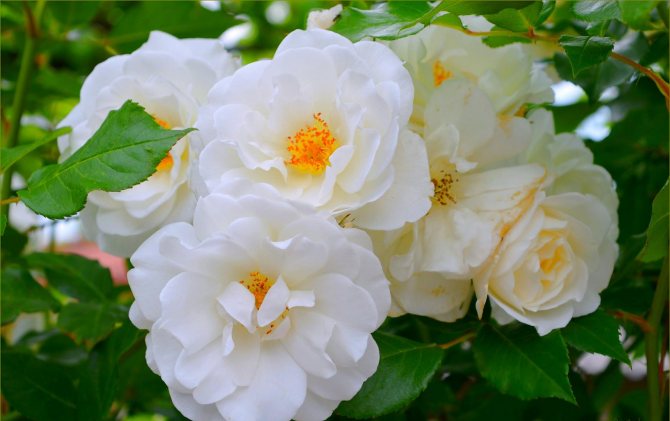
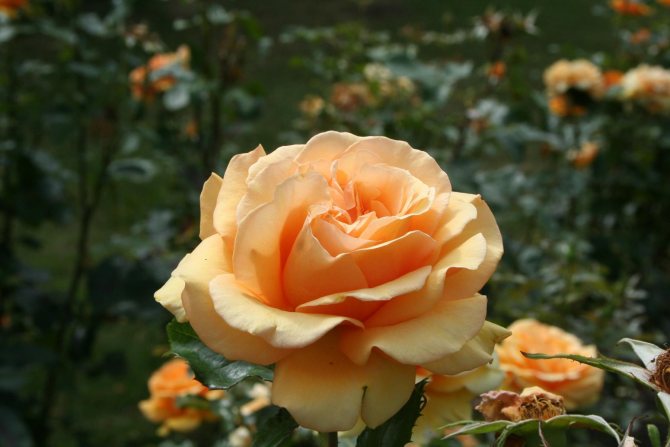
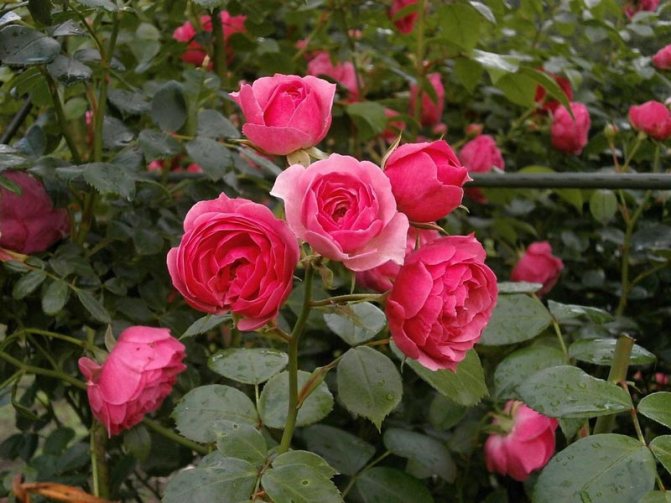
Tea roses (Tea) belong to the old class of roses. They are re-flowering climbing shrubs with smooth shoots or sparsely large red thorns. Tea roses:
- leaves - shiny dark green or light, medium size, lanceolate (oblong with a pointed tip);
- flowers - smell of various spices, semi- or densely double-shaped, located singly or in bunches of three, bloom on annual or biennial shoots;
- coloration - usually pastel shades: white, yellow, pink, apricot.
They are characterized by a pointed bud, which opens in a spiral, and the edges of the petals curl outward. This shape has become a classic in modern roses.
Used in protected areas as species and for border decoration.
Tea or scented roses first came to Europe from Asia in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Presumably from China. Their distinctive feature was an extraordinary aroma that resembled the smell of tea. Perhaps this scent explains their name.
There are other versions as well. Some argue that their shape made them call roses tea. The blossoming flower looks like a bowl from which the Chinese drink tea. Others believe that the "tea house" corresponds to the name of the country "China" (China). Still others say that the seedlings arrived on clippers (high-speed sailboats), which brought tea to Europe.
A native of southern latitudes, it was difficult to take root in a more severe climate. She didn't like the changing seasons: short summers, cold autumn and spring, low winter temperatures. Breeders have gone to great lengths to accustom them to temperate climates. They succeeded. But tea roses are still very afraid of frost, they must be well covered for the winter or grown in greenhouses and greenhouses. Therefore, they feel comfortable only in the southern regions of our country.
Examples of popular varieties of tea roses:
- Lady Hillingdon;
- Maman Cochet;
- Duchesse de Brabant;
- Mrs. Foley Hobbs.
Landing
The tea rose is a thermophilic plant. Therefore, when choosing a place for planting, one must think about the comfort of the rose. And she feels good where there is a lot of sun. Ideal when there is sun in the morning and a little shade in the afternoon (southeast).
The landing site must be protected from piercing winds and drafts. In this case, it is necessary to ensure free air circulation. This will prevent the rapid spread of fungal diseases, to which climbing varieties of tea roses are very sensitive.
For climbing varieties of tea roses, use supports and trellises. If you are going to use tea roses as a hedge, then the distance between the planting holes should be at least half a meter.
Think in advance how you will insulate roses for the winter, whether additional structures are needed for this. If so, leave room for them. Red tea roses planted on heavy soils have a more intense smell, so plant them on slightly acidic loams. If you have light soil, add dried clay, sod and humus to the planting hole.
In temperate climates, roses are planted in spring, when the weather is stable and warm without recurrent frosts. In southern regions with warm winters, they are planted in the fall.
Given the weak frost resistance of tea roses, immediately after planting and watering, the soil around the plant is mulched with sawdust or peat. This prevents the roots from freezing and drying out.
Selecting and acclimatizing a room rose
The first thing to do in order for a room rose to please for many years is to choose a healthy plant.
The quality of a mini rose is determined by two criteria:
- Outward appearance. You should not purchase a flower if dry, darkened or yellowed elements are noticeable in the foliage. The soil should also be evaluated, it should not be dry or with a white coating. If traces caused by pests are visible on the back of the leaf, such a plant cannot be purchased. You should also ask how long the rose is on sale, the longer, the worse for its general condition.
- Blooming. If all the flowers are in full bloom, it will be difficult for the plant to tolerate transplantation and adaptation. Better to give preference to a bush with buds.

Indoor mini-rose acclimatization includes the following steps:
- Transfer. A pot with special holes and drainage is required. It is better to use a soil for roses as a soil. The procedure itself is carried out by the transshipment method.
- Pruning. Before transplanting, all the buds are cut off in order to preserve the strength of the plant, then it will take root more easily.
- Quarantine. The mini rose pot should be placed in a place well protected from direct sunlight. This requires good ventilation and isolation from other indoor plants.
- Spraying. It is produced with a weak solution of an insecticide to prevent disease and prevent pests. You can also use any growth promoter, such as Epin.
Watering
Before rooting, the planted rose is watered daily. Then the number of waterings is reduced. The tea rose is susceptible to fungal diseases; it does not need waterlogging. Therefore, adult bushes are watered no more than once a week, but with plenty of water (at least a bucket). Water is poured at the root, trying not to get on the leaves and flowers. Delicate tea rose petals do not like water droplets falling on them, as they lose their shape and color.
With a lack of water, the buds become smaller, and the smell weakens. Therefore, in dry summers, the frequency of watering is increased.
Tea rose - cultivation
Tea rose (or Chinese) was named so for its unique delicate aroma, reminiscent of the smell of freshly brewed tea. According to another version, the name comes from the fact that only this variety can be used to make a delicious tea drink. The useful qualities of the Chinese beauty do not end there. Tea rose petals are used in cosmetology. And you can also make delicious jam from them.
The Chinese rose is also loved for its beautiful appearance. Bushes with flowers of a wide variety of shades adorned European gardens and parks as early as the 19th century. Growing a tea rose is troublesome these days, but the result is worth the effort. The beauty is demanding on soil and watering, does not like winds and thanks for the opportunity to soak up the morning sun.


Tea rose - varieties
Many breeders were inspired by the beauty of the Chinese beauty and created all of her new colors and shapes. Currently, there are more than 150 of them. The best varieties of tea roses:
- Rosemary harkness
- a shrub with a height of 1-1.5 with delicate orange flowers, with a salmon tint. The variety, like all roses, loves the sun and is resistant to rain. - Blue moon
- a hybrid with bluish-lilac flowers. It has an unusual silver tint in the sun. In addition to excellent decorative qualities, the variety is resistant to pests. - Parade
- Curly tea rose with double hot pink flowers with a red center. The flowering is very abundant. Blooms in waves several times per season. - Flammentanz
- also curly litter, but with bright red flowers.Gardeners love it for its rapid growth and long flowering. - Duchesse de brabant
- the favorite variety of the 26th President of the United States Theodore Roosevelt. He often wore scented light pink roses in his buttonhole.


Fertilizer
A tea rose without fertilizing with mineral and organic fertilizers will not reveal all its charm - it will not be so fragrant and bright. She needs three obligatory feeding:
- in April - nitrogen fertilizers;
- during the formation of buds - potash, a week later - mullein or horse manure;
- in August, after the first flowering - phosphorus-potassium and organic fertilizers.
The rest - as needed, depending on her condition. Frequent feeding can change the scent of the rose, making it weak and not so pleasant.
Tea rose - planting and care in the garden
The tea rose is extremely finicky, planting and caring for it must be carried out according to strict rules. Only then will the Chinese beauty delight you with lush, long flowering and fill the garden with an enchanting aroma. You need to take into account absolutely everything:
- landing place;
- soil quality;
- climate;
- landing technology;
- irrigation and fertilization regime;
- pruning rules;
- possible diseases and pests.


How to plant a tea rose?
Planting a tea rose is carried out in the fall, no later than 2-3 weeks before the onset of frost. In milder climates, it can be planted in spring, when the night frosts have passed. The rose grows well in slightly acidic loamy soil without a close occurrence of groundwater. If there is a lot of sand in the soil, then a little clay or sod is added to the soil before planting. Loves the morning sun and does not tolerate strong winds.
If your site has a high groundwater level, then the tea rose needs an elevation. Before planting, a complex mineral fertilizer is introduced into the dug soil and loosened well. Soak the seedlings in water for 8-10 hours. Then gently place the seedling in a hole about 30 cm in diameter, straightening the roots. Cover with soil, creating a small bump and water abundantly.


How to care for a tea rose?
The tea rose loves good self-care. It includes:
- Abundant regular watering. Approximately every 3-7 days, depending on the climate. Lack of moisture affects not only the size and number of flowers, but also the intensity of the scent.
- Correct pruning.
- Regular feeding with alternating organic and mineral fertilizers.
- Taking care of the rose in winter. The Chinese rose does not like cold, although modern varieties have become more frost-resistant. For the winter, the rose must be cut, buried and, if the winters are harsh, then covered.
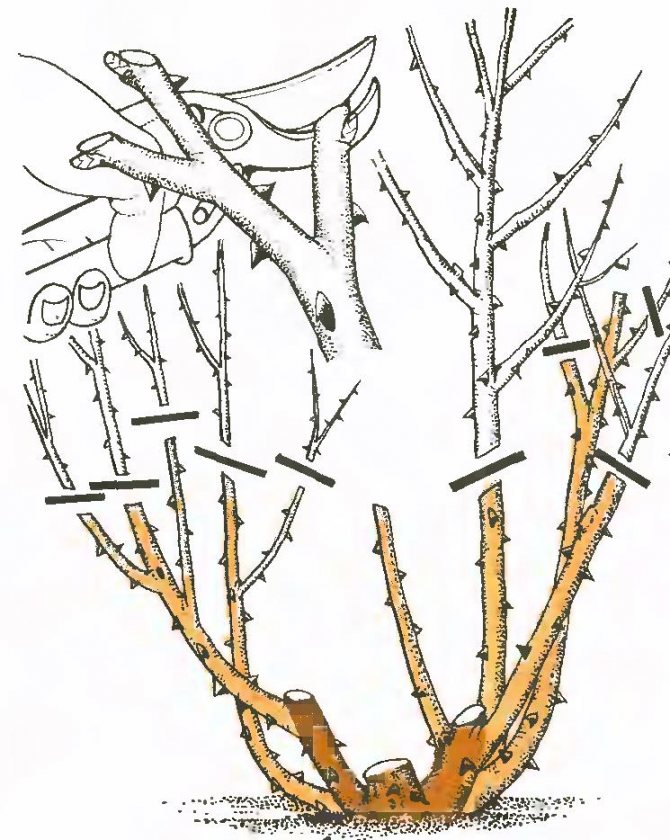
How to prune a tea rose?
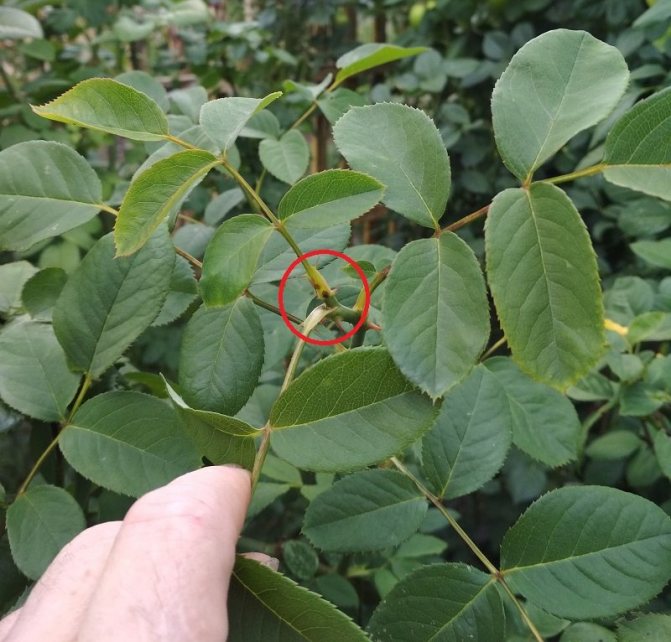
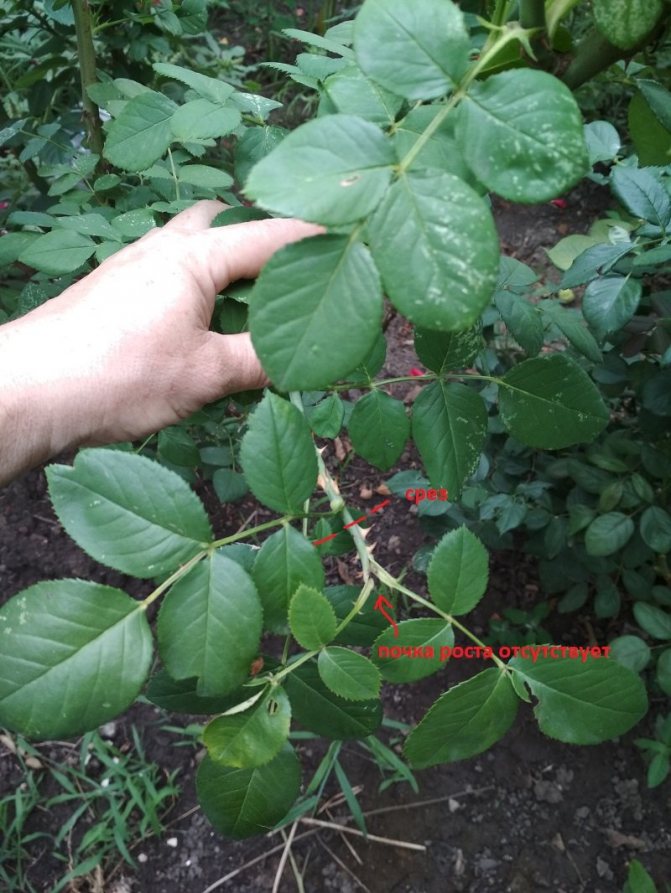
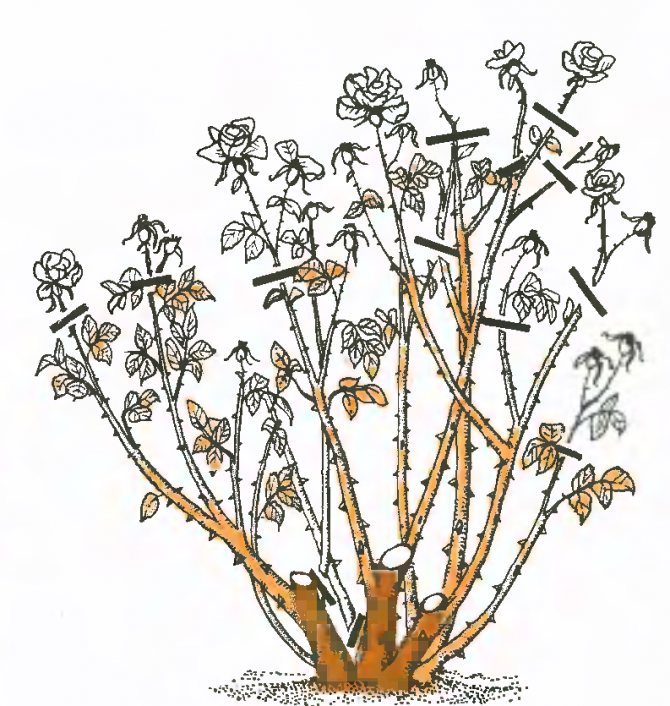
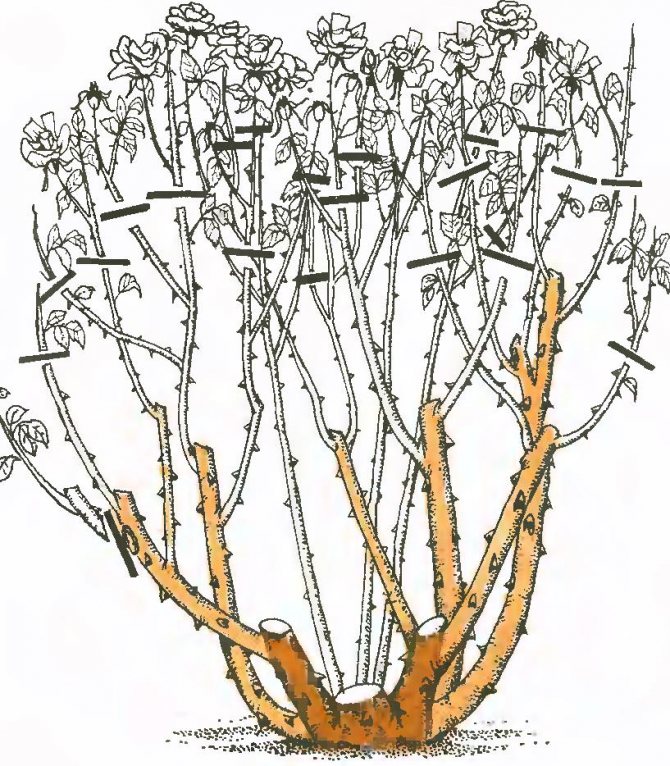
The tea rose is pruned three times a year. The first is in the spring. Sick and damaged branches are cut off, as well as those that are too long to form an aesthetic appearance. Cut off no more than 2/3 of the length of the shoots. In summer, faded buds and strongly overgrown branches are cut off from the rose, thus stimulating new flowering. Autumn pruning prepares the rose for winter. A slightly oblique cut is made above the swollen bud located on the outer side of the branch, at a distance of 0.5-1 cm. The place of the cut, if desired, can be treated with garden pitch.


How to feed a tea rose?
Top dressing of tea roses is carried out several times per season. These flowers are in dire need of fertilization. Some varieties do not even bloom without them. The first fertilization is in the spring. The emphasis should be on the nitrogen needed by the plant to grow. Then add potassium. During flowering, the rose needs complex mineral fertilizers for lush color and intense aroma. You can also feed it with organic matter - urea, compost and humus are suitable.
How to propagate a tea rose?
Tea rose propagation is made:
- Cuttings.
For this, cuts with 3 buds are placed in a jar with water and a root formation stimulant dissolved in it.Planting with potato tubers or in a greenhouse is possible. - Taps.
You can divide both spray and curly roses. In the spring, one healthy shoot is chosen from one bush. On its lower side, a small incision is made in the area of the eyes and pinned to the soil with staples in several places. Sprinkle with earth, leaving 2-3 buds on the surface. - By dividing the bush.
The procedure is carried out in the fall, digging a bush and dividing it into several parts, each of which will have a full-fledged root and shoot with buds. Plots are planted according to the standard scheme.
Diseases of the tea rose and their treatment
The wild Chinese rose is highly susceptible to the influence of diseases and pests, which is why it is on the verge of extinction. Its cultivars have stronger immunity. The main diseases of the tea rose:
- Powdery mildew.
The reason for the appearance is the drying out of the soil. White or gray dust appears on the bushes. The treatment is carried out with the preparations "Raik" or "Fundazol". - Gray rot.
Covers the buds with a white coating, which causes them to rot. It appears due to excess moisture. Such bushes are treated with a solution of "Euparen Multi" - Bacterial cancer.
It affects the roots of the rose, so getting rid of it is problematic. More often, the plant is simply dug up and destroyed, and the planting site is treated with copper sulfate.
The tea rose is rightfully considered the queen of the garden. Its lush bloom delights the eye for a long time. And the indescribable aroma flutters for several tens of meters. Breeders have bred many varieties with strong immunity, however, both bushy roses and their curly cousins require close care, otherwise the Chinese beauty blooms little and for a short time, and with mistakes in care it disappears altogether.
Pruning
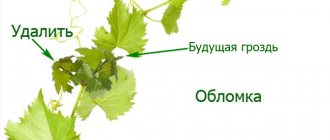
To give the tea rose bush an aesthetic appearance, the faded inflorescences are removed, the stems and lashes are shortened by a third of the length. If this is not done, then during the flowering period the branches will sag under the weight of inflorescences and buds.
Curly tea rose varieties are not pruned too low, otherwise the plant will lose its climbing ability and become bushy. Be sure to remove frostbitten and old skeletal branches. Pruning allows free air circulation within the bush. This is necessary to exclude fungal diseases. Pruning will make the flowers appear larger and the aroma more intense.
Leaving after main pruning
Roses that have undergone the basic pruning procedure should not be immediately exposed to the sun and warmth. Before the leaves appear, trimmed indoor beauties are best kept in a room with a cool temperature of about 10-11 degrees and in diffused lighting. They can be rearranged to bright lighting and room temperatures only after the first leaves appear.
Watering after pruning for a room rose should be very gentle. Waterlogging at this stage poses a very big threat, and the complete drying of the substrate may prevent the plant from releasing full-fledged strong branches. Top dressing is not renewed until the roses begin to actively develop. It is worth paying attention to the humidity of the air: high humidity in the first weeks after pruning increases the risk of spreading diseases and affecting indoor roses with fungal infections.


Caring for indoor roses after pruning. <>
Diseases and pests
A common tea rose disease is powdery mildew. Its manifestation is white bloom on leaves and stems. At the first signs of the disease, the bush is immediately thoroughly treated with a systemic fungicide.
But this is not the only misfortune. Rosebuds can become covered with a gray bloom - this is the sporulation of a fungus that causes gray rot. This disease occurs with excessive moisture, and spreads rapidly, like all fungal diseases.
If gray plaque is found, the plant is treated with a systemic fungicide, for example Euparen Multi. This drug is effective not only against gray mold, but also against powdery mildew.At the same time, it destroys the spider mite.
Bronze beetles love to feast on buds. They do this in the evening, and during the day they hide under lumps of earth. Therefore, the only effective way to deal with them is to collect them by hand in the evening under the light of a flashlight or early in the morning.
How to prune a climbing rose
Not all summer residents know how to prune climbing roses in spring. The problem is that a climbing rose has thin twigs, which are very confused with each other, crawl onto fences, onto plants growing nearby. Therefore, first you need to eliminate all those branches that are weaving in the wrong place. How to prune a climbing rose in the spring so that it retains its splendor?
First you need to do sanitary pruning. The topmost shoots need to be removed only up to the first bud. And the side ones should be cut off no further than the second or third kidney. Do not worry, the overgrown branches will be more beautiful and prolific.
If in the summer the bush loses its neatness and sluggish faded buds appear on it, then it is advisable to cut off such branches to the first healthy leaf. Immediately treat the cut site on the stem with garden varnish for quick recovery.
Pruning climbing roses in spring will solve not only the problem of forming a neat bush, but also makes it possible to remove branches affected by the disease. Therefore, it is better to finish the work before the plant begins to actively return to life.
It is necessary to carefully examine and remove the branches, broken by frost, they still will not come to life. In order not to seize too much, you need to remember the rule of the upper kidney. It consists in the selection of several main branches. They need to be cut from the top to the first bud. Cutting the shoots below is strictly prohibited.
Wintering
It is very difficult for a tea rose to survive the winter in central Russia. She is thermophilic. If there is insufficient cover, it will die.
- Before wintering, cut off all diseased shoots. They collect them and fallen leaves, and then burn them.
- The bush is mulched high with compost or peat, this will prevent the roots from freezing.
- The whips of the curly tea rose are removed from the support. Roll up in a ring. Lay on spruce branches.
- A frame is erected above them, burlap is placed on top, and a film on it is fixed with improvised materials.
- The ends of the shelter are left open for air circulation. Close when a stable subzero temperature is established.
Frost resistance: how to prepare a tea rose for the winter cold
The most important step in preparing a tea rose for winter is choosing the right time for cover and pruning. If you dig in or cover the rose too early, then you weaken its immunity, and it will die from the very first illness. If it is too late to prepare, the rose risks dying from the cold.
The best time to prepare your rose bushes for winter is late fall. But the exact date is hard to say, because the climate can be different. The starting point for starting preparation can be a mark on the thermometer at 0 degrees.
The first thing to do to prepare roses for wintering is to cut off the longest shoots. 6 buds are left on the shoot so that the rose can grow again next year. After that, you need to inspect the remaining shoots. If you find areas of watery or other color, they must be removed.
After that, the rose needs to be covered. To do this, you can dig in the rose with the surrounding earth, covering the roots and part of the stems. During this procedure, the soil is saturated with air, which subsequently acts as a heat insulator, keeping the ground from freezing.
Differences from other roses
According to the classification approved in 1976 by the World Federation of Rose Society (WFRS), all roses are divided into the following classes:
- wild;
- old garden;
- modern garden.
The tea group of roses belongs to the class of old garden roses. They are bush and climbing. They have beautiful flowers in pastel colors. But the pedicel is thin, drooping. All varieties of this group are characterized by low frost resistance.Therefore, growing them outdoors is problematic. They grow well in pots.
But they became the parental forms for many other groups of roses, which are devoid of its flaws. The most popular of these groups are hybrid tea roses. They borrowed from the tea rose the perfect flower shape, delicate aroma, and from the remontant endurance. Therefore, when growing roses in central Russia, it is better to choose varieties of roses of the hybrid tea group.
Why are roses called tea roses?
The tea rose was introduced to Europe from China in the 19th century. This variety got its name due to the aroma inherent exclusively in roses of this species. The scent of tea rose vaguely resembles tea, and China is known to be the birthplace of tea. The tea rose was brought from China along with tea on ships, popularly called "tea clippers". One of the versions interprets the appearance of the name of a tea rose by the fact that an incompletely opened flower of such a rose looks like a Chinese tea bowl. This is the only rose variety that can be used to make a wonderful tea drink.


Application in landscape design
In the southern regions, tea varieties of roses can also be used for landscaping areas. In more northern regions, this is too risky.
Shrub varieties of tea roses look good both as single plantings in flower beds, and as group plantings along the paths or the wall of the house. Climbing varieties of tea roses decorate the walls of houses and gazebos. For them, special supports are erected - pergolas.
Don't forget that tea roses are whimsical, delicate plants. Pests love them, they are susceptible to fungal diseases, and have poor winter hardiness. Therefore, placing them on the site, strive to make them comfortable, and it is convenient for you to serve them.
What kind of roses are pruned in the fall?
Floribunda
In this species, flower buds are placed on the shoots of this year. For pruning a bush, two pruning methods are recommended. Such pruning called combined.
Some of the branches are cut, leaving up to 10 buds, this pruning ensures early flowering. The rest of the branches are greatly shortened, leaving 3-5 buds, thereby causing the growth of new shoots, they will bloom later.
Polyanthus roses
Mature shrubs of this species should have 7-8 main branches. The rest of the branches are deleted. The middle of the bush must be cleaned. By pruning, a spherical shape of the bush is achieved.
In autumn, the shoot is cut off by a third, and 1-2 buds are left at its growth. This species blooms on the shoots of both the past and this year.
Miniature roses
Miniatures are pruned, leaving 5-7 buds on the shoot, trying to give symmetry.
Park roses
The park rose has flowers laid on the branches of the previous year and this one. Autumn pruning will stimulate the growth of new shoots. Weak, unhealthy branches are removed. Forming the skeleton of the bush, the main branches are cut to 15 cm.
Climbing roses
Climbing varieties are pruned to completely cover the required object, form the desired crown, and ensure long flowering.
Climbing varieties are divided into two types:
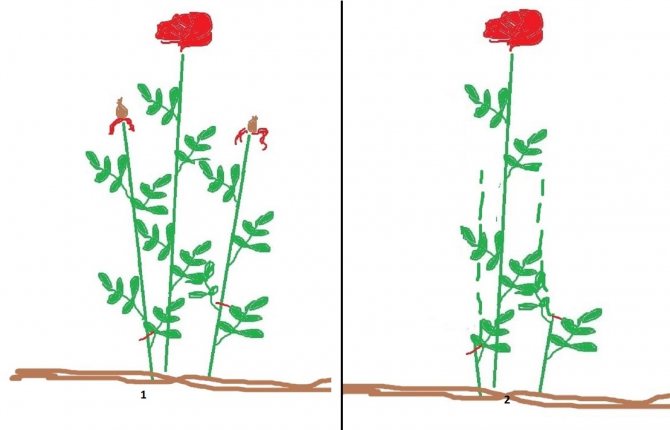
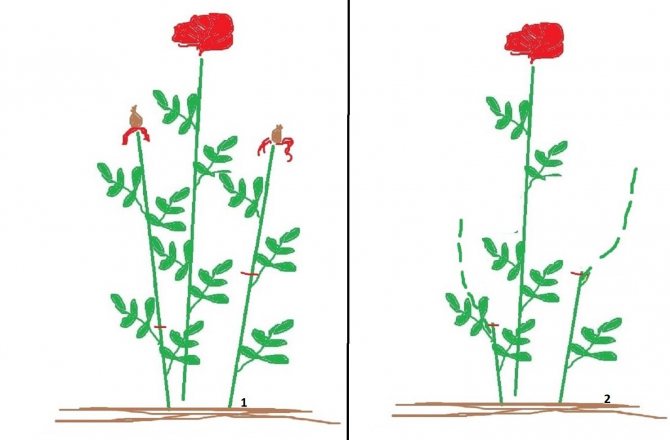
- Small-flowered Rambler have long (up to 4 m), thin, flexible shoots, as well as large inflorescences of small flowers blooming on the shoots of the last year. These shoots do not bloom again. Therefore, after flowering, they are cut off to the base of the soil; 3-4 new shoots grow from the soil to replace them. In autumn, Rambler are not drastically pruned, removing only leaves, remnants of inflorescences, damaged branches.
- Climbers - the second group of climbing roses, the shoots of which are thick, strong, up to 2.5 m long. They bloom once a season. They differ from Rambler by the formation of several basal stems, and they bloom due to growths on old shoots. In autumn, weak stems are removed, and young shoots up to 4 years old are left. It is best to leave 3 new replacement shoots and up to 7 old, flowering stems.
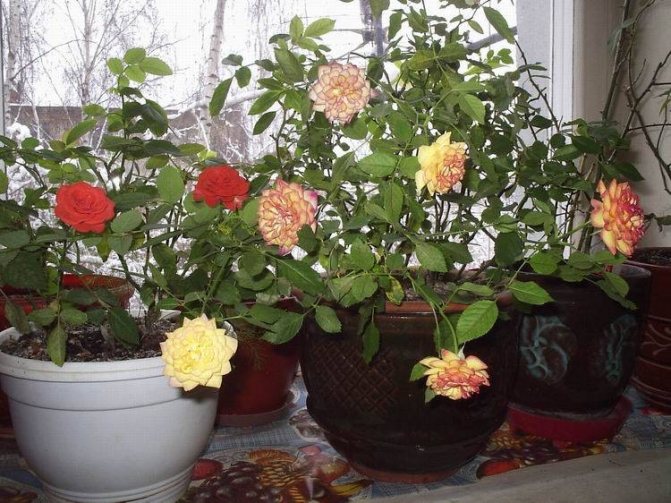
Growing at home
For the cultivation of indoor tea roses, a special land is bought. You can compose it yourself. To do this, mix:
- soddy clay soil - 2 parts;
- peat - 1 part;
- coconut substrate - 1 part.
Buy and transplant a rose in the spring. From November to February, the plant is dormant. For this period, it is better to move the flower pots to the basement or garage, that is, to find a stably cool place (from 1 to 3 degrees Celsius).
It is better to place it on the southeast or southwest windows. Optimum temperature: 18 to 20 degrees. In the summer, you can take it out into the air. Avoid drafts. Remove wilted inflorescences in time to prolong flowering.
During the budding period, foliar dressing is carried out. For these purposes, you can use the fertilizer "Bud", it prolongs the flowering phase of the plant. Before wintering, the number of watering and dressing is reduced. In November, the rose is sent to rest until February.
In March, they are transplanted into prepared soil, pruned and returned to a permanent place. They gradually begin to water and feed.
The origin of the room rose and its features
This small plant is no different in appearance from its garden counterpart, except for its compactness. Belongs to the Rosaceae family.
Mini roses rarely reach a height of more than 50 cm. Small leaves are located on a strong dense stem with thorns. They can be glossy or matte, but they always have carved edges.
The size of the flower itself depends on the species: stamped, climbing, ground cover, bush. The latter are most often used for breeding indoors. The flower can be of very different colors - from snow-white to deep burgundy.
Usually, several varieties of indoor roses are bred in the house at the same time, which bloom, replacing each other, all year round.
The life of a plant with full care is up to 25 years.
China is considered to be the homeland of the mini-rose, therefore, although there are versions about its origin from Southeast Asia or even Europe, it is called Chinese. The rich smell of tea gave her another name - the teahouse.
Adaptation of a tea rose when transplanting from a pot or container
The first steps before transplanting a flower from one pot to another involve creating the conditions in which the plant was previously kept. For some time, it will take to withstand the characteristics that are familiar to him: air temperature, watering regime, lighting and humidity, in order to provide the rose with the fastest adaptation. At this time, it is recommended to water the plant with settled, not cold water, the leaves cannot be washed - only sprayed.
You can transplant a rose according to the lunar calendar, on the growing moon. The soil is pre-prepared in the new pot. This can be a homemade mixture or pre-purchased potting soil.
The optimal size of a new pot is determined independently, based on the diameter and height of the container that contained the flower. The only thing is that it should be several centimeters larger than the container (pot) in diameter.


A new location for the tea rose can be provided with a drainage layer to remove excess moisture and a drain hole.
The transplant process itself is as follows:
- water the rose well beforehand, give time to soak,
- carefully remove the plant with an earthen lump by turning the pot over,
- sprinkle with earth around the edges and compact properly,
- put a pot with a rose in an unlit place for the day,
- after that, the tea rose can calmly stand on the balcony or windowsill.