We study the structure of plants at school in biology lessons. Surely everyone remembers how they examined the incision of the bulb under a microscope. Every person knows that plants have: roots, stems, leaves, peduncles, fruits. A plant is an organism that, when properly grown, works harmoniously. Each organ has its own function and a failure in the work of one organ will invariably entail changes in the development of the entire plant organism. When growing plants, it is important to know what function this or that part of it has. In this article we will take a look at the structure of a bow.

Onion
General structure of onions
Everybody knows onions. This important vegetable is grown and consumed in large quantities. Onions are a two-year-old crop that belongs to monocotyledonous plants. The onion family has a non-standard plant structure. He does not have a clear distinction between the root, stem, and other parts of the plant. If you ask a novice gardener where the stem of this vegetable is, I think it will be difficult to answer, and the bulb will be called the fruit. In fact, this is not the case. Let's take a closer look at each organ of this plant.
Root system
Roots are an important organ of any culture. It is with them that the vital activity of plants begins. Thanks to the roots, the plant absorbs moisture and nutrients from the soil. The root system anchors the vegetable firmly in the soil. The death of the root means the death of the rest of the bush.
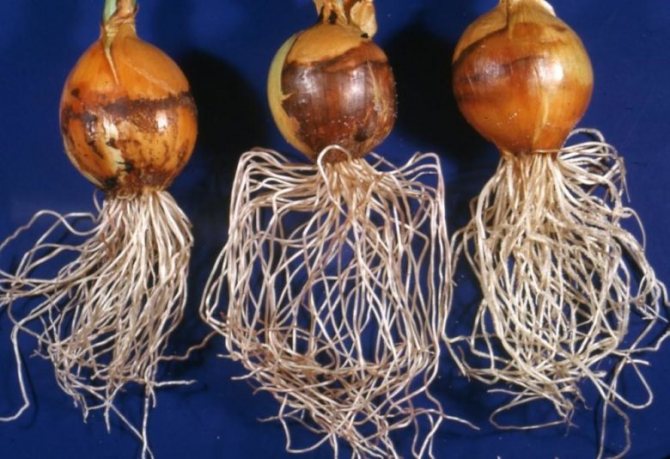


Onion root system
The root system of an onion does not have a central (main) root, but consists of a branched system of adventitious roots. The rhizome of onions looks like thin strings, but they hold the vegetable firmly in the ground. However, the vegetable does not like planting too deep, heavy soils, so choose areas with loose, light soil in an open, sunny place. The onion root system is divided into several types of roots, each of which has its own purpose.
- clauses
- contractile,
- pulling roots.
The roots of a vegetable have a one-year life cycle, and the next year they grow again. The external structure of the rhizome is similar in tubers and bulbs. Some plants have bulbs and tubers: hyacinths, tulips, lilies, daffodils and many more.
The onion stalk looks much more unusual and interesting.
Sensitivity to onion lacrimation
Why doesn't the bow make everyone's eyes sting? The reason lies in the individual characteristics of the structure of the visual apparatus.... Statistically, men have fewer receptors on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes, so they can more easily tolerate irritation when cutting bulbs. The older the person, the thicker the surface of the epithelium of the mucous membranes and the lower the sensitivity to irritating factors.
The response to onion lacrimator varies with various eye conditions... With keratoconjunctivitis dry, called dry eye syndrome, the sensitivity to the sulfur compounds of onion juice decreases dramatically until it disappears completely. In inflammatory and infectious processes, on the contrary, there is an increased release of lacrimal fluid in response to lacrimator substances.
Stem structure
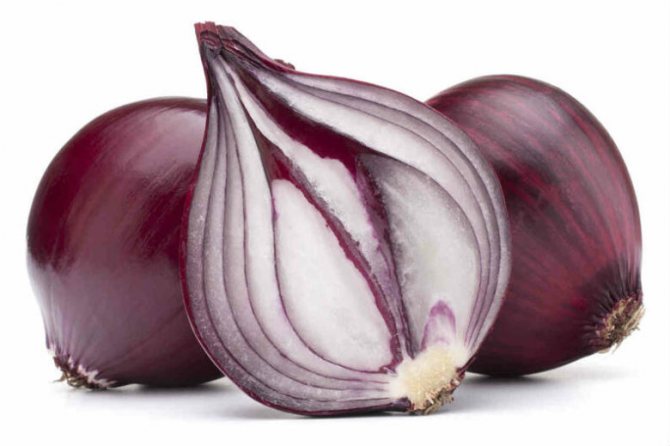


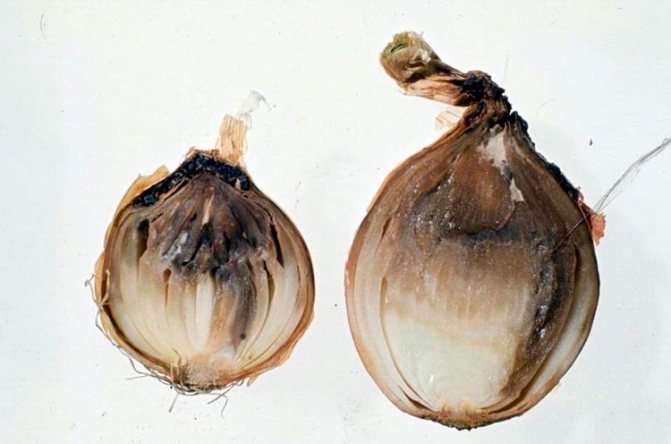
Cutaway onion
When you cut the onion to prepare the dish, you probably paid attention to the seal at the bottom - this is the bottom. Such a bottom is formed when the onion is propagated vegetatively from the set.The bottom is the hardened remnants of the bottom of the mother's bulb. Bottom - actually onion stalk... From this shortened stem, very unlike the standard stems of plants, buds are laid from which the leaves grow.
Onion leaves are its aerial part, they are also eaten with pleasure. Feathers, like the bulb, contain many nutrients. They are a great source of vitamins in early spring.
Leaf structure
The leaves of onions are tubular, hollow inside. They are tapered with pointed tips. Leaves grow vertically, straight up. They have a rather dense structure and do not require support. The color of the onion feather depends on the light and the variety. Leaves can have colors from light green to dark green. Feathers have a slight waxy coating that protects the feather from adverse weather conditions.
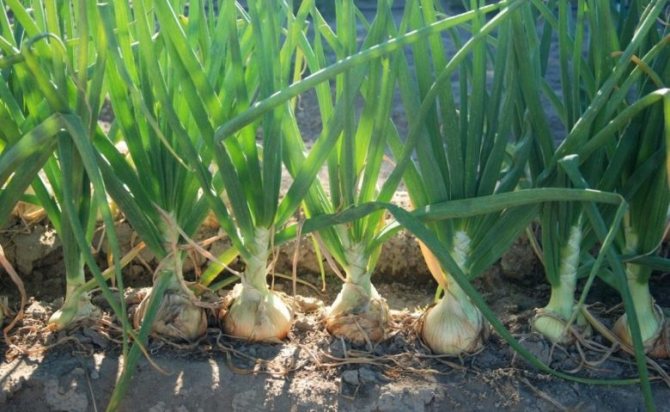


Onion leaves
As the plant grows, the leaves change, at first they are small, delicate in texture and quite mild in taste. During this period, onion feathers are the most delicious. With the growth of the root crop, the leaves also grow, becoming larger, taller, but at the same time denser and tougher, keeping in an upright position. However, the taste does not change for the better, the feathers acquire a spicy taste. By the end of the growing season, the onion feather is no longer suitable for human consumption, it becomes rough, sinewy and tasteless. The toughest are the leaves that have grown from the outer scales of the bulb.
Interestingly, it turns out that the leaves of the onion are not only green feathers, but, surprisingly, the bulb also consists of leaves.
Variety of species
Nature has taken care of the variety of varieties of this culture. The types of onions that are found in vegetable gardens are divided into edible and decorative.
True, the word "bow" has different meanings. When asked what it is - bows, the fashion world will answer: "This is the name of beautiful, properly selected clothes." But we are talking about the onion that is used for food.
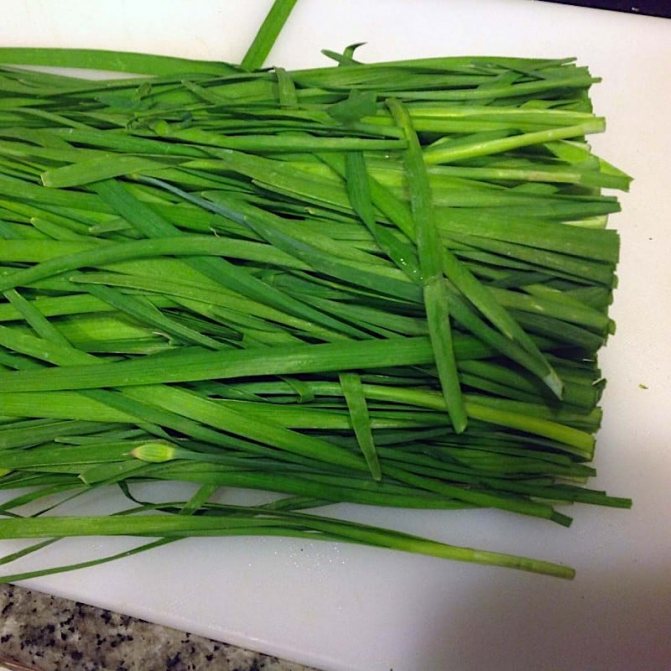
Green
These are arrows of young onions. The green mass is collected and eaten even before the turnips are formed. The largest amount of nutrients is found in the feathers of green onions. They are rich in ascorbic acid, potassium. Microelements, B vitamins, zinc are of particular value.
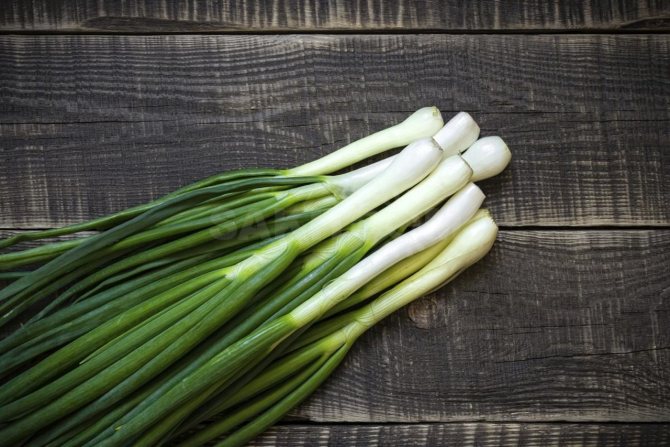


Green onions
It is easy to organize a vitamin bed in a room environment. A large onion is placed in a tight bowl of water. Roots and feathers will appear on the windowsill, in the light after 3-4 days. After 10-14 days, the first greens are already cut. Of course, a plant grown in the ground is healthier.
Batun
Biologically, winter onions are similar to onions: they have the same pipe-leaves. But the batun has a longer feather. It is more massive, wider than that of onions.
Greens contain twice as much nutrients as other green onions. Batun is grown specifically for greens. Over the summer, it is cut three times due to its high yield. Does not form bulbs as such. The underground part of the stems is called false bulbs. They do not ripen, they taste good.
Note! The main value of the batun is the feather.
Multi-tiered
Rare, tasty, unusual-looking onion. Homeland - Mountain Altai, Siberia. Other names: viviparous, Canadian, Indian, as well as walking and Egyptian.
It starts to grow like a bastard. Then each feather lengthens, thickens, at the end it throws out nigella seeds, airy bulbs. They grow, each forming the same bulbs at the end. The result is a multi-tiered design that is attractive and nutritious.
The plant is eaten raw, but we especially love pickled and pickled multi-tiered onions, fried in oil with chilli peppers.
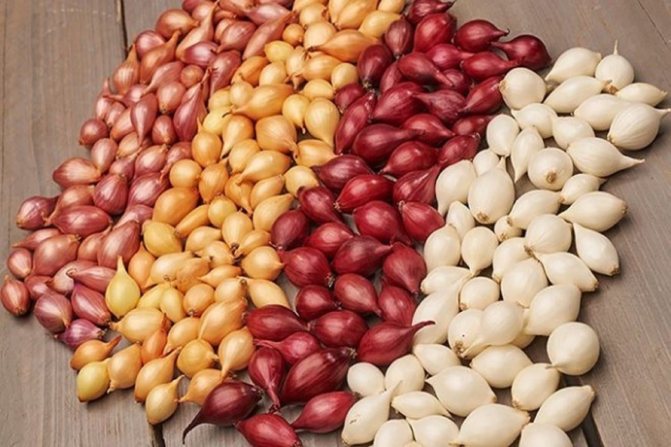
Shallot
Biologically, this is the same onion, but more juicy, tender, with a spicy point, incredibly rich in composition. Low calorie content allows the product to be used in dietary nutrition.In pickled form, it is preferred by French gourmets.
Outwardly, it is smaller than onion, the shape is more elongated, the weight of an average bulb is 15-45 g. Frost-resistant culture (withstands up to -5 ° C), suitable for cultivation throughout Russia.


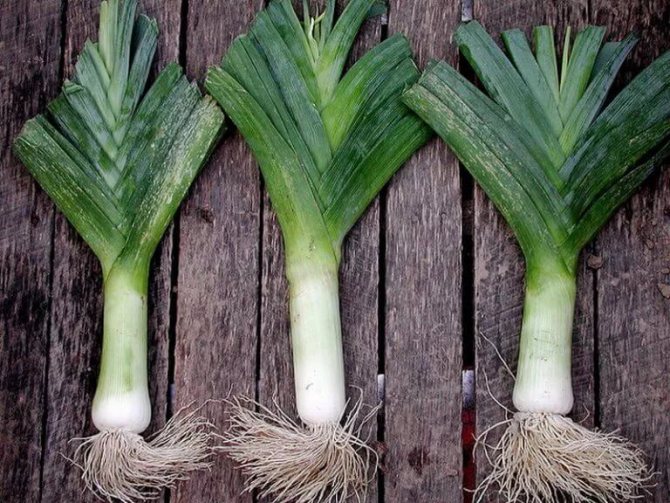
Leek
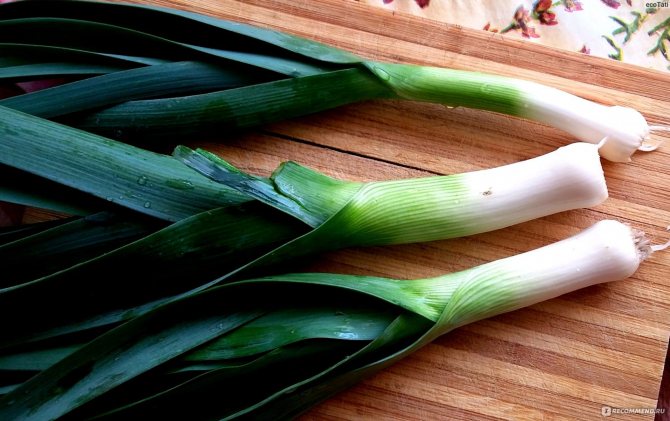
Leek
The herbaceous biennial plant with gigantic leaves is called the "pearl onion." It is impossible to understand what an onion is using the example of a leek, since it does not form on it. But the stem is strong and flexible, the leaves are juicy, actively growing throughout the season. They give the dishes a spicy-sweet taste that is completely unique in cooking.
Bulb structure
Many people mistakenly believe that the bulb is the fruit of a plant. However, as paradoxical as it sounds, this is a modified escape.
Remember! Tuber and bulb are modified shoots
To understand this, let's analyze the structure of the bulb. To do this, you need to look at a cutaway onion. This section shows that the bulb consists of scales of different thickness. Outside, they are dry, thin, we call them bulbous husks, but inside they are juicy, thick, fleshy. The thickness of the flakes increases in proportion to the center. These flakes - false underground onion leaves... The outer scales dry out and coarse, protecting the root crop from external influences. The color of the leaf scales is different - from white, red, to purple. The color of the husk depends on the variety of the root crop. Accordingly, the flesh is the same color as the rind.
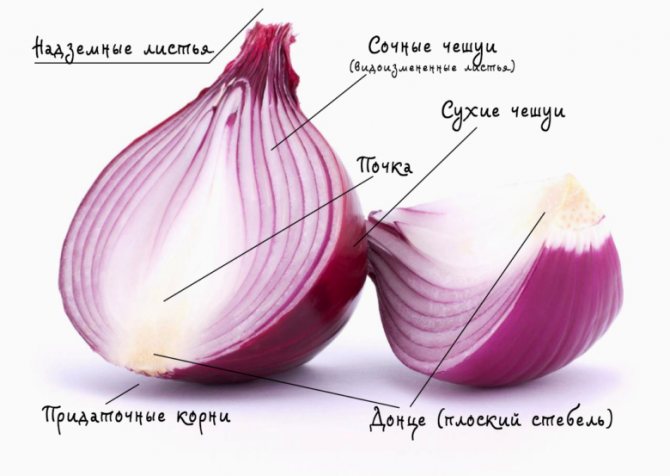

Internal structure of the bulb
The taste of the vegetable also varies. There are varieties that can be eaten fresh, they are so soft, sweetish in taste. And there are varieties with a pungent, pungent taste.
The bulb retains nutrients and moisture reserves. Thanks to this, onions are able to survive periods of drought without any problems. Unlike rhizomes and tubers of plants, the bulb serves as a kind of storage for the substances necessary for the plant for life in unfavorable periods. In rhizomes and tubers, such substances are deposited in the plant stem. From the bulb, by placing the bottom in the water, a wonderful green feather is grown, there are so many nutrients in it.
On the bottom in the center of the bulb, buds are laid, from which flowering shoots then grow.
Which way is the best
Most of the considered methods may not suit everyone, and not only technically, but also physiologically. For example, not everyone has a gas mask, diving mask or appropriate goggles, and regular ones are unlikely to work, since they do not block access to the nose and eyes. But if you have these items, be sure to use them: this method has many fans.
It is not always possible to wash onions under cold running water or keep them in the refrigerator. For example, if you decide to go outdoors with friends, such methods will not be available. But you can talk and sing songs in the process as much as you like!
In winter, it is undesirable to open the windows too often for airing, and you have to cut onions regularly, especially if you have a large family or guests often come. And the fan may not save you. Therefore, chewing gum, fresh parsley or sniffing coffee beans will be the most convenient way (although, unfortunately, not for everyone).
Yet seasoned chefs say that the most effective methods are running water and placing the onions in the freezer.
The structure of the flowering shoot
At the very end of the growing season, flowering shoots appear from the middle of the bulb. During this period, the onion has already completed the formation of the bulb and does not grow new leaves. The number of peduncles depends on the variety and size of the grown root crop. Peduncles look like smooth tubes, hollow inside, green. They are quite strong and can reach a height of as much as 130 cm. Peduncles are also called arrows of an onion, and the process of growing them is called shooting.
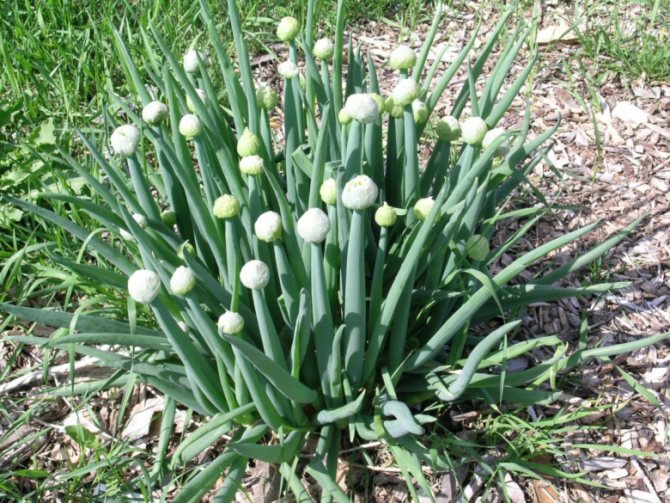


Onion stalks
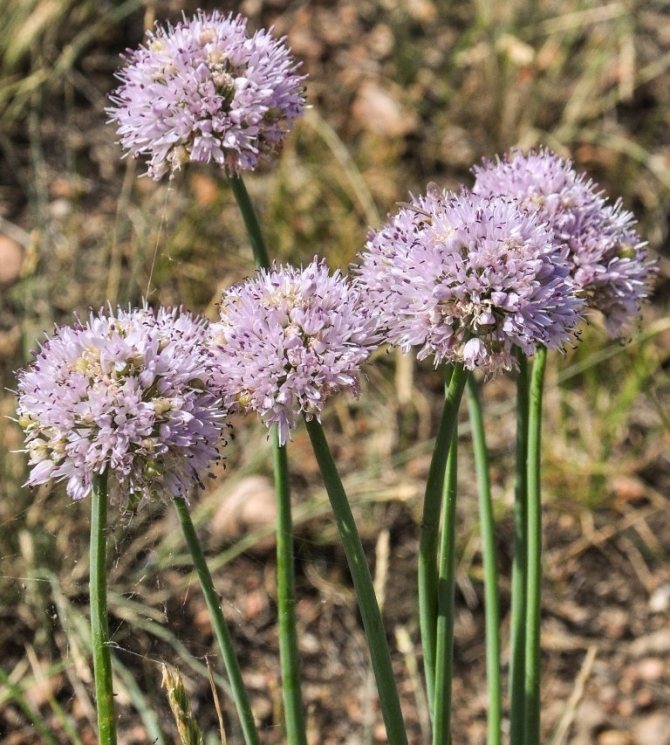
At the top of the arrow are the flowers, collected in neat balls. The peduncle is capable of producing photosynthesis, which feeds the flowers, from which the seeds then ripen. Onions bloom very nicely, during this period they even look like ornamental plants, and sometimes gardeners specially grow ornamental onions.
Flower structure
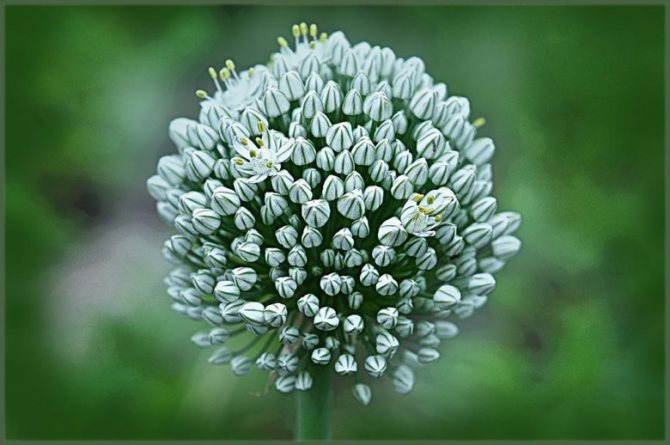


Onion flowers
Flowers of the onion family on long stalks, when closed, resemble a tulip. They are collected to the peduncle, and together they look like a ball or umbrella. The flowers consist of six white petals, the center is greenish. The size of the flowers is no more than 1 cm in diameter. A flower ball can contain up to several thousand flowers. Each flower has 1 pistil and six stamens. Onions bloom up to 35 days, and each flower lives up to 7 days. Different types of onions have very beautiful peduncles, flowers of yellow, blue, purple color. The flowering time of onions is mid-summer, depending on the variety and region, it is July-August, and the fruits ripen during August.
Fetal structure
If the bulb is not a fruit, then what is the fruit of this plant? Onion fruit - it's small dry seed boll, in which up to six seeds ripen, usually 2-4. The seeds of this plant are small, black, for which they were called nigella.
Interesting fact... Onion seeds are very lightweight. 1000 seeds - it is approximately 1 gram.
They have a triangular pyramidal shape. The culture is successfully propagated by seeds and bulbs (sevkom), is capable of self-pollination. Seeds ripen up to 60 days, depending on the variety. After ripening, you can collect the seeds to sow them in the spring or even before winter. After all, autumn planting gives good results and a very early harvest.
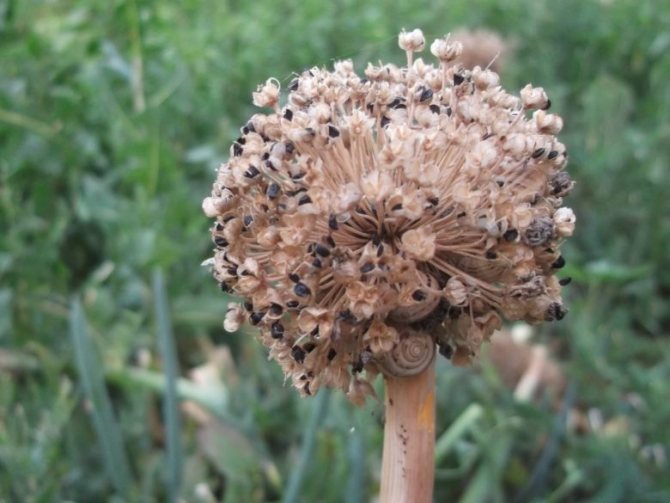


Onion seed pods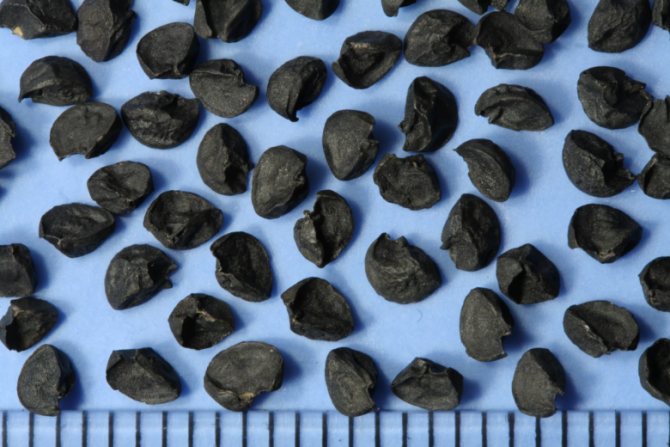

Onion seeds
Arbazheiki planting rules
Sowing is carried out in the prepared soil in a single-row method or in 2-3-row tapes. In the tape, 8-12 cm are left between the rows and 20-25 cm between the tapes.
In the first method, in a row between the bulbs, the distance can be different:
- When planting "shoulder to shoulder", the planting density is high, since the distance between the sets in a row is 1.0-1.5 cm. With this planting method, 2 thinning is carried out:
- at the first thinning, the distance is increased to 4 cm, and the young onion-feather is used for food;
- after 25-30 days, a second thinning is carried out, leaving a distance between young plants of 7-10 cm.
The second planting method is private. Sevok is planted at a distance in a row after 8-10 cm, between rows - 20 cm. Thinning is not carried out. Arbazheyka is placed in the furrows vertically up to a depth of 4 cm, covered with soil by 2.0-2.5 cm from above and slightly compacted with the palm of your hand.



























