms, it is better to throw them away, but if you find pests immediately after they appear, then you can deal with them by treating the crinum on the leaves with an insecticidal solution.
The scale insects are also destroyed with an insecticide solution, but since these insects are reliably protected from any poisons by the shell, it is necessary to remove adults from the plant before processing with a cotton swab dipped in alcohol or soapy water.
The fight against spider mites is carried out with acaricides, since these pests are not insects, but arachnids. By the way, drugs such as Aktellik, Aktara, Akarin and Fitoverm are insectoacaricides and perfectly cope with all the pests of krinum.
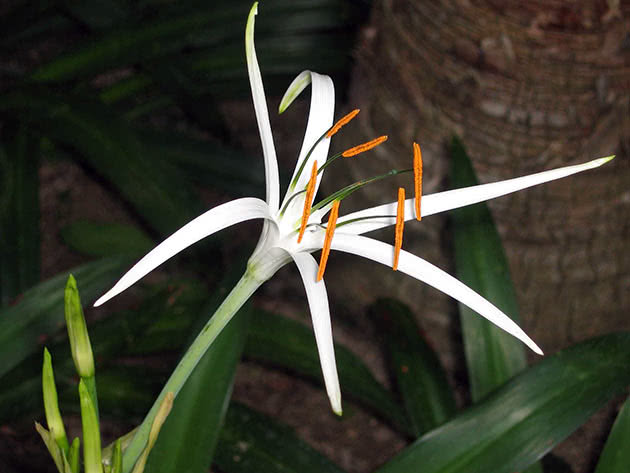


In the photo: Flowering krinum in the open field
Of the diseases, one should beware of such fungal infections as anthracnose and staganosporosis, or a red burn. Anthracnose develops rapidly in warm and humid conditions, and a red burn can be diagnosed by red spots and stripes on the leaves and bulbs of krinum. Both of these diseases are treated with a solution of Fundazole or another fungicide of a similar effect.
Popular species and varieties for the Moscow region
The most popular types:
- "Broadleaf",
- "Ceylon",
- "Rough",
- "Makovana",
- "Lugovoy"
- "Pleasant",
- "Bell-shaped"
- "Maiden",
- "Majestic",
- "Asiatic".
The most hardy hybrid variety, which will feel great in the summer cottages of the Moscow region, is Powell's crinum. Our climate suits this species well, but for the winter period it will need a reliable shelter or wintering indoors.






























