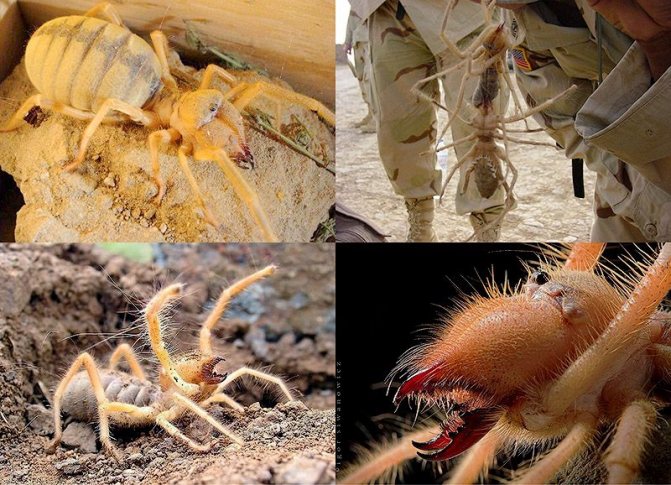
The phalanx spider has several names - solpuga, bihorka, phalanx, camel spider, Solifugae - and is a rather unpredictable animal. To begin with, this is not a spider. Outwardly, they are very similar to spiders - the structure of the limbs, their location and the presence of chelicerae, therefore they were attributed to arachnids. About 1000 species of phalanges are known.
0
See all photos in the gallery
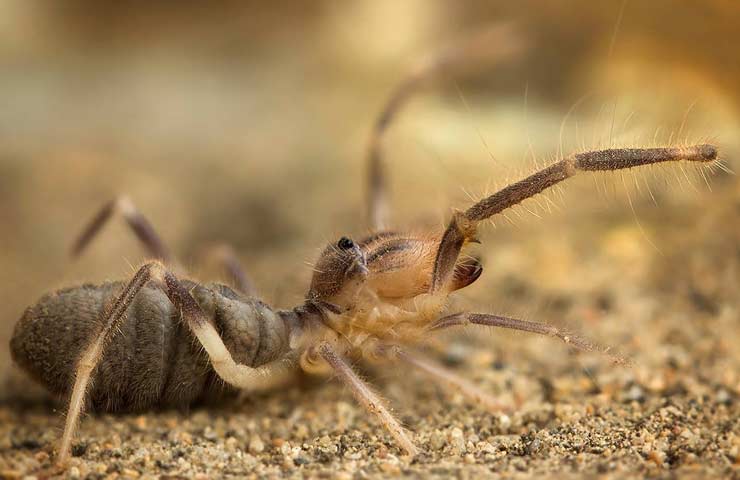
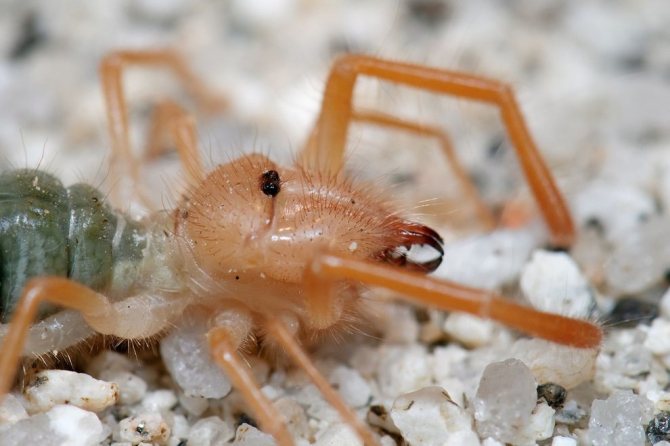
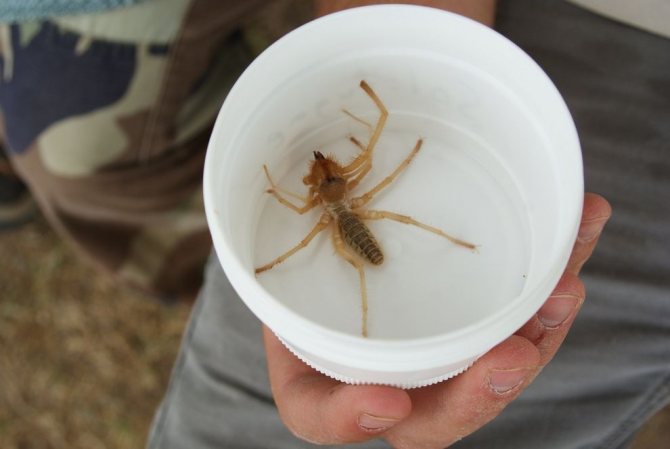
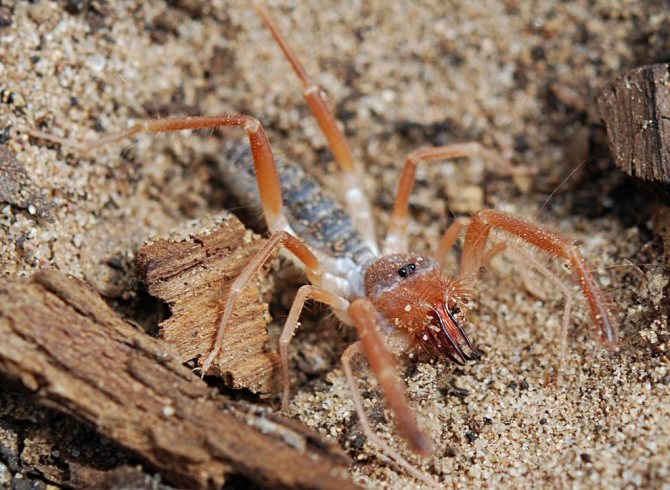
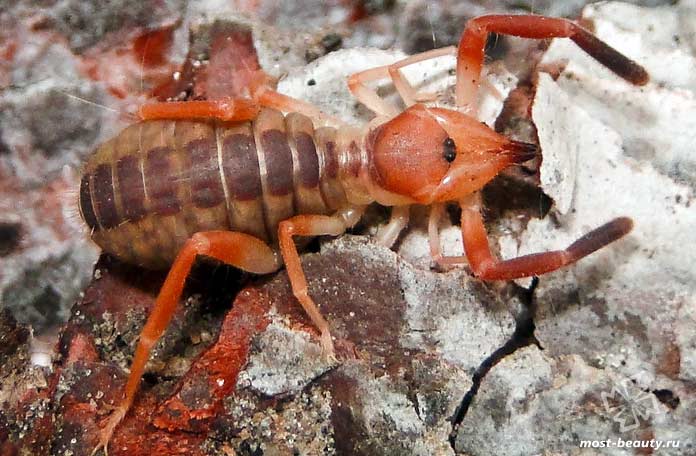
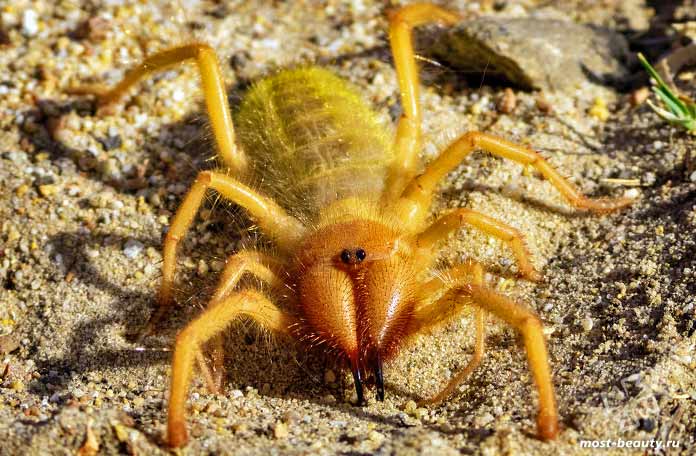
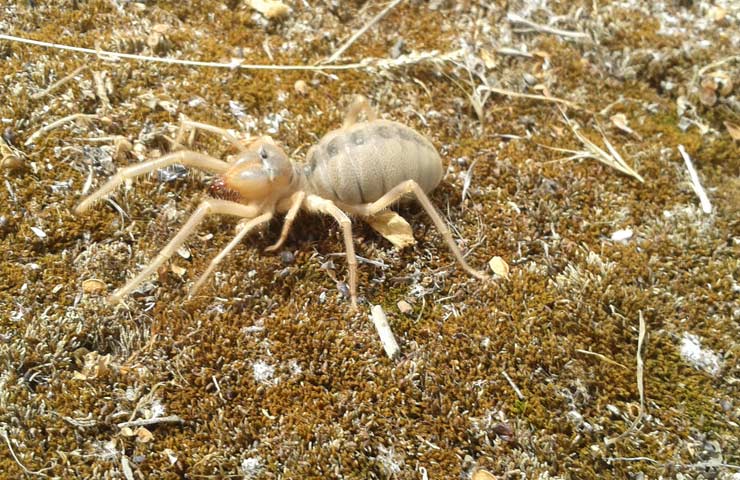
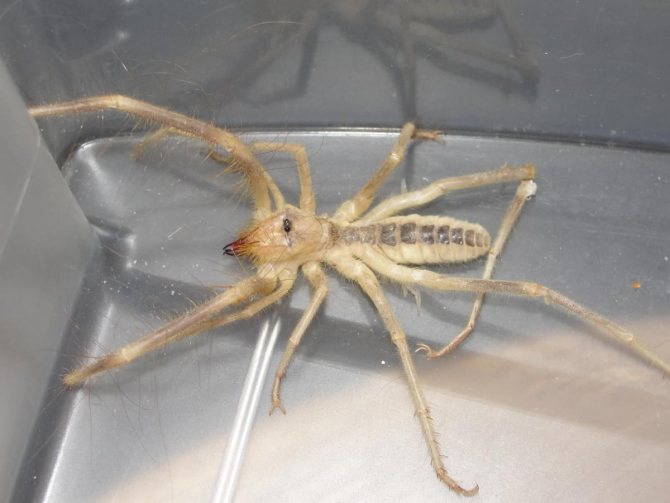
The appearance of the solpug is quite unusual. Their body length reaches 5-7 centimeters, but there are also small species that do not exceed 15 mm. Their entire long body is covered with numerous hairs and bristles, which give the saltpug an even more menacing appearance.

0
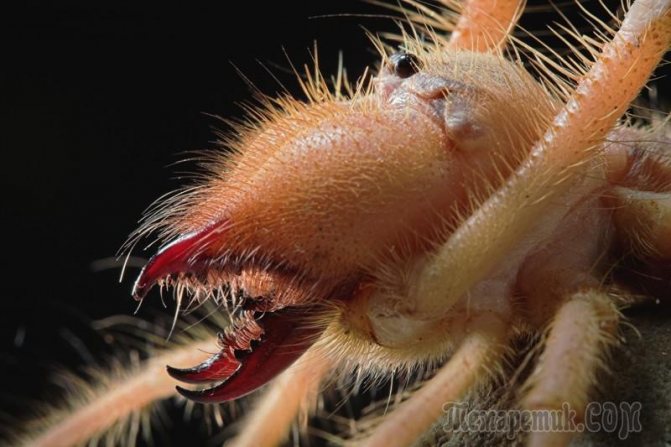
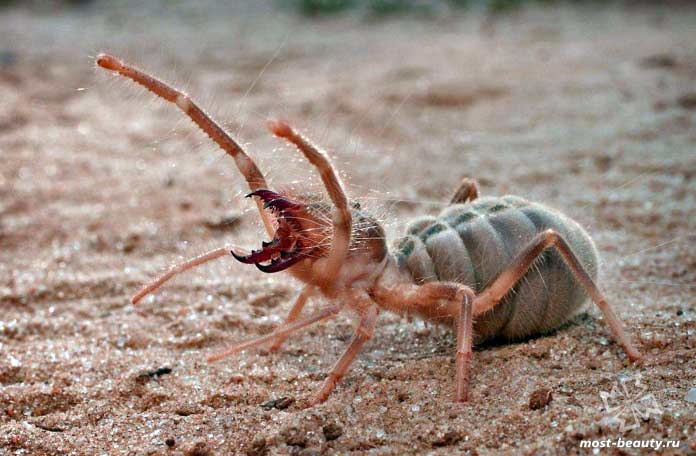
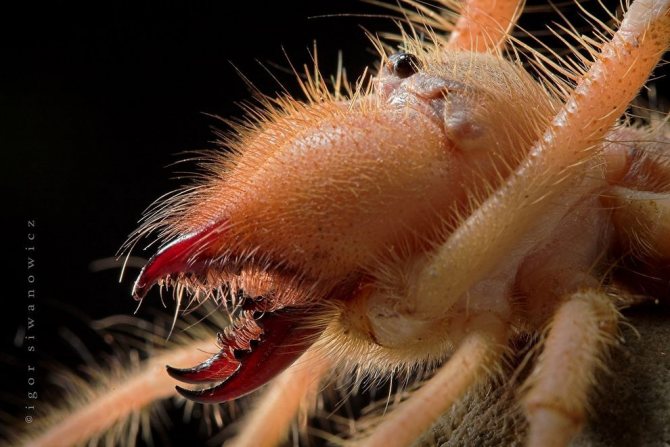
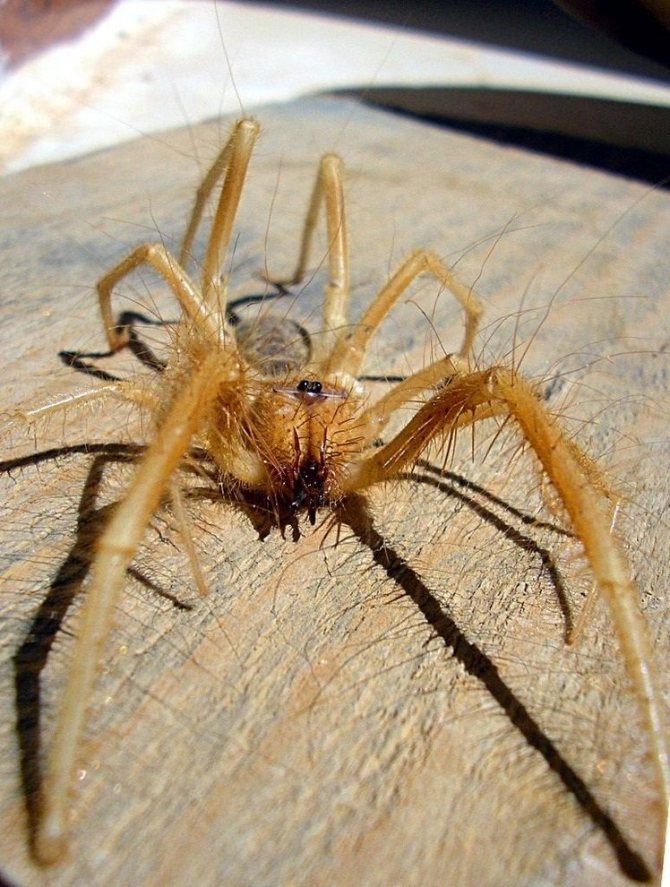
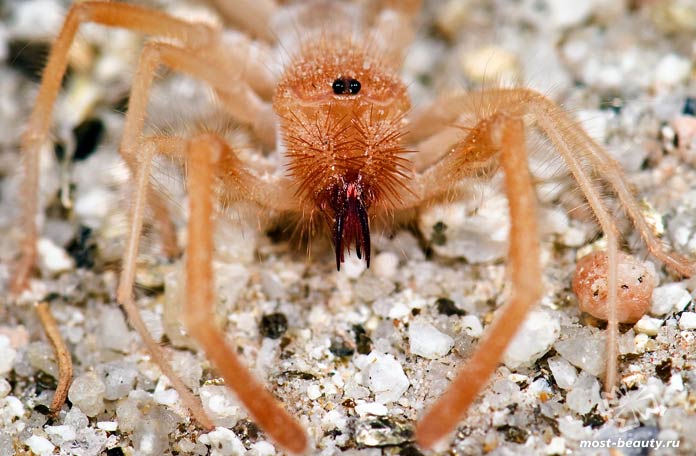
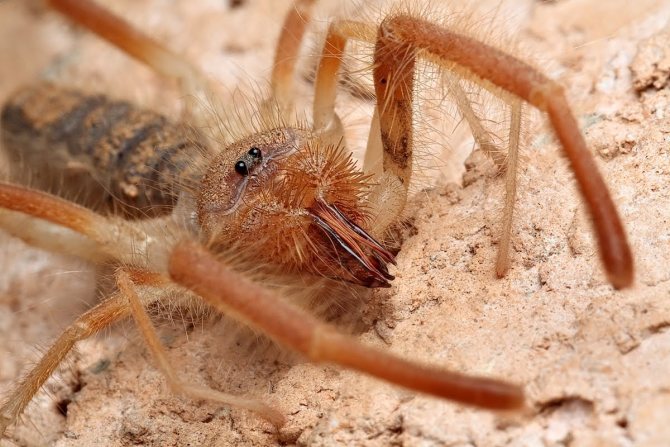
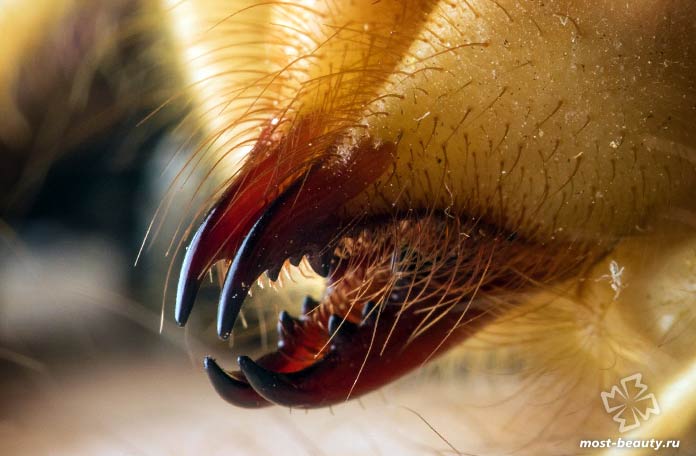
Salpugs are very peculiar - in their way of life and structure, both signs of high development and primitive features are combined. For example, their body structure and limbs are very primitive, and the tracheal system is the most developed of all arachnids. One of the hallmarks of a phalanx spider is its powerful chelicerae. In the structure of each chelicera, 2 parts are distinguished, which are fastened by a joint. As a result, the chelicera looks like a crab claw, which is noticeable in the photo below. On the chelicerae of the phalanx there are teeth, the number of which depends on the species of the arachnid. The chelicerae of the solpugi are so powerful that they allow it to cut off the hair and feathers of the victim, cut the skin and cut the bones of birds. In case of danger, the phalanges squeak or chirp piercingly due to the friction of the chelicerae against each other. The color of the phalanx spider is determined by its habitat, and solpugs live in desert and arid areas, therefore most species have a characteristic color in whitish, yellowish and brown tones. As an exception, variegated individuals are observed.


0
Where did the name phalanx (solpuga) come from?
In Russian, the word "Solifugae", which is the Latin name for the phalanx spider, is translated as "escaping from the light of the sun." The population of South Africa has other definitions for this arthropod class of arachnids: "barber" or "barber". These concepts are based on local beliefs that the underground phalanx shelters are lined with animal hair cut by camel spiders with the help of their powerful chelicerae (mouth appendages). The name "solpuga" is based on a free reading of the Latin name of the order to which the phalanxes belong.
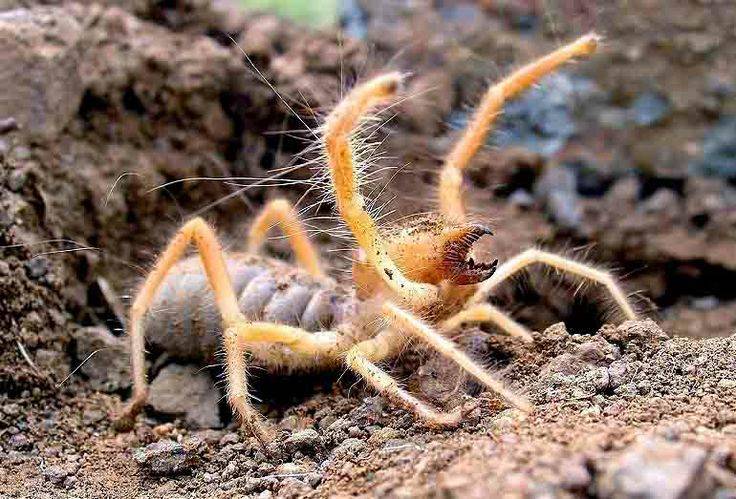


Phalanx spider (solpuga) - description, structure, characteristics, photo
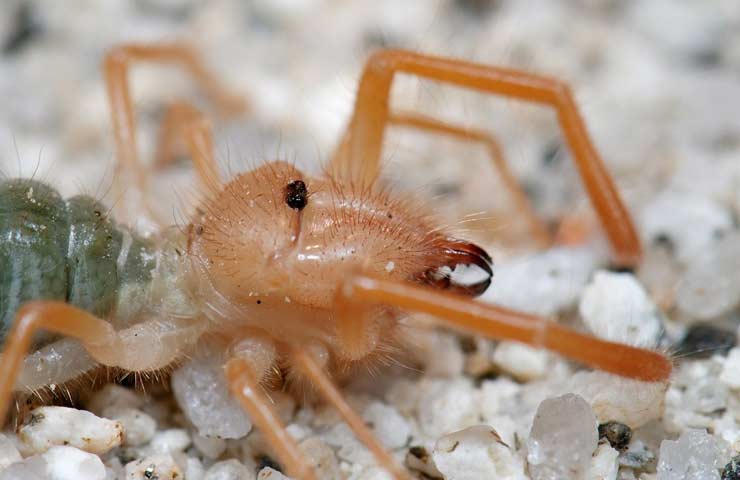
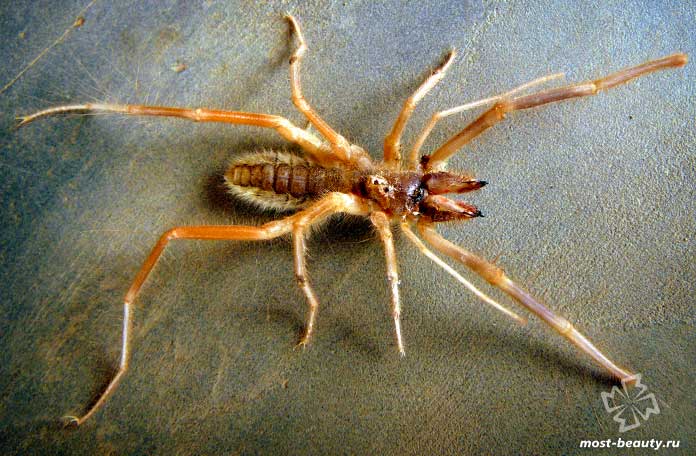
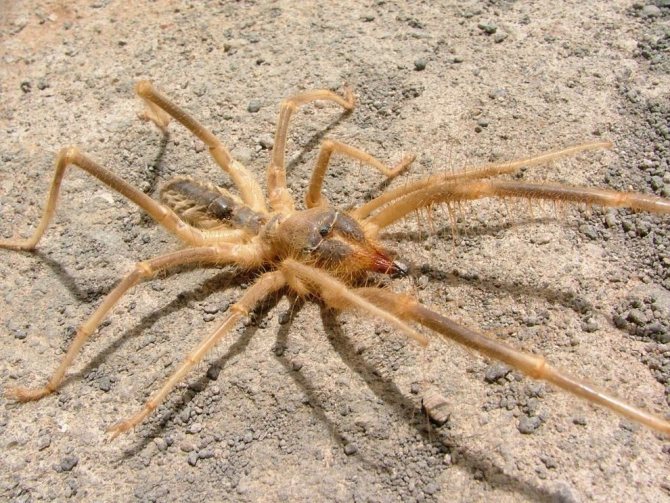
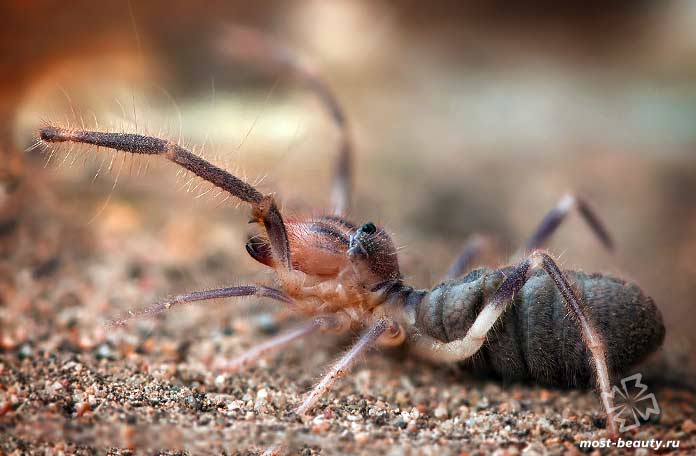
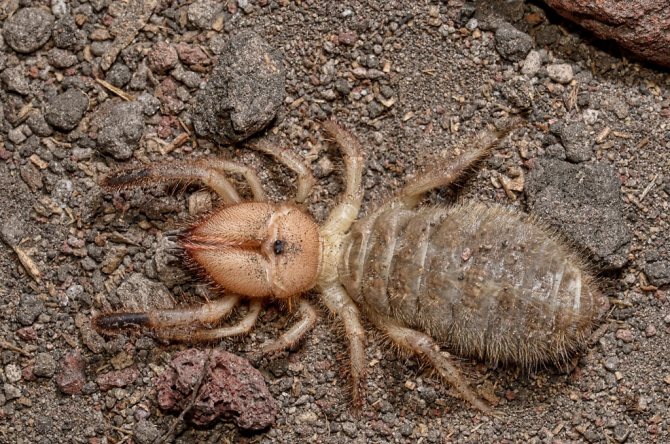
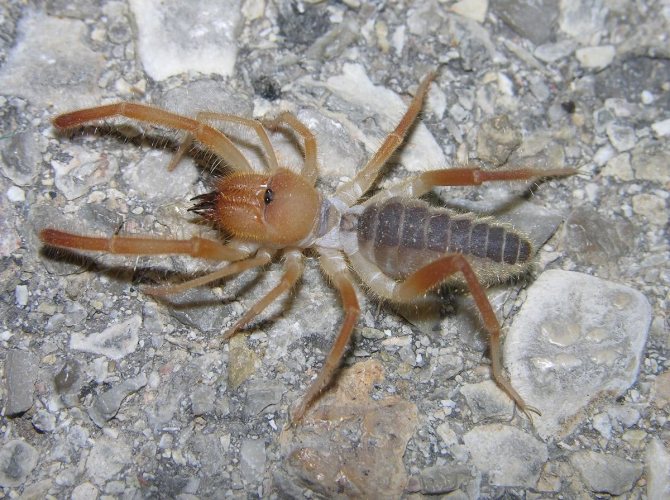
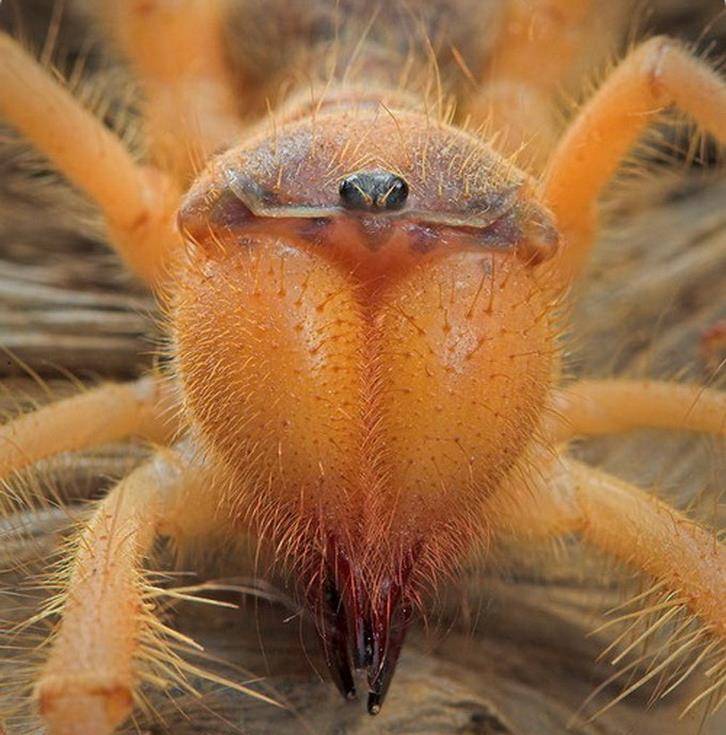
The phalanx spider can reach a length of 7 cm. The cephalothorax has a dissected structure. On its front section, covered with a strong chitinous shield, there are two protruding eyes, large chelicerae (oral appendages) with powerful ticks, short pedipalps with sensitive appendages, and walking legs. In total, the solpugi (phalanx) has 10 legs.
Unlike the front legs, which perform a tactile function, the hind legs of the solpuga are equipped with tenacious claws, between which there are peculiar suction cups. Thanks to this arrangement of limbs, camel spiders easily climb vertical surfaces.


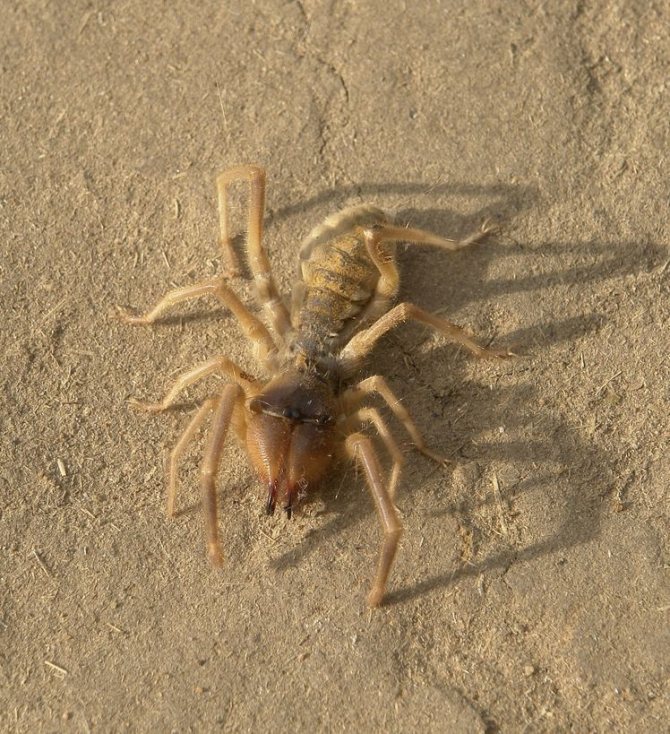
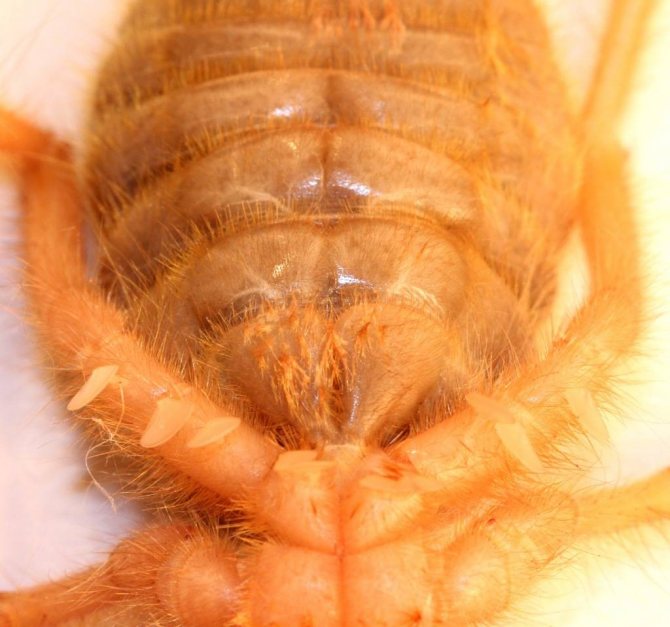
The large abdomen of the fusiform phalanx consists of 10 complex segments, each of which is formed by a solid abdominal and dorsal part and is connected to the cephalothorax like a waist.
Salpugs have well-developed tracheal respiration, consisting of powerful longitudinal trunks and a system of small branching air vessels with spiral thickening of the walls that permeate the entire body of the camel spider.


The entire body and appendages of these arachnids are covered with a huge number of fine hairs and bristles of varying thickness and length. Such an unusual "hair" cover of the solpugi, combined with the large size and fast movements of the phalanges, give them a rather formidable look, which allows them to scare off a potential enemy.
In addition, with the help of chelicera, solpugs can make gnashing or squeaky sounds designed to intimidate the enemy.
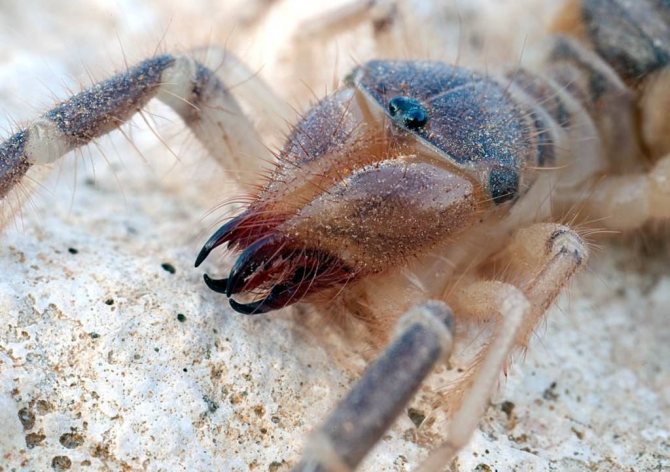


One of the hallmarks of a phalanx spider is its powerful chelicerae. In the structure of each chelicera, 2 parts are distinguished, which are fastened by a joint. As a result, the chelicera looks like a crab claw, which is noticeable in the photo below. On the chelicerae of the phalanx there are teeth, the number of which depends on the species of the arachnid.
The chelicerae of the solpugi are so powerful that they allow it to cut off the hair and feathers of the victim, cut the skin and cut the bones of birds. In case of danger, the phalanges squeak or chirp piercingly due to the friction of the chelicerae against each other.
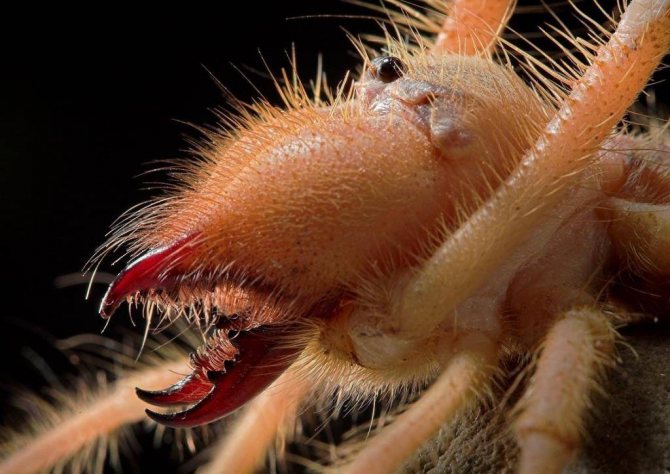


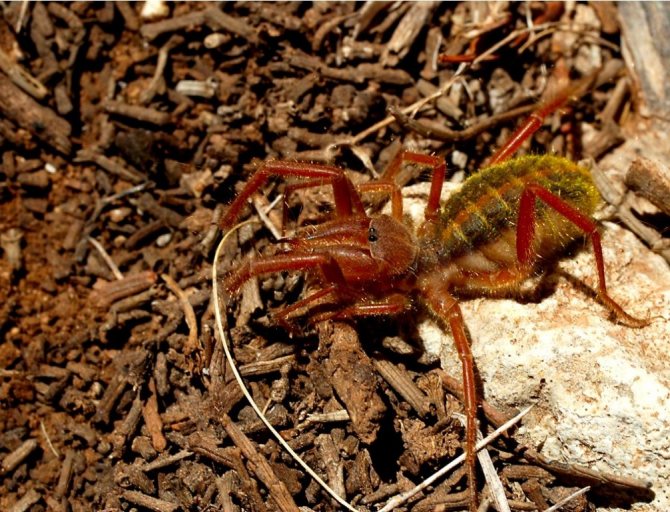
The color of the phalanx spider is determined by its habitat, and solpugs live in desert and arid areas, therefore most species have a characteristic color in whitish, yellowish and brown tones. As an exception, variegated individuals are observed.
Body size and structure
Common signs, or what all phalanx spiders look like:
- the body is divided into head, chest and abdomen;
- the body and limbs are covered with villi;
- two eyes are visible in the center of the head;
- mandibles-jaws, resembling claws;
- 6 pairs of legs;
- a pair of front paws performs a tactile function.
Animals can grow up to 10 centimeters. The hind limbs have claws and suckers, thanks to which the phalanges can move along planes at any angle of inclination.
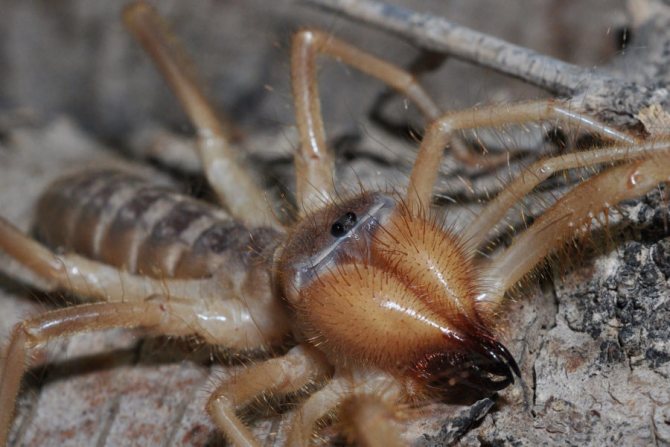


Types of phalanges (solpug)
The 13 families, which form a large order of phalanges, are subdivided into 140 genera, which include almost 1000 species. Among the representatives of camel spiders, the most famous are:
- Common salpuga (South Russian salpuga, common galeod) (Galeodes araneoides)
represented by large individuals: their body length can reach 6 cm in females and 4.5 cm in males. The lower part of the abdomen and cephalothorax are sandy yellow. The top of the back is gray and brown. Powerful chelicerae are able to withstand the weight of a camel spider's own body. The common salpuga is an active nocturnal predator that digs holes, hides under stones, in holes thrown by rodents or in crevices of the ground. These individuals are omnivores, and can attack scorpions and other spiders. The common saltpug is listed in the Red Book of the Astrakhan region.
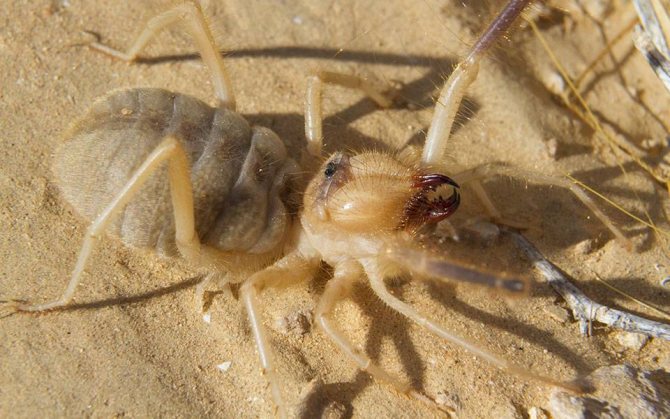


- Transcaspian salpuga (Galeodes caspius)
has a brownish red coloration of the cephalothorax and a gray abdomen, on which dark stripes are clearly distinguished. The size of these arachnids reaches 6.5-7 cm. These camel spiders live in Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
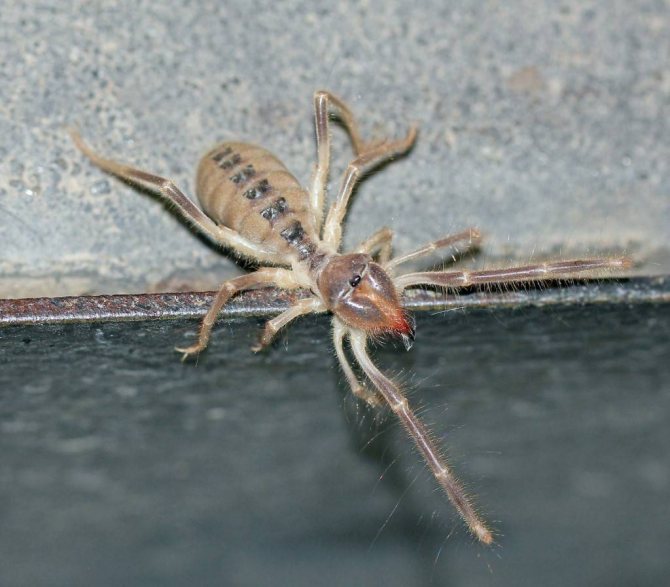


- Smoky salpuga (Galeodes fumigatus)
is the largest representative of the phalanx order. The body size of individual individuals can exceed 7 cm. The upper part of the abdomen of the solpuga, in the middle of which a grayish-brown strip is visible, is painted in an olive-smoky color. The cephalothorax has a bright yellowish-buffy tint. The phalanx lives in Turkmenistan.
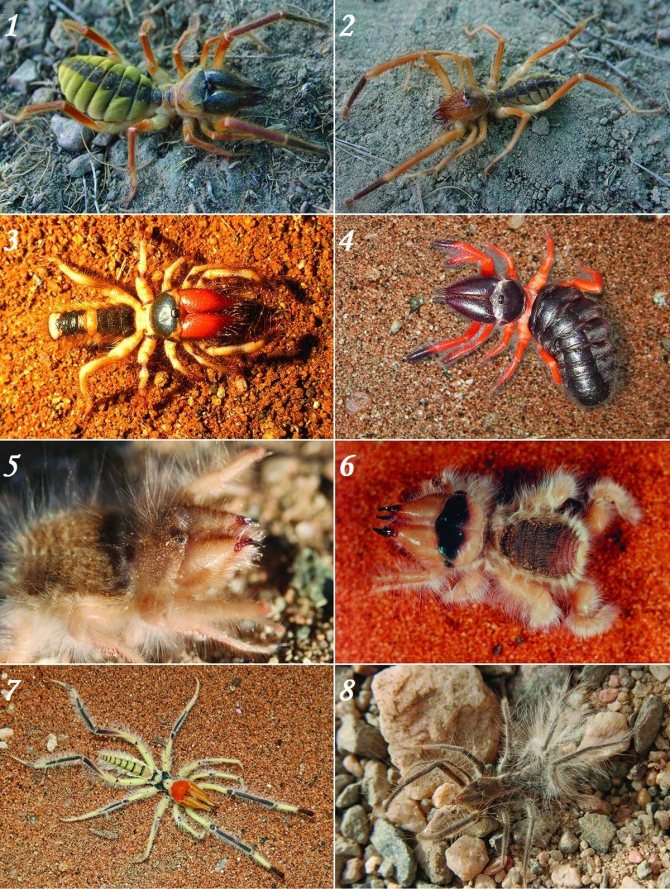


Types of camel spiders in the photo:
1 - female camel spider Galeodes caspius fuscus (lives in Kazakhstan)
2 - male camel spider Galeodes caspius fuscus (lives in Kazakhstan)
3 - Rhagodes solpuga (lives in Kenya)
4 - Rhagodes solpuga (lives in India)
5 - salpuga Hexisopus (lives in Namibia)
6 - Salpuga Chelypus (lives in South Africa)
7 - salpuga Metasolpuga picta (lives in Namibia)
8 - Salpuga Zeria sericea (lives in Namibia)
Smoky / Galeodes fumigatus
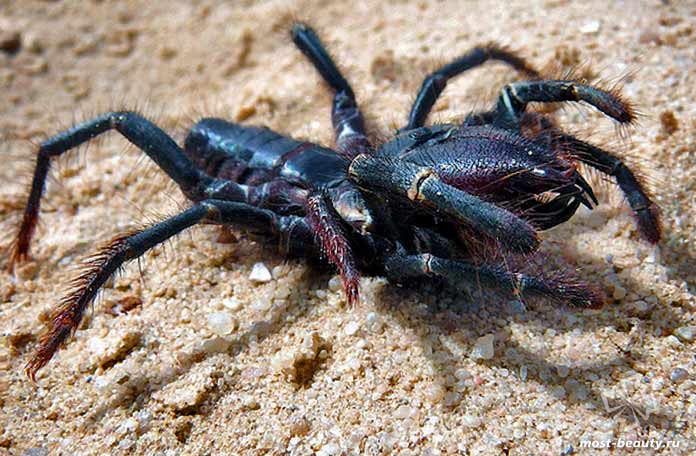


The inhabitant of the desert regions of Turkmenistan has a dark brown color. There are also completely black individuals. Such a view, of course, can be scary.
They grow up to 7 cm in length, and therefore are considered one of the largest representatives of the genus Galeodes. They hunt down their victims at night, during the day they hide in burrows. Some individuals use the same burrow, but most find a new refuge every day.
Move quickly with walking legs. To this ability we add that they easily overcome obstacles with a vertical surface.
Where does the phalanx spider (solpuga) live?
Phalanges are typical inhabitants of desert, semi-desert and steppe regions with tropical, subtropical and mildly temperate climates. Single species of solpugs have adapted to the conditions of wooded areas. The distribution area of this family includes India and Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Bhutan, the African continent, the countries of the Balkan and Iberian peninsulas. On the territory of the post-Soviet countries, solpugs are found throughout Central Asia (Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan), the North Caucasus, the Transcaucasus and the Crimean Peninsula. Phalanges are absent only on the Australian continent and the icy expanses of Antarctica and the Arctic.
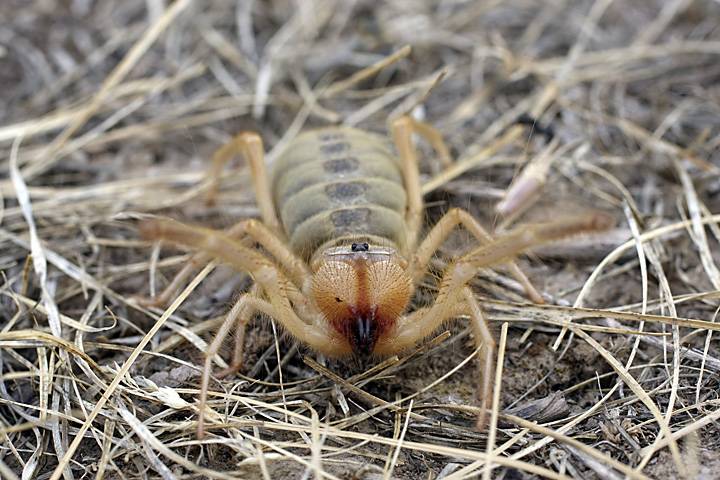


Most species of camel spiders are active nocturnal. They wait out the heat of the day in shelters, which can be abandoned dwellings of small rodents, stone deposits or self-dug burrows. Many individuals use one shelter for a long time, although some of the solpugs prefer to find a new place each time.
Habitat
Solpugs prefer warm regions: arid steppes, deserts, subtropics, tropics. A large army of voracious predators populated all continents, with the exception of Australia and Antarctica. There are 80 species in North and South America, 16 in North Africa, and 100 in the southern part of the African continent. Up to 200 species are found in Eurasia.


Countries where they are familiar with solpugs:
- Pakistan;
- India;
- SOUTH AFRICA;
- Algeria;
- Morocco;
- Greece;
- Spain;
- Kazakhstan;
- Tajikistan;
- Turkmenistan;
- Kyrgyzstan;
- Azerbaijan;
- Georgia.
Favorable places for the spider phalanx where it lives in Russia:
- Crimea;
- Astrakhan;
- Volgograd region;
- Kalmykia.
Individual representatives can be found in the northern regions.
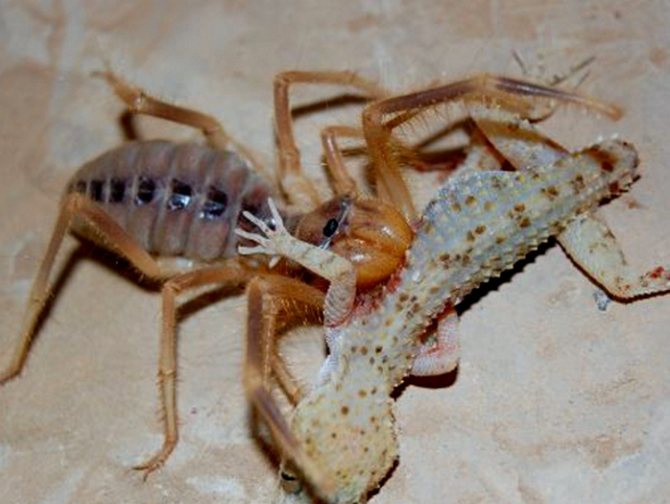
What does a solpuga (phalanx) eat?
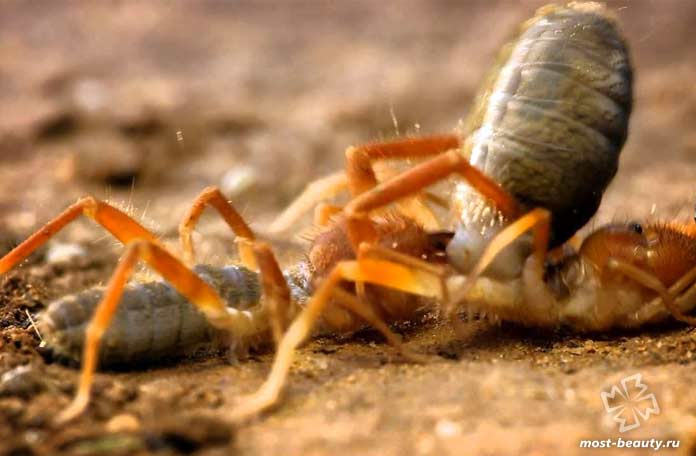
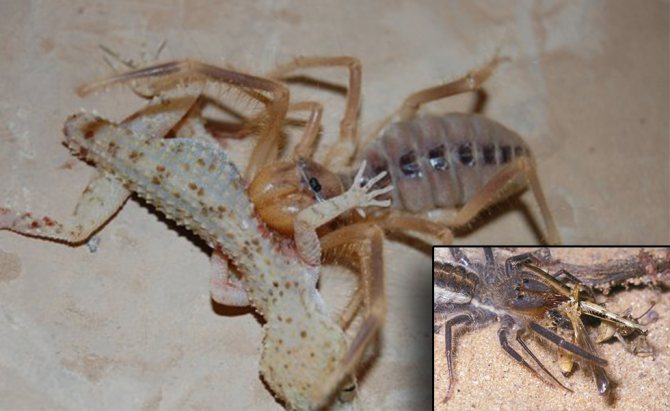
Salpugi spiders are typical predators and are characterized by pathological gluttony. Despite the fact that the phalanges lack venomous glands, their diet includes large insects and even small animals. The main food for these arachnids is various centipedes, wood lice, termites, scorpions and spiders. Large species are able to cope even with lizards, small birds and small rodents.
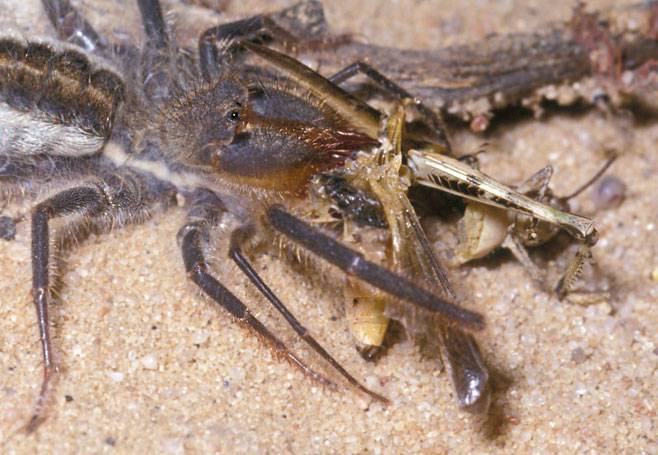


Solpuga eats a grasshopper
Camel spider (phalanx): reproduction
During the mating season, the male phalanx, by the smell emitted by the female, searches for her, after which mating occurs. Then the male has to hide urgently. This is due to the fact that the "lady" begins to show signs of aggression and is able to eat her former "gentleman".
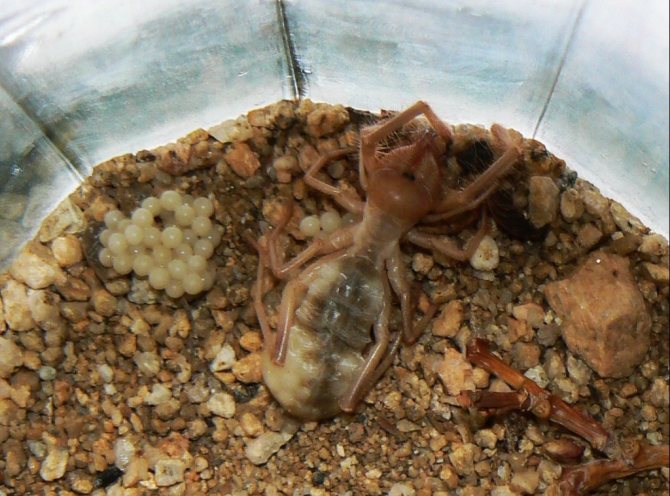
After fertilization of the salpuga, the female begins to feed intensively and lays from 30 to 200 eggs in a previously dug hole. The development of new individuals begins in the mother's oviducts. Therefore, soon small phalanges are born, covered with a transparent, but strong and flexible film (cuticle).
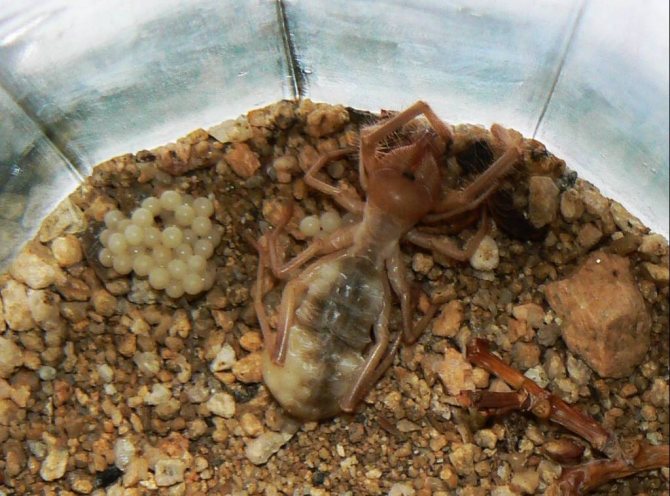


The first days the solpugi are motionless. They acquire the ability to move independently after the first molt, which comes after 14-20 days. Then the young growth begins to grow with hairs characteristic of this species.The mother is with the cubs until they get stronger, and at first provides them with food.
The life of camel spiders is subject to strict seasons. With the onset of cold weather, the phalanges fall into deep hibernation and, in this form, experience unfavorable conditions.
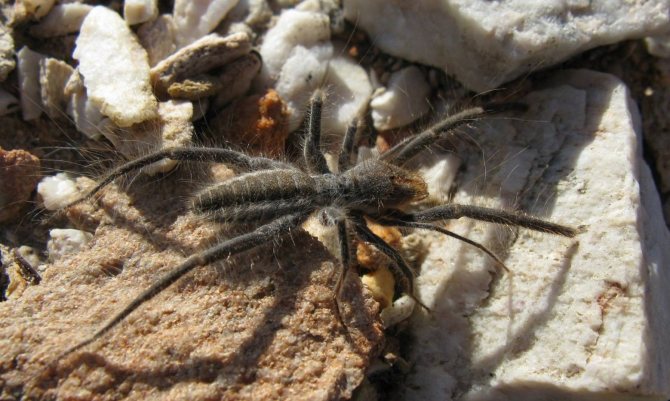


Pairing
Mating games take place at night. The female attracts males by smell. Fertilization is sperm. Before mating, the young female is so inert that the "boyfriend" has to drag her along. After fertilization, the phalanx becomes brisk. If the male does not have time to escape from her, he risks becoming a victim.
The development of embryos begins inside the solpuga. After a while, the female lays eggs in a previously prepared burrow. Cubs are born with a thin chitinous cover, extremely vulnerable, motionless. The mother protects them until the first molt, brings food. After 2 weeks, the cubs molt, increase in size, acquire a characteristic color, and the shell hardens.
How many young phalanges shed before growing up, how long they live later, is not known for certain. An approximately adult individual lives for 1 year.
Keeping the phalanx at home
Today it has become fashionable to keep a spider solpugu at home. To make such "pets" feel comfortable, you need a spacious terrarium with a heater that provides the required temperature and a small drinking bowl. The bottom should be covered with a layer of soil and pebbles up to 15 cm thick so that the solpugs can dig their own burrows. It is also advisable to sketch out twigs and pieces of bark, creating conditions close to natural. Care must be taken when cleaning the terrarium, although these arachnids do not have venom glands, their bites are quite painful. The large phalanx is capable of biting through human skin. The solpuga spider does not have poison glands, but rotting pieces of food can get stuck on its teeth, which, when bitten, can get into the wound and cause infection.
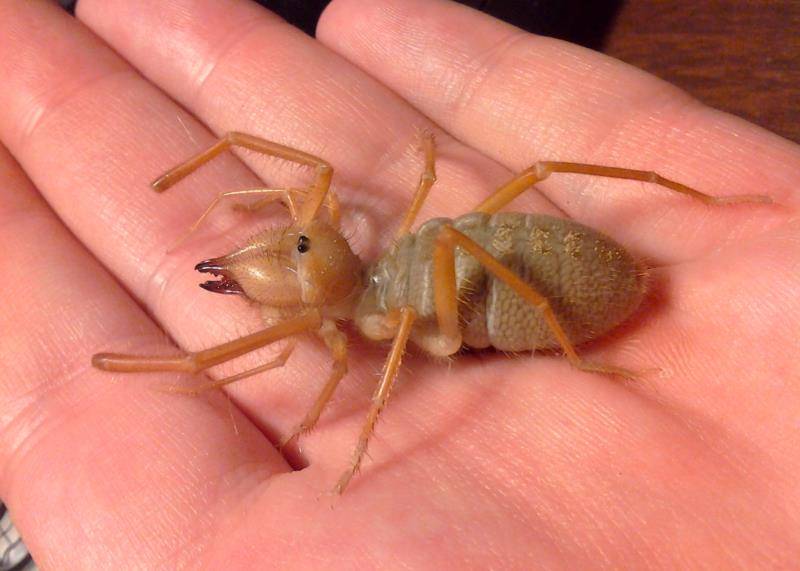


Interesting facts about the spider phalanx (solpuga)
- The phalanges have other names, for example, "camel spider". It is due to the habitat of the phalanges. And the specific shape of the body, which allows them to move at a speed of up to 16 km / h, and perform acrobatic jumps reaching 1 meter in height, served as the basis for the nickname "wind scorpion".
- Feeding "pets" at home should be moderate, as captive phalanx spiders can consume food indefinitely. There were even cases of their death from overeating.
Did you like the article?