Quails are considered one of the most popular birds for domestic breeding. The most common are English white and black breeds, as well as Manchu golden, Australian tan, tuxedo, pharaoh and about 60 hybrids based on them. Most of them are raised for eggs, and only quail of the Pharaoh breed are intended for meat production.
Below we give the main characteristics and a detailed description of the main breeds intended for breeding in the home farm.
- Features of the
- Features of the
- Features of the content
- Care features
- Features of the breed
- Characteristics
Origin of the species and description

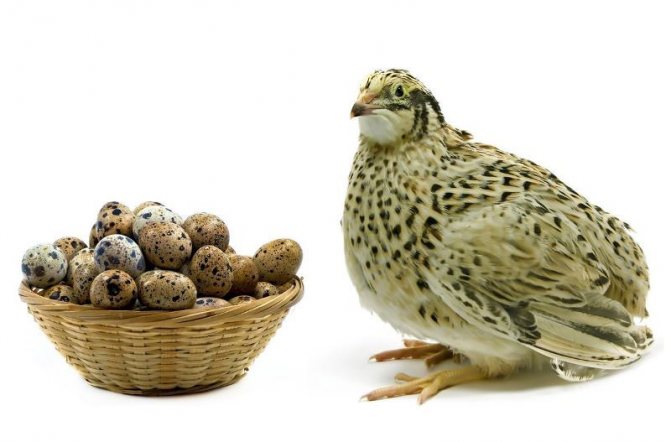
Photo: Quail
Quail (or common quail) is a bird that belongs to the pheasant family. This family includes eight extant species. Pheasants are a diverse family with birds of varying sizes, lifestyles, and habitats.
Various birds have the following traits:
- polygamy;
- birds do not form long-term pairs; the male, as a rule, has several females;
- pronounced secondary sexual characteristics of males;
- their color differs from that of females, is brighter;
- notch at the posterior edge of the sternum, short phalanx of the hind digit;
- spurs, rounded wings.
Birds of the family rarely fly, although they know how to do it. Due to their heavy, but elongated body structure and mobile neck, they run fast and prefer to nest in families on the ground, in tall grass or bushes. Because of this lifestyle, they often become the prey of large and small predators, and also become the object of human fishing. Pheasant meat is highly valued in the game market.
Fun fact: Some pheasant species can interbreed with each other.
During nesting, males fight to leave offspring. The eggs are laid in a nest - a depression in the ground, insulated with dry leaves and grass. Some families form small flocks.
Manchurian quail: breed description
Outwardly, the Manchu quail is similar to the Japanese one with the only difference that it has golden plumage rather than brown (Figure 11). But the main advantage of the breed is its versatility.
Birds have a fairly high egg production, but they gain weight well and are suitable for breeding for meat. In addition, female Manchu quail can be crossed with males of other breeds to improve characteristics.
Characteristics
The main characteristic of Manchu quails is their versatility. They bring quite a lot of large eggs, and females can be sent to slaughter a year after the start of egg production.


Figure 11. Features of Manchu quails
In addition, birds are unpretentious in terms of keeping, tolerate climate change well and are undemanding to feed.
Appearance and features


Photo: Quail bird
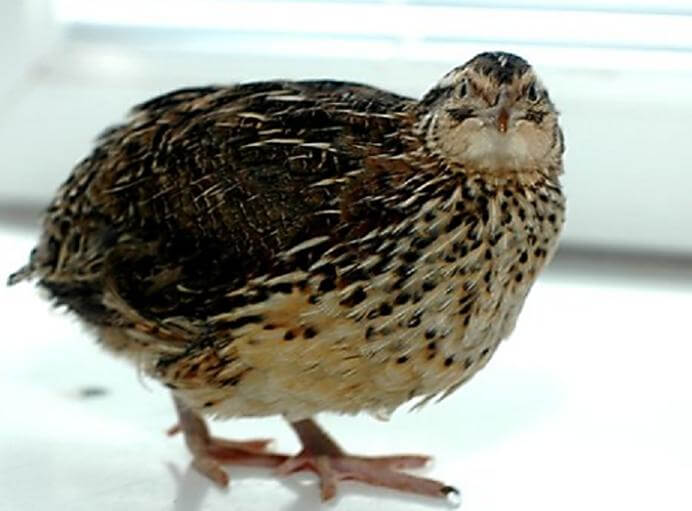
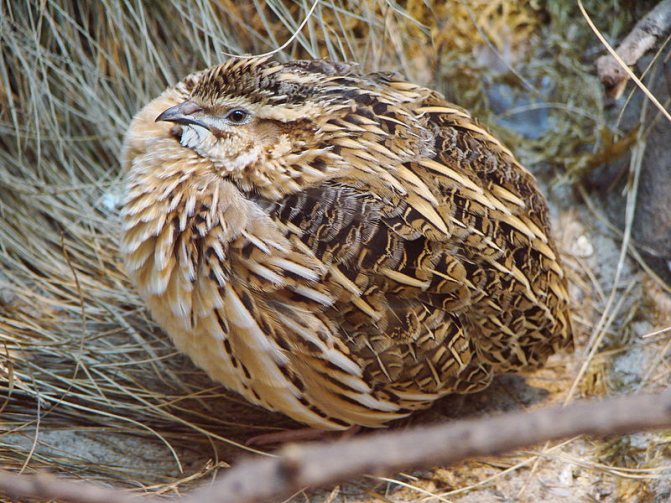
Quail is a small bird, about 16-22 cm.in length. The weight of the female is about 91 grams, the weight of the male is 130 grams. The plumage of the bird is gray, with small white blotches - this color allows it to better camouflage in dry grass. The head, back, tail have reddish, yellow stripes, and there are long white arches above the eyes. The body of a quail is as compact as possible so that it can better camouflage and run fast. A teardrop streamlined body shape, short tail and pointed wings allow her to gain acceleration while running. Feathers are not adapted to humid climates, but they provide thermoregulation, cool the body in the heat.
Video: Quail
Quails have short wings that completely cover their body, a small head and a long thin neck. Their massive legs allow them to run quickly, overcome obstacles and dig into the ground in search of seeds or to build a nest. Despite the claws on their paws, quails do not know how to defend themselves against predators. Distinctive features of males and females appear as early as the third week of life after the emergence of the chick. Males grow faster, grow larger and gain weight.
Interesting fact: Unlike other species of the pheasant family, neither male nor female quail have spurs.
Males differ from females: they have a reddish breast (while in females it is white), yellow markings above the eyes and at the beak. They themselves are larger in size, but still prefer avoiding predators than fighting. Male claws are longer and stronger because they need them to fight with each other during the mating season.
Quail meat breeds and their characteristics
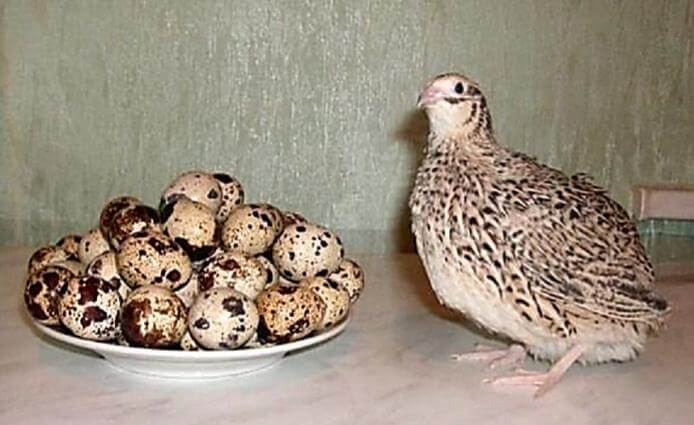
For breeding quails for meat, only two breeds are used - Pharaoh and Texas white (Figure 1). The birds were bred by the method of selection work. The description of Pharaoh quail primarily concerns their weight. The weight of an adult individual reaches 300 grams, which is a lot for such birds.
At the same time, the pharaohs are distinguished by low egg production: females bring no more than 200 eggs per year. At the same time, the large weight of the carcasses makes the breeding of this type of quail quite profitable.
Get meat quail: where to start
For breeding for meat, you should first study the suitable types of quail and their characteristics. Since there are only two species of birds in this direction, the choice will not be difficult.
You also need to take care of the containment room. Birds of the meat production direction are small, and for their maintenance they are equipped with cages. Such content greatly facilitates the care of the livestock, and the birds gain weight faster.


Figure 1. Meat quails: 1 - Pharaoh, 2 - White Texas
But the key attention will have to be paid to feeding. For meat quails, a special diet is provided, which is aimed at a quick gain in live weight. First of all, the diet includes vitamin complexes and mineral supplements, as well as fresh herbs.
Features of the
Since the pharaohs and Texas white birds are referred to as meat breeds of quails, let us dwell on their physical features and characteristics.
The main differences between meat quails from other species are:
- Relatively large carcass weight. Adult pharaohs can reach 300 grams, and Texas whites can reach 400 grams.
- Fast weight gain, which practically does not depend on the conditions of detention.
- Demanding feed: meat quails should be fed complete and balanced for weight gain and disease resistance.
Otherwise, meat quails are no different from other species. However, it is worth noting their relatively low egg production, which entails difficulties in breeding young.
Productivity
In color, the pharaohs coincide with the Japanese breed, but they belong to birds of meat productivity, although the egg production in females is quite high. It is the pharaohs that are used to produce broilers.
Where does the quail live?


Photo: Quail in Russia
It is a very common bird that has become popular as a game bird in many countries around the world.
It is distributed in:
- Europe;
- North Africa;
- Western Asia;
- Madagascar (birds often stay there for the whole year without flying due to the small number of natural enemies);
- in the east of Lake Baikal and throughout central Russia.
Common quail, which is common in Russia, is divided into two types: European and Japanese. Japanese birds are domesticated in Japan and are now raised in poultry farms for meat and eggs, so their numbers in the wild have been reduced. European quail is most common. Due to the nomadic lifestyle, the bird flies long distances for the sake of nesting. Nests are located as far as Middle Iran and Turkmenistan, where it arrives in early April. To the north - to the central zone of Russia - flocks of quails fly in early May with already grown chicks.
Interesting fact: In Russia, they prefer to hunt for quails precisely during their flight to warm regions for the winter quarters - many birds rise into the air and are easy to get through. For such hunting, trained dogs are used, which bring the shot bird to the hunter.
The bird prefers to settle in the steppes and fields, rather than in the forest. This is due to its tendency to a terrestrial lifestyle, moreover, they build nests in the ground. Quails love an arid climate, do not tolerate too low temperatures.
Quail meat and egg breeds
Virginia quails are also quite often used for cage keeping. The birds grow medium-sized, they have a short beak with a curved tip, long claws on their legs, but no spurs.
Virginia quails are quite common in zoos and home gardens, as they multiply quickly, do not require special conditions of maintenance and are very productive.
A distinctive feature is considered to be an unusual appearance. (Figure 6):
- There is a white and black stripe from the neck to the forehead;
- In the upper part of the neck there are black feathers that form a kind of rim;
- The back of the neck is covered with white feathers;
- The top of the torso is reddish brown and there are light stripes at the bottom of the torso.


Figure 6. External features of Virginia quails
In natural conditions, they settle on agricultural land, in thickets of bushes, in meadows and in rare forests. Like many other quails, Virginia quails live in pairs.
The female is engaged in the construction of the nest, which is looking for a suitable place on the ground under a high tuft of grass. One clutch contains from 8 to 14 eggs, and the incubation period lasts up to 24 days.
Note: The chicks of Virginia quails, like other species, grow very quickly and reach sexual maturity. However, male, female and chicks stay together until next spring.
By the method of artificial selection, many hybrids with a wide variety of colors have been obtained. They are great for cage breeding as ornamental birds, as well as for meat and eggs.
Content requirements include:
- It is necessary to place a box with a mixture of ash and sand in the cages;
- On one side, there is a small box with a bedding for laying eggs (one female is capable of laying from 40 to 60 eggs per season);
- After laying, all eggs are collected and placed in the incubator;
- If the birds are kept in an open-air cage with conditions close to natural conditions, the female can hatch the eggs herself. But in this case, during the incubation period, it should be isolated from the male, since he will interfere with incubation.
After hatching, the quails are fed with a mixture of bran and boiled egg yolk. You can also feed grated carrots and fresh herbs. After a few days, you can give compound feed and simply. After reaching two weeks of age, the chicks begin to feed the grain mixture.
Features of the
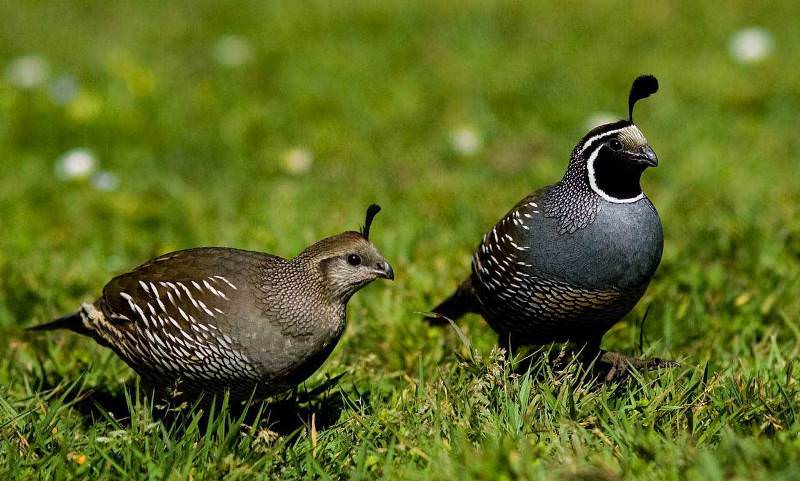
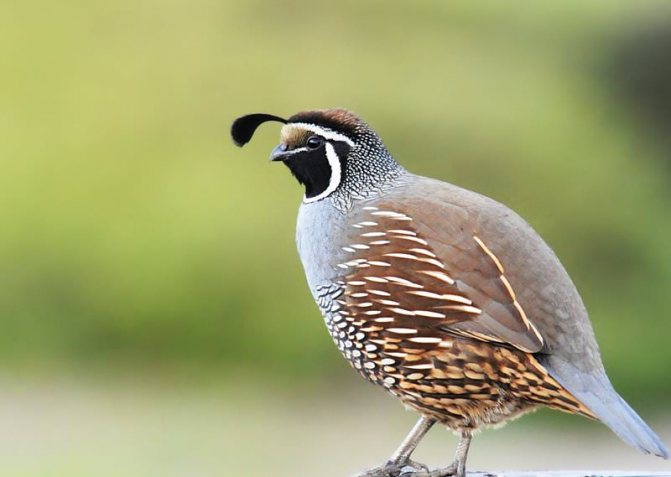
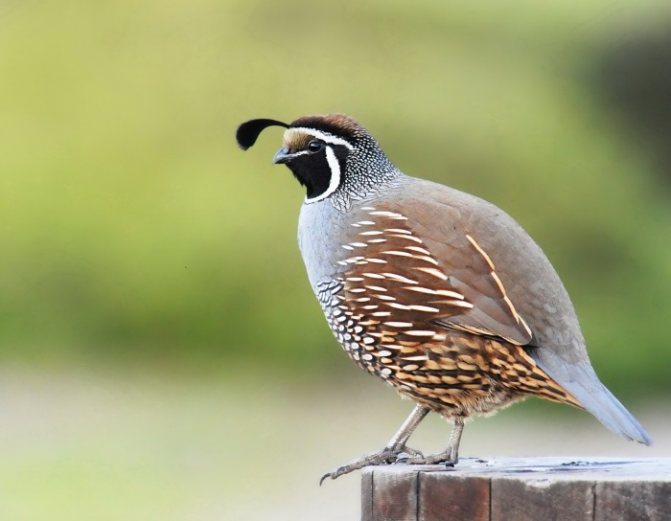
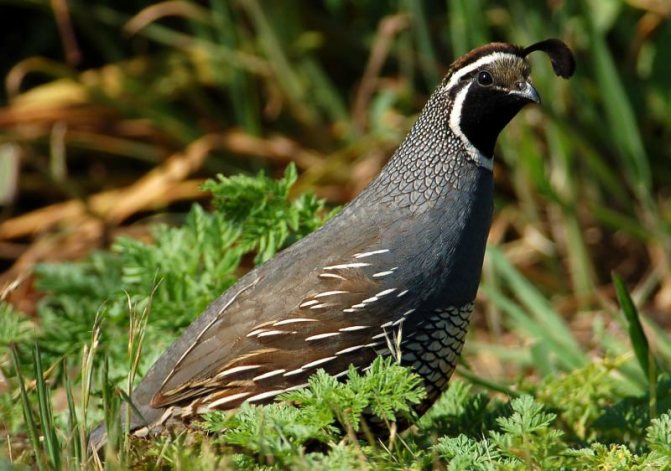
Another popular breed is the Californian quail. These birds are known for their crests. An external feature is also a short and slightly curved beak, as well as a stocky body.
The color of the California quail on the forehead is white-yellow, and a white stripe goes to the back of the head. The rest of the plumage is black-brown. It should be noted that the plumage of females is more ordinary-looking than that of males (Figure 7).


Figure 7. External features of California quails
Californian quails can be bred in open-air cages and cages, and the hatched young after reaching puberty go into flocks. At night, they sit on poles, which must be equipped in an aviary or cage.
California quails also have some breeding characteristics.:
- Pairs must be kept separately, and after hatching young birds, they can again be united into flocks;
- Females have good egg production, but their instinct for incubation is poorly developed, so it is better to place eggs in an incubator;
- It is important that even with artificial breeding in one clutch there can be many unfertilized eggs or weak chicks.
They are very sensitive to heat, so the room for keeping them must be heated. Otherwise, the care and maintenance of this breed is the same as the rest.
Main characteristics
Egg quail meat and their characteristics fully meet the requirements of poultry farmers for breeding these birds. They have a fairly large weight (200-250 grams) and are suitable for slaughtering for meat. At the same time, such quails are distinguished by intensive egg-laying, and the products can be sent for sale or used for hatching chicks.
Like other species, meat and egg quails consume little feed and can be kept in cages without free range.
Productivity
The most productive meat and egg breed is the Estonian quail (kaitavers). This is a meat-egg hybrid bred on the basis of a Japanese breed. Live weight and egg production remain at the level characteristic of most species, but a distinctive feature of Estonian quails is the high hatchability of young stock.
You will learn full information about the existing quail breeds, the peculiarities of their life, keeping and feeding from the video.
What does a quail eat?


Photo: Quail laying hen
Quails are omnivorous birds that spend a significant part of their lives in the harsh conditions of central Russia. Therefore, their diet is balanced - these are seeds, cereals, green grass (quinoa, woodlice, alfalfa, dandelion, wild onion), roots and insects. In the wild, the chicks of these birds eat the maximum protein food: beetle larvae, earthworms and other "soft" insects.
With age, the bird switches to a more plant-based diet - this is due to the fact that the body stops growing and needs a lot of proteins. While it is important for chicks to grow up quickly and start flying in order to get ready for a long flight between countries and continents in a month. Chicks that do not eat enough protein food will simply die during the flight or fall to predators.
Since quails are widely used as poultry, their diet is slightly different from the usual "wild" one. Chicks are given cottage cheese mixed with the protein of a hard-boiled egg as protein and calcium. Sometimes corn flour is added there so that the mass does not stick together.
Adult birds are fed ready-made quail feed - chicken feed is not suitable for them. It includes all kinds of vitamins and bran to make the birds fat and lay eggs. Instead of feed, you can mix corn and millet grains, sometimes adding boiled eggs and cottage cheese.
Interesting fact: Due to their omnivorous nature, birds can digest boiled chicken meat, so they can replace worms and bugs from the "wild" diet of quails.
Birds are also fed the herbs they are accustomed to, including mild homemade green onions, which strengthens the weakened immune system of poultry. In winter, which they are not used to, it is preferable to give chopped dried grass, which is mixed with regular feed.
Also, quails in the wild and at home can eat:
- fish bones or fishmeal;
- sunflower seeds, whole grains. Their birds are found in agricultural fields;
- peas, crushed shells;
- salt.
- shredded shells or whole thinned shells as a calcium supplement.
Now you know what to feed the quail. Let's see how a bird lives in the wild.
Quail breeding recommendations
In order for the birds to bring a good "harvest" to their owner, it is necessary to strictly observe the basic rules of maintenance and care:
- The room in which the birds will be kept should not be too cold or too hot. The optimum temperature is 18–20 degrees for the quail. There should be no drafts in it, but at the same time it should be well ventilated.
- The room should not be too bright. Bright light can be stressful, causing birds to peck at each other.
- No other animals or birds should be kept in the quail room. Neighborhood with other individuals can negatively affect egg production.
- The height of the cage should not be more than 20-25 cm.
- Laying cages must be equipped with an egg collector.
- The cages should have drinkers and feeders.
For feeding birds, they usually use chopped wheat... The diet should also include: chalk, meal (from soy or sunflower), fish flour, vitamin and mineral supplements. In order for quails to grow up healthy, there must always be a large amount of water in their cells.
Experts recommend placing small containers of sand in the cages once a week. In them, birds will be able to clean their feathers. In addition, such sand baths will have a positive effect on their mood.
Young quails must be kept in separate cages. The size of the cage for chicks is much larger than for adults. This is necessary in order to place lamps for heating and lighting in them. In order for the chicks not to die of hunger, the lighting in the cages must be left on around the clock for the first 21 days of their life. So they can always find food.
Features of character and lifestyle


Photo: Male and female quail
Quails are peaceful birds that have no means of protection other than camouflage. In the springtime, they go to agricultural fields, where they feed on crops and dig up vegetables. On such a diet, birds quickly get fat, which is why they often die in flights. Birds prepare for flight when the air temperature begins to drop below zero degrees. By this time, the chicks have already grown stronger and have learned to fly, so the quails get lost in large shoals. But in regions where freezing temperatures prevail, quails can settle for whole years, although instinctively they are predisposed to flights.
Migration of birds can take several weeks - during such "marathons" only the strongest birds survive. For example, from Eastern Siberia, some species of quail fly to India for the winter, which takes them three and a half weeks. Towards the end of the warm season, quails flock into small flocks (sometimes these are whole families with chicks and polygamous parents) - this is how they warm up at night. From the southern regions of Russia, they fly away in September and closer to October.
Due to their weak wings and the constitution of the body that is not conducive to flight, they make frequent stops (unlike the same swallows or swifts).Because of this, birds become endangered by predators and hunters - by the end of the migration, about 30 percent of birds die. The tenacious paws of birds are especially necessary for them when searching for seeds and insects in the hard soil of central Russia. But they do not tolerate pollution of plumage, therefore, the daily "habits" of birds include cleaning feathers and cleansing their nest from unnecessary quarrels. In the same way, by cleaning the feathers, they get rid of cutaneous parasites.
Each female has its own nest - only males do not have it, since they are mainly busy on duty, looking for possible danger. The nest is a small hole in the ground, which birds dig with massive clawed paws. The hole is laid out with dry grass and branches.
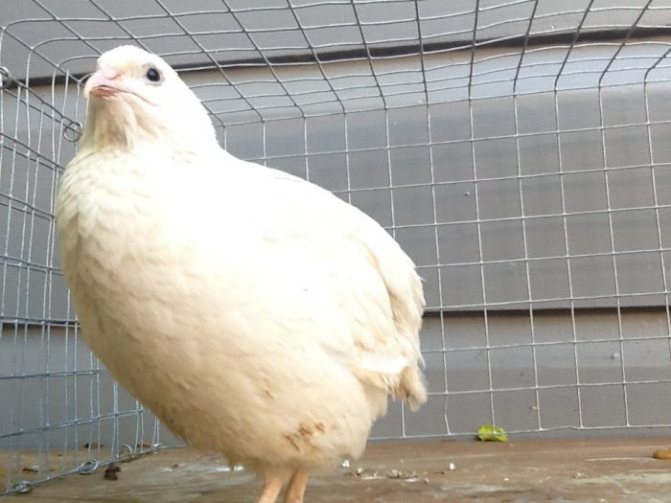
Texas quail: breed description
The Texas white quail is also called the American albino. It has white plumage and only on the head and back can there be small blotches of black color (Figure 9).
The main value of this breed is that it is used to obtain high-quality dietary meat. With a relatively low feed intake, birds gain weight quickly and do not require special housing conditions.
Care features
The unpretentiousness of the Texas quail made it one of the most popular among poultry farmers. For maintenance, standard cages are used, and for feeding, you can use almost any feed that is on the farm.
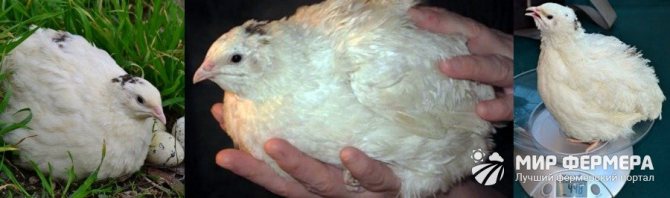

Figure 9. Meat productivity of Texas quails
Despite its moderation and unpretentiousness to feed, the Texas breed is characterized by rapid weight gain. Adult females can reach a weight of 400 grams, males are slightly smaller.
Characteristics
A distinctive characteristic is not only heavy weight and unusual white color, but also skin color. Most quails have dark plumage, so the skin has characteristic shades.
White Texas quails are special in that they have fair skin, which significantly increases the presentation and cost of carcasses.
Productivity
Like the other beef breed, the Pharaohs, white Texas quails, with a relatively large weight, have a low egg production. However, this does not diminish the value of the breed, since the eggs obtained from several females are sufficient both for eating and for raising young animals.
Social structure and reproduction


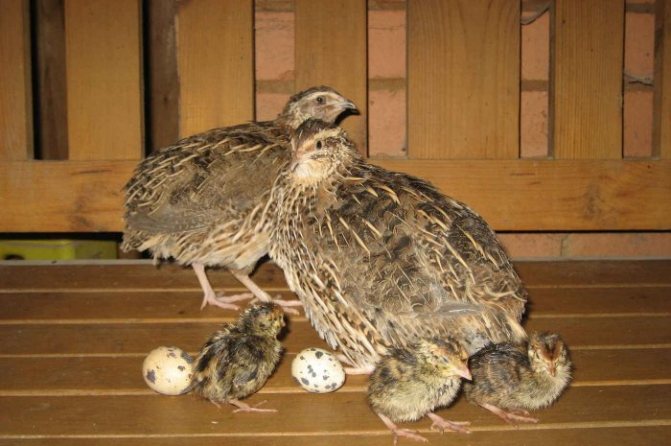
Photo: Quail chick
Birds nest in flocks of 15-20 individuals. This amount allows them to be more likely to avoid collisions with predators and survive during the onset of severe cold weather. They are mainly composed of a flock of females and several males, which fertilize several quails. In May or June, when the quails feel the increasing heat, their breeding season begins. Males look for partners and arrange fights, which can be expressed both in peaceful singing (the best "singer" will get the right to mate), and in fights that are fierce.
Interesting fact: Quail fights, along with cock fights, are popular with people, but they are not so bloody due to the lack of spurs on their paws.
Sexual maturity of the female occurs at the age of one year - this is quite late for rapidly developing birds, but the late age is compensated by the number of chicks that one quail can produce. The female digs the nest and equips it for future offspring. The nesting of a flock depends on how fertile the land is - often they are located near agricultural fields.
To arrange the nest, the quail uses not only branches and grass, but also its own fluff. A bird can lay up to 20 eggs at a time, which is a lot compared to chickens (three times more). The male does not take any part in caring for the female, but she does not leave the nest for two weeks, even in case of severe hunger and thirst. During the incubation period, females are most vulnerable to predators.
Chicks hatch independent and strong, already at the age of one and a half months they become full-fledged almost adult birds. From the first day they are looking for food on their own, they are able to escape from the predator. Mothers often form a kind of "nursery" in which a group of quails looks after a large brood.
The developed maternal instinct has given quail mothers one interesting feature that is observed in many sedentary birds (for example, pheasants and partridges). If a small predator such as a weasel or a fox appears nearby, the quail still leaves the nest, but pretends that its wing is injured. With short flights, it takes the predator away from the nest, then flies up high and returns to the clutch - the animal is left with nothing and loses its trail of prey.
Quail life in nature
These birds are partially migratory. In countries with a mild climate, they remain all year round, in regions with severe winters, they migrate to warmer places. Usually the mating season for quails begins in May - June. Getting to the nesting sites, the birds begin to do everything possible to attract a mate. Throughout the year, quails lead a secretive lifestyle, but in the spring everything changes. Males begin courtship. They begin to scream loudly, expressing their willingness to fight for their partners. As a rule, such a show of force ends with its use. In this case, 2 males begin to fight until 1 of them retreats. The victorious male is eliminated from further courtship games and mates with only 1 partner. He does not participate in raising chicks.


In countries with a mild climate, they remain all year round, in regions with severe winters, they migrate to warmer places.
The fertilized female immediately proceeds to arrange the nest right on the ground. First, she digs out a small bowl-shaped depression. Further, the female carefully covers it with grass. Thus, a neat little nest is formed. Usually, females choose places in dense vegetation, where they and the brood will be less visible to predators. Usually a quail bird lays 9-10 eggs, but sometimes there are up to 20 eggs. Their shells are brown-speckled, which makes them almost invisible on the ground.
Natural enemies of quail


Photo: Quail in nature
Quails are food for many predators of the forest and forest-steppe.
First of all, these are:
- foxes. They attack quail at night, when they are not able to evade the attack into dense grass. Foxes are one of the main enemies of quail, since it is they who predominantly maintain the population of these birds in the norm;
- wolves. These large predators rarely leave the forest zone, but during periods of famine they are able to hunt down quails. Although, due to their large size and sluggishness, wolves can rarely catch a nimble bird;
- ferrets, weasels, ermines, martens. Dexterous predators are the best hunters for these birds as they move as fast as quails. But most of all they are interested in chicks;
- falcons and hawks. They prefer to follow flocks of birds during seasonal migration, thus providing themselves with food for a long period of time;
- hamsters, gophers, other rodents. Quails themselves are not of interest to them, but they do not mind eating eggs, so sometimes they ruin the nests if they can get to the hatched eggs.
Natural enemies do not threaten the number of quails, which cannot be said about hunting, since because of it the species of an ordinary quail could disappear.
Common wild quail
Common quail inhabits vast areas. She lives in Europe, Asia up to Lake Baikal, West Africa. This bird prefers to settle in fields and open spaces where there are tall grass and bushes. Quails almost do not fly, they lead a terrestrial life.But from the northern regions for the winter, this species flies to the south. When agriculture began to develop, quails moved closer to man and his crops.
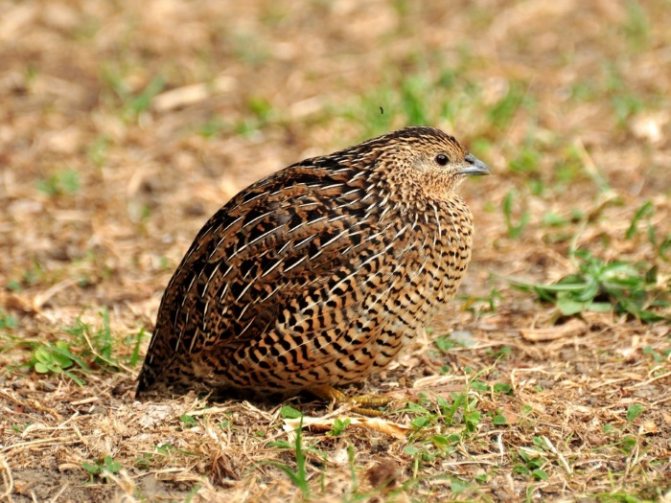
The appearance of the quail is not remarkable at all. This is a small wild bird with camouflage plumage that runs very fast, hiding from enemies. Here is a brief description of the common quail and its biological characteristics:
- The body length is 16-20 cm.
- The mass of the bird is 80-145 g.
- The wingspan is 32-35 cm.
- The body is compact, set at a slight angle to the surface of the earth.
- The head is small, without a comb.
- The beak is strong, slightly elongated.
- Quail feathers in ocher shade.
- A pattern in the form of dark brown transverse stripes and specks covers the back of the head, neck, back, covering feathers of the tail.
- The male has red cheeks and chin, a black neck.
- The female has a throat and cheeks of light ocher color, sometimes almost white, black and white specks (streaks) are present on the goiter and on the sides of the body.
- The male has a beautiful voice, he makes an original low sound.
You can see the appearance of birds in more detail in photos and videos. The number of wild quails is constantly decreasing. The main reason now is not fishing and hunting, since the species is under protection. The fields and steppes, where quails are used to living, are intensively developed with the use of heavy equipment, the area of land developed by man is growing. Crops are treated with mineral fertilizers, herbicides and pesticides. Birds die from poisoning wounds, falling under cars and for many other reasons.
Keeping in captivity
Involuntary features
Common wild quails get along well in captivity. The only thing is that no one keeps them until 5-6 years. After 1-2 years of life, quails bring fewer eggs, and males fertilize them worse.
The quail begins to rush in 1.5 months after birth. Up to 300 eggs are obtained from one layer per year. They are valued for their nutritional composition enriched with vitamins and minerals.
They began to breed common quails at home in ancient China. Next, the trend moved to Japan, where they found out the benefits of quail eggs and meat.
In addition to the edible properties of quail eggs and poultry meat, its manure is used as a fertilizer rich in nitrates. Some internal organs and bone cells of common quails have found use as a component of Asian medicine.
Common quails feed on what they eat in nature.


Optimal temperature conditions
As a heat-loving bird, the quail loves temperatures from 18 to 25 degrees. At lower rates, he may die, high rates - he will begin to lose plumage.
The number of eggs dispensed and the weight of an ordinary quail depend on the comfortable temperature.
It is imperative to provide ventilation of the room where wild quails live. This will help get rid of the ammonia that quail droppings give off.
Cell
To prevent the bird from flying around the house in different directions, it is closed in cages. Housing for common quails can be purchased ready-made or designed on your own. The last option is considered in the article "Building a cage for quails with our own hands."
Any type of cage must meet the requirements:
- height - at least 20 centimeters;
- it is recommended to cover the top with a soft cloth - it will protect shy quails from injuries that they can get when jumping during danger;
- the floor of the cage is made with a slight slope at one angle, where the eggs roll as a result.
The size of the cage depends on the number of birds. It is calculated according to the principle: for every 10 quails - 0.2 square meters. For ordinary quails raised for meat, the cage is made a little larger.


Lighting
The activity of common quails is associated with the length of daylight hours. For them, it is necessary to organize a regime of light and darkness.
Wild quails sleep about 4 hours a day.But it is impractical to do the night mode for this period, since the birds will wake up hungry and eat more food than the norm. This can cause the goiter to stop working. It is better to break the night cycle into parts of 2 hours each with the same break between them.
There is no need to illuminate ordinary quails with strong streams of light. For a cell with an area of 40 by 100 centimeters, one 40 W light bulb is enough.





































