As a rule, most gardeners grow zucchini in a seedless way, immediately planting seeds in open ground.
However, if you want to get an earlier harvest (by 1-2 weeks), then you can try first sowing zucchini seeds for seedlings to grow at home and then planting the seedlings on a garden bed in open ground.

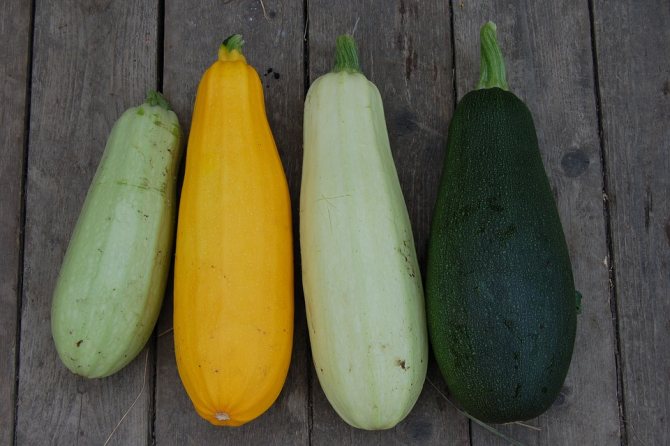
Description of zucchini and an overview of varieties
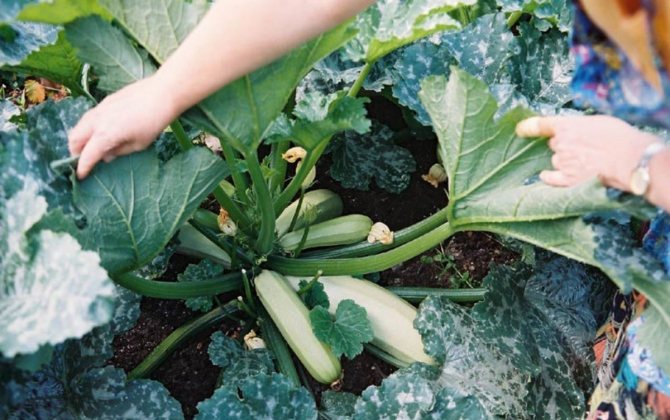
Zucchini forms a powerful bush up to 70 cm high, sometimes more, on which oblong yellow, dark green or white fruits grow. Only 7-14-day-old young fruits are eaten. Older fruits are much larger, but they become tough and practically unsuitable for food. They are used to feed livestock, but their feed value is low, because the fruits of squash of any age are low in calories. But this quality makes them simply indispensable in the diet of a person for losing excess weight.


Four different varieties of zucchini
100 g of zucchini gives only 27 kilocalories. Of the nutrients, it contains the most potassium - 240 mg. There is iron, organic acids and a set of vitamins C, PP, B and carotene.
Self-pollinated zucchini varieties
Used for growing indoors, in the absence of pollinating insects:
- Cavili.
- Parthenon.
- Jellyfish.
Early varieties
- The ball.
- Tsukesha.
- Aeronaut.
Late varieties
- Calabaza.
- Spaghetti.
Old varieties
- Gribovskys.
- Odessa.
- Kuldzhinskie.
- Greek.
How to organize garden beds on the balcony
To grow a large crop of zucchini, pay attention to the location of your balcony. Depending on which side the future garden is located, start planting.
- The balcony is located on the south side. Planting can be done in early spring (late April - early May).
- If the balcony faces west, then it is better to postpone the landing until the end of May.
- When the balcony is facing the north side (it is especially bad if it is not protected from the wind), then it is better to postpone the landing, at least until the summer.
The distance between the seedlings of zucchini is at least 70 cm.
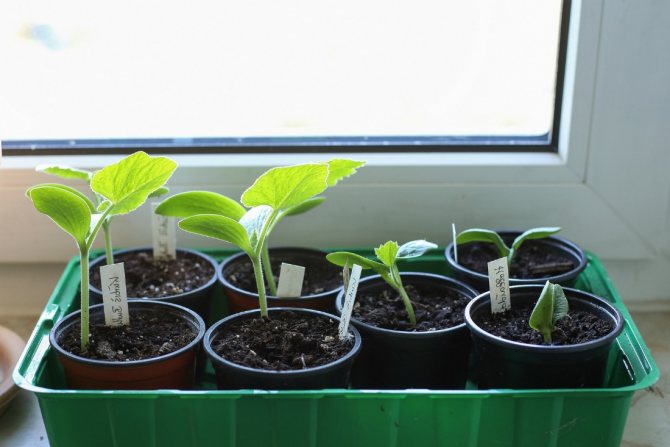
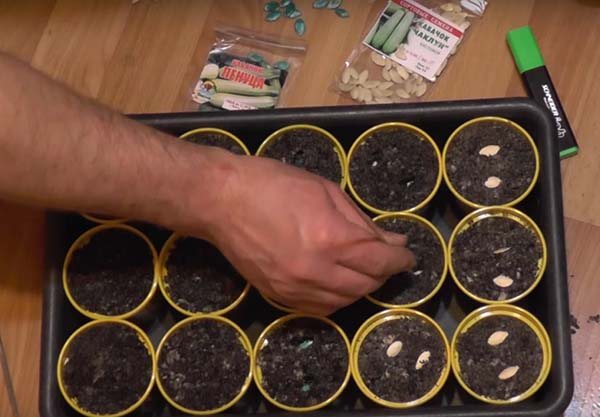
Growing marrow seedlings
The first fruits of zucchini are ready for food already 50-60 days after germination, so in the central and southern regions they have time to ripen even when planted in a seedless way, directly by seeds into the ground.
However, the first harvest is not the entire harvest. Zucchini are able to bear fruit throughout the warm period until the coldest days. Therefore, the earlier they are planted, the more harvest they will give per season. And for early planting, they use the seedling method even in warm regions. In addition, zucchini are thermophilic. The optimum growth temperature is 18-25 degrees. And for a quick and friendly seed germination, an even higher temperature is required - 25-28 degrees, which happens outside only by the beginning of summer.
Container
Zucchini forms quite powerful shoots, so it needs a soil volume of at least 350-500 g. If you need a little seedlings, it is best to use rectangular cut-off packages for dairy products. They are cut off, several holes are made at the bottom to drain excess water. It is better not to wash the packs - there is an assumption that the colony of lactic acid bacteria improves the background of the soil microflora and prevents the competing pathogenic microflora from settling. How exactly this works at the microbiological level has not yet been described by science.But in practice, many years of experience have shown that plants grow better in such packaging, this is a fact.


Can be put in a drawer for easy portability
Planting each plant in a separate container is called "closed root" cultivation. This means that when transplanting into open ground, the plant will not need to be removed from the common box, damaging the roots, but it will be possible to transplant it from a separate container along with the ground, without touching the roots at all. With such a planting, the plants do not get sick and immediately start growing.
This is especially important for zucchini because they don't like transplants. For the same reason, they are not dived (intermediate transfer).
You can use any other container of a suitable volume - plastic cups, pots, cassettes with cells, etc.
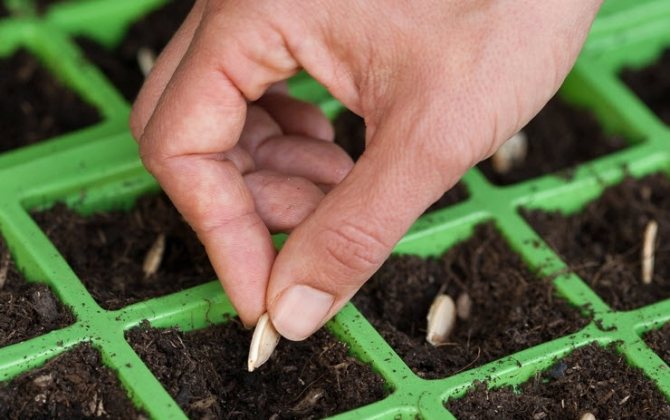


These cassettes have holes in the bottom to drain excess water.
You can avoid problems with the preparation of the soil and the search for containers and save time by buying ready-made peat pots in specialized stores or firms.
Seedling soil
Zucchini are demanding on the soil. Scanty sandstones, clean peat and heavy clay soils are not suitable for them. The soil should be nutritious, loose and free-flowing. And should not, when dry, become hard and form cracks.
Most often, the soil for them is prepared according to the following recipe:
- 1 part of good garden land.
- 1 part of forest, compost or manure humus.
- 0.5 parts of peat - as needed to make it friable.
Adding 0.5 liters of wood ash to 10 liters of the mixture will provide the plant with all the necessary elements for growth, except for nitrogen, which is not in the ash. All other substances may be in the soil, but something may be missing, but in the ash they are 100% guaranteed.
It is better if the soil was prepared in the fall and stored in the cold. Then it is cold sterilized. Ice crystals formed when water freezes in the ground break up the particles of the earth, and when it thaws it becomes softer and friable.
The earth is brought in from frost in advance so that it warms up the entire massif to a temperature of at least 25 degrees.
Timing
Seedlings are ready for planting in open ground at the age of 30–35 days. Based on this, the timing of planting seeds for seedlings is calculated for each region. It is taken into account that zucchini is a thermophilic culture and can be planted when it becomes at least 15–20 degrees outside. For example, if in the southern regions it is May 1, then seeds are planted for seedlings 30–35 days before this date, March 25 - April 1. If in southern Siberia it is June 1, then seeds for seedlings are planted on April 25 - May 1.
Seed preparation
Seeds are prepared in the same way both for planting seedlings and for planting directly into the garden.
First, the seeds are disinfected by placing them in a pink manganese solution for 20–30 minutes. Then the seeds are washed and germinated at a temperature of 20-25 degrees. A cloth is placed on a plate, seeds are placed on it and the top is covered with a cloth. The seeds lie until they begin to hatch. All this time, the fabrics are not allowed to dry out, moistening with water as needed.
Seed preparation for sowing


Before sowing, it is imperative to decontaminate the seeds. Many pathogens of zucchini diseases can be contained in the embryos of plants, therefore, the seed material must be disinfected. To do this, the grains can simply be soaked for 20 minutes in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate.
Heat treatment is more effective, which helps not only to disinfect the seeds, but also to accelerate the emergence of seedlings. To complete this procedure, you must:
- soak the seeds for 20 minutes in hot water (+50 degrees);
- immerse them in cold water for 1 minute;
- pour the seeds for 12 hours with a solution of trace elements;
- rinse the grains and leave in the refrigerator for a day.
This manipulation "awakens" the seeds and makes them more resistant to disease.
Some gardeners also choose to germinate their seeds to make sure they are germinating.
Outdoor cultivation
Zucchini is unpretentious in care. It will give a small crop even in an unfavorable year with minimal care. But in order to get a full-fledged crop, it is necessary to fulfill the requirements of agricultural technology and care.
Priming
Fertile areas, closed from the wind, are taken away for zucchini. With a serious approach, the soil is prepared in the fall, bringing in 10 square meters for digging. 50–70 kg of humus, manure or semi-rotten compost, and 200–300 g of superphosphate.
In the spring, the site is dug up again and top dressing is applied - 150 g of ammonium nitrate and 200 g of potassium salt per 10 sq. m.
If the soil is loose and warms up well, the zucchini is planted on a flat area. If the soil is clayey, heavy and cold, the ridges are poured from a loose mixture of humus, sod land, compost, peat and garden soil in proportions. which will ensure the looseness of the soil.
Landing
The intervals between zucchini can be different - 60 by 40 cm, 50 by 50 cm. The main criterion is that one plant should have about 1 square meter. m. On good soil, zucchini are planted in the holes in the usual way. If the soil is sparse, sandy, or heavy clay, the land for squash can be significantly improved. Holes are dug 20–25 cm deep and 35–40 cm in diameter. 5–7 liters of manure are poured at the bottom, which is covered with earth. Seedlings with a lump of earth are placed in a hole and covered with loose soil in such a way that the hole is slightly below ground level. This is done for the convenience of watering, so that the water does not spread during watering. After planting, the hole is poured abundantly and covered with mulch - peat, humus, compost, rotten dark sawdust, etc.


Soon they will grow and cover the entire area
Mulch plantings need to be watered much less often, since mulch does not allow moisture to quickly evaporate even in the heat.
Watering
Zucchini are demanding on soil moisture. The frequency and amount of watering is determined by the summer conditions and location. You can not leave the zucchini without watering in dry soil - the fruits become lethargic, the ovary and foliage dry out, and with abundant watering or rain after a drought, the ends of the fruits begin to rot.
Therefore, the basic rule is to keep the earth constantly in a moderately moist state. But during the fruiting period, zucchini need more moisture, and the volume of water for irrigation is increased.
Top dressing
If the soil is filled with fertilizers in autumn and spring, fertilizing is practically unnecessary. Also, little or no additional fertilizing is needed on initially fertile soils - fat chernozems and fat black loams.
At the same time, it is important that the predecessors are not related to pumpkin squash - cucumbers, squash, pumpkins. Related species take out the substances necessary for this particular type of soil from the soil, and it is they that may not be enough for the zucchini later.
The lack of nutrients in the soil is immediately visible on the weak development of the plant and fruits. Then zucchini must be fed every 10-12 days.
Organic feed
Fresh mullein or slurry is diluted in an amount of 1.5-2 liters per 10 liters of water.
Poultry droppings are also used in a proportion of 0.5 liters per 10 liters of water.
It is better if the solution will stand for 1-2 days. Then the water is saturated with oxygen and more substances from organic matter will dissolve in the water, passing into a form more accessible to the plant.
Mineral dressing
Dilute in 10 liters of water
- 30 g ammonium nitrate or urea
- 40 g superphosphate or 20 g double superphosphate
- 20 g potassium salt
- 30 g of nitrogen fertilizers (nitrate or urea) and 100-150 gram glass of wood ash.
Before feeding with any fertilizers, the zucchini are spilled with plain water to avoid scalding the roots. Solutions of any fertilizers are watered at the rate of 1 to 3 liters per plant, namely:
- 1 liter for young bushes 20-30 cm high
- 2 liters for more developed bushes with ovary
- 3 liters for an adult bush.
After each watering and feeding, the mulch washed off with water is raked on damp ground or a portion of new mulch is added.
Such doses and compositions of dressings are recommended by serious sources, which are based on many years of agronomic experiments carried out at scientific experimental stations. The plant converts all fertilizer substances into others that are useful to the human body. But, for example, excess nitrogen in top dressing can lead to the accumulation of harmful concentrations of nitrates and nitrites. Therefore, gardeners try not to abuse unnecessary dressings, including organic ones, because they contain large amounts of nitrogen. It is better to lose it in the harvest, but it is guaranteed to get a pure, healthy product. Otherwise, the composition of a rich harvest will not differ in any way from the mass grown in large farms, where the quantity and appearance of the harvest is at the forefront.
Harvesting
Zucchini fruits should not be allowed to overgrow. Overripe large fruits older than 12-14 days take on a lot of nutrients and moisture, thereby inhibiting the formation and growth of new ovaries. Therefore, harvesting is a nursing operation. Eatable zucchini 8–12 days old must be removed by cutting with a sharp knife, thereby accelerating the growth of new ovaries. The fruits are harvested about once a week.
Care rules
With sufficient lighting, squash does not need artificial light. However, frequent cloudy weather during the growing season or cold rainy summers make it necessary to use fluorescent lamps at the rate of 200 watts per square meter. It is also very important to shade the vegetable crop from too much exposure to sunlight.
Zucchini need systematic feeding with a solution of mullein diluted in a ratio of 1: 5, or chicken manure with water in a ratio of 1: 10. As a rule, such dressings are used no more than three times a month. You can alternate the introduction of organic matter with fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. Plants should be watered abundantly and regularly, exclusively at the root, to prevent sunburn on the leaves.
If at the stage of mass flowering cold and rainy weather is observed for a long time, which reduces the years of pollinating insects, then it is necessary to carry out artificial pollination. For this purpose, pollen from male flowers must be applied to the stigma of female flowers.


Growing zucchini in biofuel greenhouses
This is an old method that was widely used in cold regions to grow not only zucchini, but also other crops and seedlings. Now it is rarely used for many reasons:
- Time consuming, requires hard physical work.
- The main biofuel - manure is not as readily available today as it used to be.
- The large supply of zucchini on the market all year round makes difficult battles for the harvest of early zucchini meaningless.
But you need to know this method. The master's business - you can apply it today.
The principle of heating such a greenhouse is fresh manure, which, when decomposed, "burns", releasing heat. In autumn or spring, a pit is dug 50–70 cm deep over the entire area of the future greenhouse. At the end of March, it is slaughtered with manure. On top of the manure, garden soil is scattered with a layer of 12-15 cm. Flexible elastic arcs made of wire or glass reinforcement are placed above the greenhouse so that at the highest point it is no higher than 50 cm. If higher, there may not be enough heat to heat a large volume of air. A transparent film is pulled along the arcs.
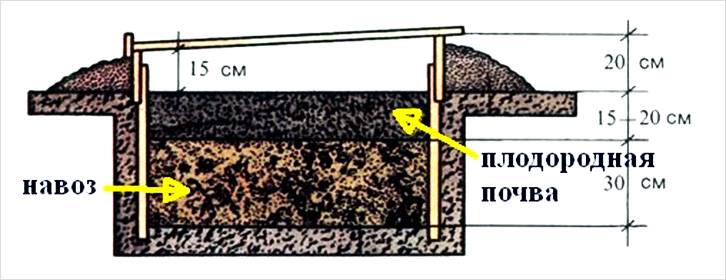

The frames at the top can be replaced with arcs
Sometimes, instead of arches, a wooden box 20-30 cm high from the surface of the garden is placed around the perimeter of the greenhouse. It is covered with frames with glass or foil.
For any type of greenhouse, you need to have additional shelter at hand - several layers of non-woven material, fabric, synthetic winterizer, light old clothes, etc., which cover the greenhouses in case of severe frosts.
Before planting seedlings from home, heated greenhouses or seeds in such greenhouses, biofuel is “turned on” by spilling boiling water - about 10 liters per 1 square meter. m. The greenhouse is immediately closed to save heat. Manure heated with boiling water should "catch fire" and begin to generate heat, self-heating up to 50 degrees inside. The process will go on until the manure is completely rotted. This is the secondary value of the method - after using manure as biofuel, high-quality humus remains.
To control the temperature inside the greenhouse, a thermometer is placed on the soil.
Zucchini are planted in holes 25-30 cm deep, which are made directly in the manure. The hole is covered with prepared soil from a mixture of garden soil, humus, peat or loose sod land to make the mixture friable. Add 150-200 g of wood ash to 10 liters of the mixture.
Seedlings are planted in a hole along the root collar. Seeds - to a depth of 1-1.5 cm.
Watering is rare, once every 10-12 days with warm and even slightly hot water, but not higher than 40 degrees.
With the onset of warmth on sunny days, you need to monitor the temperature. The sun and biofuels can heat a greenhouse to temperatures above 50 degrees. The plants will simply burn out. To reduce the temperature, they do not remove the entire film, but open the corners of the greenhouses on one or both sides, more or less, depending on the temperature.
When the bushes grow and they get cramped under the shelter, it usually becomes quite warm outside. And if the film interferes with the growth of plants, it is simply removed completely. This cannot be done abruptly. There is always a different microclimate under the film, which is very different from the open mode. It's warm, stagnant air and high humidity. The plant experiences shock due to an instant change in conditions, can stop growing and get burned by winds, unusually dry air, direct sunlight and night cold. Therefore, the film is removed gradually - first, two sides are opened, then completely for several hours, then they are removed completely. During overnight hardening, the greenhouses are closed to preserve the heat of the day.
It is impossible to name the exact terms and duration of such hardening. It all depends on the climate and weather. You just need to observe the plant and the thermometer readings on the ground. In the sun, the reading of a thermometer lying on the ground should not exceed 45 degrees. This does not mean that the plants are extremely overheated - the soil at this time, as a rule, is no warmer than 20-25 degrees, and a short-term increase in air temperature in sunny weather threatens plants with thermal burns when the thermometer reads above 45 degrees.
However, an approximate hardening algorithm is as follows:
- The first 3-5 days open the ends of the greenhouses.
- The next 3-5 days open up to a third of the area.
- Then 5-7 days are opened completely for 4-6 hours a day.
- After that, you can remove the film completely.
You can leave the zucchini to grow under a slightly open film to the end, if you raise the arches so that the film does not interfere with the development of the bushes.
Soak
Have you already decided how and when to plant zucchini seeds for seedlings in order to get a good harvest in your climatic zone? Start by soaking. This procedure delays sowing a little, but allows you to determine the germination energy and germination capacity of the material.


For the first shoots to appear, place the seeds on a damp cloth. Remember that you first need to choose the right material for sowing and prepare it (pickle and calibrate). As soon as the first shoots hatch, they can be planted in the ground.
Unusual cultivation methods
This method can be conditionally called "portable". Zucchini seedlings are grown in the usual way, and then transplanted into containers of at least 5 liters, where they grow to the end.
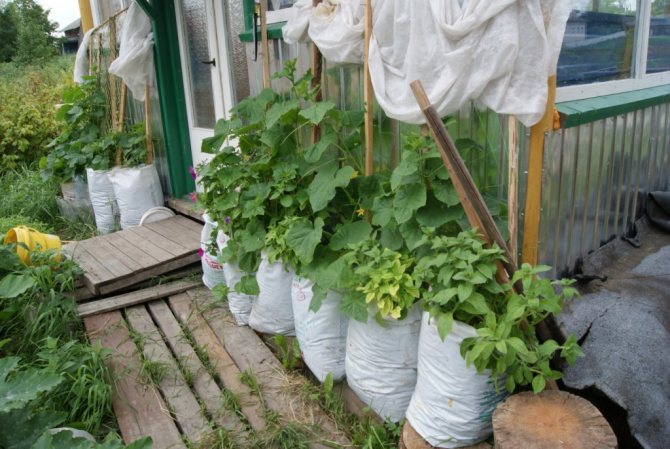
Zucchini in bags and tubs
The advantages of this method are that you can compactly place zucchini in a greenhouse or even in a living room. Then, with the onset of stable heat - 18-25 degrees during the day, they can be taken out into the street, freeing up the valuable area of the greenhouse for other crops.
The disadvantage of this method is that zucchini with this method cannot develop in full force. In natural conditions, their root system is located wide and shallow from the surface. In a limited container, they go through to form the root system in an unnatural form - to the bottom of the container in depth and limited by the diameter of the container. The soil in a container dries up much faster than in a solid massif of a vegetable garden. Therefore, you have to water almost every day. In the garden, the roots of the squash themselves find the most nutritious and favorable layer of the earth. In a closed container, they completely depend on how fertile and suitable soil they have prepared.


They look somewhat depressed
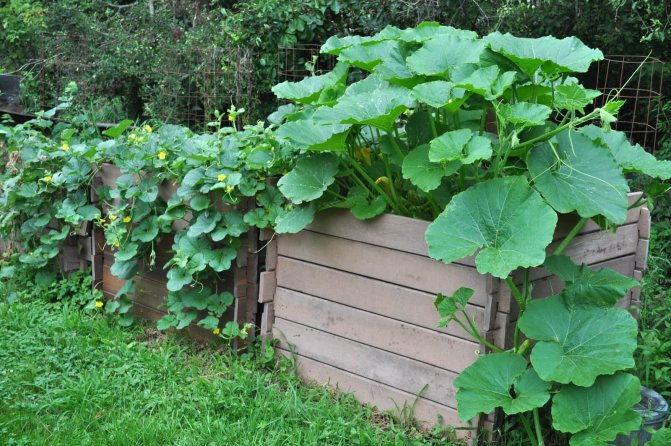
For comparison, what can look like zucchini bushes "on the loose":
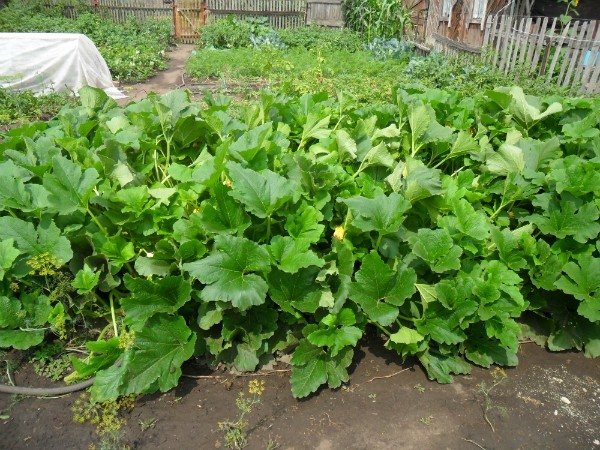


This is how normal zucchini bushes look from the middle of summer.
The most suitable soil for zucchini in closed containers:
- 1 part of garden land, black soil, loam or sandy loam, rich in humus.
- 1 part of mature manure, compost or forest humus.
- 0.5 liter can of wood ash for 10 liters of mixture.
If the garden soil is too heavy, the composition is made looser by adding no more than 10% (one tenth) of sand, 20% (one fifth) of peat.
Despite the disadvantages, this method allows you to grow zucchini in a warm place until the end or before the onset of heat. Therefore, for the northern regions, it may be the only way to grow zucchini.
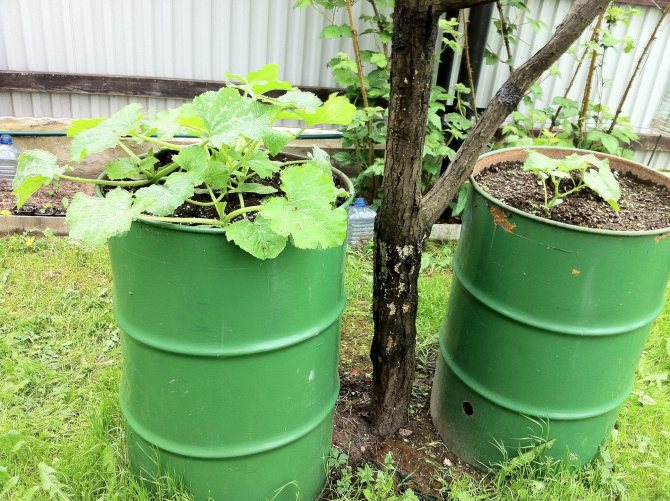
Zucchini in barrels
Sometimes squash is planted in 200-liter iron barrels.


Developing unevenly in two adjacent barrels
Zucchini barrels have more food area than sacks. But another problem lurks. The iron or plastic walls of the barrels do not allow air to pass through, and the roots lack oxygen. In the heat of the sun, the surface of barrels, especially iron ones, can heat up above 50 degrees, and all the roots near the walls suffocate and burn out.
Also, with such a planting, daily watering is required. And a simple question arises - why not plant the zucchini just in the ground exactly in the same place where the barrels are. But here, as they say, the master is the master.
Summary
Many summer residents living next to a busy highway try to reduce the danger of vegetables by liming the soil. However, I do not think that it is worthwhile to grow a time bomb in the form of a zucchini with heavy metals for yourself on the balcony with your own hands.
And yet, for those who want to try themselves as an agronomist, I recommend taking a look at the video in this article, the plot will tell you in detail about the cultivation of zucchini on the balcony. And I invite all interested readers to discuss this topic in the comments!
September 16, 2020
Balcony and loggia, Gardening
If you want to express gratitude, add clarification or objection, ask the author something - add a comment or say thank you!
Diseases and pests of zucchini
Basically, zucchini suffers from three serious diseases.
Powdery mildew
This is a fungal disease. To determine it simply by the appearance of a white bloom on the foliage. The plant looks like it has been sprinkled with flour, which is why the disease got its name. Affected leaves become brittle and eventually dry out.
This disease develops in cold, damp and cloudy weather. When the temperature rises above 20 degrees, the development of the disease stops by itself, especially with a clear sky in the sun.
Of the old means of control, it is recommended to dust the affected areas with colloidal sulfur powder. Dusting with wood ash may help. This dries up the leaf and creates an unfavorable environment for the development of the fungus.
Copper-containing preparations are also used - a Bordeaux mixture or a solution of copper sulfate: 7 g of copper sulfate and 30 g of laundry soap dissolved in water are added to 10 liters of water.
A numerous group of drugs to combat precisely fungal diseases are called fungicides. Modern fungicides recommended for use in small crop production - Topaz, etc. (there are more than 100 names today) are used in extreme cases according to the instructions on the packages.
Root rot
It appears from below on the stems. First, the root collar rots, then the lesion spreads up the stems and down, affecting the roots. The onset of the disease is determined by the appearance of brown spots. This is also a fungal disease, and the control measures are the same as for powdery mildew. Watering with cold water and sudden changes in temperature can provoke the disease.


Plant completely killed by disease
Vertex bacteriosis
It is a bacterial disease. First, it affects the fruits of squash. Determined by the following criteria:
- At the first stage, the ovary stops growing.
- Then it becomes vitreous, the top of the ovary begins to rot.
- The fruit at the leg continues to grow for some time, eventually acquiring an ugly shape.
Watering with cold water, too high humidity, unfavorable growth conditions provoke the disease.
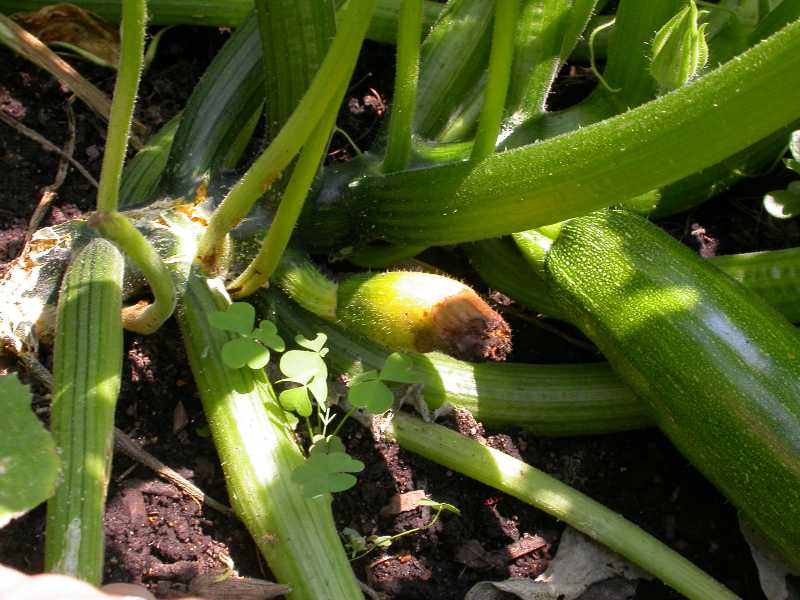


The affected fetus should be removed
Compliance with the rules of agricultural technology can be considered prevention. A strong plant, under good growing conditions, is able to withstand disease. Also, you can not injure (break, scratch) stems, leaves and fruits. The infection enters primarily through open wounds.
For the prevention and treatment of this (and other non-fungal diseases), spraying with the following folk remedies helps:
- For 10 liters of water, 1 liter of any fermented milk products (kefir, whey, fermented baked milk) and 1 tbsp. spoon for treatment or 1 teaspoon for the prevention of pharmacy tincture of iodine.
- 0.3% hydrogen peroxide solution (100 g bottle of pharmacy 3% peroxide per 1 liter of water).
Pests
Pests rarely affect the coarse foliage of zucchini. The main and most dangerous pest of zucchini is the larvae of the butterfly moth. They gnaw through the stem and settle inside, feeding on the tissues of the plant. As a result, this can lead to the death of the entire bush. It is not easy to spot them, as they live in the ground and are nocturnal. Treatment of the soil with pesticides does nothing, since poisons do not get on pests.
However, the measures to combat them are simple:
- Weed and loosen the soil regularly. This procedure, necessary in itself, destroys the eggs and larvae of the pest.
- At the beginning of the butterfly's flight, when it has not yet laid eggs, they set up sticky traps - industrial from stores or from sugar syrup, kvass, fermented juice, jam.
This will help get rid of the bulk of the pests. Single larvae cannot do much damage.
Other problems
If the zucchini weakly builds up the green mass, does not form or sheds the ovary, the reasons are most often in unfavorable growth conditions.
- The temperature is below 12 and above 30 degrees.
- Root locking due to excessive moisture.
- Drying out of the soil.
- Landing in the shade.
- Critically unusable soil, for example, among construction waste.
- Diseases.
- The bee does not fly to pollinate bee-pollinated varieties.
It is not possible to diagnose each case in absentia, but everything can be figured out on the spot, knowing the basic rules of agricultural technology.
The zucchini culture is so problem-free and grateful that somehow you don't even think about the yield, timing, etc. The only thing that bothered me was the seedling method. This is uncomfortable for me. But under a temporary shelter I plant it myself with dry seeds for the May holidays (before the earth was still cold), and they produce until the first autumn frosts ...
AndreyV
I have been planting the Kavili hybrid for 9 years now, three plants are enough for us. There is nowhere to put them. They grow like a Christmas tree, there are more fruits than leaves.In general, all imported hybrids are very productive. Our seed production falls short of them. I plant seedlings early, always on April 5, in the ground for May under the film. First, we collect small ones, then we gorge ourselves, and disgrace begins on the zucchini, hippos grow up to 70 cm and up to 4 kg, this is already for processing.
Busyasha
For me, seedlings are not a problem, I do not grow at home, but in a greenhouse. In April, I put earth + sand + compost and a little ash in liter pots. I send a seed there (I soak it beforehand) and it's all short-lived. The pots are in the greenhouse, no lighting is needed, the main thing is not to forget to water in time.
Alyonka
And now I will only plant zucchini in barrels. The Cavili variety grew in a barrel this summer. I feel sorry for the garden bed for zucchini, I save space. They stand under the sink, do not interfere with anyone. I tamp the plant waste into a barrel (full of holes) in the fall, pour the earth on top in the spring and that's it. I sow 3 seeds in a barrel, while the threat of frost sprout under the "roof" of lutrasil, then I take them off, and the three of them grow.
Cousin mom
Video: how to get an early harvest of zucchini
In summer, zucchini is consumed in small quantities. Apparently, because at this time is the season for a variety of delicious vegetables and fruits. It is not required as much as needed for a year, for example, potatoes and cabbage. But there are many great recipes for canning this vegetable, including the famous caviar. When calculating the needs of the family, you need to know that under normal conditions, a squash can give 80-100 kg of marketable fruits from 10 sq. m. And, of course, this dietary product is needed in the modern diet, as an important element of a varied and nutritious diet.




























