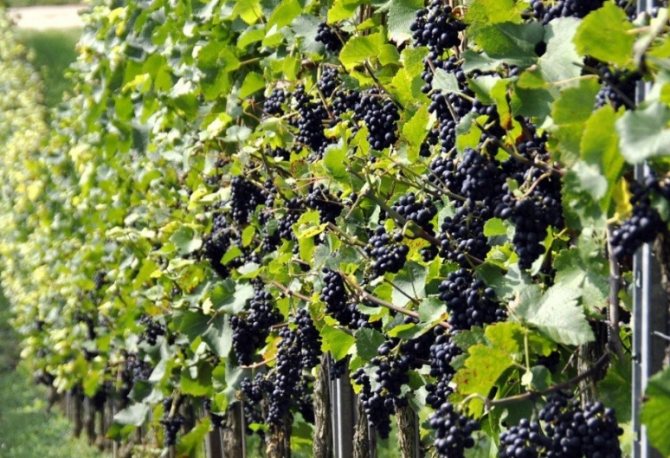
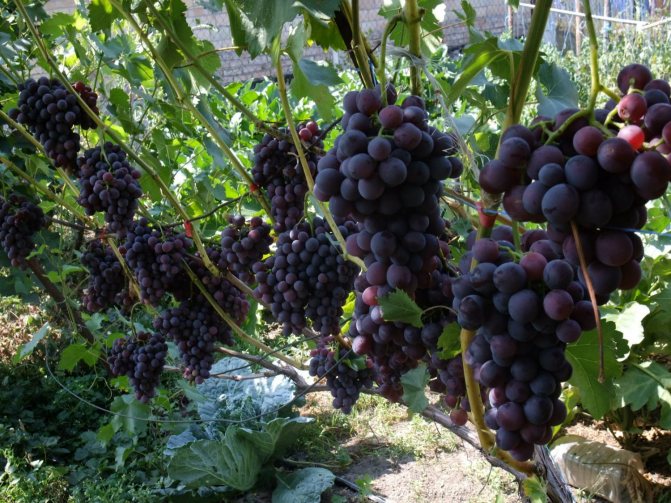
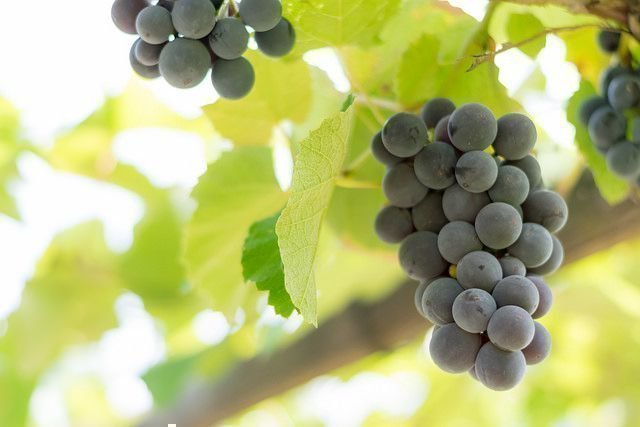
Table grapes are a favorite crop for many growers. Eating fresh grapes is very healthy, but how to keep them longer?
“Shelf life varies with table grape varieties and is significantly influenced by temperature regulation and the variety's susceptibility to decay,” says Carlos H. Crisosto of the Department of Plant Science at UC Davis. "Also, factors such as the physiological state of berries and diseases have a great influence."
Grapes do not gain sugar - what is the reason? Sour grapes.
Even with experienced winegrowers, it happens that the season is drawing to a close, and there are still unripe bunches of grapes on the vine. What is the reason, how to avoid this in the future and what to do with unripe berries in the present? Let's try to figure it out.
There are several reasons when the berries may not have time to ripen. Let's take a closer look at each.
The variety was selected without taking into account the growing conditions
Before planting any variety, it is necessary to clarify whether this variety is suitable for growing in this region in terms of ripening and climatic conditions. It so happens that the vine simply does not have enough time and warm weather to fully ripen.
During the period of grape growing, the most important factor affecting the yield and taste of the fruit is the temperature regime. As far as the temperature of the air and soil is appropriate, the resulting crop will be ultimately productive. Deviations from the permissible norms negatively affect the growth and ripening of berries.
In the northern regions, winegrowers use a number of techniques that, during the flowering period, are capable of raising the temperature by ten degrees due to accumulation.
One such technique is planting vines against brick fences or the walls of houses located on the south side. The secret lies in the fact that during the day the masonry heats up well in the sun, and at night it gradually gives off heat to the vines.
Another technique for raising the temperature is the use of black mulching materials, which are laid out between the rows and bushes of grapes. The use of black stones spread out under the bushes. All these materials serve as a kind of heat accumulators.

The winegrowers of the northern regions have their own interesting developments. They use large, sturdy black bags filled with hot water. Such bags, laid out between rows of grapes on both sides, can raise the temperature of the soil and air by 5 degrees.
Very high temperatures can also cause the grapes to lag behind the ripening period. The optimum temperature for ripening grapes is 26-29 degrees. If the temperature rises significantly to 40 degrees, then all vital processes of the vine become slower, and with a strong increase, burns appear on the leaves and fruits.
In addition, if at the time of flowering the temperature exceeds 30 degrees, the pollen becomes sterile and unsuitable for fertilization.
Overloading the vine with fruits
This can be the second reason for the immaturity of the crop.When there are more fruit ovaries on the vine than it is able to provide with the necessary microelements, this problem is observed. This applies to table grape varieties.
Such varieties need fruit normalization. If you do not fulfill the rationing of the fruits, then the harvest will not only not reach maturity, but subsequently the depletion of the bush will occur, the plant will not be prepared for wintering.


Some varieties cannot cope with a large number of berries on the vine, so they need to be removed
Pests and diseases
They can also be another reason for poor fruit ripening. In diseases, the green mass of the bush is mainly affected.
In this case, diseased leaves begin to dry and fall off. The loss of green mass leads to the fact that the process of photosynthesis is slowed down. At the same time, a very small amount of nutrients is produced, which slows down the growth of shoots, and, consequently, the ripening period of the fruits is delayed.
Excess nitrogen
With abundant nitrogen fertilization, the shoots and root system of the bush are rapidly developing. This reduces the number of fruits, the ripening period of the berries is delayed and the palatability deteriorates.
Weed plants
They can also cause poor fruit ripening. Determining their presence is easy. The vines begin to entangle the grasses and draw out all the juices from them. It is necessary to regularly weed the weeds, which draws nutrients from the soil and limits the access of sunlight to the fruits.
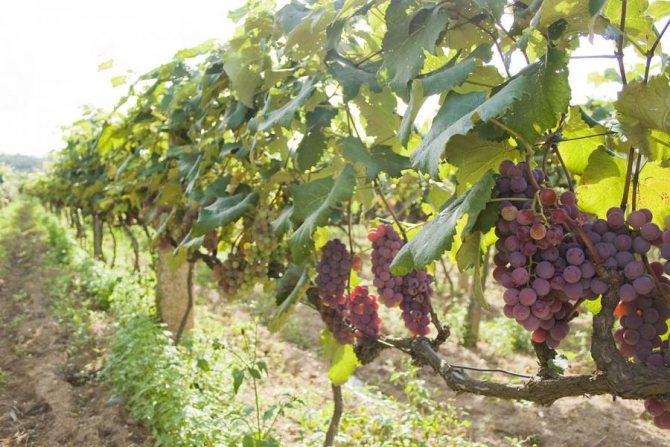


Overgrown grapes are not able to ripen the berries on their own
Chasing
One of the methods of accelerating the ripening of the vine is chasing. This procedure is the removal of the tops of shoots that have grown up to 1.5 meters. After pruning, an active supply of micronutrients begins to the adult part of the bush. This leads to lignification of the vine, which helps to successfully survive the winter.


Chasing accelerates the ripening of grapes
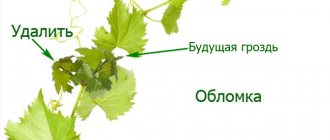
Harvest regulation: how and when to use
The normalization of the amount of the crop can be carried out before the beginning of the flowering period. It is necessary to visually assess the number of inflorescences on individual shoots. Then a certain number of inflorescences should be completely or partially removed. If this procedure is performed early, then all the nutrients will go to the left bunches.
The bush will not waste extra energy on the bunches, which will later have to be removed.
This procedure is recommended if the bushes have been bearing fruit for several years and give an equally stable yield. If the bush is young, then this procedure is performed after the flowering period, when the result of pollination is already clear, and you can see the formed brush.
The following solution would be more reasonable:
- on an adult vine, carry out early normalization during the formation of inflorescences;
- for a younger vine, normalize at the end of the flowering period, when the result will be visually visible.
- on table varieties with large hearths, where the mass of each brush is more than 750 grams, leave 1 brush for the shoot;
- for table varieties with a brush weight of 500 grams, two brushes are left on one shoot;
- in technical varieties, where the weight of the brush is 210 grams, 3-4 brushes are set aside on one shoot;
- on varieties where the mass of the brush is more than 1500 grams, one brush is left for the shoot, and on every third brush, all clusters are removed.
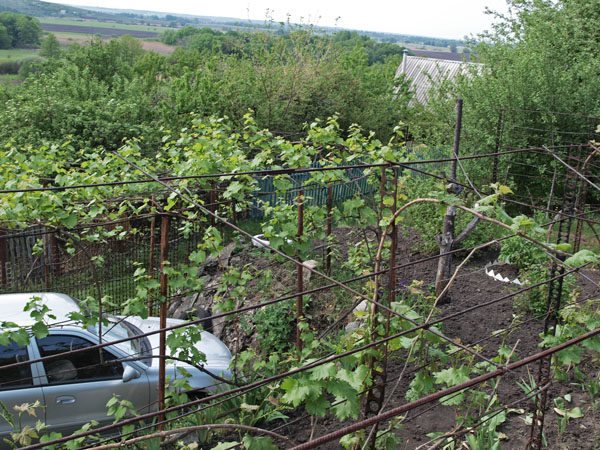


Normalization of grapes is simply necessary for the successful ripening of all clusters.
Benefits of iodine
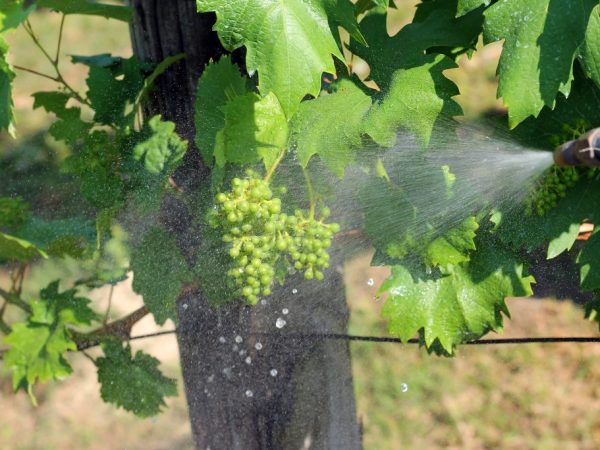


Iodine increases the sugar content of berries
Pharmayod or any other type of iodine is a powerful disinfectant that not only protects the plant, but also helps it grow. After spraying the grapes with iodine, the following occurs:
- berries are enriched with iodine - when consumed raw, a person consumes an important component for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- the sugar content of the berries increases;
- improves the quality of the peel, which does not crack even during heavy rains.
The grapes grow faster after processing. If prevention is carried out in the spring, the vineyard does not suffer from diseases of neighboring horticultural crops. Such events are suitable for both young vines and adult plants.
Maturation in polycarbonate
One of the modern methods for solving this problem is the method of constructing shelters made of polycarbonate, in which immature vines ripen in the autumn period. The essence of this method is as follows:
- it is necessary to dig a trench and cover the bottom with polycarbonate;
- trim thin shoots;
- lay the vine in a trench and cover it on top with a sheet of polycarbonate.
This design creates a greenhouse effect inside and retains a high temperature for a long time. This allows the vine to fully ripen. If polycarbonate is not available, black polyethylene can be used.
What may be troubling a child?
Excess iodine in a child's body is often accompanied by certain symptoms. In addition to a sharp bad breath, the baby may be disturbed by:
- burning throat or pain;
- bowel disorder;
- dry mouth;
- nausea and dizziness.
Doctors advise parents to examine the child's oral cavity. If the shade of the mucous membrane has become dark, this is a reason to visit a doctor.

The taste of iodine in the mouth is accompanied by dryness and bitterness (children's photos, fortunately not)
The use of unripe grapes
Do not rush to throw away unripe grape clusters with seeds. They can be used very widely and make many blanks at home:
- prepare wine;
- cook jam or preserves;
- pickle;
- prepare the sauce;
- boil the juice.
Making wine
It is necessary to shell unripe brushes in a metal container (the container must be enameled. Aluminum or copper dishes are not allowed). Berries need to be mash well. The resulting pulp must be heated over a fire to 60 degrees, removed from heat, cooled to 25 degrees, discarded in a colander and squeezed out the juice. If the juice is sour, sugar and berry yeast sourdough are added to it.
Fermentation must be carried out at a temperature of 20 degrees for a month. After two months, the wine will brighten and a sediment will form at the bottom. Drain the wine gently, leaving a residue in the container. The wine will taste unpleasant and will not taste sweet. At this point, add sugar at the rate of 100-150 grams per 1 liter, stir until the sugar dissolves completely. Then bottle it. Dessert wine is recommended to be aged at room temperature for two months before drinking.
Folk remedies
There are folk remedies to combat grape rot. As a treatment, it is proposed to use an iodine solution (1 ml per 1 liter of water) for spraying berries in the growth and ripening stages. In addition to iodine, soda, potassium permanganate, and ash are used as disinfectants. However, all these funds are effective for a short time until they evaporate.
In Bulgaria, rotting straw is used: it is poured with water and left for a week. The resulting hood is sprayed on the bushes. It is believed that the spores of the fungus living on straw supplant the fungi on the grapes.
The benefits of grapes: composition, application and unique properties
The incredible benefits of this berry are due to its unique biochemical composition, which has up to 300 components. This real storehouse of vitamins and microelements helps to increase the protective properties of the body, improve resistance to diseases and restore vitality.
It should be remembered that not only the pulp is useful in grapes. The peel and even the seeds contain a large amount of substances that have a strong therapeutic effect.
Scientific research has confirmed that grapes of different varieties and colors have different beneficial properties. They are more pronounced in dark berries than in light ones. Taste qualities and microelements and vitamins necessary for the body are also preserved in products prepared from these fruits: juices, wines, compotes and raisins.
Neither cosmetology nor the food industry can do without this product. The essential oils contained in grape seeds serve as the basis for the preparation of a number of preparations for skin, hair and nails care. It is impossible to imagine confectionery without raisins and grape syrup.
The latest research confirms that the antioxidant pterostilbene, found in sour grapes, can prevent diabetes. And lycopene, which is part of the peel of black berries, has a beneficial effect on libido, is a prophylactic agent and promotes the treatment of male infertility.
Black grapes harm and benefits for men and women
There are more than 20,000 grape varieties in the world, the bunches of which are of various shapes, sizes and colors. The variety of colors is explained by the presence of flavonoids in berries (they affect the activity of enzymes in the body, enhancing the beneficial properties and quality of food consumed).
The higher the concentration of these elements in the fruit, the darker their color and the more useful the peel. Therefore, black berries (grapes, blueberries, currants, mulberries, irga) are considered the most useful.
- sugar (glucose and fructose);
- an extensive vitamin complex;
- a large set of organic acids;
- bioflavonoids;
- pectins.
Flavonoids, in addition to the general effect on the absorption of nutrients by the body, have the following properties:
- antioxidant;
- spasmodic;
- anti ulcerative;
- antineoplastic;
- healing;
- anti-inflammatory;
- diuretic;
- bactericidal.
Due to the set of nutrients, black grapes deserve special attention. Its berries contain a large amount of antioxidants, the protective properties of which resist the formation of free radicals.
Black grapes as a preventive measure
Regular consumption of the product has a beneficial effect on human health:
- helps to lower cholesterol levels;
- prevents the occurrence of atherosclerosis;
- prevents blood clots.
When eating black grapes, blood pressure is normalized, the walls of blood vessels are strengthened, and micro-blood circulation is improved. The content of nutritious monosaccharides and their rapid assimilation in the body have a tonic and restorative effect, contributes to the normalization of metabolic processes and brain function.
What grapes to choose for diets: comments of nutritionists
When choosing the most dietary variety for weight loss or maintaining health, it is important to consider the taste of the berries, and not their calorie content. Nutritionists recommend:
Sour grapes contain more organic acids, so they are ideal for losing weight and stabilizing digestion.
Sweet and aromatic fruits contain more fructose and sucrose, therefore nutritionists recommend them for diabetes (to restore blood sugar levels) and problems with the gastrointestinal tract, but for those who are losing weight, the use of such varieties is not recommended.
Organic acids affect the composition of gastric juice, as a result of which:
- assimilation of food improves;
- increased appetite;
- the intestinal microflora is normalized;
- increased peristalsis.
The color of the berries also affects the dietary value of the product, since much less black fruits are needed to replenish the body with the necessary microelements.
By consuming small servings of grapes every day, you can regularly replenish the supply of micro and macronutrients such as potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron and zinc.
The benefits of grapes in cosmetology
Even in ancient Egypt, women were known for the wonderful properties of grapes, which help to care for the skin and keep it youthful. In modern cosmetology, preparations based on grape seed essential oils gently care for the skin, improving its elasticity and firmness, remove dead tissue, nourish, whiten and moisturize. They help to preserve beauty, youth and health for many years.
What factors contribute to the appearance
The pathogenic fungus enters grapes in the form of spores or mycelium. In order for the spores to begin to grow inside the plant and spread there, drip-liquid moisture is needed. Therefore, the grapes are most strongly affected by fungal diseases in the rainy season, with excessive watering, i.e. at high humidity.
The second important factor in the rate of manifestation of the disease is the ambient temperature. The more it corresponds to the optimal temperature for the development of a particular pathogen, the faster the disease spreads through the plant tissues.
The rate of growth of the mycelium of the fungus in the tissues of the plant determines how quickly the symptoms of the disease become noticeable to the gardener. The external manifestation of the disease marks the beginning of the last stage of its development - sporulation.
Sporulation of fungi takes place in conditions of high humidity (watering, rain, night dew). From the beginning of this stage in the development of the disease, the affected plant becomes a source of infection.
Contraindications to use
Despite all its usefulness, black grapes also have contraindications:
- The dark color makes the berry a strong allergen, so it is contraindicated for young children under one year old;
- The use of fruits and juice at the final stage of pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended;
- In case of ulcers and oncological diseases of the stomach, diabetes mellitus, diarrhea, obesity, edema, chronic constipation, acute forms of tuberculosis and colitis, the use of berries is contraindicated.
Black grapes can replace a number of foods in the diet, especially during the spring beriberi. Consult a doctor and a nutritionist, consumption in moderate doses (5-10 berries per day) will not harm the body, even with the indicated contraindications, and will keep it young and healthy. If you have an allergic reaction, you should switch to green or yellow grape varieties.
Conditions for development
Diseases caused by fungi manifest themselves under similar conditions. Consider the parameters of the external environment at which grapes can be damaged by rot:
| Disease | Air temperature | Humidity | Airing |
| Gray rot | 5-30 o C | 90-100%, spores germinate in water droplets | weak, thickened planting |
| White rot | 18-30 o C | 90-100%, spores germinate in water droplets | weak, thickened planting |
| Black rot | optimally 20-25 o C and up to 43 o C | 90-100%, spores germinate in water droplets | weak, thickened planting |
Isabel
Berries of this variety, black as midnight, are used to make aromatic wines, as well as soft drinks, preserves and jams. Isabella has a specific taste, very sour, with a strawberry flavor.
The pulp is slippery and has bones, which does not prevent amateurs from enjoying its fruits with pleasure.
- This plant belongs to late ripening.
- The leaves are glossy, richly green on top, and on the underside of a light shade, often gray due to abundant pubescence.
- Isabella's clusters are medium in size, cylindrical in shape, sometimes loose.
- The berries are round or oval, they are black with a waxy coating and thick skin.
- The growing season to full maturity takes 5-6 months.
- The bushes belong to the vigorous group.
- Isabella's popularity is largely due to her exceptional resistance to fungi and pests, including phylloxera.The main thing is to prune the bushes in time in order to prevent thickening, favorable for diseases, and improve productivity.
- This black grape is frost-resistant: it can be grown even in Siberia. In many regions, sour grapes may not even be covered for the winter. But before planting a plant in the northern regions, it is worth remembering that it is late ripening and you can not wait for the harvest.
- Isabella prefers fertile soils, with a small amount of limestone.
- It tolerates an excess of moisture relatively well, but is suspicious of drought and can throw off foliage as a protest measure.
- Isabella fruit helps against cough, strengthens the circulatory system, stabilizes blood pressure. This variety contains more nutrients in berries than other varieties of grapes. But since the 80s, this plant was "accused" of containing a lot of methyl alcohol, which is why its use was banned in Europe and the United States. In fact, the situation is not as sad as it is portrayed and the percentage of methyl alcohol in Isabella exceeds the content of this substance in other varieties by only 0.01%.


Isabella grape - late variety resistant to phylloxera
Danger of Aspergillus Rot
Until recently, this type of fungal infection of grapes was not considered the dominant disease, but after several cases of complete death of the crop, it entered the group of the most dangerous diseases. A characteristic feature of this fungus is the thermophilicity of its body, that is, the tendency to increased growth at elevated temperatures (from 31 degrees).
Risk factors for the development of Aspergillus rot include primary lesions of bunches with other fungal diseases and their colonization by fruit flies. Infected grapes become a source of infection for healthy fruit.
The disease manifests itself initially with light, and later darkening, as if depressed spots, tightening the surface of the skin and leading to its cracking. Later, a whitish bloom appears on the berries, which eventually turns into a black-brown, actively powdering mass.


Aspergillus rot is carried by fruit flies
Autumn Black
Descended from French varieties. Autumn Black is an interesting table grape and has several nice features for winegrowers and tasters in stock:
- Black or purple fruit color, oblong shape. The taste is pleasant, with a slight sourness, the pulp is juicy. The size of the berries is large, depending on their number in the bunch.
- The grape yield is high and plentiful, and the vigor of the bushes and the ripening period are related to the magnitude of the load: usually medium, but may be late.
- Conical clusters weighing up to 700 g or more.
- The plant does not tolerate strong drops in temperatures (up to a maximum of -20), and with fluctuations it becomes vulnerable to diseases, especially to gray rot - bursting berries warn about this. Even with warm winters, grapes are recommended to be covered.
- Does not like excessive moisture and the proximity of groundwater. You need to water with a little water.
- Like other types of grapes, Autumn Black responds well to mineral fertilizing and other agricultural methods of caring for plants.


Grape Autumn Black - late-ripening variety
Chlorosis
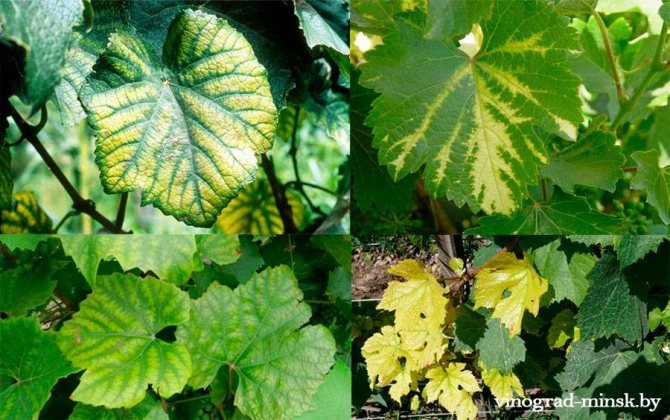


Chlorosis (grape jaundice) causes yellowing of the leaves, and only green areas remain along the main veins. With a strong development of chlorosis, the yellow color turns brown, the leaves begin to dry out and fall off. Shoot growth weakens, internodes become short, and bushes often die.
The development of the disease is mainly associated with the disturbance of plant nutrition due to the high content of lime in the soil, especially on dense heavy soils, which converts iron into a form inaccessible to plants.In addition, excessive moisture or, conversely, dry soil, excess salts, damage to bushes contribute to leaf chlorosis.
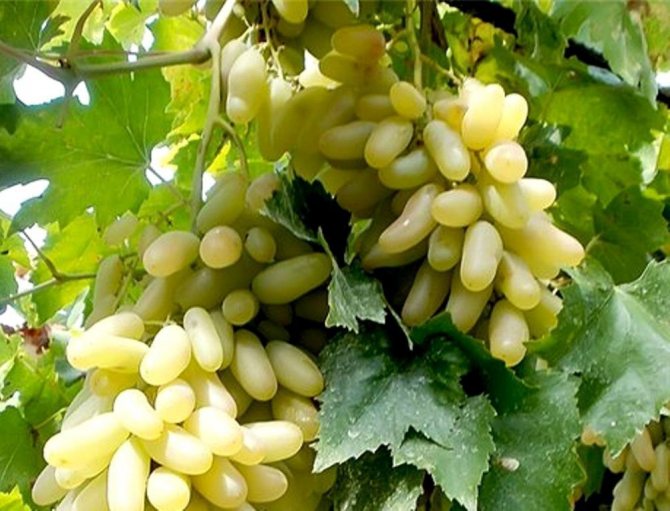
Lady fingers
This beautiful grape got its name from the elongated shape of its fruits. They brought him from Central Asia.
Gradually "Ladies fingers" spread to the southern regions of Russia and Ukraine.
- "Ladies' fingers" are guests from countries with warm climates and most of all they need sunlight and warmth. In areas with a temperate climate, good harvests come only in good years and provided that it is carefully looked after;
- The bunches of the variety weighing 400 grams or more, are not loose, but not dense, conical. The berries are large, up to 4 cm long, with a thin greenish-yellow skin, with a waxy bloom. In some fruits, large seeds may form. The taste of "Ladies Fingers" is pleasant, sugary - sweet, with a slight sour aftertaste.
- Small green leaves, vigorous bushes.
- Produces bountiful yields under good growing conditions.
- Ripening times differ depending on the climate. Average indicators: five months, at home you can pick ripe fruits a month earlier.
- Fruiting for "Ladies' fingers" is a sore point. They begin to do this only by the fifth year, although sometimes individual shoots can please the owners with a couple of bunches. Another problem associated with fruiting is its irregularity due to a bouquet of vulnerabilities to various misfortunes.
- The variety suffers from an absolute cold temperature intolerance. Already at a temperature of -10 O C, they begin to hurt, therefore, bushes cannot be left without shelter even in the warmest regions of Russia, Ukraine and neighboring countries with a temperate climate.
- Like real ladies, "Ladies Fingers" are susceptible to fungal diseases (among which the most dangerous are downy mildew and powdery mildew), especially during waterlogging and drought. In order not to lose the bushes, they must be constantly processed; and after rainy weather, carefully examine for rot.


Grapes Ladies fingers does not tolerate cold weather
Prevention measures
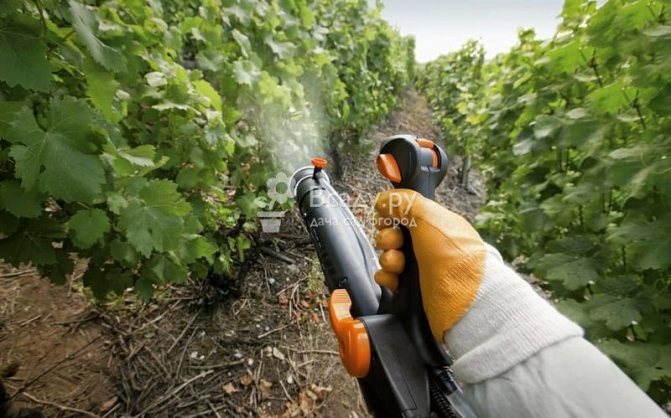
Gray rot affects shrubs in summer. Most often, the period of activity falls in July. To prevent the spread of infection and getting it on the shoots, you need to periodically spray the vineyards. For preventive measures, fungicides with antifungal action, copper-containing preparations are used. Spraying is done several times per season. The most suitable periods for this are:
- before the onset of kidney formation;
- after the formation of ovaries;
- after harvest.
Important! Chemicals are not sprayed 20 days before harvest, as they accumulate in the fruit.
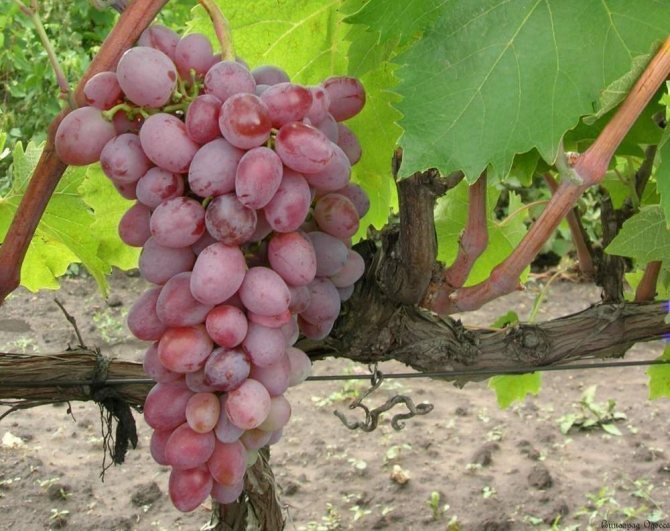
Taifi
This table variety is also named Typhoon, or Toifi. It was brought to Central Asia by the Arabs in the 7th century, and gradually spread throughout the world.
- The fruits of Taifi are large, they are oval or cylindrical in shape. The color is deep pink, interspersed with a purple hue, the inner part of the dense skin is red. The pulp is juicy, with a sweet and sour taste. There are up to 3 seeds in berries.
- The bunch is loose, large and gigantic in size.
- High level of shoot fruiting.
- Late ripening: 5-6 months pass from budding to full maturation.
- Among the disadvantages: vulnerability to powdery mildew, mildew and other fungal diseases, often becomes the target of spider mites, so it needs careful checks and treatments with special preparations.
- Like other oriental varieties, Typhoon does not feel well in frosts. Whatever the warm winter in the region, it is better to shelter Taifi from the cold, and when spring comes, do not rush to open it due to spring frosts. Better to cut vents in the shelter.
- But the typhoon is not afraid of drought.


Taifi grapes easily tolerate water shortages
Oidium (powdery mildew or ash)


Oidium is especially dangerous in hot dry summers in irrigated vineyards. Grape disease oidium infects all aerial parts of the plant. Plaque of gray powder with a large number of dark brown spots (fungal bodies). A kind of brown speck is formed on the shoots, and then large spots. With severe damage, the entire shoot turns brown and even almost black. Young berries crack, exposing seeds, dry up and crumble. Fighting the disease is possible. The easiest way is pollination with sulfur or spraying with colloidal sulfur, as well as copper oxychloride.
Complex-resistant varieties can be affected by powdery mildew to varying degrees. Czech and Hungarian varieties are resistant to powdery mildew. breeding work in this direction has been conducted there for a long time. Most Moldovan varieties are not resistant to powdery mildew or have low resistance. Novocherkassk and Anapa varieties are partially resistant to this disease.
Aligote
A white grape variety derived from the French Pinot Noir and Gue Blanc. The famous white wine of the same name is produced from its fruits, but you can also taste it fresh.
Aligote is grown all over the world, including in Ukraine, Russia and Moldova.
- The leaves of the variety are large, shiny, covered with a spiderweb fluff on the inner side, in youth they are completely covered with tomentose pubescence. The petioles are red, and by autumn the foliage turns yellow.
- The length of the cylindrical bunch is 15 cm, and the width is 10.
- The berries are medium in diameter and round, golden-green in color with dark spots and formed seeds up to 4 pieces. The skin of the fruit is thin, and the sour-sweet flesh melts in the mouth.
- Under favorable conditions and good care, Aligote ripens in 4 - 5 months, the harvest is harvested in September.
- Aligote is a European variety and is vulnerable to diseases, especially mildew, and in rainy weather it easily picks up gray rot. With oidium, things are better - grapes resist this fungus better.
- Frost resistance in Aligote is at an average level, so the plant needs shelter during the frosty period of the year.
Control methods


If the disease does appear, then it is necessary to apply the treatment of the bush and remove the damaged clusters and shoots.
Gray rot on grapes can be treated with the folk remedies described below. First, all affected parts of the plant are destroyed, then they are sprayed with a weak solution of green soap or baking soda. To prepare a soda solution, take 70 g of soda per bucket of water.
The soap solution should be 1%. Processing is carried out every 10 days. The solutions are alternated. Of the chemicals, fungicides against mildew will be the most effective, and Ronilan and Rovral in low concentration. It is desirable to carry out processing every 2 weeks. Don't forget about prevention.
They also begin to fight white rot by removing all damaged shoots and bunches. Effective weekly treatment of the bush with a 4% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
After hail or other mechanical damage to the berries, you can spray with some copper-containing preparation. Mildew and powdery mildew preparations help well in the fight against white rot.
You can get rid of black rot with the same preparations as for white. But the most effective remedy is a mixture of two fungicides: 25 g Ridomil Gold and 60 gr Tiovit Jet on a bucket of water. After 2 weeks, the treatment is repeated.
It is important not to carry out processing with chemicals during the ripening period of the berries.
Amur grape variety
These grapes can be grown not only for harvesting fruits, but also as an ornamental plant. His homeland is the Far East and China. In the wild, it grows in river valleys and on forest edges, in places growing into dense thickets.
- The Amur variety is a deciduous liana, up to 30 m long, dotted with clusters with a loose distribution of fruits. With the help of antennae, the plant, like ivy, climbs nearby buildings or trees. The bark of the liana is green, and by autumn, together with the foliage, it turns into a dark red color.
- The color of the berries is bluish - black, their skin is thick. The taste of the fruit is usually sour, but sometimes sweet specimens are found, you can feast on them without the threat of poisoning.
- You can harvest at the beginning of September and it must be done quickly, because the berries do not tolerate downtime and quickly deteriorate.
- Winter hardiness at a high level: able to withstand cold up to - 45 O C.
- Amur grapes prefers to grow on loose and acidic soils, the last point is achieved by introducing appropriate fertilizers into the soil.
- The variety needs good lighting, as in the shade, its fruits become a bait for mildew.
- The plant loves moisture and may not have enough rain, so the main rule of caring for it is constant watering.
- Grapes are used to decorate cityscapes and factories, as they perfectly tolerate industrial gas.
Taste preferences are subjective and there are people who respect and love sour varieties. This can be useful for experienced and novice tasters and winegrowers who want to grow such grapes on their site.
Grapes do not gain sugar - what is the reason? In order for ripe bunches of grapes to be sweet and juicy, you must adhere to simple rules.
In order for ripe bunches of grapes to be sweet and juicy, you must adhere to simple rules:
The grapes should not be watered while they are ripening. Otherwise, the berries will turn out to be larger, but you will face a problem - they will burst, the process of their final ripening will be delayed. In this way, you can postpone the harvesting process for a couple of weeks. For the same reason, it is not recommended to plant vegetable beds next to the vine, since the grapes have a very developed root system and take some of the moisture in these beds. It is better to plant radishes, potatoes or onions next to the vineyards, which leave earlier than the grapes have time to ripen.
Another common reason that grapes do not store sugar well is the congestion of the vine, and the plant is not necessarily overloaded with bunches of grapes, it can be hampered by extra green shoots. Therefore, experts recommend leaving no more than 40 buds after pruning grapes in order to minimize the number of shoots after wintering. If you neglect this recommendation and leave more buds, then in the spring the extra shoots will take on too much vine strength, and there will be few microelements necessary for ripening the berries, the bunches will ripen later than necessary. The situation is even worse if there are too many bunches on the vine - such a vine spends too much energy to ripen each of them, but as a result the grapes are not sweet and unripe, and there is no need to expect a bountiful harvest from this bush next year. Therefore, for each shoot there should be no more than 1, in exceptional cases, 2 bunches. If the removal of extra bunches is no longer advisable, then you can remove a third or even half of each of them, so that the rest will not lose its taste.
And sweet, if you feed the vine with some kind of fertilizer. It is believed that it is best to use ash for these purposes, which is infused in water for 2-3 days and applied to the loosened soil under the vine. Dry ash can be used in the same way. Thanks to this, the berries will become not only sweeter, but also more beautiful. Instead of ash, you can use superphosphate and potassium sulfide, using them in the same way as ash.
Diagnostic tests
The stale breath of a child, the smell of which has a persistent scent of iodine, can lead to a lot of questions from parents. Concern about the reasons for the appearance of such signs and uncertainty about the risks to the baby's health indicate the need to consult a specialist. More often than not, anxious parents go to the pediatrician. After listening to complaints, the doctor often refers the patient to an endocrinologist. The first thing this specialist will do is take an anamnesis from the words of the parents (or the child). After the information received, the endocrinologist will proceed to an external examination of the patient. According to its results, a specialist is determined with the need for certain studies.
If there is a suspicion that the specific odor of iodine from the mouth is caused by a particular pathology, the child may be sent for an ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland. A complex of laboratory tests of blood, urine and feces may be required. A blood test is taken to determine the level of the pituitary hormone, and urine is taken to determine the amount of iodine in its composition.
In the past few years, the aes-isap method has been used to diagnose iodism.
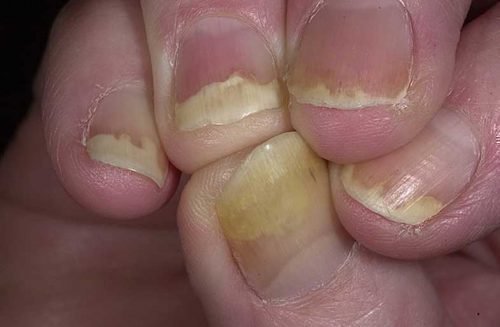

Manifestations of iodism on the nails
It consists in testing the patient's nail plate for the content of iodine in it. Its amount is determined by the length of the luminous flux that microelements emit. It can only be detected using special equipment for atomic emission spectrometry.
How to choose the right quality seeds
The process of selecting seeds for planting can be very fun, but it must be approached with knowledge. Following simple rules will help to purchase a product with the necessary characteristics, which, with the beginning of the planting season, will necessarily produce fresh young shoots.
How to choose a plant variety - general criteria:
- You should not choose high-yielding varieties, especially if you are an amateur gardener and are not familiar with the intricacies of growing them. In the overwhelming majority of cases, such plants require special conditions and much more care in comparison with simpler varieties. If growing requirements are not met, high-yielding varieties end up yielding significantly lower yields than less demanding low-yielding varieties;
- resistance of the variety to the effects of destructive environmental factors, as well as pests and diseases. Therefore, it is better to give your preference to unpretentious varieties that, although less productive, are able to withstand natural anomalies and not die;
- you should take into account the possibility of long-term storage of the fruits of the plant - the so-called keeping quality.
Signs of the disease
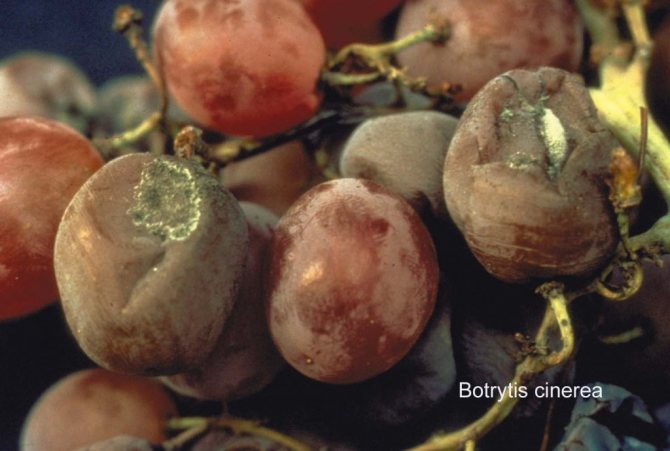
Gray rot can be identified by a number of characteristic symptoms. Among those:
- the appearance of brown spots on the leaves with a grayish bloom;
- drying out and falling of leaves during the dry season;
- dying off of the shoot bark and the formation of brown spots and gray plaque on it;
- discoloration of inflorescences, darkening, drying out and falling of flowers;
- retardation of fetal development into parts of the bunch;
- color change of berries, the appearance of a gray bloom on them, fruit decay.
Gray mold does not always affect the entire vine. It can affect a certain part of the shrub, some branches and individual clusters. In this case, the plant can be saved if diseased shoots are removed in a timely manner. If signs of the disease are observed on the entire shrub, in most cases the plant cannot be saved.