Any, even the most fertile soil is depleted over time. So that the plants do not suffer from a lack of nutrients, they must be periodically fed. To the aid of farmers comes potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) - an effective chlorine-free mineral fertilizer. It is successfully used in greenhouses and open ground, before sowing and during the growing season, allows plants to fully develop and guarantees high yields.
Description
Potassium sulfate K₂SO₄ (potassium sulfate) is necessary for fruit crops in high concentration. It is obtained from natural minerals - langbeinite and chenite. Fertilizer is used to feed plants in preparation for planting and wintering, as well as during active vegetation. Suitable for fertilizing crops grown in greenhouses and open field.
In its pure form, it is light crystals, 50% consisting of the main element. They are used dry (powder, granules) and liquid - diluted with water.


The product also contains iron, sodium, sulfur. There are very few other components, so they can be ignored.
Interesting! There is no chlorine in potassium sulfate and this is its main advantage over other similar fertilizers.
Composition and methods of obtaining
Potassium sulfate is an inorganic compound, the potassium salt of sulfuric acid, which became famous at the beginning of the XIV century. Has the chemical formula K2SO4 and a relative molecular weight of 174.24. In the scientific works of the German chemist Glauber and the English physicist Boyle, the properties of potassium sulfate and the composition are mentioned: 50% potassium, 18% sulfur, 3% magnesium, and also calcium, sodium and iron.
The substance is a powder of white or colorless crystals of a bitter-salty taste, which do not stick together during long-term storage, dissolve in water easily and without decomposition. Under natural conditions, it does not occur in a free state, but it is found in the mineral composition of deposits of double potassium salts and in the water of salt lakes. In industry, it is isolated in a fairly contaminated form during exchange reactions of potassium chloride with sulfates of magnesium, sodium, calcium or iron.
To obtain higher purity indicators of the final product, potassium chloride crystals are treated with concentrated sulfuric acid or calcined on chenite or langbeinite coal - natural minerals containing a mixture of potassium and magnesium sulfates. Under laboratory conditions, a substance is obtained by the interaction of sulfuric acid with potassium oxides and hydroxides or its salts of weak acids. Thermal oxidation of potassium sulfide or decomposition of its sulfite is also practiced.
The positive effects of potassium sulfate on plants
- When fertilized in autumn, plants survive severe frosts better and retain their viability, including thermophilic perennial crops.
- Increases the amount of vitamins and sugars in fruits, plant shoots.
- Strengthens plant immunity to diseases, especially to gray rot.


- Saturates plants that are difficult to tolerate chlorine with potassium.
- Increases the productivity of crucifers, potatoes, grapes, legumes, citrus fruits.
- Stimulates the circulation of life juices in plant tissues, evenly distributing nutrients, which contributes to the growth of vegetative mass and the development of the root system.
- When watering with a solution under the root, it activates the growth of shoots.
Which soil needs potassium sulfate?
Potassium sulfate is most needed by soil with high acidity with a pH of 5-8. Fertilizer allows you to normalize the acid-base balance of the soil.
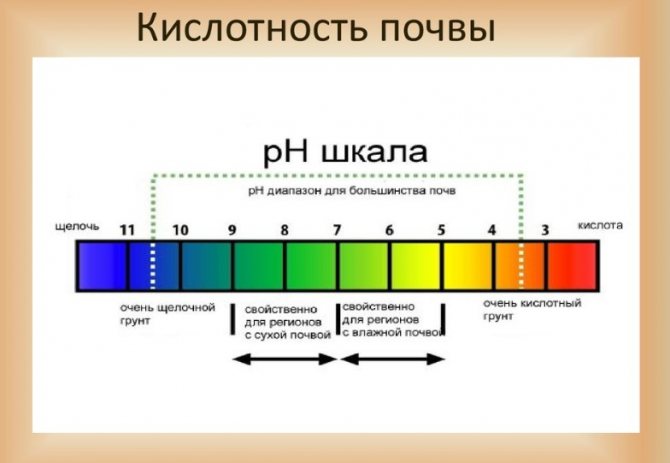

You can find out about the potassium deficiency in the soil by the following signs:
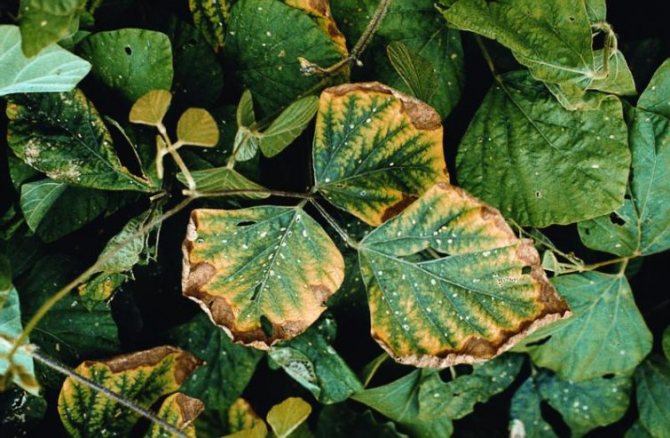
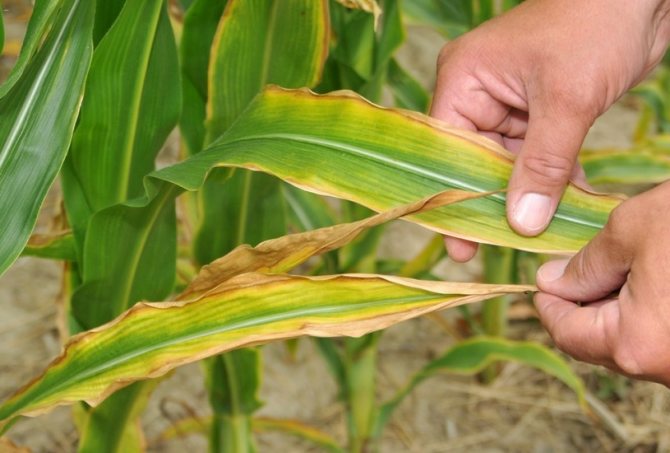
- The top and leaves of the seedling turn yellow. First, along the edges, they gradually take on the appearance of "rusty", resulting in necrosis.
- Stepchildren are actively forming.
- The lower leaves change color, curl, spots appear on them.
- The stems and shoots became brittle and less elastic.
- Vegetative growth has slowed down, yields have decreased.
- Small leaves are formed on trees and shrubs.
- The palatability of the fruit deteriorates. On the example of cucumbers, they appear in the whitening of the leaves, in the uneven color of the fruits, white stripes appear on them.
- The leaves become thinner, interveinal chlorosis is observed.
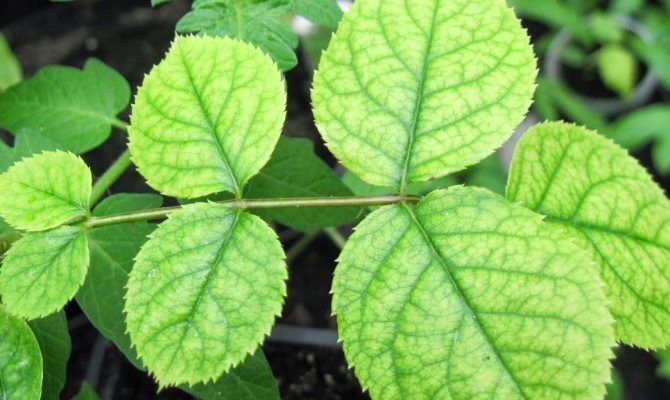


- The internode distance is reduced.
- At the roots, the tips begin to die off.
Most of all, potassium sulfate is needed by plants that consume it in large quantities during growth and fruiting, as well as sodium - beets, fruit and berry crops, sunflowers, etc.
Important! Fertilizer is applied to acidic soil together with lime.
For what crops is it suitable


It is especially important to feed such plants as:
- sunflower;
- all types of legumes (since they need a large amount of sulfur for fruiting);
- cruciferous: sugar beets, carrots, turnips, cabbage
- potatoes, scented tobacco and citruses (these are plants that strongly react to the presence of Cl);
- Strawberry;
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- eggplant;
- peppers,
- fruit trees and berry bushes.
Terms of introduction
Potassium sulfate is used for feeding throughout the season - from early spring to late autumn.
- In heavy soil, fertilizer is best applied in the fall.
- Light soils are fertilized with sulfate in the spring during the seasonal digging of the site.
- Plants are re-fertilized with potassium during their growth for full development.
- Fruit and berry bushes and trees are fertilized at the beginning of fruiting.
- Flowers are fed when the first buds open.
- Lawn grass in early autumn.
Watch the video! Potassium sulphate
The use of potassium sulfate
The formula of potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) is K₂SO₄. Well absorbed by plants, soluble in water, stored for a long time without caking. It is a white or grayish fine crystalline powder. According to GOST 4145–74, in addition to potassium sulfate (50%), the powder contains other elements: magnesium - 3%, sulfur - 18%, calcium - 0.4%. The molar mass of K₂SO₄ is 174.2592 g / mol.
K₂SO₄ is obtained industrially from natural minerals - langbeinite and chenite.
The pH (acidity) of K₂SO₄ is 5.5-8.0 units, so the fertilizer can be used on acidic soils.
Use for the vegetable garden
The use of fertilizer "potassium sulfate" allows you to solve many problems on the site. Guided by the instructions for the use of potassium sulfate, you can achieve positive results in a short time:
- Increase the level of sugars and vitamins in fruit pulp and green mass.
- Increase plant resistance to diseases.
- Improve the winter hardiness of plants (in the case of autumn feeding).
- The fertilizer does not contain chlorine, therefore it is suitable for feeding potatoes, cabbage, grapes, as well as legumes.
- Top dressing, especially with a liquid solution, has a positive effect on the development of plants.
Fertilizing the soil
Depending on the type of soil on the site, the condition of the plants, methods of fertilization are determined. The use of potassium sulfate fertilizer is most useful on peat soils, less on clay soils:
- Fertilizing sandy and peaty soils (poor in composition) - promotes plant growth. On light soils, K₂SO₄ is recommended for use in spring during processing. During the growth period, the plants are re-fed.
- When feeding into chernozems and loams with normal soil moisture, potassium promotes the growth of crops. In such soils, it is useful to bring it under sunflower, beet, trees.
- On acidic soils, the application of K₄SO₄ is combined with lime.
- It is better to feed heavy soil in the fall, trying to embed the fertilizer in the ground.
- Potassium fertilizer is usually not used on saline soils saturated with salts.
- Flowers are fertilized during flowering, while shrubs and trees are fertilized during fruiting.
- For the lawn, additives are applied in the fall in September - October.
Methods for using fertilizers in the garden
Fertilization methods depend on the type of application.
Dry
In dry form, fertilizer is applied before planting, sometimes during this process, as well as in preparation for winter.


Liquid
For liquid fertilizer, potassium sulfate crystals are dissolved in water according to the instructions on the package and watered at the root of the plants. This is the most effective method as the fertilizer penetrates the soil closer to the root system.


Spraying
For spraying, 35-40 g of dry potassium is diluted in 10 liters of water and the aerial part of the plants is sprayed with a spray bottle.
Advice! It is impossible to store the solution, therefore it is necessary to do so much fertilizer so that it is enough for 1 application.


Recommendations for different cultures
For different crops, the dosage and methods of application of potassium sulfate will also be different.
Tomatoes
Potassium sulfate is necessary for tomatoes to get high-quality fruits, since phosphorus agents contribute to the rapid growth of shoots, and organic matter - a large increase in green mass. For 1 sq. m make 20 g of top dressing when hilling and loosening. Can also be combined with other complexes, especially superphosphate.
Cucumbers
Very picky about potassium and reacts negatively to its lack. To increase the yield and quality of fruits, cucumbers are fertilized with a chemical several times per season:
- Before sowing seeds - 100g per 1 hundred square meters.
- 2 weeks after sowing seeds or planting seedlings in open ground - 200 g per 1 hundred square meters.
- At the beginning of flowering - 400 g per 1 hundred square meters.
With another scheme, fertilizers are applied at 20 g per 1 sq. m.
Beets, carrots and other root vegetables
For all vegetable root crops, potassium sulfate is applied at the rate of 30 g per 1 sq. M.
Cabbage and greens
The granules of the drug are applied during the digging of the site and during its preparation for sowing seeds at the rate of 25-30g per 1 sq.m.
Berry bushes
They are fertilized with potassium at the beginning of flowering. Around the trunk circle, fertilizer is applied to the soil at 20 g per 1 sq. m. Raspberries, currants and hawthorns respond best to such feeding.
Grapes
Vineyards are fertilized with potassium sulfate three times per season. The culture does not tolerate chlorine, therefore potassium sulfate is used. Fertilization must be done every year, since the grapes absorb a lot of this element.
For foliar top dressing, 20 g of funds are spent per square meter of vineyard. The procedure is carried out on a cloudy day, after moistening the leaves.
The required amount of the product is diluted in 10 l of water and 40 g of superphosphate is added to the solution. This is done in advance, since the last component is very difficult to dissolve.
Fruit trees
One tree consumes 200-250 g of potassium sulfate. Top dressing in dry form is applied during planting in the pit. In the future, use a liquid solution for irrigation in the trunk circle. Advice! When using dry granulate, it must be buried in the ground.
Strawberry wild-strawberry
Berry bushes are fertilized during flowering at 15-20 g of the product per 1 sq. M.
Potatoes
In dry form, potassium sulfate is added to the soil during the digging of the site at the rate of 30-35 g per 1 sq. M.
Application rates
The table below shows the rates of potassium sulfate application for different crops, depending on the timing and method of application of top dressing.
| Culture | Dosage and methods of application | ||
| In the spring, when digging a site, g / m2 | In summer, after watering or rain with solution, g / 10 l (consumption - l / 1m2) | In autumn, when digging or loosening the soil, g / m² | |
| Tomato, bell pepper | 20 | 30 ( 4 ) | _ |
| Cucumbers | 15 | 25 (3) | _ |
| Cabbage | 25 | 35-40 (3) | _ |
| Potatoes | 30-35 | 40 (0.3 l per 1 bush) | _ |
| Strawberries, strawberries, raspberries | 20 | 35 ( 3-4) | 20 |
| Ornamental shrubs, flowers | 50-100 | _ | 50 |
| Currants, gooseberries, blackberries | 20 | 20 (spraying) | _ |
| Fruit trees | 20-25 | 50 (10- 50 liters per 1 tree) | Up to 200 per tree |
Important! Tomatoes constantly need potassium, so they need to be fed with sulfate during the growth of seedlings when 3-4 leaves are formed. The second time is fertilized 7 days before transplanting into the ground. After the beginning of the formation of ovaries, the tomatoes are fertilized with potassium every 10-15 days until the end of fruiting.
Features of use
Potassium sulfate can be enhanced with nitrogen- and phosphorus-containing fertilizers, but urea and chalk cannot be combined.
Potassium from the fertilizer quickly mixes with the soil, and the plants absorb it by the root system. But this process does not take place in different soils in the same way, for example, in heavy soils with clay, the mineral is not able to penetrate into the lower layer, but on sandy and light soils, potassium is absorbed faster due to its rapid penetration into the soil. That is why fertilizer is applied closer to the roots.
Attention! On heavy soils, before the autumn digging to a sufficient depth, and in the spring, it is not recommended to deepen potassium sulfate.
Application rules
In order not to harm your plantings, when adding Potassium sulfate, you must use the instructions for use.
Fertilization of the soil can be carried out during the autumn or spring digging of the soil. But you should not give up the mineral potash feeding during the growing season of plants, if necessary. Plants can be fed with dry fertilizer or dissolved in water.
The instructions indicate which garden and horticultural crops can be fed with potassium sulfate:
- grapes and potatoes, flax and tobacco;
- citrus;
- all cruciferous;
- legumes - sulfur lovers;
- gooseberries, cherries, plums, pears, raspberries and apple trees;
- various vegetable and berry crops.
When applying any fertilizer, it is important to know the dosage and strictly adhere to the recommendations.
Here are some options:
- tomatoes, strawberries, cucumbers and flowers are enough 15-20 grams per square meter;
- cabbage, potatoes a little more - 25-30 grams;
- fruit trees, when planting, require from 150 to 200 grams per hole.
If top dressing is required during the growing season, then 10 to 15 grams per square are applied under vegetables and strawberries. You can apply fertilizer under the planting or in the furrow at a certain distance.
Potassium sulfate is also used for foliar dressing. To do this, prepare a weakly concentrated 0.05-0.1% solution and spray it in any convenient way.
For watering on a ten-liter bucket, you need to add 30-40 grams of potassium dressing. About 20 plants are watered with this solution, depending on the size.
When using potassium fertilizer, it is necessary to take into account the shelf life of the substance in the fruit. Therefore, 15-20 days before harvesting, feeding is stopped. Otherwise, instead of healthy products, poisoned vegetables and fruits will fall on the table, which can cause allergies or even poisoning.
Precautions
The fertilizer potassium sulfate does not contain any toxic components and harmful impurities. Therefore, working with it is relatively safe.
Before feeding, it is advisable to wear protective clothing and cover the nasopharynx. To do this, it is better to use a respirator in extreme cases, a cotton-gauze bandage.Eyes are protected with glasses, and rubber gloves are put on hands.
If the solution gets into the eyes, it irritates the mucous membranes. Rinse your eyes quickly with plenty of water.
Important! If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
At the end of the work, the exposed parts of the body are washed with soap and water. Clothes must be washed to remove dust from the powder. In the instructions on the package, everything is detailed.
Foliar dressing with potassium sulfate
Potassium is quickly washed out in sandy and sandy loam, as well as podzolic soils. Therefore, in the Urals, Siberia and Central Russia, including the Moscow region, fertilizers with potassium are applied by spraying the aboveground part of the plants.
In a bucket of water, 40 g of potassium sulfate are diluted and the leaves are immediately sprayed until completely moistened.
Advice! Crystals of potassium sulfate dissolve faster in warm water.
A standard (3%) solution of potassium sulfate is sprayed on crops several times per season
| Culture | Timing | ||
| The first | The second | Third | |
| Cucumbers, tomatoes | 5-6 leaves appeared | During flowering | From the beginning of fruiting |
| Cabbage | 3-4 leaves appeared | When forming a head of cabbage | – |
| Pepper | 3-4 leaves appeared | Before flowering | During fruiting |
| Beets, carrots | 3-4 leaves appeared | When forming fruits | – |
| Grapes | Before flowering | After the end of flowering | During the ripening of berries |
| Potatoes | During hilling 1 and 2 | During flowering | – |
What it is?
Potassium sulfate, also called potassium sulfate, is a concentrated feed for cultivated plants, which contains the element potassium, which is necessary for proper and active fruiting and growth of crops grown both in open and closed ground. In appearance, this substance looks like a white powder (with a slight grayish tint), consisting of a huge number of tiny crystals. These structures are bitter-sour in taste and dissolve easily in water.


Potassium sulfate in a bag
Potassium sulfate contains about 50% of potassium itself, oxygen, about 18% sulfur, a little magnesium - 3%, calcium - 0.4%.
On a note! This type of fertilizer does not contain harmful and dangerous chlorine. That is why it is ideal for those plants that are too sensitive to chlorine - for example, legumes and potatoes.


Potassium sulfate is one of the most popular fertilizers
Potassium sulfate is sold packaged in plastic bags weighing from 500 g to 5 kg. And you can buy it in any gardening store, and at an affordable price, which is important for economical and zealous summer residents who want to create a favorable living environment for their green spaces.


Potassium sulphate
Potassium sulfate prices
potassium sulfate
Compatibility with other dressings
Like all potash dressings, potassium sulfate allows you to get a rich harvest of high-quality fruits if it is used in conjunction with phosphorus. Combining potassium sulfate with superphosphate, fertilizers are absorbed more intensively:
- 10 liters of water;
- 20 g superphosphate;
- 15 g of potassium sulfate.


It is recommended to feed eggplants, tomatoes and peppers with such a solution when planting seedlings in the ground.
Nitrogen-potassium fertilizer also works well. For this, potassium sulfate is combined with nitrogen-containing dressings, except for urea. This is done immediately before the fertilization procedure, since such a mixture cannot be stored.
Important! Potassium sulfate should not be combined with urea, since ammonia is released in this case.
To deoxidize the soil, it is best to combine potassium sulfate with lime (fat). But it is better not to use it together with chalk.
Important! When combining different fertilizers, it is necessary to adhere to the correct dosage, otherwise it will lead to an incorrect chemical reaction, which can damage the plants.
Security measures
In its pure form, potassium sulfate can even be eaten.Nevertheless, it is a chemical compound and there are other elements in it that must be worked with very carefully.
Work with potassium sulfate in protective equipment. Always wear gloves, goggles and a respirator. This is necessary in order to protect the mucous membranes of the organs of vision and respiration.


If the solution comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, the site of the lesion must be rinsed abundantly with clean water and soap.
The crop can be harvested no earlier than 14 days after the last application of potassium sulfate.
Signs of a lack of sulfur in plants
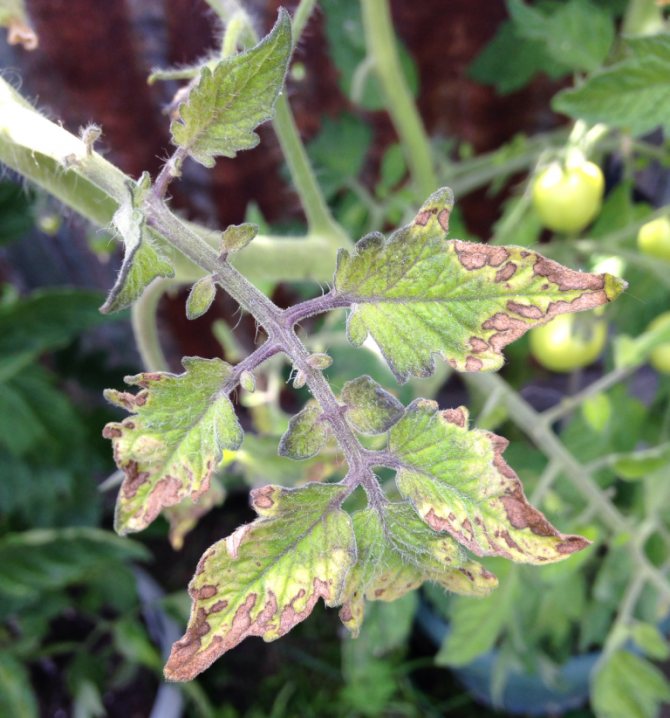
Potassium sulfate is used as a fertilizer for tomatoes, grapes, flowers, and berry crops in the event that there are clear signs of nutritional deficiencies. The lack of potassium nutrition and the element itself in the soil can be determined:
- along the dry edge of the sheet plates;
- irregular fruit shape;
- even earlier - by massively falling flowers and ovaries;
- poor pouring and ripening of vegetables and fruits.
Sulfur deficiency is visible on young leaves. Most often they are pale green. With a strong deficiency, they turn yellow and dry out. It all starts with necrotic spots. At this point, you can still help the plants and feed them with trace elements or potassium sulfate, which includes sulfur.
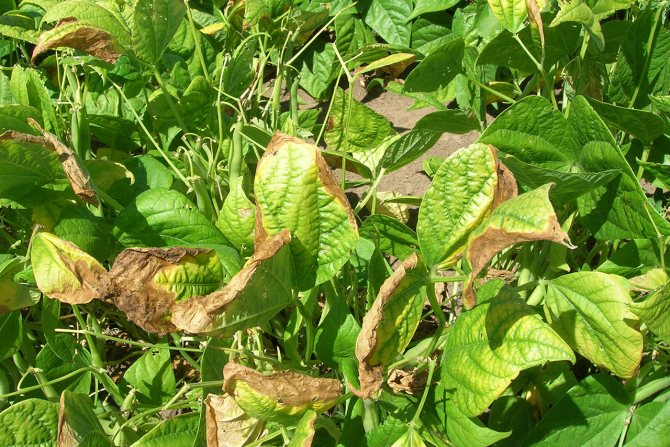


The least sulfur is in sandy soils, as well as in beds that have been exposed to excessive alkalization. With a low content of organic matter in the soil, crops will also experience a deficiency of sulfur compounds.
The lack of any macro or microelement affects the immunity of plants - they begin to hurt and are more often exposed to the invasion of harmful insects.
Storing K₂SO₄
The chemical is used not only in the industrial sector, but also in the home. It can be easily transported and stored as it does not contain explosive elements. Even though it contains sulfur, the substance is non-flammable, so it can be stored in a special container or in bulk.


The main thing is to protect potassium sulfate from dust and moisture.
Potassium sulfate is becoming more and more popular every year. It began to be used in gardening, horticulture and even home floriculture. This is not surprising, since it is a very effective fertilizer at a low cost.
Watch the video! Potassium sulphate



























