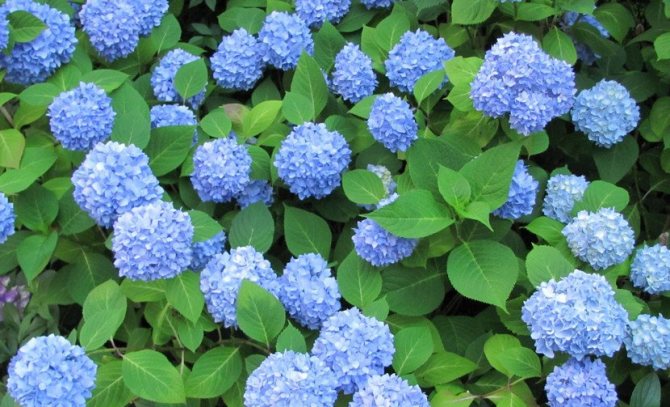
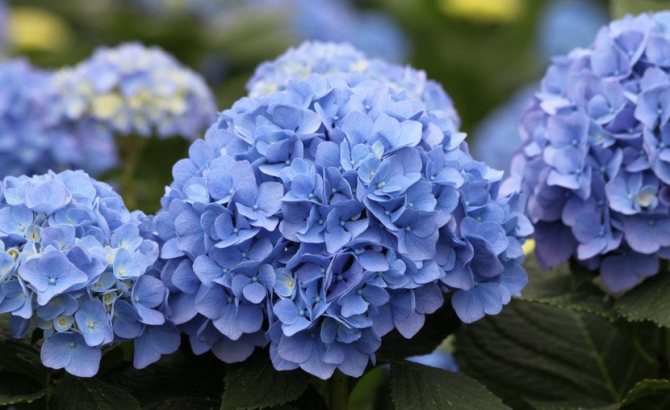
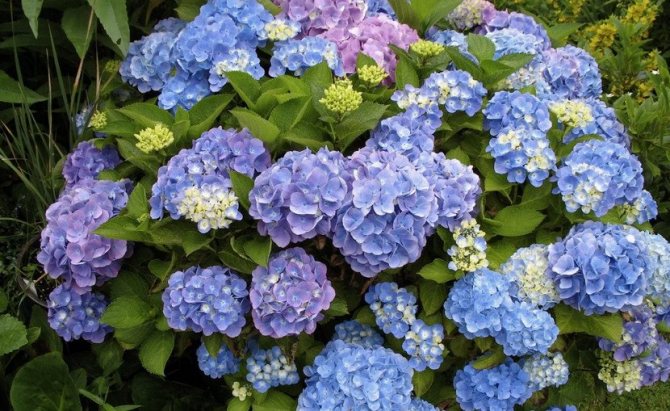
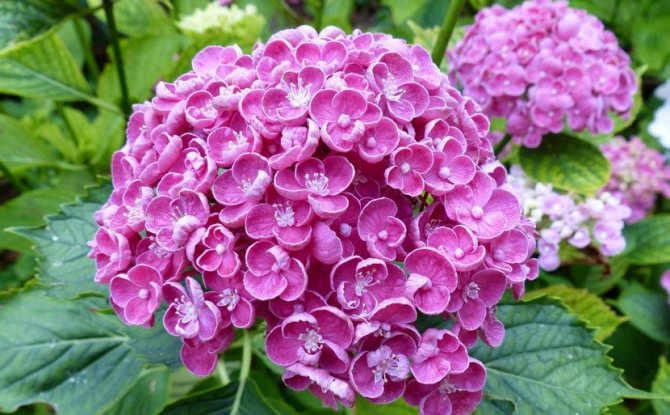
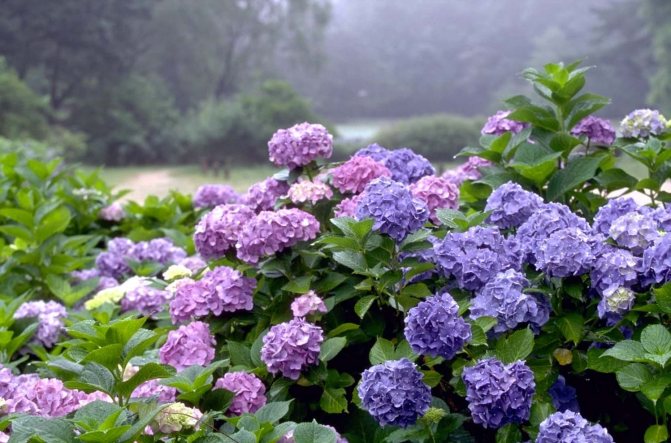
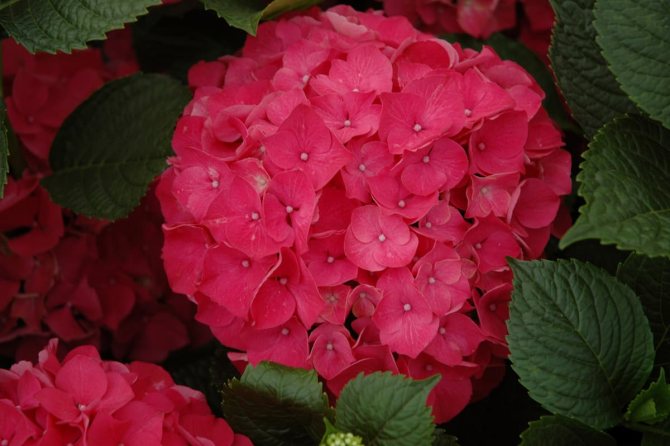
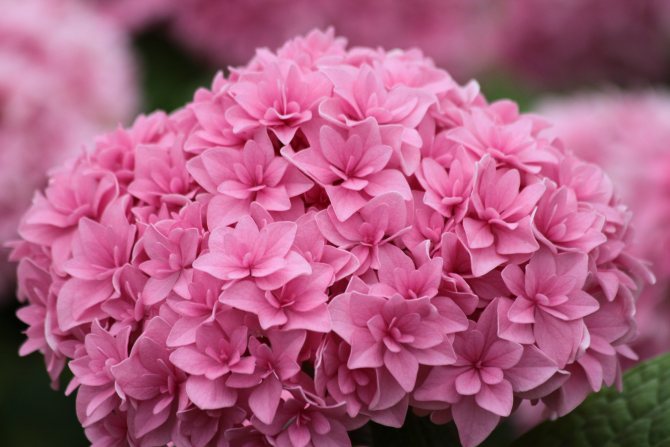
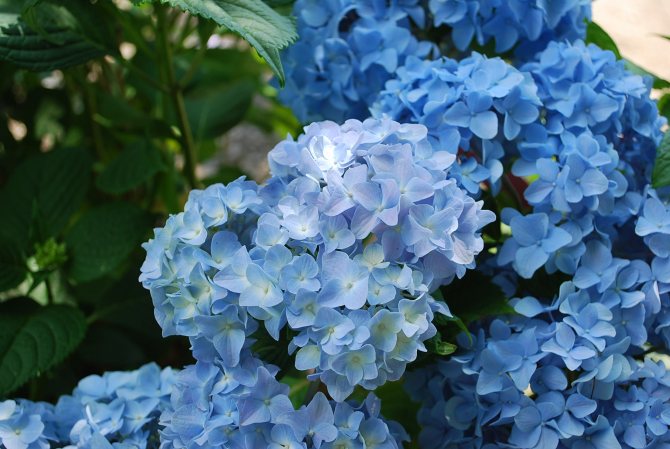
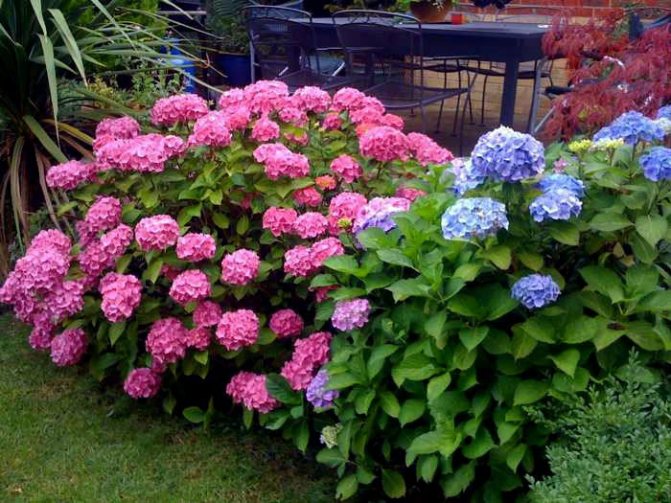
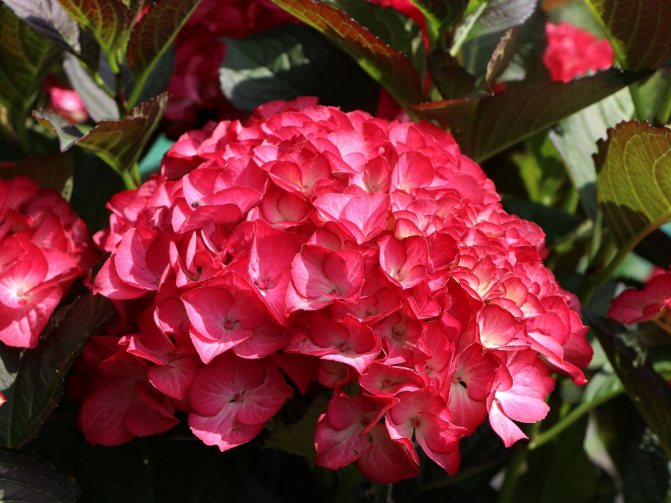
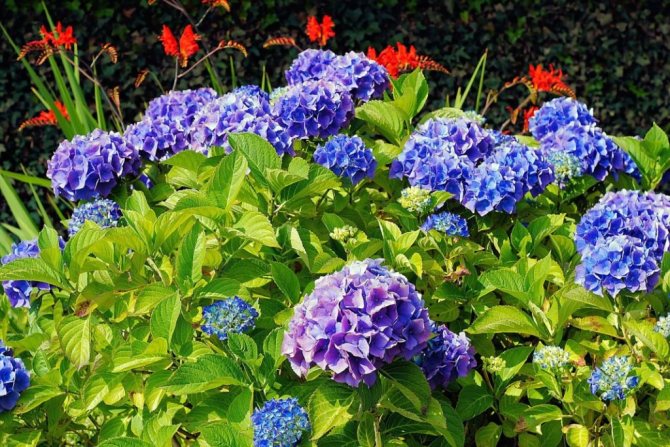
Many people want to have a beautiful large-leaved hydrangea in their garden. This spectacular shrub seems to be whimsical in cultivation in vain.
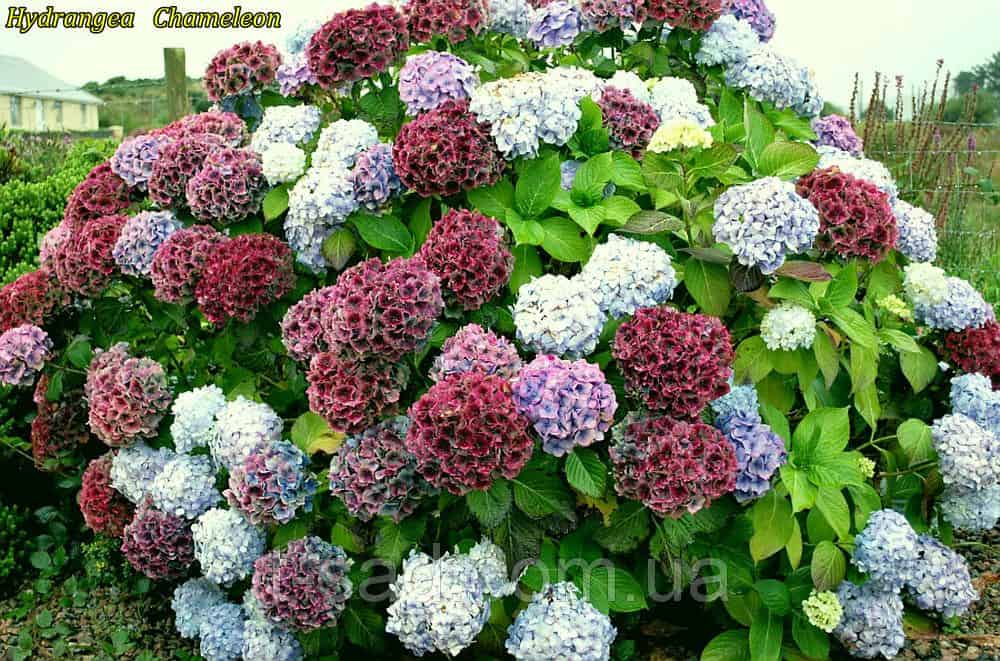

The rules for caring for broadleaf hydrangea are somewhat different from other species. By following certain agrotechnical techniques, you can avoid the frustration of losing your favorite plant.
What are the technologies for growing hydrangeas and how not to be mistaken with the choice of a variety?
Characteristics of large-leaved hydrangea
Not all garden plants can boast lush flowering combined with easy maintenance and frost resistance. Hydrangea, the name of which is translated from Latin as "a vessel with water", belongs precisely to their series, being an enviable crop for growing in private homestead plots and parks. Also widely used as a potted houseplant.
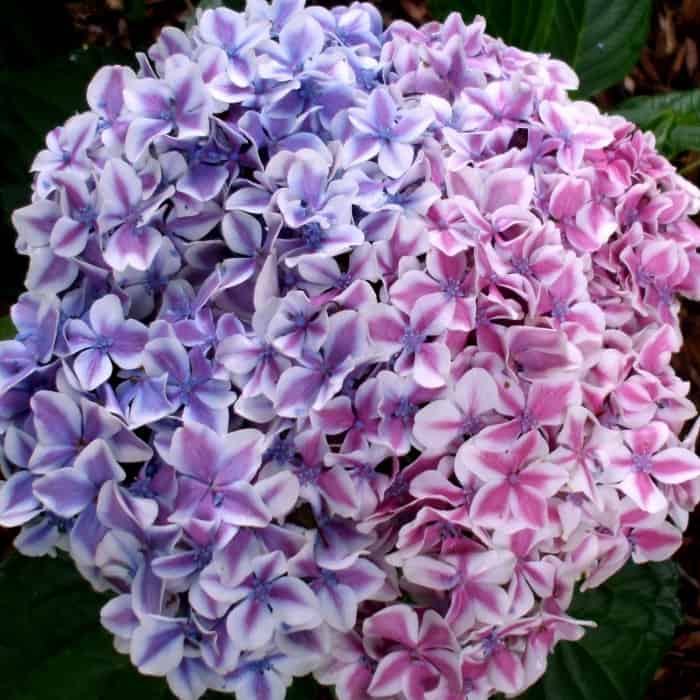
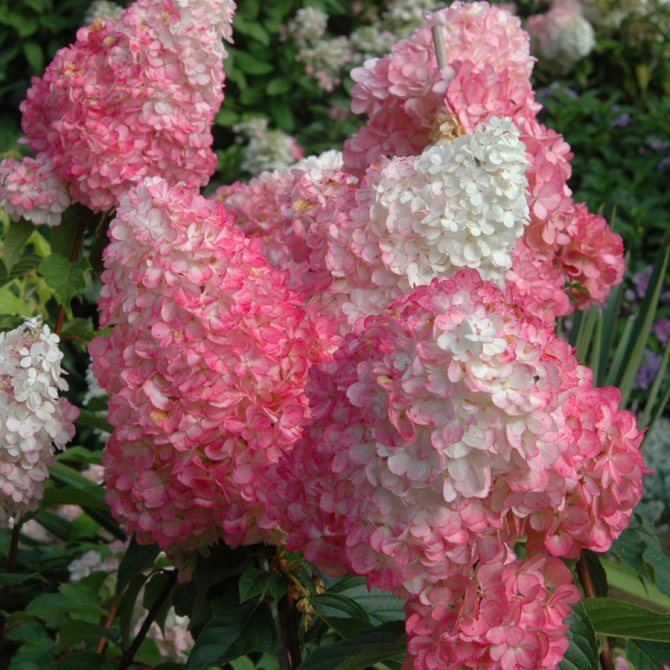
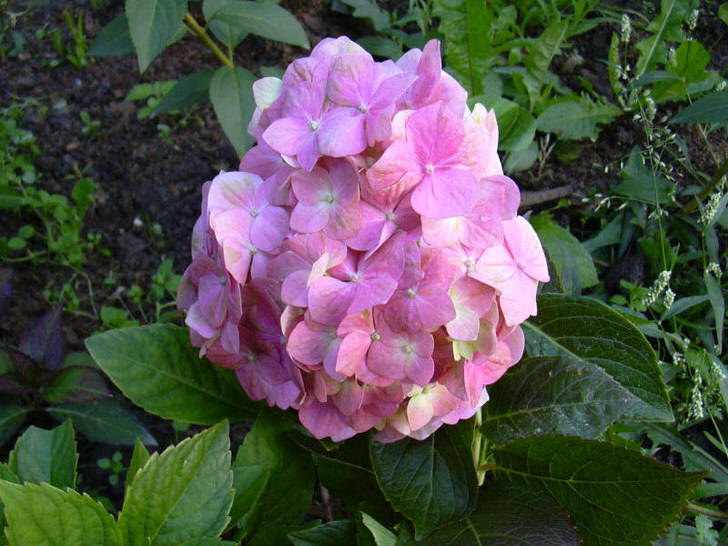
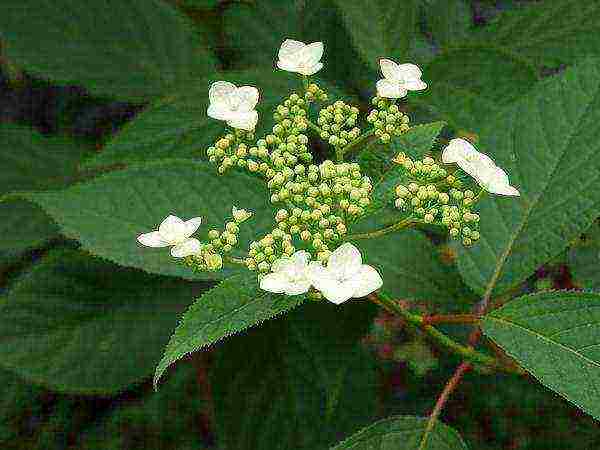
The species is a broad-leaved shrub with a round crown and a dense trunk, which lignifies over time. The main characteristic feature of the plant is its flowering - large-leaved hydrangea is capable of releasing up to 400 inflorescences on one copy. They can be painted in different shades (from white to lilac), depending on the variety, forming lush shields with large flowers. The flowering period covers July - early autumn.
Video: Growing a large-leaved hydrangea
Fertilizing and fertilizing hydrangeas
To saturate the shade of the main color of the hydrangea, ground acidity is important, so once every two weeks it can be watered with the addition of an alum mixture. It is also possible to experiment with color changes, for example to apply fertilizer only from a certain side. Do not use ash for fertilizing hydrangeas.because it can harm the plant. The best thing feed with a weak cow's solution.
For feeding, you need to complete several stages. In early spring for the formation of very fast shoulder straps. In early June, it is needed to create an effective bud set. In July, feeding is necessary to make the flowering time longer, especially useful for remontant varieties. At first, young hydrangeas must be watered with weak potassium permanganate, which protects it from the formation of rot. In the fall, hydrangea is best treated with a special Bordeaux mixture to prevent fungal diseases.
Botanical description of the species
Large-leaved hydrangea belongs to plants of the genus Hydrangia. The shrub can reach a height and diameter of 3 m, and in natural conditions grow up to 10 m. The branches are brown or red, slightly pubescent and dark green elongated leaves with serration.
Also find out how quickly a hydrangea bush grows.
Cone-shaped panicles of inflorescences of cultivated varieties reach a diameter of 20 cm and can be located on stems up to 30 cm long. Simple and ovoid leaves are colored dark green. The hydrangea fruit forms a capsule with 2–5 sections and numerous small seeds.
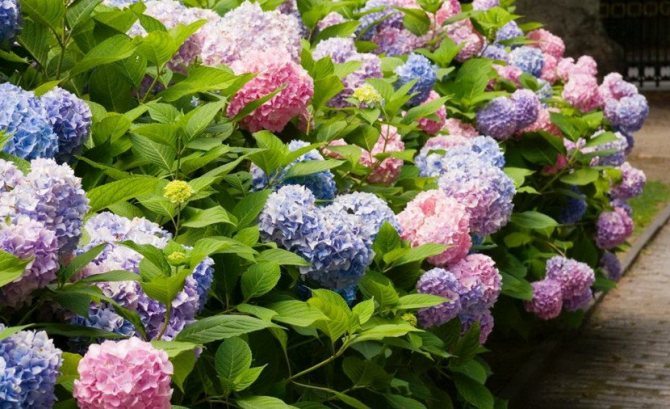


Popular varieties of large-flowered hydrangea
Large-leaved hydrangea has many varieties that are cultivated by gardeners. The most popular ones are:
- Red Sensation;
- Miss Hepburn;
- Nikko Blue;
- Countess Kozel.
Did you know? The saturation of hydrangea flowers can be adjusted by changing the acidity of the soil. The more neutral the pH, the lighter the petals.
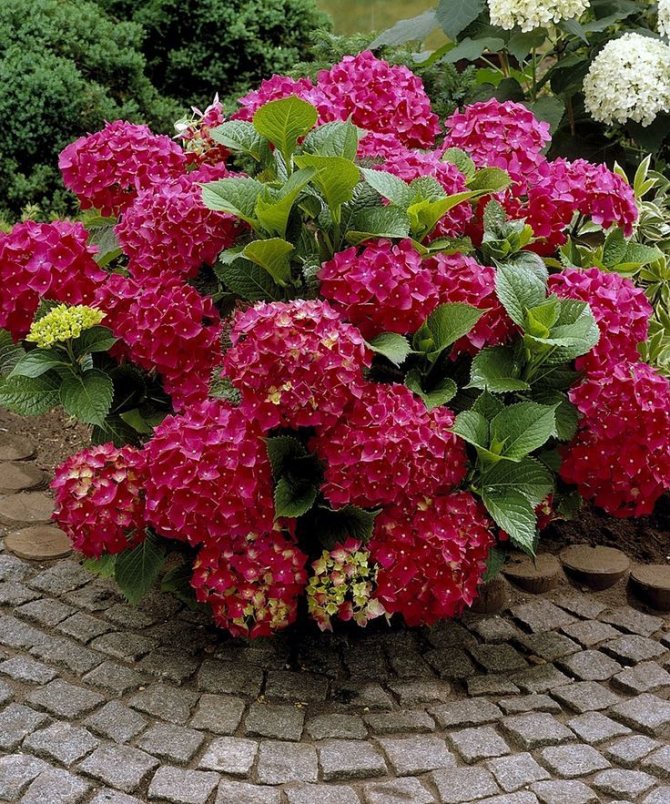
Red Sensation
Low frost-resistant variety with beautiful red flowers. The name corresponds to the appearance - large inflorescences can decorate a park or a personal plot with a bright flowering. Branches with panicles are so lush that a short bush can easily bend under their weight.
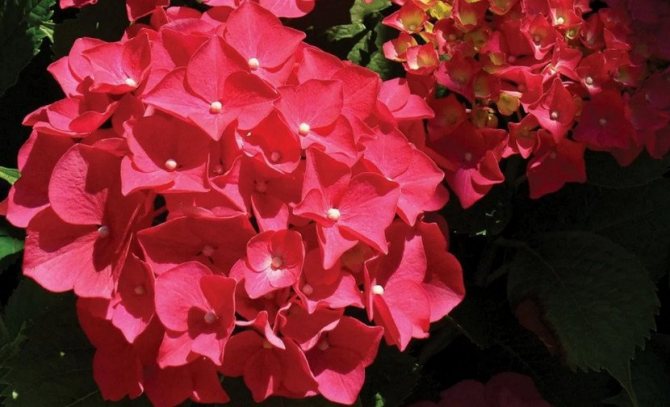


Red Sensen blooms twice a season - first on last year's branches, and then on the shoots of the current year.
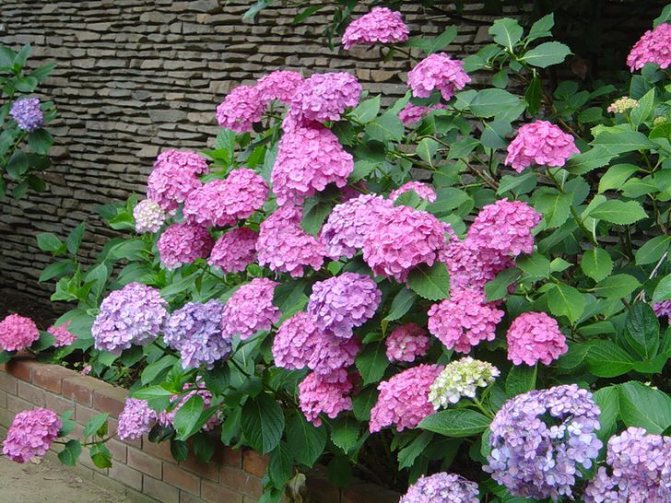
Miss Hepburn
It is a medium-sized shrub, reaching a height of 1.5 meters, with pink or purple flowers, depending on the acidity of the soil. The plant is used as a single decoration of the site. Dried inflorescences do not lose their color; therefore, they are often used in floristry.
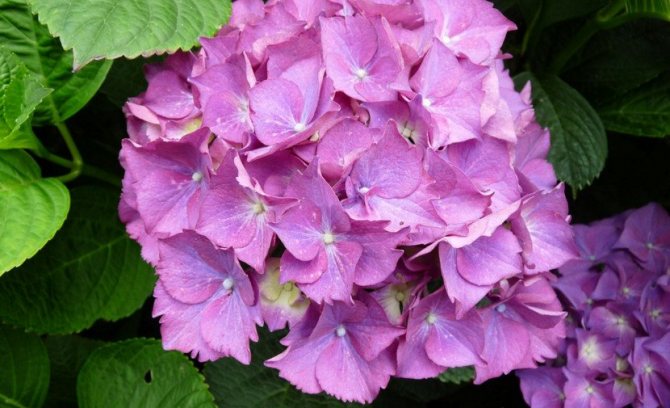


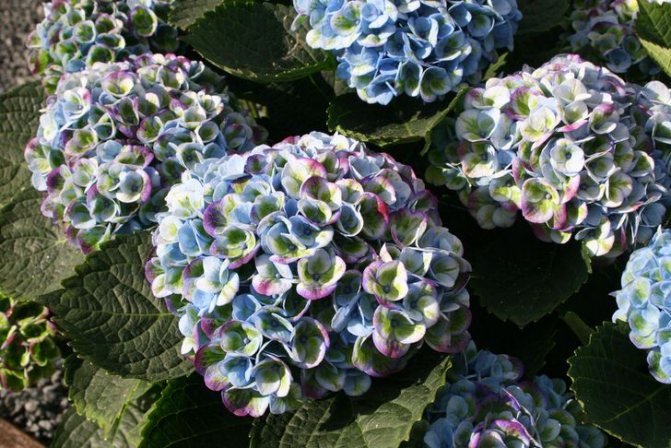
Nikko Blue
One of the few large-leaved varieties of hydrangea that can grow not only in the garden, but also at home. The bush is quite high - up to 1.5 m and the same diameter. Flowers in dense globular inflorescences are large and have a blue or blue color.


Countess Kozel
Another transcription of the name of the Kozel variety is "kossel". A cold-resistant plant that can thrive and bloom well in early July. Its pink-white inflorescences reach up to 25 cm in diameter and are supported by powerful stems. Large "balls" with flowers are complemented by large leaves, which distinguish the variety with special beauty.


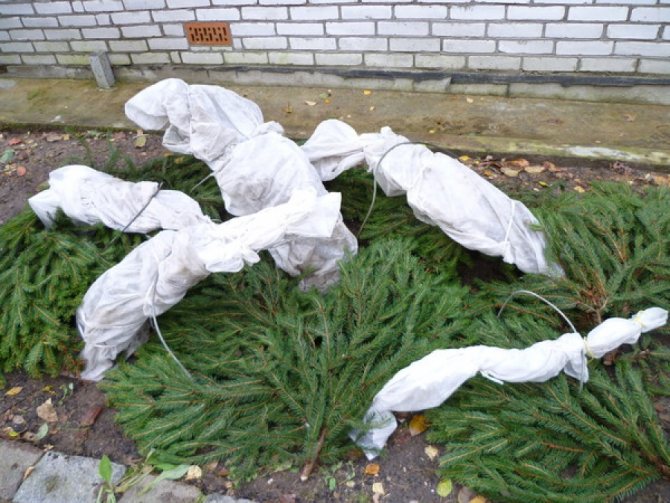
Hydrangea Miss Saori winter hardiness
Representatives of winter-hardy varieties of hydrangea conquered gardeners in our regions at the end of the last century. Today the number of such varieties has reached twenty. It should be noted that each of these varieties differs from each other not only in the size and color of the inflorescences, but also in other characteristics.
For example, winter-hardy varieties can be used as a supplement to a seasonal rabatka. Or, for example, as the main material for creating an unusual design in the garden, planting exclusively remontant representatives of the variety.


The maximum subzero temperature that a hydrangea can easily survive can also fluctuate. North American breeders have developed varieties that can safely tolerate temperatures as low as -15oС.
Their European colleagues managed to achieve an even better result. They got varieties that can withstand frost around -20oС.
It should be noted that the specified temperature range is not a limit. There are several varieties that do well at lower temperatures. The most frost-resistant variety among hydrangeas is the Miss Saori variety.
It is quite possible to recommend it for growing to amateur gardeners living in geographical conditions with rather low winter temperatures.
We watch a video about the features of hydrangea care:
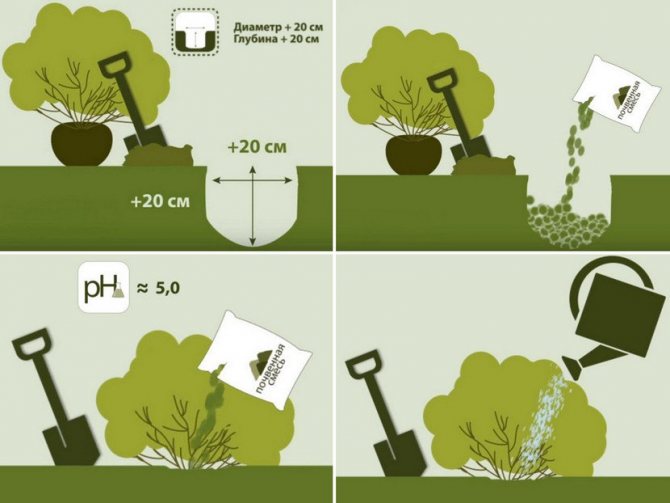
Landing in open ground
Before planting a seedling in a permanent place of growth, it is necessary to determine whether the soil, illumination, and terrain are suitable for it. Its future splendor of flowering and healthy appearance depends on it.
Important! TOthe mouth of a hydrangea should not be planted under the crown of a tree, even if it will be in the sun for most of the day. The fact is that a tree is able to "take" all minerals and moisture from the soil.
Landing dates
You can plant a young bush both in spring and autumn. When planting in spring, it is better to wait for the well-established warm weather. This usually occurs in early May, when sunny days come after snow melting and cold rains. And in the fall, a margin of time is needed for the rooting of the seedling and its adaptation to a new place of growth.


It is recommended to plant the bush in September so that the first autumn frosts do not catch the young plant by surprise and do not damage its aboveground part.
Seat selection
Hydrangea can grow both in open areas and in partial shade. In the first case, her leaves become smaller, but large inflorescences remain, in the second, the foliage becomes larger, and the flowers are smaller. The middle of a small slope, a gentle park slope, or a plain, where there will be no stagnant water after rains, is best suited.


Soil and seedling preparation
The plant prefers fertile, moderately acidic soil. In such conditions, it develops rapidly and most clearly demonstrates its best qualities in the form of large inflorescences and large dark green leaves. But hydrangea does not tolerate lime in the soil - it stops growing, after which it withers and dies.
Pay attention to information on how to help hydrangea bloom.
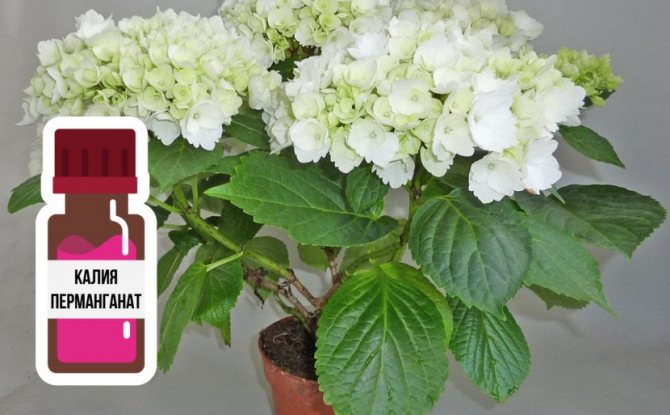
For planting, a bush with a normally developed root system is chosen. Damaged branches and parts of the roots are removed with a sharp pruner. Before planting, the seedling is immersed at the level of the root collar in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 20-30 minutes. This procedure can be done twice - in the evening, and then in the morning, just before placing in the ground.


Landing algorithm
You need to plant the plant in the same sequence as other flower shrubs. In this regard, the hydrangea differs little from its "neighbors" in the garden.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the features of feeding hydrangea with kefir.
The landing sequence is as follows:
- For two weeks, it is necessary to mulch the place for the seedling with a thick layer (about 10 cm) of sawdust or needles - this way the moisture in the ground will be preserved.
- 2-3 days before planting, dig a planting hole with dimensions several times larger than the rootstock of the seedling - usually 80 cm deep and the same diameter.
- Lay 10-15 cm of "Vermiculite" or broken brick on the bottom - this is necessary for the normal drainage of excess water, both irrigation and rain.
- Laying a bucket of humus or peat will increase the nutritional value of the soil.
- In the early morning or at sunset, place the seedling vertically in the hole and sprinkle it with soil.
- Gently tamp the earth and pour 1-2 buckets of warm water.

The main garden types of hydrangea
Despite the variety of forms, this article discusses the species that take root and grow in our latitudes. Hydrangea suffers from intense heat, many species that love partial shade slow down their growth in the sun, their inflorescences become very shallow. But there are those that tolerate heat well.


Blooming hydrangea
Large-leaved hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla)
Flowering occurs in July-August. Flowers of ordinary forms are collected in corymbose inflorescences with a diameter of up to 20 cm, flowers of sterile forms are collected in lush spherical inflorescences with a diameter of up to 30 cm in white, pink, blue.


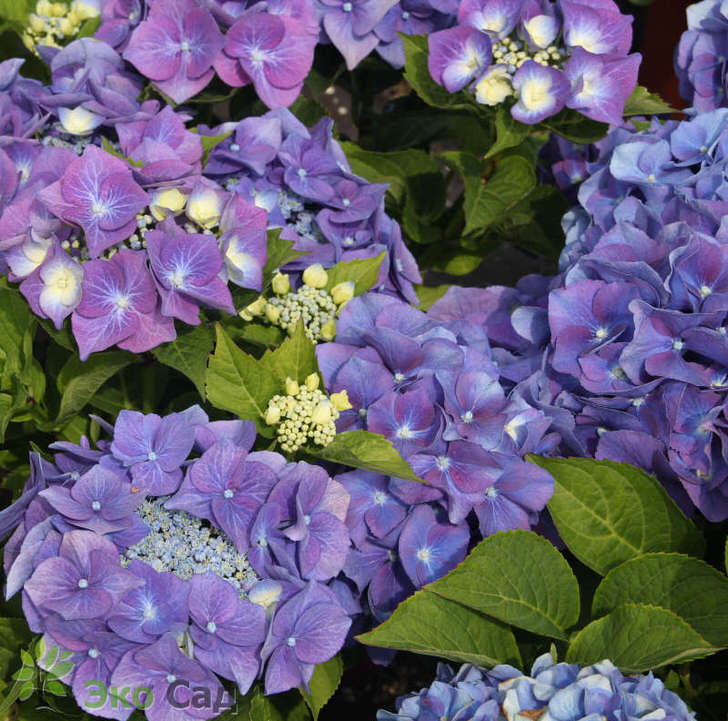
Large-leaved hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla) Shrub up to 2 m tall with large wide ovoid leaves. Heat-loving: requires shelter in frosty winters, tolerates frosts down to -10 ° C. The most common garden form in the world. The original form for potted hydrangeas. When potassium salts and aluminum sulfate are added to the ground, it allows you to get blue and blue inflorescences.
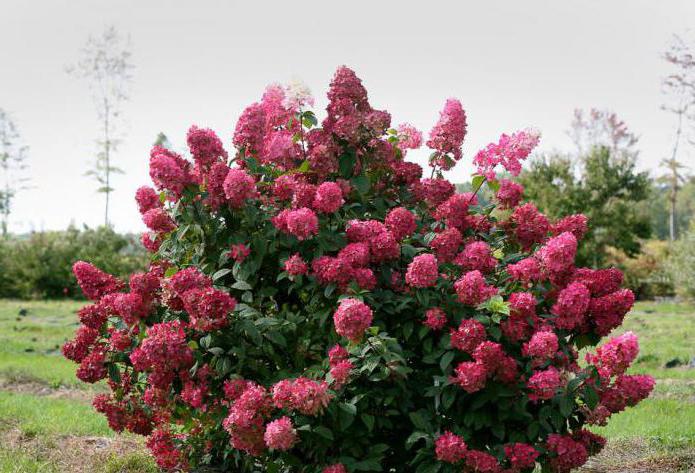
Hydrangea paniculata (Hydrangea paniculata)
Blooms from mid-summer to late autumn. Flowers are collected in dense panicles of pyramidal inflorescences up to 30 cm in length, color from light green to white, at the end of summer changes to dull purple. Shrub from 2 to 5 m in height or a small tree up to 10 m.


Panicle hydrangea (Hydrangea paniculata) Differs in durability, unpretentiousness (grows in swampy, gas-polluted places), frost resistance.
Hydrangea bretschneideri
The bush is compact, with a wide rounded decorative crown up to 3 m in height. Bloom from mid-July to August. The flowers are small, fruiting, collected in wide inflorescences in the form of umbrellas about 15 cm in diameter. The middle flowers in the inflorescence fall early, the marginal flowers bloom for a long time. The color at the beginning of flowering is bright white, towards the end - purple or reddish.The leaves are dark green, ovoid, 12 cm long. The shoots are hairy, reddish, with exfoliation of the bark in the form of thin plates; completely lignified by winter.


Hydrangea bretschneideri (Hydrangea bretschneideri). Photo from the site en.wikipedia.org The most winter-hardy variety, drought-resistant. It can be propagated by seeds.
Stalked hydrangea (Hydrangea petiolaris)
The shrub vine is attached to the support with air suction cups, reaches up to 25 m in height, in the absence of support it spreads along the ground. Perfectly braids
arches
... The flowers are white-pink, collected in corymbose inflorescences up to 25 cm in diameter, quickly fall off.


Stalked hydrangea (Hydrangea petiolaris) Abundant flowering is observed in open places, but also grows well in the shade.
Ash hydrangea, or gray (Hydrangea cinerea)
Shrub, reaches a height of 2 m. Used as a hedge. Blooms until late autumn.


Ash hydrangea, or gray (Hydrangea cinerea). Photo from the site The flowers are sterile, small, in the form of numerous shields. Leaves are oval, webbed, dull green.
Hydrangea tree (Hydrangea arborescens)
A very beautiful shrub with many varieties. Bushes up to 3 m tall, with large oval leaves up to 20 cm in length. Flowers are collected in fluffy inflorescences. Often freezes in winter, but in spring it quickly recovers and blooms profusely. This form requires heavy pruning (almost root) in April to keep the shrubs in good shape.


Hydrangea tree ‘Annabelle’ I have been growing for 10 years, blooms until late autumn, and in the flower garden is more noticeable than many of the more graceful and vibrant flowers.
What kind of hydrangeas grow in your garden? Tell us!
Catalog
Hydrangeas - sissies and spartans
Stunningly luxurious large-leaved hydrangeas make gardeners intolerable desire to have this beauty in their country house, but, most often, they cannot wait for anything but lush greenery ... Why?
That Siberia, that Alaska ...
This article is dedicated to two botanical sisters, although they were born on different continents, but for a long time they have successfully entered our gardens: Douglas spirea and oak-leaved spirea. Long ago and ...
| Hydrangea large-leaved "Miss Hepburn" (Hydrangea macrophylla ‘Miss Hepburn’) | Description: Round bush up to 1.5m high and wide. Miss Hepburn's globular inflorescences are pink on neutral soils and purple on acidic soils. They dry directly on the stems and are used by florists for dry bouquets. |
| Hydrangea macrophylla 'Miss Hepburn' | |
| Mandatory shelter for the winter or wintering in a cool room | |
| For the large-leaved hydrangea "Miss Hepburn", you should choose a place protected from cold winds with fertile, well-drained soils, acidic or slightly acidic, it does not tolerate calcareous soils at all; the soil must be constantly kept moist. For the winter, they are covered like roses, protecting flower buds from freezing, since hydrangea blooms only on last year's shoots. On acidic soils with an excess of aluminum ions, the inflorescences of the Miss Hepburn hydrangea turn purple, on those close to neutral - pink. | |
| Prefers partial shade | |
| Hydrangea "Miss Hepburn" is suitable for single and group plantings | |
| Plants are delivered at the age of 2 years, in a R-9 container. | |
| March, April | |
Together with this product you can buy:
Why don't flower shops sell hydrangea bouquets? It's just that they are probably so beautiful that it's a pity to cut them off. For garden owners in recent years, there has been no shrub more desirable than hydrangea. These are amazing bushes, immersed in white, bright pink or blue clouds of inflorescences. And the most attractive, the most delicate, the most refined of them is the large-leaved hydrangea.
Care
Further care for a young plant consists in watering, fertilizing, forming a crown and preparing for wintering.
Here you can read how and when to transplant a hydrangea to a new location.
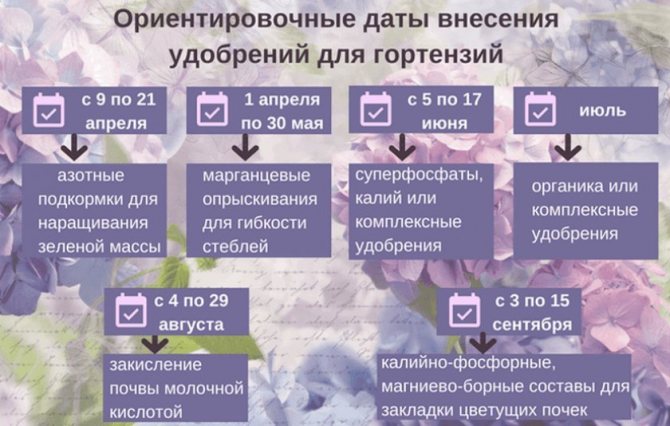
Watering and fertilizing
The approximate amount of water for each moisture-loving hydrangea bush is 20 liters per week as the soil dries. You can determine the need for watering by checking the soil moisture by digging 2-3 cm.If the ground at this level has dried out, then you can water the bush with settled and warm water - this will have a beneficial effect on the development of the seedling.


For rapid growth and lush flowering, every two weeks the hydrangea needs to be fed with aluminum-potassium solutions (up to 5 g per 1 liter of water under a bush).
Did you know? If you apply top dressing on one side of the root zone or divide the fertilized areas around the plant into sectors, you can get flowers of different shades on one bush.
You can also add a weak infusion of mullein under the trunk according to the following scheme:
- in early spring to strengthen the seedling and accelerate branching;
- in June for pouring buds;
- in mid-summer (July or early August) to prolong flowering and the formation of new buds in remontant varieties.
First-year seedlings should be watered once a month with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. It helps to fight off putrefactive bacteria and fungi.

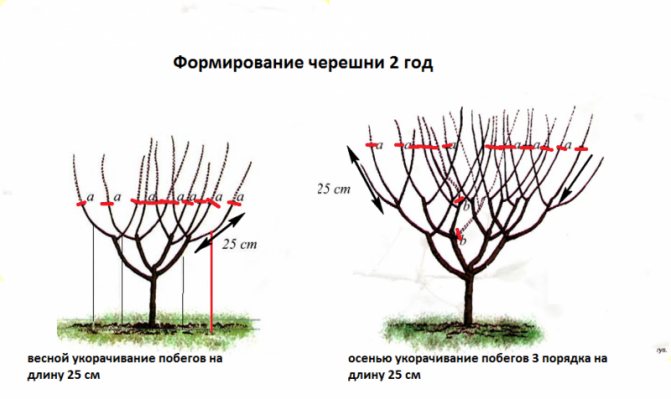
Pruning and shaping
Each gardener decides on his own whether he needs to cut the bush, because there are different pros and cons of this procedure. The plant does not require pruning, as it forms new buds in the axils of old shoots. This occurs in both remontant varieties and conventional ones. In this regard, the formation can disrupt the second flowering in the former, and the formation of buds the next year in the latter.
Trim or not
Generally, most large-leaved hydrangea varieties cannot be pruned. Repaired varieties give flowers on last year's shoots, and new shoots grow from the axils of old ones. Therefore, pruning can adversely affect the decorative qualities of the flower.
However, pruning does not affect the state of the plant itself. If you need to shorten the lashes to create landscape design or a certain variety requires it, then feel free to take a pruner. It is also necessary to monitor the safety of the shoots and remove damaged or frozen parts in time. It is best to prune last year's shoots in early spring. During the year, if necessary, only young growth can be corrected.
As you can see, hydrangea, despite its tropical origin, is quite capable of getting along in a continental and temperate climate. The main thing is not to forget about watering, to apply fertilizers on time, and then the plant will gratefully present you with flowers of stunning beauty.
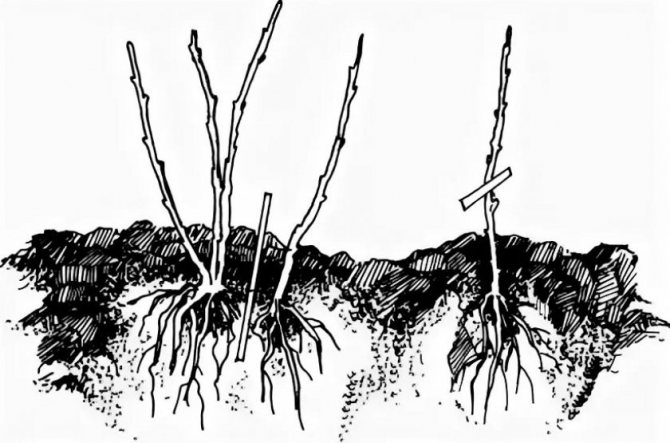
Reproduction methods
Reproduction of this unpretentious plant is done by all known methods for garden shrubs:
- cuttings;
- layering;
- seeds;
- dividing the rhizome.
You might be interested in how to change the color of a hydrangea.
Cuttings
Young, not yet lignified shoots are cut to a length of 10-15 cm in the fall, removing the lower leaves, burying the cuttings in a container with peat by 2-3 cm and leaving them in a heated greenhouse or on a windowsill for the whole winter. In the spring, their rooting is checked and transferred to a greenhouse or already into open ground.


Layers
In the fall, a strong lower branch of the bush is bent into a furrow in the ground prepared in advance and fertilized with peat, reinforced in this position with metal or plastic brackets and covered with earth.
Also learn how and how to acidify the soil for hydrangea.
Layers may appear as early as next summer or autumn, but they do not need to be touched yet. After a year, each shoot that appears will take root, which will be enough for transplanting. Each seedling is cut and planted in its own place for growth.


Seeds
The seeds collected at the end of flowering are dried, stratified in peat for 2-3 months, washed in a solution of potassium permanganate and planted in a greenhouse in early spring until viable shoots germinate. At the beginning of May, the greenhouse can be opened, the seedlings can be planted in the greenhouse, and in areas with a warm climate - in moist soil.


By dividing the bush
Dividing a bush is the fastest way to get a new and already mature plant.To do this, you need to carefully dig in the already developed hydrangea and get its root system out of the ground. The root, together with the stems growing from it, are divided into several parts (preferably two). After that, each part is added dropwise into the wells prepared in advance.

Preparing for landing
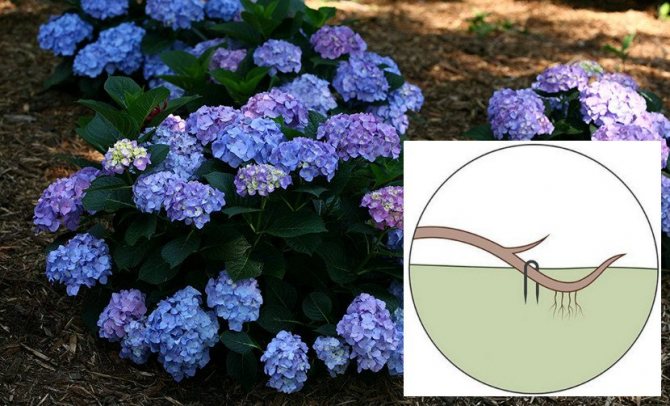
Planting of hydrangea broadleaf should be carried out on a cool gloomy day or before rain, when the bright sun does not shine, the weather is calm. The right time for this is from late April to mid-May in spring or early October in autumn. Before planting in open ground, several procedures should be carried out for better survival of the bushes.
- When planting several specimens, a distance of at least 1 m is observed between them.
- If possible, 2-3-year-old seedlings with a closed root system are selected in a nursery, planted in a mixture of sand, peat, sawdust.
- A permanent place for the bush is prepared by digging up the ground, adding peat, sand, leaf turf, humus in equal parts.
- They dig holes 35-50 cm deep and wide, in the presence of clay, loam is poured onto the bottom with sand, gravel, broken brick, crushed stone as drainage.
- A special composition is poured into the pits: for pink, red and fiery red hydrangeas with an acidity of pH 6.0 to 6.2, for blue - 5.0-5.5 pH, adding aluminum sulfate to the soil.
The next stage is the direct planting of bushes in the prepared soil.
- Releases the root system of seedlings.
- Place the roots in the hole, spreading them out with your hands.
- Make sure that the root collar remains at ground level.
- They fall asleep the roots, tamp the mound with their hands.
- Water each bush with 15-20 liters of water.
- Mulch with sawdust, needles or pine bark to a height of 5-8 cm.


Many gardeners, at the same time as planting, apply organic and mineral fertilizers to the pits, stimulating the formation of flower buds next year. They make sure that the mulch near the bushes always remains moist, this is an important condition in growing hydrangeas. During the summer, the soil is loosened 2-3 times, regularly watered and weeded from weeds.
Diseases and their treatment
Hydrangea suffers little from diseases, but it can be affected by downy mildew or chlorosis. In both cases, the leaves are clarified with their further drying out and falling off. Downy mildew is treated by washing the foliage with an aqueous solution of laundry soap.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the methods of combating diseases and pests of hydrangea.
You can add a pinch of copper sulfate to a liter of liquid. Chlorosis affects those bushes that grow in soil where there is too much limestone. Hydrangea does not need to be planted in such places, but if this has already happened, it is necessary to artificially increase the acidity of the earth by regular application of humus and peat.


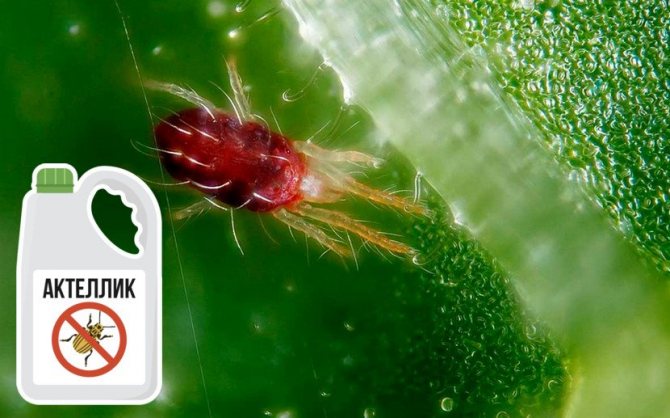
Pests and the fight against them
The only serious plant parasite is the spider mite. The rest of the insects can only accidentally get on the hydrangea from other plants or garden tools. The tick sucks the juices from the fleshy parts, after which the foliage crumbles. Insecticides - "Neoron", "Aktellik", "Fitoverm" are used against the pest for both prophylactic and medicinal purposes.


With proper and fairly simple care, hydrangea becomes a real decoration of a park or a personal plot. This plant can participate in landscape design both singly and in a group. It also looks good in compositions mixed in color and size.
What is it like
Large-leaved hydrangea (Hydrángea macrophýlla) is a shrub from the hydrangea family, the height of which is 1-2 m (indoor forms grow up to 60 cm). Slightly pointed oval leaves are dark green in color. Bright inflorescences of pink, blue, greenish or variegated color in shape can be varied. Bloom from June to October.
A heat-loving shrub with huge flower heads came to Europe from Japan in the 18th century.Until recently, the large-leaved hydrangea in our area was presented only as a houseplant. But with the development of agricultural technology, it increasingly began to appear in the open field. True, it requires a serious winter shelter. The flowering buds of the garden hydrangea are at the tops of last year's shoots. Therefore, it is very important to preserve the branches completely so that they do not die from frost. Not so long ago, remontant varieties were bred by Dutch breeders. These hydrangeas begin to bloom on the tops of last year's branches, and continue to bloom on the shoots of the current year. Thanks to this, they will be able to please us with bright colors even after a little freezing.