Home Rodents Features of wintering of a mole
In order to secure the harvest in the future and properly organize protection from these animals in the garden or garden, it is useful for farmers to learn how a mole hibernates. Indeed, very many owners of summer cottages and personal plots mistakenly believe that moles that are tired of the summer and autumn go into hibernation in winter, since there is actually nothing to harm - the harvest is harvested.

But in fact, they continue their activity in cold weather.
- Let's get to know the earthmoving better
- Are there any benefits from these animals
- Hibernation myth
- Animal diet
- Does the mole sleep at all?
- Protecting our possessions
Let's get to know the earthmoving better


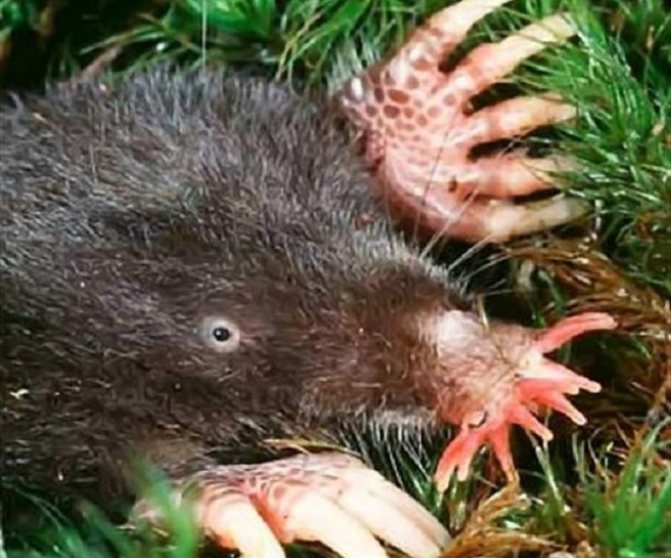
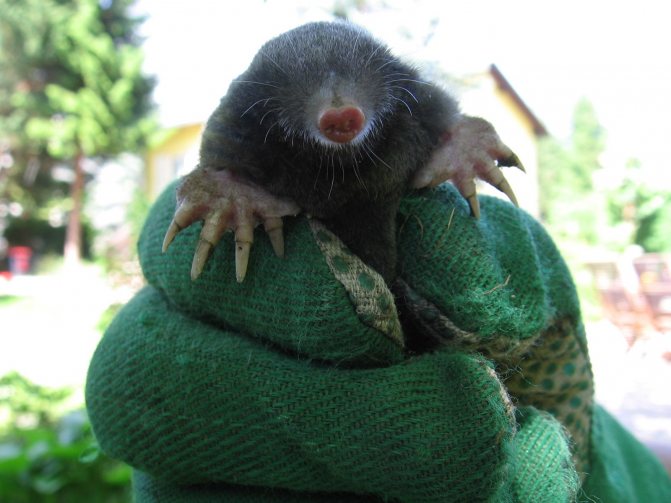
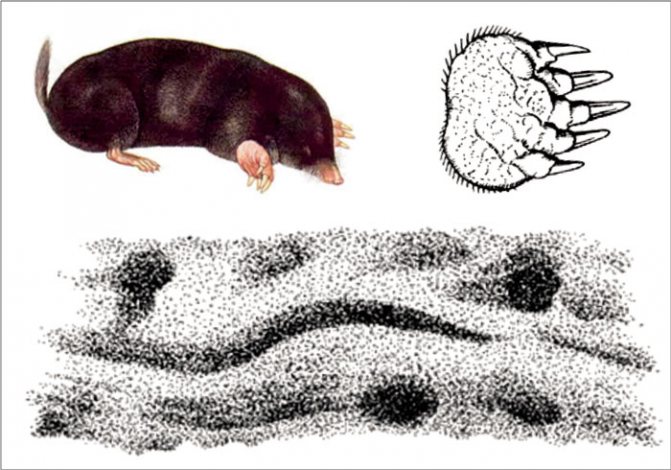
The mole is a representative of insectivorous mammals adapted to a burrowing, underground lifestyle. Depending on the species, the size of the little animal of this animal varies from 5 to 20 cm.
A few words should be said about the peculiarities of his fur coat. The mole's pile is short, soft, grows straight and lies freely in different directions, which allows the animal to move freely underground in any direction.
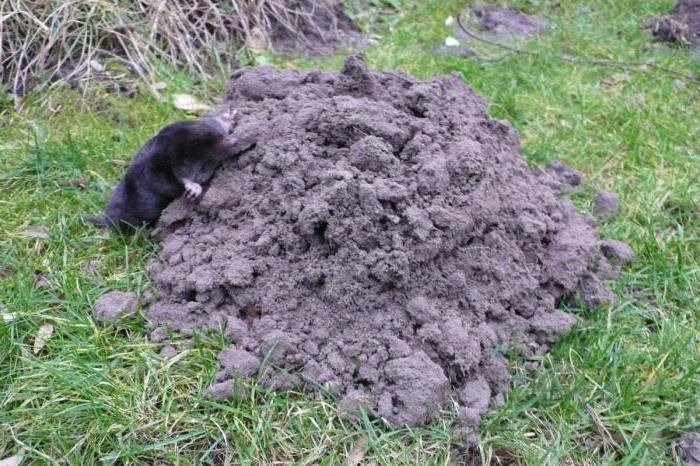
These mammals prefer to live in loose soil, which explains their "love" in gardens and fields. To feed itself, the mole lays a whole network of shallow underground passages, which can reach an area of several hundred square meters.
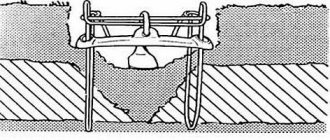
The animal equips the nest chamber at a depth of up to 2 meters and insulates it.
Hibernation myth
Since in winter, despite their warm fur coats, the moles are forced to deepen, an erroneous stereotype has formed that they are sleeping.


There are several explanations for this opinion:
- Gardeners have harvested and think that the mole has nothing to eat, so it falls asleep. This is fundamentally wrong. These mammals are predators! Both damaged tubers and roots of garden plants are just "additional losses" as a result of the hunting of these animals for bugs and worms.
- Those who know that moles are carnivores believe that since with the onset of cold weather these small predators cannot find a sufficient number of worms or insects, hibernation is the salvation for them from hunger.
- If a field or vegetable garden is covered with a sufficient layer of snow, then a person simply cannot see how the animal makes new moves.


Of course, the mole goes through very difficult times in winter. In order to survive in harsh conditions, he carefully prepares for the winter, thinks over what reserves to make for the cold period and mobilizes all resources.
However, in especially cold years, not all wintering moles are able to survive until spring.
But the frost is not very scary for these animals, because Mother Nature has awarded them with a warm fur coat that protects them from the cold underground.
The most terrible enemy of the gluttonous mole is hunger. Lack of reserves is the main reason for the death of these mammals in winter.
What eats
In winter, the mole cannot hibernate, therefore it needs to eat normally in order to maintain the normal functioning of its body.
In order for the animal to feel full, it needs to consume at least 80-90 grams of food per day. Without food, an adult mole can live up to 18-19 hours, and babies are even less. Therefore, these pests are constantly looking for a place to find food.
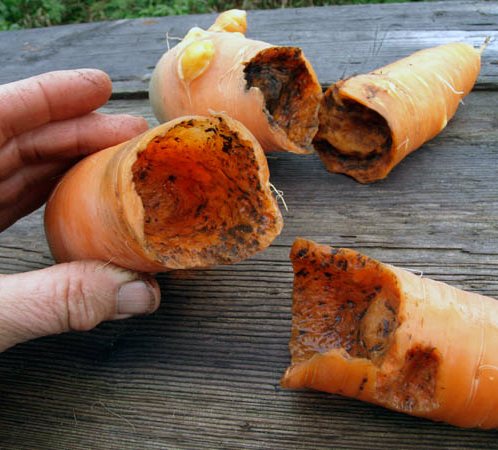


It is generally accepted that it is the feeling of hunger that increases the activity of the animal, both in spring and with the onset of cold weather.Pulling out a large number of underground passages, this mammal spends a lot of strength and energy.
As at any other time, the diet consists of earthworms, various insects, as well as their larvae, beetles, snails and similar animals.
A mouse or a shrew can enter a wide ramified system. They often use passages that have been dug by a predator. If she is stumped, then she will become food for the mole. He can also eat rodents that died of hunger, since these animals can also eat carrion.
Despite the large appetite of the burrowing animal, it is able to prepare food for itself for the winter. Mostly earthworms are used for blanks. The mole chews off the head of the worm, and the back part remains in its tunnels. Sometimes separate rooms can be used to store supplies. Otherwise, throughout its entire system of underground passages, the remains of worms will lie, which the predator will eat when there is a lack of food.
After conducting research, scientists have carefully studied the approach of these animals in preparation for wintering. More than five hundred stocked worms were found, which were found in the nest or tunnels of the mole. Of course, this will not be enough for the animal to feed all winter, but this will greatly facilitate its living during cold weather for a while, since it is difficult to find food in winter.
Animal diet
What does a mole eat in winter? Since the motor activity of the animal is still less in winter than in summer, it is not necessary to feed the cubs, and there is no sexual activity, less energy is spent, which means that the need for food decreases.


Of course, the prepared food supplies allow him to rest a little more in winter and eat less, but this does not mean that he will stop hunting. Deep underground, moles feed on all the living creatures that can be found there.
These seemingly harmless little animals are even called "underground crocodiles" because of their gluttony and the structure of their teeth - they eat everything in their path.
The main delicacies for them are earthworms, insect larvae (for example, May beetles and bear). A shrew or mouse that you meet will also not survive. Also, these predators do not disdain the corpses of rodents. Some species can eat about as much food at a time as they weigh themselves.
In the warm season, small predators stock up on earthworms. With one bite they gnaw the body of the worm into two halves, eat one, and hide the other for the winter.
Such reserves can be found all along the branched underground passages - moles feed on them during their "winter raids".
The special structure of the front legs and claws allows the animal to rake even the frozen ground in order to find food for itself. These small inhabitants of the dungeon break through new passages in order to find wintering insects, worms or snails on the surface, under rotten leaves.
How does one live
Since there are practically no signs of the vital activity of these animals (especially when a thick layer of snow falls out), how does a mole winter?
Moles do not radically change their lifestyle with the onset of winter. All this time they continue to dig the earth, only with a cold snap, they go deeper for several meters, in search of food in a new place.
With their strong, wide front paws, they clear the hardened ground without problems. The mole does not hibernate, but it always prepares its nest. Even in the fall, it drags dry moss and foliage into its burrows because this material has good thermal insulation properties. A sufficient amount of dry foliage will keep warm with the onset of cold weather.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How can you drive a mole out of the garden with folk remedies?
Since many underground passages can lead to one mole's den, some of them can be filled up with earth so that cold through air does not enter the dwelling. Thus, the animal drowns its nest, preparing for wintering. In winter, the mole sleeps the same amount of time as in the warm season, staying overnight in a warm room.
Since the animal already has complex systems of underground tunnels by winter, it can choose the most suitable place to create a nest.
For the reason of being active in winter, the mole needs to consume a large amount of food, which becomes extremely problematic, since in most other animals and insects, life is suspended.
At any time of the year, the mole eats more than 20 grams of food at a time, and then goes to sleep. After sleeping, he is very hungry, and he goes in search of food. That is why his activity is so badly harmful to vegetation on the territory of his residence, since he is looking for various insects at the root planting system.
Since it is difficult to find enough food deep under the ground, moles can rise to the surface. Usually, in autumn, a lot of foliage from trees falls on the ground, and in winter a layer of snow falls. Animals can crawl to a layer of foliage, and then move under it in search of insects, worms, snails, small larvae.
If the snow does not fall, then it is worse, and it will be much more difficult to find food on the surface.
Does the mole sleep at all?


Of course he sleeps, because, like any other creature, he needs time to recuperate. But the regime of the underground inhabitant is not at all the same as we are accustomed to observe in other animals. Since it is dark in the underground passages, these animals have no "sense of time" - they absolutely do not care what time to go hunting or sleep.
Therefore, they sleep for an hour and a half at regular intervals, up to 6-7 times a day, comfortably sitting in their insulated nest chamber. In the same chamber, moles live while rearing their offspring.
Naturally, the animal's winter sleep is longer than in other seasons, but still the feeling of hunger drives it to dig new passages and look for food.
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
To get rid of rodents, our readers advise scarer Pest-Reject
... The operation of the device is based on the technology of electro-magnetic impulses and ultrasonic waves! Absolutely safe, ecological product for humans and pets. Read more here ...
How a mole hibernates and what does it do during the cold season
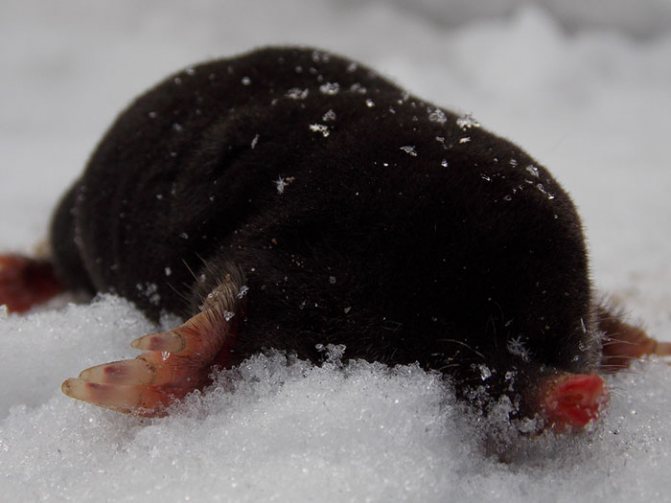
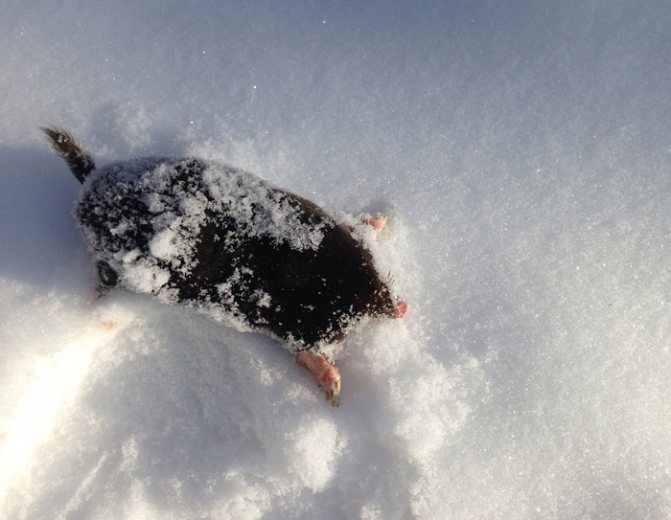
First of all, let us remember that the mole is an animal leading a predominantly underground lifestyle. In the warm season, he sometimes gets out of the dungeon through wormholes, while in winter, even having made his way to the surface of the earth, he usually remains under the snow (it rarely crawls out from under it - see the example in the photo below).
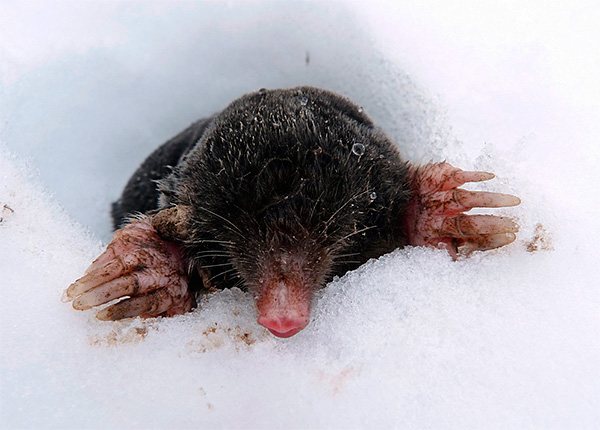


Under a layer of snow and earth, even at a relatively shallow depth, it will be noticeably warmer than on the surface of the snow open to winds. This means that the heat loss from an underground inhabitant will be less than that of animals living on the surface of the earth. The same, for example, a hedgehog in winter will freeze mercilessly, while in the underground passages of a mole, the air is significantly warmer than outside. This largely helps the moles to survive even very cold winters.
Moles overwinter in the same areas where they spend the summer. Just like in summer, they periodically dig passages, actively move along them and continue to search for prey all day long, including collecting those worms that were left here in reserve during the days of abundance. As in the warm season, after saturation, the animal returns to one of several expanded chambers, in which it rests.
Sometimes in winter, the mole makes moves under the snow, along the very surface of the soil through the foliage. This may be rational, since it is under the leaves that a large number of insects and their larvae overwinter, which the animal can profit from.


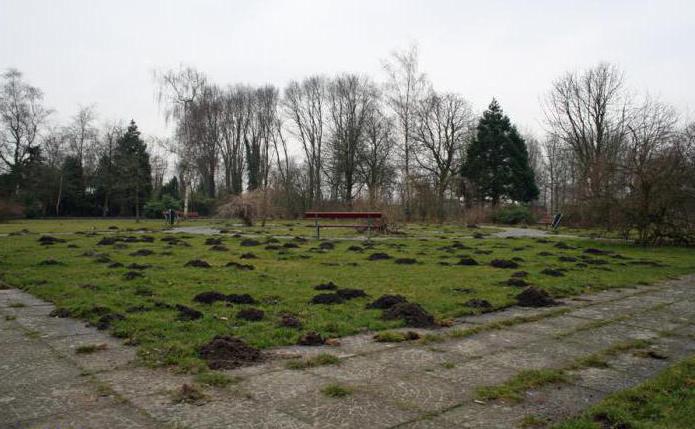
In winter, moles dig passages in the snow itself, thereby forming vents for their branched system of underground tunnels.
In winter, moles live at almost the same depth as in summer. This is due to the specifics of the creation of the passages themselves: at a depth of more than half a meter, they can no longer raise a layer of dense soil above them, and each portion of the excavated earth has to be pushed with its hind legs towards the mole, raised to the surface and thrown out. If at a depth of up to half a meter the animal is still somehow able to do this titanic work, then it becomes problematic to raise the earth from a greater depth (energetically unprofitable). Only in rare places do moles arrange nesting chambers for themselves at a depth of 1 meter.
Protecting our possessions
Since moles are active in winter and their lifestyle hardly changes, summer residents and gardeners are not delighted with such a neighborhood.
What harm does this little animal do:
- destroys useful earthworms in a state of suspended animation;
- underground passages violate the integrity of the garden;
- breaking through new passages, they cause damage to wintering plants, for example, garlic, onions, beets, etc.
In the cold season, under the snow, this activity is not noticeable, but it will be a big unpleasant surprise in the spring.
Therefore, in order to protect your garden from intruders, it is recommended to leave ultrasonic or homemade scarers for the whole winter. It is also worth keeping your traps, nets, and anti-mole trenches for the winter.


















![Mice: [name, photo and description]](https://bgn.imadeself.com/wp-content/uploads/myshi-nazvanie-foto-i-opisanie-330x140.jpg)