Plant protection from various diseases is an integral part of the care of crops grown. For this, along with folk remedies, various chemicals are also used, which include fungicides. They differ in terms of systemic remedies or local effects. The latter remain on the surface of the leaves and stems of plants and help prevent infection with fungal diseases, and do not penetrate inside. When in contact with them, the bacteria that cause diseases die, so these substances are usually called contact. "HOM", instructions for use which will be discussed in this article belongs to one of them.

"HOM", instructions for use
The drug "Hom"
The tool has long been known to gardeners, flower growers and gardeners.... It is used to protect and heal vegetables, fruits, flowers. For example, it fights well against late blight of tomatoes and potatoes, peronosporosis on cucumbers and onions, curly peach leaves, scab on pears and apple trees, plum rot, grape mildew, spotting and rust of ornamental plants.
What is Hom? It is an odorless green-blue powder, which is nothing more than copper oxychloride... It is considered an excellent substitute for Bordeaux mixture. It is enough to dilute it with water and use, while the mixture must be prepared according to a certain principle and used immediately. However, unlike her, it does not adhere well to plant leaves and is easily washed off by rain.


Did you know? In order for the solution to stay on the leaves longer, it is recommended to add milk to it - about 1% of the total volume of the solution.
Hom has long been one of the most popular remedies in the fight against fungal diseases of plants. Copper included in its composition was considered almost the only effective remedy. But with the advent of organic fungicides, the popularity of the drug is gradually fading away.
Purpose, advantages and disadvantages
The list of diseases that HOM fights against is quite large. Here are the most common ones:
- Late blight, to which solanaceous plants are more susceptible than other crops - potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants, sweet peppers, physalis, etc.;
- Peronosporosis - downy mildew, dangerous for many plants, especially for cucumbers and onions;
- Moniliosis - disease of all fruit trees;
- Clasterosporosis, coccomycosis, leaf curl - in stone fruit species.
- Mildew - downy mildew of grapes.
(+) In addition to a wide range of effects, the drug has other positive properties:
- Unlike most fungicides, it can be used at relatively low temperatures. Its actions are activated at + 9 degrees;
- In terms of safety, it is in second place, after biological protective equipment;
- After application to the surface of plants, it acts on pathogens instantly. HOM does not need time for implementation and development, such as biofungicides based on microflora.
- Subject to adherence to the norms and terms of application, it is almost as safe as biological substances.
- It is available in use, does not require special conditions and fixtures, because it dissolves easily in water.
- Suitable for many garden, garden and ornamental plants.
- Although formally refers to fungicides, it acts as a bactericidal agent on plants with a thin shell. For example, it is used to treat cucumber bacteriosis.
(-) But there is also negative traits :
- Does not cope with advanced diseases in the last stages of plant damage;
- If last year there were no diseases on the plants against which HOM is used, then prophylactic treatment is not necessary. An exception is the situation when obvious symptoms of diseases were noticed near the site, for example, on neighboring plantations.
In other cases, it is better to use biofungicides to prevent contamination.
- Washes off easily by rain. It is desirable that after the treatment of precipitation there were no two days, but preferably three. It is quite obvious that the same amount cannot be used with surface irrigation. After spraying, you can only change the root irrigation and make sure that no water gets on the stems and leaves. In this situation, drip hydration is best.
Pharmacological properties of the fungicide "Hom"
To understand the essence of the drug's effect on fungal pathogens, it is necessary to understand what copper oxychloride is and how it affects microorganisms. Penetrating into their cells, the substance interferes with the processes of mineralization of organic substances, disrupting and neutralizing them. Thus, the cells gradually die, and with them the causative agent of the disease itself. It is noteworthy that the drug is not addictive in microorganisms and acts on them 100% in each case.
Important! Copper oxychloride causes corrosion of the metal, therefore it is undesirable to use containers made of iron to prepare the Homa solution.


All these processes take place on the leaves and trunks of the plant. At the same time, the substance does not penetrate into the cells of the plant itself. Crystals of the basic copper chloride salt do not dissolve in water or organic liquids, do not break down under the influence of sunlight or at elevated temperatures. But at the same time, they are easily washed off by rain and neutralized with alkali. Without her help, the drug completely decomposes within six months, breaking down into harmless components.
In fact, "Hom" is a preparation for treating plants, which belongs to contact pesticides of an inorganic nature.
Composition, impact features
For agronomic purposes, it is produced as a crystalline hydrate, in the form of a wettable powder (SP).
HOM is characterized by chemical resistance. This is due to the low mobility of positively charged copper ions. Therefore, they, in fact, do not penetrate into plant tissues, which means they do not pose a danger to them. But when combined with biological microorganisms, the situation changes. Fungal pathogens activate the mobility of copper, resulting in their death. Such interaction is possible only with barely germinated spores, adult mature microorganisms are not subject to HOM, it cannot cope with them.
Therefore, copper oxychloride is used as a prophylactic agent or at the initial stage of plant infection, since, at the later stages of the development of the disease, the drug is completely useless. In other words, this fungicide is beneficial only, before the fungi enter the sporulation stage. As a last resort, before their hyphae fill the infected plant. That is, it must be applied when the first signs of the disease appear.
It is extremely difficult to diagnose at an early stage. In case of an error, the drug will not work. But, due to the fact that it is used at the beginning of the development of pathogens, there is time to replace it with another drug.
Arguments for using copper oxychloride - its harmful effect on many types of pathogens. In addition, the substance does not accumulate in plant tissues, therefore it is not dangerous to humans.
"Hom": instructions for the use of copper oxychloride in horticulture
To use the drug, it must be diluted in water.
To begin with, take a small volume of liquid in which the required amount of the drug is diluted. Then gradually add water, bringing the solution to the desired volume. After that, you can proceed to spraying the plants.
Fungicide "Hom", as required by the instructions for use, should be applied in calm dry weather, in the period of the least probability of rain. Make sure that the preparation evenly covers the leaves and stems of the plants. It is necessary to use the entire drug without leaving it next time.
Important! It is forbidden to spray plants at air temperatures above +30 ° C.


Plants must be processed during the growing season. If ornamental plants are to be treated, the spraying procedure is carried out before and after flowering. The drug works for 10-14 days. Fruits and berries are processed no later than 20 days before harvesting. If copper oxychloride is used in the vineyard, the application period for grapes is extended to 30 days before harvest. In general, the drug is used no more than 3-6 times per season, depending on the plant being treated.
How to use Hom for plants correctly
Hom fertilization instructions and dosage for vegetables:
- When signs of anthracnose, peronosporosis or bacteriosis of cucumbers appear dilute 40 g of powder in 10 liters of water. Liquid consumption - from 100 to 300 ml per square meter. Recommended 3 treatments per season.
- Hom is used as fertilizer for tomatoes 4 times during the growing season. Brown leaf spot and late blight are the main diseases of tomatoes. Up to 150 ml of liquid is consumed per square meter.
- Onions are often damaged by downy spores. Processing is carried out 1 time. Concentration - 40 g / 10 l of water. Consumption - 200 ml per square meter.
- To prevent the appearance of phytophthora infection on potatoes for the season carry out the processing 5 times. Solution 40 g / 10 l.
- Fruit trees require increased fluid consumption: from 3 to 5 liters per tree. You must try to process all the leaves so as not to leave a chance for the fungus. Spraying is carried out 4 times a season.
- It is important to process the grapes before the ovaries appear. Prevention is better than curing or killing the vine. In total, 3 sprays are needed.
- For decorative flowers, the concentration is reduced up to 30 g of substance per bucket of water. The number of treatments is 2.
Before processing, it is advisable to know for sure whether it will rain or not, so as not to do the same work twice and not waste the solution. Spraying is done in the evening, if there is no strong wind. During the night, the active substances of the drug manage to destroy most of the spores of the fungus. If you spray in the morning, there is a risk of leaf burns in hot weather.


Hom: the benefits of using a fungicide
Summarizing the above features of the drug, I would like to highlight its main advantages over other fungicides. First of all, it effectively fights most fungal infections of various crops in the garden, flower garden, or vegetable garden. At the same time, it does not cause addiction in pests, therefore it can be used from year to year. Copper oxychloride, if diluted strictly according to the instructions for use, can be used to prevent fungal diseases in plants.
It is simple to prepare the solution, the packaging of the drug is convenient, and the product itself costs literally a penny. In addition, it can be used with other disease control agents - it works well with almost any drug without limiting their actions.
Safety measures when working with chemical fertilizers
Hom, although not as dangerous as other pesticides, should follow these rules when using it:
- use personal protective equipment and overalls;
- do not use near water bodies and apiaries;
- do not drink, eat or smoke when working with the drug;
- do not prepare or store the drug in kitchen utensils;
- isolate pets during processing;
- if the solution gets on open parts of the body or in the eyes, rinse them with running water for at least 10 minutes, and if it enters the body through the mouth, drink a large amount of water or a glass of milk.
Fungicide "Hom": compatibility with other drugs
The drug "Hom", according to the instructions for use, is easily combined with other pesticides, as well as fertilizers and insecticides. It combines especially well with organic pesticides of the dithiocarbamate group, which avoids burns on the leaves of crops sensitive to copper. In this case, the drug receives a longer duration of action. It can also be used in conjunction with "Entobacterin", "Inta-Vir", "Fufanon", "Epin". The only thing to avoid is combinations with alkalis. Therefore, it is not necessary to spray with copper oxychloride while using lime or Aktara in horticulture and floriculture.
Appointment of the use of funds
The drug oxychom is a contact agent, which indicates the effect while it is on the surface. Covering the leaves with a thin layer, the trunk of the Hom plant prevents the penetration of a fungus or other disease, a parasite inside.
But the action lasts as long as the product is on the surface. With the first shower, the substance is washed off and no longer has the necessary protective effect.
Instructions for use indicate the possibility of application at all stages of plant development, except for flowering. But there is also one more disadvantage: Hom helps only in the initial stages of infection.
Treatment will help in the presence of pathogenic microorganisms until sporulation occurs. If you skip this moment, or start it - the required result will not be obtained.
Hom can be excellent at fighting moss on apple trees. In the garden, it will be useful if protection is needed for plums, apricots, peaches or cherries. Removes consequences and initial development:
- clusterosporiosis;
- coccomycosis;
- curliness and moniliosis.
But the use of copper oxychloride in horticulture requires a larger amount of working solution: 1 tree will require at least 2 liters, but not more than 5 liters. Good for quince and pear as well.
Recommended in vineyards, as the vine is a tasty morsel for scab, mushrooms and curl. Often affected by mildew and anthracnose. But Hom will help in this case too.
Order of use
HOM is chemically quite stable compound: active ions Cu ++ gives up reluctantly and therefore does not penetrate deeply into plant tissues. This largely explains its low toxicity (see below) and the almost complete absence of phytotoxicity. In fact, HOM gives active copper only to fungi-pests, this is the reason for its ineffectiveness against advanced diseases: parts of the pathogen organism that have invaded the affected plant remain alive; With HOM, you need to kill fungi that have just sprouted on the integument of the plant and have not yet grown into it.
The use of HOM for plant protection is carried out by spraying with a tank solution. First, as usual, the mother liquor is prepared, dissolving the dose of the SP approx. in a liter of water. The mother liquor is poured into a sprayer tank filled with about 3/4 of the flow rate (see below), water is added and sprayed.
An indispensable condition for successful processing is that there is no rain for a day (preferably 2-3 days) after it: readily soluble HOM is immediately washed off from the plants.Therefore, it is highly advisable to use HOM only in the evening: the morning dew will also wash it away. The cultivated crops must first be thoroughly watered so that after processing they have enough soil moisture for the same 2-3 days or more - irrigation water washes away HOM no worse than rainwater.
Reviews by the gardener about Oxyhom


Sergey, a gardener with many years of experience. I have been using this drug almost all my life. My acquaintance with the drug began with difficulties. In one summer season, I found information on the dangers of pesticides on the Internet; alternative methods were proposed there. This was the worst decision since my entire crop died.
I use the drug in almost all of my cultures. I try to strictly follow the instructions for use. I do not take up the remedy without wearing a work suit. The remedy effectively helps against many diseases. I advise everyone.
Marina. For a long time I tried to deal with mildew near the vineyards, but all attempts ended in failure. Thanks to the Internet, I found a lot of useful information in which they just advised pesticide products, but they were not so easy to buy. On one of the forums I came across Oksikhom.
Of course, I first read about him and found out all the pros and cons. But the most important thing is that it is at an affordable price and is always found in flower shops, unlike other drugs. True, it is more dangerous than many other means, but there is more information about it. Now you can't take your eyes off my vineyards. I recommend all gardeners to purchase this product. With it, you can get rid of the most difficult diseases. However, don't forget about safety. As you can get serious injuries.
Consumption rate of funds
The working solution is prepared immediately before spraying the infected crops, according to the instructions.
The prepared solution is used in different cultures in different volumes, as follows:
- on greenhouse tomatoes, cucumbers, the consumption rate is low and amounts to 2000 ml. 10 square meters;
- in vineyards, the drug is used at a flow rate of 1500 ml. for the same area;
- potatoes are processed at a rate of 1200 ml. 10 square meters.


A working solution is prepared immediately before spraying.
Category: "Questions and Answers"
Question number 1... Can Oxyhom accumulate in fruits?
Answer. If you follow all dosages, norms and processing times, then the drug will not cause harm. The drug does not accumulate, but may be on the shell of the fruit. This happens if you exceed the recommended spray concentration, or if you eat it before the waiting period. In this case, copper oxychloride, which is present on the surface of the peel, is dangerous. After the waiting period, the compound decomposes in air and evaporates. Then it is not dangerous. In any case, if the plants were treated with Oxykh, the fruits must be thoroughly washed before eating.
Answer. It is better to refrain from mixing with any other drugs and use Oxyhom separately from others. This means that another remedy can only be applied after a few days. If there is no other way out, then first the compatibility must be checked by first dissolving the tested substances in small amounts in a separate container, then mixing in a common container. Most likely, a precipitate or flakes will appear, which means that the preparations cannot be added together.
If, nevertheless, the connection was successful, then you should not rush into processing, it is better to withstand the mixture for 2 hours. Sometimes the reaction is slow and it takes time to be sure that it is fully compatible.
Methods for using fungicides
Fungicidal drugs can be used in a variety of ways.
Introduction to the soil. Fungicides, produced in powder form, are introduced into the soil during its digging. You can dissolve the powder in water and water it. This will help destroy the pathogenic fungi that live in the soil.Pollination and spraying. The fungicide solution can be applied to the aerial parts of plants using a sprayer. Several sprays per season are allowed, they are carried out in late autumn and early spring. Sprayers are also used to treat storage facilities and greenhouses.
Seed dressing. Plant tubers and seeds are treated with a fungicide before planting. Powder or solution can be used.
If only one agent is constantly used, the effectiveness decreases, since the pathogens of the fungi cease to react to the components of the substance. To prevent this, it is necessary to alternate the applied fungicides, strictly observing the dosage of the drug consumption. The production of fungicides is constantly growing, new drugs are being created, since it is difficult to overestimate the importance of these drugs for agriculture and horticulture.
You may be interested in: UAN fertilizer: advantages and disadvantages of the drug
Biological fungicides for plants are being developed very actively. They are strikingly different from chemicals, they are safer, and the bacteria they contain are capable of causing the death of several types of pathogenic fungi. Such funds include: Fitosporin, Fitop, Agate, Integral, Barrier. They are highly effective at low toxicity.


Composition and action
Fungicide Oxyhom is produced in preparative forms of VDG (water-dispersed granules) for LPH and SP (wettable powder) for SH. It is not compatible with other pesticides in tank mixtures due to significantly different solubility of the drug components in water.
The chemical formulas of DV Oxyhom are shown in the figure:
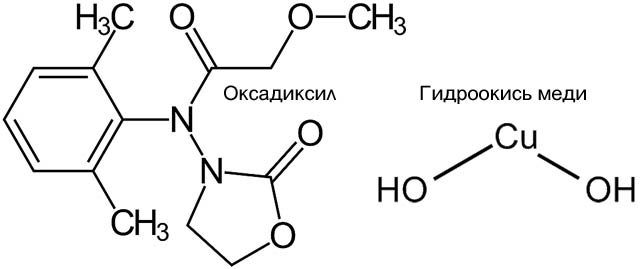

Copper hydroxide is insoluble in water. It acts on the objects of elimination as a contact poison, denaturing proteins of cell membranes and cell contents. The phytopathogen fungus dies due to a general violation of the mechanisms of biosynthesis due to plasmolysis. Copper hydroxide provides a fast action of the preparation for the fungicide - 2-3 hours - but is subsequently washed off from the treated surfaces by the first rain. However, the use of this DV is effective in the temperature range of normal vegetation of plants (15-25 degrees Celsius). At lower temperatures, the substance is washed off with dew before it acts on pathogens that slowly develop under such conditions. At higher temperatures, moisture transpiration prevails in the daytime gas exchange of plants, and the copper hydroxide film is "blown away" in places. Since copper hydroxide is a 100% contact fungicide, “windows” are formed on the treated surfaces in which infection can develop.
Oxadixil belongs to the chemical class of phenylamides. Like its “colleagues” (metalaxyl and its R-isomer mefenoxam) in fungi it suppresses the synthesis of all types of RNA, which stops mitotic cell division and prevents spores from developing. Also, like other phenylamides, oxadixil is fairly well soluble in water (3.4 g / kg), resistant to hydrolysis and photolysis, however, unlike mefenoxam, it is most effective against oomycetes (which include downy mildew fungi, late blight and Alternaria), and against real mealy grew ineffective. Volatile, saturated vapor pressure at 20 degrees Celsius 0.0033 MPa; this is a lot for a pesticide.
As a substance readily soluble in water, oxadixyl has a high systemic activity, which, in combination with its stability, gives a long-term prophylactic and protective effect. Compared to other phenylamides, it is significantly less toxic. Resistance of pathogens to both DVs of Oxychoma was not observed. However, they both stay in the soil for a long time, actively leach out without breaking down, and migrate with the soil water, having a detrimental effect on the soil microflora and microfauna, because copper hydroxide is a bactericide no less powerful than a fungicide.
General concept of fungicides
Fungicides are pesticides used in horticulture to fight plant diseases. These include products for processing plants, soil, seeds. Fungicides are divided into several types, the classification depends on the purpose, chemical properties, the nature of distribution within the plants.
Fungicide preparations are used to eliminate or prevent fungal infections of plants, as well as to combat pests of garden crops and indoor plants. The preparations can also be used to protect seeds during dressing. If you apply these funds correctly, in a timely manner, you can preserve the health of plants, prevent mycosis from developing, and increase yields.
Types of fungicides
All fungicides are divided into two large groups:
- Biological. At the heart of the funds are beneficial bacteria that can destroy pathogenic fungi. Most popular in recent years among summer residents, since they are less toxic. Biological fungicides are used to disinfect the soil.
- Chemical. The main active component of the funds are chemical compounds.
Fungicides, depending on their chemical properties, are divided into:
- organic;
- inorganic.
Inorganic fungicides are compounds of potassium, manganese, mercury, iron, sulfur, nickel, copper. Organic ones do not contain heavy metals, they are easily decomposed, therefore they have an undoubted advantage. Solutions of such drugs are easy to prepare: it is enough to dilute the product in water. Substances are easily combined with other pesticides. Inorganic drugs are incompatible with many other drugs. But organic products also have drawbacks. They are unstable, remain in the ground for only a few days or weeks, then losing their properties.
You may be interested in: Topaz - systemic fungicide
Fungicides are:
- Eradicating (therapeutic action). The death of fungi is possible after infection of the plant.
- Protective (preventive action). Introduced in advance can prevent infection.


Depending on the purpose of use, substances are of the following types:
- preparations for processing cultures during the dormant period;
- seed dressers;
- preparations required during the growing season;
- means for soil treatment;
- preparations for processing storage facilities for vegetables and grain.
For the convenience of gardeners and gardeners, modern manufacturers have developed many universal fungicides that can be used for soil cultivation and for other purposes during the growing season of the plant, and during the planting period for seed treatment.
Distinguish between contact and systemic fungicides by the way they are distributed in plant tissues.
Local or contact substances remain on the surface of the plants. They cause the death of the fungus upon contact with it. The effectiveness of the product depends on many things: the amount of fungicide used, the duration of action, weather conditions, chemical resistance. There are contact fertilizers that have a deep effect; they can penetrate through the seed coat inside.
Intra-plant, systemic fungicides, inhibit the development of pathogens, spreading through the vascular system of plants. Efficiency is determined by the rate of penetration of a substance into plant tissues. They do not depend on weather conditions.
















