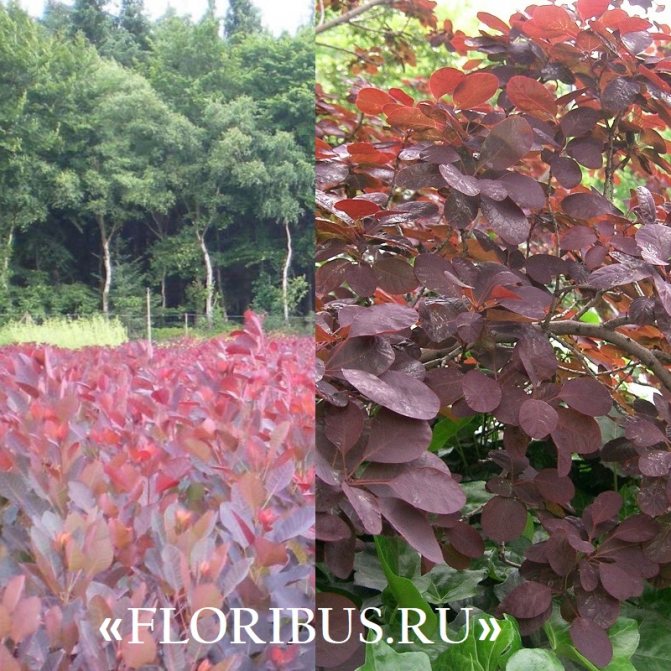
A dandelion tree, a bush in a wig - this amazing plant is not called for its outlandish appearance, which it changes throughout the entire calendar year. The catchy decorativeness and high aestheticism of the scumpia have earned the love of the designers of park and garden landscaping. An additional trump card of this decorative leafy crop is the ease of cultivation. Scumpia is not capricious, planting and caring for her is usually straightforward. Let's talk about how to properly organize this process.
What is scumpia and how does it grow

Skumpia tannery belongs to the perennial deciduous plants of the Anacardia family, or Sumach. This crop is a branchy shrub or tree, the height of which ranges from 1.5 to 5 m, depending on the variety. In the wild, scumpia is common in South Asia, Western Europe, India and China. It is also found in Russia, in particular, on the lands of the Voronezh and Rostov regions. As a garden culture, this plant gained popularity in the 17th century. and since then has been actively used in perfumery, dyestuffs and leather production.
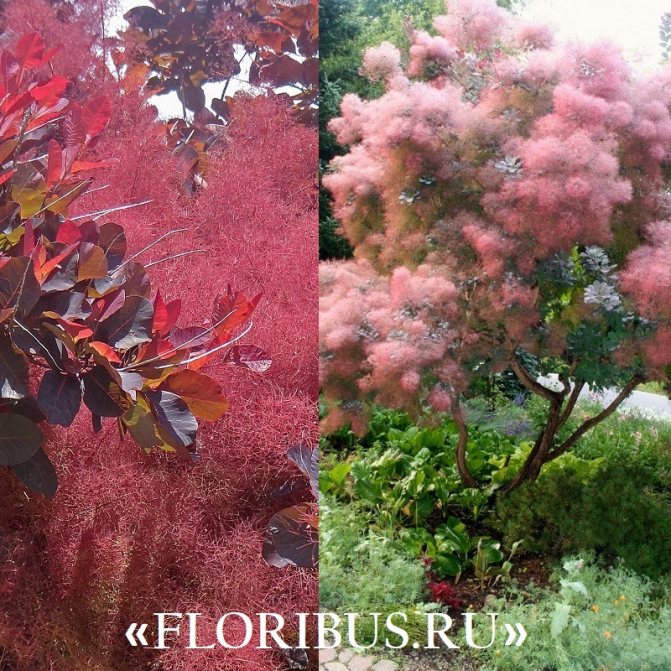
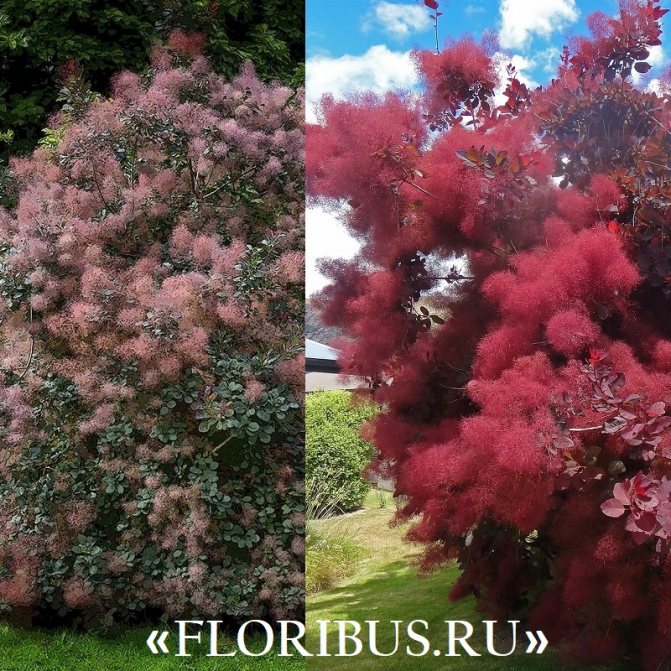
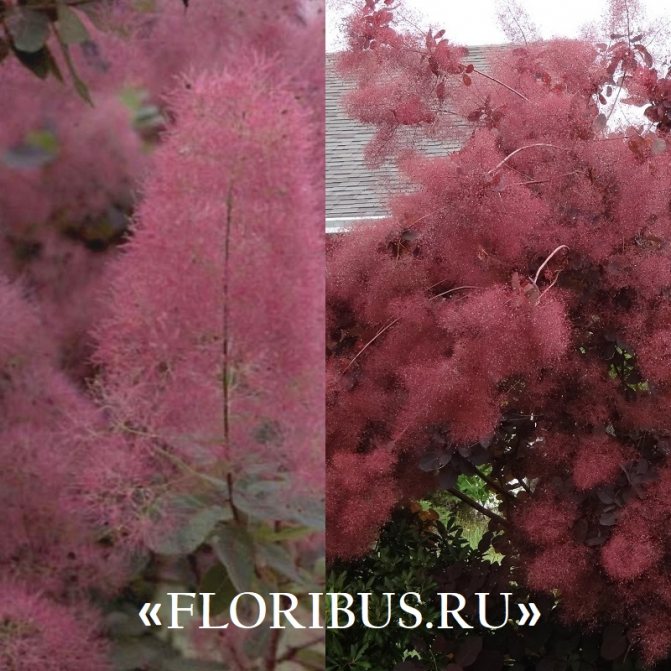
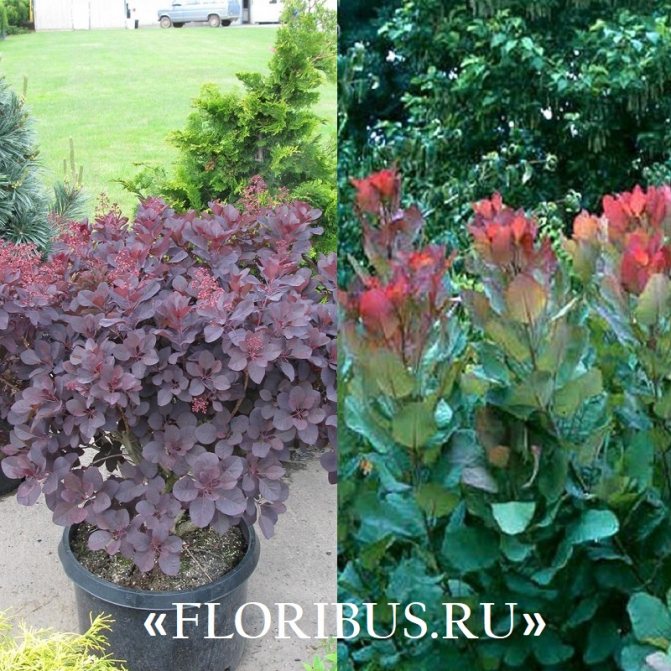
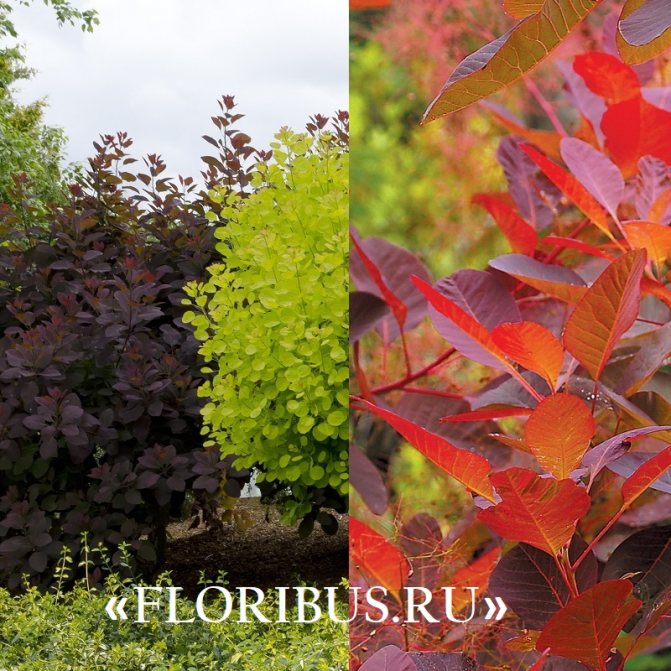
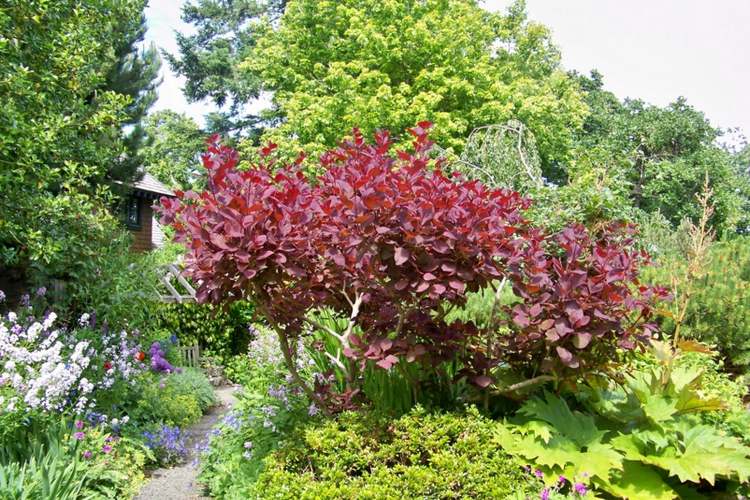
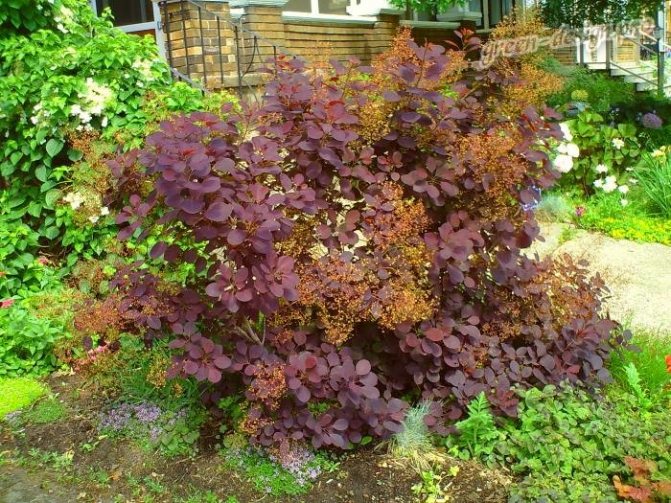
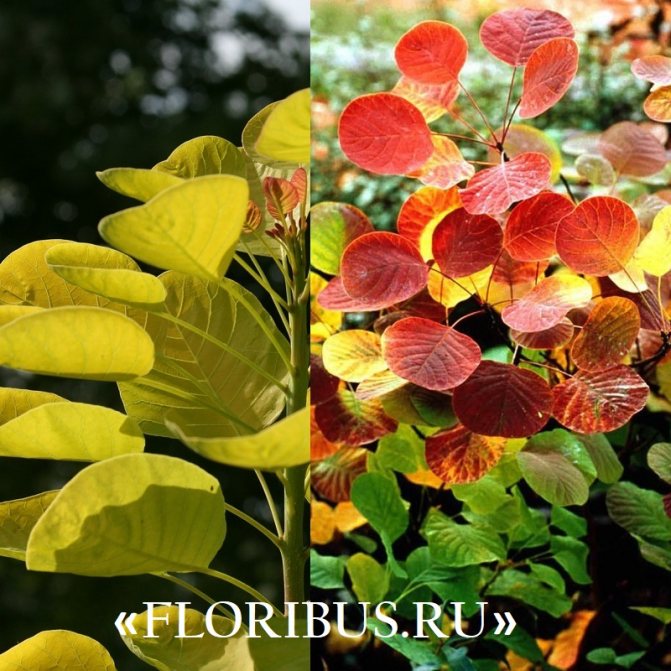
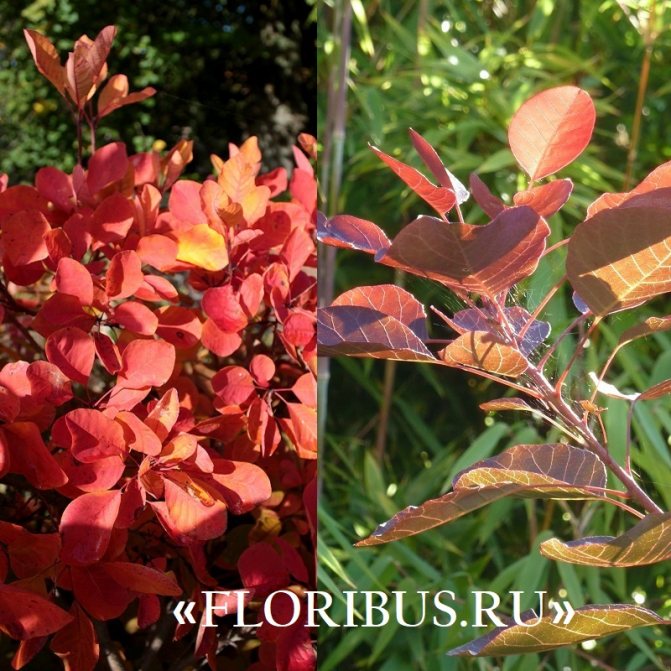
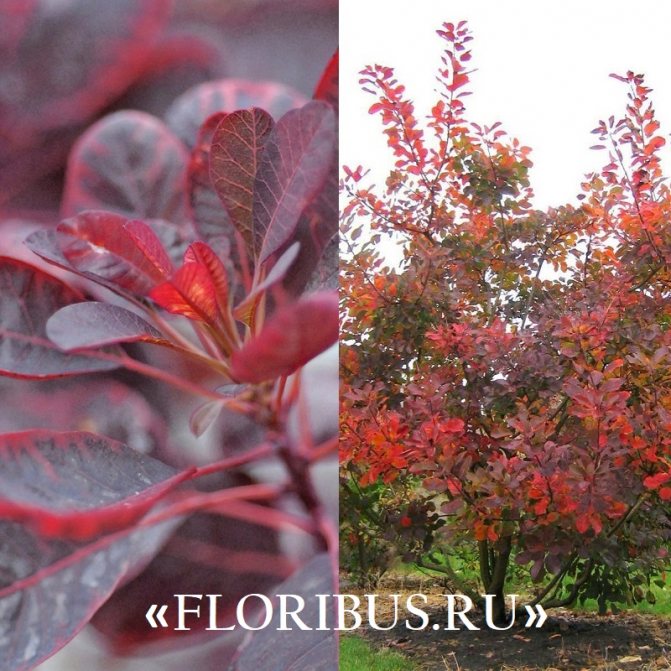
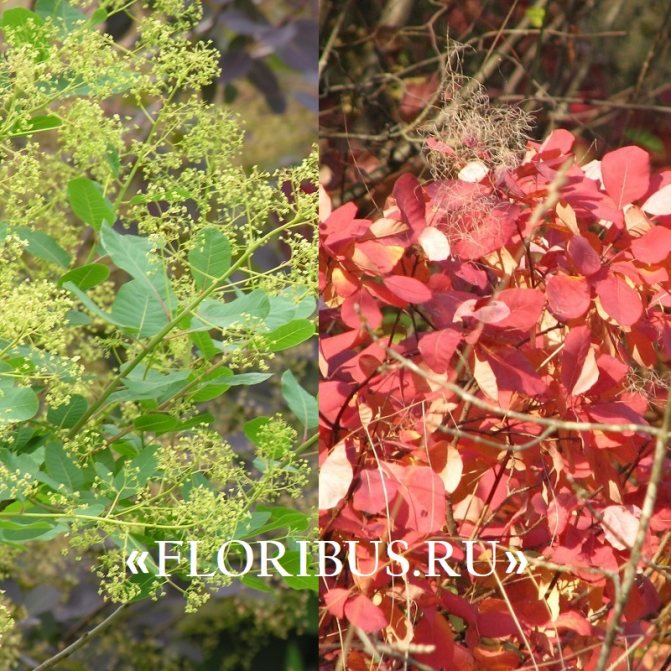
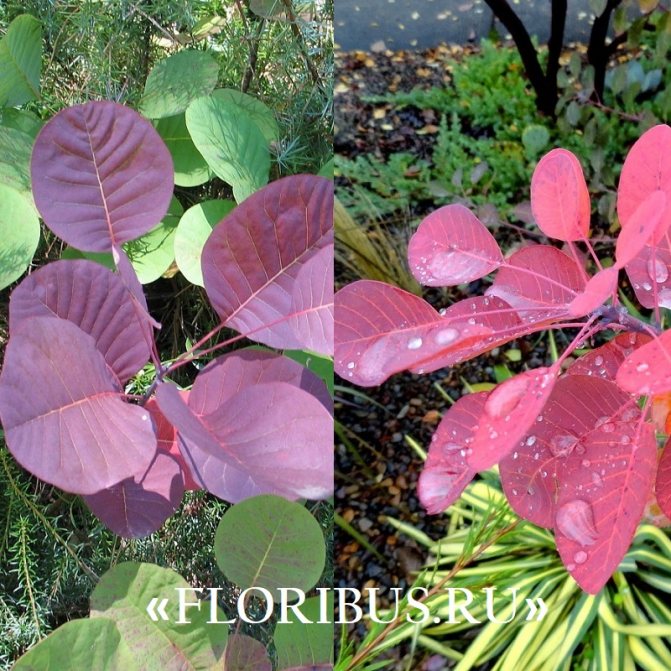
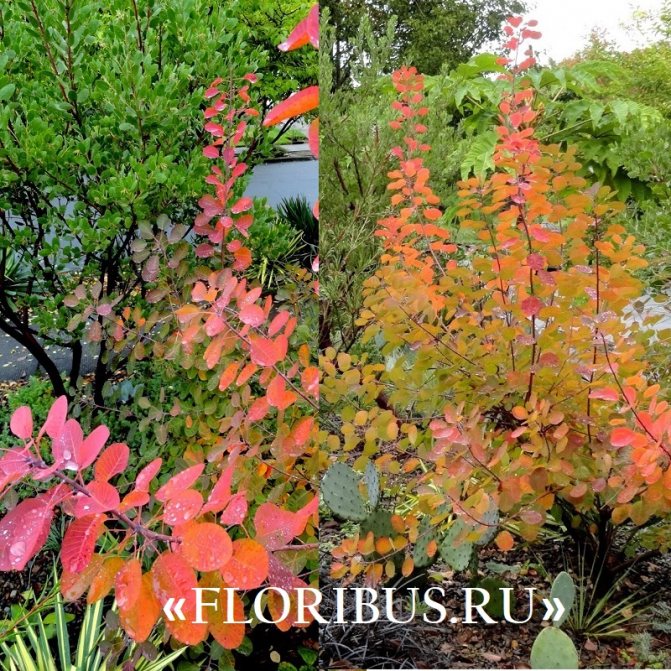
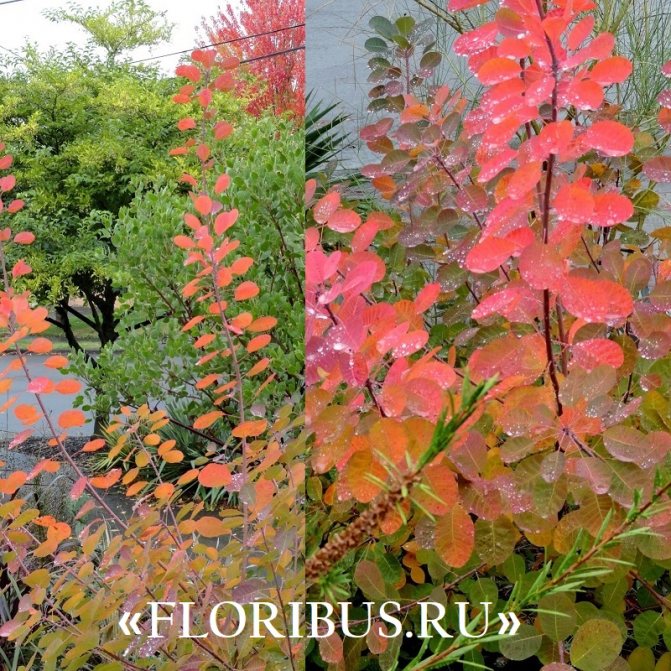
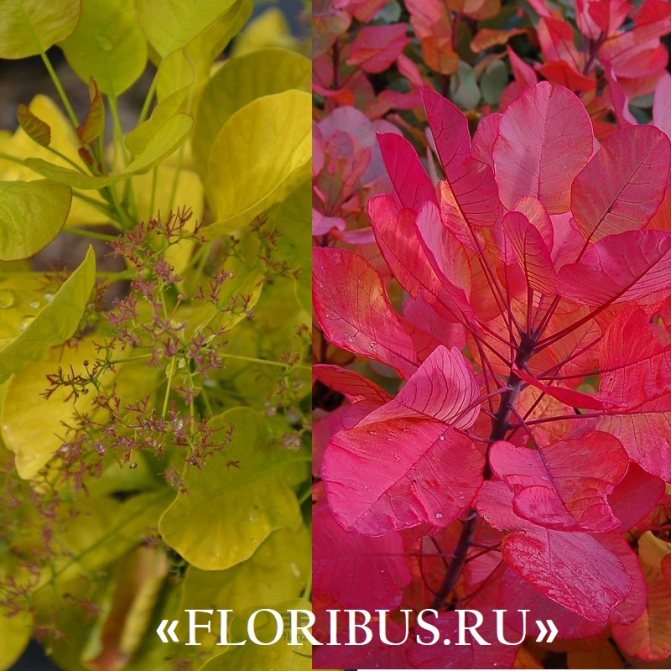
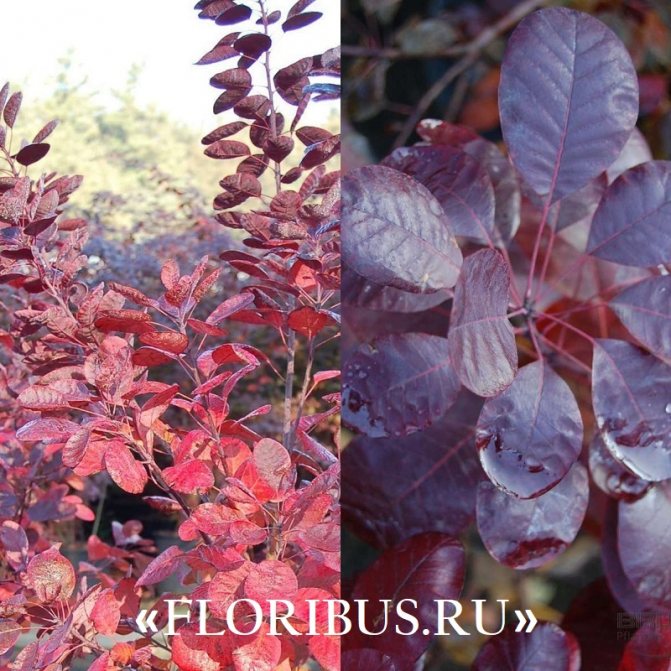
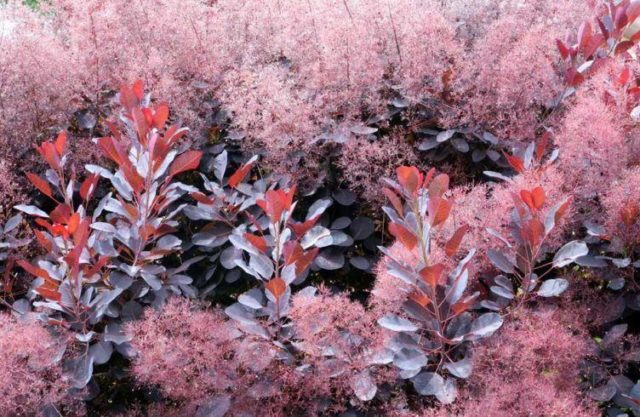
Gardeners appreciate the tanning skumpia, first of all, for its decorative effect. All types of this plant have a compact spherical or umbrella-shaped crown, which looks very advantageous on a personal plot. The leaves of the culture, bright green or dark purple in summer, attract the eye with a rich palette of colors in autumn, acquiring red, crimson and orange hues. This property of the yellowberry, as well as its unusual flowering, make it a very popular crop in landscape design.
How scumpia blooms


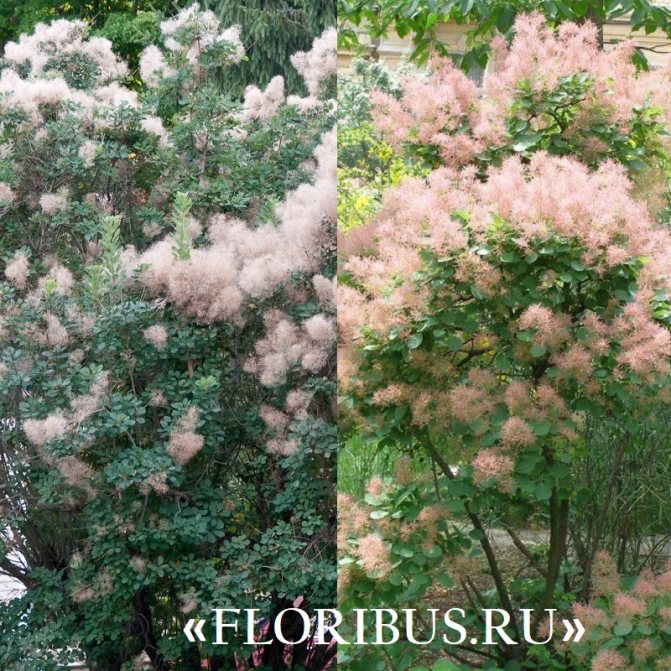
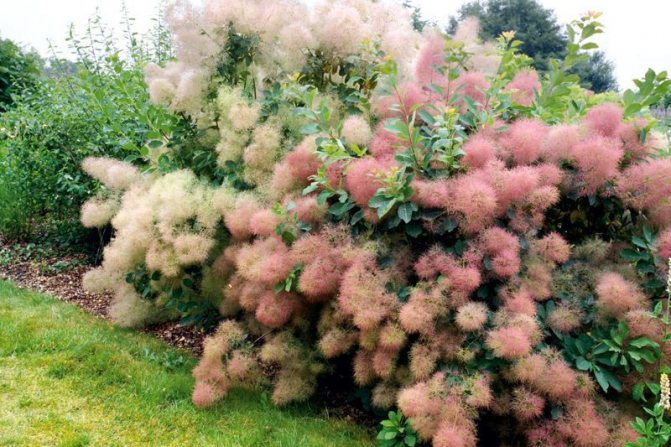
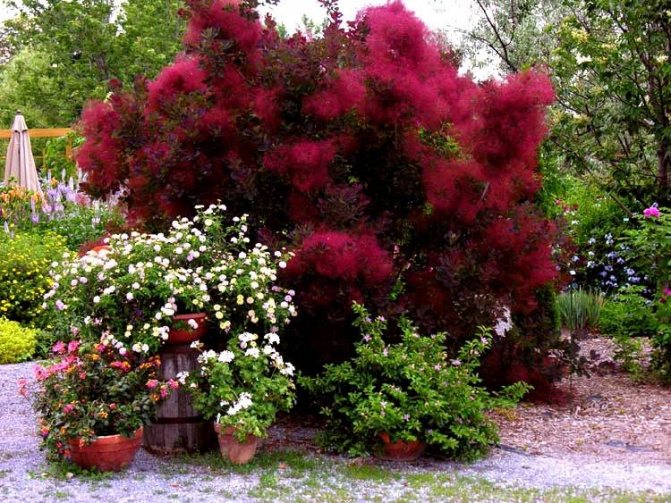
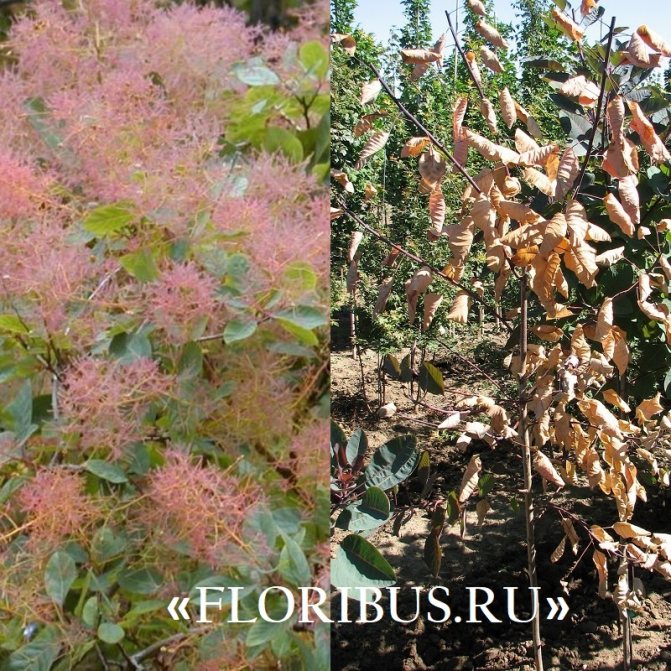
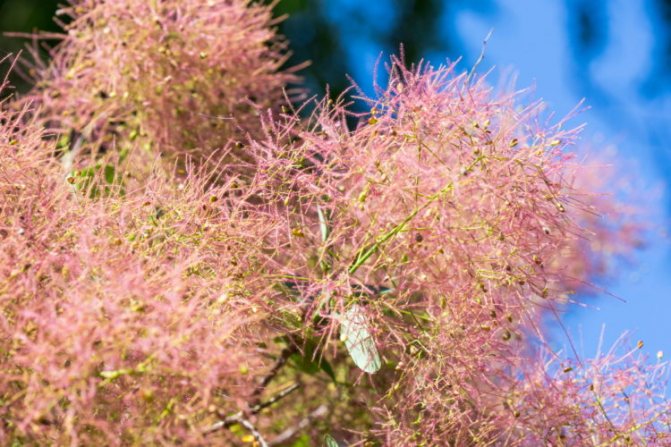
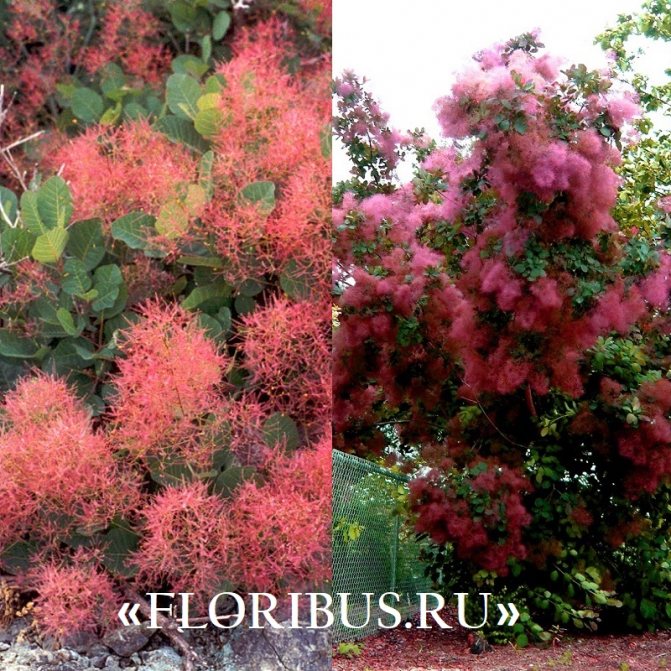
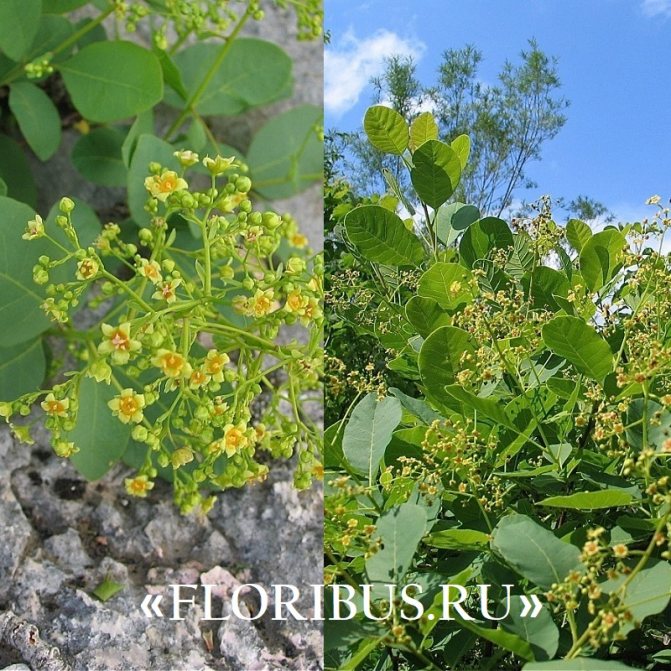
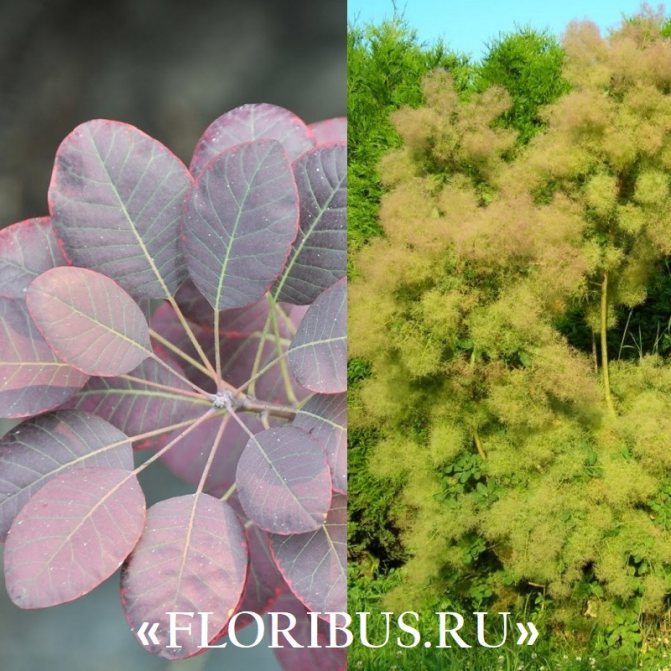
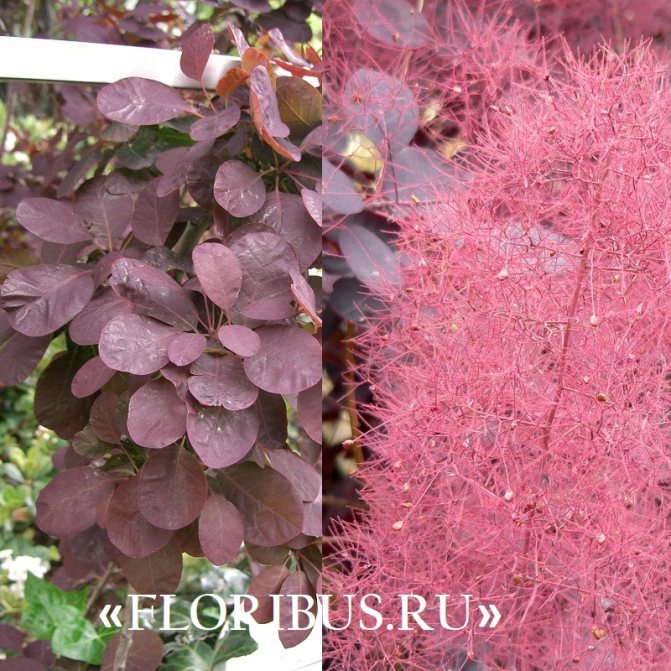
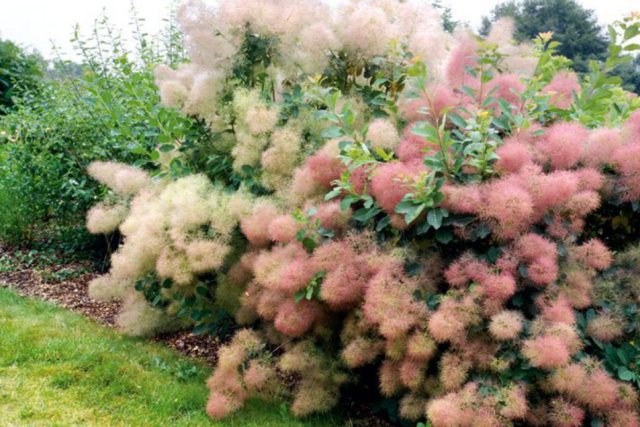
Many plant lovers prefer leather skumpia because of its spectacular flowering. In late May - early June, the culture is densely covered with paniculate inflorescences 15 to 30 cm long, consisting of small flowers of burgundy, white, greenish or pale pink flowers. The airiness and delicate color of the scumpia inflorescences, such as in the photo above, give the impression that the shrub is shrouded in haze. For this reason, the plant got its English name - "smoke tree", or "smoky tree". The Russian-speaking population calls the leather skumpia a "wig tree", as a flowering shrub evokes associations with a lush wig.
How fast the scumpia grows
Skumpia tannery lives in its natural habitat for about 100 years. The impressive lifespan of this plant is combined with rapid growth. Since the yellowberry has a powerful superficial root system, it has a peculiarity in a short time to grow violently in breadth, therefore, already by the 2nd - 3rd year of cultivation, you can count on getting a beautiful ornamental shrub. But scumpia begins to bloom much later, at 6 - 8 years old, when it reaches maturity. By this time, the plant slows down its growth somewhat, which makes it much easier to maintain its shape.
Winter hardiness of leather skumpia
Winter hardiness of tanning skumpia often becomes the reason why breeders refuse to cultivate this plant in their plots.The fact is that young shrubs and scumpia trees tolerate low temperatures very poorly and can die during the first stable frosts, if you do not worry about their shelter in time. This is especially true for imported seedlings. Specimens grown in the same country where the planting will subsequently be carried out are less sensitive to frost, but it is not always possible to find such in central Russia.
At the same time, seedlings 3 - 5 years old have a fairly high frost resistance and quite successfully winter in cold regions with minimal cover at temperatures down to -15 ° C. Winter-hardy varieties can boast even greater endurance and, when properly protected, thrive in colder climates. So, among connoisseurs of scumpia, there are gardeners who have experience in growing this plant in the Urals and in other areas with similar weather conditions. Such varieties of leather skumpia as Young Lady or Grace not only do not suffer from the Ural winter frosts, but also retain their aesthetic appearance in the summer.
Is the scumpia poisonous or not


Skumpia leather itself is not poisonous, however, the leaves of this culture contain large quantities of essential oils and tannins, which in large doses can be toxic. Untreated yellow leaf plates are not recommended for people to eat, as this can provoke poisoning. In addition, if possible, you should limit the access of pets to the bush, otherwise an inadvertently swallowed sheet of leather skumpia can lead to death of the pet.
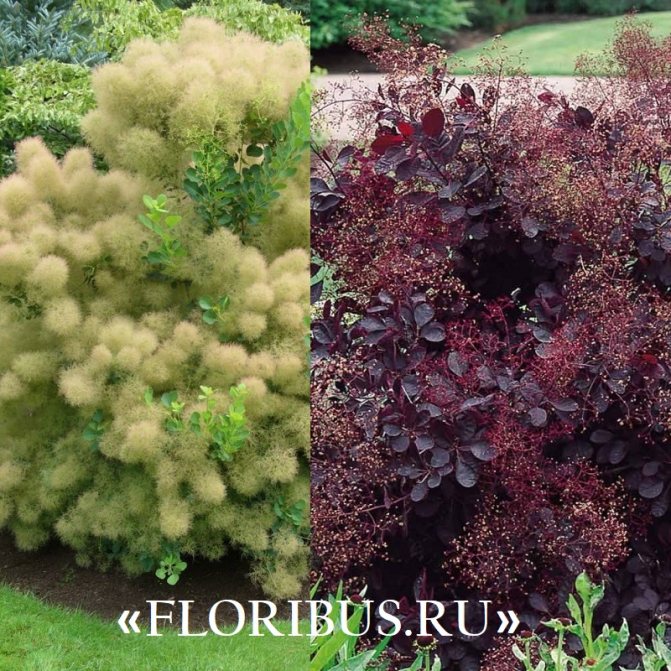
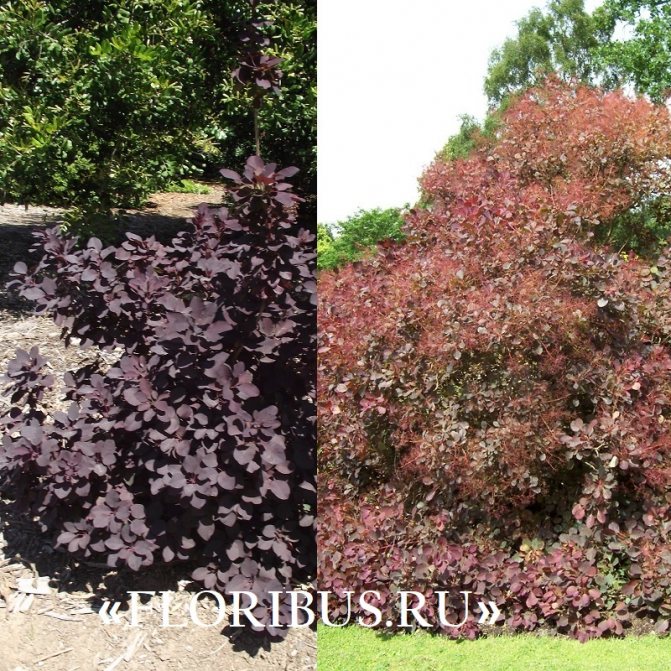
Types and varieties of scumpia with a photo
The beauty of the tanning skumpia has inspired many breeders to experiment, thanks to which new varieties of this unusual plant appear with enviable frequency. Below are descriptions of the most common types of leather skumpia and their photos.
Golden Spirit
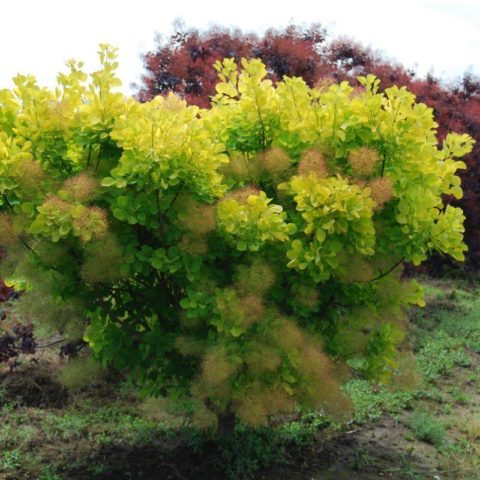


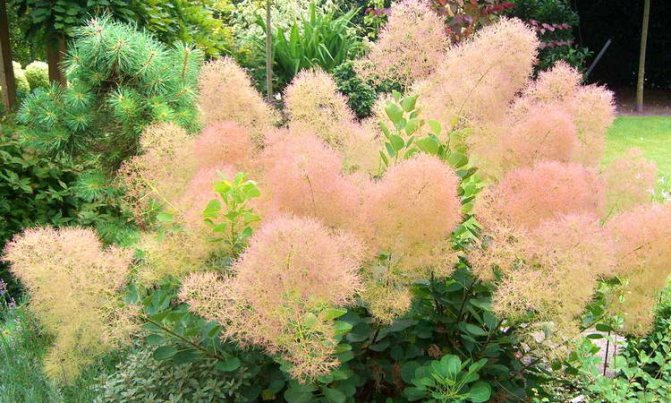
This variety, reaching 2 m in height, owes its high decorative effect to its golden-green leaves. In clear weather, the sun's rays passing through the leaf plates give the shrub a glowing effect, which is why Golden Spirit is happy to grow even in cold regions. Despite not too high winter hardiness, the culture is quite capable of surviving the frosts of central Russia with proper shelter.
Young Lady


The Yang Lady variety is considered the least whimsical of all known varieties. In addition to its luxurious appearance and lush flowering, during which the shrub seems to drown in the dawn fog, the variety has an enviable frost resistance, which makes it possible to plant and leave the leather skumpia, including in the Urals and Siberia.
Grace


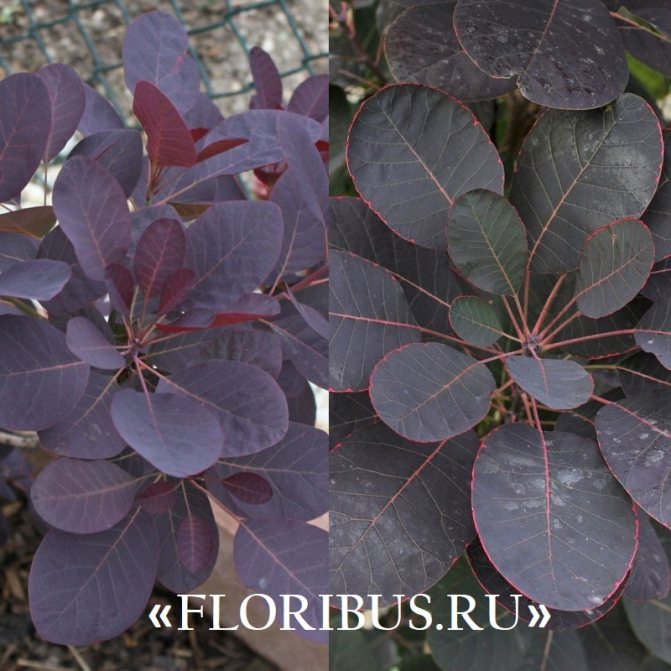
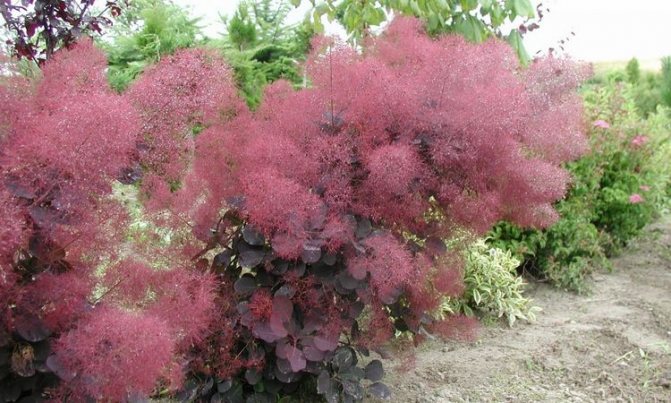
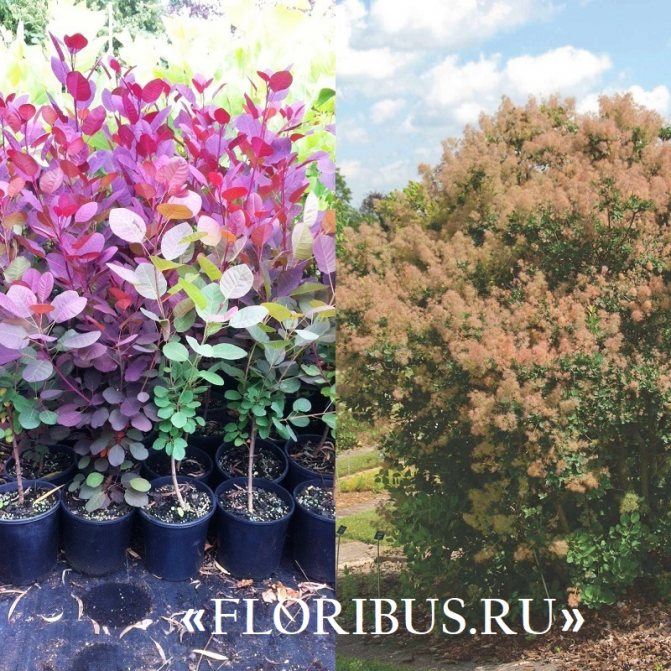
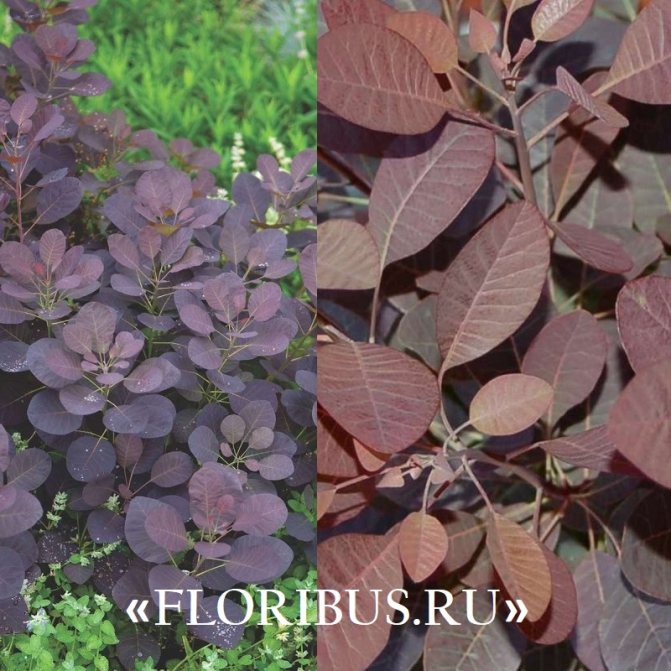
This shrub 2.5 -3 m immediately catches the eye with its dark purple foliage, which in autumn is complemented by shades of scarlet, orange and crimson. The plant blooms with airy inflorescences of burgundy color.
Velvet Cloak


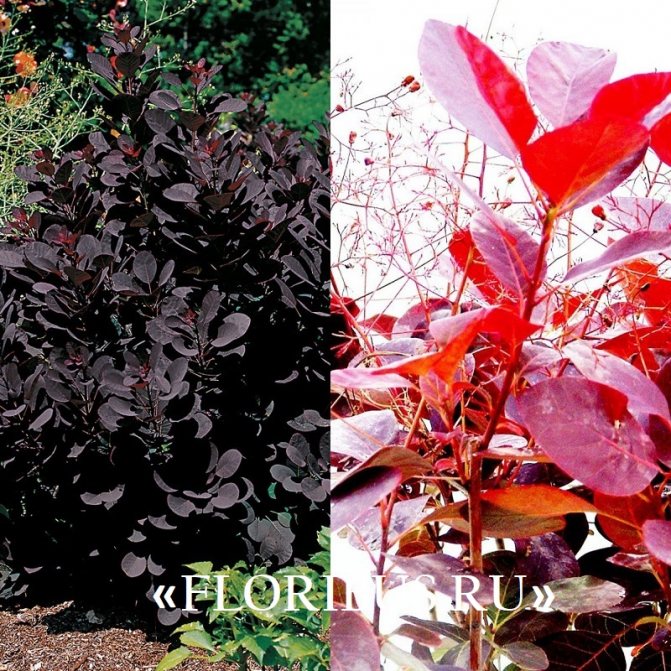
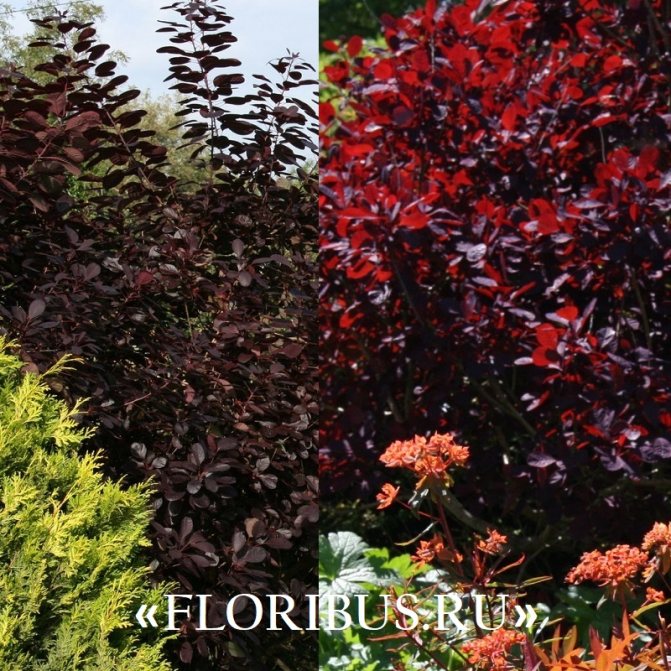
No less attractive to the eye is the Velvet Cloak variety of leather skumpia, which is remembered for its relatively small size - from 1 to 1.5 m - and blue-violet, almost black leaf plates. The inflorescences of these plants are dark pink in color.
Royal Purple


The leather variety Royal Pearl, popular among connoisseurs of scumpia, dates the shrub to a height of up to 2 - 3 m and a compact silhouette with dark purple leaves and crimson sultans of inflorescences. The culture does not tolerate frost and in cold dry winters tends to freeze to the root collar.
Botanical description
Scumpia is a shrub or tree with a spreading crown. The height of the plant is from 1.5 m to 5 m, the crown can be 1.5 m in diameter.
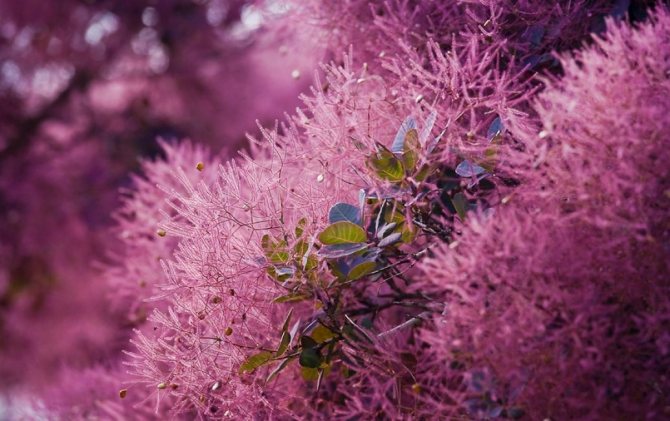


Fizegin is obtained from scumpia - an orange or yellow dye for silk, wool, leather
Scoopies are centenarians... Branching of the shoots begins at the very ground, the young bark eventually acquires a gray or reddish-green hue. Gradually, the bark flakes off. If you accidentally damage the shoot of the plant, milky sap will be released.
Rounded or oval leaves of the plant form a dense, broadly oval crown. Alternately growing leaves, 5-7 cm long, are attached to the shoots with long petioles. The leaves have a glossy sheen, whole or slightly serrate along the edge.
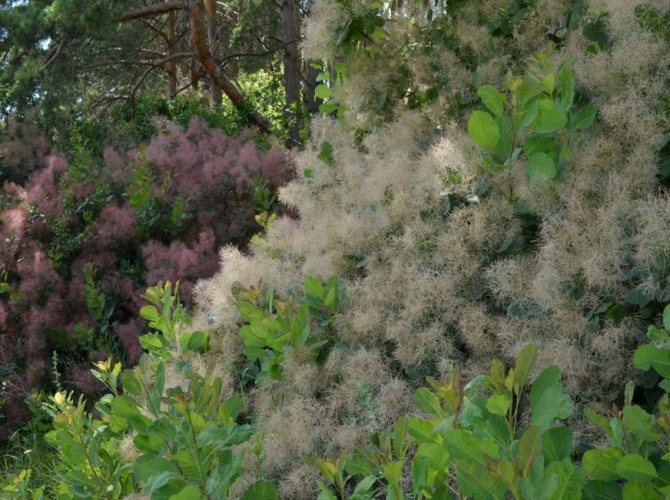


Different types of scumpia in natural conditions of growth
Depending on the type of foliage, it can be red or dark green, by autumn it acquires an orange, yellow, purple or crimson hue.
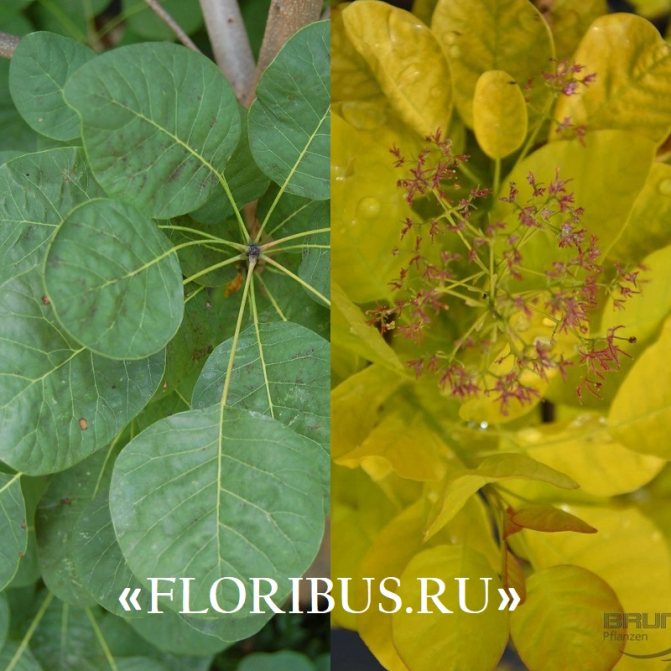
At the end of May or in the first decade of June, last year's shoots are covered with long, numerous inflorescences in the form of a panicle. They are formed by yellow flowers with a green tint. Corolla includes short, underdeveloped petals with a bunch of long stamens.
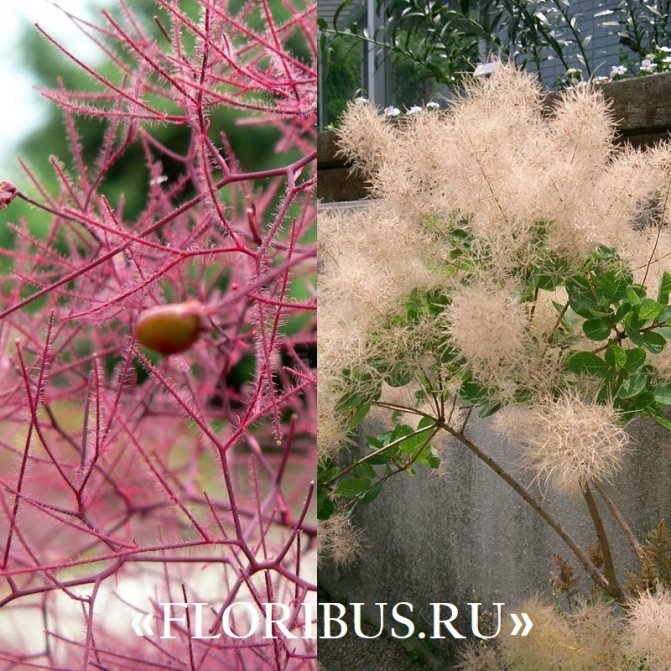
Long, fleecy pedicels, which cover the entire bush with a cloud after flowering, give the bush decorativeness.
The fruits ripen in late July, early August. Oblong drupe-fruits are black in color and practically without pulp.
back to menu ↑
See also: Euonymus: Description of the plant, species and varieties, cultivation, planting in the open ground and care, reproduction (65+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
The use of leather skumpia in landscape design
Looking at the neat silhouette of the tanning skumpia, we can say with confidence that this plant was simply created to decorate gardens, parks and green areas. Both shrubs and treelike varieties of zheltinnik look appropriate in gardens of different styles. Sumpies stand out very effectively in contrast to conifers and surrounded by other deciduous perennials. Often, different varieties of these plants are planted in groups against the background of mixborders: in this form, they not only do not overshadow each other, but, on the contrary, complement the composition.
Leather skumpies also look beneficial in single plantings, in particular, in zones that imitate the natural growing environment of these plants. For this reason, zheltinnik shrubs fit especially organically into the atmosphere of rocky gardens, coniferous rockeries and rock gardens.
Important! In addition to aesthetic purposes, detached plants are used to anchor elevations and areas that are prone to erosion.
Below are photos showing the tanning skumpia in landscape design.
Interesting information for gardeners about the scumpia


Although the "smoky tree" is mainly grown as an ornamental crop, its foliage has long been used to obtain tannins and substances derived from them. These derivatives are used in the chemical and textile industry. Deciduous pulp is used for tanning leather. "Fustik" or "yellow sandalwood" is the name given to wood of a greenish-yellow color scheme by cabinetmakers; it is used in crafts and in the manufacture of musical instruments. "Fisetin" refers to a dye obtained from scumpia, which is used in robots to dye woolen and silk fabrics, giving them shades of yellow and orange.
Foliage and branches contain a large amount of highly active substances, among which are tannin and flavonoids, essential oils and tannins, and many organic acids are also found there. These parts of the scumpia are usually brewed. The prepared broth can be used for compresses and lotions, added to baths to relieve irritation on the skin, treat ulcers and eliminate abscesses. If you rinse the mouth with such a means, then a significant decrease in inflammation of the gums and bleeding from them is noticed, the symptoms of periodontitis and gingivitis will be eliminated.If there are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as poisoning or intestinal upset, then the broth is prescribed to be taken orally, it will also help with pneumonia.
Scumpia is also used in official pharmacology, for the manufacture of certain medicines, which include tannin. These drugs are astringent and can reduce inflammation and fight germs. For cosmetic purposes, due to the fact that the bark can turn yellow, it can be used instead of henna.
The healing properties of scumpia
In addition to its decorative effect, tanning skumpia has a number of medicinal properties. Tannins in its composition, as well as flavonoids and essential oils provide the plant with the following properties:
- wound healing;
- antibacterial;
- choleretic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- expectorant.
Almost all parts of the yellowberry, including leaves, young shoots and roots, are used in folk medicine for the preparation of drugs for a wide range of diseases. According to the reviews of connoisseurs of alternative methods of treatment, lotions from the infusion of leather skumpia help with burns, bedsores and wounds, and foot baths - with increased sweating. Inside, the infusion is taken for food poisoning, disorders of the intestinal microflora and intoxication with salts of heavy metals.
Important! Means made from leather skumpia have contraindications, therefore, before using them, you should consult with a qualified representative of traditional medicine.
Reproduction of leather skumpia
Reproduction of tanning skumpia is carried out using seeds or vegetative methods, which include:
- cuttings;
- reproduction by layering;
- division of the bush.
Important! The latter method is rarely practiced due to the risk of damage to the root system of the plant and not very successful survival.
The choice of the optimal breeding method for tanning skumpia depends on weather conditions, soil quality and other environmental factors. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages, which should be considered before carrying out the procedure.
How to propagate scumpia by cuttings
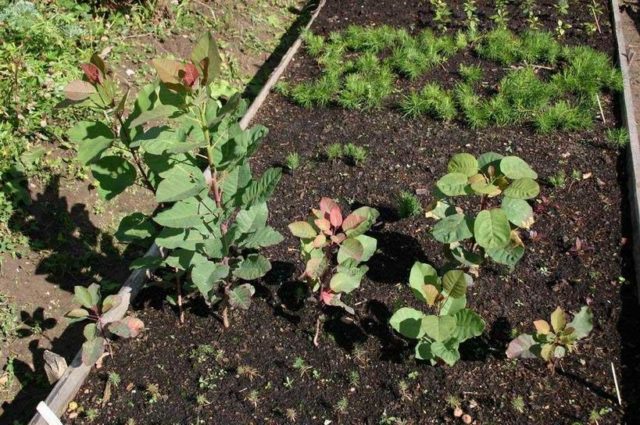


Reproduction of leather skumpia by cuttings gives good results if you know the nuances of this cultivation method:
- Planting material is prepared at the end of June - early July.
- Before planting, the cuttings are soaked in a solution of heteroauxin for 12 hours. The solution is prepared at the rate of 20 mg of the product per 1 liter of water.
- After that, the cuttings are planted in a summer greenhouse or cuttings in prepared soil of peat, turf and sand in a ratio of 1: 1: 1.
- To increase the chances of rooting, the soil under the seedlings must be kept moist. The ideal watering interval is 20 minutes.
Under such conditions, the first roots of the tanning skumpia will appear after 3 - 4 weeks. After that, you can think about transplanting the plant into open ground.
Important! With this method of reproduction, about 30 - 40% of the planted plants take root.
Layers
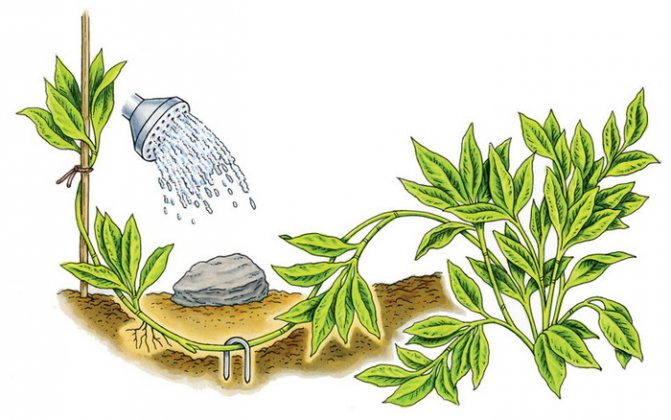
A higher percentage of rooting is observed in scumpies obtained with the help of cuttings. This breeding method is also considered the least labor intensive. To implement it, they are guided by the following actions:
- On a tanning skumpia bush, a healthy lower branch is selected and the bark is incised on its outer side.
- The branch is tilted to the ground so that the incision in the bark touches the soil, fix it at this level and sprinkle it with soil.
- The place of attachment is regularly watered until young shoots and roots appear on the branches.
- As soon as rooting occurs, the branch is cut from the mother plant and planted in open ground.
Seeds
Reproduction of tanning skumpia using seeds requires some experience and skill. The seeds of the plant have a very dense shell and germinate with great difficulty without certain manipulations.So, before planting in spring, they need to be stratified for 5 - 6 months at a temperature of 3 - 5 ° C. If planting is carried out in the fall, it is not necessary to additionally withstand the seeds, since wintering in the ground will successfully replace this procedure.
Advice! It is possible to accelerate the germination of leather skumpia and reduce the stratification time by 2 - 3 months if the seeds are soaked in concentrated sulfuric acid for 20 minutes.
Seeds are sown at a depth of 2 cm, while the autumn seedlings are not covered for the winter. The first shoots will appear a year after planting, moreover, the germination rate of seeds planted directly into the ground is several times higher than that of those that germinated at home
Planting and caring for the skumpia outdoors


Skumpia is not a very pretentious shrub that will feel good enough in almost any climate and on any soil, if you follow certain requirements for planting and caring for it.
Timing
Spring is considered the optimal time for planting tanning skumpia, however, if the seedling has a closed root system, then it is placed in the ground at any time of the year, except for winter. The only condition that should be remembered when planning a planting: the plant needs 2 - 3 weeks for rooting before the cold weather comes. Otherwise, the roots of the yellowberry will freeze and it will die.
Leather skumpia seeds are often sown in early spring, but early autumn is also suitable for this. In this case, after the procedure, seedlings germinate only the next year, regardless of when the plant was planted.
Site selection and soil preparation
As a thermophilic crop, the tanning skumpia prefers well-lit areas, so it is worth choosing a place for it with a lot of sun. The shrub growing area should be protected from drafts and away from tall trees that provide abundant shade.
Advice! It is not recommended to plant the yellowberry in the vicinity of holly and ash-leaved maples, thorns, black poplar, robinia, Amur velvet and some other plants, since the scumpia releases organic compounds into the soil that are toxic to these crops.
As for the soil, the tanning skumpia is rather unassuming to its composition, but acidic soils are not the best choice for this plant. Healthy growth and lush flowering of the shrub will be provided by slightly alkaline light soils with moderate moisture. If the planting site is located in a lowland or groundwater lies in its immediate vicinity, you should consider moving the plant to a more favorable zone.
How to plant a skumpia
The procedure for planting leather skumpia differs little from region to region and is carried out according to the following scheme:
- The recess for planting must be larger than the earthen coma of the plant.
- Before planting a seedling in open ground, soak it in water or Kornevin's solution.
- The planting hole should be watered generously using 2 buckets of water per hole.
- At the bottom of the recess, it is necessary to place a drainage layer with a height of 20 - 30 cm
- A small elevation should be poured over the drainage and a plant should be placed on it.
- After that, the planting hole must be covered with earth and carefully tamped
Important! It is not necessary to fertilize the pit before planting, since the tanning skumpia takes root better in soils in which there is no excess of nutrients.
Views
In nature, there are only 2 types of scumpia: common and American, and several varieties of this beautiful decorative leafy plant. The shrub cannot be attributed to whimsical plants, but it is advisable to follow the rules of planting and caring for it.
back to menu ↑
See also: Badan: description, types and varieties, planting and care in the open field, medicinal properties and contraindications (60+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Skumpia leather or ordinary
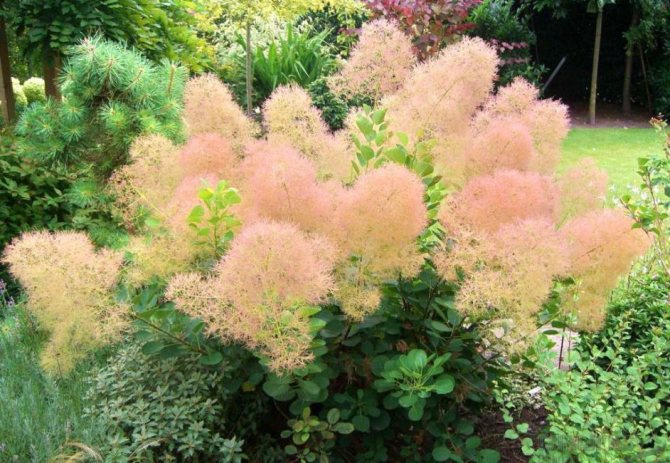


Skumpia leather or ordinary
- Sometimes the common scumpia is called juniper, due to their close proximity in nature. But this is not the case. This is a tall tree, reaching a height of 5 m. The crown is rounded, green or red foliage also has a rounded shape, another arrangement.
- The plots can be grown as a shrub. Varieties with green foliage are resistant to low temperatures, therefore they are recommended for growing in the middle lane.
- Red-leaved skumpies require shelter for the winter, otherwise they may die. In appearance, they are more attractive than their green counterparts.
back to menu ↑
See also: Magonia: holly, creeping, apollo, atropurpurea - edibility and usefulness, decorativeness, care, planting in open ground (115+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Scumpia American
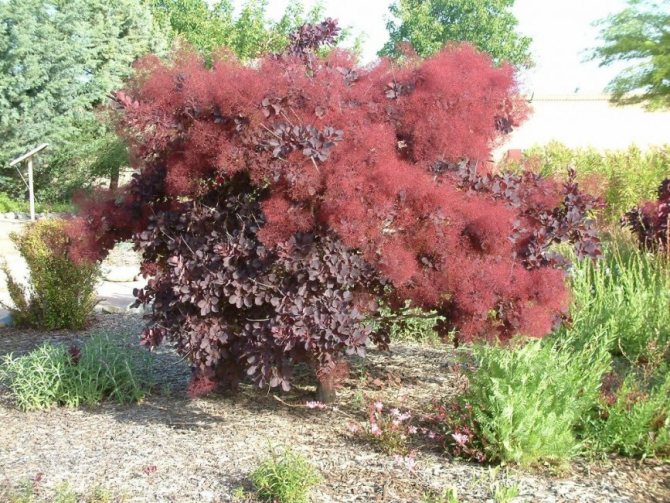


Scumpia American
- A tall plant with huge foliage in height can reach 5 m, but the inflorescences, in comparison with the common scumpia, are much smaller. The species is not considered frost-resistant, therefore it has not become widespread. The bushes are very beautiful, the view is unpretentious. By autumn, the foliage turns red.
- Some species of scumpia live more than 70 years, and some centenarians are over 100 years old.
back to menu ↑
See also: Bubbles: species, description of 18 popular varieties, planting and care (80+ Photos & Videos) + Reviews
Rules for growing scumpia
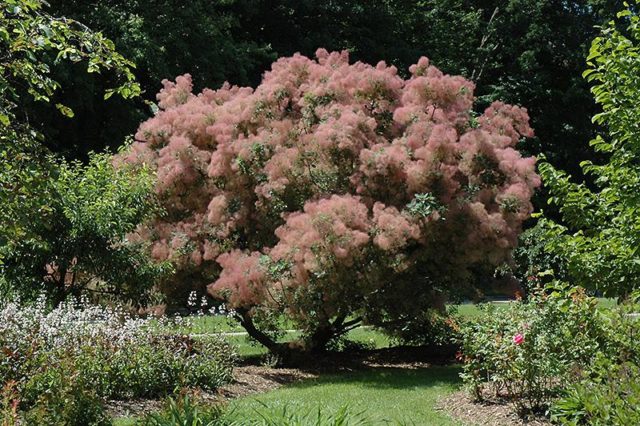


After planting, the tanning skumpia does not bother gardeners with too burdensome care and can delight with abundant, as in the photo, flowering with minimal watering, periodic pruning and feeding.
Watering
Skumpia tannery is a fairly drought-resistant plant, however, a prolonged lack of moisture negatively affects the growth and flowering of the shrub, so you should not ignore its timely watering. As a rule, the yellowberry is watered as needed, when the soil around the trunk circle dries out. In this case, water is poured as close to the base of the plant as possible so that moisture does not get on the leaves. You can reduce the frequency of watering by mulching the trunk circle, which is carried out in early spring. The mulch will help distribute water evenly and protect the roots from drying out during the dry season.
Top dressing
Although skumpia leather is quite capable of growing without any additional fertilizers, it responds well to feeding and actively uses the introduced nutrients to enhance flowering. Therefore, it will not be superfluous to apply complex mineral fertilizers to the plant in early spring, before the leaves appear: this way the shrub will recover faster after winter. In June, before flowering, the yellowberry can be fertilized again, this time replacing the phosphorus-potassium fertilizing with organic, for example, a solution of mullein or bird droppings. The plant does not need more frequent feedings.
How to prune a skumpia


Growing and caring for tanning skumpia involves periodical pruning of the plant, which is carried out every 2 to 3 years. As a rule, this is done in the spring, before leaves appear on the bush. In this case, a hygienic procedure aimed at removing frozen or old branches is combined with formative pruning. Annual shoots of a young yellowberry are cut off by 2/3 of the length - so the bush will become more luxuriant and form more branches. On older plants, branches can be safely cut to fit a stump. Scumpia will quickly recover from such pruning and will form a more compact spherical crown, and the leaves on it will be larger.
How to cover a leather skumpy for the winter
Although there are frost-resistant varieties among the varieties of tanning skumpia, the first few winters young plants need protective shelters. So, lutrasil or other non-woven material is suitable for warming the zheltinnik, which is wrapped with cling film for reliability.So that in the winter months the root system of the plant is not damaged by frost, it is worth mulching the shrub with peat or humus.
Advice! Instead of using plastic wrap, you can tie a leather skumpia with spruce branches under a non-woven material: this way the plant will be better provided with ventilation, and its branches will not freeze.
Leaves, flowers and fruits
The leaves are formed in April, and in early November (in some regions a little earlier) the veins begin to turn redder and the perennial is painted in shades from crimson to bright orange. By the way, it is in this organ of the plant that there is a dye that is used to dye cotton or silk, less often it is used in order to obtain natural yellow or orange skin. As for the red dye, it is contained in the roots and by the way, they are also quite branched and massive in structure.
Skumpia leather flowers can be seen in spring (early May). The plant does not bloom for long, usually until the end of June. At this time, inflorescences are formed, which are very small and can be yellow or green-white, as shown in the photo below:
By the way, it is important for gardeners to know that the tanning skumpia is a monoecious plant, that is, it is capable of self-pollination. Its flowers contain generative organs of both sexes, although some of them are completely asexual. Bees love nectar most of all, so it can often be found as a honey plant.
The inflorescences together form spreading panicles, no more than 30 cm long, after the scumpia fades, the peduncles are covered with long red hairs. This makes the shrub even more solemn and attractive. So it can be seen until the first frost.
After flowering, the tanning skumpia produces fruits of a green color and very similar to the buds of a plant. When they ripen, they are covered with brown streaks and become very dark themselves. Usually, gardeners and in natural conditions can see them from mid-August to the end of the month.
Common scumpia grows in almost all corners of the world where there is rocky soil. In Russia, it can often be seen as a specimen plant in parks and gardens. Wood is widely used to create musical instruments and for other purposes, as it is very lightweight, durable and does not rot in any climatic conditions.
Look at the common scumpia in the photo, which demonstrate the unusual appearance of the shrub:
Why scumpia does not bloom: causes and possibilities of elimination


It so happens that when cultivating skumpia tanning gardeners are faced with a situation where the shrub refuses to bloom. The flowers either do not appear at all, or after a short time they crumble, not having time to form beautiful paniculate inflorescences. Most often, the reason for this lies in insufficient care. So, flowering may be absent:
- due to an unsuitable planting site (the shrub grows in the lowlands or is too shaded);
- acidic heavy soils in the place of cultivation;
- excessive moisture due to the influence of groundwater or watering more often than 1 time in 2 to 3 weeks;
- fertilizer overdose (scumpia grows better in soil with natural nutrient levels).
In these cases, the situation will be corrected by correcting the conditions in which the plant grows.
If the flowers of the tanning skumpia quickly fall off after the appearance, without having time to please the colorful clouds of inflorescences, you should pay attention to their structure. There are two types of scumpia flowers:
- monoecious;
- dioecious.
The first variety is more common and implies that the flowers of the plant have both pistils and stamens. Such scumpies are self-sufficient, since pollination occurs within one bush.
Dioecious crops are divided into male plants, whose flowers have only stamens, and female plants, which have only pistils.For pollination of such skumpies, both specimens must be present. At the same time, shrubs with male-type flowers cannot boast of lush flowering and look quite modest.
Shrub diseases and pests
Scumpia is quite resistant to disease and insect damage. However, sometimes a fawn leaf beetle, a scumpian beetle and a small pistachio beetle can settle on it. To combat them, it is recommended to use insecticides, for example, Karbofos or Decis. The dosage is indicated in the instructions.
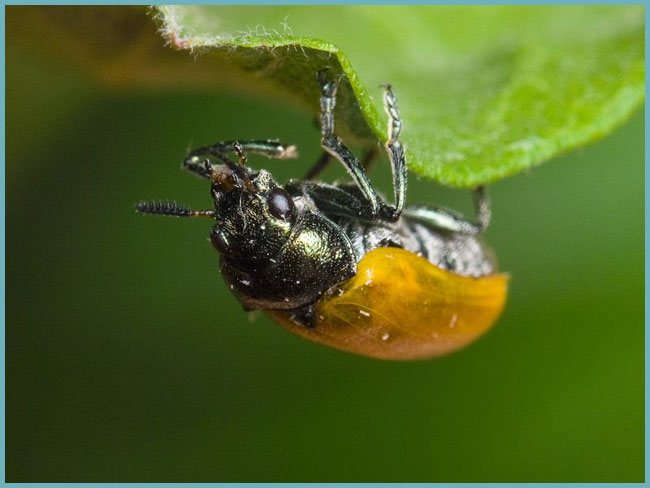


Fawn leaf beetle
Of the diseases, leather skumpia is sometimes overcome by verticillary wilting. Its source is fungi that infect shrubs through root damage. The disease is manifested by wilting leaves and gradual necrosis (death) of the shoots. Infected branches should be removed immediately, and the cut sites should be lubricated with garden varnish.
Advice. You can increase the resistance of the scumpia to verticillary wilting with good care: moderate watering, top dressing and thorough loosening of the soil.