The grape is a thermophilic crop and most of the table varieties are grown in the southern regions. For those who live in the middle lane and want to have tasty fruits and large bunches on their site, the Nizina grapes are suitable. This hybrid was bred by an amateur breeder N.V. Krainov based on two varieties - Talisman and Radiant Kishmish. What are its distinctive features?

Breeding history
The appearance of the hybrid grape variety Nizin can be called a revolutionary event in Russian breeding.
An amateur breeder Viktor Nikolaevich Krainov, a famous Russian winegrower, was engaged in the development of a new variety of berry culture, crossing the Talisman variety and Tomaysky grapes by pollination.
In 1998, the breeder received the first crop of a hybrid crop, which was later named Lowland. After lengthy trials, in 2020 a new hybrid variety was entered into the state register of fruit crops with a recommendation for cultivation in any climatic zone of the country.
Requirements for conditions
Nizin grapes, in general, are unpretentious, however, in order to obtain consistently high yields of berries, certain conditions must still be met. Let's get acquainted with the requirements for lighting, site selection, soil, etc.
Seat selection
In order for the Lowland grapes to please with good growth and impressive yields, it must be placed on an area abundantly lit by the sun. The best option for placing bushes is the south side of the garden. You should be aware that grapes growing in the shade will not bear fruit well.


The best harvests grapes of the Nizina variety will be able to please when growing in fertile black soil. If the soil in your garden is far from the quality of black soil, you will have to feed the plant well, fertilize it - and a good harvest will be ensured.
Occurrence of waters
Lowland grapes should grow in an area where there is no close groundwater. Otherwise, plant root decay is likely. It is necessary to make sure before planting that the groundwater flows at a depth of at least 2.5 meters.
Occurrence of waters
Description and features
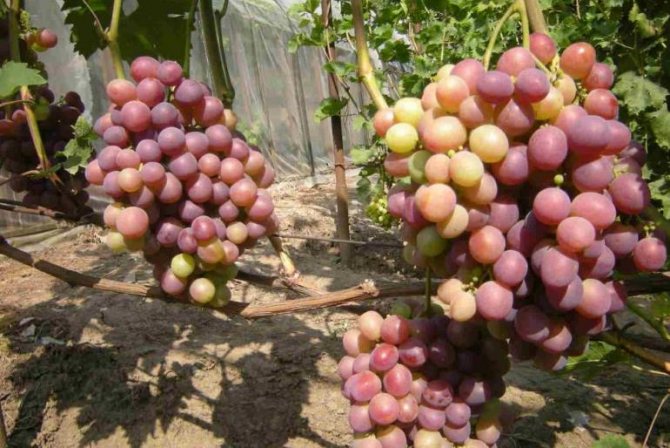
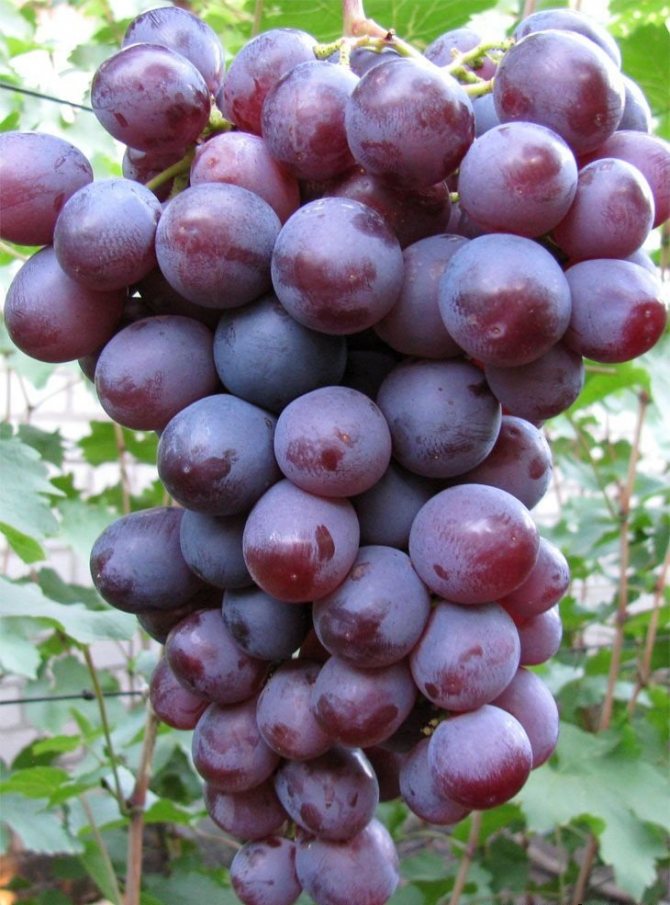
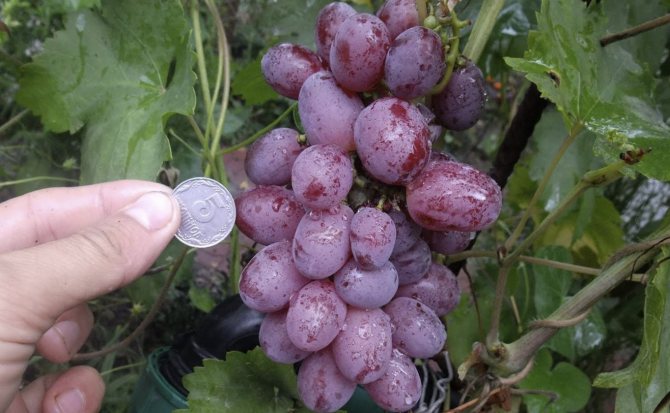
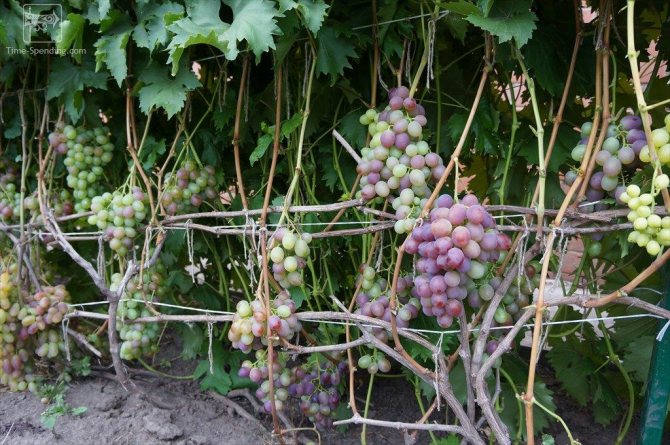
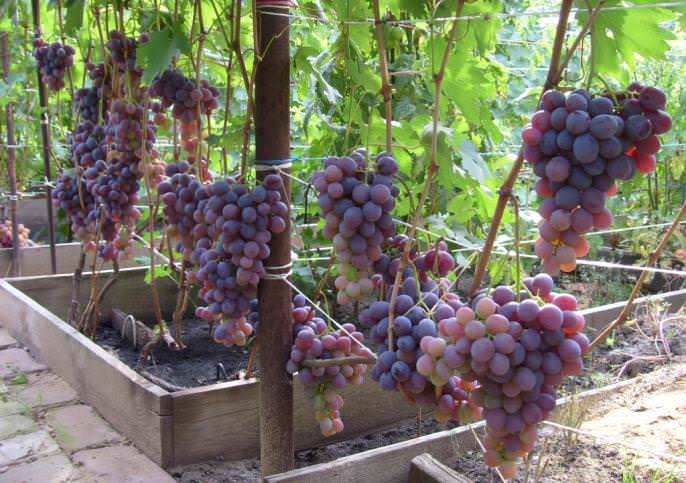
The Nizin grape is recognized as a table, a universal variety of fruit crops with early ripening of berries. The fruit crop is distinguished by high yield rates, large berries and unpretentious care.
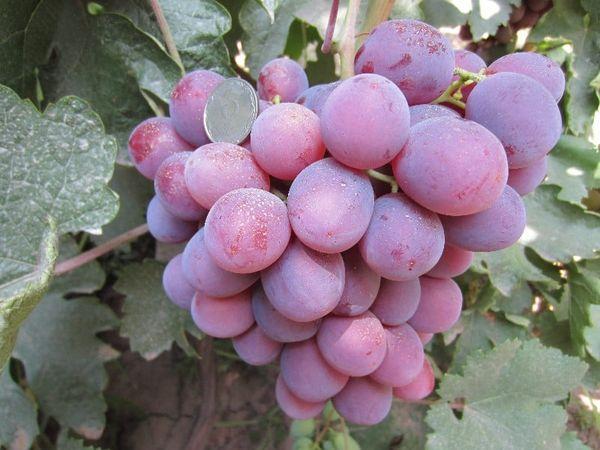


- Vine bushes are vigorous with spreading branches. During the growing season, the bush grows up to 25 fruitful shoots, on which brushes weighing from 700 g to 1.5 kg are formed, with large berries.
- Leaf plates characteristic of fruit crops, green in color with jagged edges.
- During the flowering period, clustered inflorescences with small flowers of both sexes appear. But to increase the fruiting of Lowland grapes, it is recommended to plant pollinators with similar flowering periods.
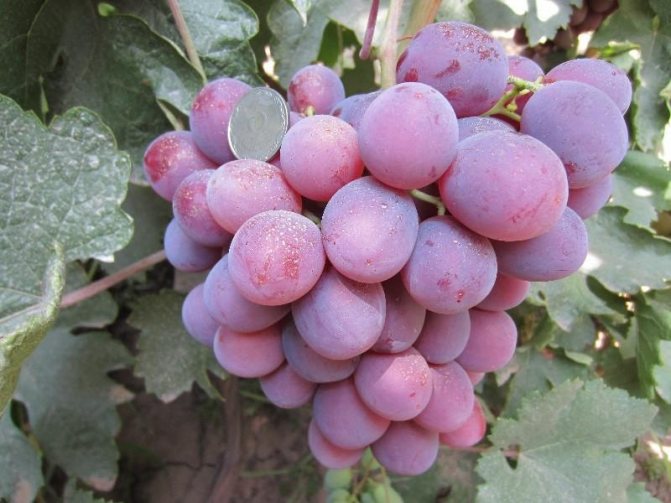
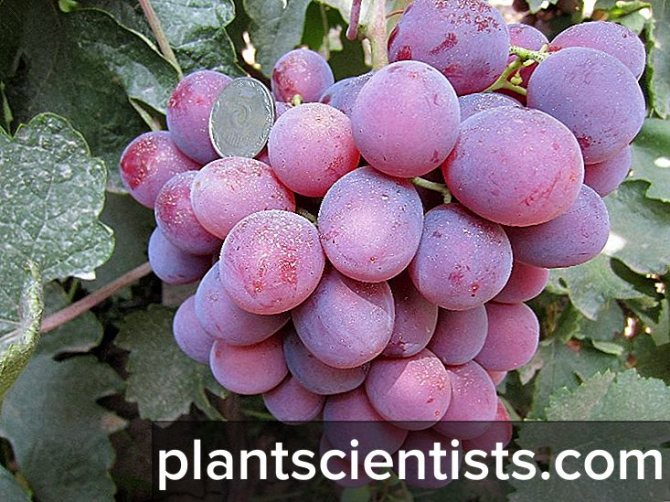
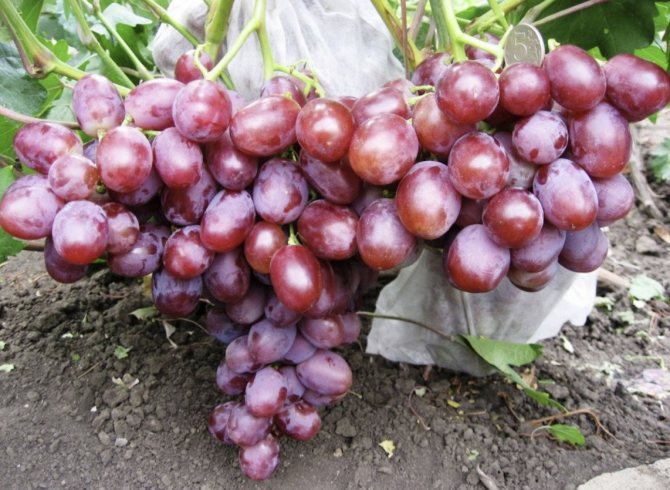
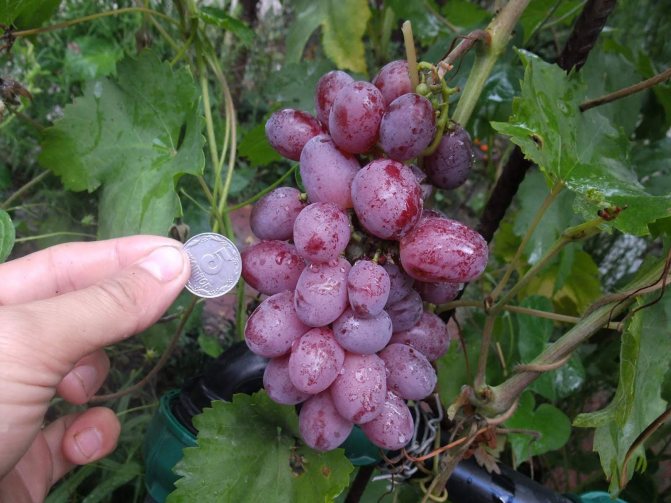
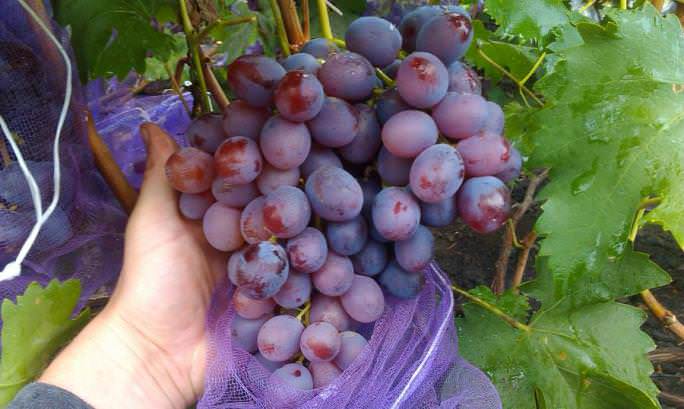
- The bunches are dense in the form of a cylinder or cone, each of them ripens more than 30 berries weighing from 10 to 12 g of a dark purple hue.
- Fruits are juicy with fleshy, sweet pulp and dense, thin skin. Ripe berries have a cherry aftertaste.
- The level of sugars ranges from 16 to 18%, acids up to 9 g / l.
Advice! The longer the grape clusters remain on the bushes, the sweeter the berries become.
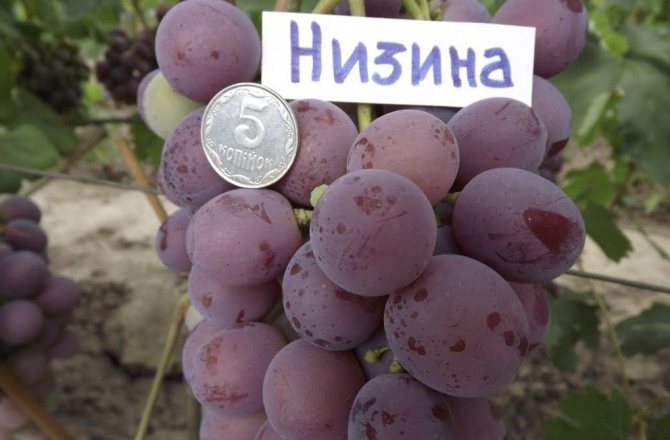
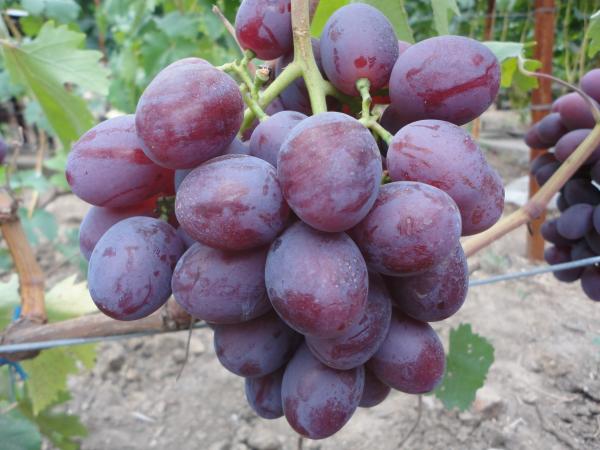
Grapes "Nizina": description of the variety
The bunches of this grape are cone-shaped. When ripening on black soil, the berries have a pronounced bluish - purple color. The bunches are very large in appearance, the weight of which is sometimes reaches about 3 kg... Beautiful oval fruits also have an impressive weight and size. The parameters of one berry are 3 by 2.5 cm, with an average weight of 13 g.
The bright red hue of the bunches does not always indicate full ripeness, since the rich color appears before full ripeness. When finally ripe, the berries darken and turn dark purple.
Among the dark varieties, Violet Early, Witch's Fingers and Ataman are especially popular.
The pulp of the berries is characterized by rich taste, fleshy and dense.
Skin with its thickness practically not felt and is eaten without a trace.
Almost no seeds, only two or three in one grape.
In terms of sweetness, the berries of this variety are superior to some similar varieties. So, the sugar content in relation to acidity is in a ratio of two to one.
Characteristics of the variety
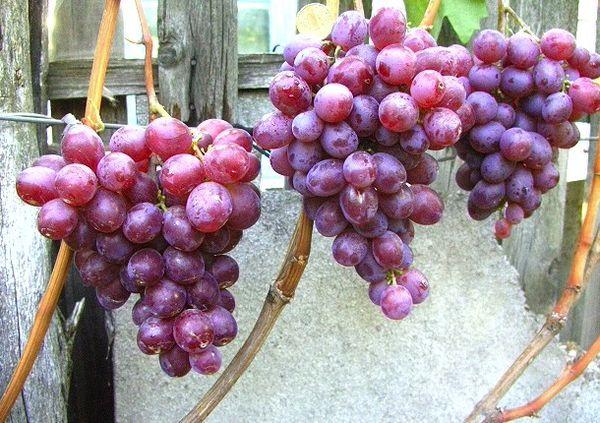
When breeding a hybrid berry crop Nizin, the characteristics of resistance to low temperatures, droughts, resistance to fungal infections and pests were taken into account.


Frost resistance
The resistance of the fruit crop to winter frosts makes it possible to grow the variety even in the northern regions.
Berry bushes calmly tolerate frosts down to -23 degrees, and with a reliable winter shelter up to -33-35 degrees.
Drought tolerance
The variety has a negative attitude towards both prolonged droughts and soil with a high moisture content.
Therefore, it is recommended to water the fruit bushes no more than 1 time in 30 days, and in case of rainy weather, irrigation work is completely abandoned.
Productivity and fruiting
Fruiting of lowland grapes begins at 3-4 years of growth and development in the ground. The ripening time of the crop depends on the weather indicators of the growing region. In hot, southern latitudes, berry picking is carried out starting from August 10-15. In the middle zone with a temperate climate, the grapes ripen in the last week of September.
From the beginning of the flowering period to the full readiness of the berries, it takes from 125 to 130 days.
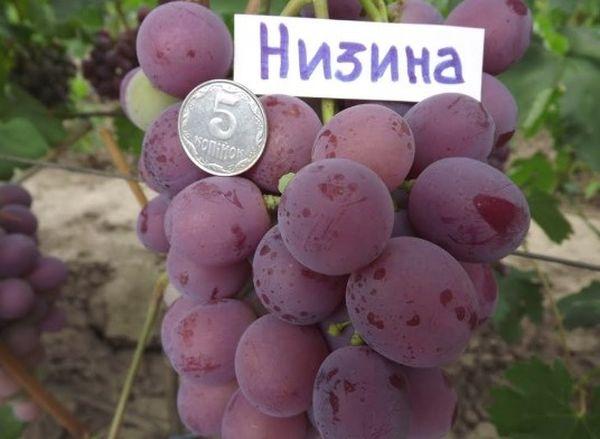


Up to 20 kg of fruits are obtained from one bush. In industrial volumes, the maximum yield indicators reach 17 tons per hectare of land.
Important! In temperate climates, it is imperative to monitor the load on fruitful shoots. An overloaded vine ripens longer, which is unacceptable for weather conditions and threatens with loss of yield.
Applications of berries
The table variety of fruit crops is recommended to be consumed both fresh and processed. Berries contain minerals, vitamins, amino acids and antioxidants that are necessary for the body to function properly and defend itself.
Juices, nectars, jams, preserves and marmalade are produced from the fruits. Also, grapes are used to make baked goods, desserts, sauces and dairy products.
Many experienced housewives freeze, preserve, dry fruits, make homemade wine and liqueurs.
Disease resistance
With proper care, lowland hybrid grapes are rarely affected by fungal, viral diseases and pests.
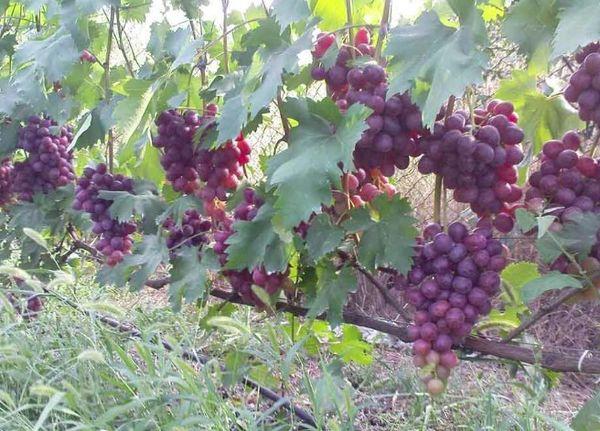


The problem faced by growers of this fruit variety is its low resistance to powdery mildew.
Pollinating varieties
To increase fruiting, professional gardeners recommend planting other varieties of fruit crops near the Lowland.
Mascot
Table grape variety Talisman is considered early ripening, ripening period from 122 to 130 sunny days. The bushes are tall, with spreading branches and large clusters, weighing up to 1 kg.The berries are large, juicy, sweet in taste, whitish-greenish in color.
The variety is distinguished by its relative frost resistance, easily tolerates winter minuses up to -23 degrees, is rarely affected by fungi, viruses and pests. The plant is not capable of self-pollination.
Laura
The variety was developed and bred by Ukrainian breeders. The ripening time of Laura grapes is from 110 to 115 days. The bunches are large, cone-shaped, weighing up to 2.5 kg. The berries are elongated, whitish-greenish in color, with a dense, juicy pulp with a sweet taste. For fruiting, neighbors with similar flowering times are needed.


Victoria
Table grape with a maturation of 115-120 days. Compact bushes with large clusters, weighing up to 700 g, and berries from 6 to 8 g of red-raspberry color. The fruits are sweet, juicy with dense pulp and nutmeg aroma. An adult bush can withstand a load of up to 30 fruit eyes.
See also
Methods of dealing with wasps during the ripening of grapes, how to protect it
To read
The variety is resistant to low temperatures and fungal infections.
Fruit crops require pollinators.
Bashkir early
The variety is designed for cultivation in cold climates, therefore it has increased resistance to low temperatures.
The bunches are small, but with large, juicy, sweet berries of a dark purple hue.
The variety is not capable of self-pollination; correct neighbors are required.
Gunna
An early ripe grape variety with technical maturity from 90 to 100 days. The clusters are small, cylindrical in shape with dark pink berries and the delicate aroma of Isabella.


The variety is excellent both for fresh consumption and for making homemade wines.
Madeleine Angevin
Madeleine Angevin table grapes are distinguished by their early ripening and varietal varieties.
The fruit crop perfectly tolerates low temperatures, which makes it possible to grow berry bushes in different climatic zones.
Pukhlyakovsky
Fruit crop with early flowering and late ripening. The bushes are tall, with powerful branches and shoots, with large cluster-like inflorescences and berries.
Fruit ripening occurs 150-155 days after the beginning of flowering.
Fruits are juicy, sweet, amber in color. Up to 17 tons of ripe berries are obtained from one hectare.
Chaush
Chaush grapes are distinguished by their resistance to drought and heat, cultivation in the southern regions is recommended.
The variety is high-yielding, with proper care and pollinators, up to 20 tons of ripe berries are obtained from 1 hectare of land.
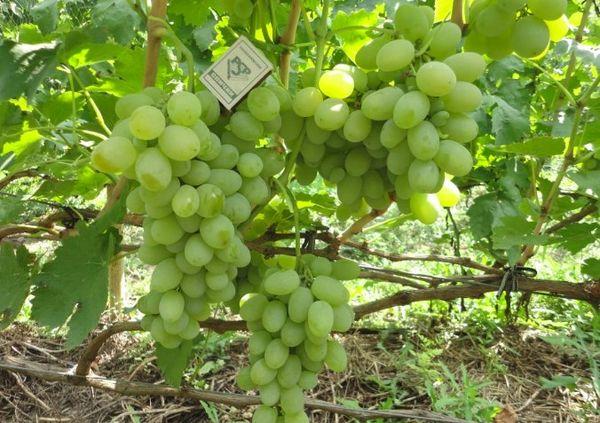


The grapes are large, greenish-yellowish, with juicy, dense pulp of sweet and sour taste.
Low resistance to temperature extremes and frost, often exposed to fungal infections and pests.
Moldavian black
A table variety of berry crops with ripening periods of up to 137 sunny days. The berries are large, purple in color, with a pleasant sweet and sour taste.
Up to 15 tons of ripe fruits are harvested from one hectare.
The variety is resistant to frost and disease, tolerates well not prolonged drought. The variety is not suitable for winemakers, it is recommended to use it fresh.
Harvesting and application of the crop
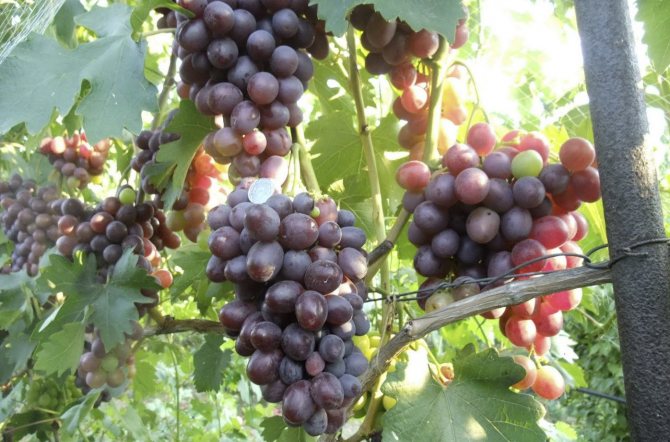
The berries of the Lowland do not have the famous nutmeg shades that are so prized in winemaking, but they have a pronounced fruity taste, which is a great rarity for grapes. The main purpose of the hybrid is fresh consumption. Many farmers include Lowland in their market collection.
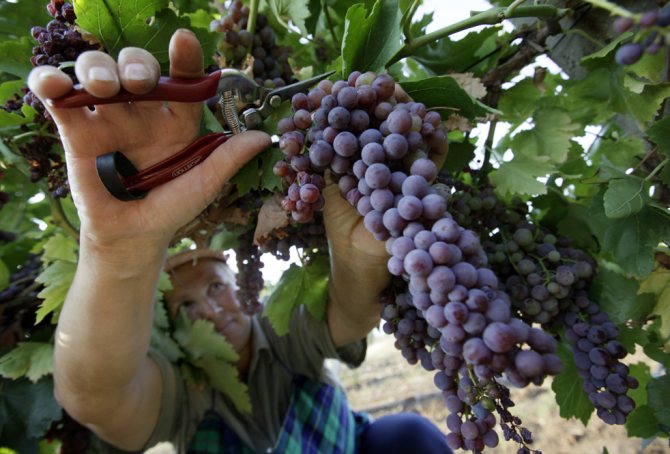


To preserve the presentation and extend the shelf life, during harvesting, hold the bunch not by the berries, but by the leg
If you plan to store, transport, sell grapes, cut the bunches carefully. Choose for this the first half of the day, when the berries have already dried out from the dew, but have not yet warmed up in the sun. When collecting, try not to damage the wax coating on the skin.Hold the brushes by the twigs and place them in boxes lined with paper. At a temperature of 0 ... +7 ⁰C, Nizin grapes are stored for 2 months, but they must be regularly checked and sorted out, removing rotten berries. Surplus crops are frozen, processed into compote or jam.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Before planting Lowland on a personal plot, it is necessary to clearly record all the advantages and disadvantages of the variety.
Benefits:
- High yield rates.
- Resistance to low temperatures and return frost, which simplifies the cultivation of fruit crops in regions with different climatic conditions.
- Annual, stable fruiting.
- Large size fruits with excellent taste.
- It is rarely affected by fungi and viruses.
- Duration of storage and the possibility of long-distance transportation of ripe berries.
Important! A distinctive feature of the variety is the full maturation of the fruitful vine.
Disadvantages:
- Prolonged drought and high temperatures increase the risk of disease.
- The bush produces a large number of fruit shoots, which increases the load on the vine and the ripening time of the berries. It is necessary to constantly regulate the shoots.
- Spreading plants require a large area for growth and development, which makes it difficult to grow in small areas and vegetable gardens.
The rest of the grapes of the Nizina variety are unpretentious, both in care and in the process of planting seedlings.
Testimonials


Gardeners of the southern regions often note this particular grape variety - Nizina. Given its features, such as the same yield or disease resistance, vineyards stop their choice on this particular grape subspecies.
Many people note the sweet taste of the berries, the characteristics of the grapes in terms of strength and juiciness. There are practically no downsides, with the exception of the possibility of flooding the bushes and an acute reaction to some types of dressings.
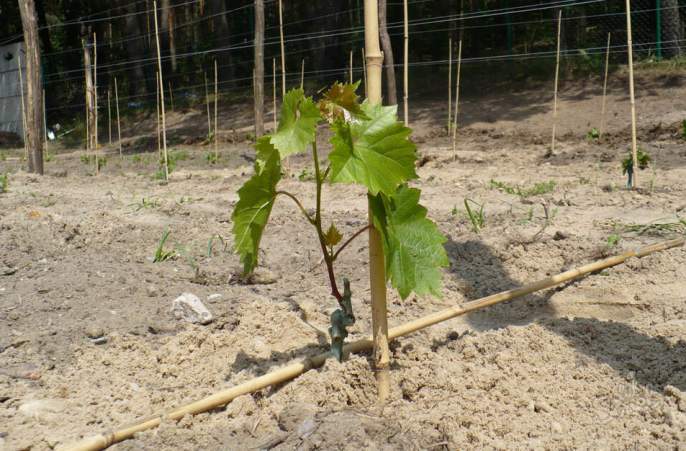
How to plant correctly
To obtain a high-quality harvest, it is necessary to choose the right place and observe the timing of planting grape seedlings.
Timing recommendations
Nizina grapes are recommended to be planted in the spring, before the beginning of the growing season. In this case, the seedlings will have enough time to adapt to a new place and root.
In the fall, planting work is carried out in the first half of September, so that before the first frost the seedlings have time to take root and prepare for wintering.
Site selection and preparation
Any grape loves sunny areas and hills, the Nizin variety is no exception.
Illumination
For planting a fruit crop, the southern sides of well-lit areas are chosen. Even a slight shading of the plants negatively affects the ripening and taste of the fruit.


Draft protection
Vine bushes do not tolerate gusty, cold winds and strong drafts, but at the same time, the plantings must be ventilated.
In gardens and orchards, buildings or fences can serve as protection against drafts.
The groundwater
The close location of groundwater is detrimental to grape bushes. Plant rhizomes quickly rot and die.
The maximum permissible groundwater level is not less than 2.5 m from the soil level.
Ground requirements
Special attention is required to prepare the soil for planting seedlings and planting holes.
Nizina grapes prefers loose, fertile soils with a low acid and moisture content.
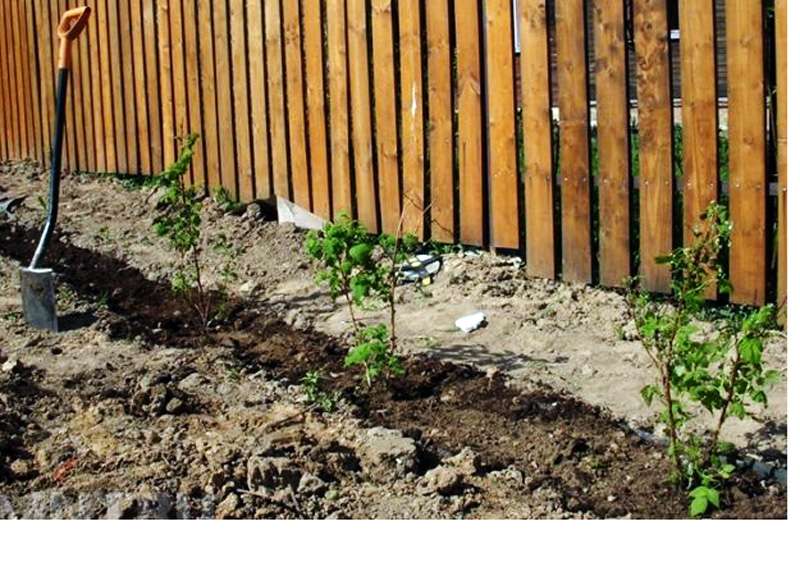
Mutual arrangement of plants
The bushes of hybrid grapes are spreading, therefore, plants require a lot of space for growth and development.
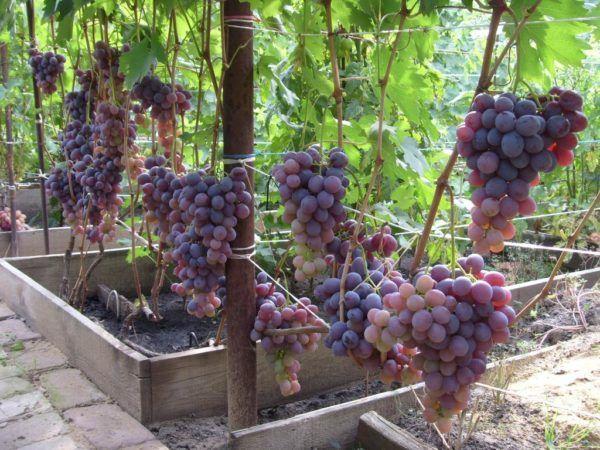


A distance of 2.5 to 3 m is observed between plantings, 3-4 m between rows. The length of a row should not exceed 30-40 m.
How to cook
The soil is prepared 4-6 weeks before planting.
- Organic matter and mineral fertilizers are added to the chernozem soil.
- The site is carefully dug up to a depth of 80 cm, debris, weeds, roots are removed, and loosened.
- Sandy soil is mixed with humus or manure, a small amount of clay is added.
- In heavy, clayey soils, compost and some river sand are added.
- Drainage is laid out in the planting holes, prepared fertile soil mixture is poured on top.
The plot is watered, and support pegs for seedlings are driven into the holes.
How to choose and prepare planting material
Varietal seedlings of hybrid grapes are purchased in specialized centers or nurseries.
- Transplanting 2-3 year old plants is best tolerated.
- The seedling is carefully examined for damage and disease.
- The trunk of the plant is even, monochromatic, the presence of green leaves or buds is required.
- The roots are well developed and moist, without damage and putrefactive manifestations.


Before planting in open ground, the seedlings are sent to a container with warm water, and left for 10-15 hours.
Advice! For the prevention of diseases and pests, rhizomes are treated with a weak solution of manganese.
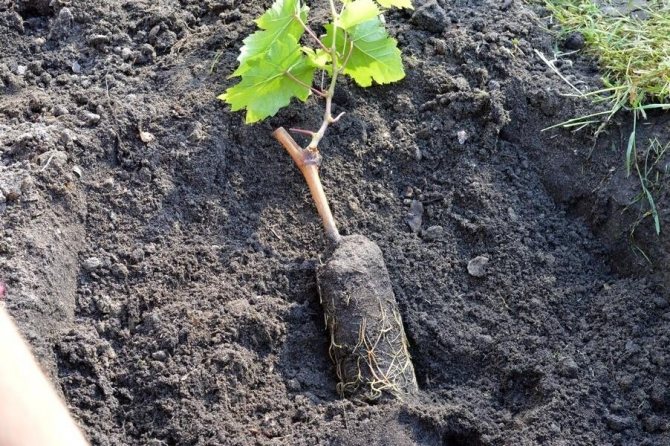
Landing scheme
Before starting planting, the roots of the grape seedlings are cut, leaving only the longest and healthiest branches.
- Plants are placed in the center of the well.
- The roots are evenly distributed in the planting pit and covered with a fertile mixture.
- The soil is tamped, the seedling is tied to a support.
- The planted plant is watered abundantly.
- The trunk circle is mulched with humus or dry grass.
See also
Description of Galahad grapes, planting and care rules
To read
Important! The voids left between the roots and the soil during planting provoke the development of fungal, viral lesions and the spread of pests.
How should you care for your vine?
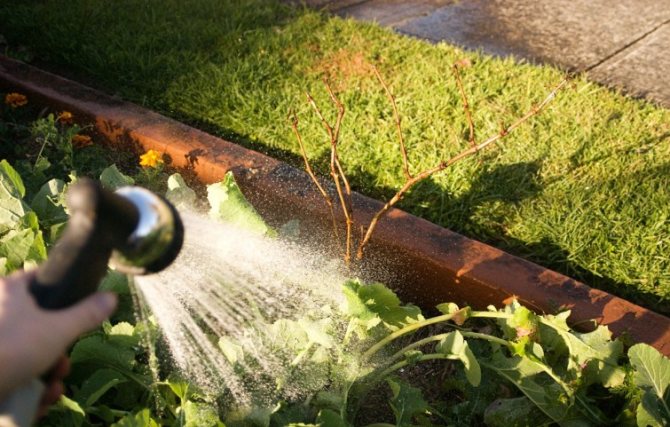
Lowland grapes need regular watering. A constant supply of moisture ensures that the yield is good. The question is especially relevant in the hot summer period. Moisture is retained well if the area near the trunk is mulched. The variety must be watered during the period of active growth and at the time of the formation of berries. Also, the shrub is watered in the fall in order to charge the plants with moisture so that tasty and sweet berries grow next year, with this procedure the bushes will not freeze in winter.
One of the main points is feeding. In mid-March-early April, the plant is fertilized in the near-stem region. Superphosphate is used as a fertilizing material, its amount is 40 g per 1 m2. In the last month of spring, nitrogenous fertilizers are applied so that the bushes have a rich green color. After the buds have swollen, a solution is prepared from the chicken droppings, and the plant is irrigated with it. In order to prepare it, you need to use 1 liter of droppings and 2 liters of water, mix and let it brew for 7 days. After the infusion is diluted with water, for each liter of infusion there are 10 liters of liquid. When watering, a liter of infusion is used for one seedling. When forming berries, it is worth resorting to fertilizers containing potassium, they are used according to the instructions. Such manipulations help the plant to produce vegetable sugar. Feeding is applied regularly and it is brought under the root system, combined with watering.
Periodically, the plant must be sprayed to prevent pests and diseases. In the autumn and spring, Anthracop will be an excellent helper in the fight against the enemies of the vineyard.
The shrub is pruned every year. The most suitable form is considered to be a fan with sleeves. This formation is less injurious to the plant. If the shoots are shortened in general, then they need to be shortened by 3 eyes, and if each is required to be shortened, then by 9 eyes. At the time of harvesting the fruit, the bunches need to be normalized.
It is necessary to cover the plant, since every year it is not known how cold the winter will be.Adult strong shrubs are not afraid of a drop in temperature, but reinsurance will not hurt in case of severe frosts. Grape growers usually propagate this variety: by layering, grafting or seedlings.
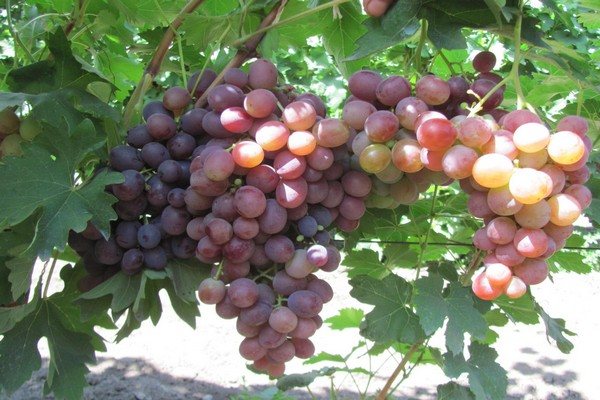


Lowland grapes: photo of the variety
Care rules
Vineyard care is not difficult, it includes watering, fertilizing, pruning and preventive treatment of the bushes.


Watering mode
Watering is carried out taking into account the climatic characteristics of the area of growing fruit crops.
The main watering schedule is 1 time in 3-4 weeks. Up to 30 liters of water are poured under each bush.
During the rains, watering is stopped, and at the time of drought, it is increased.
Top dressing
Grape bushes give a lot of energy and nutrients for the ripening of berries, so plants need additional nutrition.
- At the beginning of the growing season, grape bushes are fertilized with organic matter.
- In the phase of flowering and the formation of ovaries, the berry crop lacks phosphorus and potassium.
- During the ripening period of berries, the bushes are also fed with potash fertilizers.
The last feeding is carried out in late autumn. Humus and wood ash are added to the soil.
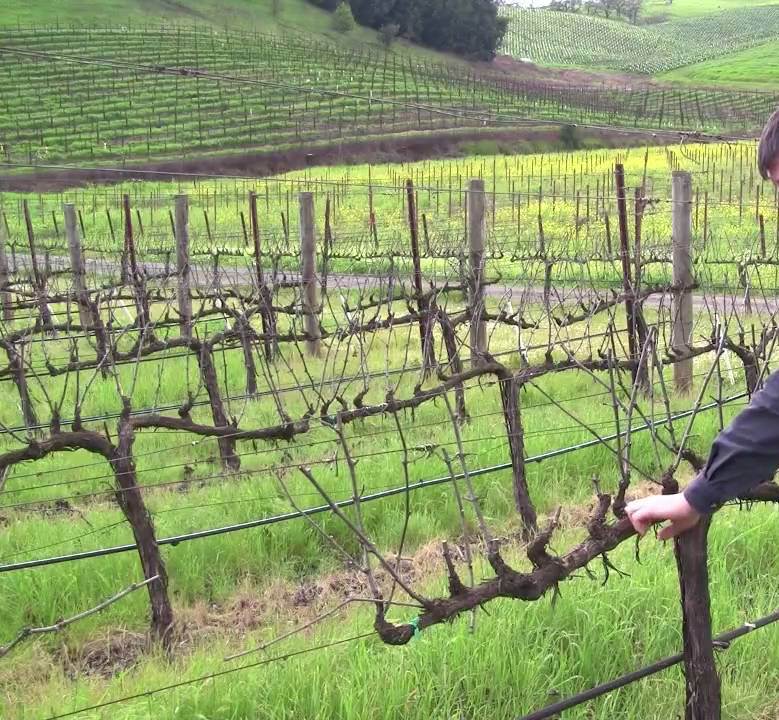
Trimming and shaping
To increase yields and correct growth, grape bushes are annually subjected to formative and sanitary pruning.
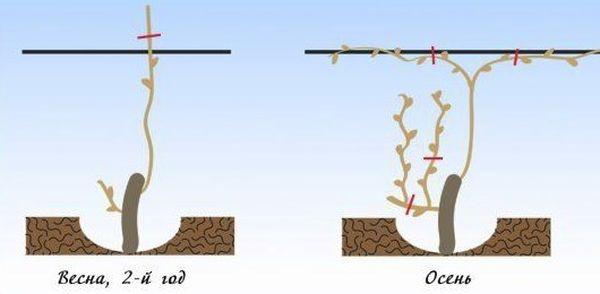

First season
In the first year of growth, the plant develops roots and the green mass builds up. All young shoots are removed, leaving 2-3 shoots.
Second
In the second year of growth, the main skeletal branches and sleeves are laid in the vine bushes. For this, 2 to 4 shoots are left on the bush, the rest are cut off.
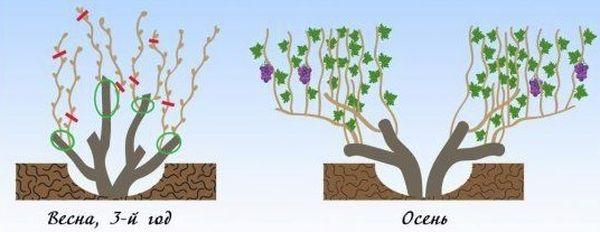
The third
At the beginning of spring, the main branches are shortened, the formed sleeves are tied to the supporting structures, the growing vine is strengthened vertically on the trellis.
Sanitary pruning is carried out every autumn, removing broken, dry, damaged and old branches and shoots.
Protection from birds and insects
Bunches with beautiful and tasty grapes often attract birds and insects that can harm the crop.

To scare away birds, scarecrows are installed, shiny objects are tied up or berries are covered with a fine mesh.
To prevent protection from pests, in early spring, the fruit crop is sprayed with insecticides.
Preparing for winter
Before winter rest, the fruit crop is abundantly watered, fed, the trunk circle is loosened and mulched with a thick layer of humus.
In regions with harsh winters, grape twigs are removed from the supporting structures and bent to the ground. From above, the grapes are covered with a film and spruce branches, when it snows, they create a high snowdrift.
Preventive spraying
In order not to lose the harvest of berries and strong, healthy bushes of grapes, preventive treatments of the bushes with chemical and biological preparations are carried out 2 times a year.


Features of the formation of a bush
Lowland grapes grow very quickly. It shoots as soon as the active movement of the juices begins. A strong growth of green mass leads to the formation of a fruiting vine. It makes up more than 80 percent of the total number of shoots.
With proper care, 2-3 clusters should remain on each branch. More brushes will weaken the plant. The hybrid has bisexual flowers, so pollination takes place inside the vineyard. No additional measures are required for the appearance of ovaries.
With proper care, timely watering and fertilization, the bushes begin to bear fruit as early as 2 years after being placed in the ground.
Advertisement 1
Reproduction methods
To increase the number of grape bushes and rejuvenate plants, vegetative propagation methods are used.
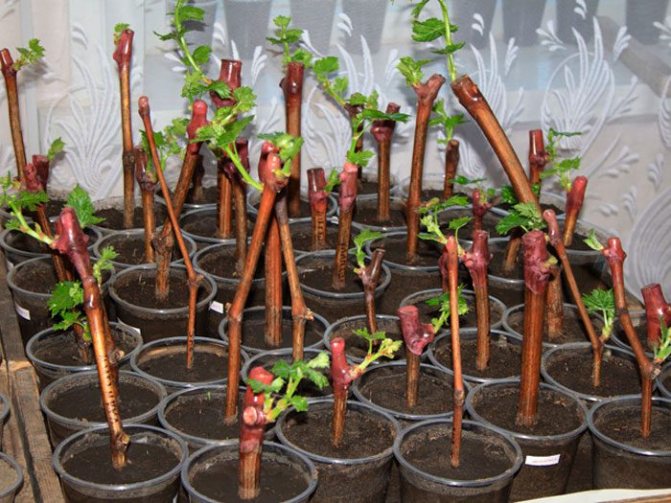
Cuttings
In the spring, from a healthy, adult bush, a strong shoot is cut off and divided into equal parts. Each cut should have buds or leaves.
The stalk is planted in a container with a fertile mixture, and at the beginning of autumn, the rooted seedling is transferred to open ground.
Graft
A young stalk is grafted onto an old grape bush. To do this, an incision is made on the bark of the guide of an adult plant, and the cutting is fixed with a special tape.
Layers
Reproduction by layering, a quick and easy way to get new seedlings. At the beginning of summer, a strong, lower shoot is chosen from a healthy bush and bent to the soil surface. The layering is sprinkled with earth, leaving the upper part of the branch above the soil surface. In the fall, the victories are dug up, and, together with the resulting roots, are separated from the mother bush. The seedling is transferred to a separate hole.

Diseases and pests
Unfavorable weather conditions and violation of the rules of care often lead vineyards to fungal and viral infections.
Oidium
Powdery mildew poses a threat to the health of fruit crops and crops. The disease manifests itself as a grayish bloom on shoots, leaves, ovaries and berries.
The process of fruit rotting is accompanied by a rotten smell.
For treatment and prevention, sulfur-based preparations or fungicides are used.
Mildew
Downy mildew affects the leaves, ovaries and berries of grapes. It appears with yellow and brown spots. The inflorescences dry out, the berries become small.
To combat the fungus, preparations based on fungicides and copper are used.
Anthracnose
The fungal infection manifests itself in the form of brown spots on the leaves, which eventually turn from the hole.


Plants are treated with Bordeaux liquid or fungicides.
Bacteriosis
The disease affects vines through contaminated soil, plant damage and pests. Bacteriosis manifests itself in the form of dark spots on berries, leaves and shoots.
For treatment, chemical and biological remedies are used.
Gray rot
The lesion manifests itself in the form of a gray, fleecy plaque on berries, foliage, buds and ovaries. For treatment and prevention, the bushes are sprayed with biological agents or fungicides.






































