Garlic pests: control methods
The main harm to garlic is caused by diseases caused by fungi. The reason for their appearance often lies in violations of agricultural cultivation techniques.
- The thickening of the plantings excludes air access to the leaves and roots of garlic.
- Excessive humidity, due to over-watering or rainy summers.
- Failure to comply with crop rotation.
- The presence of weeds and last year's plant residues.
- Inappropriate storage conditions for the grown crop.
These are just some of the reasons for the development of fungal diseases.
Why does garlic, which can scare off many insects, is itself often spoiled by pests that destroy green feathers and heads? There are more than a hundred species of these parasites. Let's list some of them.
Spider mite
When vegetables and fruits are planted on a personal plot, you need to be prepared for the fact that the plants, in particular the garlic considered in this article, may be negatively affected by such a pest as a spider mite. It seems that on the leaves of garlic cobwebs. What to do? In fact, it is a very small, about 1 mm, sucking animal.
Stems, shoots and leaves are wrapped in a white, at first barely noticeable cobweb, then it spreads, and the plant appears, as if in a cocoon. The fight against spider mites involves the following procedure:
- Wash leaves and stems with soapy water;
- Provide abundant watering. Ticks don't like moisture very much;
- After that, apply insecticides, for example, Karbofos;
- Process the soil.
Tobacco thrips
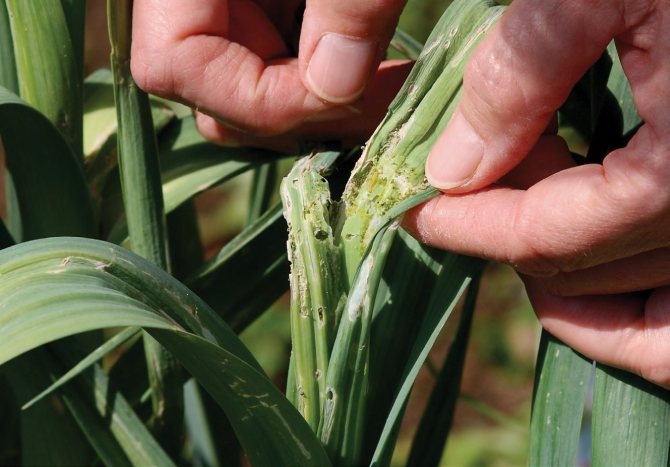
Who's chewing on garlic? Not only garlic, but also onions and a number of other plants damage the larvae of tobacco thrips. They are brown or yellow in color, their length is only 1 mm. Females lay eggs in leaf tissue. The born larvae suck the juices from the leaves and inflorescences.
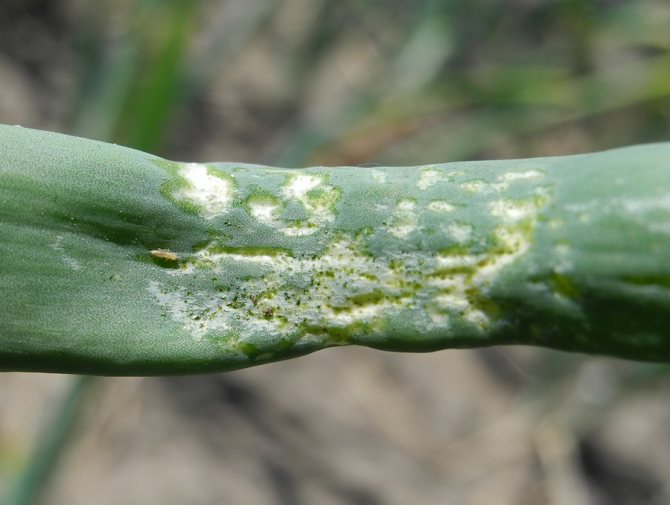

Tobacco thrips - consequences
They fight against them by alternating planted crops, disinfecting the heads before planting in hot water and loosening the earth with the addition of ash, mustard and pepper. This is a folk method.
Onion fly
Who is eating garlic in the ground? A centimeter onion fly has whitish larvae. She lays eggs under the scales of the garlic or between the leaves. The plant withers and dries up. At the same time, the heads become softer, rot, spreading a not very pleasant smell.
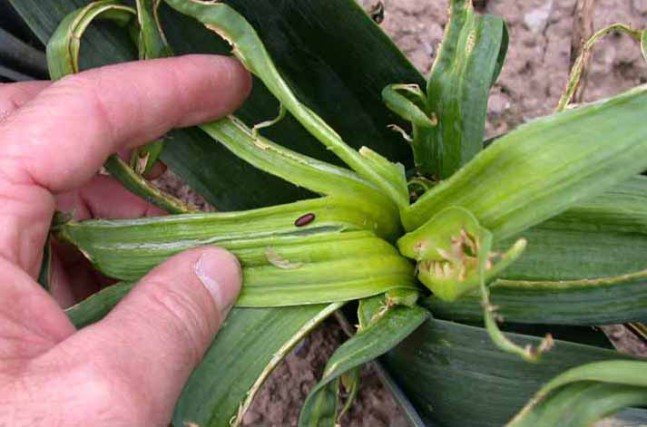


Onion fly


Garlic is planted earlier, when the onion fly is not yet flying. Also, to prevent its appearance and combat it, place garlic next to carrots and onions, pour it with a solution of salt, trying not to get on the feather. You can treat the garlic with a tobacco solution with pepper.
Stem nematode
Almost the most harmful to garlic is the stem nematode, which causes the plant to dry out completely. She can live in dry land for up to 5 years, eating up whatever she has to. It looks like a filamentous worm and feeds on the sap of the feather and the whole plant.
Its features are:
- Light stripes on the leaves;
- Then the leaves curl and dry;
- Pungent smell from garlic from the ground;
- The bottom of the bulb dries up and falls off.
Control methods - healthy planting material, disinfection of the teeth. The infected plant should be destroyed immediately, it is better to burn it. Changing the landing site helps.
The beneficial properties of garlic have long been known to mankind.Growing this crop is usually not a big deal. However, there are insect pests that can cause significant damage to plantings, or even completely deprive the crop.
Garlic pests
Pests not only damage the bulbs, but also contribute to the spread of various infectious diseases. Most often, garlic is affected by stem nematode, onion moth, aphid, onion fly, hidden proboscis, root and four-legged mites.
This small insect can harm almost any agricultural crop. Garlic is no exception. Aphids form colonies first on young leaves, sucking out juices and nutrients from them. It multiplies very quickly and is able to breed more than a dozen generations per season. These pests inflict the greatest damage on young plantings.
Aphids infect young shoots of garlic
Garlic feathers are curved, wrinkled, and later turn yellow. With a strong spread, pests affect the entire plant. In addition, insects carry spores of fungal infections. Garlic stops growing, various diseases begin. As a preventive measure, you need to systematically remove weeds and regularly carefully inspect the plantings.
Read more: Treatment of grapes with folk remedies for diseases
Stem nematode
The stem nematode is extremely dangerous for garlic. These are very small (1.5 mm) white worms. It is quite difficult to see them with the naked eye. But the results of their vital activity for the plant are very deplorable, because nematodes feed on plant sap.
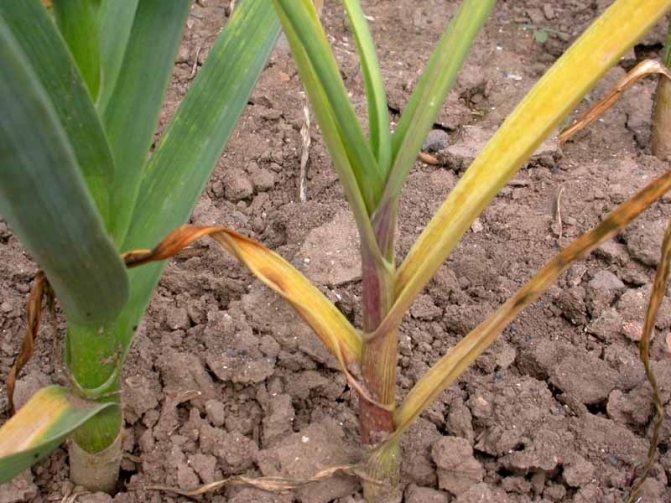
First of all, long longitudinal yellowish stripes appear on the plume of garlic, then the leaf blade curls and dries completely. The bulb acquires a pungent unpleasant odor, the roots rot, the bottom cracks and crumbles.
Nematodes live in the stems, bulbs, leaves and roots of garlic. Larvae hibernate in soil and plant debris. In the absence of plant food for nutrition, they are able to stay in dry ground in a state of suspended animation for more than 5 years. In a humid environment, they can live without food for a year. At the first opportunity, they come back to life.
A garlic bulb affected by a stem nematode cracks and darkens
Preventive measures:
- In order to prevent the attack of this pest, the soil is spilled with saline before planting the garlic (20 g of boiled salt is dissolved in a 3-liter jar of water - per 1 m2).
- The planting material is pre-soaked for a couple of hours in an ash solution. Or it is kept for a day in a solution of edible salt (3 l), to which a finely crushed fern leaf (160-200 g) is added.
- In heavy clay soils for prophylaxis, it is recommended to apply when digging in a large bucket of coarse sand and peat per 1 m2.
- For deoxidation, use chalk or dolomite (limestone) flour (300-400 g per 1 m2).
Onion fly
The insect is widespread on loam and sandy soils; it is extremely rare on acidic peat soils. This pest is similar to a common fly, only slightly smaller in size. Usually its length does not exceed 6 mm. Fly pupae in winter are in the ground at a depth of 15–20 cm.
In the spring, with the onset of warmth, the insect crawls to the surface and after 1–2 weeks lays eggs on the ground between plantings and near the root collar. After 5–8 days, larvae hatch from them, which penetrate into the clove of garlic through the bottom and then gnaw out the juicy entrails.
The onion fly looks like a common fly
After 2-3 weeks, the grown larvae leave the bulb and go down to pupate. After another couple of weeks, the cycle repeats. Thus, the onion fly is capable of producing 2-3 generations during the growing season.
The mixture is poured into 3 liters of heated water and infused for at least 2 days. You can wrap the container in a blanket for better steaming.
Then the solution is filtered, 20–25 g of laundry soap is added and diluted with water to a volume of 10 liters.
Root mite
It is an insect with an almost transparent vitreous body, not exceeding 1 mm in length. Lives in soil, damages all onion crops, potatoes and other root crops. It enters the bulb through the lower part - the bottom, gradually grinding it off the edges. As a result of the activity of the tick, white dust remains, the bottom falls off.
The root mite has an almost transparent body, no more than 1 mm in length
Females lay hundreds of eggs inside the bulb, which develop into adults in about a month. Favorable conditions are high temperatures (over 25 ° C) and humidity of at least 60%.
Heads of garlic affected by onion mites crumble like dust
Basically, the pest is dangerous for stored vegetables. Bulbs damaged during this period dry out completely.
To exclude contamination, it is recommended to dry the garlic bulbs thoroughly at a temperature of at least 30 ° C for 6-7 days before laying them for winter storage. It is necessary to carefully sort out and destroy the affected fruits.
Small pest, not exceeding 0.2 mm in length. This species prefers spring (planted in spring) garlic varieties. He not only eats root crops, but also spreads viral diseases. At the end of summer, females lay eggs on bulbs, sometimes on leaves. The larvae eat the juicy pulp. On the denticles under the husk, depressed yellow ulcer spots remain.
Small ticks are carried by the wind
The parasite is carried by the wind; it easily clings to leaves with its four paws. Weak plants with curved feathers grow from the affected planting material.
Onion moth
Not very large butterfly with a wingspan of about 14 mm and a body length of up to 8 mm. It usually flies out in early June and sticks eggs to the root collar or to the lower surface of the leaf blade.
Caterpillars appear after about 7 days and begin to gnaw the leaves quickly enough. Because of this, the plant slows down greatly in growth and cannot develop normally.
Read more: Pests of aphid cucumber leaves, treatment and control
The next generation of winged pests appears in about 30 days.
Onion moth usually appears in early June.


A beetle 2–2.7 mm in size often damages onions, but occasionally also garlic. In winter, the weevil hides in the remains of plants and under lumps of earth. It flies out in early spring and attacks bulbs planted in autumn.
Then it damages the early planting of onion crops. Females lay clutches on the inner surfaces of the leaves, the hatched larvae feed on the tender pulp. Longitudinal whitish stripes remain on the leaves. Garlic feathers turn yellow on top.
If the weather is dry, they die off.
The lurker gnaws tunnels in the stalks and leaves of garlic
Control and prevention measures:
- It is recommended to periodically loosen the soil between the rows, especially during pupation.
- It is necessary to thin out the plantings in a timely manner, rejecting damaged and weak plants.
- It is useful to sprinkle the soil between the rows with chopped wood ash, dry mustard or ground pepper.
Onion sharpener
- The thickening of the plantings excludes air access to the leaves and roots of garlic.
- Excessive humidity, due to over-watering or rainy summers.
- Failure to comply with crop rotation.
- The presence of weeds and last year's plant residues.
- Inappropriate storage conditions for the grown crop.
Fusarium disease of fruit and berry crops
No matter how much the gardener would like to avoid meeting with the pest of summer cottages, but no - the uninvited guest is right there. And all kinds of a rich harvest of fruit and berry crops disappear overnight.
Strawberry
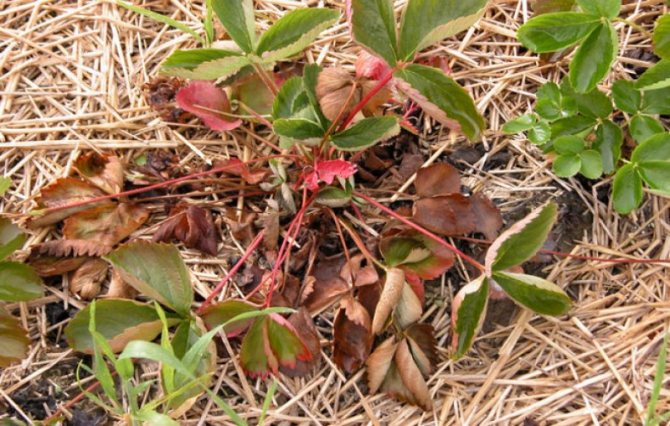
Strawberry and strawberry disease, unfortunately, is more common than one would like.Dry rot leads to the death of not only individual bushes, but often the entire plantation.
An attentive summer resident will immediately notice that something was wrong: necrosis (dying off) of the edges of the leaves, which wither, dry out, turn yellow and sag lifelessly. The petioles, together with the leaves, acquire a brown color, and when they turn black, they die off.
In this case, there is no need to talk about the ovaries - they either do not form, or, having formed, immediately die.
The whole process described takes a little more than a month, but it will certainly lead to the death of the plant.
Symptoms of the disease become visible in the ripening stage of the berries. It is during this period that strawberries experience an increased need for nutrition and moisture.
Fusarium wilting of strawberries in the photo:


The pertinent question would be: how to treat strawberry fusarium wilting? Is there really no control over this pest?
You must immediately answer in the affirmative: yes, you can cope with rot, but only at an early stage of the disease. When the leaves are just beginning to lose their natural appearance.
It is necessary to immediately treat the strawberries with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, Fundazole or Trichoderma Veride.
Diseased plants must be removed from the garden and must be burned.
Fusarium in strawberries, video:
Melon
Fungal attack is a terrible scourge for melon producers, especially in Central Asia. It is there that this epidemic most often rages. Dry rot, with the addition of all favorable factors, can easily destroy almost the entire crop of these representatives of the pumpkin family.
Affected shoots turn brown. The roots are painted in the same color. The hairs disappear on them. Then a scattering of reddish-brown spots appears, interspersed with longitudinal stripes.
A diseased melon has little chance of survival. If the fungus affects the bush during the ripening period, then the fruit does not ripen, losing its taste and aroma. And it is only suitable for animal feed, which is no less dangerous.
Temperature 22-25 ° and humidity up to 80% are the most comfortable conditions for Fusarium.
It has been verified that the most resistant to fusarium wilt are such melon varieties as Ich-kzyl 1895, Shakar palak 554, Khandalyak kokcha 14.
List of diseases and treatment
Not only pests, but also diseases of garlic provoke a decrease in the amount of the crop. No vegetable crop can be completely protected from negative external factors, so it is important to know about common diseases and methods of eliminating them.
To reduce the likelihood of developing bacterial infections, you should adhere to the following measures:
By adhering to a small number of measures, it will be possible to reduce the consequences of even such a dangerous disease as peronosporosis of garlic.
Garlic rust
The appearance of rust leads to the formation of convex orange spots on the leaves of the culture. With the progression of the disease, the spots darken, and the ground part of the plants begins to dry out prematurely. The development of rust is provoked by a parasitic fungus, whose life cycles occur on one seedling. Also, the sources of infection are post-harvest residues in the garden and perennial plantings. It is very easy to detect the development of garlic disease, with a constant external examination of the plantings, by visual signs.
There are several effective techniques to combat the spread of rust. Including:
- At the beginning of the development of the disease, it is necessary to independently pluck and destroy the infected leaves.
- When the planting is neglected, spraying with a weakly concentrated Bordeaux liquid is required.
- Garlic cloves, previously peeled from the husk, should be treated with formalin solution before planting in the ground. Then leave to air on a dry, hard cloth in the shade.
- It is necessary to plant garlic at a distance from the planting of perennial onions, which can provoke the development of the disease.
As a separate method of combating rust, it is worth highlighting the treatment of crops with a solution of copper sulfate or a fungicidal preparation Hom. It is recommended to use these substances when most of the leaf surface is covered with rust. To increase efficiency, you should mix the preparations with tar soap rubbed into fine crumbs. It is necessary to spray the seedlings at intervals of 1-2 weeks, but a month before harvesting, it is required to completely stop irrigation.
It is possible to detect the development of black mold by the presence of yellowish spots on the leaves. The development of garlic mold disease leads to a gradual darkening of spots and the formation of plaque, which is a consequence of the sporulation of the parasite. The disease progresses actively in a damp climate and constantly high temperature.


Faced with infectious diseases of garlic, you need to use countermeasures and ways to combat them. To eliminate black mold, it is necessary to adhere to the conditions of crop rotation, to apply agrotechnical methods in a timely manner, and not to neglect the timing of watering and loosening.
To prevent the disease from spoiling the crop during storage, it is important to provide suitable conditions. Usually, the infection affects fruits that are left in a warm room, as well as unripe or not completely dried. At first, the crop becomes soft, and when the fungal spores mature, black spores form in the space between the scales. With the wind, spores are carried to neighboring crops.
Fusarium garlic
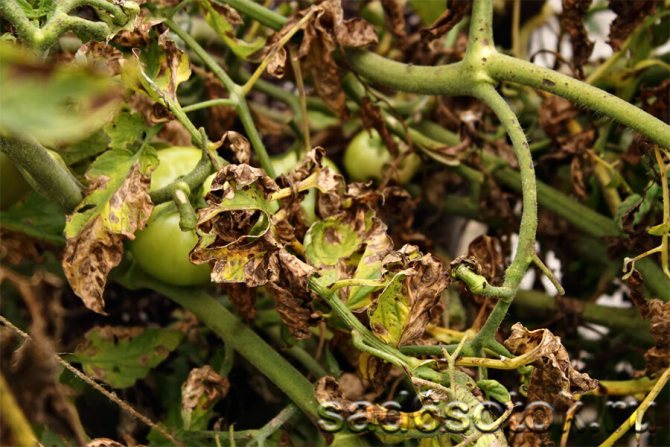
Rotting the bottom of the garlic is called fusarium. The primary symptoms of infection can be seen during intensive ripening of the crop. When garlic is infected with Fusarium, first, the tissues of the bottom are softened, after which a pale yellow or white mycelium forms on it. As a result of the impact of the disease, the root system rots, and the ground part turns yellow and withers.
Read more: Swine erysipelas symptoms and treatment, swine erysipelas
With excessive humidity and hot weather, Fusarium progresses and spreads to neighboring plants. If the disease has spread to the garlic before it is harvested, then during storage the heads will begin to dry out and over time they will completely lose their taste and useful qualities.
If fusarium occurs, it is necessary to find out the cause. In most cases, the source of infection is contaminated soil or seed. If this reason led to the disease, as a preventive measure, to protect further plantings, it is worth resorting to disinfecting the planting material with copper oxychloride or a solution of copper sulfate. To prevent the progression of fusarium it is also recommended:
- remove infected plants from the beds;
- dry the harvested crop thoroughly and store it in a cool room;
- periodically check the site for weeds and plant debris;
- adhere to basic agrotechnical techniques and rules for caring for a crop, taking into account the characteristics of a particular variety.
Horticultural crops are susceptible to disease. Garlic is no exception, it suffers from fungi and viruses. There are many diseases that can infect a plant, it is difficult to distinguish them without some experience.Photos of diseases of garlic and methods of dealing with them will help to visualize how this or that pathology looks, and to recognize the signs of diseases at the first stages. The sooner the treatment starts, the easier and faster it will pass.
Common fungal diseases of winter garlic and their symptoms:
- Fusarium. This common fungal disease can destroy an entire crop. The disease can be recognized by individual brown stripes appearing on the leaves. If fusarium is not cured in time, it will get to the head, which will begin to rot from the bottom and eventually die. If the disease manifests itself during the storage stage, white mold forms on the affected bulbs - the causative agent of the disease.
- Rust. The disease can be recognized because yellow, slightly convex, rounded spots appear on the leaves of the culture. In the future, brown-red swellings are formed on them, which turn black over time. The leaf dries up and dies off.
- Peronosporosis. Quite a dangerous disease, which is also called downy mildew. The disease is caused by fungi of the Peronospora family, which are often present in bulbs and soil. They are activated at high temperature, humidity and severe neglect of the garden. At first, the disease manifests itself as yellow-brown spots covered with a gray bloom. The lesions gradually increase in size. The fungus develops and enters the culture head. It stops growing and dies off.
- Aspergillosis. A disease known as black rot develops in bulbs when not properly stored. The head becomes soft and then dries up. If you peel off the skin, black dust will appear - spores of fungi that are able to transfer to healthy heads.
Vegetable crops are susceptible to only two diseases of this type: yellow dwarfism and mosaic. Diseases are dangerous because they do not respond to treatment. They spread quickly and are capable of destroying the entire crop, so it is important to recognize them early on.
- Yellow dwarfism is carried by aphids. The disease can be recognized by lethargic and drooping leaves - they acquire a yellow tint at the tips, become bumpy, twisted and decrease in volume. The culture stops growing and gradually dies off.
- Mosaic is a viral disease that spreads through soil, seeds, plant debris. It manifests itself in the fact that stripes and dots of a light yellow hue are formed on the leaves and stems. The feathers themselves weaken and sink to the ground. The plant gradually withers and dries up. The denticles become elongated, and you can notice their underdevelopment.
Garlic bacteriosis is a deadly disease for vegetable crops, and it affects garlic during the growth stage and during storage. The causes of the disease are premature harvesting, improper storage and insect activity.
Diseases of garlic are mostly bacterial or fungal. Most of the crop can die in neglected cases; if detected, it is necessary to urgently fight the disease.
Peronosporosis
Peronosporosis is one of the most famous and common pathologies.
Its symptoms are as follows:
- The upper part of the stem turns yellow;
- At the same time, the stem gradually dries up;
- Plant growth slows down significantly.
This fungus can easily spread to all crops, so prophylaxis is essential to avoid this disease.


Peronosporosis
The described pathology does not develop in bright light, as well as at high temperatures, therefore, the recommended prevention is as follows:
- Before sowing chives, they are warmed up in bright sun for about 2 days, it is very important that the air temperature is as high as possible;
- Also, before sowing, the soil is well cleaned of any organic residues and disinfected;
- When the crop has already been harvested, you need to warm it up in exactly the same way.
The causes of this disease are the use of already infected material for sowing, poor-quality soil cleaning from organic residues and spores of fungi that can be carried by the wind. Before sowing, the drug Tiram is used, in which the cloves are soaked for 20-30 minutes.
Bacteriosis
Another serious type of garlic disease is called bacteriosis. It can also outlive nearly the entire crop. Pathology tends to develop during the growing season of the plant and during the subsequent storage of the crop.
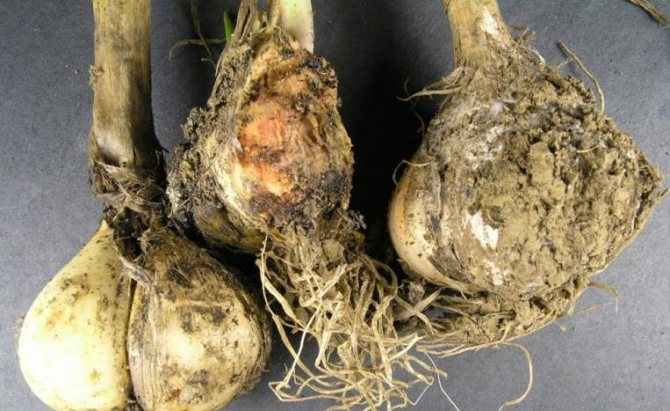


Bacteriosis
Garlic cloves do not sprout, but rot. Yellow-brown lesions appear. In other cases, the teeth become transparent, and then mucus appears on them.
Green mold of garlic (penicillosis)
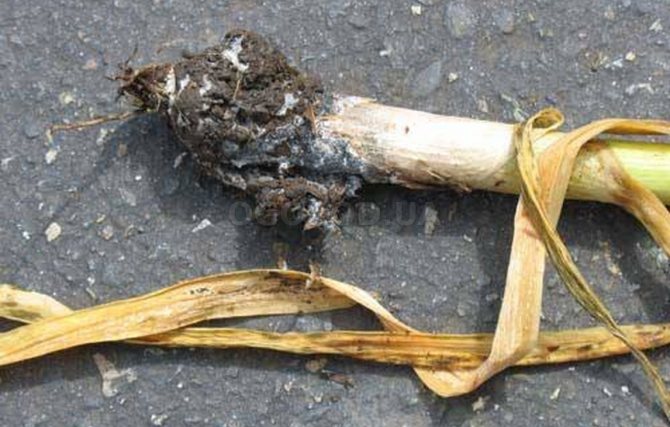


As you know, the quality of the grown crop directly depends on the quality of the planting material. And if for sowing the gardener used seeds from his own plot or purchased from a random seller, then the most careful attention must be paid to the storage of the harvested crop. It is in the repository that the disease manifests itself most actively.
If the air temperature in the room is 18 ° C and higher, then the spores of the fungus are activated and the destruction of the bulb will begin.
The lesion begins with the upper covering scales, small gray-black spots form on them - mold. Then the spores of the fungus penetrate deep into the bulb, the cloves of garlic soften.
Black mold spores rapidly increase in number and very quickly populate the entire bulb. This leads to its complete destruction. In addition, neighboring root crops become infected and, if the problem is not detected during the time, then this threatens the loss of the entire crop.
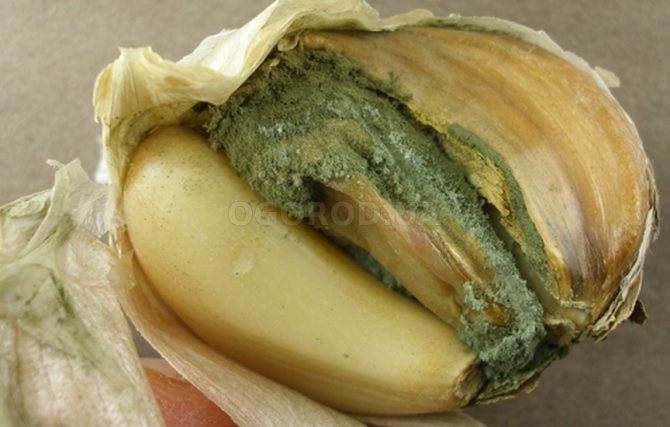


This disease also manifests itself during the storage stage of the crop. Wet brown spots form on the bottom of the bulb, and depressed yellowish marks appear on the teeth. With the development of the disease, the garlic softens, a light bloom appears on it, which later turns green.
The disease progresses inside the bulb and, when neglected, leads to the complete destruction of the cloves. The bulb becomes empty from the inside.
To prevent the spread of both types of mold, it is necessary to regularly inspect the stored crops and remove roots with signs of damage.
Prevention measures
To minimize the likelihood of infection, it is worth paying special attention to caring for the orchid. If the content of the flowers is correct, and the feeding is timely, then infection can be avoided. It is worth considering the main points:
- The place where the orchid grows should be well lit and regularly ventilated.
- Watering should be done regularly, but not watering the plant.
- The air temperature should not exceed 24 degrees.
- There must be a properly selected substrate.
- Regular pest control.
On a note! The infection loves heat very much, so the development of the fungus can be provoked by the usual heat in the room or the lack of sunlight.
It is worth checking other plants periodically if one is sick. The fungal infection is tenacious and multiplies rapidly. There is always the possibility that the fungus can spread to other plants. If at least one flower is infected, it must be isolated immediately. Can only be returned to the greenhouse after quarantine.
Cervical rot
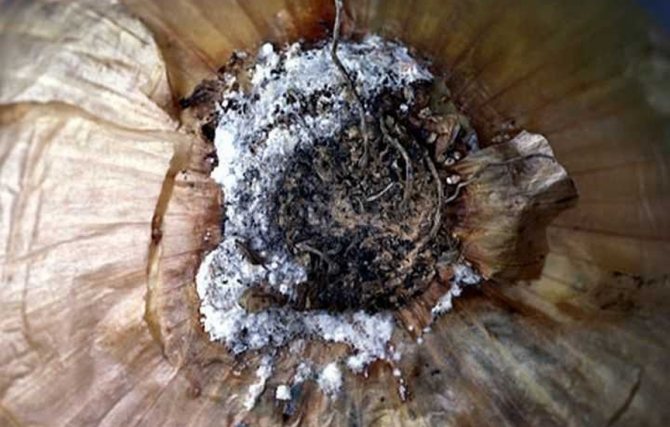


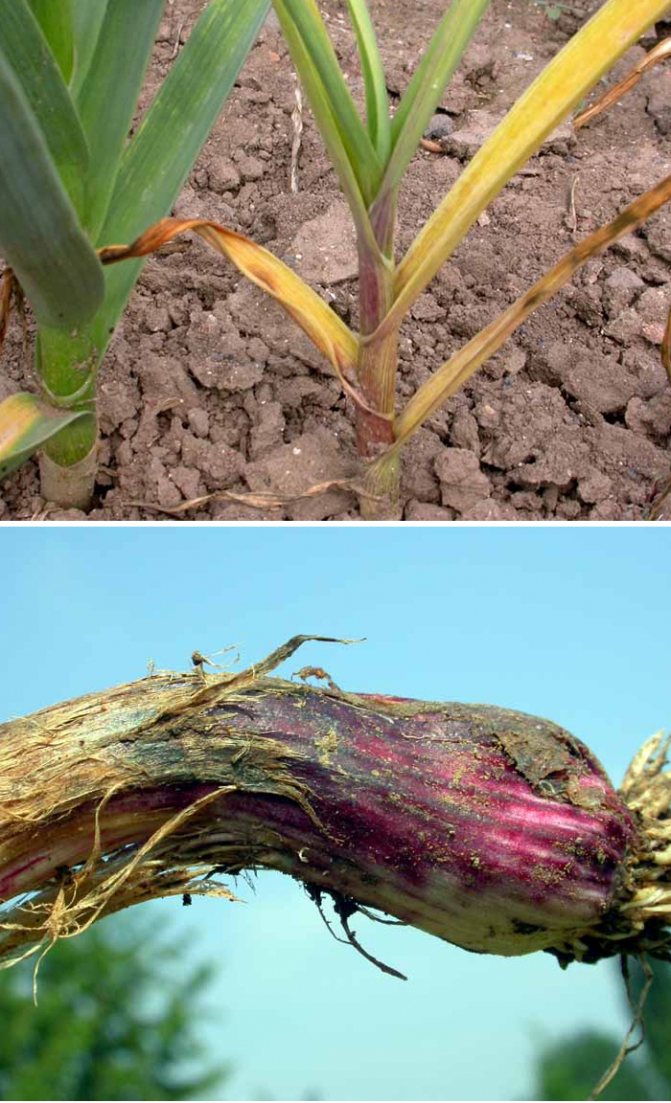
The fungus that causes this disease can infect garlic both during its cultivation in the garden and during storage of the crop. During the growing season, yellowing of the leaves begins. White bloom appears on the root crop and roots. This is the white rot mycelium. The teeth become watery and quickly rot.
The activation of the fungus is facilitated by a decrease in temperature, up to 10˚С. The pathogen overwinters either in the soil or on roots.
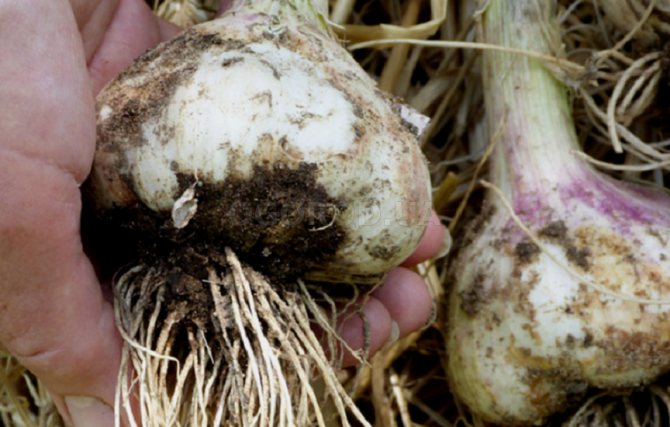


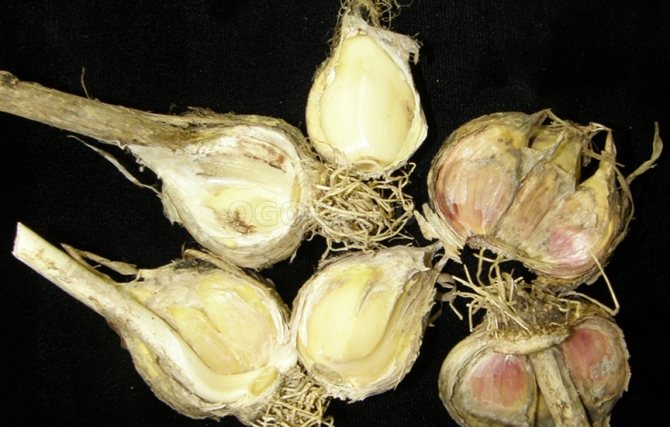
The fungus that attacks the root system of garlic is called Fisarium.Plant infection occurs both through the soil and through the seed. The first sign of the disease is yellowed leaves, followed by decay of the roots. A yellow-pink bloom appears on the roots, and mold can be found between the layers of husks. If you do not start treating the disease, the plant may die. And the increased air temperature contributes to the active development of the disease.
Treatment of the soil with the drug "Hom" (according to the instructions) will destroy the harmful fungus and protect the crop.


Garlic infestation occurs before harvest, most often during leaf lodging. Excessive soil moisture, a sharp cold snap, an excess of nitrogen fertilizers are the main causes of cervical rot.
Garlic begins to soften at the base of leaf growth, and during storage this process continues, infecting neighboring roots.
To avoid this problem, you must:
- Harvest garlic in dry warm weather.
- Dry the harvested crop thoroughly.
- Apply nitrogen fertilizers only at the beginning of the growing season.
Why do the leaves turn yellow?
Garlic leaves turn yellow most often in spring... What to do with this?
- Many gardeners notice that mainly winter crops turn yellow. This occurs during a period of low temperatures in early spring, when the plant is most vulnerable. The root system weakens and garlic draws energy from the leaves.
- Leaves may turn yellow when planted deeply. Garlic should be planted to a depth of 5-7 cm. To prevent the leaves from turning yellow, young shoots are covered with transparent polyethylene foam.
- At the first spring frosts, the plant must be treated with stimulating drugs, such as "Epin", "Zircon".
- There is another reason for the yellowing of the leaves - acidic soil. The acidity of the soil is reduced with lime.
- Leaves may turn yellow in early spring. This is due to the insufficient amount of nitrogen in the soil. What if the garlic turns yellow because of this? To fill this gap, you need to apply mineral or organic fertilizers to the soil.
- With insufficient moisture.
We recommend watching a video about the causes of yellowing of garlic leaves:
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
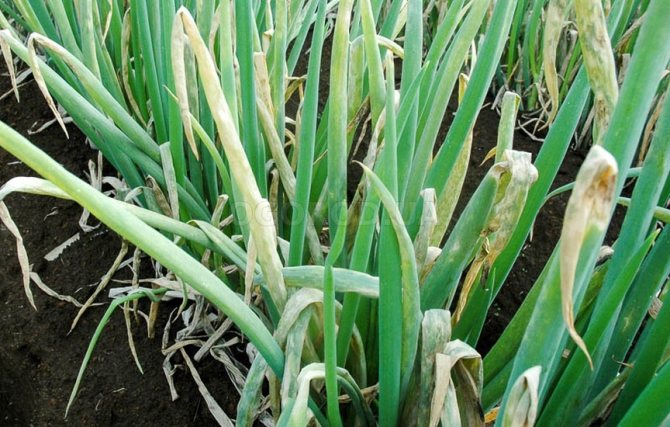


Garlic reacts to the occurrence of this disease by yellowing the tops of the leaves. The development of the plant slows down, the leaves completely turn yellow and dry out.
Most often, wet weather contributes to the occurrence of peronosporosis - in a rainy summer, garlic crops are in increased danger. And in dry hot weather, the causative agent of the disease dies.
The cause of the disease is the affected planting material and pathogens that overwintered in the soil on plant debris. In addition, the spores of the fungus are easily carried by the wind and, in collective gardens, infection can occur, even if nothing on the site foreshadowed the appearance of downy mildew.
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to thoroughly process the seed material. Warm up in the sun for 1-2 days. Can be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate or the drug "Tiram", at a concentration of 2-3%. A thirty-minute exposure of the seed in these solutions will protect the garlic from downy mildew.
Young garlic seedlings are treated with Bordeaux liquid, at a concentration of 1%.
The harvested crop must also be well dried. However, it should be borne in mind that exposure to direct sunlight will shorten the shelf life of garlic.
Non-communicable coniferous diseases and remedial measures
Burn. Solar radiation is especially dangerous for young trees. The snow cover reflects the rays, enhances the evaporation of moisture. Roots in frozen ground cannot compensate for the loss. Sap flow begins when the soil warms up to + 4 ° C, until this temperature the roots sleep. Young conifers planted in the fall can die from burns. I lost a young pine tree, we did not shelter for the winter.I noticed that glare from greenhouses, windows of houses, shiny roofs act like mirrors. If brown or yellowish spots appear on the crown, you need to look for where the bright light comes from.
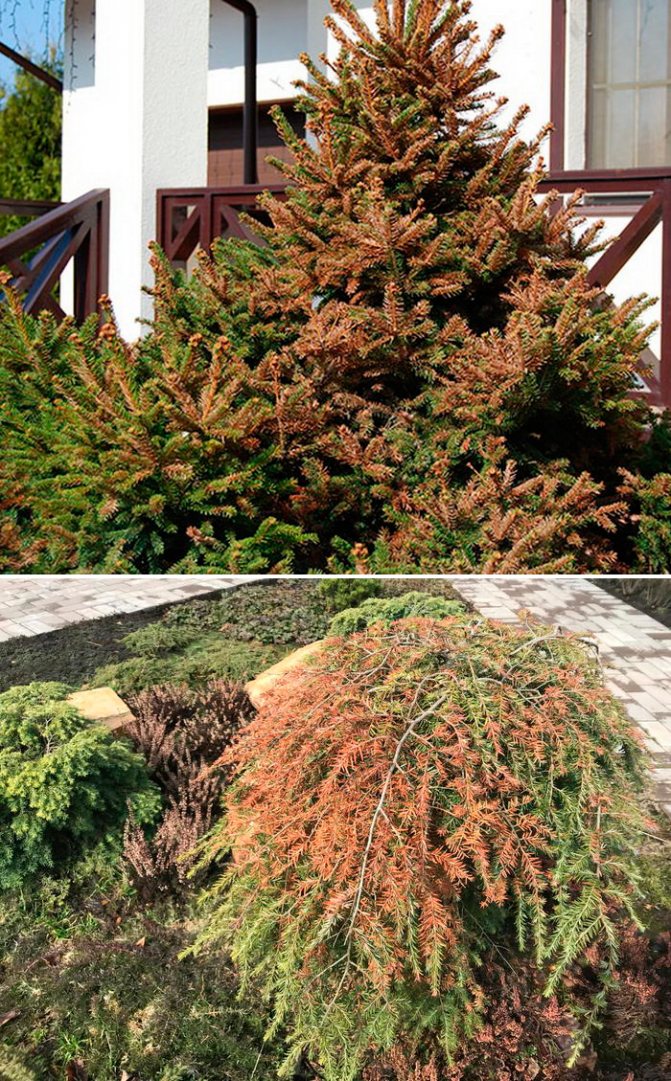


Spring sun protection measures:
- Spraying helps young trees - the branches are abundantly moistened from a spray bottle or garden sprayer.
- You can put sacking or covering material on small trees in the spring or in the fall. It will protect you from the scorching sun and drying wind.
- Scattering black earth or ash on the snow, they "start" the process of snow melting, the roots begin to absorb moisture.
When planting trees, it is important to maintain the integrity of the root earth coma. When seedlings are purchased in pots, they take root better. Pine trees are more resistant to transplanting, their needles grow after rooting. The most capricious is the forest spruce. She is usually sick for a long time, it is advisable to shade her in the spring during the first three years. From junipers I advise varieties "Skyrocket", "Blualps" (Cossack).
Other causes of yellowing of needles:
- Mechanical injuries to trees occur due to snow load, damage by animals.
- An undeveloped root system is characteristic of weakened seedlings, it is better to immediately choose a worthy planting material.
- With strong return frosts with active melting of snow, the bark cracks, it must be checked, the cracks must be covered with pitch.
- In flooded places, stagnant water provokes the development of root rot, changes the acidity of the soil.
The resistance of conifers to non-infectious lesions is increased by bioactive drugs:
- Kornevin (stimulates the growth of the root system)
- Super humisol is a balanced mixture of trace elements and minerals;
- Zircon is a complex drug;
- Siliplant is a silicon-containing chelated microfertilizer.
Timely feeding strengthens the immunity of plants well, they are less susceptible to burns, and grow faster in spring.
Rust
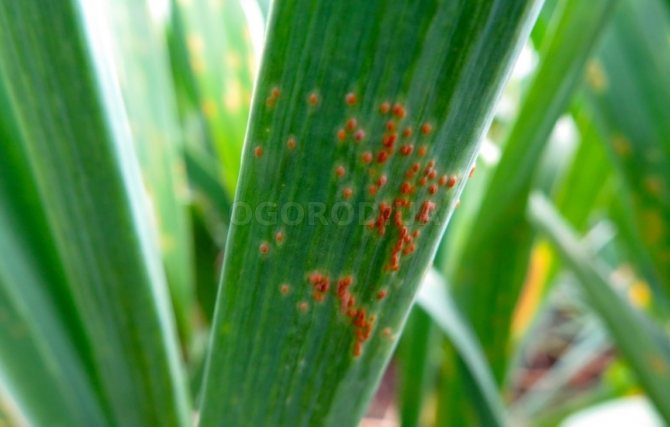


This disease is characterized by the appearance of yellow specks on the leaves of garlic. The dots increase in size and over time cover the entire surface. Damaged leaves die, the plant weakens, which leads to a decrease in the development of garlic heads.
Use healthy seed to avoid rusting on the garlic. But if signs of the disease appear, then the beds with garlic must be treated with a solution of copper sulfate, Bordeaux liquid (1%) or Fitosporin-M, at the rate of 15 ml per 10-liter bucket of water.
Treatment of the disease
Unfortunately, we must admit that it is not particularly necessary to deceive ourselves. In the fight against fusarium, especially if it has already hit the green patch, the victory goes to him.
But not everything is so hopeless. Science has developed a number of drugs, the use of which significantly reduces the likelihood of this enemy entering your area.
Drugs
When developing recommendations for the use of certain means, scientists took into account the exclusive features of plants and focused on them.
| Type of culture | Recommendations for the use of drugs |
| Potatoes | Treatment of tubers before planting (soaking) in fungicides: Baktofit, Fitosporin-M. |
| Tomatoes | Treatment of bushes with copper-containing preparations - 1% Bordeaux liquid. Under diseased bushes, the holes are treated with fungicides and spilled with Trichoderma Veride. The best fungicides for tomatoes:
|
| Cucumbers | Seed treatment before planting: Fitosporin-M, Baktofit. Recommended fungicides:
|
| Garlic | Treatment of planting material with fungicides: Hom, Maxim. Irrigation with biofungicides: Mikosan, Biosporin, Bioreid. |
| Strawberry | Treatment of bushes with fungicides:
|
| Eggplant, pepper | Preplant soil treatment:
|
| Melon, watermelons | Plant processing: Speed (during flowering, use is prohibited).
|
| Cabbage | Spraying:
|
| Flowers, including indoor | Fitosporin-M (prophylactic drug, used before planting).
|
| Recommended for many cultures | Universal potent drugs:
|
The fight against fusarium cucumber, video:
Folk remedies
To say that folk remedies will become a decisive weapon against the cunning of the garden enemy is at least reckless. After all, the root of evil lies in its secrecy - the mushroom is discovered only after it is no longer possible to help the green culture.
But to brush aside grandmother's advice is also not worth it. They have proven their life-affirming power and their complex application together with the achievements of chemists and biologists will be completely useful.
Processing recommendations:
- Infusion of black-haired (marigold). Take a bucket of warm water and half a bucket of marigold flowers. Combine and insist for two days. Filter the solution and spray on home crops.
- Wood ash infusion. Collect 3 kilograms of ash and pour ten liters of boiling water over them. Withstand two days. Spill the site with this composition.
- Cow cakes. Fill a third of the bucket with this organic matter. Pour three liters of warm water there and let stand for 2 days. Strain and add water until the bucket is full. To make medicinal feeding - 0.5 liters per bush.
- Rub 30 grams of laundry soap with shavings. Pour it with one liter of milk, adding 40 drops of iodine. Mix thoroughly and irrigate garden crops with this solution.
- Take two liters of hot water. Place a glass of wood ash with a grated bar of laundry soap there. Stir and leave the solution for two days. Treat the leaves and root area with this composition. Repeat the procedure after seven days.
- Collect two handfuls of onions (as many as possible), boil them for half an hour in ten liters of water. Cool, filter and mix with the same volume of water. Treat your garden crops with a watering can.
- Chop a head of garlic. Pour in a liter of water and stand for a day. Filter and dilute with nine liters of water. Irrigate the leaves with the solution in the evenings.
Bacteriosis
The name of the disease suggests that it is provoked by bacteria. As a result of the defeat, the bulbs rot. The presence of a viral disease in garlic can be detected by the following signs:
- at the initial stage, the fetus softens;
- the scales turn yellow or brown;
- an unpleasant odor develops, indicating defeat.
The cause of the disease is improper storage of fruits - too humid and warm indoor air. Therefore, the disease is easier to prevent than to fight it.
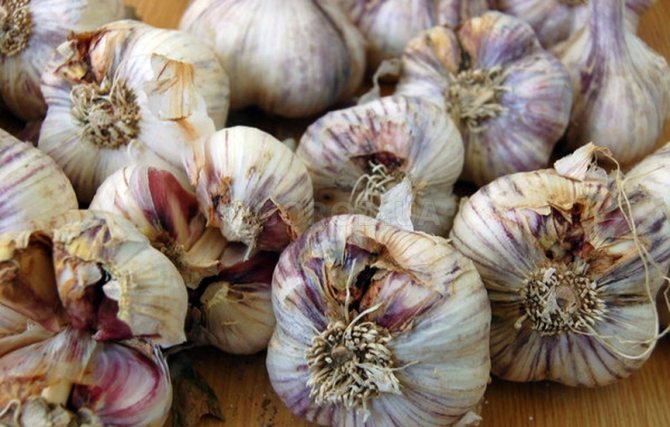


This is the name of the garlic disease caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas xanthochlora Stapp and Erwinia carotovora Holland. During the cultivation of garlic, bacteriosis is combined with fungal diseases and damages the plantings. And it fully manifests itself during storage of the crop. Defects in the form of grooves and ulcers appear on the garlic, it changes its color - it becomes yellowish.
Poor drying of root crops before storage can be the cause of bacteriosis. High humidity and high storage temperatures can also be factors contributing to the development of the disease.
Fusarium on garden crops
The most vicious and fierce destroyer of gardens and orchards does not recognize any authorities. Everything that his deadly spores penetrate is doomed to slow fading and inevitable destruction.
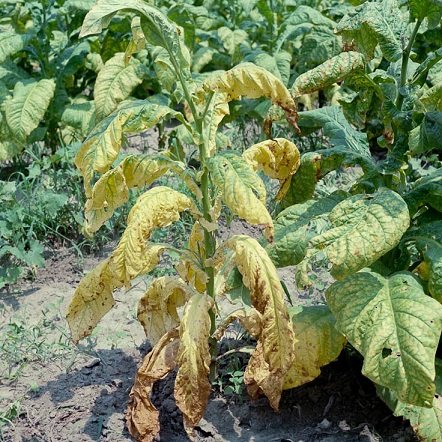
Potatoes
The damage that dry rot can inflict on potatoes is comparable only to the invasion of the Colorado potato beetle.
For potatoes, the most vulnerable period, that is, when fusarium wilting can bring down the harvest as much as possible, is considered to be the time of flowering.Although at other stages of the cultivation of this culture, there are no guarantees.
The disease occurs in waves - becoming more active during a period of high humidity.
The disease is determined by the following features:
- Lightening the upper foliage.
- At the edges, an anthocyanin color appears - a blue-violet color, such as that of blueberries, figs or eggplants.
- The leaves wither and sag lifelessly.
- The stem closer to the base acquire a brown color, and in cloudy, wet weather begins to rot, becoming covered with a pink or orange bloom.
- On the cut of thick stems, a change in the color of the feeding vessels is visible - their color becomes brown.
- A diseased plant withers in a matter of days, and when it dries up, it dies.
Fusarium potato in the photo:


But the adversity from rot does not end there. It can affect already harvested potatoes, which are poured into the cellar for storage. The disease is manifested by slightly depressed spots of gray-brown color. The pulp under them dries up, becomes like dust, forming voids. Fusarium spores accumulate in them.
Diseased potatoes are riddled with filament-like sprouts, threatening to spill over to neighboring tubers.

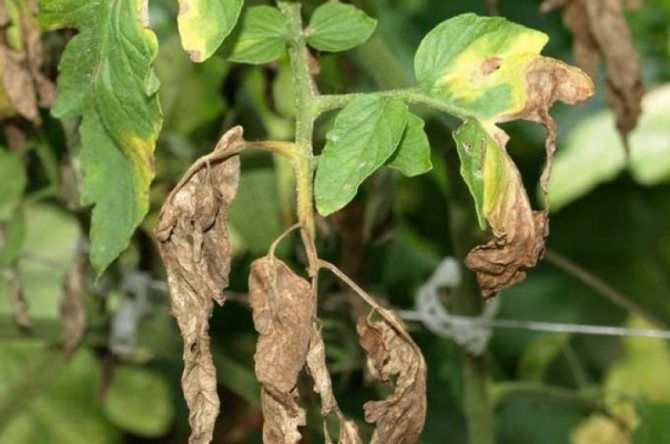
Tomatoes
Monoculture greenhouses, that is, where crops of the same species are grown, are extremely vulnerable. Having penetrated from the soil or from untreated seeds, the fungus will infect the vascular system of stems, peduncles and fruits.
There is no chance to save the harvest. The incubation period can last up to 30 days. It is even difficult to imagine how many bushes during this time can infect tomato fusarium.
External signs of fusarium on tomatoes:
- The disease begins to manifest itself from the lower layer of leaves, rising, covering the entire bush.
- Withering of the top, deformation of the petioles and folding of foliage.
- On the cut of the stem, a changed color is visible. It has become a brownish hue.
- Darkening of blood vessels is visible in the lumen.
- Leaves affected by rot turn white, turn yellow and completely lose their usual color.
Fusarium wilting of tomatoes in the photo:


Eggplant
It has been noticed that the garden attack most often affects eggplants at the flowering stage.
As in the case of tomatoes, the leaves of the lower tier begin to turn yellow, curl, wilt, and then dry out. The movement of the disease occurs from the bottom up.
Pink bloom at the base and brown vessels on the cut of the stem are perhaps the main distinguishing features of dry rot.
The channels of penetration of the fungus are known - these are soil or infected seeds. Recall that the fungus is able to retain its insidious properties for several years.
The disease enters the green organism from the soil, through mechanical damage to the root.
After the defeat, the eggplant bush may not die, but its condition will be extremely deplorable, which will certainly affect the number and size of fruits.
Fungus-affected eggplant:


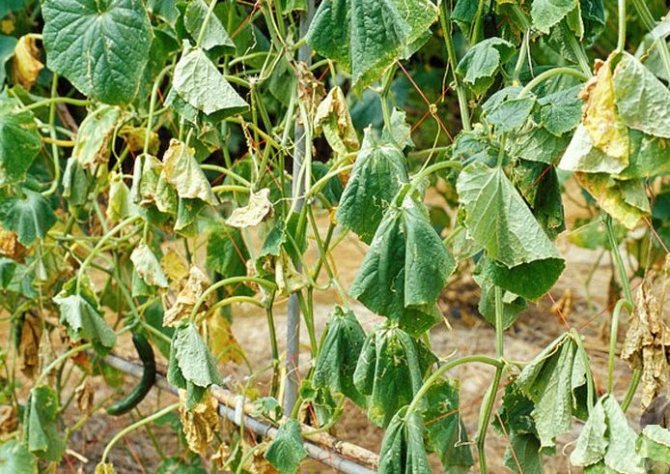
Cucumbers
The disease is dangerous both for greenhouse varieties and for cucumbers grown in the open field. Although it is worth noting that outdoors, their durability is much higher.
The first signs appear suddenly and, as it were, for no reason:
- Despite good care - watering, garter, weeding - the leaves turn yellow and dry.
- In high humidity and in rainy weather, the stems and leaves are covered with a pink bloom.
- At the stage of flowering and fruit formation, the root collar is covered with a brown color, cracks and rots, the root falls off.
The main channel for the penetration of the disease is garden soil. The most favorable conditions for its distribution are temperatures above 15 degrees and soil oversaturation with nitrogen fertilizers.
Fusarium wilting of cucumbers in the photo:


Garlic
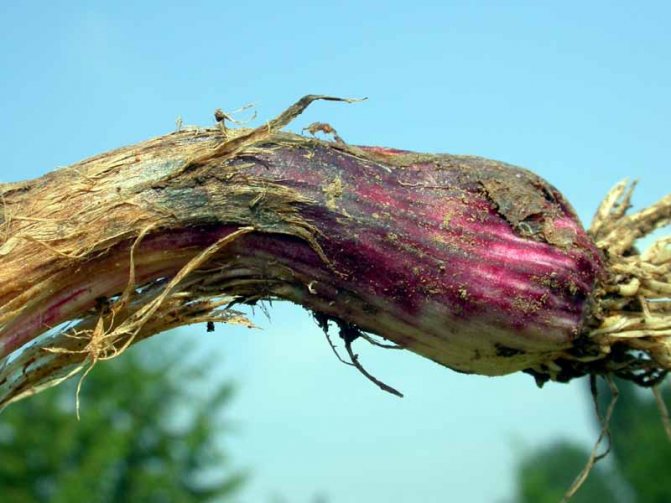
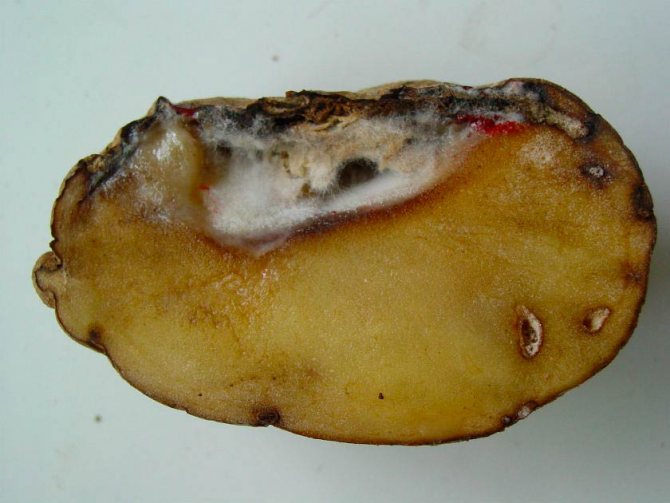
Rot of the bottom - this is how this garlic disease is called in another way.
The fantastic damage from this scourge is felt in the southern regions of Russia, where there are hot and warm summers and mild winters. Here, crop losses can reach 70 percent or more.
The problem is aggravated by the fact that garlic is "attacked" by not one, but up to eight fungi from this group at once. And there is simply no way to resist this culture in such conditions. Each of them has its own active form of suppression.
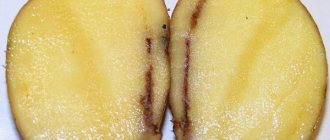
Signs of the disease:
- Painful pink coating and brown streaks on feathers.
- Rotting and death of the root structure.
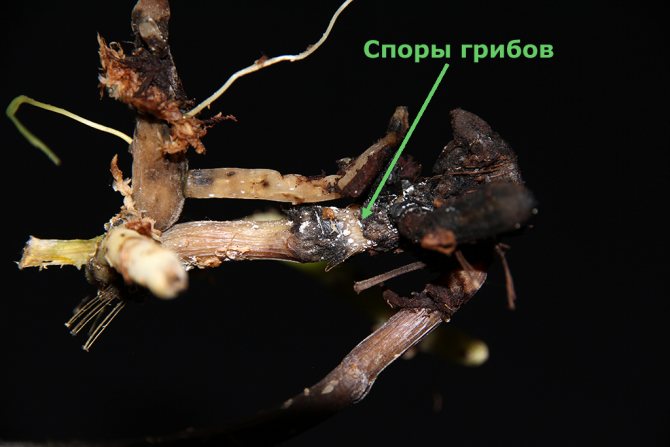
- Loss of elasticity of the bottom and its softening. The mycelium of the fungus, yellow, white or pink, appears on the surface.
- When stored, pink pads are formed between the garlic scales, and the heads themselves dry out and mummify.
Fusarium garlic in the photo:
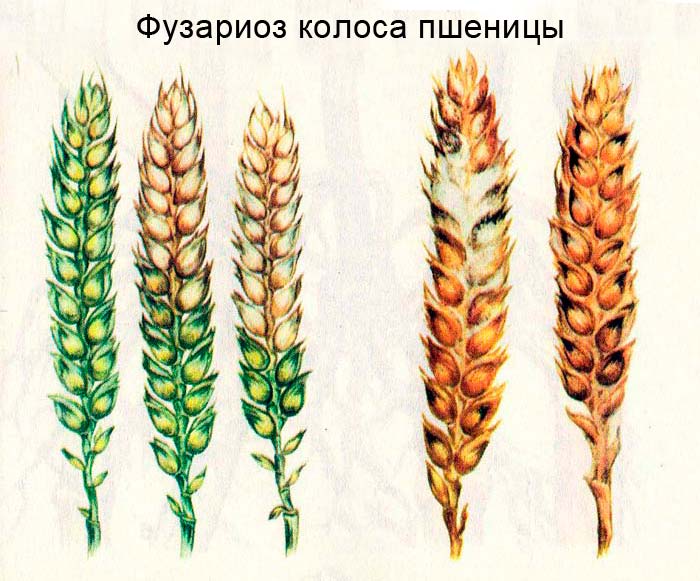
Wheat
For pathogens from the Fusarium group, it makes no difference what and how to infect. It can be both the root of wheat and its ears. The fungus spares nothing.
After the penetration of the fungus into cereals, a week later, orange-pink conidia appear on the ears - its spores. With the help of the wind, they are able to cover huge areas.
As with previous examples with other crops, a humid environment is most conducive to promoting this disaster.
When the weather is humid and hot, then Fusarium head blight can inflict a fatal blow on the future harvest, destroying up to 70% of the crop. The danger increases manifold precisely during the period of ear formation.


It is especially worth emphasizing that eating foods made from diseased grains significantly increases the likelihood of penetration and accumulation of the most dangerous mycotoxins in the body.
Wheat root rot can be caused by the same fungi from the genus Fusarium - Fusarium oxysporum, which persist in the soil for a long time.
Signs of the disease:
- Low germination and slow growth.
- Loss of natural color.
- Low ear mass.
- The destroyed rhizomes of wheat are black in color.
Fusarium root rot is capable of destroying 30% of the area in a season.
Fusarium spike of wheat in the photo:


Root (or onion) tick


She wakes up in the second half of May and lays eggs at the base of garlic leaves or on the ground, in close proximity to garlic and onion plantings. The hatched larvae penetrate the inside of the garlic head and eat the young juicy scales. The plant slows down growth, then withers and gradually dries up. The root crop itself softens and rots, emitting a very unpleasant odor.
To prevent the harm that the onion fly can cause, first of all, you should:
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Place garlic beds next to carrot crops.
- Plant the garlic as early as possible. (This applies to spring varieties.)
- Do not plant garlic after onions.
- Pollinate the plant and the ground around it with deterrents. A mixture of ash and tobacco is suitable for these purposes, to which you can add ground pepper or dry mustard.
- Water the garlic with a saline solution: 250 g / 10 l of water. This volume is spent on 1.5-2 square meters. m. sown area. Carry out the first treatment when the feather grows 5-8 cm. Repeat three times, every two or three weeks.
To spray garlic beds against onion flies, you can use the following infusion:
- 250 g makhorka or tobacco;
- 3 liters of hot water;
- 2 tsp ground red pepper;
- 2 tbsp. l. liquid soap or dishwashing detergent.
Pour the makhorka with hot water, add pepper and leave for three days to infuse. For greater efficiency, the container with the contents can be wrapped with something warm. After the time has elapsed, strain the mixture, increase the volume to 10 liters and pour in liquid soap. It is used for better adhesion of the solution to the leaves.
The revitalizing procedure should be carried out every 10-14 days, starting from the emergence of shoots.
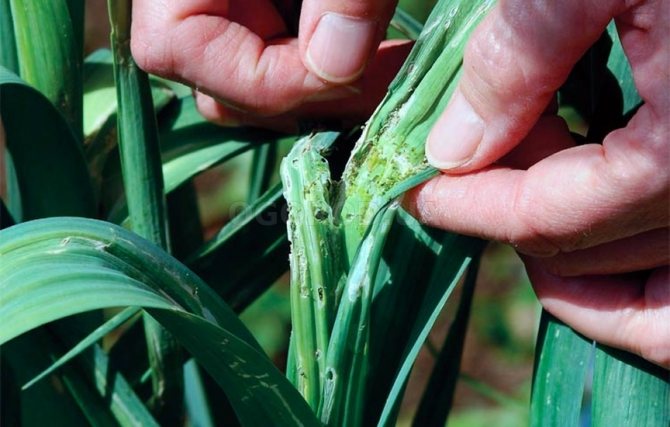


This pest prefers dry and warm weather. It hibernates in the ground, and starts flying with the onset of warmth. The onion moth lays eggs in garlic beds or between leaves, at their very base. The first generation of caterpillars appears in May-June.Longitudinal stripes on the leaves of garlic testify to their vital activity.
Preventive measures:
- Compliance with the timing of the alternation of vegetable crops.
- Destruction of the tops of last year's harvest.
- Deep autumn tillage.
- Processing garlic during the growing season with Iskra, according to the instructions.
Against the onion moth, it is possible and necessary to use the same folk remedies as against the onion fly.
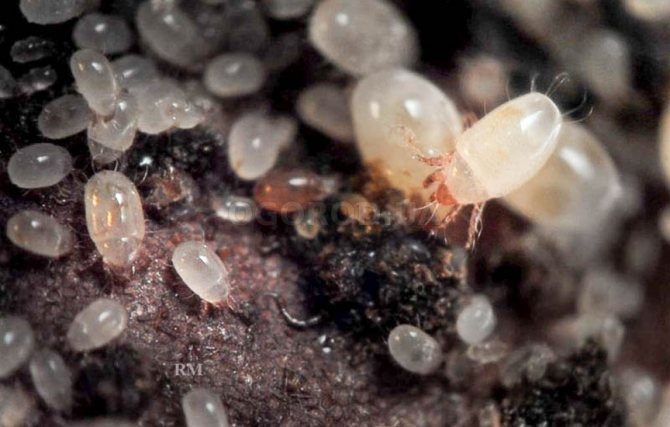


This pest is ubiquitous. The defeat occurs to a greater extent in the storage, but it happens that damage to the plants is also caused during the cultivation of garlic on the site. It enters the garden bed together with the planting material.
Penetrating into the bulb through the bottom, the tick eats up the fleshy scales, which leads to decay of the root crop.
In order not to bring the insect to the site, it is necessary to purchase healthy planting material. It is also necessary to burn plant residues to monitor the cleanliness of garden tools.
The storehouse, where the garlic will hibernate, is subjected to treatment with sulfur dioxide, which is formed when burning the "Gamma" checkers. Disinfection will be effective if the room is hermetically closed and the processing time is 2 days.
Garlic nematode
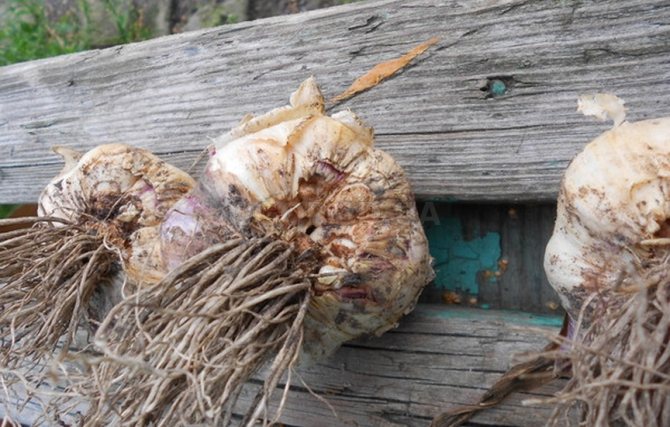


A parasitic worm, small and threadlike, causes significant harm to garlic beds. There are three types of nematodes.
The appearance of the stem nematode is accompanied by yellow-brown spots on the leaves. The aerial part of the plant is twisted and deformed.
When infected with a root nematode, neoplasms (galls) appear on the roots of garlic. Their diameter does not exceed 2 mm. Close inspection of the head of garlic can also reveal light brown egg-laying.
The root nematode is more difficult to recognize. It develops in close intertwining with fungal and viral diseases. When garlic is damaged by a root nematode, the following occurs:
- the growth of adventitious thin roots stops;
- inclusions of a color uncharacteristic for the root system appear on the roots: yellow or brown;
- the appearance of garlic indicates a deficiency in moisture and nutrients.
To protect garlic from uninvited guests, you should take preventive measures:
- Purchase seed material in specialized stores.
- Remove self-seeding garlic.
- Keep the garlic plantings clean.
Weeds and seedlings from random crops are most often host plants for nematodes.
The prevention of the horse nematode includes the alternation of vegetable crops. (Sowing after carrots, beets.)
If a root-knot nematode is damaged, garlic can be returned to the same bed no earlier than after 5 years.
Against stem nematodes, when planting garlic in the fall, it will protect the soaking of the seed.
- Water. Chives are kept for 24 hours in water with t = 20˚С.
- Manganese solution. A 5% solution of potassium permanganate is prepared and seed material is immersed in it for a day.
- Formalin. You will need a solution with a concentration of 5%. Garlic is kept in it for 12 hours.
The effectiveness of these methods is 95-98% and increases the adaptation of the plant after planting.
Tobacco thrips
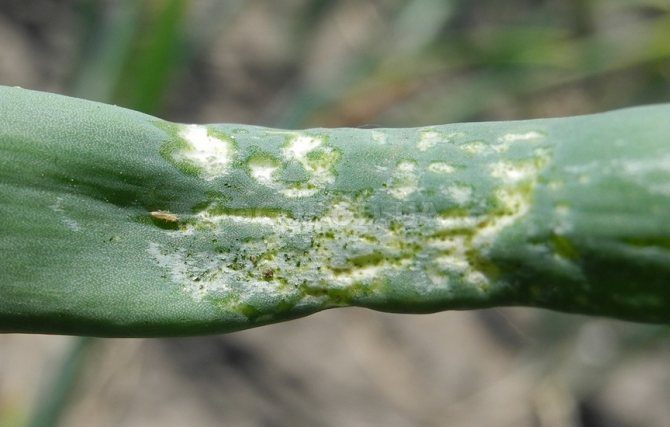


The insect is a microscopic organism of light yellow or dark brown color. Its dimensions are barely 1 mm. Females of thrips lay eggs in the soft tissues of the leaves, and after 3-5 days larvae appear from them. They feed on the sap of the plant and deprive it of nutrients. Garlic begins to stunted, the stems become sluggish. The parasitic insect hibernates in the upper soil layer.
To avoid the appearance of a pest on garlic, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Destroy plant debris.
- Work the soil deeply.
- Intersperse the crops of garlic and the beds with carrots.
When thrips appear, you can spray the plants with celandine infusion. Insist 1 kg of dry raw materials in 10 liters of water for 2 days.