In marshy areas and near water bodies, a large number of very unique flora grows. One of the most widespread and famous is sphagnum moss (translated from Greek “Natural sponge”). It has useful and unique characteristics. The fact of birth is dated a very long time ago - the first pharaoh was not yet born, and a specific representative of the plant world has been growing on Earth for many hundreds of years.
The culture got its name due to its high hygroscopicity - the ability to absorb moisture.
Where sphagnum moss grows
Of course, it is more correct to speak not about one type of moss, but about a whole group of sphagnum mosses. In any locality, at least some of their species are always found. All sphagnums are similar in structural features, living conditions, in appearance, differing in color (there are always green mosses, there are reddish, brown ones), and some other features.
But for most of us, the exact species of moss is not so important. They are all very similar in structure and properties.
Sphagnum moss grows in raised and transitional bogs, in swampy and swampy forests, fills lowlands where water can accumulate.
Harvesting and storage of a marsh plant
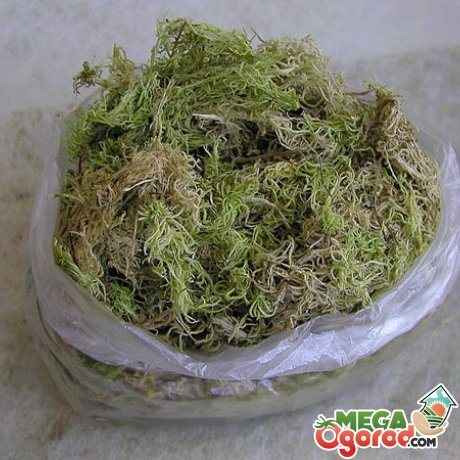

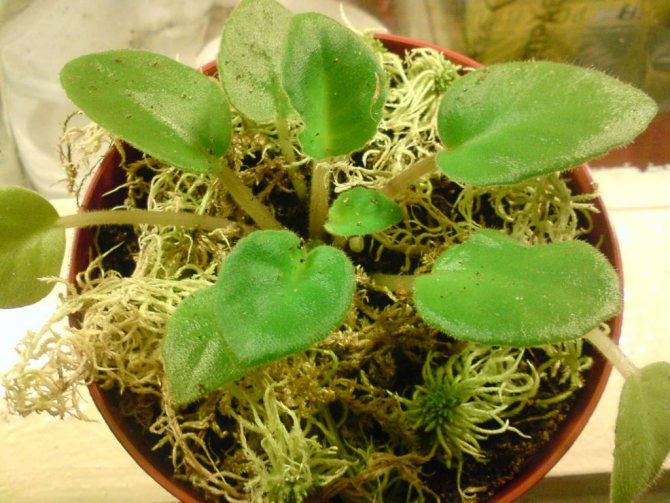
Moss can be harvested at any time of the year. Only the upper live branches are taken, carefully cutting them off with scissors or a knife. You can and completely remove the grass by hand. The best place to collect sphagnum is near the trees. After collecting, the moss is squeezed out, removing the brown parts from it, clearing it of debris, needles. Keep the plant moist by placing it in plastic bags and leaving it in the cold.
The stems are dried by hanging them on hangers or spreading them out on fabrics.
This will allow him to maintain elasticity. It will also be well blown out. For protection from the weather, sphagnum is placed under a canopy. The plant dries slowly, acquiring a white color over time.
After that, the material is placed in paper bags, keeping it at room temperature. It is necessary to use raw materials within a year. You can harvest sphagnum even in winter by digging it out from under the snow. It does not lose its beneficial properties from frost.
More information can be found in the video:
External appearance and photo of sphagnum moss
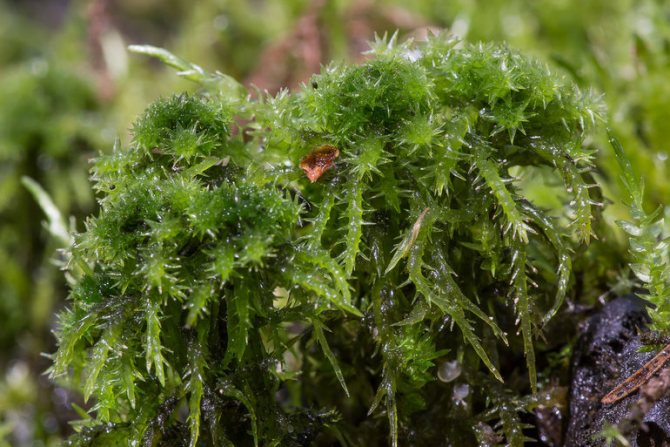
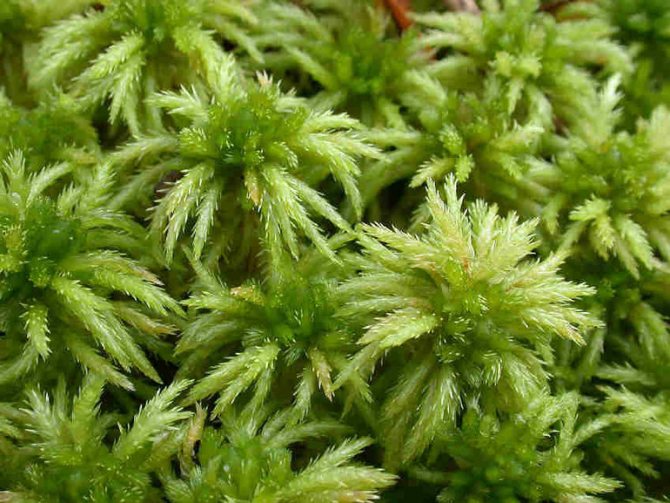
This bright green carpet in the photo is sphagnum moss.


Sphagnum moss in the forest
And the reddish moss shoots in the next photo, too.


Sphagnums may look like this
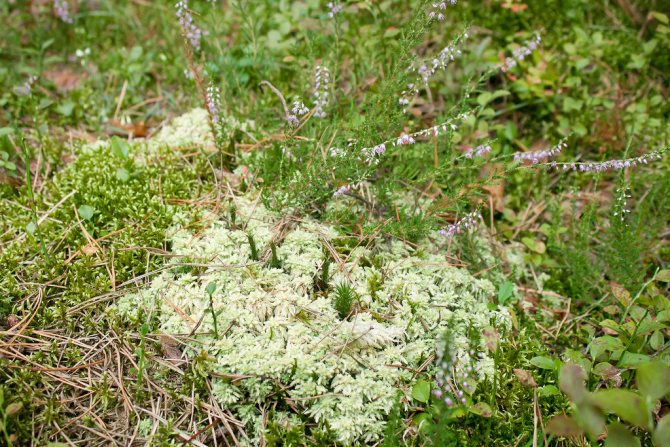
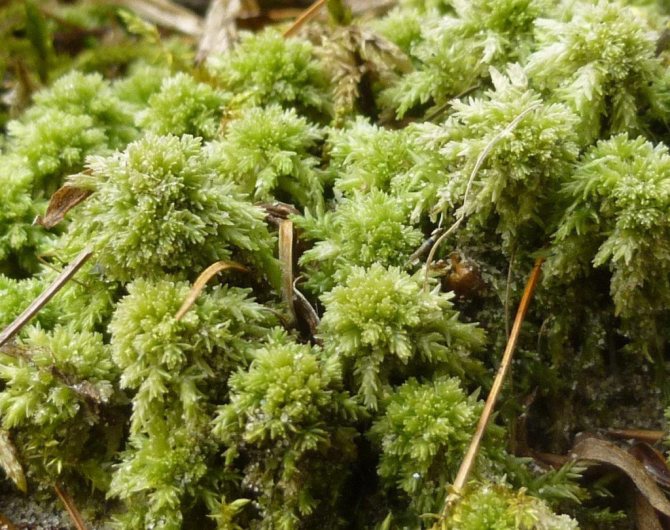
And in this photo of sphagnum moss, it is a pale green pillow and grows in a pine forest. By the fall, there is not much moisture in it, so it turned white.


Sphagnum pillow in a pine forest
The stem of the moss is erect, rather long. It has many side branches sticking out to the sides, densely covered with small scaly leaves. There are also leaves on the stem, but there are fewer of them.
At the top, the branches are twisted and form a head. It is she who is the hallmark of any sphagnum moss. On separate branches in the head, organs with sex cells are formed - antheridia with spermatozoa and archegonia with eggs. Some species - monoecious - have them on every plant. In dioecious, the male germ cells develop on some, and female - on other specimens of moss.


Heads of woven branches are a hallmark of sphagnum moss
The development cycle of sphagnum moss is similar to that of other mosses. On a gametophyte plant, germ cells are formed. After their fusion, a sporogon is formed at the site of the egg, in the capsule of which spores mature. The germinated spore will give rise to a new gametophyte.
Sphagnum moss is constantly growing on top. And it constantly dies off in its lower part. He is always on the move - up towards the light. And the dying bottom turns into peat.
Actually, only the top of the shoot is green at the moss. The part below it, immersed in water, looks whitish. And below the moss turns light brown.


A bunch of sphagnum taken from a moss pillow
Rhizoids - thin filaments that replace the roots of moss - do not have sphagnum. He does not need them, because moss spends most of its life in water and sucks it up with the entire surface of the body. And if there is not enough water, it is able to actively store it.
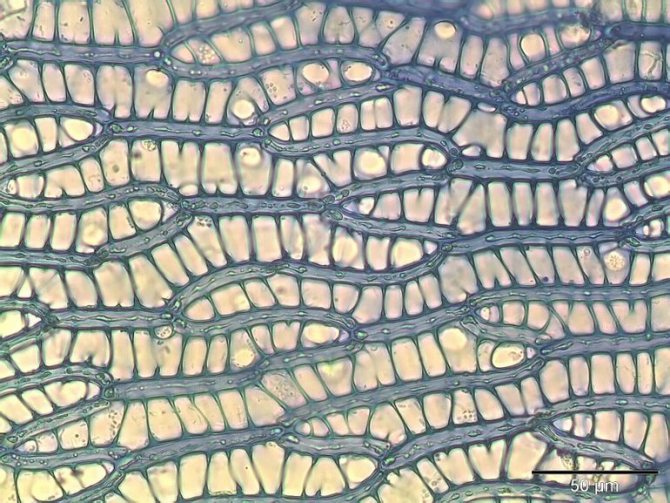
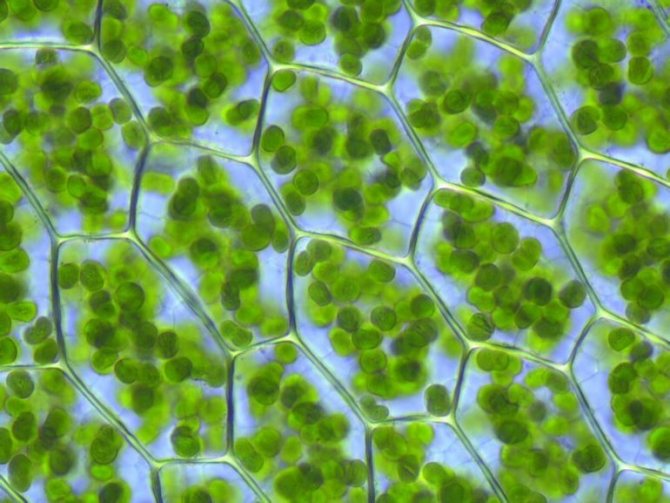
Under a microscope, you can see that not all sphagnum moss cells are filled with living contents. Many of them are dead and are connected to the external environment by pores. It is thanks to such cells that sphagnum moss can store water, which is 20 times more in weight than the plant itself. Like a sponge!
It is from here that its scientific name comes - "sphagnos" in Greek and means a sponge. And why did this moss - green or reddish in its upper part - get the Russian name "white moss"? The fact is that when the moss dries out, dead cells lose water and are filled with air. Then the moss turns white.
Description
It should be said that the structure of sphagnum moss is similar to other representatives of the species. In the process of growth, unbranched erect shoots are formed, which are collected in pillows or dense turf. Their height, as a rule, is no more than five centimeters. There is no real stem. The elements that correspond to them are called phyllidia and caulidia. Through the gaps between these parts, most of the salts and water, which is necessary for normal life, enter. Phyllidia, as a rule, consist of one cell layer. Rhizoids play the role of roots. Through these branching multicellular filaments, water with useful compounds dissolved in it is absorbed from the soil. However, with age, rhizoids lose their ability to "conduct" and serve only for support and anchoring in the substrate.
Read also: How eggs are processed by sanpin

How sphagnum moss creates swamps
Yes, that's how it creates! In some lowland this moss appears and grows. And it absorbs water. And then it grows, forming a layer of peat under it. You look - in place of the lowland there is already a solid carpet of sphagnum, sometimes already higher than the surrounding area. And the moss begins to settle further, displacing other plants. And the fact that the soil in its habitat is always wetter and more acidic, that it is good for moss, but not for others. And the fact that the moss grows very amicably - after all, its stems stick out to each other with their branches sticking out in all directions.
And now, in place of the sphagnum carpet, there is a small sphagnum bog, which will eventually turn into a real raised bog. Dying sphagnum contains a significant amount of organic acids. They pass into the composition of peat, preventing its further decomposition, preserving the deposited organic matter. The swamp grows displacing the surrounding forest.


Sphagnum swamp
I will definitely tell you more about the role of swamps in nature and our life later. In the meantime, I recommend subscribing to blog updates so as not to miss new articles.
Blank
When collecting moss, do not pull it out together with the bottom. For the correct workpiece, the top is trimmed with scissors. In this case, the remaining part will be able to give shoots. Collected moss at home must be doused with boiling water. This is done to eliminate insect larvae and eggs. At the same time, the properties of moss are not lost. Raw materials are dried outdoors in sunny weather with a slight breeze.The use of dryers is not recommended. If the preparation is carried out for subsequent use for medicinal purposes, then the raw material is kept in the air until it is completely dry. After that, it is broken and put into a dry container. If it is intended to be used for decorative purposes or as a filler for animal cells, then the plant should not be completely dried. In this case, the raw material is stored in the newspaper. You can also keep dry moss in the freezer. They put it there in green and get it out if necessary.
Read also: How to make a flying cup
- View the full image
Where and how sphagnum grows
Useful properties and application in medicine
Sphagnum moss in floriculture
Harvesting and storage of a marsh plant
Plants growing in bogs differ from others in structure, in their properties. Sphagnum moss is one of those grasses that, having adapted to terrestrial life, have retained some features of aquatic crops. The representative of bryophytes firmly takes its place in nature, sharing its useful properties with humans.
Many are familiar with peat moss - sphagnum, meeting with it while walking in the forest. When walking on a beautiful moss carpet, your feet gently sink into it. At each step, a person feels moisture, as the climbing shoots absorb moisture from the soil, air, retaining it in their cells. But moss is the material from which peat masses, brown coal, have been formed for thousands of years. Sphagnum thickets play an important role in the regulation of the hydrological regime of the territories.
Useful properties and uses of sphagnum moss
Moss in medicine
A number of substances useful for us have been found in the chemical composition of sphagnum. First of all, it is a natural antibiotic from the group of phenols, a unique substance and the name given in honor of the moss that created it - sphagnol. A number of organic acids, also characteristic of moss, have an antibiotic effect.
The property of moss to absorb large amounts of liquid can also be used for the benefit of humans! After all, this is real natural cotton wool! Moreover, unlike ordinary cotton wool, sphagnum moss also disinfects the wound.
Probably, people began to use moss to treat wounds, including purulent ones, as well as burns, frostbite, back in time immemorial. And from time to time he remembered this in difficult times of wars.
Not only the partisans of the Great Patriotic War used sphagnum instead of cotton wool. The doctors of the prosperous (as is commonly believed) Great Britain during the years of the world wars also remembered about him. Which, however, is not surprising - cotton does not grow in England, and cotton wool had to be transported from across the seas. And in the oceans - enemy submarines ...
When they noticed that moss not only absorbs blood and pus, but also helps to heal wounds, they began to understand. And they discovered the antibiotic properties of sphagnum.
And now its use in pharmaceuticals, medicine, and other areas related to human health is becoming more and more diverse. For example, on the basis of sphagnum, highly efficient water filters are made.
Moss as a means of survival in difficult conditions
It is not at all useless to know about the beneficial properties of sphagnum moss to everyone who is in nature - mushroom pickers, tourists. Anything can happen. And it is far from always possible to get medical help quickly. But you can start treatment right in the forest if you know how to do it.
The sphagnum moss will stop the blood from the wound. It will be useful to wash the burn with water squeezed out of the sphagnum bundle. Or attach moss to the burnt place. It is very nice to put a sphagnum pad under the splint applied to a broken arm or leg - this will both alleviate the pain and help avoid swelling.
To eliminate the unpleasant odor from the shoes, it is enough to put a few sphagnum stalks there as insoles.By the way, this will also help to cope with such a difficult-to-treat disease as foot fungus!
The water flowing from the sphagnum bog can be drunk completely fearlessly. It is usually a little dark because it is infused with peat. But there are no pathogens in it - a biological filter made of sphagnum mosses has tried!
In the fight against swamps, as well as in many ways, Europe has overtaken us ... And now, when the understanding has come of how useful sphagnum bogs are for nature in general, and for human health in particular, they (bolts) are beginning to be restored there. And sphagnum moss is bred! Although, "to restore" something in nature is much more difficult and costly than "to preserve".
We have ... No, of course, the importance of sphagnum bogs is recognized. They are guarded. At least in words ... In fact, they often “don't get their hands on it”. And it turns out our eternal - "as always."
Moss - to help the gardener
Both gardeners, and especially those who breed indoor plants, often use this marsh moss. Lovers of rare orchids cannot do without it at all. Orchids form many aerial roots and require moist air. Try to create such conditions for them in a modern apartment! But the raw sphagnum moss, laid next to it, makes it easy, releasing the stored water into the air.
And those who go on vacation can entrust the "watering" of the flowers to the sphagnum - just wet the moss and overlay it with a plant in a pot. The soil will remain moist for a long time.
For germination of seeds, the hostesses used this moss, and this experience was adopted by gardeners. And for good rooting of cuttings, chopped sphagnum stems can be mixed into the soil.
But you should not use peat from a sphagnum bog in the garden and in the garden! Indeed, due to the abundance of organic acids, such peat strongly acidifies the soil, which is unacceptable for most cultivated plants.
Moss in construction
And sphagnum moss is also used in the construction of wooden buildings. Logs of a log house are laid on it (as well as on cuckoo flax). Due to the peculiarities of its structure, moss has a low thermal conductivity and reliably insulates the interior from the outside cold. Sphagnum moss also disinfects logs from pests (for example, from a fungus).
But it is important to consider that the moss should not be too wet, and at the same time - too dry. Dry moss will crumble. And too damp, laid in the wall, instead of insulation and disinfection, perhaps, will contribute to decay!
So sphagnum must also be properly dried. Actually, having a choice, I prefer “white moss” - sphagnum “red moss” cuckoo flax. But, if for some reason there is no choice, then it is still better to take sphagnum for construction not directly in the swamp, but somewhere nearby, in a swampy spruce forest. Here it contains less water, and it will be easier to dry.
Dried moss should be tested for moisture. To do this, take a bunch of moss, twist it into a flagellum and spread it out on level ground. If the moss crumbles during twisting, it is overdried and requires soaking. If the flagellum does not unwind, the moss is not yet completely dry. The flagellum of normally dried sphagnum should unwind by about half.
Lay the moss as follows. A bunch of moss is taken, loosened a little and laid on the logs. Then you need to press it slightly with your palm. The next portion of moss is stacked so as to overlap the previous bundle by five centimeters. The thickness of the moss layer should be about one and a half centimeters.
This is such a wonderful moss that lives in our forests and swamps - sphagnum moss! And if you remember that together with him, on the swamps he created, such a magnificent berry as cranberries also grows - I think you will agree that the author "sang praises" to the marsh moss is not in vain!


Cranberries and sphagnum moss in the swamp
Best regards, Alexander Silivanov
Looking forward to your comment!
You can subscribe to news and keep abreast of events on the blog by simply clicking on the picture
Use in horticulture and animal husbandry
Florists use moss when growing young shoots or to save sick specimens. Due to the hygroscopicity of the "sponge" moisture is effectively retained in the substrate. The plant is especially often used when caring for orchids. To grow shoots, the moss is scalded, cooled and squeezed. Then it should be spilled with the prepared mineral liquid fertilizer "Kemira Lux", squeezed out again and placed in a plastic bag. When closed, the moss must be kept for four days. Every two months, an orchid should be transplanted into a soil freshly prepared in this way. When its roots reach five to seven centimeters, the plant is placed in a pine bark substrate. Sphagnum moss is also used to protect plants from frost in the garden. As a hygiene product, sphagnum is used in cages with hamsters, rats, guinea pigs. Such a natural filler perfectly copes with odors, disinfects and absorbs moisture.