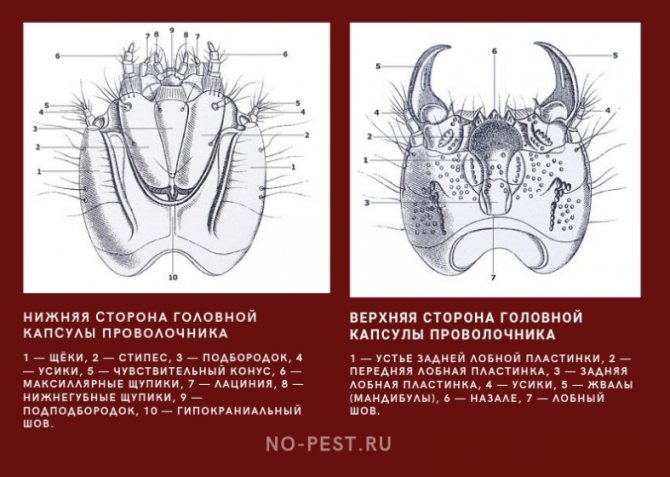
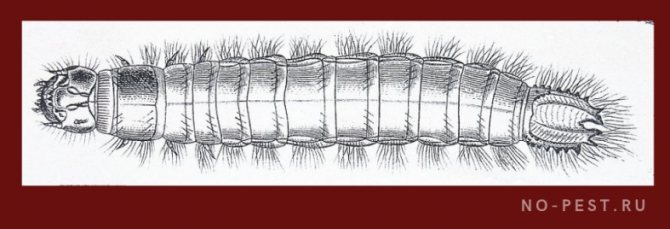
The larvae of the click beetle, called wireworms, infect potato tubers and cause serious damage to the crop. The fight against the pest is complicated by the fact that they live in the ground, so it is quite difficult to detect and remove them.
Therefore, every gardener should understand where the larvae come from, thoroughly study the characteristic signs of its appearance and learn how to get rid of the wireworm on a potato plot before starting to grow a vegetable crop.
The danger of the wireworm as a potato pest
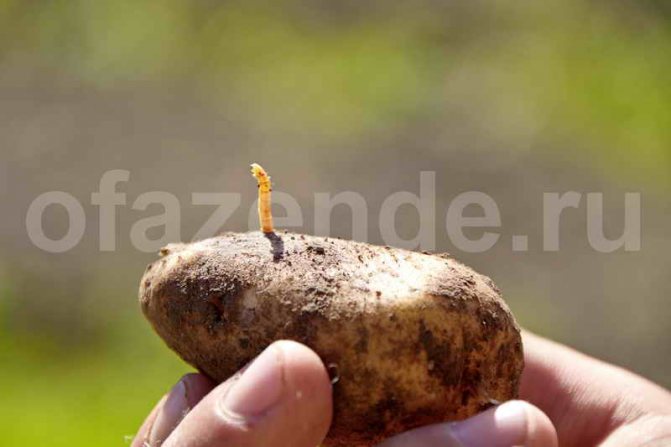
Wireworm is an extremely dangerous pest for horticultural plants. Most often, it damages potato plantations, although sometimes it can also be found in tomato beds, and even in vineyards. With the help of strong mandibles, the larva bites into the pulp of the tuber, making numerous moves in it.
Unlike the bear, the wireworm is not able to eat large amounts of potatoes.
But it damages potatoes, which is why they are affected by fungal and bacterial infections.
Even if such a tuber externally retains its integrity, it can be damaged internally. And when stored among healthy root crops, it causes them to deteriorate. Thus, a large amount of the crop intended for winter consumption can die. The pest also damages thin roots and young shoots of potatoes. In the area where there is a wireworm, the condition of the plants deteriorates, and the yield decreases by 40-60%.
Description
In the vegetable garden, agricultural crops have two most dangerous enemies that are capable of destroying the crop if you do not wage a war with them. One enemy attacks the tops, the other operates underground. These are beetles: Colorado and clicker.
And the nutcracker is worse than the Colorado, in my opinion. You can see him and wage war in the open, but the larvae of the second, living underground, can be much more dangerous.
This beetle, which has about 10 thousand varieties, is united in one name - "clicker". It spreads across all continents. His presence was seen even in the highlands, above five thousand meters.

These beetles were united into one group due to the fact that when jumping, the beetle produces a very characteristic click. It is this sound that allows you to identify the pest in the garden.
One has only to overturn the insect on its back. The clicker beetle will immediately emit a characteristic sound, rolling over on its stomach.
It is very important to know this feature of the clicker, since they are very diverse in their appearance. These insects differ quite strongly depending on the habitat.
The sizes of the clicker insect also differ: you can find an individual from a meager size of 1 millimeter to large beetles up to 6 centimeters in length.
They are united by only two factors: in case of danger, they are able to make a jump and the similarity of the larvae, called "wireworms".
Some types of click beetles:
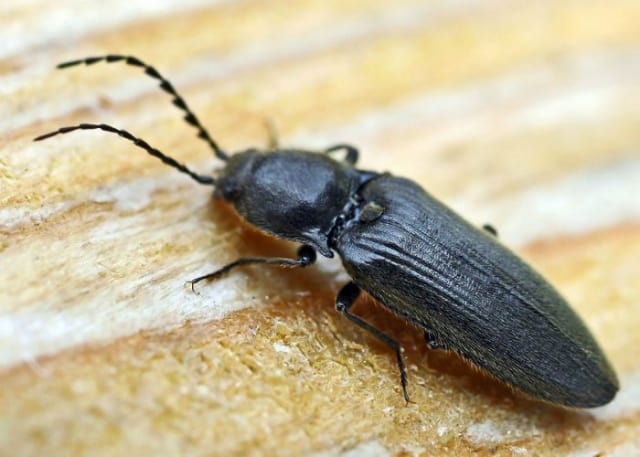
- hairy


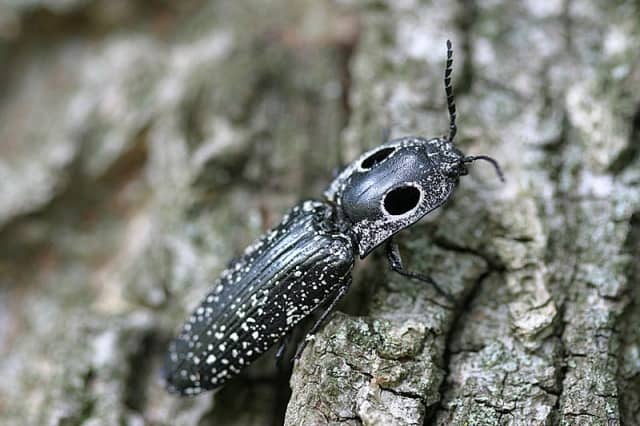
- ocellated


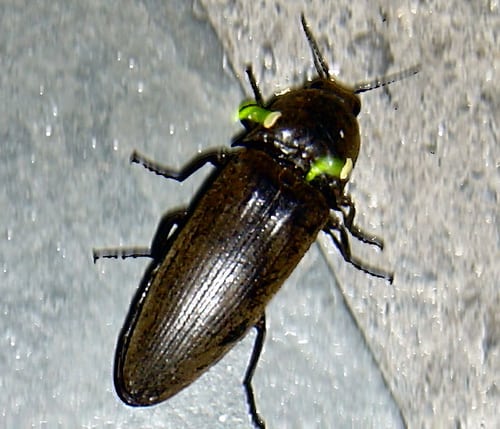
- jamaican bioluminescent


Not much is known about biological features. Most of the information is available about individuals living in Eurasia. Their American relatives have been little studied, and little is known about the inhabitants of the tropics.
But on the other hand, it is precisely established that the insects themselves do not pose a danger to agronomy, only the larvae are the enemies of garden crops.Moreover, most of the wireworms (larvae of this beetle) cause serious harm to crops. Other larvae are direct predators, devouring various living creatures underground.
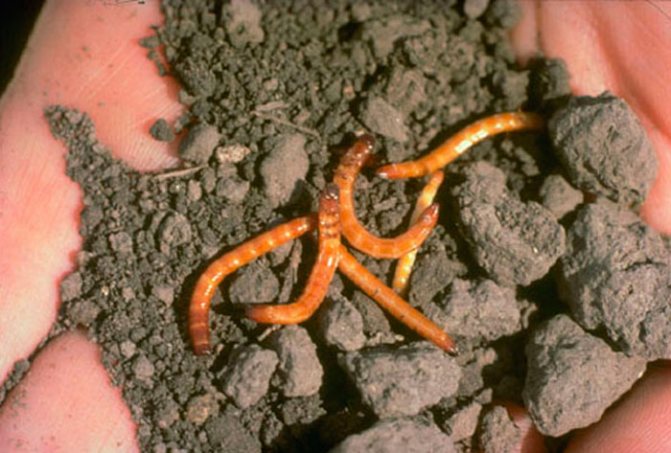
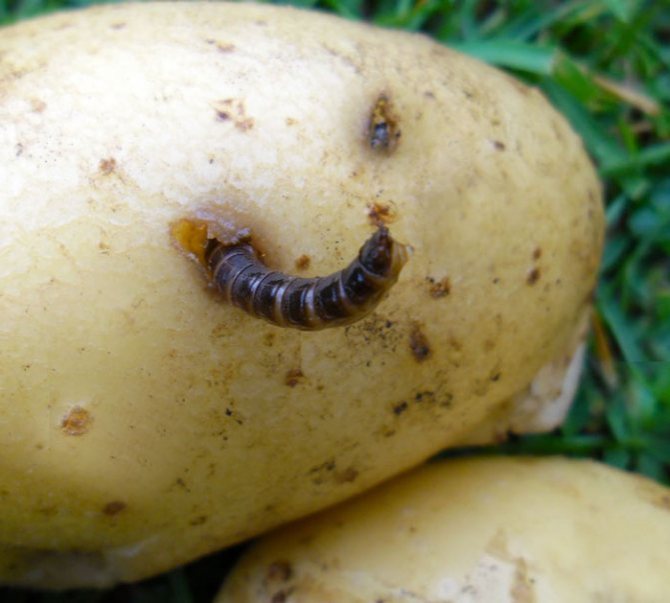
Although wireworms are different in size and color, they are united by the presence of a chitinous hard shell and shape: these are all worms.
Because of their chitinous shell, these worms resemble pieces of wire - hence their name.
Perhaps the most vicious pests are the wireworms of three varieties of the click beetle:
- Dark nutcracker


- Sowing striped
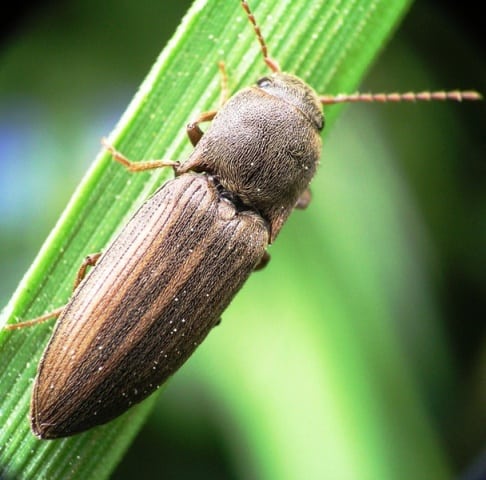


- Steppe


How to spot a wireworm in an area
Wireworms are the larvae of all beetles of the click beetle family. They look like small brownish or beige-yellow worms, up to 2 cm long. Their body is divided into segments, the first 3 of which have small legs. With the help of them, the wireworm moves through the soil. The pest has a pair of strong mandibles on its head, which help it to bite through the shell of roots and root crops. The body of this "worm" is dense and hard, it is not so easy to crush it with your fingers.
Since the larvae live in the ground, they can only be detected by indirect signs. Plants affected by wireworm have fewer stems than healthy plants. If the bush is severely affected, then signs of wilting can be seen on it. Stems and leaves lose turgor, look lethargic and drooping. Individual plants are most often affected. Less often, whole groups of affected plantings can be found. To make sure, they dig in the potatoes and examine the tubers.
Agrotechnical measures
There are a number of agrotechnical techniques that can be used to prevent wireworm infestation of the garden land or to minimize the damage to it.
This is the correct crop rotation, ensuring the required level of moisture, maintaining the acid-base balance of the soil, and controlling weeds.
Important points
If infected bushes were found in the garden, they must be dug up immediately. Spoiled tubers and tops are disposed of (it is better to burn). The place where the infected potatoes grew is treated with insecticides. If among the dug out potatoes there are seemingly healthy ones, they cannot be stored for storage. Inside, they can be attacked by a pest.
Application of lime
Although the use of lime can scare off the larvae of the click beetle, it is not recommended to use it in a potato field. This culture reacts to lime with the appearance of a disease such as scab. To prevent its occurrence, it is better to use wood ash, chalk or dolomite flour. These substances are introduced during planting in 0.5-1 glass in each hole or for digging, 0.5-1 kg per 1 sq.m.
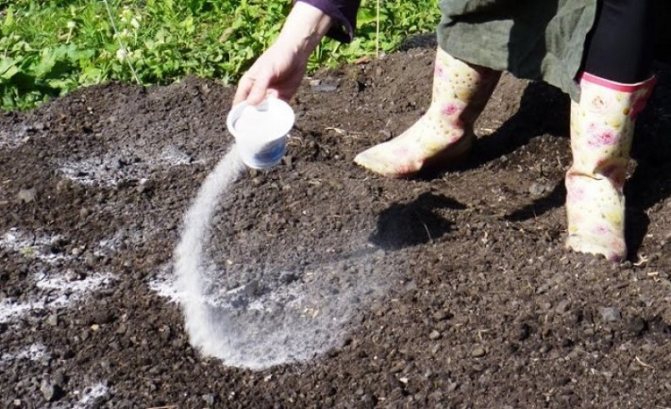


Ash is used to combat the wireworm.
Site cleaning
Since the pest is able to feed not only on potatoes, but also on the roots of others, including weeds, it is necessary to maintain cleanliness in the beds before and after planting vegetables. It is necessary to remove bluegrass and wheatgrass from the site, which are the favorite food of the clicker. Do not leave damaged or small potatoes in the ground. Remove any plant residues in a timely manner, it is better to send them to compost or (if there is a suspicion of infestation) to a fire.
Crop rotation
Crop rotation is an important part of agriculture. By changing the location of vegetables on the site in places, the gardener complicates the task of pests to find their favorite crop. It is difficult to completely remove the wireworm from the site in this way, but in combination with other measures, its presence can be minimized.
Timely hydration
For the larvae of the click beetle, potatoes are not only a source of food, but also a source of moisture. In dry soil, tubers are damaged by the pest to a greater extent than in a wet substrate.Moisture control may not drive away or scare away pests, but it does keep more tubers intact in areas where wireworms are abundant.
No thickening
Land in which the roots are close to each other and tightly intertwined is the most attractive for the wireworm. He easily finds a source of food in such soil. Therefore, it is not recommended to locate potato fields near lawns, lawns with weeds and abandoned areas densely overgrown with weeds. It is undesirable to plant bushes of cultivated plants close to each other. This makes it possible for the larvae to easily move from plant to plant and damage entire areas of garden vegetation.
What is used for preventive treatments?
It is possible to reduce the likelihood of the appearance of beetles on the site and stop their reproduction if you follow the simple rules of agricultural technology: change the types of crops, do not plant the same ones constantly in one place. Do not plant carrots, daikon, beets on infected beds - crops that also target click beetles.
Destroy weeds that wireworms like to settle on - wheatgrass, chicken millet, sedge. In the fall, it is good to dig up the soil, roll over the earth so that the insects are at the top and freeze in the cold. Apply nitrogen fertilizers, ash to the soil, monitor the acidity of the soil. To plant calendula and marigolds next to potato beds and in aisles, they should scare away pests with their smell.
If you decide to grow potatoes, you need to take care of its protection from wireworms even before planting. You should purchase any drug produced by the industry, or use a folk remedy.
A source
Application of chemistry
Unlike the implementation of agricultural practices that help reduce wireworm damage to vegetables, the use of chemical plant protection measures makes it possible to completely get rid of it. Chemically synthesized preparations kill not only the larvae of the pest, but also the eggs of beetles. They are highly effective, but it must be borne in mind that they produce a negative effect not only on harmful insects, but also on beneficial soil inhabitants.
Among the drugs recommended for the destruction of the wireworm are the following: Aktara, Provotox, Pochin, Zemlin, Bazudin, Prestige, etc. They are introduced into the soil before planting, they are treated with tubers, and the aerial part of the plants is also sprayed with solutions prepared according to the instructions on the package ... Since these insecticides are toxic to both humans and animals, they are used only when the site is massively infected. If the invasion by the wireworm is of a local nature, it is advisable to use biological agents.
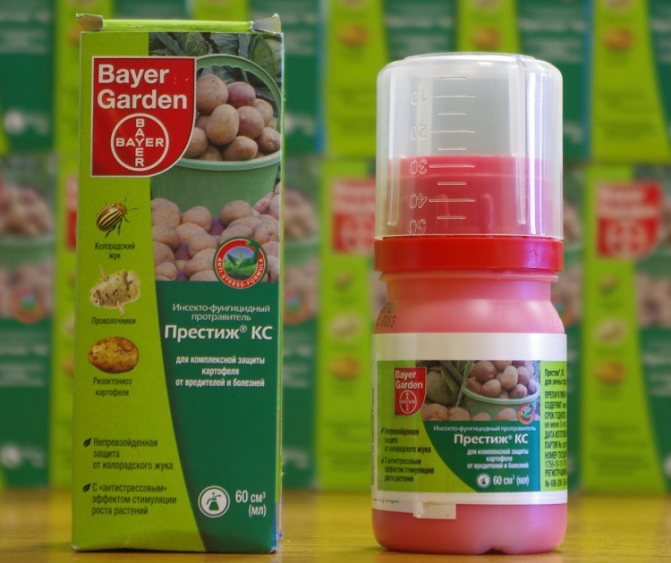


Prestige is used to combat wireworms.
Method 10. Coniferous needles
Conifers also help fight wireworms. It is better to collect the needles just before planting potatoes - two days in advance. Branches of young pine trees are considered the best option. During planting, potatoes are first placed in the furrow, then ash and humus are poured, and from above the entire furrow is covered with pine branches.


Defeating the insidious wireworm is possible only by combining different methods of struggle. Of course, a more reliable result will be "shown" by combinations with chemicals - Provotox, Barguzin, Medvetox, Zemlyan, Aktara, Prestige. But since all these funds are very poisonous, you need to apply them strictly according to the instructions and wait for the required time before harvesting.
Biological drugs
Biological methods of pest control are becoming more widespread. They imply the use of entomophages - insects that feed on their own kind. The wireworm has natural enemies in nature. These include, for example, a predatory nematode.
You can bring it to the site using a drug called Nemabact. Treatment of potatoes before planting and the substrate with this preparation leads to the fact that microscopic nematode worms gradually exterminate the larvae of the click beetle. There is no need to expect an instant effect from this method, but in the long run it pays off.
Eco-friendly control methods
Most of these methods involve the installation of various kinds of traps for these individuals.
Cereals are sown two weeks before the start of planting tubers. Cereals are sown in nests, a handful in one place. As soon as the seedlings have appeared, they are harvested along with the larvae.
Set up traps. To do this, by mid-April, holes are dug in the still cold soil. They put rotted straw or grass in them.
Then the trap is moistened and covered. In just a couple of days, it will be full of larvae. The trap is taken out and burned. Then they put it again. For several times, you can significantly reduce the pest population on the site.
Lures and traps
The use of baits allows you to get fairly quick results, but at the same time does not pose the threat of poisoning the soil and its many inhabitants.
Cut potatoes or other vegetables soaked in an insecticide solution are used as baits. They are placed in the garden, buried in the ground. After a few days, they are dug up along with the pests that have climbed inside and destroyed.
It can be effective to identify pests by organizing places convenient for their wintering. In autumn, heaps of vegetable tops or mowed grass are left in the beds. Before the onset of constant frosts, they are lifted and examined. Most often, in such places, not only a large number of wireworms accumulate, but also the larvae of May beetles and other pests. Plant residues are burned along with all insects found in the heap.
Dig up the soil in the garden in the fall and remove the weeds
You can discuss as much as you like the pros and cons of digging the soil, its necessity, but if a wireworm is wound up on the site, these works are on the list of mandatory. Moreover, you cannot delay, start processing the site immediately after harvesting, until the larvae have time to go deep into the ground for wintering. Removing pests from there will be problematic.
Arm yourself with a shovel and carefully dig up the entire area, go deep, in fact, the further the better. Be sure to select all the roots and wireworms that come across. The process of destruction will be completed by freezing, which the pests cannot tolerate. Birds also will not refuse such a generous treat. The larvae themselves, in the absence of root crops and weeds, will have nothing to eat, so they will simply die of hunger. Of course, in this way it will not work to destroy all pests, but about 90 percent may well die.
Important! Do not ignore the spring digging, it makes it possible to destroy new pests and old ones that have not been killed.