Bordeaux liquid for beginner gardeners seems like something incomprehensible and difficult to use. Experienced ones will say that there is nothing complicated here. And they will be right. Having cooked yourself for the first time according to these instructions, you will understand that everything is quite simple. The main thing is to properly prepare it so that the processing is beneficial.
Security measures
When working with such a solution, you should adhere to safety rules. For humans, the Bordeaux mixture is moderately toxic. During maintenance work, you should wear:
- respirator,
- glasses,
- latex gloves.
If this solution enters the gastrointestinal tract, weakness, dizziness, nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal pain, thirst, and indigestion appear. Each person's reaction to contact with the mixture may be different. There is a possibility that the temperature will be below 36 degrees. It is recommended to rinse the stomach with warm, boiled water. Without using a respirator, you can feel chills, irritation of the larynx, fever up to 39 degrees, sweating.
Gardening Tips
To use the product for medicinal and prophylactic purposes, your crops will need equipment.
If you have a lot of plantings and spraying is a long, impressive work, it is better to purchase a special sprayer, into which you can pour any substance. But if there are few plants and you rarely do processing, such expenses are not necessary. Use a regular bottle with holes in the lid as a spray bottle.
Being engaged in such processing on an ongoing basis, it will be more profitable to buy ingredients in bulk - for example, a bag of each. It will be cheaper, and you can prepare a pesticide at any time without the distraction of going to the store.
Security measures
Remember that Bordeaux liquid is very dangerous for humans - you cannot inhale it, touch it, and even more so you should beware of getting the solution into your eyes or mouth.
To prevent this from happening, take the following protective measures:
- dress in clothes that you do not feel sorry for and that are not used in everyday life - they should be closed, not leave skin patches in sight;
- wash such clothes separately;
- in a set of such a "shape" buy thick rubber gloves and goggles;
- it is highly desirable to have a respirator, but if not, be sure to cover your mouth and nose with a mask or tight collar.
The history of the creation of the Bordeaux mixture

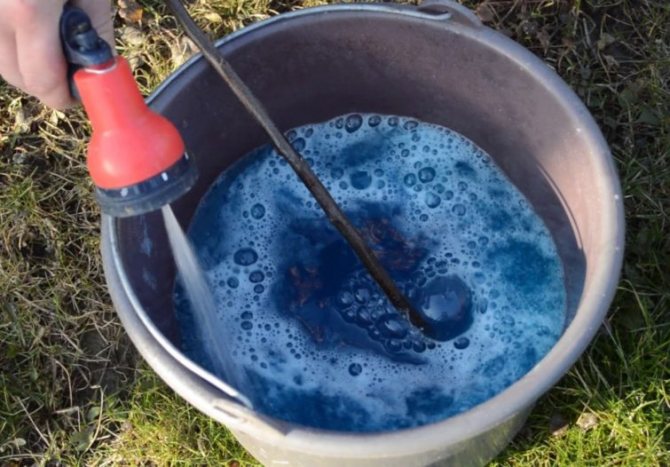
Bordeaux liquid in a plastic bucket. You can cook in any dish except iron. Photo: Good-Tips.PRO
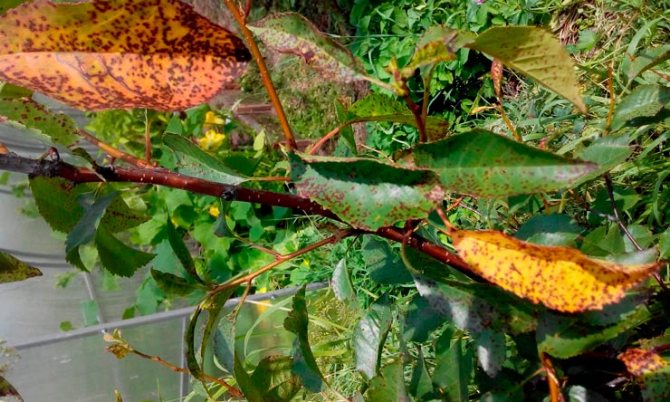
It has long been noticed that copper sulfate is harmful to all kinds of fungi. It is not for nothing that copper sulfate is sold in stores as a separate product - the chemical is used to treat wood from decay during construction and carpentry. Being impregnated with copper sulfate, wood is less susceptible to rotting and the appearance of mold in damp places: basements, cellars, attics, baths, etc.
But it is easier to process logs and boards with copper sulfate - the tree already perfectly absorbs copper compounds, but it turned out to be more difficult to get live plants to keep copper sulfate on the leaves. It is for the retention of copper sulfate on the stems and leaves of plants that lime, or rather lime milk, serves.Slaked lime supplements copper sulfate and a new compound is formed called Bordeaux mixture.
For the first time, the French botanist-inventor Pierre Marie Millardé developed and applied a mixture of copper sulfate and hydrated lime. The fungicide was originally used to protect and treat vineyards against the mold Plasmopara viticola, which is the cause of mildew.
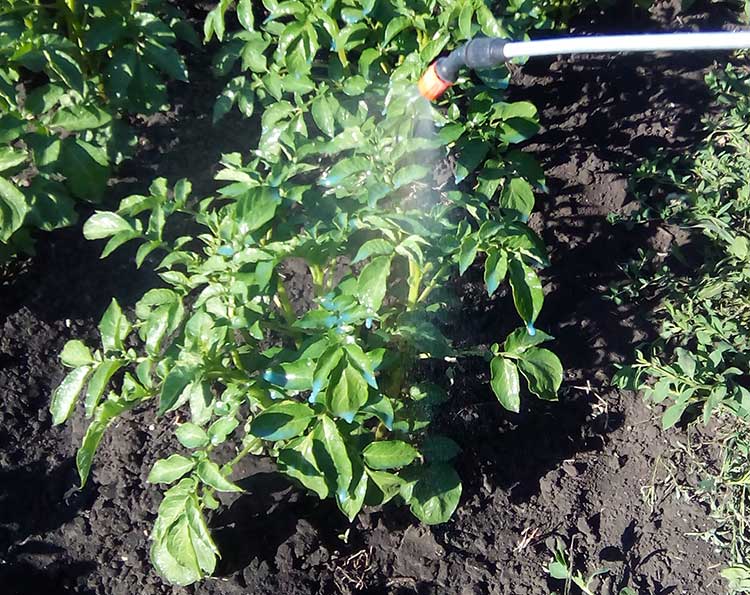


Spraying a potato bush with a Bordeaux mixture for the prevention of late blight. Photo: Good-Tips.PRO
Now the range of application of the Bordeaux mixture has expanded significantly, in addition to vineyards, the Bordeaux mixture is beneficial for the treatment and prevention of fungal diseases in plants:
- macrosporiosis, late blight (tomatoes, potatoes);
- mildew (grapes);
- spotting (raspberries, strawberries, strawberries);
- rust, scab, fruit rot, powdery mildew (fruit and berry crops);
- septoria, peronosporosis, anthracnose (cucumbers, onions, garlic, carrots).
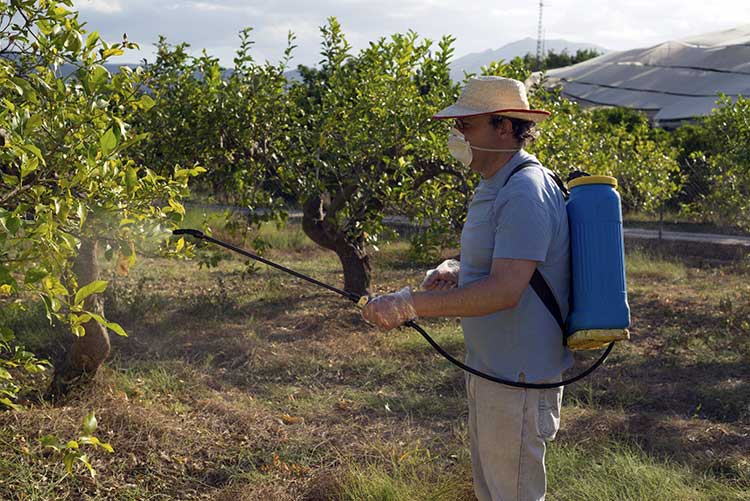


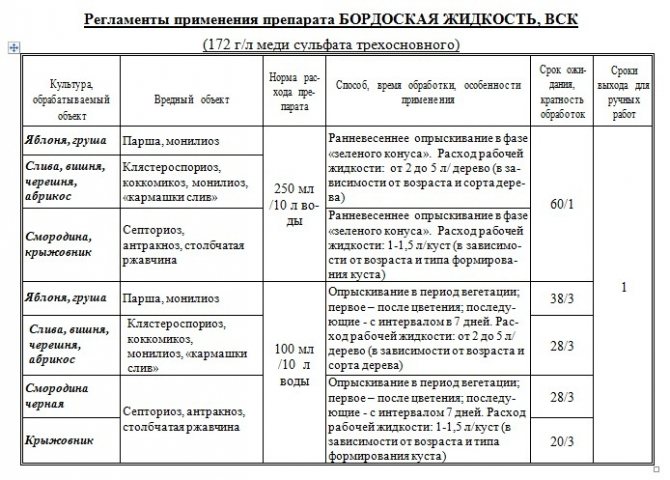
Processing of fruit trees with Bordeaux mixture. Initially, Bordeaux mixture was used to treat grapes, now the scope of application of the fungicide has expanded significantly. Table. Protection of fruit and berry and vegetable crops from diseases using Bordeaux mixture
| Cultures | Diseases | When to process. Frequency of processing |
| Perennial fruit crops | ||
| Pome fruits: pear, apple, quince | Fruit rot, leaf rust, scab, phyllostictosis, moniliosis, black cancer, powdery mildew, leaf spots. | Before the beginning of the spring growing season and after the leaves have completely fallen off, the plants are treated with a 3% solution of the Bordeaux mixture. During the growing season: in the bud extension phase and after flowering, spray with 1% Bordeaux mixture solution. The rest of the time - as needed. Stop processing 2 weeks before harvesting. |
| Stone fruits: cherry, sweet cherry, plum, cherry plum, peach, apricot | Coccomycosis, leaf curl, moniliosis, clasterosporium disease. | Before the beginning of the spring growing season and after the leaves have completely fallen off, the plants are treated with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid. From the budding phase to the beginning of flowering and in the phase of the onset of ovary growth, they switch to spraying with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture. Apricots and cherries are highly sensitive to the Bordeaux mixture (deformation and cracking of the fruit is observed). It is better to treat them with a 0.5% Bordeaux mixture solution. Stop processing 2 weeks before harvesting. |
| Berry crops | ||
| Grapes | Mildew (downy mildew), anthracnose, black rot, rubella, cercosporosis, melanosis. | The bushes are treated with a Bordeaux mixture in the phase of leaf deployment and during the growing season once every 2-3 weeks for the purpose of prevention and from other concomitant infections. |
| Gooseberries, raspberries, currants, blackberries, wild strawberries and strawberries | Leaf spot, leaf rust, anthracnose, septoria, black rot. | Berry growers have a shorter growing season, therefore, during the season, 2-3 treatments are carried out with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture before bud break and before flowering begins. The third treatment is carried out mainly after harvesting. |
| Vegetables | ||
| Cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins, beans, tomatoes, cabbage, onions, garlic, peppers, eggplants, potatoes | True and downy mildew, root and root rot of seedlings and adult plants, fusarium wilting, anthracnose, late blight. | For the first time, seedless vegetable crops are sprayed with a Bordeaux mixture in order to prevent fungal diseases in the phase of mass shoots. The second spraying is carried out with the deployment of 2 or 3 true leaves. On seedlings, the first spraying with Bordeaux mixture is carried out 2 weeks after planting. For processing plants, a 0.5-1% solution of the Bordeaux mixture is used. In the subsequent growing season, spraying with Bordeaux mixture is carried out according to the recommendations and at the first manifestations of the disease. |
Precautions
When using a solution of copper sulfate and lime, you must follow the safety rules:
- Prepare the mixture for spraying and handle plants with gloves, respirator, headgear and special protective clothing.
- Do not drink, smoke or eat anything while working with the mixture.
- Do not spray the mixture near fruits that are to be harvested within 2-3 weeks.
- Wash all fruits, vegetables, fruits, berries before use.
- Do not treat plants with Bordeaux mixture during their flowering, in strong winds, rains and abundant dew.
- Do not mix the solution with other fungicides and preparations.
- Do not add soapy water to the mixture to improve adhesion.
- The last spraying is carried out in the fall 2 weeks before harvest.
What is Bordeaux Blend
The formula of the substance: СuSO4 • 3Cu (OH) 2 = copper sulfate + calcium hydroxide. If the composition is prepared correctly, then it has high adhesion and is retained for a long time on the crown and leaves of crops.
Bordeaux liquid - a combination of 3 substances:
- lime powder;
- copper sulfate;
- water.
After dilution, the solution acquires a pale blue tint. The main component of the mixture is copper. Its lack does not affect the formation and fruiting of plants in the best way. To a greater extent, this applies to plantings on peaty and acidic sandy soils.
Copper in the composition of this preparation is an important trace element for the full formation of plants. If the culture grows on soils with its deficiency, then growth slows down, yield decreases, branches and leaves are deformed. Therefore, processing with blue mixture serves as an excellent way to fight diseases and additionally nourish the plants.
Benefits of Bordeaux liquid
Many gardeners regularly use Bordeaux mixture due to its versatile properties and significant benefits. Its chemicals instantly come into contact with the plant. The undoubted plus is that the mixture is not washed off by rain.
The protective characteristics of the Bordeaux mixture last for about 30 days, which is an advantage over other similar formulations. It is required to use the drug in early spring or late autumn - this is a prerequisite for its effectiveness.
The liquid has a high efficiency against a variety of pathogenic microorganisms and pathogens. Recommended for scab, rust, black rot, late blight, leaf curl, melanosis.
Disadvantages of Bordeaux liquid
Bordeaux mixture belongs to the group of pesticides with high contact action, therefore careful processing is necessary to combat diseases in the garden. The drug cannot be combined with organophosphate liquids, as well as mixtures that break down in an alkaline environment.


Benefits of Bordeaux liquid.
If you use the preparation for spraying annually, then there is a high accumulation of copper in the ground and in the garden plants themselves, which provokes bad ovaries and the death of young seedlings at the beginning of the season.
The disadvantages of using the mixture include phytotoxicity for garden crops during their active growth, from April to August. An active oxidative reaction when spraying Bordeaux liquid during rain causes burns and cracks on the crown of plants.
Due to the copper content, the mixture is unsafe for human well-being. Experts strongly recommend the use of respirators when diluting the product and treating the garden. This will help avoid chemical poisoning. For the same purposes, it is necessary to carry out work with the liquid only in calm sunny weather.
Bordeaux liquid instructions for use
Bordeaux mixture in spring is effective for prophylactic ("blue") spraying: during the period of swelling or the beginning of budding, plants are treated with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid. During the active growing season (when the plants already have leaves), a weaker, 1% solution of the fungicide is used.
Bordeaux liquid must not be mixed with other preparations, or used simultaneously with other fungicides.
In autumn, Bordeaux mixture is used in a more concentrated form (3%) than in early spring processing, since the foliage is opal, and you can not be afraid of burns. Autumn spraying will protect pome (pear, quince, apple) and stone fruit (cherry, apricot, plum) trees from fungal diseases.
Bordeaux cucumber liquid
Just like tomatoes, cucumbers are sprayed with 1% Bordeaux liquid (1.5-2 liters per 10 square meters). The first prophylactic treatment is carried out at the stage of 2-3 true leaves, then repeated 2-3 times with an interval of 10-12 days.
The last spraying with Bordeaux liquid must be carried out no later than 20-25 days before harvest.
Bordeaux liquid for potatoes
The first treatment is carried out before planting potatoes: the tubers are sprayed with 1% Bordeaux liquid 1-1.5 hours before planting. Then, when the potato bushes reach a height of 15-20 cm, the spraying is repeated at the rate of 0.5-1 l of the mixture per 10 sq. M. The treatment is repeated after 12-15 days.
Bordeaux liquid for grapes
In the “green cone” phase (the bud has not yet blossomed, the green tip is only visible), the grape bushes are sprayed with a 3% Bordeaux liquid. During the growing season, use a weaker, 1% solution of the drug.
It is necessary to spray the leaves of plants both from the outside and from the inside.
Bordeaux currant liquid
Currant bushes (also gooseberries, raspberries) are treated with Bordeaux liquid to prevent spotting. The first spraying is carried out in early spring using a 3% solution; for the next 2-3 treatments, a 1% solution of the drug is prepared.
Bordeaux tomato / tomato liquid
If tomato seedlings show signs of disease (gray, brown or black spots on the leaves), spray the seedlings with 1% Bordeaux liquid using a spray bottle.
For the prevention of late blight and other diseases, spraying tomatoes with Bordeaux liquid is carried out from the end of June to the beginning of July (or 2 weeks after planting) at the rate of 1.5-2 liters of solution per 10 square meters. In total, the plants are sprayed 3-4 times with an interval of 10-14 days.
Bordeaux strawberry liquid
After the snow melts, garden strawberries must be treated with a 3% solution of Bordeaux mixture (0.5-1 l per 10 sq. M). Then, in the stage of leaf regrowth, the spraying is repeated, reducing the concentration to 1%. The following procedures are carried out at the beginning of the emergence of buds and after harvest (in these cases, a 1% solution is also used).
Bordeaux tree liquid
In the spring, before bud break, trees are sprayed with 3% Bordeaux liquid (10-15 liters per adult and 2-3 liters per young tree). Then, in the "green cone" phase, the treatment is repeated with a 1% solution of the preparation, the next spraying is carried out after the trees have flowered. Further treatments are done with an interval of 10-15 days, and their number should not exceed 6 sprays per season.
As an alternative to the Bordeaux mixture, you can use drugs of a similar effect, which also include copper oxychloride (Polychom, Oxyhom, etc.). Such agents are able to heal "from the inside", deeply penetrating into plant tissues. In addition, they can be mixed with other substances.
Calendar for treating the garden from diseases and pests Plan of protective measures in the garden.
How can you replace the drug analogs of the drug?
The popularity of this tool among professionals and amateur gardeners is due to its relative safety, availability, versatility and high efficiency. However, this fungicide is not unique, and there are many analogues on the market for such preparations. The table provides information on pesticides that can be used to replace Bordeaux liquid:


| Drug name | Manufacturer | Release form | Active ingredients | Human hazard class | Benefits |
| Cuproxat | Nufarm | Liquid | Tribasic copper sulfate | 3 |
Does not precipitate. |
| Abiga Peak | Agricultural chemistry | Copper oxychloride |
| ||
| Hom | Technoexport | Powder |
Compatible with other similar drugs. Not addictive to pests | ||
| Polychom | Green Belt | Copper oxychloride, polycarbacin |
| ||
| Oxyhom | Soyuzagrokhim | Copper oxychloride, oxadixyl |
|
Preparing liquid at home


The scheme for mixing the components and obtaining the finished composition consists of several stages:
- the original weighed portions of copper sulfate and quicklime dissolve with stirring in a small amount of hot water. A separate container is taken for each solution. Slaking of lime is not carried out in plastic buckets, since they can melt, and metal containers are not suitable for dissolving copper sulfate and storing Bordeaux mixture;
- both solutions are diluted with water to a volume of 5 liters, after which they are mixed;
- a solution of copper sulfate is poured in a thin stream into a continuously stirred solution of lime;
- the finished mixture is an opaque blue suspension. Its suitability for treating plants should be checked by measuring the pH with litmus paper. If an acidic environment is found, a small amount of lime mortar must be added to the Bordeaux liquid. The readiness of the drug is evidenced by a weak alkaline or neutral medium.
The colors of the litmus indicator: in a neutral medium it does not change color (yellow paper), in an acidic medium it acquires a crimson tint (some mistakenly consider it red), in an alkaline medium it shows a blue coloration.
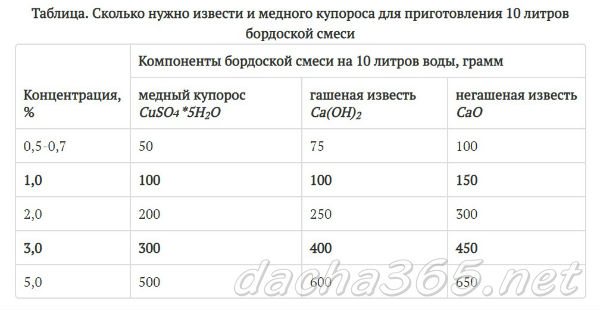
Mixing ratios (for a final volume of 10 l):
- copper sulfate - 100 g (1% solution) or 300 g (3% solution);
- quicklime - 100 g (1% solution) or 300-500 g (3% solution).
After preparation, the drug should be used immediately (do not insist), until the fine particles of copper hydroxide are combined into larger conglomerates. Periodic stirring maintains the dispersed state of the solution. Long-term storage will lead to sticking and settling of hydroxide particles, which will clog the sprayer nozzle. To keep the mixture for use for a couple of days, add 5-10 g of sugar to it.
The process of preparing and using the liquid, see the video:
It will be cheaper to buy the ingredients for the Bordeaux mixture separately. A ready-made kit, including all components and litmus paper, is simpler, but more expensive.
Application features, dosage and consumption
The suspension of the preparation is applied to the surface of plants in early spring and summer by spraying. The prepared solution is poured into a tank, which is then pressurized (manually or from a carbon dioxide cylinder). Spray the mixture evenly on trees and shrubs, trying to get the liquid on all sides of leaves and branches.


Features of using the tool:
- the composition should be sprayed carefully, avoiding spills on yourself and on the ground;
- before work, you must make sure that there are no people without protective clothing (especially children) and animals in the spray area;
- do not carry out work with a high probability of precipitation;
- application should be done strictly downwind.
The number of treatments is:
- before the appearance of the kidneys - 1 (3% solution);
- during the growing season - 3-4 (1% solution);
- the frequency of processing (the period of validity of the liquid) - 10-14 days.
Mix consumption:
- for trees (fruit and berry, deciduous and coniferous) and large shrubs - 15–20 liters per 100 m2;
- for medium shrubs and grapes - 10-15 liters per 100 m2;
- for small bushes (strawberries, potatoes) - 5-10 liters per 100 m2.
Large trees that have external signs of fungal infection can be sprayed with a 1% solution of the mixture at the rate of 10-15 liters per tree.
The liquid remains an effective and cheap drug for the treatment and prevention of green plant diseases. Its widespread use in horticulture is facilitated by the availability of components and ease of self-preparation. The versatility of the product allows for joint processing of most plants and contributes to the overall health of the site.
Bordeaux mixture how to cook
What is important to know:
- first, two aqueous solutions are prepared in different containers, i.e. you need two containers
- Bordeaux liquid can only be diluted in enameled (no chips), glass, wooden, plastic dishes; it is unacceptable to use aluminum, iron, galvanized dishes
- dissolve copper powder in hot water, then cool, adding cold, lime - immediately in cold
- mix only cold solutions
- check lime for quality
- the effectiveness of the mixture being prepared depends on the ratio of the components
What you need to make Bordeaux liquid
- two buckets: one for 5 liters, the other for 10 liters
- a piece of gauze for straining and a sieve
- wooden stirring stick
- iron nail
- kitchen scales with an accuracy of +/- 1 g (if all components are purchased separately, not in a set)
Preparing a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid
The industry offers us ready-made - weighed and packaged mixtures. The package contains two plastic bags - one with copper sulfate CuSO 4, the second - CaO quicklime.
To prepare a 3% concentration of Bordeaux liquid in a volume of 10 liters, you need to take: 300 g of copper sulfate and 400 g of quicklime (CaO).
- Pour 1 liter of hot water into a 5 liter bucket and add copper sulfate, mix well with a stick, then add very cold water to a solution volume of 5 liters.
- Extinguish lime: pour 2 liters of cold water into a 10-liter bucket and add quicklime. Mix well - lime is extinguished: CaO + H2O = Ca (OH) 2
- Add cold water to a volume of lime milk of 5 liters.
- From the first bucket, pour the dissolved copper sulfate into the milk of lime in a thin stream.
- We get 10 liters of a 3% solution of bright blue color, without flakes!
- We check the reaction of the solution: we lower the iron nail and look - no copper plaque should appear on it.
- We filter the solution through a fine sieve or cheesecloth folded in 3-4 layers.
- Pour the solution into the sprayer, work.
Bordeaux fluid without errors
The safety of your fruit and berry crops, vegetables and flowers actually depends on the quality of lime.
The correct quicklime (fluff), when extinguished with water, will rapidly dissolve with the release of heat (therefore, you need to dilute lime only with cold water). If the dissolution process is weak and a lot of sediment with limestone flakes is formed, the lime is of poor quality (poorly burnt or stored for a long time). In this case, you need to take more lime, but it is better to just take a fresher and higher quality one. The fact that it is necessary to add lime shows the formation of a red plaque on the nail - separately prepare a solution of milk of lime and add to the total volume of Bordeaux liquid until repeated tests with the nail show that it remains clean, without red plaque.
If you do not fix the solution, then Bordeaux liquid has an acidic reaction and can cause burns to the leaves.
When adding lime milk, pour it into the Bordeaux liquid in a thin stream, stirring the solution evenly with a wooden stick.Initially, we pour the copper solution into lime, and not vice versa!
If you buy a ready-made Bordeaux mixture, then in the set, in addition to copper powder and lime, there is a litmus test. It is more correct to determine by indicator paper, because if you add too much lime, the nail will not be coated with copper, but the solution will reduce the fungicidal properties.
Preparation of a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid
To prepare 10 liters of a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, you need to take 100 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of lime. The cooking technique is the same as for a 3% solution.
Structure
Bordeaux mixture is an aqueous solution of copper sulphate and slaked lime (solution of copper sulfate CuSO4 5H2O and calcium hydroxide Ca (OH) 2).
During the mixing of milk of lime and copper sulfate, a reaction occurs, during which copper sulfate is formed, which destroys fungi and suppresses the vital activity of pathogenic organisms.
Often a 1% Bordeaux mixture is used, which consists of:
- copper sulfate - 100 g;
- slaked lime 100 g, if quicklime - 150 g;
- water - 10 liters.
Dosage
Next, let's talk about how to dilute Bordeaux mixture... This process must be approached very responsibly, since each plant needs its own dosage of the agent. In this case, it is important to observe the dosage of the agent. If the wrong dosage is chosen, then irreparable damage to the plant can be caused.
The CORRECT dosage for 10 liters of water should be taken with slaked / quicklime and copper sulfate in the following proportions:

Consumption calculation
Processing with Bordeaux mixture different plants and trees implies the use of a certain amount of solution. It is different for each culture:
- For 1 young tree up to 6 years old, 2 liters of the mixture is used.
- For fruiting plants, 10 liters of the mixture is taken.
- For 1 shrub, 1.5 liters are used.
- For the prevention of diseases in grapes, raspberries and strawberries, 1.5 liters per 10 square meters are used. meters.
- For tomatoes and cucumbers, spend 2 liters. by 10 sq. meters of landings.
- 10 sq. m. planting melons, watermelons, onions or beets use 1 liter of solution.
Pros and cons of using
The positive effect of the drug on seedlings is due to its properties:
- quickly affects the bark of trees, their leaves;
- is not washed off by rain;
- in permissible concentration it is harmless to plants;
- protects against infection within a month after spraying.
The disadvantages of the fungicide include:
- Impossibility of interaction with pesticides, phosphorus-containing organic substances, as well as with compounds that can dissolve in alkali.
- Dependence of the degree of efficiency of the solution on the intensity and quality of foliar spraying of seedlings.
- Negative impact on vegetation due to the accumulation of copper in the soil. When the permissible concentration of a trace element is exceeded, the plant begins to wilt and eventually dies.
- The danger of penetration of active chemical elements into groundwater, which can lead to an imbalance of the entire ecosystem.
- The content of the poison in the solution. If it enters the respiratory tract and the human alimentary tract, irreversible processes are triggered in the body; death is possible without medical assistance.
- Possible plant burns due to improper preparation and use of the mixture.
- Difficulties in using the liquid due to incomplete dissolution of lime, since solid particles clog the spray gun.
Features of tillage
The soil is treated with fungicide in the fall, during the preparation of the land for winter. The procedure allows you to rid the land of pathogenic flora.
Before processing, the following activities are carried out:
- remove fallen leaves and weeds;
- loosen the soil, break earth clods.
The solution is introduced by watering the soil or spraying bushes and trees.


Negative soil changes due to improper use of Bordeaux liquid
The Bordeaux mixture contains copper, which can accumulate in the soil over time. It is displayed very slowly. An excess of a trace element in the soil leads to the fact that the leaves of plants acquire a brownish, brownish tint, their roots grow poorly. Iron deficiency provokes looseness of the structure of the leaves, the appearance of lateral branches of the roots.
Prevention of fungal diseases with the help of the mixture must be done correctly, strictly observing the dosage of the drug and the frequency of application.