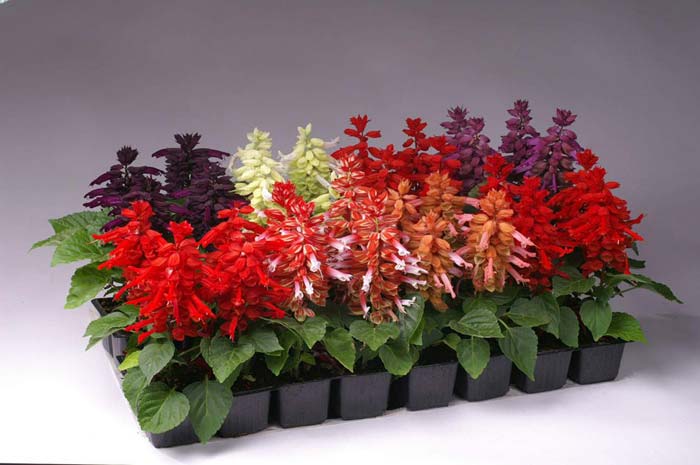
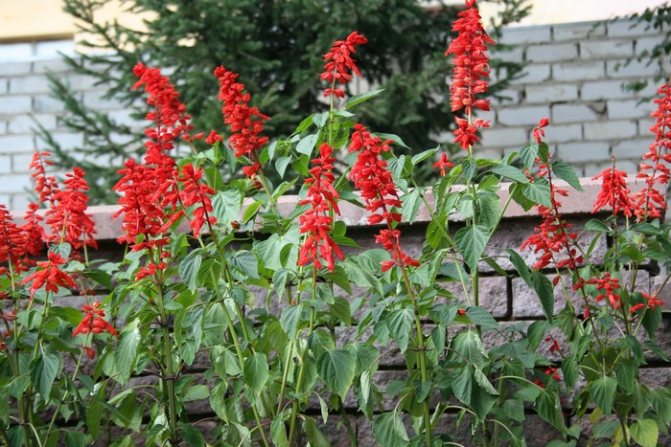
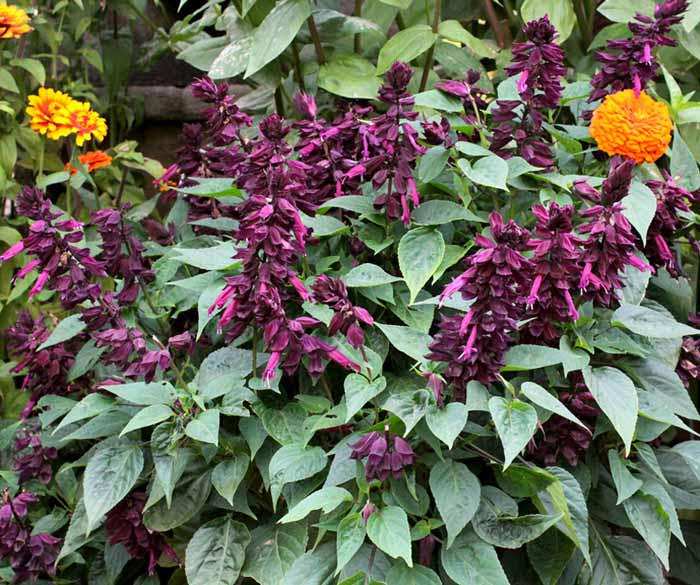
Sage in Latin is called Salvia, it is under this name in Russia that the decorative variety of this plant is known. Salvia appeared in Europe several centuries ago, they belong to the Lamiaceae family and exist in nature as perennials. To avoid confusion, it is customary to divide plants of this species into two groups and call only medicinal species as sage, and decorative salvia. The cultivation of perennial salvia in temperate climates has its own characteristics, because this plant is of tropical origin. Despite the plant's increased love for heat and sun, hundreds of species of cultivated sage can exist without problems in flower gardens and flower beds in the northern country.

Photos of perennial salvia flowers, a description of popular varieties can be found in this article. Here you will learn about the seedlings of this plant and how and when to plant it, how to care for flowers, what to do with salvia in winter.
Growing features
Location: Most species require a sunny location. Salvia sticky puts up with partial shade. Many species are drought tolerant.
The soil: the best soils for them are dry, lime-rich, permeable, not too light. Glutinous salvia grows best on rich and moist soils, and glittering salvia grows best on moderately fertile and loose ones, blooms poorly on moist and rich soils. Salvia forest on heavy soils rots and loses strength.
Care: After the main flowering, cut the forest salvia completely, and then the plant will bloom in late summer. Fertilization also contributes to the second flowering. Shorten Salvia officinalis by 2/3, then the plant will be more compact. Remove the shoots.
Care Tips
Salvia grows best in a well-lit, sunny, warm place protected from the wind. The soil should be neutral or slightly alkaline, relatively fertile, with the addition of coarse sand or fine gravel for good water permeability. Before planting salvia, add some vermicompost or compost to the soil.
The plant does not tolerate stagnant water, which leads to root rot, but overdrying the soil is also unacceptable. In soil that is too wet or too dry, the plant will stop growing. Beautifully flowering ornamental varieties are fertilized once a month with mineral water-soluble phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, which stimulates abundant and long-lasting flowering.
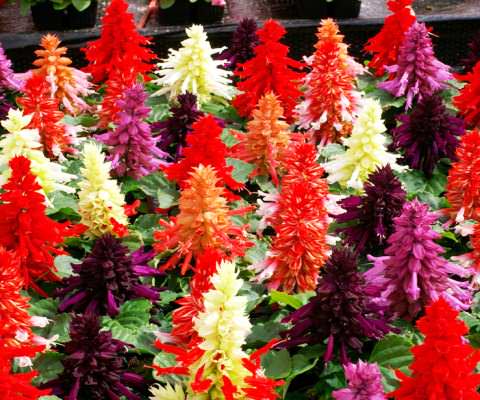


Salvia sparkling
Cold-hardy varieties tolerate frosty winters well if their root system is covered. To do this, mulch the ground around the bush or pour a layer of leaves, needles. In early spring, the plant is pruned, leaving 8-10 cm above the ground. Pruning contributes to the formation of a beautiful bush shape and stimulates the growth of new shoots. Perennial sage propagates by dividing the bush, preferably in the fall after flowering and by rooting stem cuttings.
Reproduction
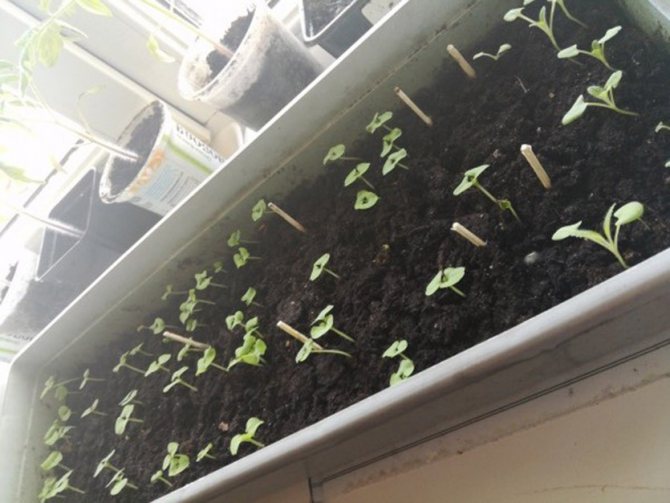
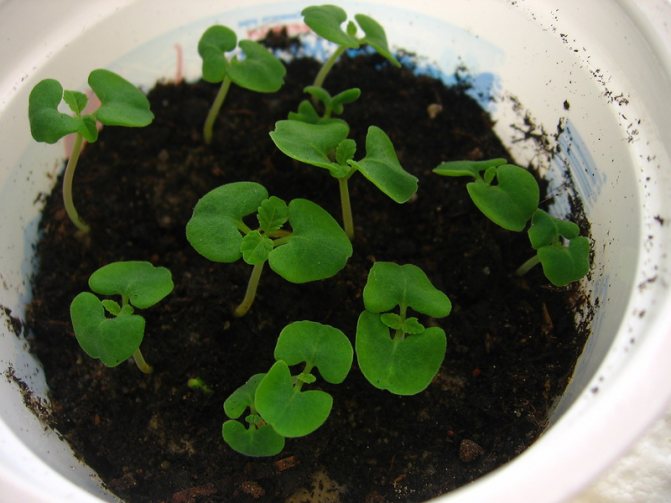
Annual and biennial species of Salvia are propagated by seeds, which are sown in spring and before winter. Seeds of glittering salvia are sown in February - early March in boxes. Seedlings usually appear on the 10-15th day. Seedlings dive twice. To obtain strong seedlings, the second pick is carried out in 9 cm pots. In April, they are taken out to greenhouses for hardening. They are planted in a permanent place in early June, after the end of spring frosts, keeping the distance between plants 20-25 cm.Seasoned seedlings transplant well.
Perennial species are propagated by seeds, stem cuttings and bush division. Planting is best done in late August - early September. Young plantings in the first winter require shelter.
When and how to sow seeds for seedlings
One- and two-year-old salvia can be planted with seeds or seedlings. For some species (eg shiny), only the second breeding method is suitable. You need to start in mid-February. The deadline for sowing salvia in boxes is the beginning of March. For hybrids, this may be a later time. You need to check with the data indicated on the seed packaging.
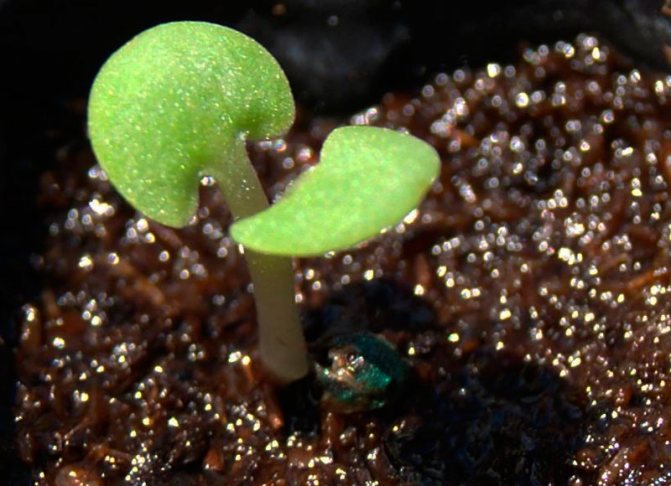
Salvia soil requires loose, moisturized. Seeds should be spread over its surface and sprinkled with a thin layer of earth. The container must be covered with foil, glass or newspaper, placed on a sunny windowsill. Periodically, you need to moisten the crops using a spray bottle. The temperature required for germination is + 22 ... + 24 ° C. Under these conditions, you can wait for the first shoots in 7-10 days.
Attention! The seeds of culture do not germinate amicably, but this is a feature of Salvia, and not errors of agricultural technology.
Seedlings, which have 2-4 true leaves, must be dived into the pots, keeping a 5 cm distance between the seedlings. The cotyledon (first) leaves are buried in the ground. The second picking procedure takes place about 3 weeks after the first. For each sprout, you need to take a separate container with a diameter of 10-12 cm. After the formation of the 5th true leaf, the bush is pinched so that it is more lush. From the beginning of April, the seedlings are hardened, gradually lowering the night temperature to + 10 ° C.
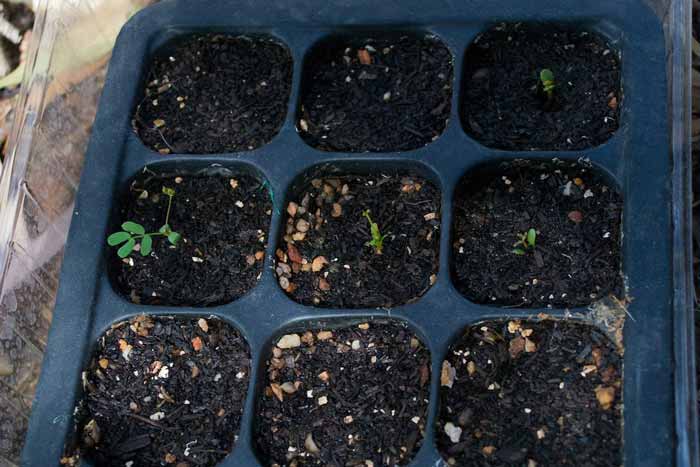


Planting salvia
Use of ornamental sage
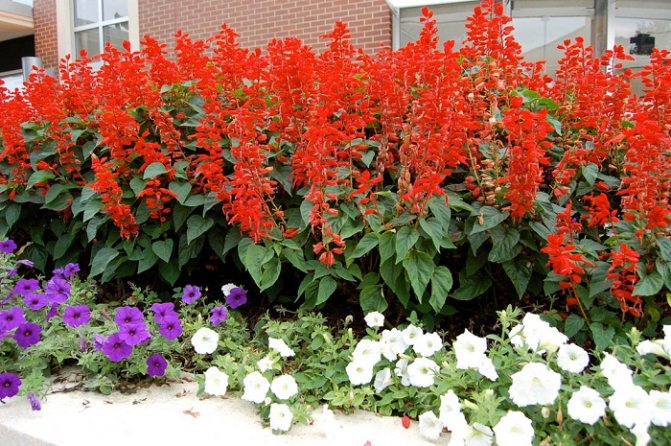
Most sage plants are used in landscaping. Brilliant sage is very effective in ceremonial compositions, flower beds, flower beds. Cultivars with compact habit are good for growing on balconies, in pots, flowerpots and containers. Much less often this species is planted in mixborders, however, it deserves wider use in mixed compositions, since it allows you to create bright spots that are decorative for a long time.
Ethiopian sage is suitable for group plantings against a background of stones: unusually beautiful and large rosettes of pubescent leaves in the first year of the growing season, and huge airy inflorescences in the second. Sage bright red, mealy, green, whorled, sticky, meadow and oak are good in mixborders and groups. Their loose inflorescences do not give bright color spots, however, a variety of shades of lilac-blue gamut, large, picturesque bushes, excellent compatibility with other perennials make it possible to successfully use these species in landscape compositions.
Compact sage - dandelion-leaved and Jurisic's sage - look great in the foreground of mixborders, and can be recommended for rockeries as well. Sage is rarely used for cutting, however powdery sage is great in arrangement. Its dark blue velvety inflorescences retain decorativeness in water for a long time, and when dried, they are an excellent material for winter bouquets. In dry compositions, you can also use faded whorled sage (Purple Rhine variety with purple cups) and green sage. The tops of the shoots of the latter are dried in bulk in the sand, while the spectacular purple or bright pink color of the bracts is completely preserved.


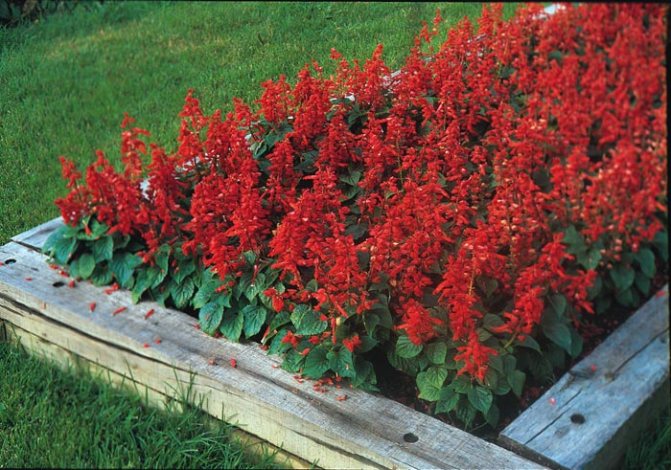
A flower bed from Salvia.
Pests and diseases


Fungal diseases do not harm salvia. The main problem for the plant is insects. Whiteflies, aphids, thrips, spider flies, slugs and snails harm the decorative species of plants and can lead to their death.
Whiteflies when planted closely with vegetables, they move to flowers. These small white butterflies infect the leaves and form a white coating on them, they suck sap from the plants. This insect very quickly covers a large area of plants.In the absence of chemical or biological protection, they lead to the death of flowers.
When the appearance aphids, you need to immediately take protective measures, this insect multiplies very quickly and in a short time can destroy a large area of salvia plantings.
Thrips almost impossible to see as they are very small. When this insect appears, the leaves curl and dry out. Insecticides are used to control thrips.
With the defeat of salvia spider mite, diseased plants are removed and burned.
Slugs and snails They eat tender salvia leaves and use special traps to combat them. The slate and bark under the plants help to get rid of these pests. For minor lesions of slugs and snails, you can remove it by hand.
The best protection against pests is prevention, which is carried out periodically throughout the growth of the plant.
Views
Decorative
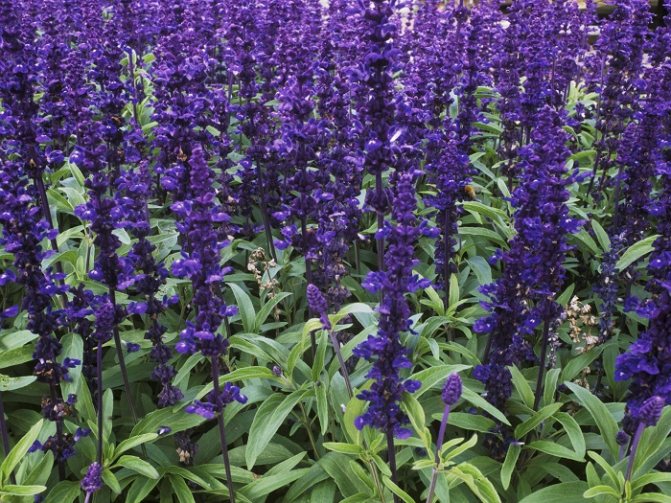
Forest salvia (Salvia sylvestris) - cold-resistant ornamental plant. It blooms in early summer with blue and purple flowers of different shades. Many varieties and hybrids have been created on the basis of this species: Blauhugel, Mainacht, Lye End, Viola Klose, Rhapsody in Blue - with blue flowers, Rose Queen - with pink flowers, Schneehogel - with white flowers.


Forest salvia 'Mainacht'.
Salvia lavender, narrow-leaved, or Spanish (Salvia lavandulifolia) - extremely ornamental plant with silvery foliage and delicate purple flowers in May-June. Used in cooking. Winter hardiness.
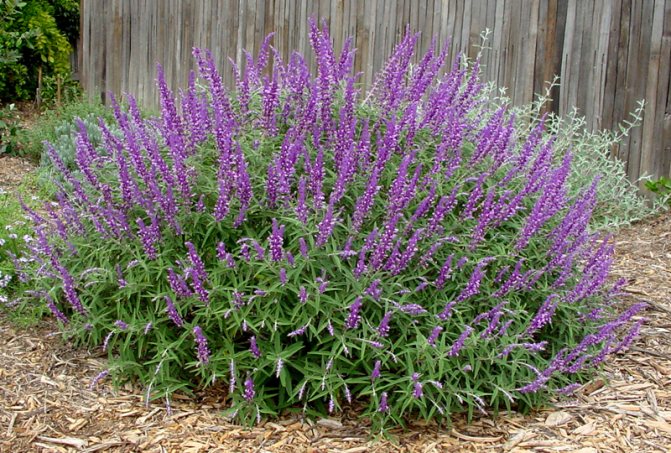
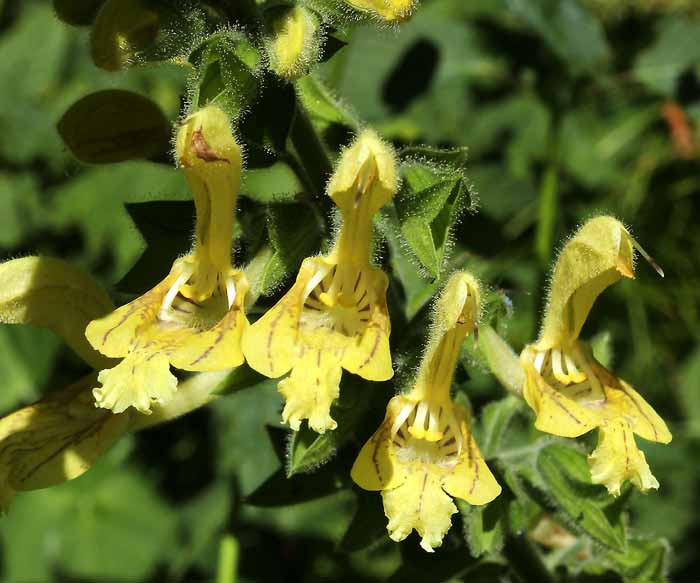
Salvia oak (Salvia nemorosa) - unpretentious cold-resistant plant. There are known varieties with purple (Caradonna, Marcus, Ostfriesland) and pink (Plumosa, Rose Wine, Schwellenburg) flowers.


Salvia Dubravnaya.
Salvia meadow (Salvia pratensis) - with purple, pink (Lapis Lazuli) or white (Swan Lake) flowers in the first half of summer. There are known varieties of the Haematodes group.
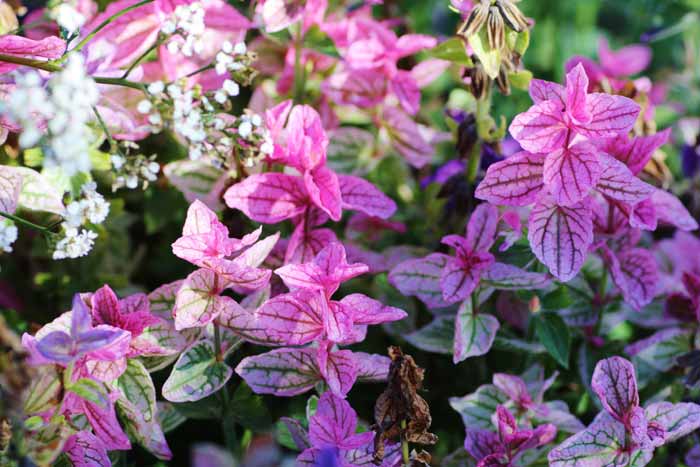
Salvia verticulata - extremely decorative and rather cold-resistant plant with bright purple flowers. Bloom from July to autumn. The Purple Rain variety is known, as well as the Alba variety with white flowers.
Mealy salvia (Salvia farinacea) - an ornamental thermophilic plant that blooms luxuriantly from summer to autumn. The flowers are bright blue. There are known varieties of Victoria. In colder regions, it is recommended to grow as an annual.
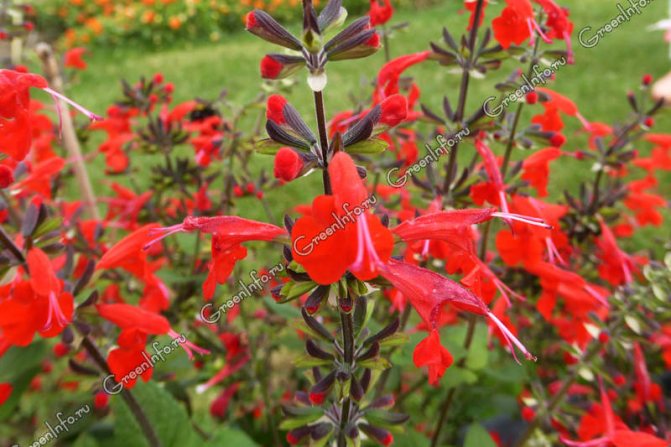
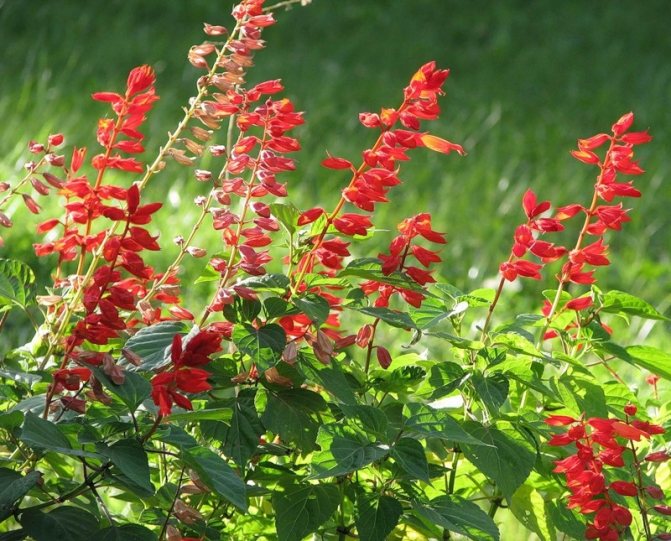
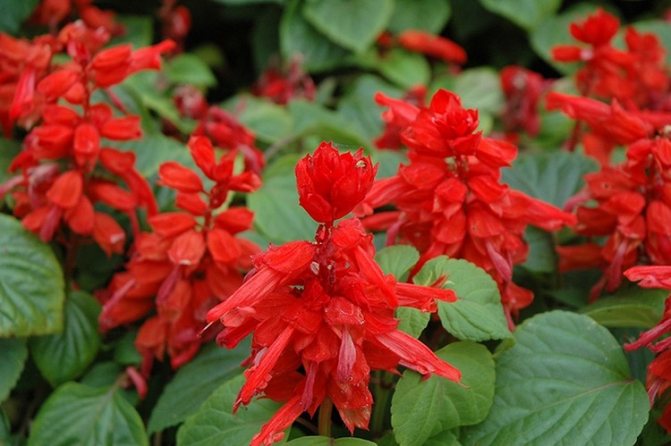
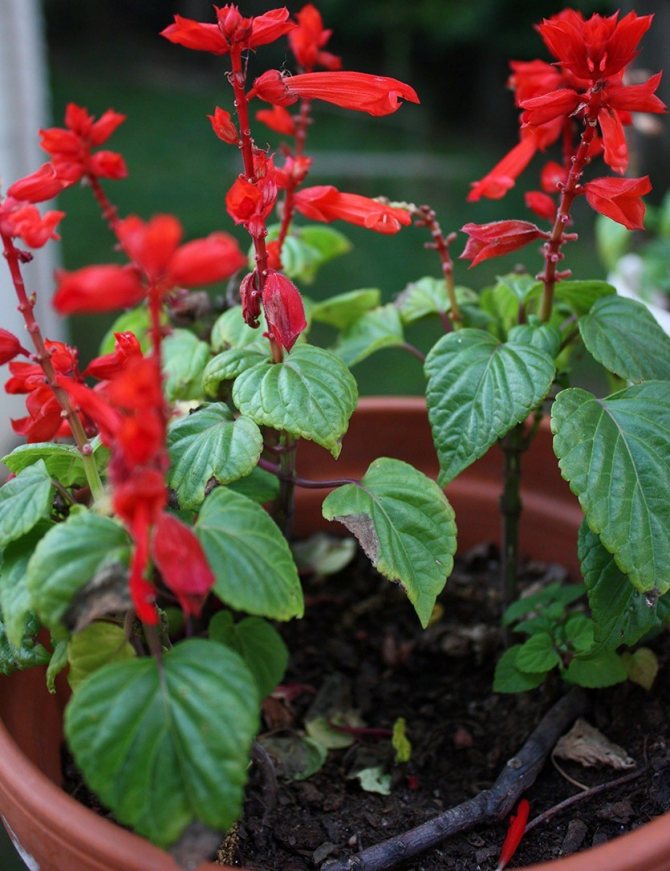
Salvia red (Salvia coccinea) Is a thermophilic biennial plant from South America that loves heat and moist soils. It blooms in late summer - in autumn with white, pink or red flowers. In culture, varieties of red varieties are more common: Lady in Red, Forest Fire.
Small-leaved salvia, or myrtle (Salvia microphylla) Is a charming thermophilic shrub from Mexico. Pale green oval leaves that give off a blackcurrant scent when rubbed in your hands. Bright red flowers appear on the plant in mid-summer, flowering continues until the first frost.
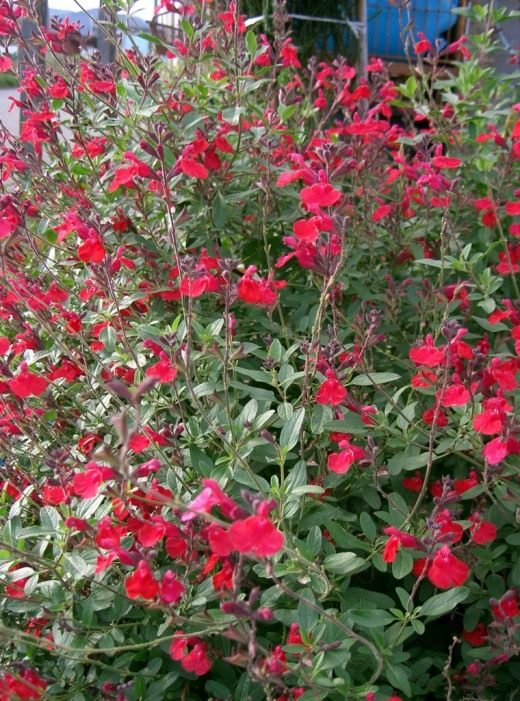


Small-leaved salvia, or myrtle.
Salvia discolour Is a very original plant from Mexico. The bluish black flowers remain half hidden in the silvery calyx.
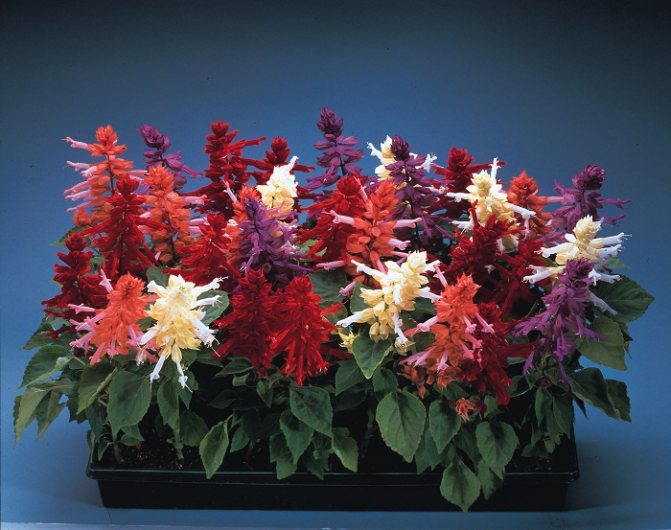
Salvia brilliant, brilliant (Salvia splendens) - the most popular salvia in Russia, grown as an annual. Blooms from June until frost, color - from orange-red to dark purple. Prefers moderately moist soils.
Medicinal and spicy species
Sage officinalis (Salvia officinalis) - medicinal plant and spice. Comes from the Mediterranean region and the Balkans. Winter-hardy shrub with dense velvety leaves and blue-purple flowers. There are less cold-hardy varieties with burgundy green (Purpurascens), creamy green (Aurea), creamy burgundy green (Tricolor), and golden yellow-green (Icterina) leaves.


Sage medicinal (Latin Salvia officinalis).
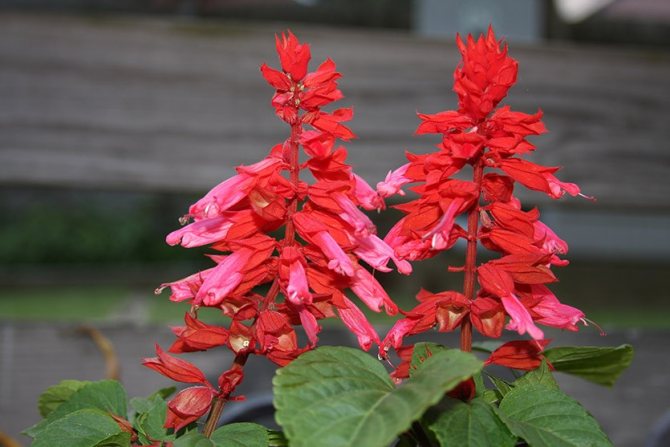
Sage elegant (Salvia elegans) - a tall plant (up to 1 m) with red funnel-shaped flowers that appear at the end of summer. If you rub the leaves of these sage leaves, you will smell a fruity smell. Used in cooking, such as fruit salads. Known varieties: Scarlet Pineapple (with the scent of pineapple), Tangerine Sage (with the scent of tangerine).
Planting a plant in open ground
The grown and matured seedlings are rooted in late May or early June. By this time, the threat of night frosts usually has passed. The place should be open, sunny, and the ground should be light. Before flowering, salvia is often moistened as the soil dries out. After flowering, watering is reduced. Also, care consists in loosening the earth, applying fertilizers.
Attention! Do not overuse nitrogen fertilizers so as not to worsen flowering.
Growing salvia by seedling is not so much a troublesome process as a lengthy one. However, a beginner can also cope with it. But the effort will not be wasted. In the open field, flowers will delight you until autumn. After that, you can transplant the salvia together with an earthen clod into a pot and put it at home. Flowering will continue in indoor conditions.
Benefit
Sage is especially beneficial for the female body, as it contains female phytohormones. Sage treats frigidity and has a good anti-aging effect. In ancient times, infusion of sage leaves and juice were given to women with infertility, because it strengthens the walls of the uterus and promotes successful conception. Helps reduce anxiety during menopause. Eases the course of many inflammatory gynecological diseases.


Mealy salvia
An infusion of dry leaves helps:
- As an expectorant for various bronchitis.
- Helps with kidney disease, it is a good diuretic.
- It also helps with gastritis, sore throat, gum disease, toothache.
- Has a hemostatic, astringent effect.
- Strengthens memory and helps maintain clarity of thought.
- Fights fungal skin diseases, relieves psoriasis symptoms.
Be healthy! Looking forward to your advice!
Origin, history of Salvia
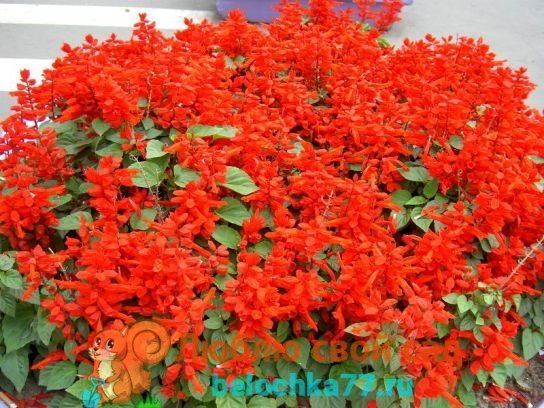


Salvia (in Latin - sage) belongs to the Lamb family. The literal translation of the name "salvus" is to be healthy. Since ancient times, it has been known as the "sacred herb" and is valued for its healing properties. This flower has been used for medicinal purposes since ancient Egypt. The homeland of the plant is America and Eurasia. Salvia is the name for the decorative forms of this flower, which have common ancestors with sage.
- In Europe today, sage is called salvia. In the wild and cultivated form, this plant is found in almost all countries and continents, except Australia.
- The American Salvia group is annual and grown in warm climates.
- The Mediterranean group of these plants is more winter-hardy and has a huge variety of varieties.
The third group of this flower includes cold-resistant varieties, which are most often found in the temperate climatic zone of Europe. They grow even in shady places and require a little cover during the winter. Abundant flowering in varieties of this group occurs in the second year of life.
The genus Salvia is so widespread that there are more than 900 varieties of this plant. For ornamental cultivation, the most commonly used salvia brilliant and brilliant salvia.
Description of the plant Salvia (sage)
The concept of "salvia" could come from one of the concepts of the Latin language:
- salvare, which means "to save";
- salvus, translated as “to be healthy”.
The word “salvia” literally translated as “the herb of life”. It has been used to treat many diseases. In Russian, the concept of "sage" appeared only in the 18th century. They began to grow this plant to obtain raw materials from which various drugs were made.
Salvia can grow up to 30-150 cm in height. This is due to the type of shrub. The appearance of the plant also depends on it.
The stem of all varieties of grasses and shrubs is tetrahedral. The leaves are arranged opposite each other in pairs.
Scopes of the plant:
- medicine;
- cooking;
- production of essential oils;
- decoration of summer cottages and garden plots.
Planting salvia seeds for seedlings
The process of sowing seeds takes place with the following stages:
- the planting container is filled with expanded clay or drainage in one layer;
- it is covered with the prepared substrate, leaving the extreme side up to 2 cm;
- the earth is abundantly moistened with water from a fine spray;
- seeds are scattered over the soil surface; by lightly pressing the hand, the seeds are pressed into the soil;
- sprinkle on top with a layer of earth 2-3 mm;
- moisten the soil with a sprayer;
- cover the planting container with foil or glass; put in a dark place.
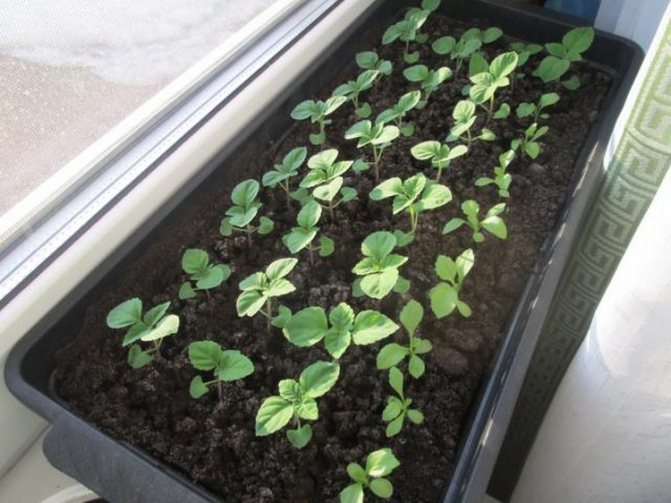


Growing flowers from seeds
Salvia sparkling purple


Salvia the lush Salvia the dwarf Burgundy


Salvia the sparkling Carabinieri
Sowing time
Perennial salvia is propagated by seeds and vegetatively, using cuttings or dividing the bush. But annuals and biennials can be grown only from seeds, both by seedlings and by direct sowing into the ground.
In open ground, seeds must be sown before winter or early spring, since the growing season of the plant is quite long. Under unfavorable conditions, seed germination is delayed, and sprouts that have hatched in time die from frost, therefore this method is practically not used by experienced growers.
The best option is to grow salvia through seedlings.
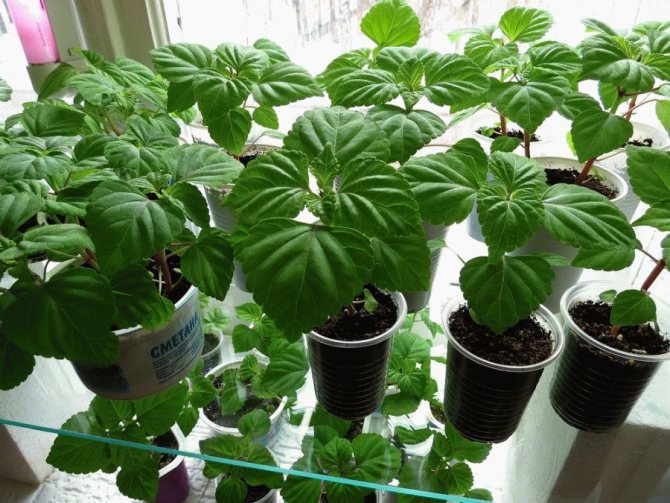


Salvia seedlings
As a rule, 3-4 months pass from germination to flowering, and in order to admire the flowers at the beginning of summer, seeds should be sown in February, the latest date is mid-March. Sowing later is only suitable for hybrid species that have early flowering. When choosing hybrids, keep in mind that their seeds are not suitable for planting material, and you will have to buy again in the store next season.
Soil preparation
Salvia grows best on fertile light soils with an acidity of pH 6.0-6.5. On clay and poor organic soil, plants branch worse, form scanty peduncles, and lose their bright color. For seedlings, you can purchase a ready-made soil mixture or make it yourself by mixing garden soil, peat and washed sand in equal proportions.


Fertile soil must be mixed with peat and sand
Such a substrate must be warmed up in the oven to destroy harmful spores and weed seeds.
Sowing seeds


Sparging seeds with oxygen or air
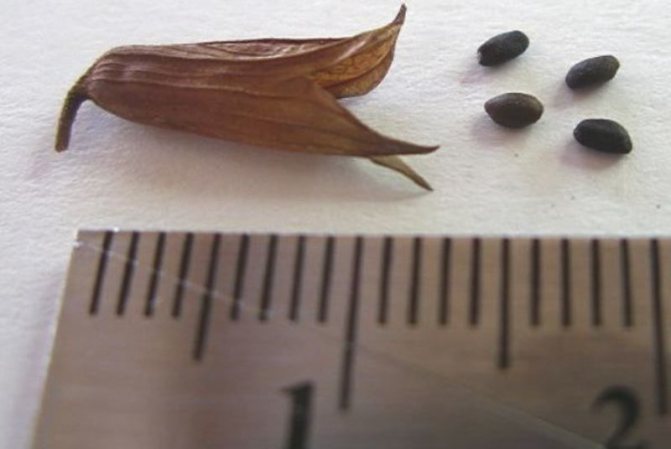
Salvia has very small seeds, and many agricultural firms supply them for sale in granular form. Such seeds are more convenient to sow, in addition, the granules contain various substances useful for sprouts, but the shell slows down germination. This should be taken into account when calculating the sowing time, especially if the seedlings are grown for sale.
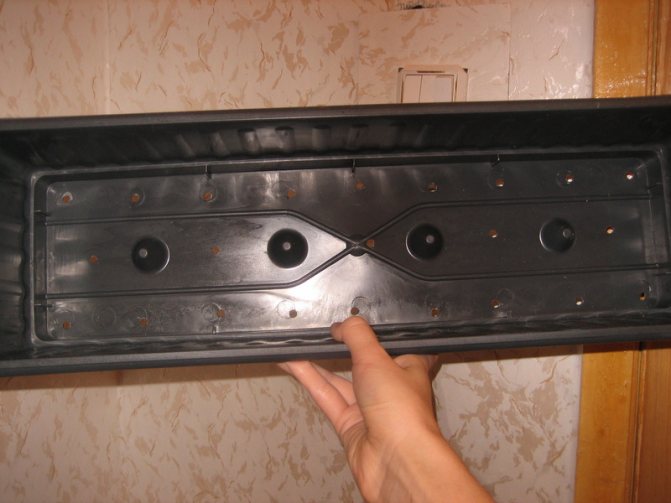


Seedling box has multiple drainage holes
Step 1. A layer of expanded clay or small pebbles for drainage is poured into the planting container, and a prepared substrate is placed on top. It is not necessary to fill the box to the top, the side should remain about 2 cm.
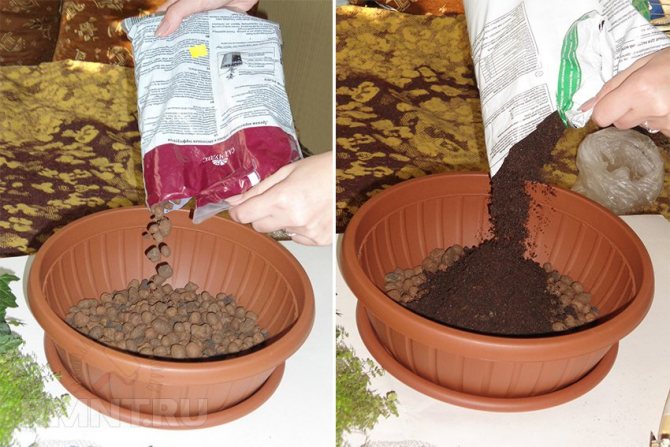


The photo shows a layer of expanded clay and the process of filling the substrate into a container for seedlings
Step 2. The earth is abundantly moistened and seeds are scattered over the surface. Many people mix them with coarse sand - it turns out more evenly. After that, the seeds are lightly pressed into the ground by hand, then sprinkled with earth by 2-3 mm.


Seeds mixed with sand


Conveniently sow seeds by spreading them into grooves with a toothpick


An example of filling sown seeds with a small amount of soil
Step 3. Crops are moistened from a spray bottle, the box is covered with glass or foil and placed in a warm place away from sunlight. Until the first shoots appear, maintain a constant temperature of +20 .. + 25 degrees. Depending on the variety, seedlings begin to appear 15-30 days after sowing.


We cover the container with a lid or glass
Growing seedlings
When mass shoots appear, the container must be rearranged to a bright place, for example, a windowsill.Since the daylight hours for seedlings should last at least 12 hours, and in February the days are still too short, backlighting is organized for seedlings in the morning and evening hours. This condition is mandatory, since with a lack of light, the sprouts quickly stretch and weaken, and it is impossible to get strong plants from them.


Seedlings should have enough light
Moisturizing should be regular but moderate. The glass is removed for only a few minutes a day for airing, in order to create an optimal moisture environment for the seedlings. For irrigation, use a spray bottle or pour water into a pan, from where it will gradually be absorbed into the substrate. With an excess of water, the bases of the sprouts rot and turn black, so carefully inspect the plants every day.
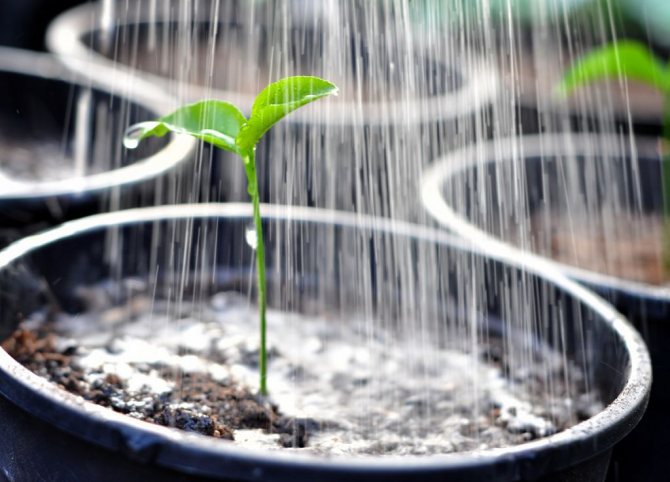


Do not overmoisten the soil
Advice! If the plants start to rot, you need to remove the shelter from the box and sprinkle the surface with sifted wood ash.
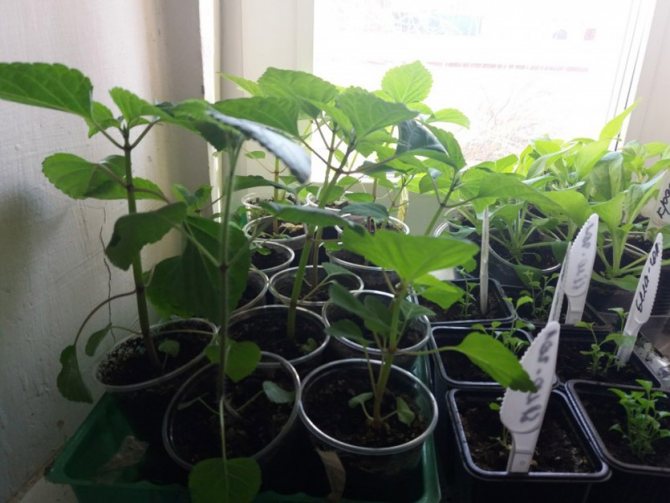
In order for the seedlings to quickly take root in the open field, its root system must be well developed and strong. Double picking helps to achieve this. When the seedlings have 2 true leaves, they are dived for the first time, transplanted into a more spacious container. A distance of 4-5 cm is left between the plants. The stems should be deepened to the cotyledonous leaves.


Salvia's pick
The second pick should be performed three weeks after the first. This time, the seedlings are distributed in individual cups or pots with a diameter of up to 10 cm. After the development of the fourth leaf, the growth point is pinched - this stimulates the development of lateral shoots. Around the same period, the seedlings begin to harden, taking them out overnight in a cool room with a temperature of about 10 degrees.
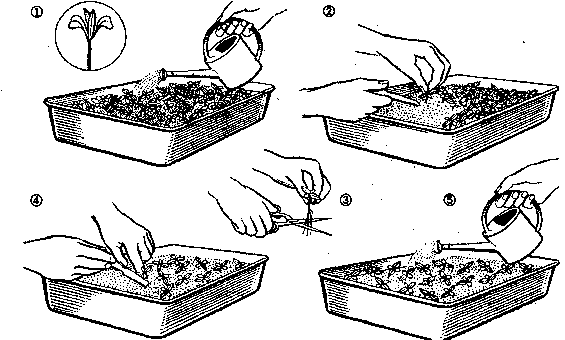

Seedling picking - scheme
Sage varieties
Since this article mostly dealt with medicinal sage (vegetable), we will consider varieties that are suitable for different climatic zones and have excellent taste and irreplaceable medicinal properties.
Sage Breeze
This variety is included in the State Register of the Russian Federation, it is recommended for consumption fresh and dried (young shoots and foliage), it is used for the preparation of desserts, salads, soups, sauces, meat, fish. Plants of this variety reach about 60 cm in height, with erect shoots and dense foliage. The leaves are pubescent, dentate at the edges. In the second year after planting, the bush of the variety reaches about 280 g. Flowers are violet-blue in color. Seeds are small, brown-black in color.
Sage Aibolit
Like the previous variety, it is included in the State Register of the Russian Federation. It is consumed both fresh and dry. The plant is larger than the previous one, 60-120 cm tall. The leaf is dark green in color, finely toothed along the edge, wrinkled, has strong pubescence. It is customary to use the variety in the second year after planting, after a month from the beginning of the growing season. But it is not as persistent in winter as the previous variety, so in the middle lane it is better to cover it for the winter.
Sage Nectar
The variety, included in the State Register of the Russian Federation, is very popular when combined with cheese and in aromatic culinary compositions. Its height is about 100 cm, the stem is erect. Foliage color is light green with pubescence. The flowers are blue-violet.
Sage Patriarch Semko
The variety is used dry and fresh; it has been included in the State Register since 2000. The height of this variety is 50-80 cm. Erect, stiff stems at the bottom. Dense foliage up to 10 cm long. To the top of the shoot, the leaves are smaller. The seeds are in the form of a ball, the flowers are blue-violet.
I also recommend another author's excellent article on this wonderful plant.
Sage: planting, growing, care
Sage, aka salvia, is another excellent representative of ornamental and medicinal plants. It belongs to the glorious genus of lamines, which gave rise to many beautiful and useful flowers. I love its beautiful, narrow foliage and blue flowers.After articles by one author about sage, I wanted to learn as much as possible about such a familiar and beautiful plant. It turned out that the shapes and colors of sage are different: from the usual to the most outlandish and extraordinary. There are 700 different sage species in the world.
Sage is a perennial, but there are both annual and biennial species. Sage inflorescences are collected in panicles or spikelets. Stems are erect, can branch and reach a length of 120 cm.
Sage is an excellent helper in cooking and medicine. In ancient Rome, it was used in the treatment of many diseases, today it is just as relevant.
What to do after flowering
One-year and two-year-old salvia after flowering do not require special care. Some varieties can bloom again after cutting the flowers. The introduction of top dressing allows you to quickly form new flower stalks.
When growing perennial salvia, the plant requires formative pruning. Without pruning, young shoots stretch out and form empty spaces.
After flowering, it is necessary to remove all flowers, and a haircut is performed before wintering and at the beginning of the growing season. Lignified shoots are removed, leaving a few centimeters with young greens and buds.
After the autumn pruning, the area is mulched with compost, foliage, dry small grass. Young perennial salvia is covered with dry foliage, spruce branches.
In cold winters, the rhizome can be dug up and placed in a box and placed in the cellar until spring.
Characteristics of salvia
Retreat refers to the perennial representatives of the flora. But in the latitudes of our country, they often survive as an annual or biennial flower. Only a few varieties can successfully overcome winter conditions. The stems can grow up to 1.20 m. The leaves are either whole or whole. The lower side of the leaf is slightly white. At the end of the stem, the colors are collected in the form of a wheel or broom. Flowers long about 15-20 cm. They are white, deep, red and violet. By the end of flowering, the salvia develop fruits in the form of four small nuts. They can be obtained already in 30 days after flowering. All seeds are not lost over the course of 5 years.


Popular varieties and varieties of brilliant salvia
The brightest is the red variety. Its red flowers look especially beautiful in the fall. Popular varieties with red flowers: Salvator, Red Arrows, Fiery Star, Sahara. White differs in inflorescence of lower density. Her flowers are creamy. Violet variety - dark flowers have a velvety appearance, making them look very catchy. Brilliant salvia with a pink color - the corolla of flowers is also velvety, thanks to its dense pubescence. The inflorescence is average in density between the white and red varieties.
Salvia brilliant - a rather troublesome plant to grow. However, the result is worth it. Flower beds and borders will acquire a special charm if the centerpiece is the brilliant or sparkling salvia. Its bright flowers will delight the eye until the beginning of the winter cold.
Healing properties
Sage is capable of disinfecting, anti-inflammatory, hemostatic, diuretic and antipyretic effects. In this regard, it is suitable for the treatment of a number of diseases:
- pathology of the stomach and intestines (ulcer, gastritis, spasms, diarrhea);
- dysfunction of the respiratory system (tonsillitis, bronchitis, catarrh, pneumonia);
- trauma (frostbite burns, ulcerative and bacterial skin lesions);
- diseases of the teeth and gums (gingivitis, stomatitis);
- problems in the genitourinary system (ovarian dysfunction, adnexitis, endocervitis, etc.);
- skin diseases (acne, dermatitis, increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, etc.) ..
The use of medicines made from sage helps people. Ointments, sprays, syrups and tinctures based on it are often recommended by doctors. Sage is especially effective in treating sore throats and skin infections. It should be remembered that these funds are effective only as part of a comprehensive therapy.
Sage essential oils are used to relieve headaches and prevent the effects of stress.
This herb can increase the secretion of female sex hormones, so it should not be prescribed for women with fibroids, polycystic ovary disease and endometriosis, in which there is a hyperfunction of the gonads. It is also not recommended to use preparations based on this plant while carrying a baby and breastfeeding.
Not all types of salvia are suitable for the preparation of medicines. At the same time, both medicinal and decorative varieties are able to delight gardeners with beautiful flowering until mid-autumn. The main thing is to create suitable conditions for growing the plant.
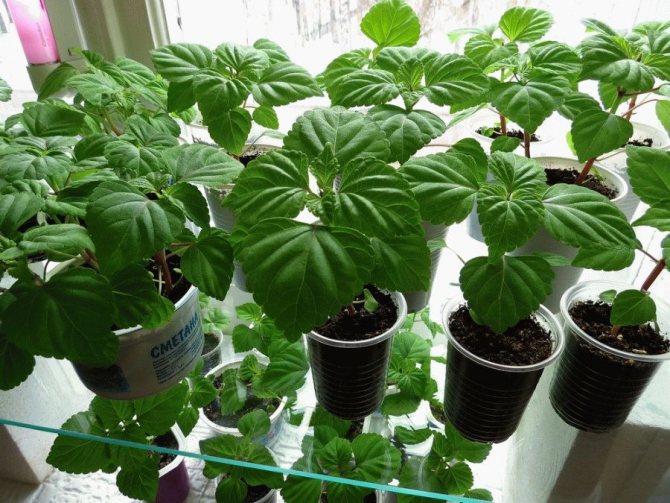
Salvia seedlings picking
Salvia seedlings are a real "slow-witted" in matters of growth - it comes to picking only a month and a half after sowing. If you got a "very fast" variety, focus on the leaves - you can dive the salvia when two true leaves are formed on each plant.
Gently pry off the sprouts with a fork or small picking spatula and transplant them into separate containers. Salvia seedling pots should be about 10 cm in diameter and 15-20 cm deep. The soil will do the same in which you sowed the seeds.
After the dive, gently water the bushes and cover them from the direct sun with a newspaper - for the next 2-3 days they will be in a state of stress, and the sun's rays can burn them. Continue to water the cut salvia seedlings 1-2 times a week.
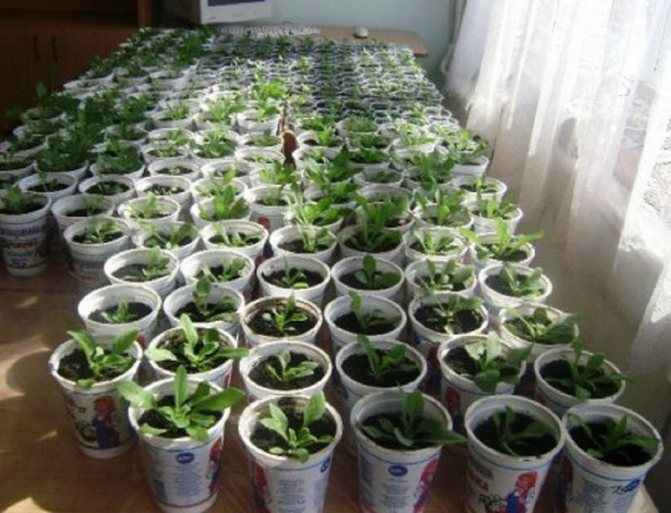


Sowing and caring for Salvia perennial
It is not difficult to grow Salvia perennial on your own at home. One-year and two-year-olds are propagated by seeds. For perennials, the vegetative method is more suitable - by dividing the root or cuttings. Some species, for example, Salvia brilliant, can only be grown by seedlings, as shown below in the photo of perennial Salvia flowers.
The main care consists of the following activities:
- moderate watering, which should not be abundant;
- loosening the soil to enrich it with oxygen and remove weeds;
- fertilization at least 2 times per season - in spring and before flowering;
- pruning to make the bushes decorative and tillering;
- shelter for the winter with spruce branches with preliminary soil mulching.
Perennial Salvias rarely get sick. Pests such as slugs, aphids, thrips, and ticks can pose a real danger to them.
When to plant Perennial Salvia
Planting Salvia with perennial seeds can be carried out both in autumn and spring. The autumn time for planting must be chosen so that the seeds do not have time to germinate before the snow.
In spring, it is better to do early planting in March-April, covering the area with foil to create a greenhouse effect. If planting is carried out in May, then there is no need to cover with foil.
Propagation by cuttings is done in the middle of summer. For this:
- the stems are cut into a length of 12-15 cm;
- they are lowered into a transparent container with water;
- after the roots grow back up to 1-2 cm, the cuttings are transplanted into pots with light soil;
- watered periodically;
- ventilated, maintaining the temperature at about +20 0 С.
After 2-3 weeks, the cuttings can be transferred to a permanent place.
In regions with a short summer, Perennial Salvia is propagated by seedlings, having done (as in the photo) planting seeds at the end of February in boxes with prepared soil.
Seed treatment
Before sowing seeds in spring, it is recommended to soak them in a growth stimulator or hold them in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and then dry them. You do not need to do this before planting in autumn.
Preparation of soil and containers
Salvia perennial loves light fertile soils of normal acidity. If the soil is clayey, it is recommended to dig it up by mixing with sand.
It is advisable to enrich the soil before planting in open ground. To do this, in the fall, on the territory of the future planting of Perennial Salvia, compost and phosphorus-potassium mineral complexes should be decomposed. Add nitrogen fertilizers in the spring.
It is necessary to choose a sunny place, as this plant needs a lot of light and heat. An exception is the Salvia glutinous variety - it grows well in partial shade.
For planting seedlings, use a wide container, preferably with a water tray. After the first leaves appear, the seedlings are seated in separate pots or glasses filled with peat.
Planting Salvia perennial
When growing Salvia with perennial seedlings, seedlings are planted in open ground, maintaining a distance of 25-30 cm between them according to the following scheme:
- In the prepared hole from the pot, carefully transfer the seedling along with the ground.
- They are installed vertically and covered with fertile soil.
- A little compacted at the base and watered with water.
To maintain the purity of the species, the planting of bushes of different varieties of Salvia perennial must be carried out much further from each other.
Seedling care
The seedlings should be planted according to the following scheme:
- Fill the box with light soil and water.
- Spread the seeds at a distance of 5 cm from each other, or mix with sand and pour evenly into the box.
- Sprinkle the soil on top about 1-2 cm.
- Cover with foil or glass for 2-3 weeks.
At first, the seedlings of Salvia perennial should be closed from direct sunlight. It is necessary to create an air temperature of about +25 0 C. Seedlings should be periodically ventilated and sprayed with water. After sprouting, remove the film and put the box in a sunny place.
When the first true leaves sprout, dive the seedlings.
Dive
In order for the seedlings to develop their root system, to receive more light and nutrients, a pick is carried out - they are transplanted into separate glasses, immediately rejecting weak seedlings. Before picking, you need to water the seedlings with water so that the roots are easier to separate from the ground.
The picking process is simple:
- Pour potting soil into the pots.
- Make a depression with a pencil or finger.
- Pry the seedling with a special spatula and remove it from the ground.
- Pinch off 1/3 of the rhizomes (some gardeners do not).
- Place carefully in the prepared hole.
- Cover with earth, lightly tamping.
- Drizzle with water.
- Place in a dark room for 2-3 days.
Do not feed 6-8 days after the pick, so that the plant will strengthen itself in new conditions.
In open ground, seedlings are planted in early June.







































