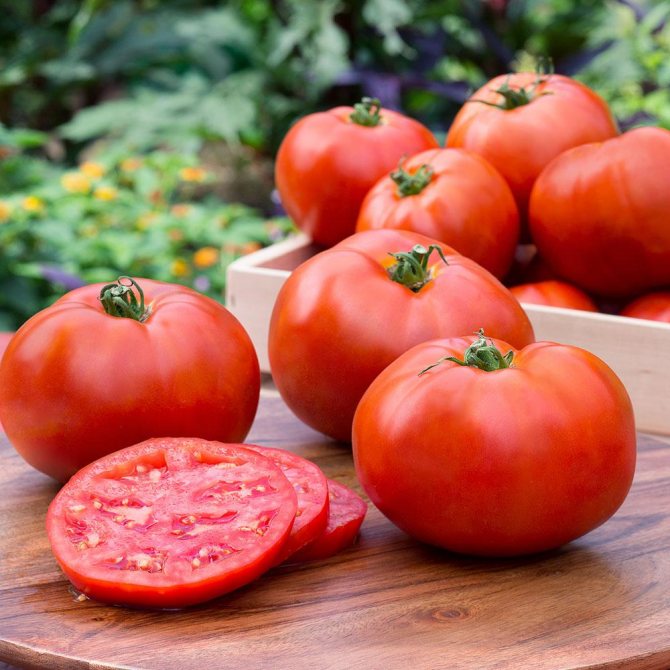
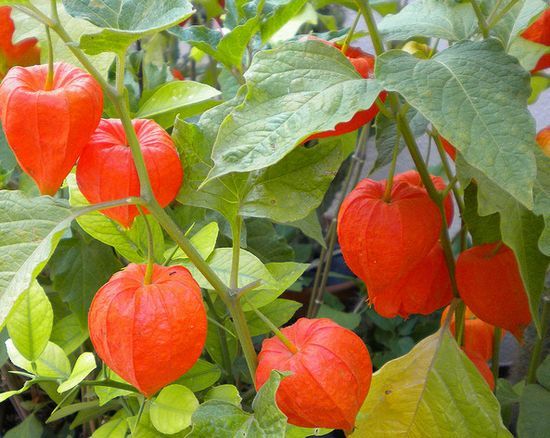
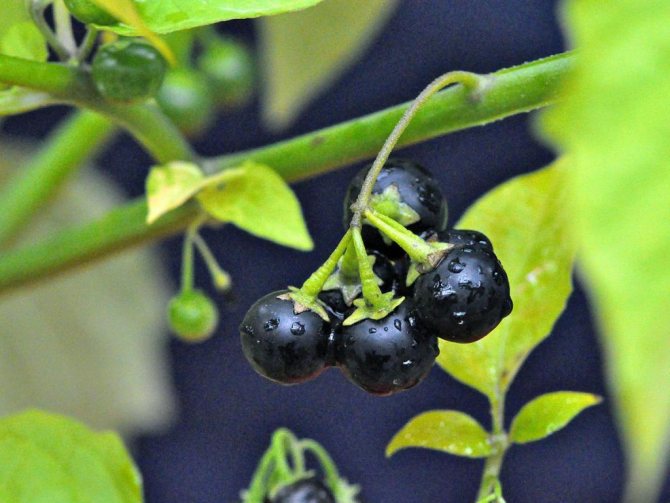
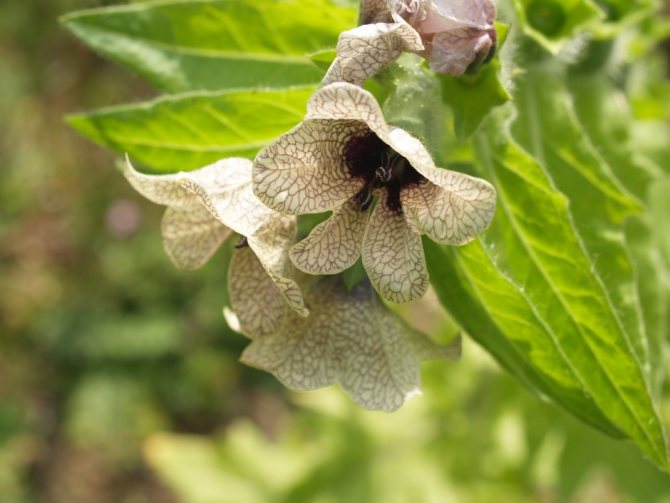
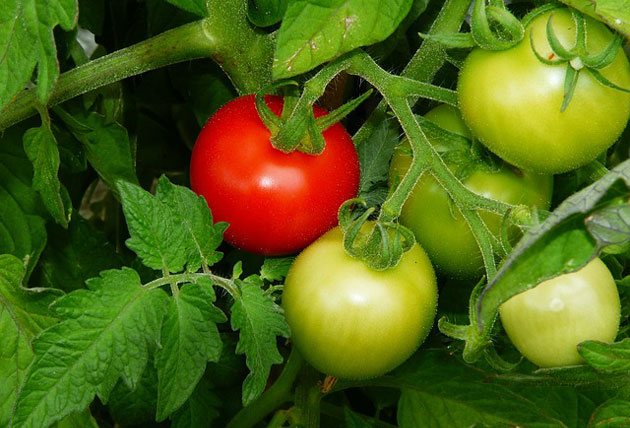
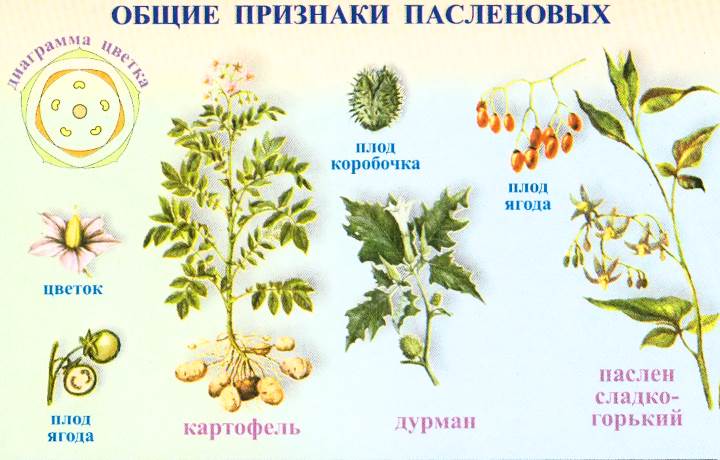
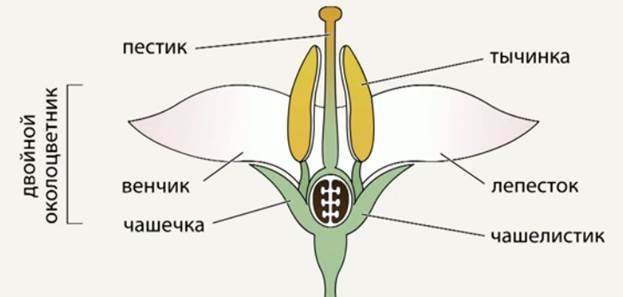
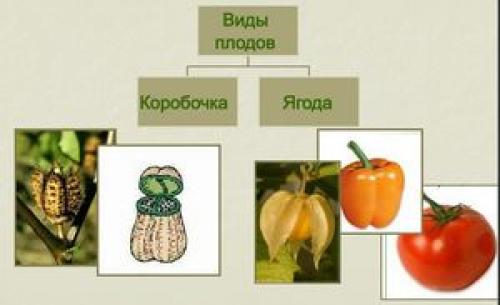
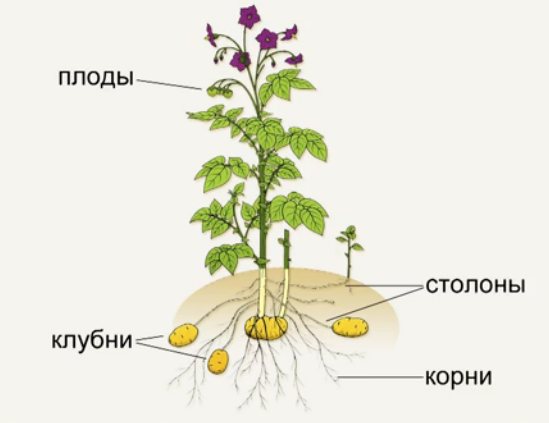
Plants of the Solanaceae family are found all over the world. They bring together annuals and perennials that grow in the wild and within home gardens. Insects take part in pollination. But it can also be animals and birds. In South American countries, a greater number of modern species of solanaceous plants are concentrated, the list of which includes many different species, including vegetable crops.
- 2 Healing properties
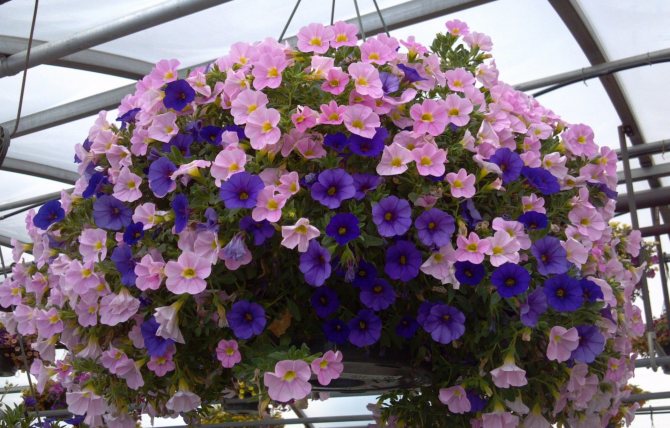
- 3 Ornamental crops
Indoor nightshade: the secret of the attractiveness of the plant

In their natural environment, nightshade is most often found in regions with a warm climate. Its homeland is South America, where it reaches a meter in height. In some countries, such as Australia, the plant is being destroyed because it is considered a weed. Despite this, indoor nightshade attracts plant lovers.
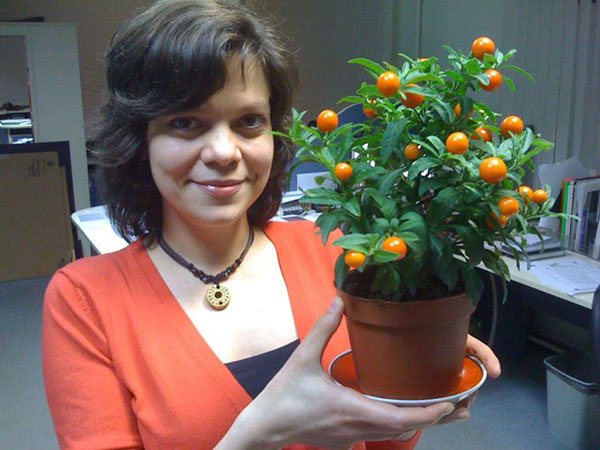


The flower grows to about 30 cm. From the side it resembles a small bush. The oblong lanceolate foliage has a rich dark green color, against which clearly pronounced veins are visible. The edges of the plates are distinguished by a wavy frame, which gives the bush a spectacular look.
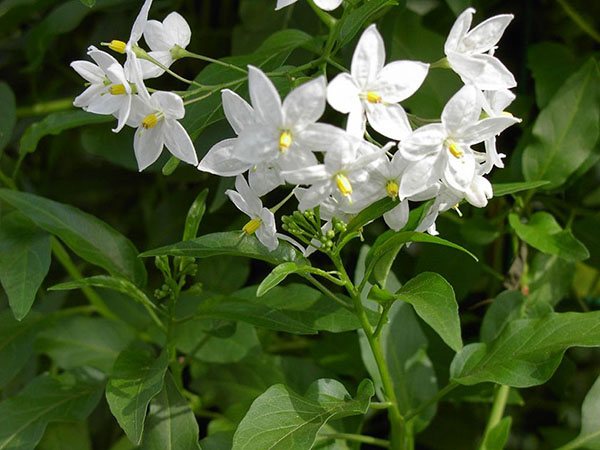


During the flowering period, buds appear on the branches of the indoor nightshade. They can grow in inflorescences in several pieces or singly. Interestingly, flowering takes place at different times of the warm season, but the berries appear in the winter. Their size is about 1.5 cm. Ripe color can be from bright red to orange. From the outside it looks very nice. Against the background of dark green leaves, scarlet beads shine with bright lights, which are kept on the shoots for several months. They do not fade or fall off.
Among the popular varieties of plants, the decorative indoor nightshade "Three-flowered" is especially appreciated. During the fruiting period, brushes of homogeneous berries appear on the branches, which are the decoration of the living room.
Cultural plants of the Solanaceae family
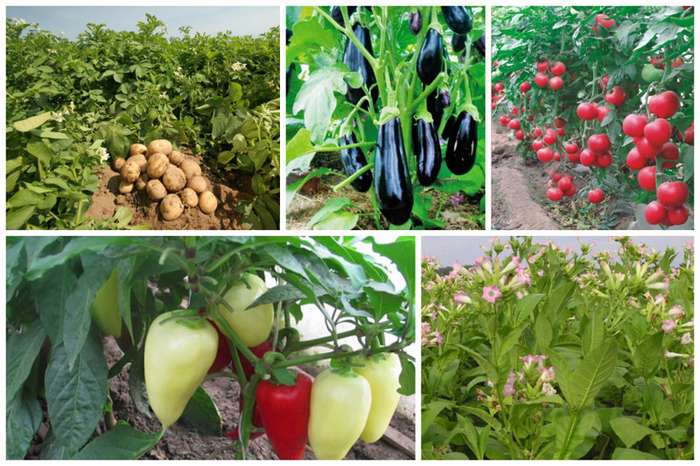
The family can be divided into wild and cultivated plants. Cultural ones are obtained from wild ones using scientific methods: selection, genetic engineering, creation of hybrids. What concerns cultivated nightshades:
- potatoes;
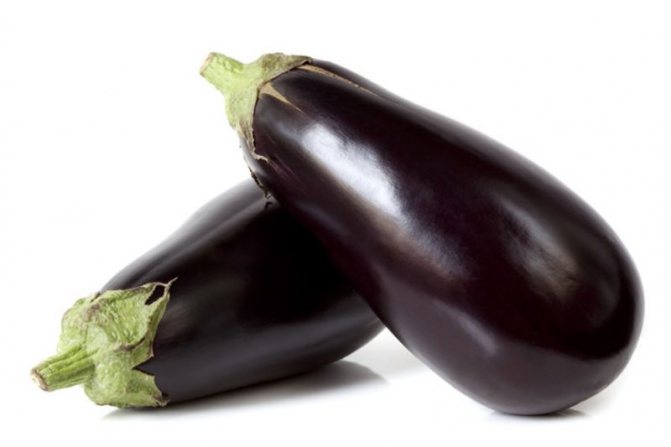
- eggplant;
- tomatoes;
- capsicum;
- smoking tobacco.
They have long been grown by humans for food, animal feed, medicines, cosmetics, cigars and cigarettes.
Solanaceae are plants that people encounter on a daily basis. Wild and cultivated members of the family are beneficial in the composition of medicines and food, and decorative species transform the home.
Simple rules for growing berry mosaic at home
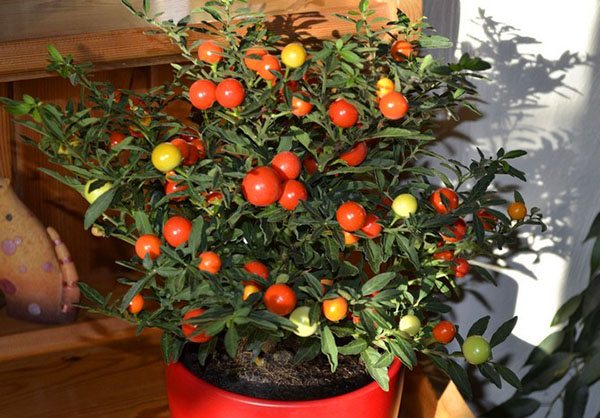


Growing culture on your windowsill is easy. She feels great in a variety of soil. The main condition is that the soil must be loose. Often, fans of home crops grow indoor nightshade from seeds, carefully observing its development. The process begins in late May or early June.
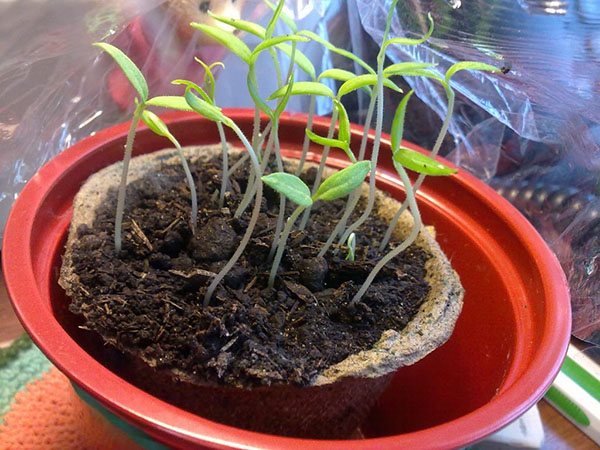


Place the seeds evenly in small containers filled with suitable soil. Then they are covered with a layer of sand of about 1 cm and irrigated with a spray bottle. The containers are covered with plastic wrap and placed in a room where the temperature is at least 22 ° C. It should also have a lot of daylight.The first seedlings will turn green on the ground in about 14 days. When they get stronger, and there will be 3 leaves on the shoots, the sprouts dive into other containers.
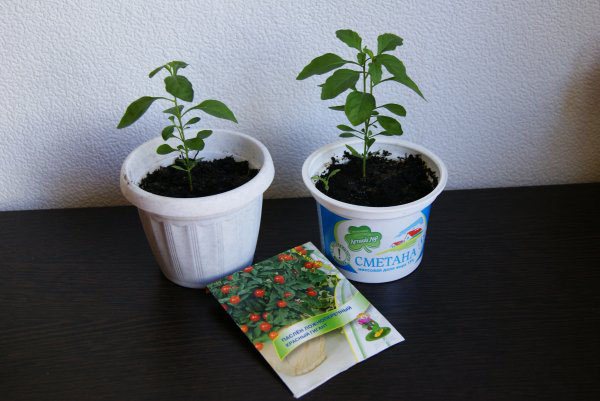


After 30 days, the grown seedlings are transplanted again, but already to a permanent habitat.
The last dive is carried out when the nightshade bushes grow up to 15 cm in height.
When the plant takes root, you need to know the rules of how to prune the nightshade and not harm it. The procedure is performed several times a year. In late February or early March, all shoots of the culture are shortened by a third of the main length. It is best to do this during the ripening period of all berries, and when the foliage turns yellow.
For the effective formation of the indoor nightshade bush, additional pruning is carried out in April or early May. The procedure is repeated before the blooming of the buds. To increase the bushiness of the culture in the fall, new shoots are pinched to the branches where there are no buds and fruit ovaries. As a result, a cute decorative ornament, strewn with bright fruits, will appear on the windowsill.
Growing


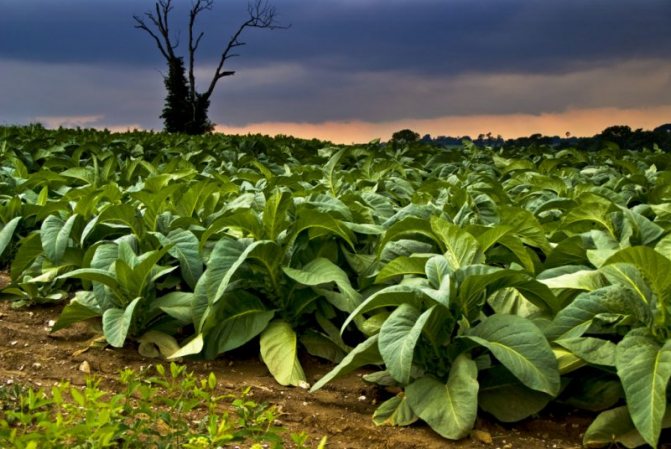
Most of the tobacco plantations are located in North America, India, China and Asia Minor. On the territory of the former Soviet Union, it is cultivated in the Transcaucasia, Crimea, Krasnodar Territory, Moldova, Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan.
At first, tobacco seedlings are grown in open ground or special nurseries. When they grow up to 13-15 cm, they are transferred to plantations. After about 40 days, the leaves are harvested. On average, the entire process takes 15-17 weeks.
A smart approach to caring for indoor nightshade
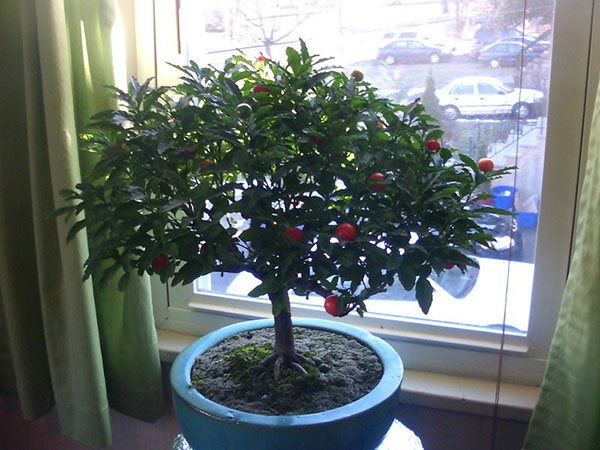


Since the plant came to Europe from tropical countries, its conditions must correspond to its natural habitat. A reasonable approach to caring for indoor nightshade at home leads to a remarkable result. Exotic berries will become an exquisite decoration of the living space, turning it into an oasis of peace and pleasure.
The basic rules of care are to create suitable conditions for the culture, which include:
- lighting;
- humidity;
- temperature regime;
- watering;
- top dressing.
Let's consider in detail each procedure to grow an exotic flower at home.
Adequate amount of light
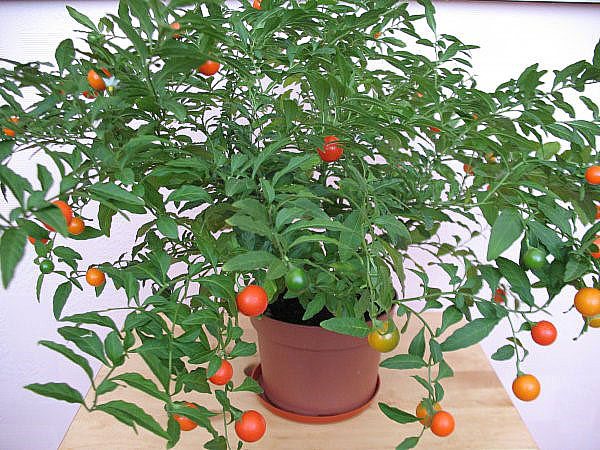


Practice shows that proper lighting directly affects the decorativeness of the nightshade. Throughout the season, the plant needs diffused light. Therefore, it is placed on windows facing east or west. When winter comes, the flower feels wonderful on the south side. With insufficient light, nightshade develops poorly and bears a small amount of fruit.
Reasonable temperature and humidity control


For the successful development of a tropical plant indoors, it is necessary to maintain an optimal temperature regime. In spring and summer, it is in the range from 18 to 25 ° C, and in winter 12 or 15 ° C is allowed. If the temperature regime is violated, the flower will lose all berries and foliage. This is one of the reasons why nightshade leaves fall at the most inopportune moment.
The plant does not like drafts, therefore, when airing the room, it is better to remove the culture pots to another place.
Since nightshade is native to the tropics, it needs regular spraying. Also, the pot with the culture can be placed in a shallow pan with moistened drainage material. The main thing is that there is no direct contact with water. Insufficient air humidity has a detrimental effect on the development of culture. Therefore, gradually losing vitality, nightshade dries up and may eventually die.
Application
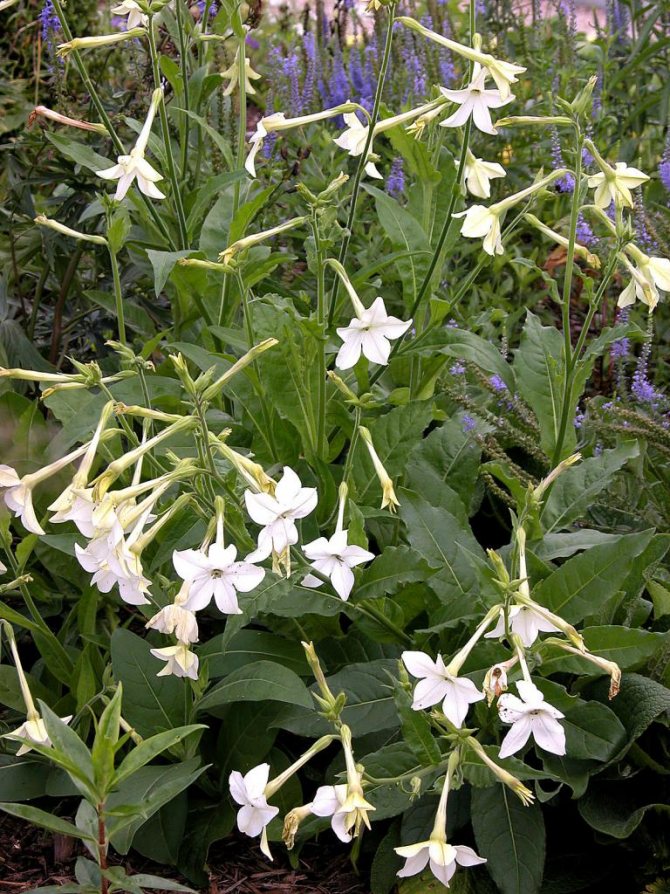
The use of tobacco is very diverse. He finds a place in medicine (traditional and folk), the chemical industry, gardening and even cooking. The plant was successfully adapted for some household needs.
For smoking
This is the primary role of tobacco in the world's most profitable industry. On sale tobacco products for every taste.
Cigarettes and pipes have become popular again among smokers. Therefore, the market is supplied with many types of packaged tobacco of any kind with a variety of aromatic and flavoring additives. They often drastically change the taste of tobacco. A separate niche of the market is occupied by hookah tobacco.
At home
Some varieties of crops perform a decorative function, for example, winged tobacco... It is often planted in gardens for beauty purposes only.
In agriculture, the plant improves the quality and fertility of the soil, so it is often planted in the fields before sowing wheat or rye. Tincture of tobacco helps control pests (aphids, red fleas or thrips).
The strong smell of the plant scares away moths, so some housewives use it to preserve woolen things.
It is interesting! Some chefs use tobacco as an ingredient in their dishes. At the XV International Cigar Festival in Havana, guests were offered such unusual dishes.
ethnoscience
Tobacco has been adapted for the treatment of many diseases. Some even use it against tuberculosis and hemorrhoids.
The most popular recipes are as follows:
- Crushed leaves are used to treat colds.
- A decoction of tobacco is used against skin diseases.
- Raw materials insist on vodka and take for dizziness and nausea.
- Tobacco ointment serves as a pain reliever.
- Tincture of cigarettes is used to get rid of subcutaneous ticks.
Invisible enemies of the tropical beauty
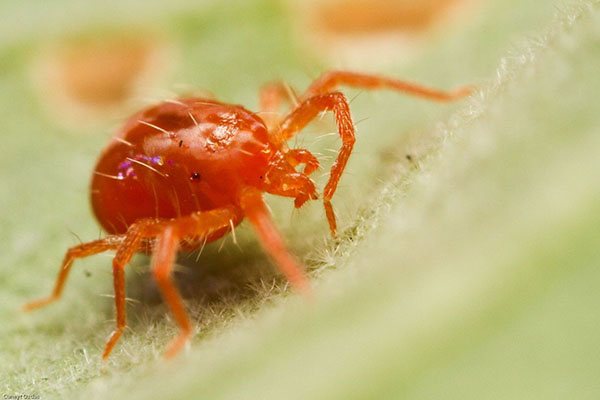


Exquisite sheet plates of indoor nightshade attract the attention of pests:
- whitefly;
- red spider mite;
- orange aphid.
Often insects settle on them, reproduce and suck out juices. The plant begins to ache and lose its decorative effect.


The miniature whitefly, which slightly resembles a moth, loves to feast on the juice of the culture. It leaves sugary traces on the leaves, and larval clutches on the back of the plate. If everything is left to chance, the leaves will begin to curl, turn yellow and eventually fall off.
Another "uninvited guest" of the flower is the spider mite. Its favorite habitats are the back side of the leaf plate. Pest-caused diseases of the indoor nightshade are manifested in the formation of miniature specks on the foliage. Over time, they turn into stains that spread throughout the culture.
In a similar way, the plant infects orange aphids. It settles on the back of the plates that grow on the tops of the shoots. As a result, the foliage turns yellow and dries over time. To stop the process of crop disease, you need to get rid of pests with the help of special preparations. And then the indoor nightshade will delight the owners with its lush greenery and bright berries all year round.
Tips for caring for indoor nightshade - video
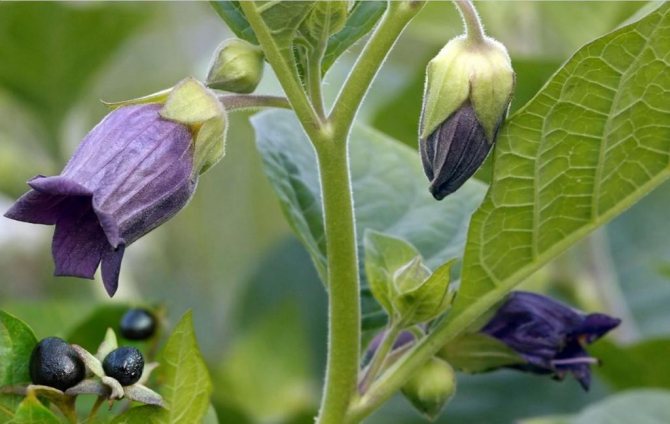
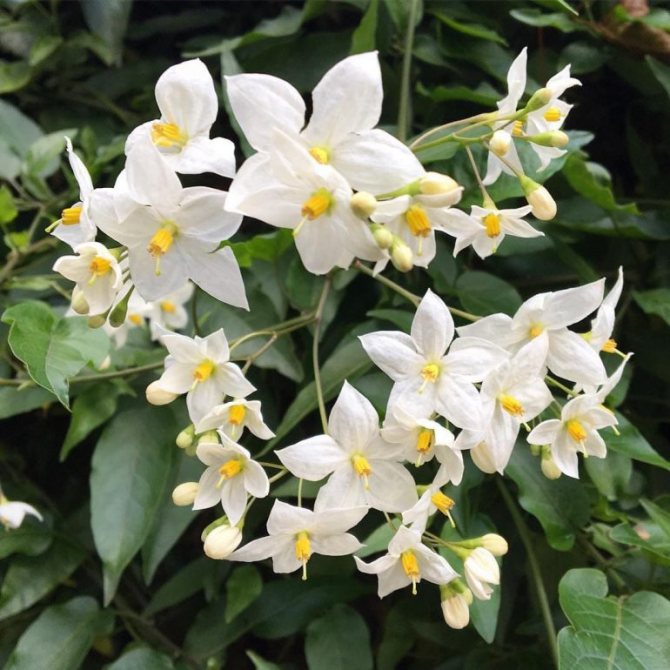
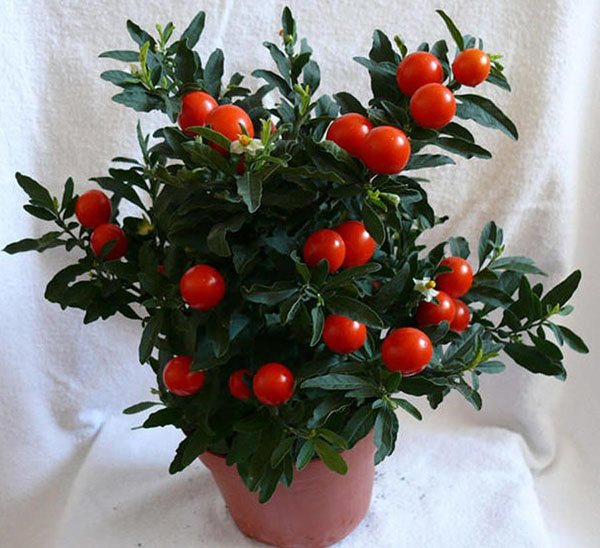
Solanum (Solanum) is popularly called by the people: nightshade, coral bush, indoor cherry, Chinese cherry, Cuban, Jerusalem.
Houseplant nightshade is a low evergreen deciduous shrub native to South America and Madeira with oblong glossy leaves.
Unusual nightshade preserved all year round: the branches are simultaneously showered with flowers, a green ovary and bright orange ripe berries, which are really very similar to cherries.
Unfortunately, such a bright representative of the nightshade family is poisonous... It cannot be kept in a house where there are small children who can pick and taste the poisonous berry. If the nightshade fruits are not eaten, then there is nothing to be afraid of - the plant will not be able to bring any harm.
Wild plants
Indoor nightshade: examples of care and the main varieties of plants
The nightshade family consists of cultivated representatives and wild-growing ones.The latter category includes:
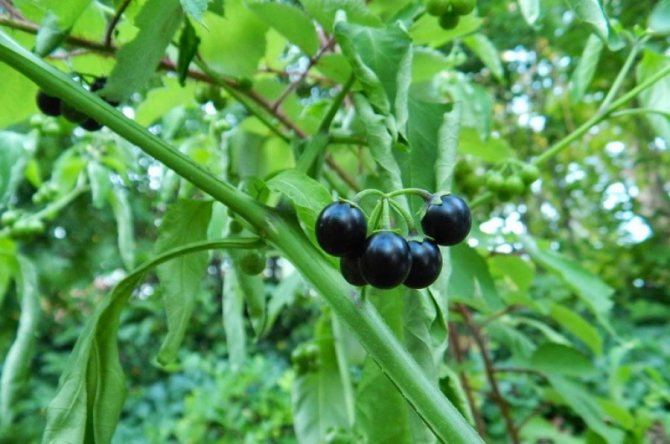
- nightshade black;
- bittersweet nightshade;
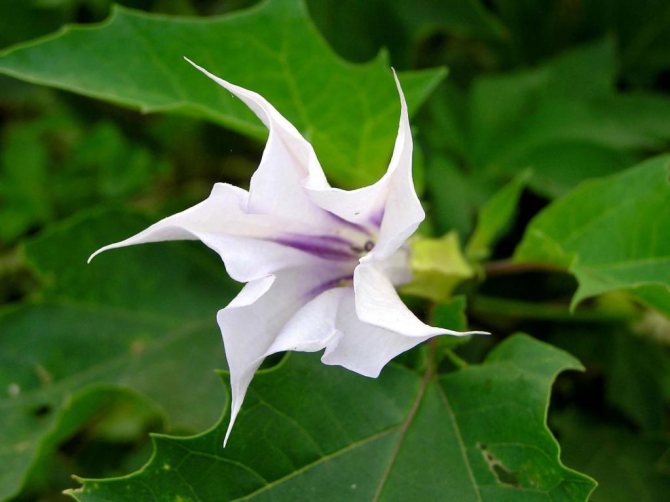
- dope ordinary;
- belladonna;
- henbane, etc.
Most nightshades are wild plants.
Medicinal plants of the Solanaceae family
Due to the high content of alkaloids, most of the wild-growing members of the family are poisonous. However, the poison is successfully used in pharmacology in small concentrations. An example of medicinal poisonous plants:
- belladonna;
- tobacco;
- henbane is black;
- mandrake;
- dope;
- scopoly;
- bittersweet nightshade;
- black nightshade;
- bird nightshade.
Not poisonous:
- chilli pepper.
The resulting alkaloids (hyoscyamine, scopolamine, atropine) are used to treat gastrointestinal diseases, peptic ulcer disease, diseases of the urinary system, asthma, and cholecystitis. In folk medicine, tincture and decoction of the root, powder from dried leaves are used.
Varieties
In the tropics and some areas with a temperate climate, more than 1,700 species of saltanum grow. But we will consider only two of them, which are most often grown at home.
False Nightshade - S. pseudocapsicum. Erect evergreen shrub, growing up to 120 cm. Leaves with short petioles, oval or lanceolate, glabrous and slightly wavy.
Flowers are white, small, with five petals; fruits are round, red or yellow up to 1.5 cm in diameter. Originally from about. Madeira For indoor cultivation, undersized forms of decorative nightshade were bred.
Pepper nightshade - S. capricastrum. Much smaller in size than pseudo-pepper, it has smaller berries and more tender shoots, green with a grayish tinge. At home - in Uruguay and southern Brazil, grows in forests. The most popular varieties are Craigii - with colorful fruits and Variegatum - variegated variety.
Characteristics of the nightshade family
Solanaceae are a family of plants with 115 genera and more than 2,700 species for 2019. People encounter many of them every day: indoor flowers, common vegetables, tobacco and medicinal plants.
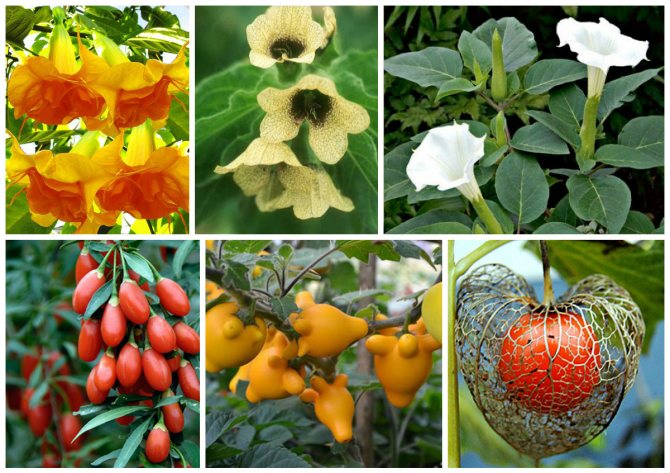


Solanaceae
Representatives are divided into three life forms:
- herbs;
- shrubs (erect and creeping);
- trees (nightshade or acnistus).
Together with the "bindweed" family, they form the general order of the nightshade.
Features of nightshade plants
Mostly representatives have a delicate pleasant aroma. Poisonous species are partially covered with glandular cells and exude a pungent odor.
Important! Most nightshades contain solanine. This poisonous alkaloids is not harmful in small concentrations. The maximum amount is found in unripe fruits with green peels (tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, etc.). Therefore, green fruits and tops cannot be used for livestock feed. During heat treatment, solanine is destroyed.
A dangerous dose of alkaloids is found in henbane, dope, and belladonna. Poisoning provokes fever, headache, dizziness, diarrhea. With a prolonged reaction, the function of the thyroid gland is disrupted, the tissues of the digestive organs are damaged, and vision deteriorates.
Actions in case of poisoning: call an ambulance, then drink water with some absorbent and induce vomiting.
Conditions of detention
Caring for an indoor nightshade flower suggests an optimal spring-summer air temperature for solanum about +15 + 25 ° С. With the approach of cold, the bush will need to lower the temperature level - to +13 + 15 ° C. Lighting also plays a huge role. It should be borne in mind that nightshade loves bright light, but not heat.
Humidity level It is advisable to measure the air in the room with a hygrometer - it should not be below 60%. In case of insufficient humidity, it is necessary to spray the plant daily and place it in a tray with wet expanded clay or pebbles once a week.
Origin and distribution
The spread of tobacco began in the 1st century. BC e.on the territory of America, but did not go beyond the continent until the arrival of the Europeans. The situation changed when in 1492 H. Columbus landed in America and the Indians brought him gifts, among which were dried tobacco leaves.
It is interesting! The sailor Rodrigo de Jerez, who traveled with Columbus, is considered the first smoker in Europe. The Spanish Inquisition considered that the man, from whose mouth and nose smoke comes out, possessed by the devil, and de Jerez was imprisoned.
At the beginning of the 16th century, when the Spaniards created the first tobacco plantations, the plant began to spread throughout the world. Soon, successful promotion of smoking began in high society, although in some countries and cities (the Ottoman Empire, Bavaria, Zurich and Saxony) tobacco was banned, and smoking was punishable by up to the death penalty.
In Russia, tobacco first appeared under Ivan the Terrible. At first, smoking was popular among representatives of the Russian nobility, but Tsar Mikhail Fedorovich issued a decree banning tobacco. Only under Peter I was smoking legalized.


Reproduction
Homemade nightshade can be grown from seeds or cuttings. Depending on the method of planting, the fruits can be more or less large. When growing from seeds the bush usually grows strong and bears excellent fruit. When propagation by cuttings the plant takes longer to adapt and root in new soil.
Nightshade seeds are sown in late February - early March using this substrate composition:
- peat 1 part;
- clay soil 3 parts;
- sand 1 part;
- drainage.
Nightshade kernels sown at a distance of 20 mm from each other, pressed into the ground by 1 cm, watered and sent to a windowsill with good lighting. When will appear seedlings (after 8-10 days), they need to be shaded a little. Within a week, when young shoots gain strength and release 2-3 leaves, they are transplanted into separate containers. Grown 10 cm plants pinch the top, remove side shoots, giving the bush the shape of a ball.
Your old dream to know: how to grow ginger on a windowsill? We've turned it into a valuable article.
Read about the rules of caring for asparagus at home with us.
LYUBODAR - a portal for self-knowledge and development


Nowadays, in the diet of people there are a lot of different food products, although, of course, many of them are artificial, industrially created and it is impossible to call them a full-fledged food. Sooner or later, many people come to this conclusion, who have at least a drop of common sense left. But not everyone knows and thinks about the benefits of vegetables that they eat every day. People are used to thinking that apart from the presence of nitrates and pesticides in vegetables (a side effect of modern agriculture), vegetables are healthy by default, because these are food products created by nature itself for our food. Alas, this opinion is erroneous, not all plants growing in the wild are useful for humans, the same applies to vegetables that people are used to seeing almost daily on their table.
The tomato and cucumber salad has become a classic for us. However, just three hundred years ago, these vegetables were not familiar to our ancestors. How much our diet has changed and whether it is so beneficial to have international food on the table can be seen in the example of nightshades.
What are nightshades?
Solanaceous plants (tomatoes, potatoes, paprika, chili, bell pepper, eggplant and others) are favorite vegetables of the Slavs, Europeans and Americans. What is harmful in them? Solanaceae contain solanine. Solanine is an alkaloid that causes diarrhea, head and joint pain, lack of will, insomnia, nervousness, depression, dizziness, stomach cramps and cardiac arrhythmias. They can also cause gastrointestinal and neurological disorders. Solanine slows down the breakdown of acetylcholine and is a neurotransmitter.
The result is muscle numbness.Solanin also contributes to malfunctioning of the thyroid gland, chronic joint pain, leaky gut, and depression. The calcitriol in nightshades causes the intestines to absorb calcium from food, but too much of it leads to elevated blood calcium levels. The body stores excess calcium in soft tissues, tendons, cartilage, kidneys, and skin. This can lead to osteoarthritis, coronary artery disease, bone spurs and pain!
Dr. Norman Childres (Ph.D., founder and chairman of the Center for the Study of Arthritis and the nightshades) first became interested in nightshades in the 1950s. He was a gardener scientist who discovered that diverticulitis was caused by nightshades.
Naturopath Garrett Smith says avoiding nightshades reduces arthritis pain, muscle pain, gallbladder problems, and insomnia.
Norman Childers: Solanaceae are members of the Solanaceae family of over 90 genera and 2,000 species. Tobacco also belongs to this family. It has been used for several centuries, but now many are abandoning it because of the harm it causes to health. Products from the nightshade family include tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and all peppers except black pepper, which belongs to another plant family, the Piperaceae. Mexican tomatoes are also nightshade, popular in Central and South America. Why are nightshades literally called "night shadows" in English?
According to some sources, the Romans used nightshades in the preparation of poison for their enemies. When a person drank a poisoned drink, the shadow of a long, eternal night fell on him - he was dying.
The Solanaceae family is a large group of plants, consisting of 92 genera and over 2000 species. These include beautiful flowers such as petunias, succulent vegetables, addictive tobacco, medications such as scoplonin, which is found in insomnia pills, and many poisonous plants such as belladonna with black berries, which forbid children from eating, as well as bad smelling henbane.
What problems arise with nightshades?
Norman Childers: Because of several poisonous plants in this family, people in the past were wary of eating potatoes, and some older people still believe that tomatoes are poisonous. For more than a century, livestock breeders did not allow their cattle to eat nightshades growing in the fields. Farmers sent their children to pluck nightshades. The shepherds are well aware of Jen Autry's famous song "Low Datura." Livestock owners watched the animals eat these herbs, get sick and die. Tomatoes were once known as "crayfish apples". And tobacco for a long time caused obvious damage to the health of smokers, until the authorities, and now the media, began to fight it.
What do you offer people; what is your specialization?
Norman Childers: The question arises: are the little-studied nightshades a health threat? Nowadays, potatoes and tomatoes are the main vegetables; along with peppers and possibly eggplants, they are part of the daily diet of many people.
I drew attention to the nightshade problem in the 1950s when my doctor told me that hot peppers could cause inflammation of the colon, which resulted in surgery. As a vegetable grower, I researched the nightshade family and eliminated these foods and tobacco from my diet.
My health problems, including arthritis, disappeared. My colleagues noticed that I had cured arthritis. They began to follow "my" diet, and, having received positive results, in the end, turned to me: "Why don't you help other suffering people?" Therefore, by personally gathering information and posting several announcements with questions, we ended up receiving over 400 positive dietary reviews (72 and published a book called Nightshades and Health.Subsequently, the Center for the Study of the Effects of Solanaceae on Health was established; We have distributed thousands of copies of The Child's Arthritis Diet (originally revised) and are now publishing Newsletter, reaching 4,300 subscribers.
What advice can you give to people who are trying to give up nightshades?
Norman Childers: It's not easy to do. A strong motivation is needed in the form of a desire to get rid of pain and disease, or you just need to strive to avoid these plants and possible health problems. If the average person eats nightshades from time to time, he can safely do so for many years. But nightshades like herbal drugs - like tobacco - are addictive. The more of these drugs a person uses, the sooner problems arise, and the more serious these problems are. Some people are more sensitive to nightshades, especially people with arthritis and the elderly. But in our time of massive consumption of nightshades, fried potatoes and pizza, even children and adolescents, like adults, are forced to take medications for headaches, asthma, inflammation, etc. Parents are worried about their children.
The effects of nightshades are subtle, and heart problems, circulatory problems, or even cancer can occur suddenly. Tobacco is known to cause cancer, and tomatoes have enjoyed a similar reputation in the past, but unlike tobacco, it's hard to tell if other nightshades can cause cancer since everyone eats them. Comparative analysis is not possible. All nightshades contain narcotic and drug-like chemicals. All nightshades are more or less addictive.
Summing up, I can say: we have found that completely eliminating all nightshades can completely or partially eliminate many serious diseases. This conclusion is based on our experience. Based on 45 years of experience healing tens of thousands of people, we assume that nightshades and tobacco are the number one problem these days. Researchers should pay closer attention to these plants, the effects of which are clearly underestimated.
Think about it! For many millennia, the Slavs and Europeans lived without nightshades (tomato, potato, eggplant, sweet pepper, etc.)! These plants were brought from America only about 400 years ago! What did our ancestors eat before? Were they starving? Let's remember what our ancestors ate before the appearance of nightshades in Russia and start feeding on these plants, including wild plants!
Obviously, it is beneficial for someone that our entire diet consisted of nightshades, which cause addiction, are poisons in large doses, affect mental state, reduce the level of awareness and slag people's bodies, making them sick and dependent on medicine!
Let's return to the traditional Slavic food products and plants that grow in our area and are much more beneficial in every sense for our physical, psychological and spiritual health!
Also read the article “CAUTION: POTATO! HOW AND FOR WHAT THE POTATO WAS IMPLEMENTED: +++ Helpful article? Tell your friends and subscribe to the newsletter for key new articles. Thank you! The subscription form is in the upper right corner of the page. +++ Other useful articles and materials: