The main - Botany - Houseplants - How ferns reproduce
Ferns are the most ancient plants that have been growing on Earth since ancient times. There are approximately 11 thousand fern species in the world. In home floriculture, plants are used for their beautiful leaves. They don't bloom. Indoor, tropical and subtropical plants are grown; outdoors, bushes from temperate latitudes are used for planting.

The rich "hair" of the plant compensates for the lack of flowers.
Fern types for home cultivation


Living conditions are not important for this evergreen plant - it exists perfectly in swamps and meadows, as well as in shady forests of a tropical climate. Some species can live only in a room, while others thrive in low temperatures, surviving the winter months in the ground.
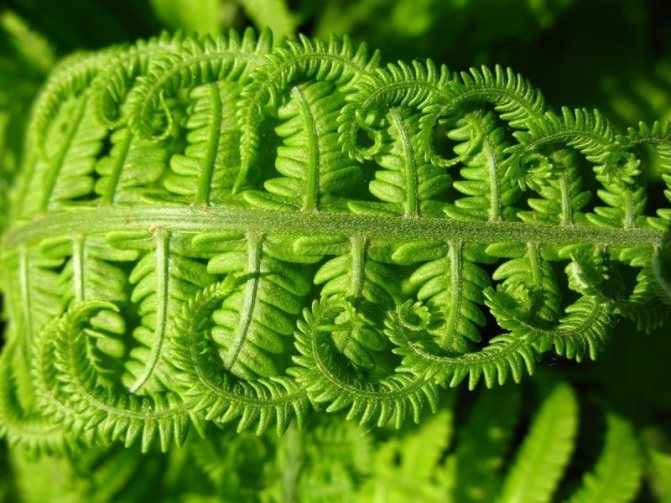
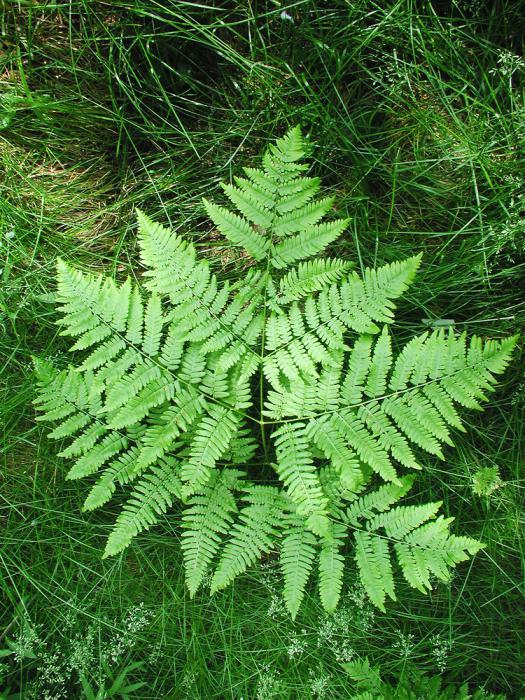
Any kind of fern consists of 2 structural parts - rhizomes and chic, openwork, striped deciduous plates.
Most of the shrub species have dissected-feathery leaves, but some varieties are distinguished by accrete leaves, which can be of various shapes and specific sizes.
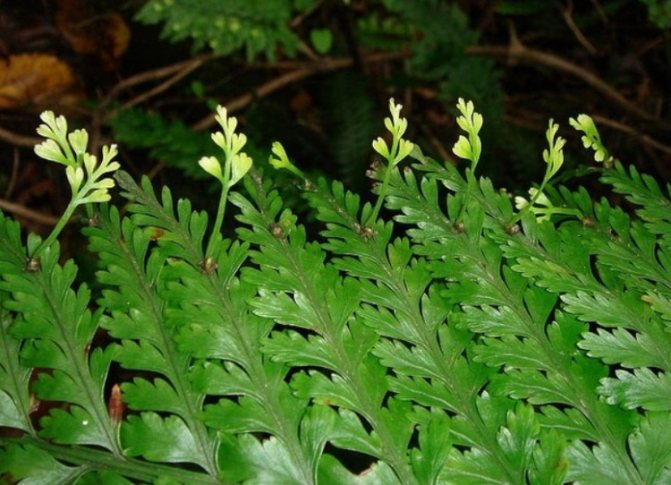
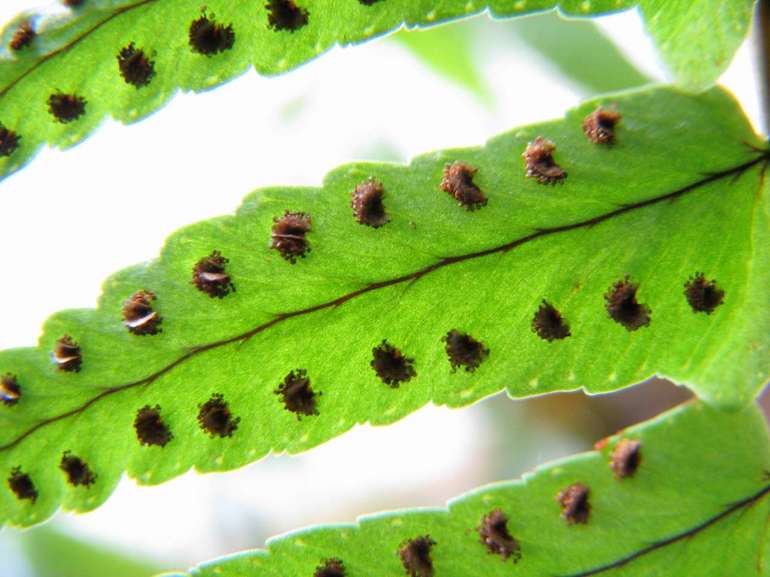
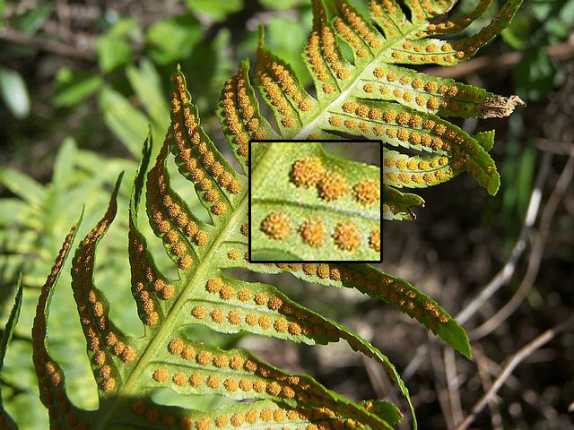
There are many legends where on the night of Ivan Kupala people go to look for and collect flowers of a mysterious fern. But no matter how hard they try to find the cherished color, it simply does not exist in nature. The fern does not give color, it does not form seeds and fruits, and the swelling of the scales on the underside of the leaf plate is the spores with which the wondrous plant reproduces.
There are not many varieties of ferns that can be grown at home. Among them are the most popular varieties:
It requires partial shade and a humid climate. For home cultivation, such fern varieties from this line as bulbous, nesting and viviparous are suitable.
It has the property of reaching up to 1 m in height with its crown. At the same time, rigid leaf plates outwardly begin to resemble palm leaves. Suitable for cultivation are the Brazilian variety or the Humpbacked Blehnum.
The stems of the shrub are graceful, of fine structure, but distinguished by their strength. For the rapid growth of the bush, shade, high humidity and optimal air temperature are required. The best option for growing the variety would be a greenhouse or a special greenhouse. Among the species of this variety, Tender, Venus hair, Radi and Melkovolosisty prevail.
Refuses to grow if other species of flora are nearby. It requires a lot of space and increased attention. Flying plants have a strongly dissected appearance, due to which the shrub receives an interesting openwork effect.
Differs in a thick root system. Thanks to this, the people called the plant hare or squirrel legs.
The foliage of the bush is dissected, the rhizomes are located on the surface, which gives rise to the feeling of a creeping plant. Feels great in rooms with dry air.
In favorable conditions, it reaches 3 m. It is grown for the decoration of voluminous rooms.
The owner of large, bladed leaf plates.In appearance it resembles huge deer antlers.
Therefore, before planting a plant on your site or in a pot, you should choose one of the varieties. Each of the types is distinguished by the originality and grace of the leaf plates.
Fern species and varieties
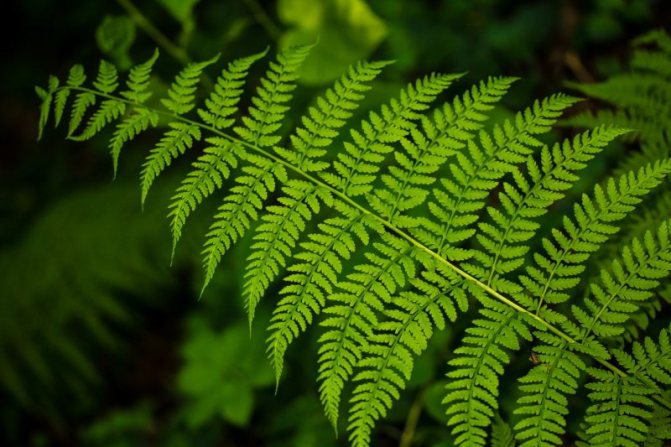


There are a huge number of groups and varieties of ferns.
Asplenium.
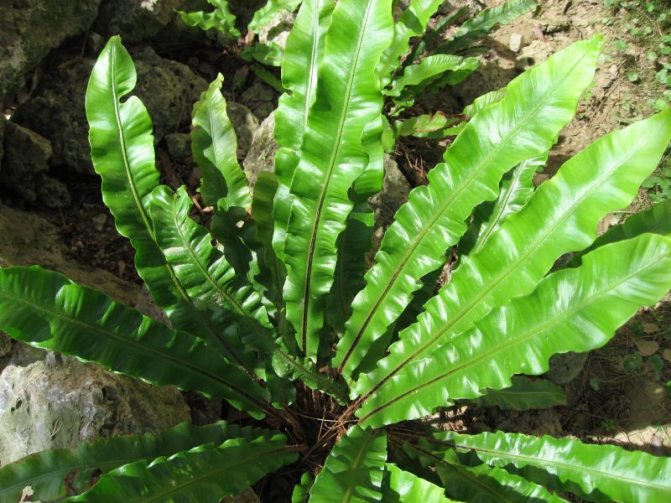


Known for his love of rocky surfaces. Forms a separate family. The description is as follows: rounded, leathery leaf blades on thin twigs. The most famous are two types: wall and northern. The first is often found on the walls of old stone buildings. It grows mainly in stone crevices. The northern loves the rocky places of northern Europe and Asia.
Woodsia.
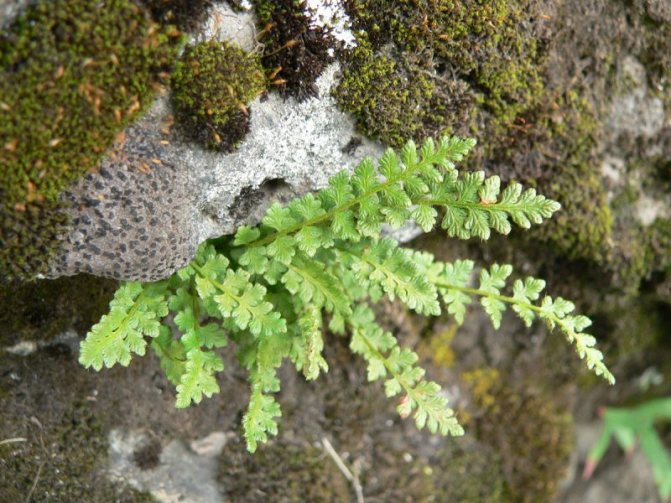


Belongs to the asplenius family. A low-growing fern, characterized by "fluffy" foliage - thin leaves grow from a small root, from which smaller leaves diverge in two directions. It has several varieties (Elbe, multi-row), which differ in the size and density of the leaves.
Kochedyzhnik.
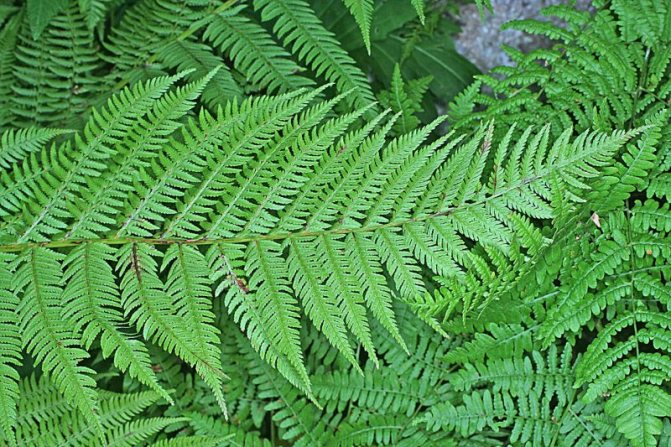


Also belongs to the Asplenium family. This variety has about 200 varieties. Of these, the most famous is female, Chinese-reddish (with red veins). Description: tall shrub with delicate, light leafy feathers.
Multi-rower.


Like the previous groups, it is part of the Asplenium family. It differs from the previous ones in the width of leafy branches, in love for the dense shade of a wooded area. Such varieties are known: Brown's multi-row, tripartite, bristle.
Interesting: indoor fern
Bracken.


Belongs to the cyatein family. Popular for its unpretentiousness - varieties of this group are found on all continents of our planet: tundra, wasteland, wooded thickets. He is not there except in the desert and steppes. It differs from other varieties in the huge size of leafy branches - up to one and a half meters.
Osmund.


Forms its own family. One of the most ancient fern species. In ancient times, they grew on all continents, but today they are found only in the Caucasus, in the forests of East Asia and North America. The following varieties are known: Asian, Clayton, royal. Loves shade and swampy terrain.
Scraper.


Belongs to the asplenium family. Its distinctive feature is a love for land and a lot of light, unique in its family. The leaves are leathery, dense, in contrast to congeners. Prefers limestone rocks.
Common types of fern include Ostrich (the shape of the leaves resembles ostrich feathers), Telipteris (characterized by lush greenery), Fegopteris, Shchitovnik, Onkolea.
Fact. It was ferns that many thousands of years ago had a kind of woody plant varieties. Trees died over time, and their wood went deep into the soil, compressed and survived to this day in the form of coal.
The choice of soil and container for growing


In order for the planted sprout to take root perfectly, it is necessary to choose the optimal flowerpot and soil in which the plant will grow. The primer can be purchased in a specialized store, or you can make it yourself. But in order to sow spores into the ground, you should check that there are special components in the ground.
For the optimal composition of the soil substrate, the following list of ingredients will be required:
- River sand and brown peat. To combine a soil substrate, you will need 1 part of sand and 3 parts of peat.
- Leafy soil, river sand and peat in a ratio of 1: 1: 3, respectively.
River sand and leafy earth are taken in identical proportions (1: 3).
For good rooting and rapid development of the root system, you can also use soil for violets.It contains the optimal amount of all the nutrients required for planting a young fern sprout.
It is imperative that the planting soil be loose, well permeable to nutrient oxygen and introduced moisture.
For planting spores, the soil requires specific preparation. Initially, the earth is sieved, all large stones and solid particles, various debris are removed from it. Experienced gardeners recommend disinfecting before rooting.
To do this, rinse the soil with a weak solution of Potassium Permanganate and put it in one layer on a baking sheet in the oven. The soil should be sterilized within a few hours. Only after that you can prepare the landing container. If the fern is propagated by spores, then for sowing you will need a shallow, rectangular pot made of plastic or glass.
When planting plant sprouts in ordinary peas, you can select any options. A clay container is perfect. It has the ability to absorb moisture. And as necessary, give it back to the soil. But you shouldn't overfill the pot. This situation can provoke the development of a fungal infection, which is very problematic to be eliminated from a clay pot.
You can also use plastic containers for planting. But it must be remembered that it is very unstable and does not allow air to pass through. Therefore, it is worth choosing large pots, but so that they are half the total volume of the fern branches. And in order for the plant to receive a sufficient amount of air, it is worth loosening more often.
Reproduction methods
Since ferns do not bloom, they do not propagate by seeds. These plants are spore-bearing. Therefore, their reproduction often occurs by spores, which serve as a substitute for seeds. In order to breed ferns with spores, you need to carry out the following manipulations:
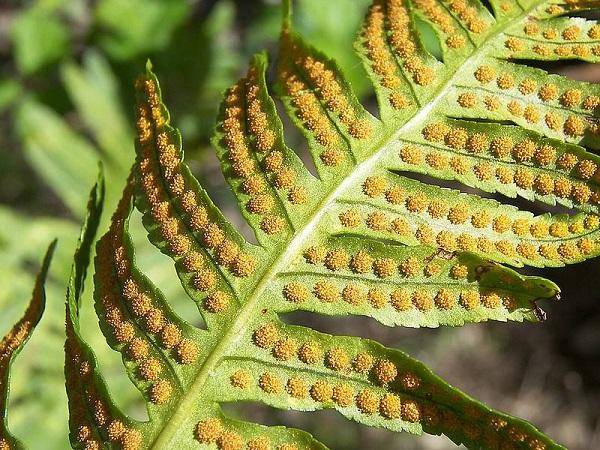
- collect ripe spores. Spores in these plants are located in special formations - sporangia. When the spores mature, the sporangia acquire a brown color. Please note that each species has its own rate of maturation of the propagation material. Also, spores can be located pointwise in the sori. When ripe, they turn brown;
- storage them until ripening. Spores must be carefully cut from the frond and placed in a paper bag, in which they dry and ripen. The bag itself should be well closed, as spores are highly volatile. The package is opened only before planting the spores in the ground. Ripe spores are brown powder;
- planting in the ground.
In order for the cultivation of planting material to be successful, you need to choose the right soil. For ferns, soil can be purchased at a flower shop. Also, the earth can be prepared by hand. For sowing spores, the soil can contain various components. Often, soil is used prepared from the following components:
- sand and brown (high moor) peat. This primer is prepared by mixing the components in a 1: 3 ratio;
- sand and leafy earth (1: 3);
- leafy earth, sand and peat (1: 1: 2).
You can also use violet soil here.


Plant spores differently from other flower seeds. Before planting spores, prepared or purchased soil must be sieved to remove solid and large particles from it. Also, before planting a house, experienced florists recommend sterilizing the ground. There are various ways to do this. But the easiest way to sterilize is to steam the earth.
Planting spores in a shallow glass or plastic pot. Wet soil is placed in a container and tamped a little. After that, the spores must be evenly distributed on the soil. They should not be sprinkled with earth. It is enough just to water.
You can also use a fern sprout for breeding at home.This is the so-called vegetative propagation. Here, fern sprouts are used, which look like long and fluffy arrows. Fern also reproduces by layering. Some fern species can also reproduce with leaf stalks and brood buds. But there are very few such plants.


Vegetative propagation methods depend on your preferences and the availability of this or that formed planting material.
Vegetative reproduction is carried out only in spring or autumn, when the weather is cool. It will allow the plant to develop and grow quickly. Under these conditions, in just a few weeks, the planted shoot will take root and begin to develop.
For reproduction in a vegetative way, plants with one growth point cannot be used. After dividing the bush and planting the resulting material in the ground, thorough watering is carried out.
Features of reproduction by spores


Growing a plant with spores is a rather laborious and problematic way to get your own specimen. It is usually used by experienced breeders. The method is divided into several stages:
- Preparation of planting material - seeds can be purchased at a flower shop or in an online store. You can also collect spores yourself. They are collected from an adult plant, simultaneously with sporangia. The assembly is carried out at the moment when the sporangia acquire a brown tint. To make them fully ripe, immediately after harvesting, they are placed in a paper envelope or bag. After a short period of time, the spores mature and spill out on their own.
- Planting spores - drainage is laid out on the bottom in containers prepared in advance. The soil substrate is poured out from above, which is neatly leveled, compacted and moistened. After this, the spore is sown. Place the glass on top of the container. This is required to create a microclimate for the plant for the fastest germination.
- Care for sprouted seedlings - you need to adhere to +22 C, as well as humidify the air well. Before the appearance of the first true leaves, it is forbidden to disturb the resulting moss.
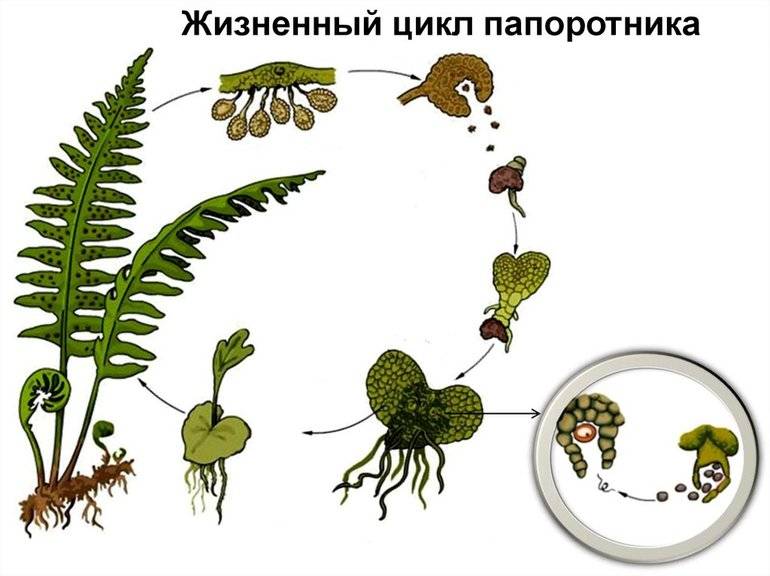
Reproduction methods
Fern, regardless of the variety, grown indoors, can reproduce in the following ways:
- disputes;
- shoots;
- dividing the bush;
- accessory kidneys.

Let's consider the above mentioned methods in order.
Reproduction by spores
Fern propagation by spores is one of the most laborious and time consuming method of reproduction. It can be divided into several stages:
- seed preparation;
- planting disputes;
- growing seedlings and caring for them.
Fern spores can be purchased at a specialty store, or you can try to collect them yourself on an adult plant, along with the sporangia in which they form. Sporangia are cut off when they are slightly brown. For full ripening, they are removed in a paper envelope. After a while, the spores will mature and get enough sleep. This will be the seed that needs to be planted.


The next point is soil preparation. A special soil medium for violets is best suited. It should be mixed with one part sand and three parts peat. The resulting arrogance must be brought to a monotonous state, remove large parts of the soil and sift well several times. Then the soil for sowing spores must be disinfected. To do this, it is sent to the oven for four hours, where it is kept at a temperature of one hundred twenty - one hundred sixty degrees.
You can use wooden, glass or plastic containers as a planting container. The main thing in them is to provide holes for the drainage of excess fluid. Now the prepared substrate is poured into the boxes for planting.The thickness of the soil should not exceed four centimeters. The soil is lightly tamped and well moistened, after which spores are sown and covered with glass. The air temperature at which the seedlings should appear should be constant, about twenty-three degrees. During the period of spore germination, the soil is moistened exclusively through the sump. Planting should also be regularly ventilated and condensation removed from the inside of the glass.
With proper care, fern spores germinate within a month. Visually, you can see that the surface of the substrate is covered with a green bloom resembling moss. These are spores that have sprouted, but since they do not yet have a root system and they are attached to the soil exclusively by rhizoid hairs, it is necessary to organize good care for them. The air temperature should be maintained at about twenty-two degrees and soil moisture. Germinated spores are left under glass until leaves appear and take root. The process of root formation and the appearance of the first leaves takes about two months. Now the seedlings need to be hardened. To do this, they must be opened for a couple of hours every day. After the fern grows up to five centimeters, you can replace it by watering through a tray for spraying from a spray bottle. It should be carried out at least once a week, since seedling growth should be carried out in a humidified environment.
Note that fern seedlings need room to grow. Therefore, they should be dived. It is recommended to make the first pick before the roots are formed. The second, and, if necessary, the third, as the seedlings grow. After transplanting, the seedlings need to be sprayed frequently so that they quickly adapt and take root. This should be done several times a week.
At the age of five to six months, seedlings can be transplanted into individual flowerpots. And after another couple of months you will admire a beautiful decorative flower with gorgeous greenery.
Vegetative propagation
Shoots, division of the bush, adventitious buds - all these are methods that relate to vegetative reproduction. All, without exception, types of indoor ferns have this ability. Any florist will be able to cope, having previously read the necessary information.


The next point is the reproduction of the fern by dividing the bush. There are certain requirements. Firstly, they start this type of reproduction only in the spring. Secondly, only adult, well-developed fern flowers are used. Technically, it works like this:
- an adult fern is watered abundantly and, after softening the soil, is removed from the flowerpot;
- the roots are carefully cleaned from the ground;
- a sharp knife separates the roots between the sockets;
- the resulting cuttings are planted in a previously prepared fertile and light soil;
- further care is the same as for an adult plant.
Accessory buds are formed on formed petioles. They can also be used for self-propagating ferns at home. But, adventitious buds are not formed in all varieties of indoor fern. Therefore, this method cannot be applied to everyone without exception. The reproduction technique by the kidneys is as follows:
- the buds are carefully separated from the petioles;
- planted in a nutrient soil under glass;
- maintain a constant high air humidity in the germination tank;
- when the roots are formed, the bud is carefully transplanted together with a lump of earth into an individual flowerpot.
The scions are long, fluffy arrows that form periodically on the fern bush. They are also used for breeding. To do this, you need to bend the shoot to the soil, pin it and provide good moisture. If possible, it is better to use moss for rooting. Within a month, the shoots will form roots and begin to form the ground part.After another month, it can be separated from the mother bush and planted in a pot.
Note that vegetative breeding methods are carried out in early spring.
Fern propagation by dividing the bush


Dividing a shrub using this method is very easy. It is just right for those new to this business. The day before the procedure, you need to water the plant well. The next day, put the flowerpot on its side and roll it over the surface. This will make it possible for the earthen coma to move away from the walls of the flowerpot. After gently turn the flowerpot over and the fern will quickly leave its place of residence along with a whole lump of earth.
Now you need to inspect the entire plant. It is necessary to select equal parts of the shrub so that at least 2-3 full-fledged sockets remain on each side, as well as a well-developed root system.
It is prohibited to divide a shrub that has one rosette.
This is due to the fact that a plant lacking rhizomes does not take root. The same can be said about rhizomes without growth buds. With a precise movement, a clod of earth is cut into equal parts. The resulting delenki are placed each in a separate flowerpot with new soil. Further growth of the shrub depends only on the care of the plant.
How ferns of Vyatka forests reproduce
Vyatka forests. The nature here is so pristine and poorly studied that, according to local residents, there is a "Bigfoot" here. Particularly attractive is the left bank of the Vyatka River, not affected by agricultural agriculture, where the entire territory is occupied by floodplain meadows and forests. The grass cover of this plot of land is multi-tiered and quite varied. Ferns are not the last place in it.
Most often in the Vyatka forests there are such types of fern as the fern, cochin and bracken.


On plots of land with constantly moist soil, whole fern spruce forests are found. It's amazing how ferns of Vyatka forests multiply: openwork fern leaves are attached to the spruce forest and grow without touching the ground. This spectacle is especially beautiful in autumn, when the fern leaves turn yellow and, against the background of green fir trees, form fancy laces woven by nature.
Lighting, humidity and temperature for the plant
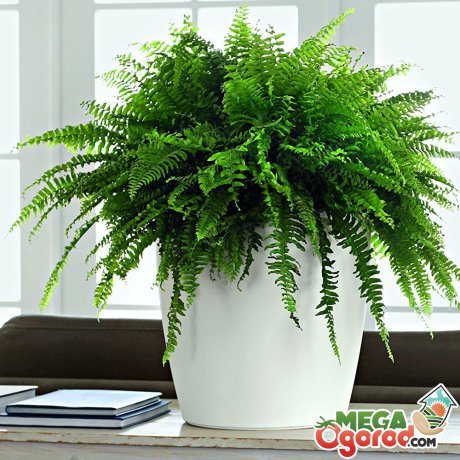


In order for the shrub to develop quickly and build up the ground crown perfectly, it is recommended to adhere to certain requirements:
- Lighting - Ferns of any species require a lot of ambient light. The bush can live in the shade of other plants, but then its appearance will not be so bright, noble, and the shade will not be saturated. But at the same time, the direct rays of the luminary scorch the delicate petals of the plates. Therefore, it is recommended to choose such an arrangement for the flowerpot so that the sun's rays fall on the plant in the morning and in the evening, and the shrub remains in the shade in the midday heat.
- Temperature - the most suitable temperature for a fern to live - +16 .. + 23 C. In winter and summer, degrees in the room where the plant is located, noticeably increase. Therefore, it is worth spraying the area next to the bush. This will saturate the leaf plates with nutrient moisture. The minimum temperature at which a fern is able to survive is +5 C. A further decrease in degrees will only lead to the death of the bush.
- Humidity - spraying the plates must be carried out every day, especially in winter, when the room is overdried by heating devices. To increase the humidity, you need to take a small towel and wet it and place it on the battery.
The formed microclimate is not only suitable for the plant, it will also be favorable for people.
Care


Ferns grow well indoors, but there is not always sufficient humidity there for their successful development (especially in winter).Spraying helps to increase the level of humidity in the room, or you can place a container with a fern in a tray with pebbles and water.
Ferns love humid places, but they can also withstand a short period of drought. At this time, their growth may slow down and slightly change color and brown, but when the drought is over, they will return to their previous appearance.
Watering and feeding the fern


Fern watering is very important. For the introduction of nutrient moisture, it is necessary to prepare settled, slightly warm water. Distilled as well as pre-harvested rainwater is ideal. Tap liquid will not work. It contains harmful substances that provoke the formation of dark spots on the leaf plates.
In the summer, it is necessary to water much more often than in the winter time.
You should not wait for the coma to dry completely, it is worth watching when the soil dries up a little and re-add water, but so that there is no oversaturation and stagnation of water in the soil.
Top dressing is very important for the plant. It is necessary primarily when there is an intensive build-up of green mass in the spring and summer. If the nutrients are completely absent or are introduced in the missing volume, then the plant first loses its color, and then completely dies.
Fertilizing, starting in spring, every week. For this, complex fertilizers are used. The only thing to stop feeding from the end of October until the first days of February. During this period, the plant is at rest, therefore, not only fertilizers, but also watering are sharply reduced.
Adult plant care
The fern has a very picky character, otherwise it simply could not survive for more than 400 million years. Moreover, the most persistent is the common ostrich, which is very common on the territory of the Russian Federation. It perfectly tolerates the harsh Russian winters and is able to grow calmly at home in a pot.


The most important condition for successful development is regular watering, which is somewhat reduced in winter. Sprinkle the leaves with water at least once a week. Ferns need feeding once a year, in the spring. The culture can easily grow at a distance from the window, because it does not like bright sunlight.
The plant is transplanted every 1-2 years, as soon as it becomes cramped in the pot. This can be understood by raising the pot (often the roots begin to sprout into the drainage holes) or by piercing the soil with a long wooden stick with a diameter of 5-7 mm: if it clings strongly, then it is probably time to change the container.
Fern is an unusual plant that attracts flower growers with its unusual foliage, unpretentious nature and history. There are more than 10 thousand species of ferns in the world, among which it will not be difficult to find a suitable option.
All about plant transplant


The plant is transplanted annually. This is due to the fact that the fern is a fairly large specimen of flora, so its root system within 12 months has time to completely fill all the free space in the flowerpot. The transplant is carried out by the transshipment method. This is the most gentle way to reduce trauma to the root system.
The process of transporting a plant to a new flowerpot should be carried out at the beginning of the growing season, in the first days of the coming spring. Otherwise, if the shrub is transplanted in the fall, then the fern will be sick for a long time, which can provoke the death of the bush.
For transplantation, a new land and a new flowerpot are taken.
The latter should be at least 3 cm smaller than the previous container. This is necessary so that the fern rhizomes have much further development.For transplanting in a day, it is also worth watering the plant as before reproduction of the shrub by the method of division. The next day, a clod of earth with a flower is safely removed from its habitat and transported to a new flowerpot, in which drainage is laid out in the first layer in advance, and then the earth is placed. After setting in the center of the plant, you can fill in fresh soil along the entire remaining perimeter and tamp it thoroughly. It is imperative that the plant is watered abundantly after planting.
Additional home methods
The spore propagation method is quite difficult for inexperienced growers, so you have to look for other options. The easiest way is to simply divide the mature plant into several pots. For this, a work surface and tools are prepared. The table is covered to avoid contamination. You will also need:
- several containers for seating;
- priming;
- drainage;
- water;
- Activated carbon;
- knife.


The plant is removed from the pot, the roots are freed from the old soil. If the fern has a rosette bush shape, then it is simply divided into separate units. With a common root, you should cut off a part of it with small roots and a pair of buds on top. The damaged area is rubbed with activated carbon. After that, drainage is placed in the pots, a layer of soil is about 5 cm and the plant is placed, and the empty areas are covered with soil and tamped. The last step is to water abundantly. Usually the plant takes root well and is not a hassle.
Another way is to reproduce by shoots. After wintering, the fern can release arrows, which are crowned with a miniature brother of a large plant, but without a root system. For rooting, a container with wet moss is placed under the shoot and pressed to the surface. With regular wetting of the moss lump, the plant quickly grows roots. Once it is sufficiently rooted, the arrow can be cut off.
The last option is brood buds, but they appear only in single ferns, for example, such as mnogoryadnik or kostinets. They form daughter plants on the fronds, which can be carefully separated from the main one and placed in a container for germination. It is best to use moss again instead of soil, and the vessel will need to be covered with a lid and placed in a shady warm place. Babies give root shoots within 2-3 weeks. After about a month, they can already be planted in flower pots.
Diseases and pests, the fight against them


The fern is susceptible to disease, like any other indoor flower. In order to prevent the emergence of pathogenic bacteria and the invasion of parasites, it is worth following the conditions of care and constantly monitoring the condition of the plant.
The following diseases are distinguished, which most often affect the fern:
- Decay of the root system - initially the problem is reflected in the foliage, it begins to turn yellow, then turns brown. In order to prevent the formation of a fungal disease, it is necessary to correctly add the amount of nutrient moisture and prevent waterlogging.
- Gray rot - on any segment of the shrub, as well as on the soil substrate, there is a pile of gray plaque. To save the bush, you need to quarantine it, away from other plants from the collection. Remove all damaged parts. if possible, disinfect the soil and spray the branches with chemicals from mold.
- Anthracnose - Brown stains form at the ends of the leaf plates. All diseased leaves should be removed from the plant, and healthy ones should be treated with a fungicide. In this situation, it is recommended to reduce the introduction of nutrient moisture somewhat, and also to remove the spraying for a while.
- Spotting on leaf blades - brown oozing spots form on the foliage. To save the pet, it is worth completely removing all affected areas, also reducing watering to a minimum and spraying with chemicals.
Views
Modern ferns are represented by more than 11 thousand different species, which are distributed around the globe. They grow in a wide variety of places: swamps, forests, fields and even deserts. Moreover, their appearance is as diverse as the places of growth. For example, in the tropical forests of South America, you can even find giant tree ferns that look like palm trees.


All ferns grown in the wild or grown in the garden and at home can be divided into two groups:
- gametophytes or sex plants. They are represented by females and males. These species often grow in the wild;
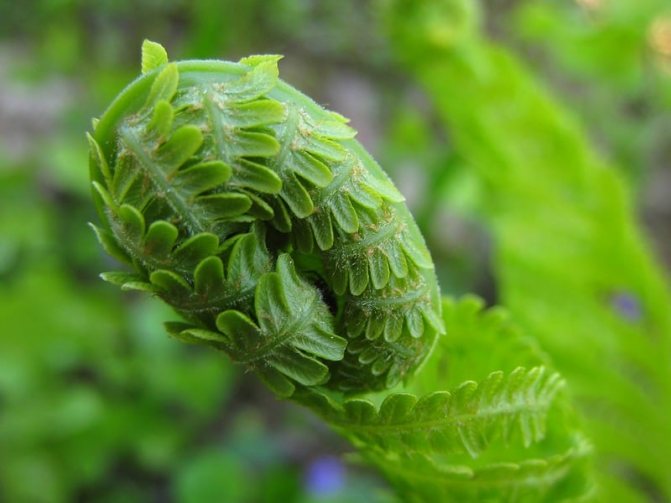
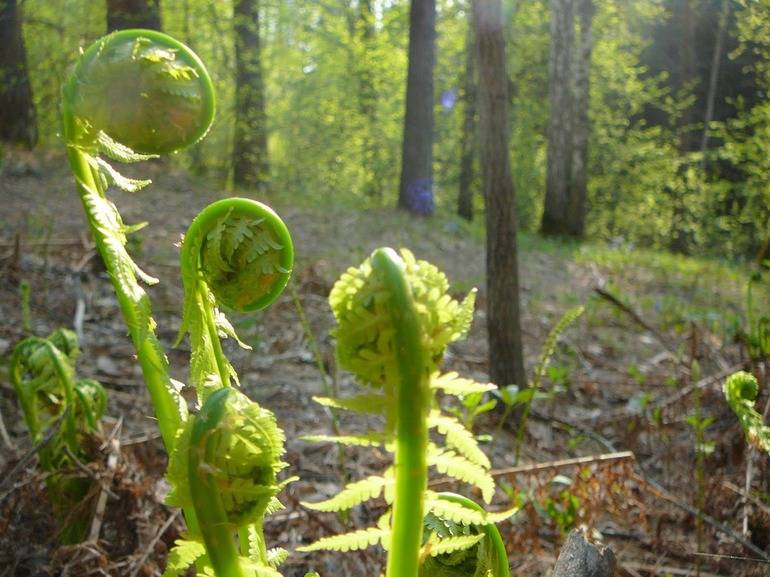
- sporophytes are asexual plants. Sporophytes grow in temperate and subtropical climates. Their characteristic feature is a sheet plate rolled into a spiral. It is these features that made sporophytes frequent residents of the house as decorative indoor flowers. This is due to the fact that the structure of the leaf of a plant can have a different appearance.
The following types of ferns are great for indoor growing:
- maidenhair. It is a graceful plant that forms feathery fronds, which are located on dark brown thin petioles. The leaves are characterized by fine dissection. Shades well. Has a simple care and rapid development, due to which the house quickly grows to a large size;
- asplenium. This indoor fern is characterized by a shiny leaf surface that has a light green color. The fronds have a solid, not divided into separate segments, structure. Therefore, they have a majestic and very beautiful appearance. A central vein runs in the center of the sheet. It darkens over time, which makes it more expressive;
- nephrolepis. Several species of this plant are grown at home, which differ among themselves in the size and shape of the leaves. Sori with spores are placed on their underside. Like Asplenium, it has simple home care;
- platycerite. The structure of this flower is characterized by two types of frond: sterile and spore-bearing. It is not recommended to touch the surface of the leaves, as this can disturb their silvery edge.


These are the most common indoor ferns in the home. But besides them, blehnum can be grown in the house. This flower, if the care was organized correctly, can reach a height of one meter. Leaves are formed quite dense and tough. Also dawallia or hare's foot often grows in pots at home. As an indoor flower, it is very attractive, as the plant forms beautiful shaggy rhizomes that hang from the pot. They look like a rabbit's foot, which gave the fern its second name. Growing this flower at home is also quite simple.
If desired, you can try to grow other types of ferns at home. The main thing is to know what kind of care they need at home.
Application in interior design
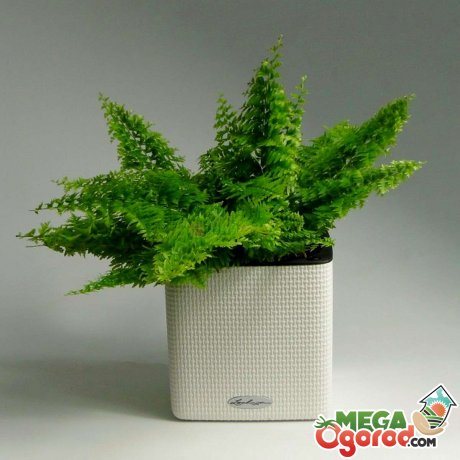


Growing a fern at home allows you to give the room a specific tropical atmosphere. The shrub looks interesting when planting plants in hanging pots. In addition, installing a flowerpot on a shelf or stand fills the room with coziness.
Placing a fern at home always attracts guests of the room. The shrub becomes the highlight of every room. Additionally, the bush saturates the room with air, creates a favorable temperature balance. The plant disinfects the indoor air from dust and other harmful toxic substances. Its delicate leaves hide noise, improve a person's mood.
Therefore, people who grow an amazing mythical plant in their home are always cheerful, full of energy.
Thus, the Fern is an unpretentious plant that can be easily propagated.Various methods are used for the process of obtaining a second copy. In order for the bush to actively develop, certain care and maintenance manipulations are performed.
More information about growing indoor ferns can be found in the video:
What is fern
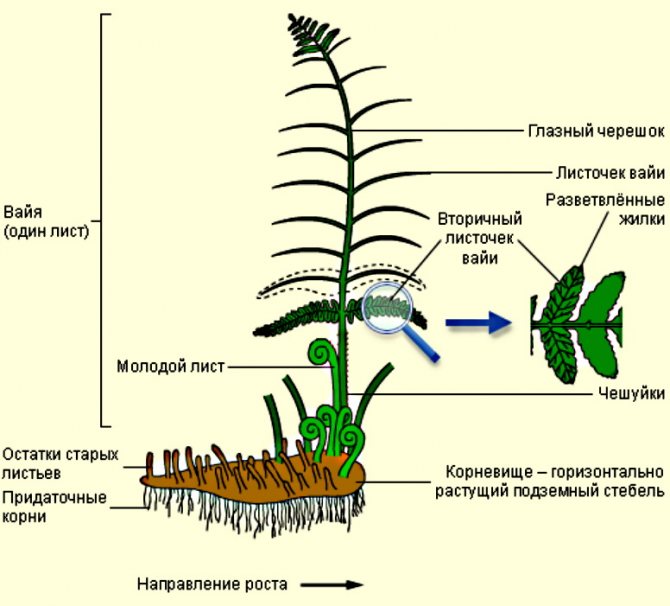
Along with the usual plant organ rhizome in ferns (Polypodióphyta), instead of stems, leaves, peduncles with seed pods, a leaf-like shoot developed, which received the scientific name frond. Spores form on fronds, with the help of which one of the ways of reproduction and development of ferns occurs.
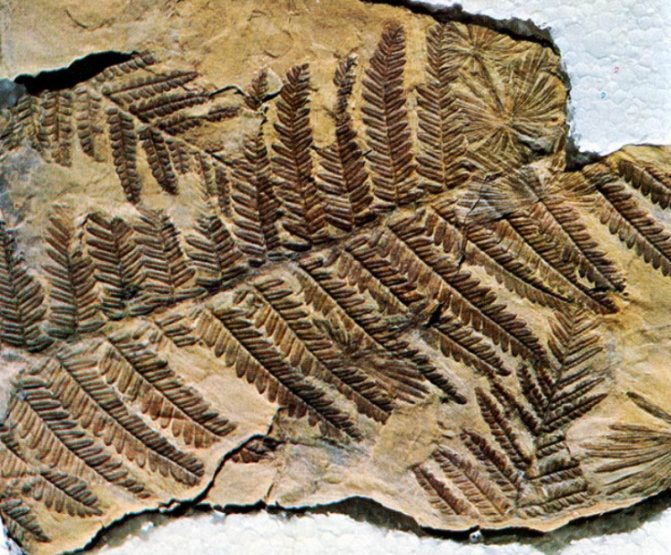


Fern print on stone
Currently, about 10 thousand perennial fern species have been identified on Earth. In the temperate climate of Russia, they grow in moist shady forests, they are grown as a garden crop. The most widespread European species of Polypodióphyta are the ostrich, bracken, and duckweed. Bracken fern is harvested in early spring, soaked, dried and used as a food product.
For your information! Growing bracken in a garden can negatively affect pets. The green parts of the plant contain toxic substances that are dangerous to them.
The tropical species Polypodióphyta are distinguished by a large variety of wai, and can have tree-like forms. Some of them grow high above the ground on the branches of other plants. In cold climates, the cultivation and reproduction of heat-loving ferns and fern-like plants (horsetail, lyre) is carried out at home.
Among the popular indoor ferns, the Aspelium stands out, with shoots resembling a green fountain; Blehnum, whose frond grows like the leaves of a palm tree; Nephrolepis is a lover of large free space; Disconia is a tall plant for office space; Platizerium, the fronds of which are like deer horns.
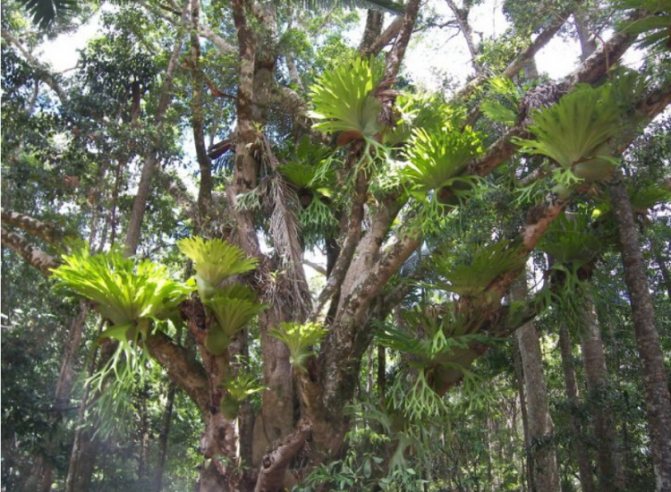


Tropical Platizerium on the branches of a tree
The necessary conditions

The first ferns appeared 400 million years ago, but over time, most of the varieties of this tropical culture ceased to exist. The main reason for the extinction of tropical plants is considered to be global climate change.
Today, according to encyclopedic reference books, there are more than 10 thousand species of ferns in nature, some of which can be propagated and grown at home.
For the successful cultivation of indoor plants, it is recommended to carefully study the description and properties of the cultivated crop. So, indoor fern is a shade-tolerant and moisture-loving culture. According to experts in the field of indoor floriculture, the success of the reproduction of a tropical flower depends on the correct timing of this procedure. The optimal period is mid-spring.
Please note that a flower growing in inappropriate conditions will be difficult to breed and root. For this reason, it is recommended to carefully monitor the air temperature and humidity level in the house. If the air in the room is dry, the plant will not take root. The fern needs diffused lighting (sunlight or artificial), infrequent feeding, moderate watering and frequent spraying of foliage.
The oldest plant on earth
Ferns are considered the most ancient plants that have existed on Earth since time immemorial. They appeared about 400 million years ago (middle of the Paleozoic era). But their features and unique properties (for example, high adaptable ability) allowed them not only to survive many species of the animal world, but also to become the most extensive group of spore plants represented on Earth today.


At the moment, there are about 11 thousand species of ferns. Moreover, some of them are grown at home. Here they are prized for their decorative beautiful leaves.Often, growing at home is typical for those species that grow in the wild in the climatic zone of the tropics and subtropics.
Do not believe the beliefs and expect flowering from this plant, because ferns reproduce by spores and in a vegetative way. Flowering involves the formation of seeds. Since ferns do not bloom, they do not form seeds either. The leaves of ferns are called frond.
These are the features these relict plants have.
Home Fern Care Video
In this video, an expert will tell you how to properly care for a fern at home.
According to many gardeners, the reproduction of ferns by spores is one of the most difficult and time-consuming processes. On the inside of adult leaf plates, brownish dust can be found - these are spores. The spores will serve as seeds for the propagation of a tropical flower.
Take a plastic bag and collect the spores in it. Pour a mixture of sand and crushed peat into a plastic container, distribute the spores evenly over the entire surface of the soil. Remember to moisten the soil well. To create a favorable microclimate, the container must be covered with glass.
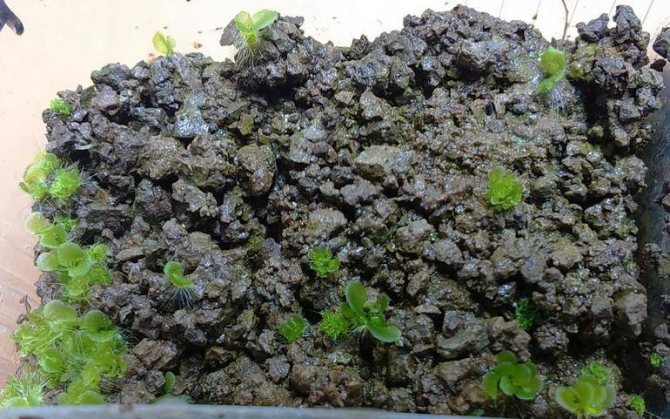
After 1–1.5 months, the first shoots will appear in the form of thick, bright green moss. As soon as the first leaves begin to hatch, you can open the container.
Young plants can be planted when three leaves are formed on each stem.
By dividing the bush
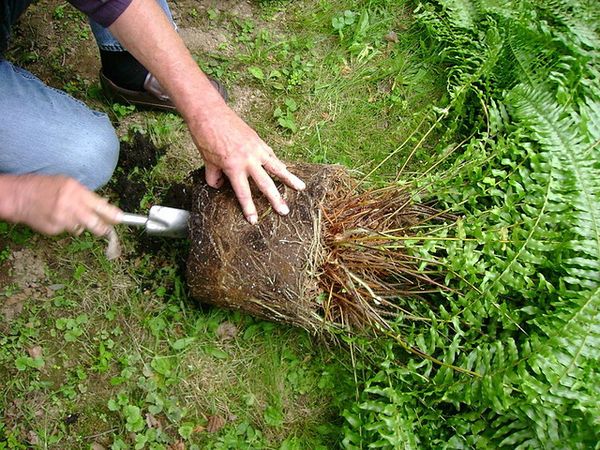


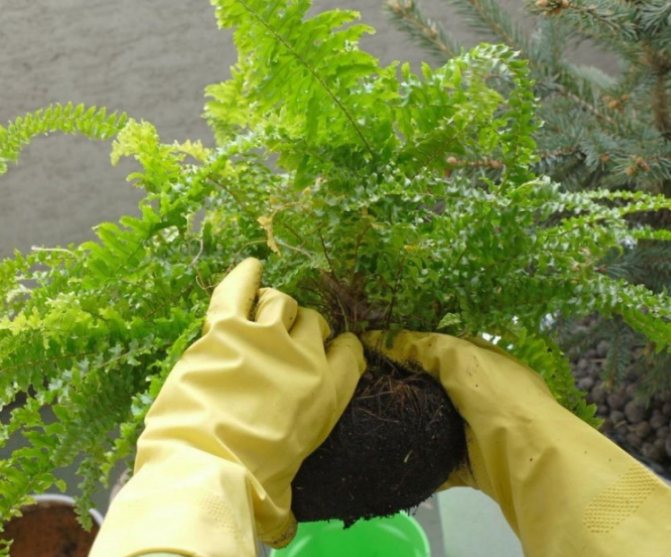
It will not be difficult to propagate a fern by dividing a bush if you first familiarize yourself with the advice and help of seasoned gardeners. Before proceeding with the transplant of an indoor flower, you should carefully examine it. In order for the bush to be divided into several fragments, each part must have a root system and 2-3 sockets. It makes no sense to share a bush with one outlet, since single outlets do not take root.
Upon completion of the division of the rhizome, each fragment is planted in a separate flower pot. Remember to keep an eye on soil moisture and air temperature. For fast and good rooting, it is necessary to adhere to a temperature regime in the range of + 18 ... + 22 ° C. Overdried soil, low air humidity, too low or, conversely, high air temperature in the room will lead to the death of transplanted ferns.
Vegetatively
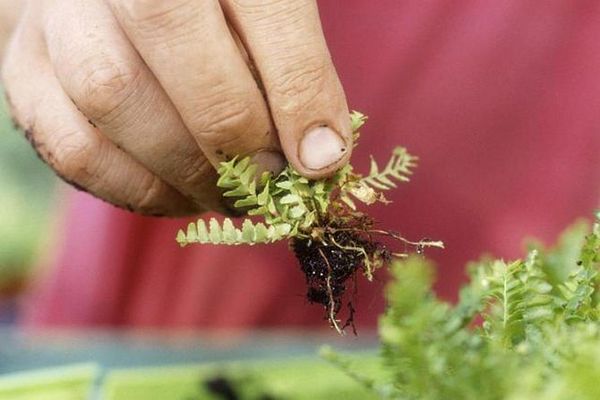


Reproduction by lateral buds and processes is referred to vegetative methods. But these methods of breeding indoor flowers are not suitable for all types of fern. For example, reproduction by brood buds is often used in the process of growing pemphigus, maidenhair, doriopteris palmate, etc.
How to grow a fern from brood buds, you ask? Let's consider this method in stages.
Carefully remove the brood buds on which the roots have formed from the leaves. Place the collected material in a special container covered with glass. It is important to maintain a high level of humidity inside and an air temperature of around + 24 ° C. It is recommended to transplant it into separate containers only when the young shoots get stronger and new leaves begin to form on them.
The shoots, which are long arrows on the fern leaves, are also used for propagation. Take a container with nutrient soil, place it nearby with a flower, bend the shoot to the soil and fix it.
It is necessary to separate the shoot from the mother plant in 1–1.5 months, when the roots are formed.
Fern propagation is the process of breeding a spore ornamental plant at home. Initially, it was considered a wild plant that grows exclusively in natural conditions.Today, many summer residents are engaged in breeding ferns in order to create an attractive landscaping of the garden area. Of the 11 thousand species, only 2,000 varieties are considered domesticated, which are propagated not only naturally, but also by seedlings, shoots.
Vegetative propagation of ferns
In a vegetative way, garden ferns, some houseplants and sex crops most often reproduce. Among the indoor species, the most suitable for dividing the root are maidens, pellets, leaflets, nephrolepis, pteris. Plants are propagated in the fall during the transplant process or in the spring, when the vai have not yet grown.
Plants that have only one growth point are not suitable for division. The root system is carefully cut with a knife between the sockets. Each split plant should retain a portion of the root system. The division procedure is performed only in cool weather. Plants are planted in the ground and watered thoroughly. When propagating in the fall, plants are also systematically watered.
Some species reproduce vegetatively, by means of brood buds on leaf stalks. Brood buds are transplanted into a greenhouse, for example, an aquarium. The greenhouse maintains constant humidity. When the plants take root, they are transplanted with part of the soil to a permanent place. There are very few plants that reproduce in this way, one of them is the bulbous bulb.
Reproduction of ferns. Vegetative reproduction. To consider the main vegetative breeding method of ferns - division, we are obliged to conditionally divide them into two groups:
1.having sprawling (most often superficially) rhizomes with single fronds growing from them. Such plants form clumps in which it is difficult to recognize each individual specimen;
2. forming a semblance of a rosette, bundle or compact group connected by a single short rhizome.
Plants of the first group are planted, dividing the sprawling rhizomes. It is advisable to choose the end segments - they have actively growing buds of renewal. In a simplified, plant-friendly version, it is possible to separate a part of the layer of the general curtain without fine division into separate pieces of the rhizome.
In plants of the second group, for large forms, it is possible to separate the lateral rosettes, and for small ones, a simple separation of the excavated specimen.
The best time coincides with the time of transplanting - early spring (beginning of growth). At other times, division is undesirable.
Some fern species such as Cystopteris bulbifera and Polystichum setiferum have the ability to form growth buds on leaves (fronds). This is easy to take advantage of by bending bulbous fronds to a wet substrate. Fern reproduction photo:
disputes1 Reproduction of ferns. Spore reproduction. All ferns can be grown from spores - microscopic cells that are used for reproduction. On the underside of the frond of an adult plant, it is easy to see small tubercles, arranged randomly, in rows or strokes. Sometimes they form a solid crust or encircle the edge. These structures are called soruses - sporangia are collected in them, in which spores are formed. Some species have special spore-bearing fronds.
The maturity of the dispute is judged by the browning of the sori. Collect them together with a part of the leaf and put them to dry in a paper bag, which is kept in a cool dry room or in a refrigerator and opened immediately before sowing. The periods of preservation of the viability of spores of different ferns vary greatly: from several days to 15-20 years.
For sowing, the spores are separated in a draft-free room. To do this, you need to knock on it without opening the package, from which the spores spill out. If the spores have not separated, then the sori are scraped off with a knife. You can also collect spores from a fresh green leaf. The spores are extremely small and look like a brown powder.Each sample is processed separately, after having thoroughly washed and dried hands. The table and the instrument are periodically washed. If the measures to maintain sterility are not followed, then spores of different types will mix.
Sowing spores can be done at any time, but with a lack of light and heat in the temperate zone, the best period is the end of winter - the beginning of spring.
Spores can germinate on any moist substrate, but a slightly acidic environment is required for successful seedling development. Usually the following mixture is used: high-moor peat, leaf soil, sand (2: 1: 1). All components must be carefully prepared: both the very small and the largest particles are removed from them. The thoroughly mixed substrate is sterilized to destroy seeds and spores of other plants, pathogens and pests. (Breeding ferns)
Steaming is the best method of sterilizing soil without disturbing its structure. The substrate is placed on a fine sieve, placed over boiling water and covered with a lid. After 2-3 hours after it is moistened, the procedure is finished (in total, it takes about 3-4 hours). After 2-3 days, the potting mix is ready. Store it in a clean container with a closed lid.
For seeding, you can use deep “Petri dishes” with tight-fitting lids or small translucent plastic containers covered with glass. I must sterilize any dishes
otvet.
How ferns reproduce in nature
Ferns usually reproduce naturally by spores or brood buds. During the entire life cycle, plants go through the sporophyte and gametophyte stages. Sometimes, with the spread of the root system and the increase in new organisms, independent dispersal occurs through the genital branches. In such places, an overgrowth appears, which arises in the place of a spore pocket.


The reproduction process is simple: sporangia are formed on fronds, in which spores develop with a single set of chromosomes. Once ripe, the spores are spread by water or wind. The fern reproduces by spores only under favorable temperature conditions. Getting into such conditions, the overgrowth germinates, then it is fixed on the surface with the help of rhizoids. Subsequently, in the lower part of the plate, sex cells develop with sperm and eggs. After full maturation, fertilization and the birth of a zygote occurs. The embryo feeds on the germ until it finds its own roots. Thus, a real shrub grows from the embryo or gametophyte.
Features of the structure of fern leaves
Ferns belong to the group of higher spore plants. Their leaves are actively involved in the process of photosynthesis. Fern spores form on the lower part of the leaves, with the help of which the sporophytes reproduce safely. There are species in which spores form on certain spore-bearing leaves or at the very top of the frond.


Depending on the species, the shape and structure of the leaves, as well as their size, differ. There are pinnately dissected forms, and there are solid ones. Leaves are also curly, up to thirty meters long, but this is in species found in natural conditions.
However, regardless of the varieties, they all belong to unusually beautiful plants that are very popular with flower growers.
How can fern propagate in the garden
In gardening, several types of fern propagation are used: bush division, seedlings, spores, root buds. Previously, sporangia was collected in order to ripen spores at home. The breeding process consisted in the preparation of planting material, which is stored in tightly sealed envelopes and planted in moist soil.
After planting, the seed tray is covered with dense polyethylene or glass to create the necessary microclimate. The first shoots appear in 20-30 days.Shoots of rhizoid greens are treated 3 times a day with an epin solution. Protallium or fern seedlings are planted in separate peat glasses, which will absorb excess moisture when watering. When the sprouts reach 5-10 mm, the seedlings dive. For 6 months, 3 transplants are carried out, then at the age of 8 months the fern is planted in a flower bed or flower pot.


A street plant is planted by dividing the bush, which is dug up in early spring. Dig holes in advance, then divide the main bush into several small parts. Before planting, cut off the rotten parts of the plant and sprinkle it with earth. Daughter shrubs begin to develop after a week of acclimatization on a new land. This feature of fern breeding is noticeable by the weekly lethargy of the branches, which goes away after rooting.
It is not always possible to collect planting material in the form of spores on time or to purchase a quality product in a store. However, seedlings may not grow if they do not provide comfortable conditions for the microclimate and soil.
What conditions are necessary for the reproduction of ferns
Basically, comfortable conditions for the favorable development of the plant are high controlled humidity in the room or moist soil outside. The optimal time for the start of vegetative reproduction of a fern is early spring with a constant positive air temperature. Bushes are also planted in the summer after rain, when the ground does not require additional moisture. The fern does not dominate over third-party plants, therefore it can coexist with various types of shrubs.


The less often the gardener plans to water the plant, the further the bushes are planted in the shade. The plant takes root and develops well under any kind of lighting. When planting on the sunny side of the site, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the bush and soil. Rapidly withering branches are a clear indicator of a lack of moisture and vitamins. Effective watering like a summer shower after sunset from a shallow watering can will make the fern lush and vibrant. It is worth noting that in the shade the ferns are more branched, while in the sun they grow in compact bushes with light greenery.
Bracken fern
The name "bracken" for this species of ferns did not arise by chance - its leaves are too similar to huge eagle wings. Bracken leaves can reach up to 1.5 m in width and up to 1 meter in height. The plant has medicinal substances for health - it contains catechins, flavonoids, phytosterols, carotene, riboflavin and nicotinic acid. Therefore, it is widely used in cooking and pharmaceuticals.


Do you want to know how the bracken fern reproduces in order to grow it at home? The easiest way to do this is to do it vegetatively - by digging up or acquiring a plant along with thin cord-like rhizomes. Early spring is most favorable for transplanting, but a fern transplanted at the end of summer can take root quite well.
Bracken fern also reproduces by spores. They ripen in late July and early September. During this period of time, you can try to peel spores from an adult plant and dispel them in a humid place in your area.
Bracken fern is unpretentious in care - does not require additional feeding, easily tolerates frost and lack of moisture.
Knowing how the bracken fern reproduces, it can be easily grown in your garden. The plant is very decorative, unpretentious and has the ability to grow quickly, which won the hearts of flower growers.
How to propagate a fern by dividing a bush
An effective way to propagate a shrub, which can be done in any warm season of the year, is to divide the bush. To begin with, the day before planting, the roots of the plant are poured abundantly with water. According to the description and reproduction scheme, ferns are planted to a depth of 20-30 cm, although the planting hole is dug 50-70 cm deep. I cover the bottom with rubble mixed with a substrate and fertilizers.The bushes are divided into 4 small parts so that the roots are not severely injured. There should be 2 or 3 rosettes on each part of the plant. Rhizomes without growth buds will take a long time to take root or may not take root.
The roots are carefully spread over the substrate at the bottom of the hole, then sprinkled with earth. After planting, the fern is watered and sprayed with a diluted solution of phytoncides from insects. In the first year of growth, a root circle is made for watering and the roots are mulched with hay or large sawdust. If the leaves begin to turn yellow or rusty, you need to fertilize with compost or mineral fertilizer. Watering methods should be alternated: shower from a watering can 2 times a week and 1 root watering. A pick is done only when necessary, if the bush is not accepted or the soil is too heavy, acidic.


Scheme and description of plant reproduction
Fern propagation takes place with the help of seeds.
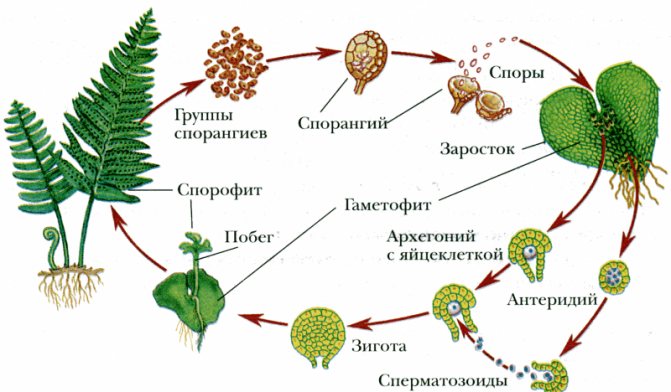

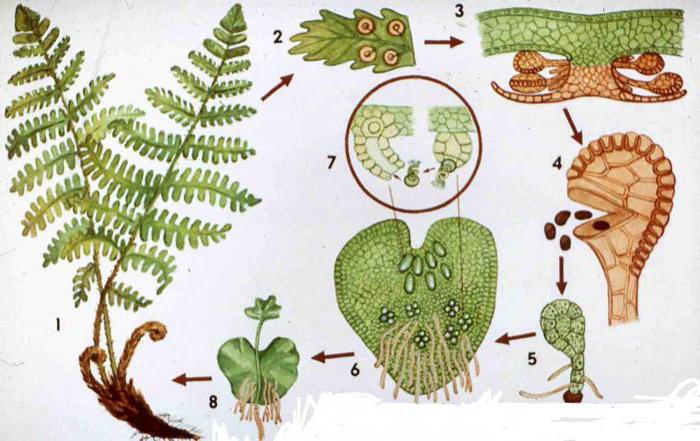
The fern propagation scheme is as follows: on the lower side of the fern leaf there are sori, which, when ripe, are separated from the leaf plate. Sporangia in the sorus ring burst, scattering fern spores around them. Then a small green plate is formed from the spore, growing into the soil. This overgrowth is attached to the soil by rhizodes, has male and female reproductive organs. As soon as water gets on the plate, for example, after rain, fertilization occurs: in the female organs (archegonia) there is an egg cell, to which spermatozoa move from the male organs (antheridia) drop by drop, and fertilize it. It turns out a full-fledged embryo, attached to the germ, from which it feeds during development. Then a plant grows over time.
How to propagate a fern with spores
Growing ferns from spores is a rather laborious process of cultivating a shrub, which requires special care until the first transplant. Planting material is purchased in company stores, although the process of collecting sporangia can be done on your own.
Spores can be planted at any time of the year if the planting is for indoor fern production. Outdoor spore plants are planted in early fall or spring. Spores are scattered over the surface of the wet soil, then sprinkled with a layer of earth 3-4 cm. The kidney is sprayed from a spray bottle and covered with glass, cling film so that condensate collects inside. After the appearance of the first shoots, the coating is removed in the daytime, and when the protallium appears, they are planted in pots.


Until the first leaves form, the seedlings are kept under glass and opened for 2-3 hours. With frequent and moderate watering 2-3 times a week, the sprouts will quickly grow. The room needs a constant positive temperature of + 20-23 ° C. Wild varieties are more adapted to emergency conditions, but it is difficult to guess the time for collecting sporangia in the forest. This is not the most efficient way of fern propagation, but with proper care and preparation of the planting material, a healthy plant can be grown.
Fern structure and development
The main phase of the life cycle is the sporophyte.


Features of the structure of the sporophyte:
- not long roots extending from the main oblong rhizome. The primary root dies off quickly, and small roots grow stronger, buds form on them;
- shoots - formed from the buds on the roots, are the main way of fern breeding;
- leaves - grow from the root;
- sporangia, collected in small bunches called "soruses" - small green lamellar capsules with spores - the second way of fern breeding.
Life Cycles:
- Asexual plant. A full-fledged seed-producing fern shrub.
- Disputes. Seeds from the boll trapped in the soil.
- The outgrowth. A small green plant attached to the soil, producing male and female cells at once.
- Gametes. The stage of reproduction, fusion of cells of different sexes.
- The embryo.Formation of a new asexual plant.
On a note. The green mass of the fern is not usually called leaves, since in structure it is completely different from the usual foliage of flowering shrub plants.
Is it possible to grow a fern from seeds
In no case should fern spores be confused with seeds. Planting material is prepared independently. As soon as sporangia are formed on the lower leaves, several branches are pruned. The spore sacks will not have time to open, and when they mature, they will be ready for drying. The seeds are removed from the sheets and dried under gauze in a low-humidity room. Fern propagation by seeds begins in mid-March or late April.
The seeds are planted in the ground when they can be crumbled to the touch. The method of growing a shrub is almost no different from a spore one, except that the spores do not always germinate and most of the planting material dies at the stage of development before the protallium. In the first 2-3 months, watering is carried out 1-2 times a week. The minimum temperature for planting outdoors is allowed up to + 10 ° С, in the room up to + 15-18 ° С. At the age of 6 months, they are transplanted into new soil, fed with phosphates. At the age of 1-2 years, the bushes are divided into seedlings.


Sexual fern generation
Once in favorable conditions, the spores grow and form an outgrowth - a small plant that is a sexual generation, the so-called gametophyte. The outgrowth looks like a small green plate, reaching 1 cm in diameter. In the lower part of the outgrowth there are rhizoids, with the help of which the tiny plant is fixed in the soil. In the outgrowth, female and male genital organs (archegonia and antheridia) are formed, in which eggs and spermatozoa develop. Since the overgrowth is tightly pressed to the ground, drops of dew or rain linger under it. In this water, sperm "swim" to the eggs. When they merge, fertilization occurs, and a new plant subsequently develops from the formed zygote, which immediately gains growth, turning into a powerful fern.
>
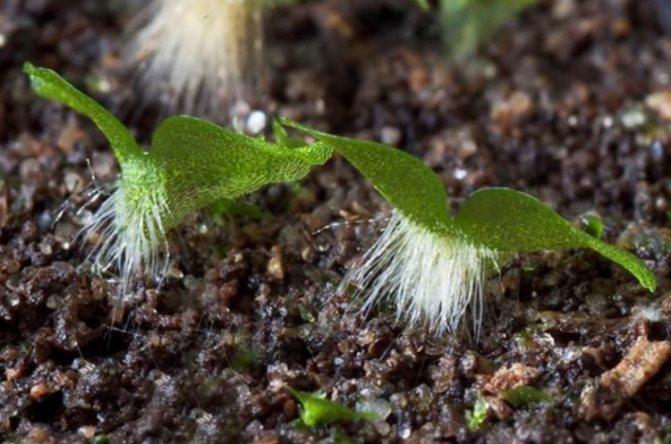
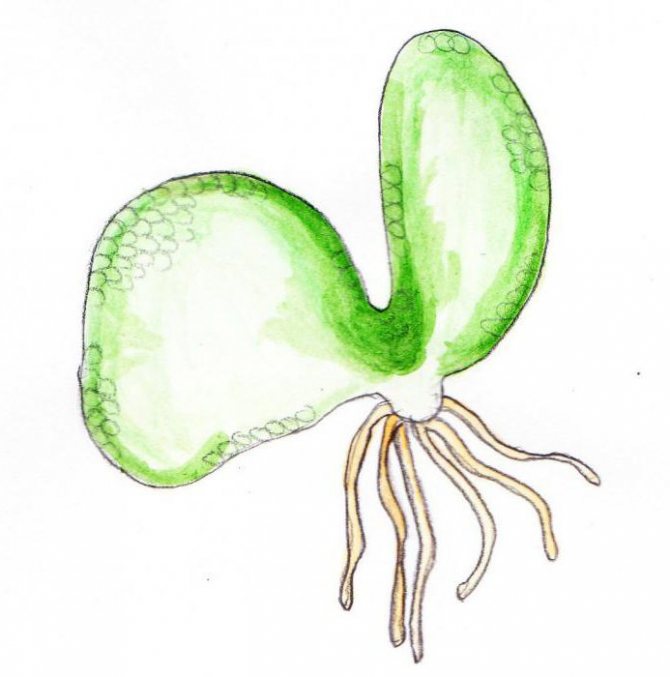
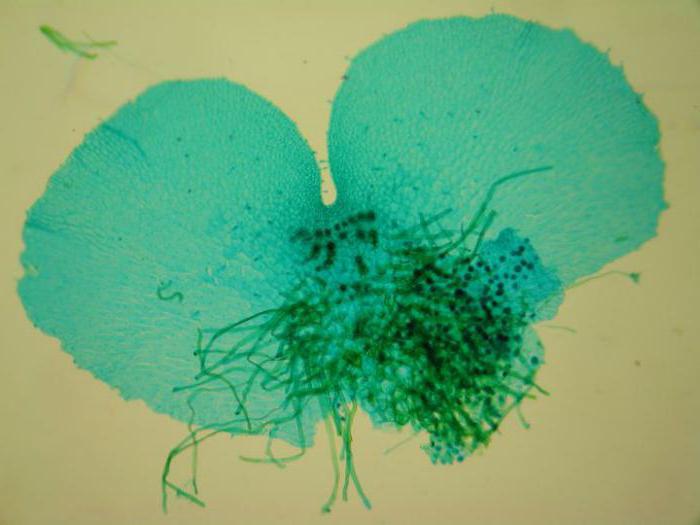
What is an outgrowth
The result of the development of spores is an outgrowth. This is an individual of the sexual generation, which is the next link in the fern development cycle. For a long time, scientists did not even know about its existence. The thing is that the overgrowth is very small in size - only up to a centimeter in diameter. Outwardly, it is a heart-shaped green plate. The germ develops on the soil, to which it attaches with the help of rhizoids.
As the gametophyte develops, the organs of sexual reproduction are formed on its underside. Sex cells of two types mature in them: eggs and sperm.

Artificial reproduction
The fern is a very interesting and peculiar plant, so it is not unusual for many people to try to propagate it right at home.
Germination of spores


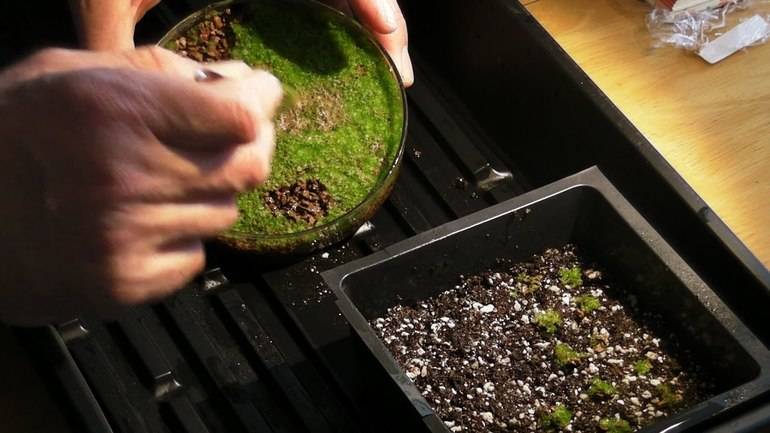
This is a tricky way and quite difficult to master. Therefore, according to the stories of the gardeners themselves, they often simply divide the fern bush into separate parts with roots and buds, and then plant them in favorable shady places in their garden.
However, not all fern species are able to reproduce vegetatively. Some of these plants are characterized by a single growth point, and no additional buds appear on them.
Thus, for the reproduction of this species, it remains to germinate spores, otherwise it will not work to multiply it. As you already know, after the spore germination, the fern will go through the entire life cycle, and only then a new individual will be born.
It should be told in what sequence the germination of fern spores should be carried out.


- A leaf of a mature plant, covered with brown bumps (spore sacs), must be cut off and placed in a paper bag. Not in cellophane;
- A package with a leaf should be put in any warm place for a day, not forgetting to shake it periodically;
- When the spores finally ripen and fall out of their bags, you need to take them out of the bag and place them in a prepared nutrient mixture consisting of sand, peat, coal and crumbled greens;
- The dishes with the mixture and germinating spores should be placed in a humid and warm place with a temperature of at least twenty-five degrees Celsius. The surface should be moistened at regular intervals with a spray bottle and in no way allowed to dry completely. To improve the effect and reduce moisture evaporation, the container must be covered with glass.
After the first shoots appear, watering is done with greater responsibility, because at this stage of development, moisture is the predominant component of the whole process. In the absence of water, fertilization of the egg will not occur, and all preparations will go down the drain. After all, growing a fern from a spore is a real work.
Ecology.
Most temperate ferns prefer damp, cool, shady forests with abundant leaf litter or north-facing slopes of deep ravines with percolating groundwater. Some species (calcephiles) are confined to limestone substrates, others (acidophiles) grow best on acidic soil. Epiphytes occur in the tropics, i.e. ferns that inhabit tree branches. Species with waxy leaves, thick hairs, or overlapping scales are found on dry rocky slopes, stone walls, and even in deserts. At the other extreme, ferns with scarious leaves, consisting of a single layer of cells; the lack of devices to prevent water loss limits their distribution to places constantly shrouded in fog or wetted by the spray of waterfalls.
Ferns are found from the Arctic Circle to the equatorial jungle. Rainforests are richest in these plants. For example, on the island of Jamaica approx. 500 species of ferns; their number decreases to the north. In the United States, ferns are most common in the southeast. Here, in a strip from 1800 m above sea level to the subtropical coastal lowlands of Florida, there are approximately 150 native fern species. The ancestors of some of them survived in the Blue Ridge Mountains when much of southeastern North America was inundated by the sea; the ancestors of others came to this region from the tropics via a land bridge that once existed between Florida and the Caribbean.
Stem
it can be creeping or vertical, completely or partially underground, sometimes it reaches a height of 25 m and is crowned at the top with a rosette crown. In many species, for example, in the bracken, aerial leaves branch off at certain intervals from the highly branched underground stem (rhizome), forming extensive dense thickets in the glades. porous plants differ from seed plants by the absence of cambium in the stem, i.e. a special layer of constantly dividing cells, therefore, annual rings are not formed in them, and growth in thickness, the conducting capacity and strength of the trunks are limited even in tree ferns. The main supporting function is performed by thick-walled cells of the cortex and the adventitious roots braiding the stem along its entire height.
Fern life cycle stages
Several stages are required for the emergence of a new young sprout. The life cycle of a fern is a combination of all phases, from the inception of life to the stage of maturity, when the plant is already capable of giving rise to a new life. The cycle is closed in nature.
The stages of the life cycle of a fern are arranged in the following sequence:
- Spore.
- Gametophyte (outgrowth).
- Eggs, sperm.
- Zygote.
- The embryo.
- A young plant.
When all the stages are passed, the young plant, having developed and strengthened, will be able to repeat this cycle for the birth of the next generation.
Description of the plant


Ferns are often used for landscape decoration. They are unpretentious in nature, very beautiful and diverse. Ferns are sometimes called eagles for their feathery foliage pattern, reminiscent of the wings of an eagle. One of the most widespread types of fern is "Shitovnik". Ferns are the largest class of lymphoids. They look like mosses, but they are not.
This handsome man has many useful qualities. The protein contained in them is easily absorbed by the human body and gives it tone. Its beneficial effect on the human nervous system is also known.
Northern China and the Far East are considered the birthplace of ferns. However, the most exciting thing about this representative of the flora is the procedure for its reproduction, called the development cycle.
Where are the sporangia located
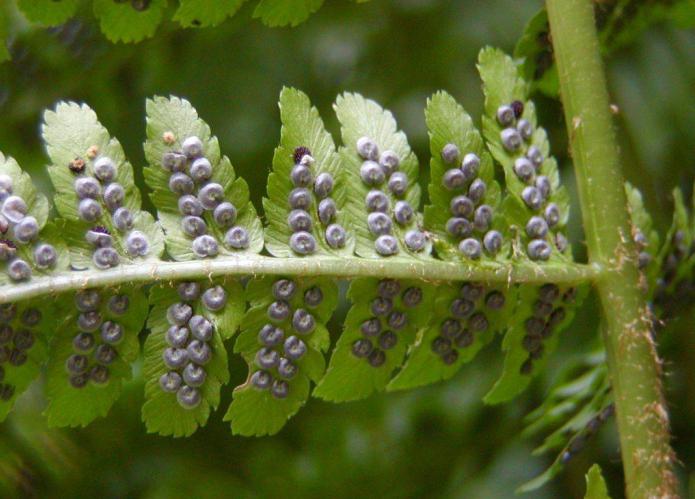
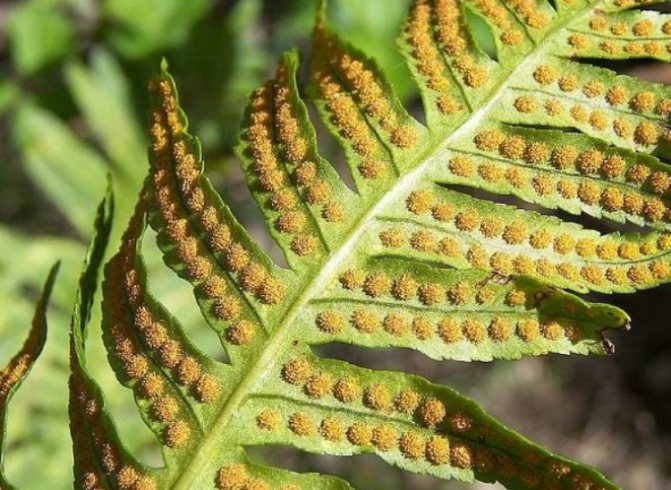
The next stage in the fern development cycle is the maturation of the organs of asexual reproduction. They are called sporangia. These structures appear as small brown bumps located on the underside of the leaves. From above, they are additionally protected by membranous "covers". Fern sporangia are collected in groups called sori.
At the end of summer, these structures darken. This means that the sporangia are ripe. Then they open, and thousands of small cells pour out into the ground. This is controversy. In the presence of sufficient moisture, they immediately begin to germinate.


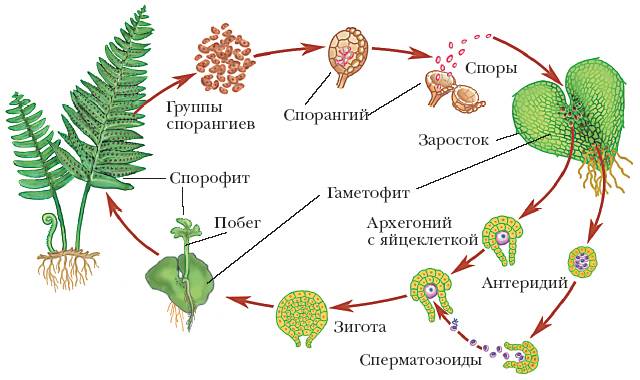
Reproduction.
The life cycle of ferns includes the change of asexual generation (sporophyte) and sexual generation (gametophyte). Sporophyte is a fern familiar to everyone, i.e. a plant with a root, stem and leaves, and the gametophyte is a thin heart-shaped plate, often less than 15 mm in diameter, called a growth (protallium). A strip of specialized cells in the wall of the sporangium - a ring - breaks its wall when it dries, and spores spill out. Each of them, once in moist soil, can form a green growth that feeds on photosynthesis and absorbs water and salt from the soil by hair-like rhizoids present on its lower surface. In structure, the outgrowth does not resemble the sporophyte that gave rise to it, but rather the thallus liverwort from the bryophyte department. On the underside of the outgrowth, the genitals (gametangia) are formed, and in them - gametes. Male gametangia - antheridia - contain spermatogenic tissue surrounded by three to four epidermal cells, while female gametangia - archegonia - are flask-shaped structures, in the enlarged abdomen of which a single egg cell develops, and the narrow "neck" (neck) is filled with the so-called. nalc cells. The latter are destroyed when archegonia ripens. Spermatozoa are spirally twisted cells that can swim thanks to their numerous flagella. Released from the antheridium, they penetrate into the archegonia neck, and through it - to the ovum. One of them fertilizes it, and the resulting zygote grows right inside the archegonia. The young sporophyte developing from it parasitizes for some time on the protallium, but soon forms its own roots and green leaves: the life cycle ends.
Sporophyte can multiply not only by spores, but also in another way. When the leaves of the crooked corn-leaved plant fall on the ground, new baby plants form on their tops. As a result, large colonies (clones) can quickly emerge. Bulbous tuberous buds develop bulbous-like bodies with a supply of water and nutrients in two fleshy leaves. Falling to the ground, they take root and give new sporophytes. Many ferns form long stolons ("whiskers") with scaly leaves. At certain points, they take root: here daughter plants arise.
All ferns - ferns, horsetails and lymphoids - have a similar life cycle.
They reproduce sexually and asexually. For them, as well as for bryophytes, the alternation of sexual and asexual generations is characteristic, but, unlike mosses, the asexual generation predominates in ferns - the sporophyte. It is the sporophyte that forms perennial rhizome grasses.
On the leaves of the fern, special organs are formed - sporangia with spores:
Fern sporangia
In sporangia, thousands of small spores develop, which are carried by the wind and, under favorable conditions, germinate, forming a haploid gametophyte - an outgrowth. The germ is the sexual generation of the fern, it looks like a small (up to several centimeters) heart-shaped plate, has rhizoids for attachment to the soil, and is not divided into organs.
Outgrowth
Rhizoids at the outgrowth
On the outgrowth, male and female genital organs are formed - antheridia and archegonia. In the antheridia, male germ cells are formed - spermatozoa, and in archegonia - female ones, eggs. After rain or heavy dew, the sperm swim up to the archegonia and fertilize the egg. Despite the fact that ferns live on land, fertilization is possible only in water.
When a sperm and an egg merge, a zygote is formed, from which a new sporophyte grows.
A young sporophyte that has grown from an outgrowth
Ferns have another way of reproduction - vegetative, by dividing the rhizomes into parts.
Plaunas
Plaunas are the oldest ferns. Nowadays, these are perennial herbaceous plants with long creeping stems, densely planted with hard leaves. Roots extend downward from the stem, and branches with spore-bearing spikelets grow upward. These spikelets form haploid spores, from which very small, 2-3 mm, colorless outgrowths with rhizoids grow. They live underground for 3 to 15 years, forming a symbiosis with mushrooms, and only after that antheridia and archegonia are formed on them. After fertilization, a new sporophyte grows from the zygote, just like in ferns.
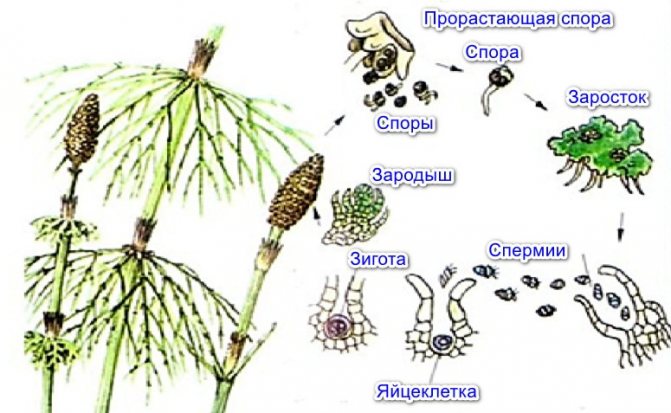
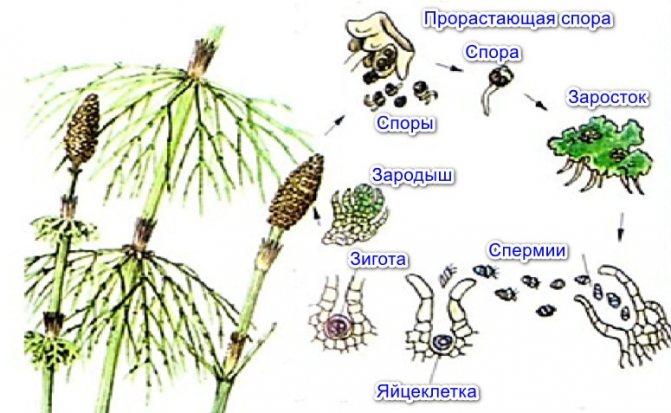
Horsetails
Once upon a time in antiquity, horsetails were huge trees up to 10-20 m high with powerful trunks. Horsetails are currently perennial herbs that grow in damp forests, wet meadows and swamps, especially on acidic soils.
Horsetails have a perennial hibernating rhizome with adventitious roots, from which aerial, similar to small fir-trees, shoots with whorled leaves grow every year.
Horsetail stems are tough and contain silica, and are even used for grinding wood and metal. In early spring, a spore-bearing stem grows upward from the rhizome of the field horsetail - an arrow - thick, pinkish. It consists of nodes and internodes, and is hollow inside. In the nodes there are accreted, chlorophyll-free, reduced leaves, they cover the growth zones rich in sugar. In Russia, these arrows were used for food.
Horsetail
After the spores mature and spill out, the stem dies off, and green leafy shoots grow to replace it.
Horsetail
Small outgrowths with archegonia and antheridia grow from the spores, fertilization occurs in water, after which new sporophytic individuals grow out of them.
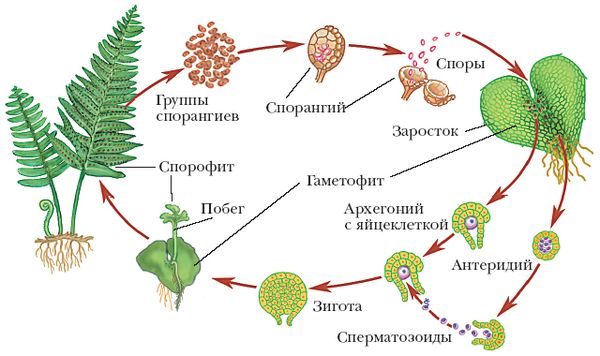
All ferns - ferns, horsetails and lymphoids - have a similar life cycle.
They reproduce sexually and asexually. For them, as well as for bryophytes, the alternation of sexual and asexual generations is characteristic, but, unlike mosses, the asexual generation predominates in ferns - the sporophyte. It is the sporophyte that forms perennial rhizome grasses.
On the leaves of the fern, special organs are formed - sporangia with spores:
Fern sporangia
In sporangia, thousands of small spores develop, which are carried by the wind and, under favorable conditions, germinate, forming a haploid gametophyte - an outgrowth.The germ is the sexual generation of the fern, it looks like a small (up to several centimeters) heart-shaped plate, has rhizoids for attachment to the soil, and does not divide into organs.
Outgrowth
Rhizoids at the outgrowth
On the outgrowth, male and female genital organs are formed - antheridia and archegonia. In the antheridia, male germ cells are formed - sperm, and in archegonia - female, eggs. After rain or heavy dew, the sperm swim up to the archegonia and fertilize the egg. Despite the fact that ferns live on land, fertilization is possible only in water.
When a sperm and an egg merge, a zygote is formed, from which a new sporophyte grows.
A young sporophyte that has grown from an outgrowth
Ferns have another way of reproduction - vegetative, by dividing the rhizomes into parts.
Plaunas
Plaunas are the oldest ferns. Nowadays, these are perennial herbaceous plants with long creeping stems, densely planted with hard leaves. Roots extend downward from the stem, and upward are branches with spore-bearing spikelets. These spikelets form haploid spores, from which very small, 2-3 mm, colorless growths with rhizoids grow. They live underground for 3 to 15 years, forming a symbiosis with mushrooms, and only after that antheridia and archegonia are formed on them. After fertilization, a new sporophyte grows from the zygote, just like in ferns.
Horsetails
Once upon a time in antiquity, horsetails were huge trees up to 10-20 m high with powerful trunks. Horsetails are currently perennial herbs that grow in damp forests, wet meadows and swamps, especially on acidic soils.
Horsetails have a perennial hibernating rhizome with adventitious roots, from which aerial, similar to small fir-trees, shoots with whorled leaves grow every year.
Horsetail stems are tough and contain silica, and are even used for grinding wood and metal. In early spring, a spore-bearing stem grows upward from the rhizome of the field horsetail - an arrow - thick, pinkish. It consists of nodes and internodes, and is hollow inside. In the nodes there are accreted, chlorophyll-free, reduced leaves, they cover the growth zones rich in sugar. In Russia, these arrows were used for food.
Horsetail
After the spores mature and spill out, the stem dies off, and green leafy shoots grow to replace it.
Horsetail
Small outgrowths with archegonia and antheridia grow from spores, fertilization occurs in water, after which new sporophytic individuals grow out of them.
It's time to move on to the fern development cycle
The main stages of fern development
From sporangia, when spores mature in them, they begin to fly out. The sporangia themselves are surprisingly adapted for this. When the disputes in them are already ripe, the sporangia crack in a special way, and often, even also turn outward. Spores from this spill out and fly in the wind. Spores are very light and through the air they can, like dust, fly away a considerable distance from the fern, from the frond where they were formed.
From the spores, when they fall on wet soil, the next generation begins to form. Recall, by alternation, a sex generation should grow out of disputes. It is completely different from asexual. Remember the compliment that the old woman Shapoklyak gave to Gena the crocodile? She said, "It's good that you are green and flat." This is how the sexual generation of the fern can also be characterized - a tiny green plate about the size of a marigold, a little like a heart.
The main thing that this small, flat, green heart has is not on the top side, but on the bottom. Thin strings extend from the underside of the gametophyte - this green flat heart. These are not roots - these are rhizoids, the very rhizoids that you can hear about in algae or bryophytes.In gametophyte (reproductive generation of ferns), there are no real roots. It attaches to the soil by rhizoids - the same attachment organs that were found in ancient plants - its ancestors.
We will also see more important parts here, for example, small sacs in which the eggs should ripen, because we have a sexual generation in front of us. We have to find where the germ cells are formed here. So, the eggs mature not far from the cutout that makes our record look like a heart. Nearby, but closer to the edge, are other bags. In these sacs, which run along the edge, sperm mature. And here, it is clear why, the gametophyte has such a structure and why it is so flat.
After rain, water flows under a thin plate and remains there for some time. A humid environment is formed in which sperm from their sacs swim to the eggs. So, before us is a gametophyte. This gametophyte - bisexual, that is, it is hermaphroditic, and a moist environment is formed under it, in which the sperm swims across this water film to the egg. This means that fertilization takes place and where the eggs have just been, zygotes are already formed, that is, fertilized eggs, the first cells of the new future organism.
Population conservation
Although this type of fern is quite widespread, its population is gradually decreasing. There are several reasons for this. One of them is massive deforestation. The male shieldworm is one of those vulnerable plants that have very sensitive roots and therefore are difficult to tolerate any human intervention in their environment.
In addition, this plant is a constant collection item. It is harvested as a medicinal raw material, and some tanners use shitnikov for tanning and dyeing leather.
Paleobotany.
Ferns are one of the oldest land plants. They have been known since the Paleozoic era (about 350 million years ago) and were especially abundant in the Carboniferous period (the remains of fern-like ones that lived at that time formed deposits of coal). The most primitive families of this group are completely extinct, and they can only be judged by the fossils. The ancient families of Osmundaceae and Marattiaceae are now represented by very few species. All other modern families appeared no earlier than the middle of the Mesozoic (about 150 million years ago), and the number of species in them has decreased since then, except for the family of centipedes (Polypodiaceae), which unites the most common living ferns.
Propagation of male shieldworm
This fern species has mastered quite large territories and is found almost everywhere - from Scandinavia to the Mediterranean, in North America and even in the Arctic. It is widespread in Russia as well. The male shieldworm prefers coniferous and mixed forests, where there is high humidity and little penetration of sunlight.
Most of all, fern thickets were found in places with a predominance of such trees as aspen, linden, birch, as well as in spruce-fir forests. Less commonly, this plant can be found in pine forests, since moisture is very poorly preserved there. In mountainous areas, the shrimp grows on slopes sheltered from the wind and in rock crevices.


Sheet
- the most visible part of the fern. In all species, except for aquatic ones, the leaves are first coiled, and unfold as they develop. Their final sizes and shapes are quite varied. They are usually pinnate. From a common petiole, as, for example, in nephrolepis, small leaves extend on both sides. Often they are divided into leaves of the second and third orders (this is observed, in particular, in mutant forms of the same fern). yi births common in greenhouses Cyathaea
,
Cibotium
and
Angiopteris
reach a length of 5.5 m and a width of more than 90 cm.The representative of the tropical family Schizaea dwarf reaching Newfoundland resembles a small cereal with leaves twisted in a corkscrew. Another unusual example is the genus
Vittaria
, whose representatives have long cord-like fringed leaves hanging from the branches of palm-shaped saber. Liana fern leaves
Lygodium
entwine support plants, and in some tropical species of the family Gleicheniaceae, long forked leaves are covered with sharp thorns and form almost impenetrable thickets.
Usually the leaf is used in ferns for photosynthesis and for the formation (on its underside) of reproductive structures - spores. They are formed in sporangia, which are located either openly or protected by the folded edge of the leaf or by special outgrowths of its epidermis - the veils (Indusia). In some species, sporangia are formed only on specialized leaves in the middle part of the frond (Clayton's chistostomus), at its apex (for example, in the acrostica multiforme) or on entirely spore-bearing leaves of special shape, sometimes losing the ability to photosynthesis.
Fern structure
The common fern plant we see is the asexual generation, or sporophyte. In almost all ferns, it is perennial, although there are few species with an annual sporophyte. Ferns have adventitious roots (only in some species they are reduced).
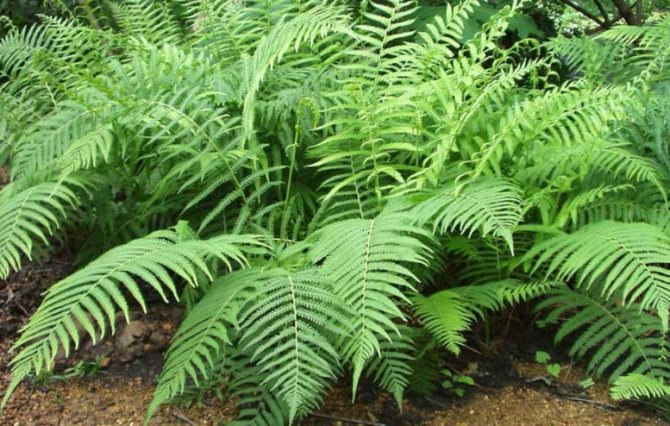


Ferns - photo
Foliage, as a rule, prevails over the stem in weight and size. Stems are erect (trunks), creeping or curly (rhizomes); often branch. Our forest ferns (ostrich, bracken, male fern) have a well-developed rhizome with numerous adventitious roots extending from it. Above the ground, there are only large pinnately dissected leaves - fronds.
A young leaf is cochlearly folded, as it grows, it straightens. In some species, leaf development takes three years. Fern leaves grow at their top like stems, indicating their origin from the stem. In other groups of plants, leaves grow from the base.
In size, they can be from a few millimeters, up to three or more meters in length, and in most species they perform two functions - photosynthesizing and spore-forming.
Fern breeding
On the underside of the leaf there are usually brown tubercles - sori with sporangia located in them, covered with a thin film on top. In sporangia, as a result of meiosis, haploid spores are formed, with the help of which the fern reproduces.
A haploid outgrowth, gametophyte, a small green heart-shaped plate, up to 1 cm in diameter, develops from a forest fern spore that has fallen into favorable conditions. The outgrowth grows in shaded, humid places and attaches to the soil with rhizoids. Antheridia and archegonia develop on the underside of the gametophyte.
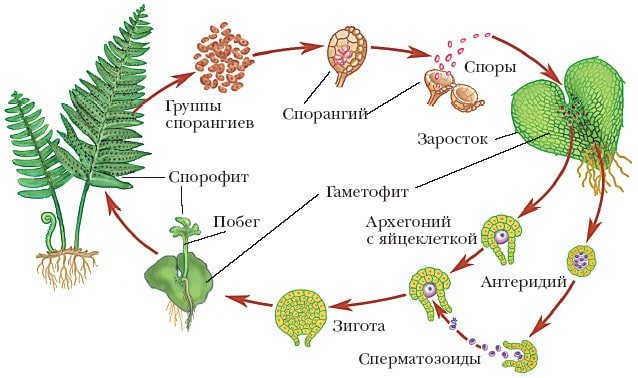

Fern breeding process
Fertilization occurs only when there is sufficient moisture. The sperm move along the water film to the archegonia, which secretes certain chemical stimulants such as malic acid. A diploid sporophyte develops from the resulting diploid zygote. Initially, it grows as a parasite on the gametophyte, but soon it develops its own roots, stem and leaves - it becomes an independent plant. This completes the fern development cycle.
The "conquest" of land by ferns turned out to be incomplete, since the generation of the gametophyte can exist only with an abundance of moisture and shade, and an aquatic environment is necessary for the fusion of gametes.
Asexual and sexual stages during reproduction
The fern is the result of asexual generation. Consider the sequence of the life cycle of a fern.
In order to start a new life, an adult plant should have spore sacs on the back of the leaf, in which the spores will mature. When the spores are ripe, the sac will burst and spores will fall out of it. Under the influence of the wind, they will scatter in different directions and will germinate when hit on favorable soil. This stage is very important, because without it the plant would not be able to exist. As a result, a process will appear - a gametophyte - a sexual generation of a fern. It is shaped like a heart. This heart has thin threads at the bottom - rhizoids, with which it attaches to the soil. The germ of the fern is bisexual, with small sacs on it: in some, eggs ripen, in others - sperm. Fertilization takes place with the help of water.
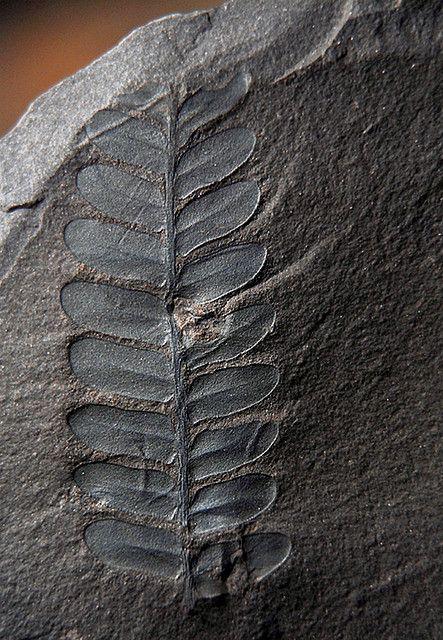


Since the seedling is very small and has such a peculiar shape, this contributes to the slow drainage of rainwater and its retention below. Thanks to this, the sperm can swim up to the eggs and fertilize them. As a result, a new cell appears - a zygote, from which a sporophyte embryo is formed - the result of a new asexual generation. This embryo consists of a haustorium, which in its appearance resembles a leg growing into an outgrowth, and at first consumes from it the substances necessary for its growth. After a while, the first leaf of the embryo appears, which serves as the beginning of the development of the fern.
Thus, the asexual generation predominates in the fern life cycle, which gives life to a new large and long-lived plant, and the sexual generation is small and rapidly dying off. Moreover, it is necessary for fertilization.
Sexual reproduction and its features
For self-propagation of a fern at home, it is necessary to collect spores that have been freed from the shell and sow in the right place. This area should be well hydrated. The condition for the successful conception of a new plant is a high level of humidity.


For cultivation, it is recommended to use a mixture of peat, sterilized soil and charcoal in a ratio of 8: 2: 1, respectively. The resulting mixture is filled in a small pot almost to the top, then it is thoroughly tamped, sprinkled with brick chips. Stones are thrown into this crumb. The top of the pot is tightly covered with transparent glass. The entire structure is placed in a pan with settled water. Growing temperature 21 degrees. The place should be darkened.
The first outgrowths appear in a month, after another two - the fertilized small ferns let out the first leaves.
Appearance
Representatives of the order of ferns have spread throughout the world. They have a different appearance of leaves, are environmentally unpretentious, while more like moist soils.
The fern has a root system, stem and leaves. He has no seeds. On the inner side of the leaf, below, there are spores in sporangial sacs. Fern leaves are called "fronds", they are not like the leaves of other plants. They look as if several branches were laid in one plane and attached to the stem. Their color can vary from light green to dark green.


Fern, not counting the root system, consists of frond, sorus and Indusia, where sorus is a bunch of sporangia, Indusia is an outgrowth resembling an umbrella that covers the sorus.
The most beautiful and the simplest
The most common varieties for cultivation are remarkable for their extraordinary beauty. The common ostrich is famous for its large leaves resembling ostrich feathers in appearance. Eagle's leaf plates resemble eagle feathers (hence the name). The Nippon kochedzhnik can pleasantly diversify the green massif with the unusual color of its deciduous plates: they are pearl-gray, with reddish veins. Maidenhair (Venus hair) grows with a lush cap of pale green color.Azola with small leaves can be a decoration of the reservoir. Asplenium (Kostenets) flaunts with long sword-shaped leaves.
One of the most ancient plants on Earth, the fern is incredibly diverse and beautiful, and it rewards those who grow it with dignity, giving a special charm and originality to the collections of flora lovers.
Plaunas - structure
Plaunas were widespread during the late Devonian and Carboniferous periods. Many of them were tall, tree-like plants. At present, a small number of species (about 400) has survived compared to the past - all these are small plants - up to 30 cm in height. In our latitudes, they are found in coniferous forests, less often in swampy meadows. The bulk of the lyre are inhabitants of the tropics.
The common species in our country is the club-shaped lymphoid. It has a stem creeping along the ground, from which needle-branching lateral shoots extend vertically upwards. Its leaves are thin, flat, arranged in a spiral, densely covering the stem and lateral branches. The growth of lymphoids occurs only at the point of growth, since there is no cambium in the stem.
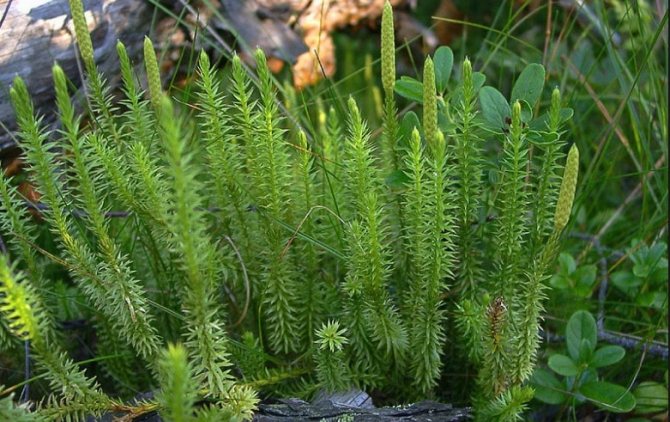


Year-old plow - photo
Reproduction of lymphoids
At the top of the stem are special leaves - sporophylls, collected in strobilus. Outwardly, it resembles a pine cone.
The germinating spore produces an outgrowth (gametophyte) that lives and develops in the ground for 12-20 years. It has no chlorophyll and feeds on fungi (mycorrhiza). The change of sexual and asexual generations in horsetails and lymphoids occurs in the same way as in ferns.
Fossil ferns formed thick coal seams. Bituminous coal is used as a fuel and raw material in various industries. It is used to produce gasoline, kerosene, combustible gas, various dyes, varnishes, plastics, aromatic, medicinal substances, etc.
How to propagate a fern
Higher and lower groups of plants
Plants are divided into higher and lower groups. They differ in their habitat. Higher plants "came out" on land and spend their life cycle on earth. These plants include ferns. Terrestrial plants have a clear division into root, stem and leaf.
However, it cannot be said unequivocally that ferns have completely moved away from the aquatic habitat, since a free-living gametophyte is involved in their reproduction process and the spermatozoa necessary for the fertilization process can exist only in the aquatic environment.