"Black leg" is a concept familiar to almost everyone who is engaged in agriculture. They designate in a simple way a group of diseases that have some similar symptoms. In fact, these are different diseases - either fungal, or bacterial, sometimes viral, caused by a variety of pathogens.
Plants are most vulnerable in the initial period of their vegetative development. Therefore, it is the seedlings of tomatoes, peppers, flower crops, etc. that need special attention in order to timely prevent the "black leg". It is better to insure against such a misfortune in advance - it is better to prevent than to fight.
I will tell you how to correctly diagnose the disease and ensure a competent selection of methods and means - either early preventive protection, or the fight against an illness that has already hit the seedlings.
Black leg in tomato seedlings: control measures and treatment of the disease
Amateur gardeners who practice growing tomatoes from their own seedlings know how much time and effort have to be spent in the spring on different stages of such a difficult activity.

The same gardeners or greenhouse workers who buy seedlings talk about the considerable costs associated with the purchase of planting material. Therefore, when tomato seedlings disappear without turning into a fruiting plant, the gardener experiences a lot of negative emotions.
Diagnosis of infection
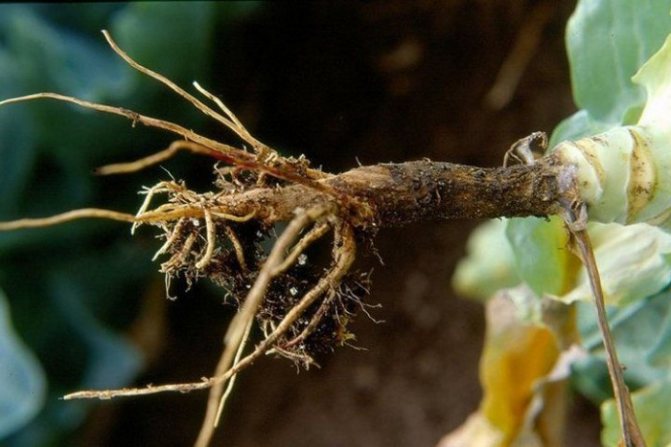
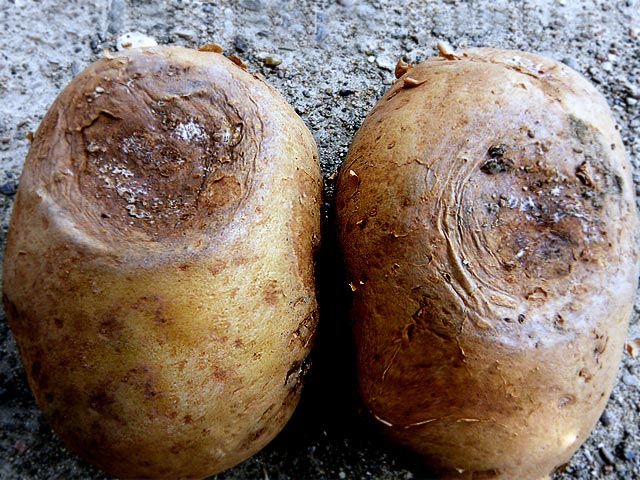
The bacteria that provoke the development of the blackleg spread from the stem to the tubers, turning them into a rotting mass that exudes an unpleasant odor. The color of diseased potatoes varies from light to dark.
A characteristic viscous liquid with a strong unpleasant odor flows out of the cracks of the affected tubers, and a void forms inside them.
Outwardly diseased potatoes are characterized by cracks and dark skin. As a rule, it is possible to diagnose a black leg only after the emergence of shoots. The foliage immediately turns yellow and falls off, the stem also turns yellow and dries out over time. Under its own weight, the stem is capable of breaking, and in the place of the break, signs of decay are clearly visible. At the same time, the potatoes themselves are easily pulled out of the ground.
Related article: Young potatoes, fried whole and in skins
The most common signs of seedling disease
It is difficult to say what "kills" tomato seedlings more often: diseases, pests or inept actions of the workers of the tomato beds themselves. You need to be able to recognize what causes tomato seedlings to die - what to do depends on the diagnosis.


abnormal thinning and elongation of the stem (reason: lack of light or violation of the temperature regime);- discoloration of leaves, their drying and falling off (reason: very wet soil or poor lighting);
- drying of the tips of the leaves (reasons: dry air, salinity of the soil or water hardness);
- white or off-white spots on leaves and stems (reasons: too aggressive sunlight or fungal disease septoria);
- blackening of the stem of the seedlings at the bottom (reason: black leg fungal disease).
Symptoms of the disease
Signs that a potato is affected by a black leg are:
- yellowing and falling foliage;
- the stem and root turn black, at the site of the lesion they easily come off;
- lag of diseased bushes in development;
- with severe damage, the disease from the stem passes into the root, tubers;
- the junction with the root crop rots, has a pungent unpleasant odor;
- in the rainy season, after flowering, the stem of the potato acquires a dark green color, and when pressed on it, emptiness is felt;
- initially, the fruit becomes covered with brown spots, after which its tissues darken and rot.
Black leg is a disease in which the symptoms are clear from its name
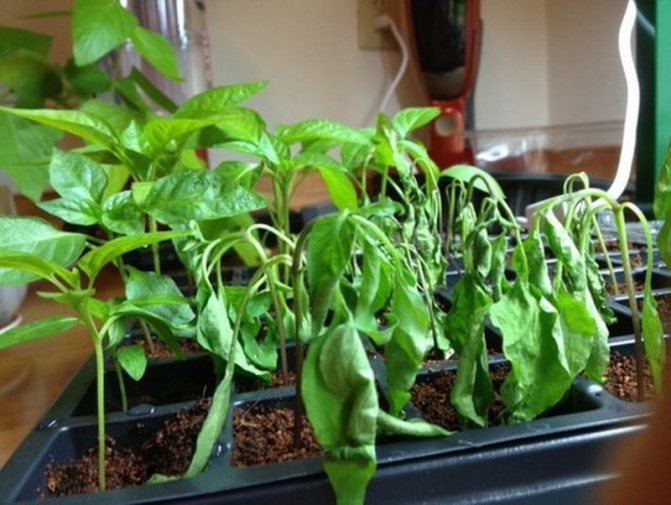
The fungal disease "brown rot", better known to tomato growers under the name "black leg", can very quickly destroy all young seedlings. First, a dark brown color appears in the plant in the area of the hypocotal knee, then a putrefactive abscess appears in this place, then the lower part acquires a pronounced wateriness and softness, and in the end the seedling simply breaks down. So tomato seedlings die from the fungus - what to do in this case will be discussed later in this article.
Symptoms of the disease
The fact that the potato is infected can be judged by yellowed and falling leaves. Sick bushes develop poorly. After defeat, the stem turns black, then the root and tubers begin to rot. A strong unpleasant odor emanates from the place where the trunk connects to the fruit. The affected parts come off easily.
You can understand that a potato is sick with a black leg if:
- in rainy time, after flowering, the stem turns dark green;
- as a result of pressure, one feels that it is empty inside;
- first, brown spots appear on the root crop, and then it darkens and rots.


The reasons for the development of the "black leg" and factors of its provocation
Much less often, the root cause of the development of such an unpleasant disease is the sprout fly.


Although the black leg in tomato seedlings in this case does not arise because of the flies themselves, but because the larvae of this pest, which are in boxes with seedlings, eat the roots and the bottom of the stem of the tomatoes. The larvae appear in the soil with the compost made from animal humus.
Factors accelerating the development of the blackleg fungal disease:
- excessive moisture in the earth;
- too densely planted seedlings;
- lack of lighting;
- freezing;
- poor ventilation;
- lack of a pick.
Seeing on a sunny day that the seedlings show a sluggish and lifeless look, you need to immediately think about why the tomato seedlings are missing, and start processing the seedlings for treatment for black leg. In this case, the tomatoes can still be saved. If the darkening has already manifested itself, then, most likely, the plant will disappear. In this case, you just need to try to protect other seedlings from infected plants.
Description of the disease
Blackleg is considered a dangerous disease that affects vegetables such as tomatoes, cucumbers, potatoes, cabbage and many others. It is caused by parasitic fungi that can persist in the soil for several years. Blackleg disease is mainly found in seedlings grown in greenhouses and hotbeds.
When a plant is affected by this disease, a darkening of the root part of the stem is observed, which subsequently leads to thinning, forming a constriction, decay and then death. Infected stems can survive, but they will greatly lag behind in growth, get sick and will no longer be able to give a good harvest.
The disease is caused by pathogenic fungi in the soil. They "eat" weakened plants, for example, at the moment of emergence of sprouts on the surface or after their pick. Therefore, during these periods, it is necessary to carefully examine the seedlings for the timely detection of the disease.
The fungus is located in the root collar of the sprout, blocking the nutrition of the leafy part. Leaves wither, curl, begin to fall off.The stem of the seedlings becomes lethargic, soft, it has a black leg, the gardener does not know what to do with such sprouts. To the touch, they are either too soft or, on the contrary, fragile. Without treatment, they rot.
Disease control technique
To prevent a black leg from appearing in tomato seedlings, control measures should be based on competent prevention.
Preparing seeds for planting
It is best to choose seeds that are classified by the manufacturer as resistant to brown rot infestation. This must be indicated on the package. For example, tomatoes of the "Gift" variety are not afraid of fungus, therefore, when growing seedlings, an amateur agronomist does not have to think about how to process tomato seedlings from a black leg and how to save seedlings. Even at the stage of seed preparation, they should be treated with a solution of humic acid or potassium permanganate to destroy the theoretically having a chance of the presence of fungal spores. Or at least thoroughly pour over boiling water. You can read about the preparation of tomato seeds for sowing seedlings here.
Preparing the land for tomato seedlings


If there are no pathogenic fungi in the soil, then in the future the black leg on tomato seedlings will not show itself - what to do for this, the science of agricultural technology knows. It is necessary to take "clean" land in the fall, which did not have the experience of growing tomatoes, potatoes or peppers on it. Leave it on the street for the winter, so that it “freezes” well. In the spring, before planting tomato seeds, the soil must be “roasted” in the oven or oven at 130 degrees for half an hour. Instead of roasting the soil, you can steam it: supply steam from boiling water to the ground for an hour.
Then the tomato planting site should be spilled with a solution of potassium permanganate or soda ash, or colloidal sulfur should be added to the soil about 5 grams per square meter. When the seedlings begin to sprout, you can sprinkle the soil on top with a two-centimeter layer of dry sand, wood ash, or a mixture of these. Such soil cultivation will eliminate subsequent worries about why tomato seedlings are sick - what to do with the blackened legs of the seedlings. It would be even better to purchase ready-made neutral acid soils in the store. But this is very costly when a lot of seedlings will be grown.
Read also: Grow pepper seedlings in diapers at home
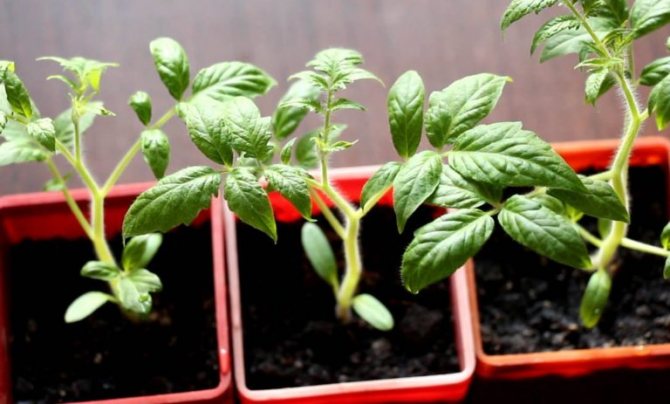
Growing tomato seedlings


Gardeners who know how to save tomato seedlings from a black leg will never allow the sowing to thicken. If we are talking about a greenhouse, then constant airing of the seedlings should be ensured, and if possible, it should be taken out into the air during the daytime. But you also do not need to allow drafts. Watering should exclude too much moisture in the soil, so it is better to water the tomato seedlings in the morning, which will allow the soil to dry out before nightfall. In addition, you should observe a temperature regime that is comfortable for seedlings (18-20 degrees), give the tomato seedlings enough sunlight and periodically loosen the soil.
It is the absence of excessive moisture and drought that will allow the gardener to forget what the treatment of black leg in tomato seedlings is as unnecessary. It is better to germinate seedlings in peat pots, cups or cassettes made of plastic or polyethylene.
The use of folk remedies
If infection could not be avoided, and, despite preventive measures, a black leg was still found in the seedlings, what should be done? First of all, it is necessary to carefully remove the damaged plant along with a part of the adjacent land in order to prevent the spread of the infection to the nearby seedlings.
After that, pour the remaining seedlings with an ash solution (2 glasses per 1 liter of boiling water, leave for 6 hours and dilute in a bucket of water). Many gardeners recommend feeding with a mixture of slurry, chicken droppings and mullein. This will help increase the plant's resistance.
There are many examples of black leg disease affecting seedlings. How to deal with it? Watering with special solutions. To do this, use 1% Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate (5 grams per bucket of water) or a solution of potassium permanganate. Watering is carried out at the rate of 1 liter per 1 square meter.
In order to dry the soil, you can add a mixture of sand and ash. It also promotes the formation of new roots above the affected area.
The black leg has been known among the people for a long time and it would be strange if there were no ways to deal with it. Unfortunately, the truth is that if the fungus has chosen the seedlings, then it will practically not be possible to save the plant. The only thing that needs to be done is to urgently transfer the greens that have not yet been touched by the disease into a new dish. That is why the popular experience is mainly aimed at preventing the conditions of the appearance of the black leg in the same way than at treating it.
So, for example, it will never be superfluous to use potassium permanganate. It does not harm plants and will not affect human health in the future (when the harvest will be eaten), but at the same time it effectively disinfects the soil. Processing is carried out with a weak solution of potassium permanganate with water (in the proportion: 3 grams per 10 liters of water).
The so-called soil calcination is widely used among the people. For this, metal dishes are filled with soil. Pass the earth a little with boiling water and leave it in the oven for 30 minutes at a temperature of at least 100 degrees Celsius.


Those who have a lot of experience in growing seedlings often sprinkle the topsoil with coal or ash, which slightly dries the base of the plants and inhibits the growth of fungi. Sometimes they take the practice of periodically watering the seedlings with soda. To do this, a teaspoon of soda is diluted in a glass of water and poured over the soil in a bowl.
Another recipe widely spread among the people for the prevention of rot in plants is the use of river sand. It is also calcined in the oven (ideally, it is also cleaned of impurities using a coarse-grained sieve). The grains of sand allow excess moisture to pass through well and "breathe" perfectly, which is detrimental to the fungus.
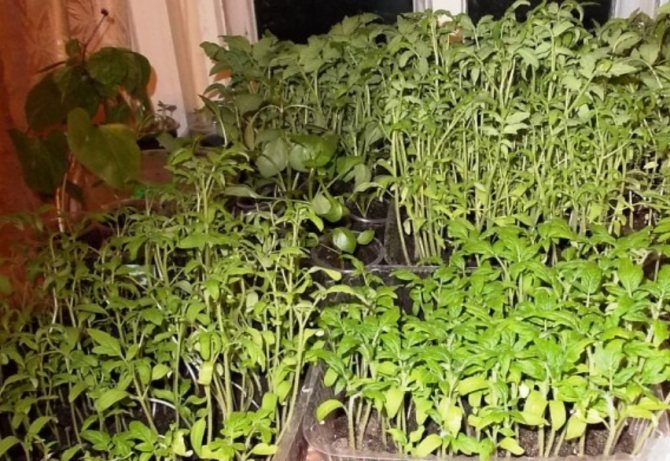
Black leg: how to save seedlings from black leg. Black leg is a real scourge of seedlings, most often it affects seedlings of crops such as tomatoes, bell peppers, eggplants, cucumbers, various types of cabbage, radishes, lettuce, and from flowering plants - petunias and others grown through seedlings. In this article, we will talk about what a black leg is and how you can deal with it, including in the most effective ways, as well as how to prevent its appearance, that is, about preventive measures.
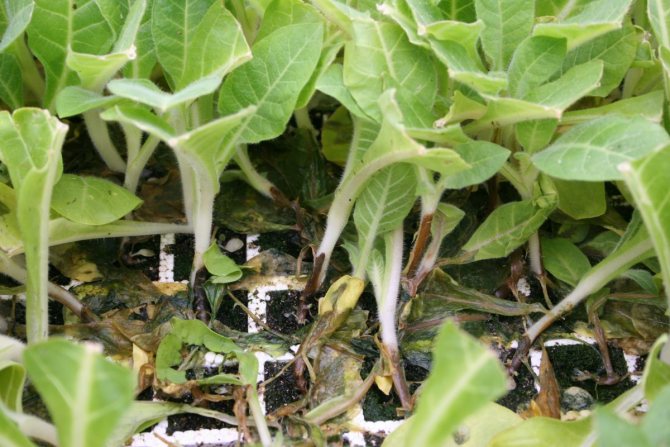


Black leg on tobacco seedlings.
In the first place - dusting the soil with wood ash or wood soot with a layer of literally a few millimeters. Gardeners claim that the black leg does not develop on such soil, and the seedlings grow beautifully.
In second place is watering the seedlings with a solution of ordinary baking soda - you only need one teaspoon of soda per glass of water, this volume is enough for a square meter of the seedling box, and you need to water it once a week.
In third place is the soaking of seeds in Epin's solution, while the ampoule is dissolved in a liter of water and the seeds are soaked in it overnight, gardeners claim that such seedlings are not affected by a black leg.
So, it is clear that a black leg can be dealt with both through competent preventive measures, that is, to prevent its appearance at all, and with the help of various means of dealing with it. But do not think that this disease is not worth focusing on. The black leg is very dangerous and if you miss the moment of mass destruction of seedlings, it will be impossible to return the lost days, and the seedlings will only have to be thrown away, so be careful about this disease.
If the black leg has already appeared
In the case of the manifestation of a black leg, it is necessary to remove the diseased plant along with the soil.
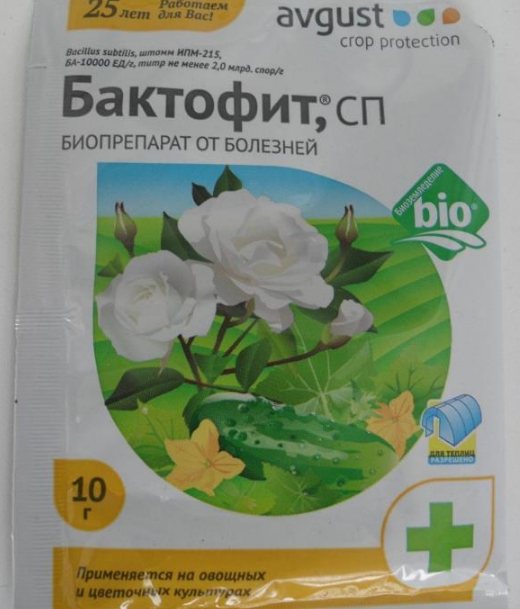
Healthy seedlings growing next to it should be evacuated to non-contaminated soil.In the event of blackening on the leg of tomato seedlings, gardeners are looking for how to water tomato seedlings from a black leg and turn to special antifungal drugs. These include: "Baktofit", "Fundazol", "Fitolavin", "Planriz" or "Fitosporin".
Fitosporin - a remedy against blackleg


Fitosporin, produced in the form of a paste and powder, is ideal for tomato seedlings because it is a natural biological agent, not a chemistry. Its basis is beneficial bacteria that can "eat" the fungus that provokes the development of the black leg. This drug is introduced into the soil to disinfect it from the fungus, the seeds are treated with it and it is taken if the question arises: how to spray tomato seedlings from diseases of the fungal group.
Folk remedies in the fight against black leg
Connoisseurs of folk remedies, when they notice that a blackfoot is developing in tomato seedlings, what to do, they ask their grandmothers. Those recommend spraying infected seedlings and watering the soil with onion peel infusion. You can wash the site of infection on the stem with vodka diluted with water. The solution should be weak in strength: one in ten. Also used is the treatment of affected seedlings with potassium permanganate, copper sulfate in the form of a solution of 5 grams in a liter of water or a solution of baking soda - a teaspoon per 200 grams of water.
What if the fungus reaches the seedlings?
To prevent the disease of seedlings with a black leg, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of the disease and create conditions unfavorable for the development of the fungus.
- Purchase seedling soil from specialized stores. If you take it from the garden, be sure to ignite or freeze it, additionally spill it with potassium permanganate or Fitosporin solution.
- Do not neglect pre-sowing seed treatment, unless you have inlaid or other purchased seed that is guaranteed to be processed by the manufacturer. For this, you can also use "Fitosporin" and other drugs with a similar effect. Many people use a solution of potassium permanganate. For most crops, a 1% solution is used, for some (pepper, cabbage, pumpkin) - 2%.
- Allow the soil to dry sufficiently before sowing seeds.
- Respect the spacing between seeds that is recommended for your particular crop.
- Air the seed box after sowing.
- Observe the watering regime. It is better to water abundantly, but rarely, so that the soil can dry out on top;
- Sprinkle a thin layer of sand or ash on the soil.
- Dive seedlings in time.
- Apply top dressing in the same composition and in the amount recommended for a particular type of seedling. Do not overfeed plants with nitrogen fertilizers.
Another effective measure for the prevention of blackleg is the choice of varieties of tomatoes, peppers and other vegetables that are resistant to fungal diseases.
If you notice that the seedlings have begun to hurt with a black leg, you need to take measures to combat this scourge without delay.
- Remove the affected plants: they are unlikely to be saved, but the rest of the seedlings from them can become infected.
- If the seedlings are old enough, plant them in different containers.
- Treat the places where diseased plants grew with a solution of potassium permanganate (0.2 g per 1 liter of water) or a solution of "Fitosporin". Try not to get on healthy seedlings so as not to burn them.
- Treat the soil of healthy plants everywhere with a solution of Fitosporin. If the seedlings are very young, apply the solution drip, strictly under the root, preventing it from getting on the leaves of the seedlings. Mature seedlings can be sprayed completely with the fungicide solution.
- Sprinkle ash over the soil in the seedling container. River sand can be used instead of ash, but ash will give the best effect, especially when mixed with charcoal.
- Eliminate the factors contributing to the development of fungi: normalize watering and temperature conditions, dive seedlings if necessary.
For the treatment of diseased plants and the prevention of black leg disease of healthy seedlings, you can use a solution of copper sulfate (0.2 g per 1 liter), Bordeaux liquid (11%).
Of the folk remedies for combating black leg in seedlings of vegetables and flowers, soda has proven itself well. A teaspoon of this product must be dissolved in a glass of water and treated with a spray bottle or simply watered. Soda treatment is carried out weekly.
A blackening leg in seedlings of vegetables and flowers is a sign that the plant is sick. Such symptoms are caused by a number of ailments of a fungal nature. Diseased plants will have to be removed, but healthy seedlings can still be protected from infection. If urgent action is taken, most of the crop can be saved.
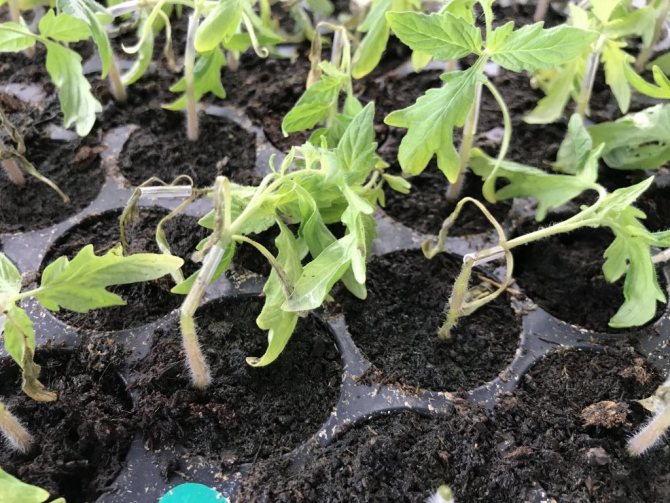
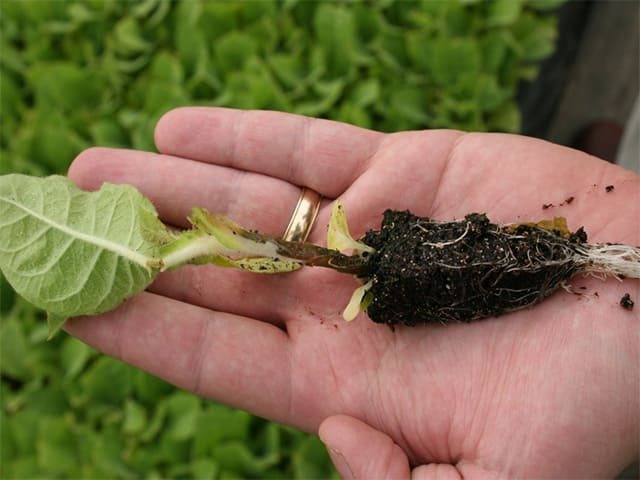
The fact that the black leg has befallen the seedlings is not difficult to notice. Initially, the base of the stem darkens slightly, but every day the color is closer to black. Therefore, it is very important to pay attention to the development of the disease in time. If you closely monitor your seedlings, you can save many sprouts.
First, you need to immediately come to terms with the fact that infected seedlings can no longer be saved. The fungus will develop until it completely destroys the seedling. As a rule, such a plant does not have long to live. After about a week, the stem will weaken so much that the sprout will not stand up and will fall off.
Secondly, you need to carefully examine each seedling. Any blackening, even if in doubt, is a sign that it is most correct to plant such a sprout separately from others. The same seedlings, in whose health you are sure, urgently dive and transplant to a new place.
The fungus is so small that it cannot be seen with the naked eye at first. When it becomes noticeable, then, in most cases, it is too late to do something. Therefore, the transplanted sprouts still require prompt processing. To do this, you can see a variety of drugs in garden stores.
If the transplanted seedlings grew already without a cover at the time when rot started up nearby, then for the first time they need to be provided with warmth and no drafts, otherwise they will take root badly. In a few days, when it becomes clear which seedlings survived, you can return to the previous conditions.
It is very important to organize the correct watering for the surviving plants. It will consist in the fact that drugs should be added to the water to combat harmful microorganisms. Diluted mixtures with "Maxim", "Fitosporin" or "Baktofit" are well suited. It is not bad to water the soil with special preparations "Alirin-B" and "Gamair" in compliance with the proportion: 4 tablets for every 10 liters of water. If everything is done correctly and in a timely manner, then part of the seedlings can be saved.
What it is?


Root collar rot or black leg rot is a common fungal disease that usually affects seedlings or young plants.
The causative agent of the disease is the pathogenic fungus Olpidium or Pythium, which lives in the surface layers of the soil. Usually, it feeds on dead plant tissues, but with high soil moisture and high air temperatures, the fungus can spread to the roots and root collar of living plants.
After penetrating the root system, the mycelium begins to absorb nutrients that enter the plants, due to which it grows and affects an increasing part of the seedling.
Most agricultural crops are susceptible to the disease, but seedlings of tomatoes, cabbage and cucumbers, indoor and garden ornamental flowers are more often affected. Infection occurs only under favorable conditions, with increased soil acidity. The fungus develops only on weakened plants, but when the mycelium grows too much, the disease can spread to strong and healthy seedlings.
Diagnosis of infection
In most cases, it is possible to identify the disease only after the potatoes rise. Just by examining it, you can see the changes that have occurred. As for the leaves, they are:
- lose melatonin;
- turn yellow;
- curl;
- dry up.
Dangerous microorganisms infect the stems. They turn yellow and wither after a while. The bacteria then spread to the tubers. Gradually, everything turns into a soft, rotting and fetid-smelling mass. The appearance of diseased potato fruits becomes dark in color. A foul-smelling liquid flows from the cracks that appear, and a void forms inside. In hot weather and high humidity, the disease develops quite rapidly, everything can happen in 4-6 days.
Reasons for the appearance
Fungal spores can stay in the ground for a long time and be activated only when favorable conditions are achieved.
There are several reasons for the appearance of a black leg in seedlings:
- Increased acidity of the soil.
- Soil moisture is more than 85-90%.
- Too low or high temperatures, a sharp change in climate.
- Failure to comply with the seedling watering regime.
- Dense planting of seedlings.
- Wrong pick.
- The use of a low-quality substrate for growing seeds.
- Poor quality seed, selection of a weak variety of tomatoes.
- Insufficient illumination in the room.
- Constant drafts.
It is believed that blackleg, unlike other diseases, is easier to prevent than to cure. After infection of seedlings with root rot, it is almost impossible to save the plants, which is why the fight against it comes down to competent prevention.
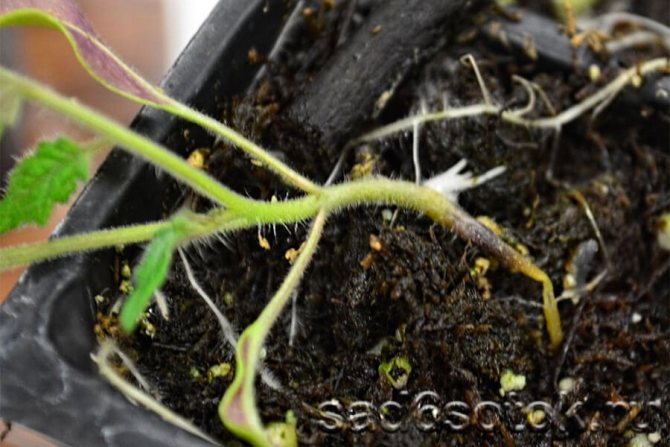
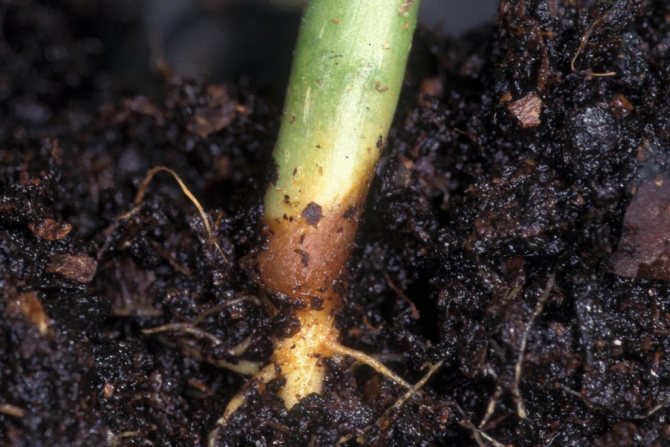
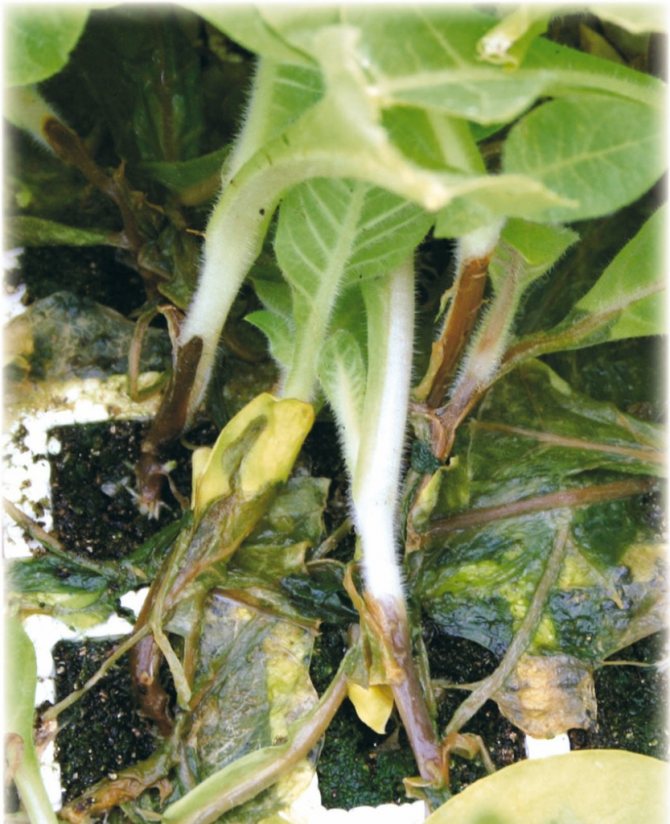
The first symptoms of infection appear even before the leaves form on the seedlings. First, a slight darkening appears at the bottom of the stem, and then a characteristic blackness develops throughout the lower part of the plant.
The seedlings stop growing, and the already formed leaves curl and dry out. Due to the fact that young seedlings are not yet resistant to diseases, the death of the plant occurs within just a few days.
The fungus absorbs all nutrients and water from the soil, causing the seedlings to fall to the ground, where tissue decomposition occurs. In the later stages of the disease, the stem and pre-root part looks like a thin black thread.
Read also: Pear - Just Maria: variety description, photos, reviews
Causes of the disease
There are quite a few reasons for the formation and active development of such a disease as black leg of seedlings, it may be the soil deliberately infected with black leg fungus; excessively thickened crops, when moisture stagnates for a long time at the base of the seedlings, which, in combination with above-zero temperatures, gives the prerequisites for the development of the disease;
excessive soil moisture, when moisture simply does not have time to evaporate and be used by plants; lack of fresh air - when the gardener, fearing a draft, does not ventilate the room at all; an excess amount of moisture in the soil, combined with an abundance of heat - these are ideal conditions for the rapid development of black leg seedlings;
If one or more of these conditions take place, then sometimes only seven days are enough from the beginning of the development of the black leg to the complete blackening of the stems of the seedlings and the death of the seedlings. If you take such seedlings in your hands, you can feel with your fingers how the stems are very softened or, conversely, are characterized by increased fragility.
Mushrooms belonging to the genera Olpidium, Pythium, or Rhizoctonia cause the formation of a black leg. All these harmful fungi live in the topsoil and consume dead plant tissue. At high humidity, fungi cease to feed on dead tissues and begin to feed on living tissues, or they can feed on both tissues at the same time. So, it is the root collar of the seedlings that is at risk during this period.


Thickened planting promotes the development of black leg on seedlings
Pathogens are fungi that live in the ground up to 2 centimeters deep. The basis of their nutrition is the remains of plant tissues. Under favorable conditions for reproduction, they begin to feed on living tissues of plants. Some of the causes of the disease are:
- Infected seeds used for planting.
- Contaminated soil.
- Increased acidity of the substrate.
- Planting too dense.
- Improper watering, lack of drainage system, which leads to high humidity.
- The closed room is not ventilated, insufficiently lit.
- A sharp change in temperature.
- Excess nitrogen fertilizers.
It is interesting that the fungus can be in the soil for a long time and not affect the seedlings in any way. When these favorable factors appear for him, he begins to amaze them.
| Fitosporin Biological product based on the action of natural bacteria. They have a depressing effect on the fungus and allow you to get rid of it. Prepare the solution 2 hours before use. Dilute at the rate of 2 g per 1 liter of water. Water the seedlings at the root |
| Maxim A fungicide with a broad spectrum of action. Prepared at the rate of 2 g of the product per 1 liter of water and mix thoroughly. You need to treat by watering at the root. The frequency of application is indicated on the packaging. |
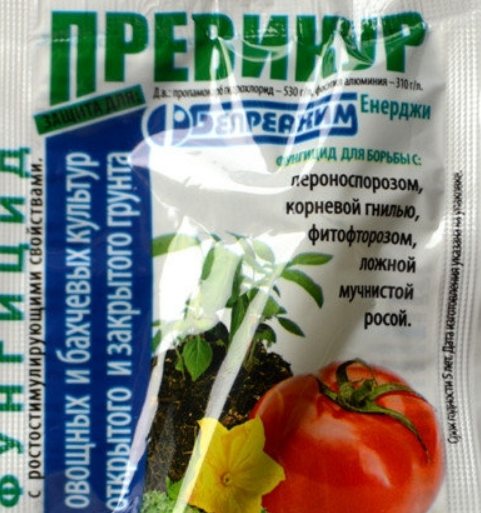
| Previkur A product with growth stimulating properties and preventing overgrowth of seedlings. It also inhibits the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Prepare a solution at the rate of 10 ml per 6 liters of water. Watering at the root and cultivating the ground part of plants and soil, plus this control measure in a universal spectrum of impact |
| Baktofit Biological fungicide with a wide range of applications, good for many pathogens. Differs in safety of use. It should be cooked at the rate of 3 ml per liter of water. Apply by watering under the root part |
| Planriz A biological product that effectively affects almost all fungal diseases. It is used both for soil treatment and for preventive treatments. Cooking should be at the rate of 25 ml per 5 liters of water. Spray the entire surface of the soil and water the tomatoes at the root |
Control methods
Treatment of the black leg is effective only in the early stages of the development of the disease. The fungus progresses rapidly on seedlings, so in most cases it is simply impossible to save the seedlings. It is noted that recovered plants subsequently lag behind in development, bear fruit worse and gain green mass.
When root rot is detected, the following measures can help:
- It is necessary to completely stop watering, and also remove all affected and weakened seedlings. If planting is too frequent, it should be thinned.
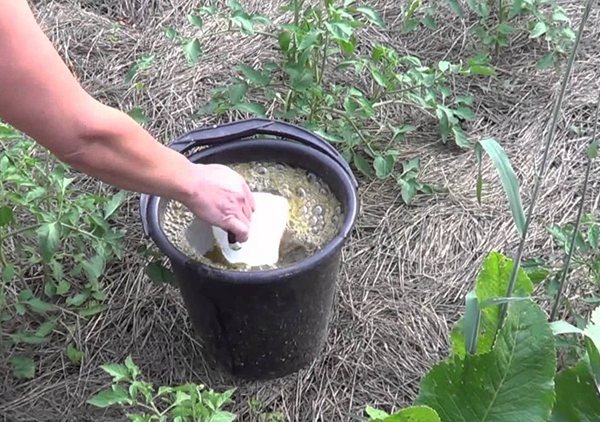
- It is imperative to disinfect the soil. For this purpose, you can use a 1% solution of potassium permanganate, Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate or formalin. Before processing, the soil must be loosened to provide access to the middle and deep layers of the substrate.
- If the soil is acidic, it is recommended to add wood ash, crushed coal (at the rate of 0.5 kg of the product per 1 m 2) or milk of lime (0.2-0.4 kg per 1 m 2).
- The stems and surface parts of the roots are treated with a biological fungicide. For this purpose, Fitosporin-M is used (5 g of the drug per 10 l of water), Fitolavin (20 ml per 10 l of water) or Trichodermin (100-150 ml per 4 l of warm water), the treatment should be carried out at intervals of 10-12 days ...
If blackleg has developed on one or more plants, the tomatoes should be transplanted into separate containers to minimize the risk of spreading the disease. For picking, you can use both peat pots and plastic containers. The main condition is to introduce fresh soil, previously treated with a disinfectant solution.
Traditional methods
You can fight black leg seedlings using folk methods. They have low efficiency, since systemic fungicides are needed to destroy mycelium and spores.Some methods can be applied as additional measures.
For example, the soil and green parts of the seedlings are sprayed with vodka diluted in water in a ratio of 1:10. However, in case of infection, an infusion of onion husks or marigolds is often used for feeding and watering with regularity every 3-4 days.
Fight
The most important rule for all gardeners who want to protect their plants is to pre-prepare the soil in which the seeds will be planted.
However, this is true mainly for a self-prepared mixture. Experienced gardeners are accustomed to steaming the soil in order to surely destroy the harmful larvae and pathogens that are abundant in the upper layers of the soil. For this, a colander is usually taken, the soil mixture is placed in it and dipped in boiling water for about 15 minutes. This is enough to completely sterilize the future soil.
After this procedure, the mixture should be given a little "rest". This is done so that the soil regains its useful properties. Seeds can be planted about 2 weeks after steaming.
It is worth paying attention to the acidity of the soil. For example, chernozems are not afraid of high acidity, since, due to the content in them of a large amount of humus, they easily compensate for this deficiency. But loamy soil needs to be extinguished. Lime is best suited for this.
Purchased soil is most often initially prepared in order to immediately sow seeds of garden crops into it. The acidity of the purchased soil mixtures is balanced, so no additives are required.
High soil acidity is another significant factor that contributes to the rapid development of fungal diseases and damage to growing greenery.
By the way, today on sale you can find many seeds of garden crops and flowers, which are protected at the genetic level from the influence of blackleg and some other diseases. You can clarify the details with a knowledgeable seller or prepare yourself and search for information on the worldwide network about the properties of the desired seeds (the manufacturer indicates this information on the package).
Peat tablets, which are very popular among gardeners, are perfect for planting horticultural crops and flowers. In fact, it is almost impossible to overmoisten them, since peat perfectly absorbs moisture, and the excess is passed through the tablet. And the methods of production of the peat base themselves imply treatment with antimicrobial drugs, which makes them practically sterile.
Yes, after the seedlings in peat tablets grow up, it is very easy to dive, since the sprout is transferred to a new place along with the base in which it grew.
If you use the soil again, but already purchased, prepared for planting seedlings, then it is also well processed and is practically guaranteed safe in terms of the development of decay. However, it is often noted that it can still contain eggs of small pests that will cause inconvenience to small sprouts.
Read more: Pinot Noir grapes and its varieties: description of varieties Gris, Blanc, Fran, Meunier, photo
Perhaps the most important mistake many amateurs make is planting seeds before any reasonable time. In the struggle for a fast harvest, crops are often sown at the wrong time. Plants stretch out quickly, but due to a lack of light (which is a frequent occurrence for central Russia, not to mention the northern regions), they turn out to be weak and stunted. In such a situation, they become easy prey and the most favorable environment for lightning-fast fungal infection.
Due to the high prevalence of black leg, there are a sufficient number of different means that gardeners use to prevent the development of putrefactive processes in their seedlings:
- Trichodermin is one of the most famous and effective drugs. It effectively fights not only the fungus that causes the black knife disease, but also more than 60 types of other microorganisms that can harm the flora. It must be introduced into the soil strictly according to the manufacturer's instructions. If a large number of seeds are planted in one container, then it must be used almost without fail.
- Experienced gardeners often use seed soaking prior to planting in their practice. The easiest way is to use a weak solution of potassium permanganate. The seeds are placed in cheesecloth and then in a solution. On sale you can find special preparations that are also suitable for disinfecting seeds of garden crops and flowers. Among the well-known and available: "Maxim", "Fitosporin", "Vitaros".
- For tomatoes and peppers, you can use "Epin" (1-2 drops are diluted in 100 ml of water, and the seeds are placed for at least 12 hours). Remember to rinse the seeds thoroughly with running water after soaking. By the way, it will not be superfluous to treat the seedlings with "Fitosporin" right before planting them in an open area.
- "Immunocytofit" and "Epin-Extra" are immunomodulating drugs. You can use them to grow a strong and disease-resistant crop.
- Try not to plant the seedlings tightly together. To do this, when the first shoots appear, try to dive them right away, without regretting. The closer the shoots crawl out to each other, the more moisture it will collect at the soil surface. The fungus will be able to multiply unhindered and, if inactive, will destroy first the weakest seedlings, and then the entire crop.
- If the black leg nevertheless befell your seedlings, then the whole sprouts need to be treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid. It is possible to dissect slightly damaged samples in the same way. The fungus during processing can die on them, and the culture will survive.
- From time to time, you can treat the plants with a weak solution of potassium permanganate until it becomes noticeable that they have been ill.
- In addition, you need to follow the basic rules of caring for plants. For experienced gardeners, they often already work at the instinct level. With a little experience, you can inadvertently create favorable conditions for the development of a black leg.
- So, the main reason for the excessive reproduction of the fungus is excessive moisture. It is often advised to water the seedlings rarely, but abundantly, than vice versa. With this method, a clod of soil quickly passes water through itself into the deep layers, and the upper part remains moderately moist for a long time.
- It is important to subtly feel the line between ventilation and draft. It is worth removing the cover from the greenhouse soon enough after planting the seeds. These procedures are quick at first, but each time they must get longer. It is important to remember that an open draft is very harmful for weak seedlings. So you can destroy all the seedlings.
- You can even ventilate the seedlings with the vents open in the room. On the contrary, such procedures will only temper the seedlings. Just do not leave the dishes in a ventilated place.
- When ventilating a greenhouse, you also need to know the rule that you cannot remove the cover immediately after watering. A sharp jump in humidity and a drop in temperature are extremely unfavorable for green spaces.
Read more: Hedgehogs for weeding potatoes do-it-yourself drawings
And take the practice of regularly loosening the soil. Firstly, it is very useful in the fight against blackleg. Since this fungus feeds on the surface dead tissues of plants, frequent loosening will not create too much "food" for the development of pathogens.
Another plus from this procedure is the delivery of air to the roots.As you know, the more breathable the soil, the better the plants grow in it. Thus, you will kill two birds with one stone. And after planting seedlings in an open area, you can go through your seedlings about once a week and loosen the ground around them well.
By the way, in order for the earth to pass air better, you can sprinkle it with sand on top a little after each loosening. Then, watering the sprouts, you can be sure that the soil will not turn into a dry and hard lump, which completely prevents air from reaching the roots.
The biological products used show excellent effectiveness in the fight against black leg. So, for example, we can recommend that you add Trichodermin to the soil, which perfectly suppresses various pathogens, including the black leg.
Fitosporin
It is recommended to process seeds before sowing in Fitosporin, Planriz, Baktofit or Fitolavin 300. Spraying with such agrochemicals shows effectiveness not only as a prevention of this disease, but also at the first signs of activation of this fungal pathogen.
As a prophylaxis against the appearance of a black leg, various charcoal-based products can be used. You can purchase these products from gardening stores, or you can make your own from wood ash.
You can fight the black leg with Bordeaux liquid. Spraying and processing the land with Bordeaux liquid should be carried out in full accordance with the instructions for a particular agrochemical. This solution is not absorbed by the plants, so it does not degrade the quality of the grown crop.
However, in the event that the application rates of this chemical agent are not observed, this will invariably lead to problems with the growth of horticultural crops, up to the complete destruction of plants and loss of yield.
Another great way to combat this disease is potassium permanganate. If, when cultivating the land, it is necessary to make the most concentrated solution, then when spraying the plant, try to use a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and immediately after treatment, water the plants from the rain.
The preventive measures taken will ensure you get rid of this disease. It is recommended in spring or autumn to shed the earth with a solution of Carbation, which is prepared at the rate of ten liters of solution for processing one square meter of beds. The drug must be diluted in full accordance with the instructions for this tool.
Blackleg
It is also possible to introduce Tiazon, which is mixed with sand in a ratio of one to three, and 100 grams of the resulting sand mixture is introduced into the soil per square meter. As mentioned above, the fungus that causes the black leg loves moisture, so it is not recommended to water the seedlings and not plant it excessively thick.
Do not create a greenhouse effect, and the seedlings must be watered with a solution of potassium permanganate immediately after their appearance. And remember that spores of the fungus that cause this disease can survive for many years. That is why if you know that the ground is infected with a black leg, it is forbidden to use such soil for seedlings.


In thickened plantings, diseases spread very quickly.
| Dolomite flour and wood ash Mix the ingredients in equal proportions. Use fine ash. Sprinkle lightly over the surface. Distribute it evenly |
| Infusion of marigolds Pour a glass of flowers with a liter of hot water. Insist for a day. Pour to the root. Also spray the surface of the soil |
| Eggshell Grind dry shells. It should become powder. Sprinkle on soil. Treat all the soil under the seedlings, pay special attention to places near the stems |
| Baking soda Prepare a solution at the rate of a teaspoon per glass of water. Stir until completely dissolved. Spray the soil and water the plants under the root. Carry out work once a week |
| Potassium permanganate Prepare a solution at the rate of 0.2 g per liter of water. Stir the liquid well. Water with a solution of potassium permanganate at the root. Do not disturb concentration, so as not to burn the root system |
| Copper sulfate Dissolve 5 g of powder in a glass of hot water. Add liquid so that the volume is 1 liter. Water the plants at the root. Also treat the soil surface with a sprayer |
Preventive measures


Competent prevention allows you to minimize the risk of infection of tomato seedlings with root rot.
It is always a set of activities, including the following methods:
- To prevent the formation of moisture at the root collar of plants, it is recommended to sprinkle the soil with fresh river sand.
- Control the acidity of the substrate, do not use the soil with high acidity or alkalinity. To do this, you can purchase specialized soil for tomatoes.
- Observe the mode and volume of watering. After the procedure, the surface of the earth must completely dry out; moisture stagnation must not be allowed. The recommended water temperature is 22-25 degrees.
- When using plastic wrap and other types of seedling shelters, it is imperative to ventilate the room.
- It is best to use peat pots or tablets to provide the oxygen needed for root development and health. When using plastic containers, drainage should be done.
- Carefully select seed, purchase seeds only from certified stores and choose disease-resistant varieties.
- Seeds and soil should be treated before planting. It is not recommended to apply humus or manure, as they may contain fungal spores.
The transience of the development of the disease is aggravated by the fact that young plants do not yet have strong immunity and resistance to diseases. To prevent infection, it is necessary not only to observe prevention, but also to make growth enhancers, as well as all the necessary fertilizing for the full development of tomatoes.
Root rot or black leg in tomato seedlings is considered one of the most serious diseases of this vegetable crop. In the case of infection of plants with this fungus, it is rarely possible to save the seedlings, and the surviving individuals grow poorly in the future and lag behind in yield. Preventive measures can reduce the risk of infection to a minimum, but if the disease cannot be avoided, it is extremely important to take the necessary measures in time.
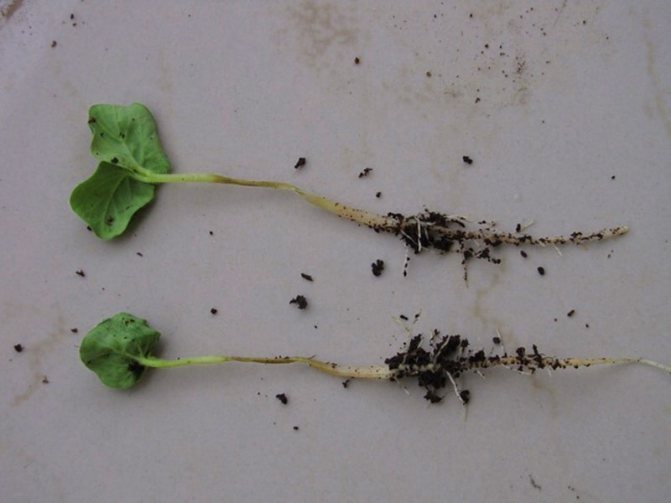
Causes of defeat and external signs of "black leg"
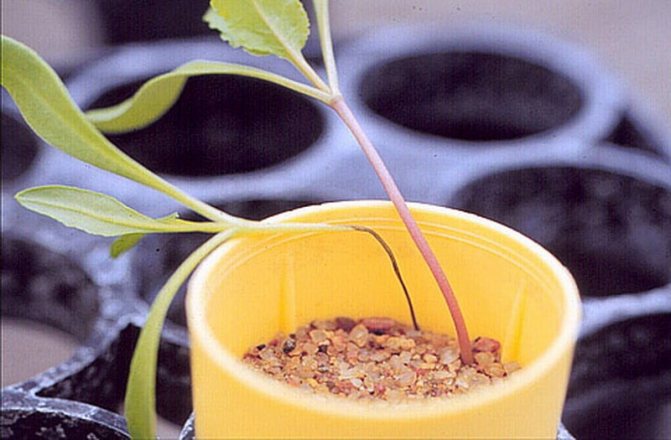
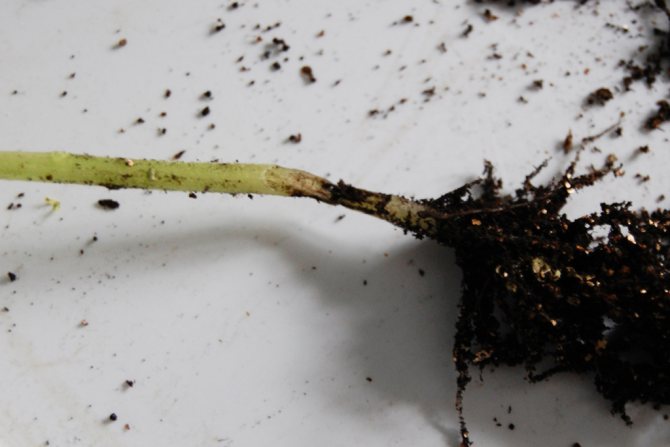
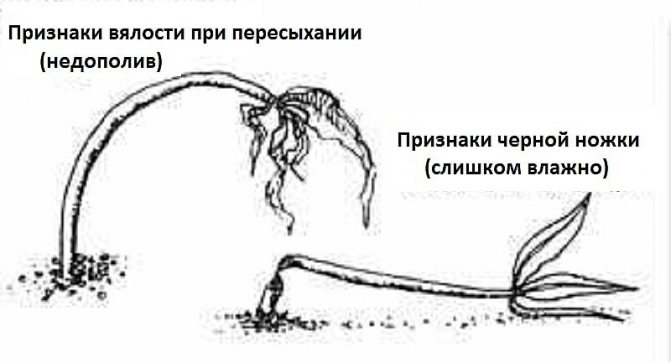
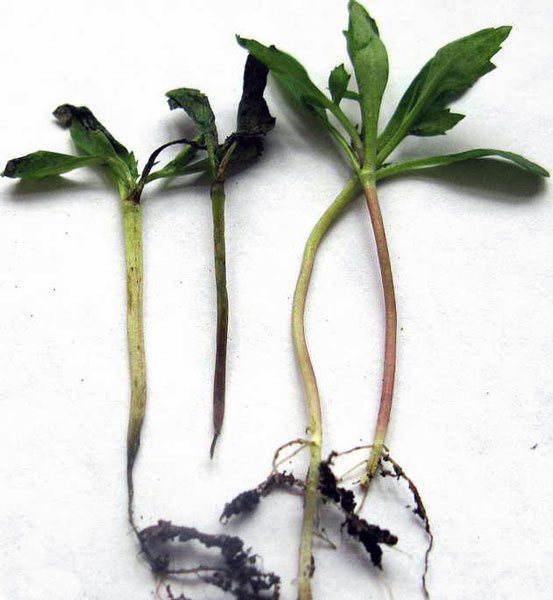
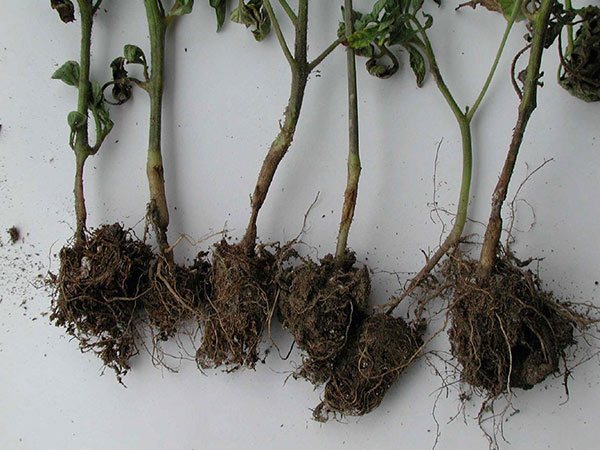
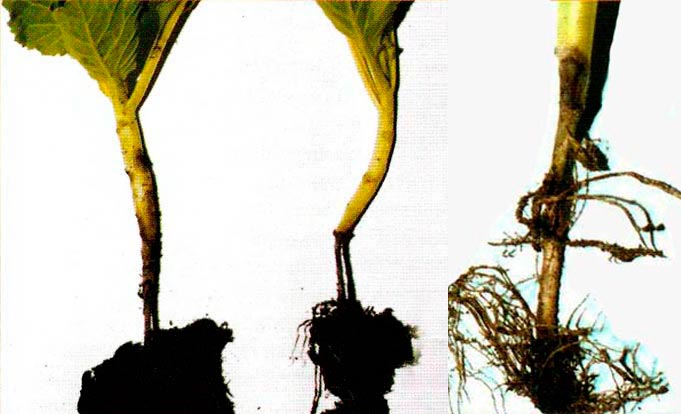
Disease "black leg" affects a young plant - a seedling, or rather a seedling. Outwardly, it is characterized by darkening and narrowing of the stem in its lower part. Due to the cessation of sap flow, the affected sprouts of seedlings wither and "lie down", then destruction or decay of the horse system is observed.
There are only three reasons for the defeat of plants by the "black leg" - fungal, or bacterial, or viral infection.
Fungal infection
Everyone knows that the soil is inhabited by many lower fungi - saprophytes, feeding on organic residues. The following types of Olpidium (Olpidium), Pythium (Pythium), or Rhizoctonia (Rhizoctonia) and etc.
Indoors (greenhouses, hotbeds, potted plants), mushrooms have the most favorable microclimate, in which they multiply many times faster. Accordingly, for large colonies of fungi, more nutrition is needed, and microorganisms become insufficient. And therefore, the roots and shoots of young plants - vegetable or flower seedlings - go into nutrition.
Freshly cut seedlings suffer most of all, since they have damaged roots and microcracks on the stems. It is these places that become tidbits for settling a fungal infection.
a) Molds
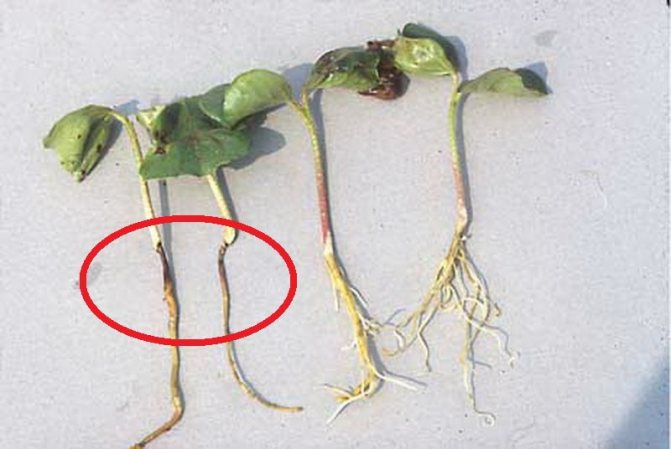
When affected by mold fungi, the disease develops slowly. Lesions are small. In the initial stages, the affected plant stem can be dark green, dark gray, later black.But most of all, the roots are damaged, they can be completely destroyed by fungi. Lack of roots is a characteristic sign of fungal mold infection. In this case, the seedlings can be saved (see control measures below).


"Blackleg" in seedlings caused by molds
b) Aggressive fungi of the genus Fusarium
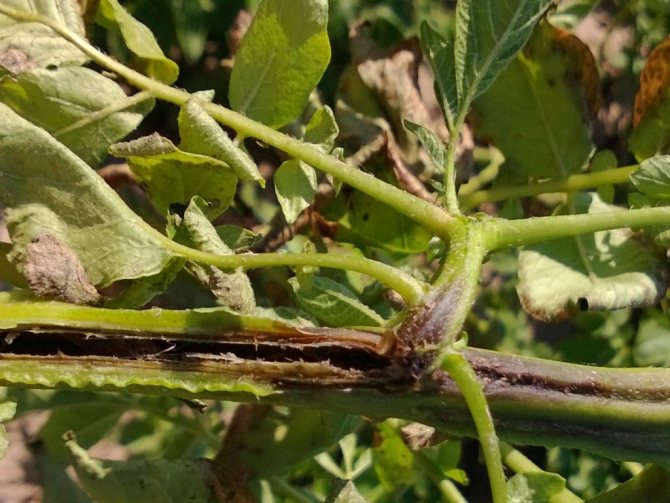
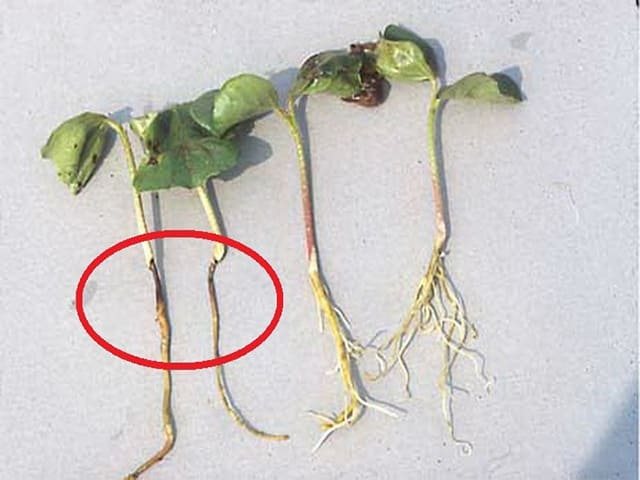
There are also more aggressive fungi, for example, the Fusarium genus. They are considered the classic cause of blackleg development. Penetrating through the wound into the stem of the plant, Fusarium releases a strong dose of toxin, which leads to tissue necrosis. The defeat process is fast - from several hours to two days. Outwardly, the lesions are obvious - the seedlings fall and the leaves wither. The constriction in the area of the root collar has a denser structure; one or more dark rings can be observed on the stem - this is the mycelium. The roots are not damaged, they remain intact.


"Black leg" in seedlings caused by fungal infection of the Fizarium species
This mushroom, in fact, is a predator - it does not settle in the plant, lives off of it, feeds on it, and after destroying the seedling, it immediately leaves it. In this case, it is not possible to save the seedlings. Appropriate measures should be taken in advance (see protection measures below) - seed dressing, use of "clean" soil, etc.
c) Mushrooms of the genus Alternarium
More often conifers are affected. Symptoms and protective measures are similar to the attack of seedlings with Fusarium fungi.
Bacterial lesion
a) Erwinia bacteria
These bacteria cause bacterial rot. Like molds, they feed on organic matter in the topsoil. Unlike fungi, the disease develops slowly, the disease is diagnosed already in adulthood. The first signs are that the leaves become more rigid and acquire a yellowish tint. There are varieties of this bacterium - E. carotovora (causes rot of tubers and "black leg") and E. Atroseptica (causes soft rot with a characteristic foul smell). Soft rot affects the lower part of the stem, at the base, the stem changes in color - it becomes dark green, dark brown, or black. The inner tissues of the stem soften, turning into mucus. It is mucus that indicates the bacterial nature of the disease.


Blackleg caused by bacterial contamination
b) "Fermentative bacteria"
Seedling lodging and root rot can cause fermentative bacteria. They live in unripe manure or in soils with a high peat content. In such soils, an increased temperature is observed, and the roots of the seedlings "burn". When the root withers and weakened, bacteria begin to attack the plant. This process is called "fire blight".
Viral lesion
Viral infection is extremely rare. Outwardly, the lesions look like dry ulcers on the root part of the plant stem. It is introduced along with the seed material. The plant cannot be saved, viral diseases cannot be cured. Plants are subject to complete elimination, along with the soil.


"Blackleg" caused by a viral infection of the plant
Causes of the appearance of a black leg in tomatoes
After examining the "falling" plants, you can see that the tomato stems are thinning near the ground, as if they were damaged by earwigs, which often settle in containers with seedlings.
A thin stem signals that a fungal disease called black leg has struck the tomato seedlings. This disease destroys vegetables that are grown by seedlings in greenhouses and greenhouses.


The disease is caused by several types of fungi living in the ground. Fungi spread at the root level, passing from one plant to another, which leads to the appearance of new foci of the disease.
The causative agents of the disease remain in the ground, on plant debris and on seed. The disease severely damages vegetable crops, spreading to seedlings of radish, cabbage, and swede. An ailment can be provoked by: dampness, low temperature, too dense plantings, poor lighting. It is very important that the seedlings have enough light. Foil can be placed behind the seedling boxes to improve lighting.
Read also: Raspberry Brilliant: description of the variety, photos, reviews, cultivation


Having found out the cause of the seedling disease, you need to take urgent measures to combat this disease. To begin with, you should change the watering rules: water abundantly, but infrequently, and it is better in the morning, so that the soil has time to dry out a little before the evening. From generous, but rare watering on the surface of the earth, excessive dampness will not be diluted. With such irrigation, by the evening, the upper layer of the earth will already dry out, and at night, when it is cool, the seedlings in places of contact with the ground will be dry. Thanks to this, the seedlings can be saved and the spread of the black leg can be avoided.
When growing tomato seedlings in a greenhouse or greenhouse, it is necessary to ventilate the structure more often to avoid excessive dampness.


If a black leg begins to appear in tomato seedlings, you can sprinkle sand around the stems of the tomatoes. Then, during irrigation, water will quickly go into the ground, and its surface will remain dry.
After drying the soil, the seedlings are watered with a solution of potassium permanganate or special preparations are used so that the black leg of tomato seedlings disappears faster. To prevent this ailment, Trichopolum tablets (1 piece per 1 liter of water), whey, Fundazol, herbal decoctions, copper preparations are used.


Often, gardeners themselves endure all diseases with the soil or with boxes in which vegetables were kept in winter, and in the spring, without disinfecting and steaming them, they decided to grow seedlings. This contributes to the appearance of a black leg in seedlings growing in these boxes.
Causes of occurrence
Subject to a good temperature regime and, most importantly, humidity, you can avoid plant diseases and grow good seedlings. But one has only to water the sprouts too abundantly and often, as this will immediately create the most favorable conditions for the fungus to begin to transfer to the stems of healthy plants.
Do not forget that at first the seedlings need to be covered with a lid in order to create ideal conditions for the seeds for early germination. But this is another reason for the appearance of the black leg. If you do not remove the cover to ventilate the seedlings, this contributes to the stagnation of too humid air, which can affect the uncontrolled spread of fungi and the destruction of healthy seedlings.
There is only one reason for the disease of seedlings of vegetables and flowers with a black leg - infection with a fungus. It is often found in the soil used to grow seedlings. Often the reason is the use of unhealthy seeds: if they are taken from a sick plant, then growing healthy seedlings from them will be problematic.
If you took the soil for seedlings from the garden, and besides, from the garden where representatives of the Solanaceae family used to grow, then the risk of infection of seedlings with a black leg will be quite high. Calcining or freezing the soil, treating it with fungicides or other disinfectants reduces the hazard, but does not completely eliminate it.
Seeds collected by you yourself or purchased from another gardener may also be sick. Treatment with "Fitosporin-M" and similar preparations, etching with a strong solution of potassium permanganate will help to rid them of the fungus. But even these measures do not give a complete guarantee that the seedlings will not get sick with a black leg.
Sometimes infection occurs from containers in which diseased seedlings have already been grown. The use of peat tablets or pots will help to avoid trouble.
The fungus will develop well, mercilessly mowing seedlings of tomatoes, peppers and other plants, if favorable conditions are created for it: high humidity and warmth.
The factors accompanying the emergence and spread of the black leg are:
- improper watering when the topsoil remains wet for a long time;
- lack of ventilation. Most often this happens immediately after sowing the seeds, when they need to create a greenhouse effect for their germination. Some gardeners neglect the advice 1-2 times a day to raise the glass and ventilate the "greenhouse";
- improper ventilation: with a sharp temperature drop, the risk that the seedlings will not be able to resist infection increases;
- too dense sowing of seeds: moisture evaporates poorly, it becomes warm under the "crown" of seedlings, as a result, the most favorable conditions for the fungus are created;
- if you did not dive the seedlings in time, then it is not at all more comfortable for it than with too dense sowing;
- increased acidity of the soil contributes to the development of the fungus;
- the occurrence of an ailment can provoke an excess of nitrogen fertilizers.
By eliminating the factors contributing to the development of the black leg, you will protect it from disease, even if it turns out that spores of a dangerous fungus live in the ground.
The causative agent of the black leg disease is bacteria and fungi that are in the soil, which for the time being do not manifest themselves until the factors that provoke their activity appear. This can be high soil moisture, lack of lighting, overly thickened plantings, poor ventilation, excessive fertilization, or sudden temperature changes.
Under such conditions, rapidly accumulating in the soil, the causative agents of the disease first cover small areas, and then the entire seedlings are affected by the black leg disease. How to deal with it when the first signs appear, you need to find out in advance in order to suspend and prevent the spread of the disease in time.
Read next: Caterpillars On Cabbage Folk Remedies (10 Useful Tips)
Better yet, take care of preventive measures that will help avoid such troubles.
How to deal with the disease
You can talk a lot about measures to combat the black leg, but you need to start with disinfecting the earth. Droot for seedlings is frozen and fried. The soil must be prepared in the fall, taken where tomatoes and other nightshade crops have not grown, and keep it outside all winter, freeze it, and in the spring this soil mixture must be calcined on the stove.


After calcining, the soil and seeds must be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate. For processing, the seeds are placed in a gauze bag and dipped for half an hour in a solution of potassium permanganate. Then, without removing from the bag, the seeds are washed, dipped in clean water, and dried.
Sowing seeds should be started only when the earth dries well and begins to crumble. Waterlogged soil will contribute to seedling disease.
The black leg damages not only tomato seedlings, but also other vegetable crops, for example, cabbage. The disease occurs unexpectedly and rapidly damages all seedlings. If the ailment has already arisen, then measures to combat it must be taken immediately, otherwise the root collar will rot.
In addition, the leaves curl up and turn yellow. Damaged plants appear weakened and are easily pulled out of the soil.
The disease progresses on acidic soils and massively destroys seedlings. To prevent disease, seedlings must be properly looked after. To do this, before planting seeds, colloidal sulfur (5 g / m²) and potassium permanganate (5 g per 10 l) are introduced into the soil.


Having found damaged plants, it is necessary to immediately remove them along with the soil, while capturing a certain number of healthy seedlings in the neighborhood, and the place of removal must be well disinfected. When transplanting seedlings into the garden, they carefully examine it, rejecting all diseased plants. It has been noticed that seedlings in peat-humus pots are much less likely to suffer from black leg. Therefore, it is better to grow them either in these pots, or in plastic cups, or in cassettes.In such a container, they almost never get sick and do not have to be treated.
Prophylaxis
The first step in disease prevention is preparing seeds and tubers for planting. Disinfection and hardening will help remove spores of fungi and pathogenic bacteria from them. For this, chemical, biological agents, natural humic acids are used.
For planting potatoes, only healthy tubers are selected, without spots and dents. They are pre-soaked or sprayed with fungicides or Fitosporin-M. Then germinate in the light for 14 days.
Reduces the risk of blacklegs by pre-preparing the soil for planting. For seedlings, a loose, water and air-permeable soil is prepared. Additives of vermiculite, coconut fiber, calcined river sand do not make the substrate heavier.
Often the soil for seedlings from your own plot has an acidic or slightly acidic reaction, and acidic soil is a favorable environment for the reproduction of fungal spores. Reduces the acidity of ash, lime, dolomite flour.
It is advisable to steam the soil before planting. This is especially important if there have been outbreaks of the disease in previous seasons. After processing, the cooled soil is spilled with a solution of any biological product, for example, Baikal-M, and left for a week so that the soil "breathes" and useful living microorganisms settle in it.
Not all gardeners pay attention to the containers in which the seedlings are grown. The walls and bottom of reusable drawers, pots or containers must be thoroughly brushed to remove dirt residues, washed with soapy water and rinsed well.
Dense crops should be avoided. If you need to grow a lot of seedlings, but there are few containers, then you will have to dive early or thin out, removing weak shoots.
With early sowing - in January-February, the seedlings must be illuminated. Boxes with tender shoots are not placed on cold windowsills and drafts.
Water the plants sparingly, as the topsoil dries up. Water for irrigation is used slightly warm so as not to overcool the roots.
The greenhouse or film shelters in which the grown seedlings are planted are regularly ventilated. They monitor the moisture content of the soil - they loosen it and do not fill it.
Fighting with a black leg is very difficult. After all, the disease can develop rapidly and completely destroy plants in 1-2 days. Therefore, proper seedling care is the main way to prevent infection.
You will learn more about black leg disease from the video.
A plant disease called blackleg or soft rot is most common on tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, cabbage, cucumbers, lettuce, radishes, and other vegetables. This disease also affects the stems of ornamental plants and flowers (for example, petunias, asters). Do not shun, pathogenic and tubers, affecting, for example, potatoes.
This infection manifests itself as darkening and subsequent rotting of plant tissues, and can also cause yellowing and curling of leaves.
Reasons for the formation of a "black leg"
Top fertile soil layer infected with pathogenic infections
Too thickened crops
Lack of fresh air, with excess heat and humidity
Sudden changes in air temperature
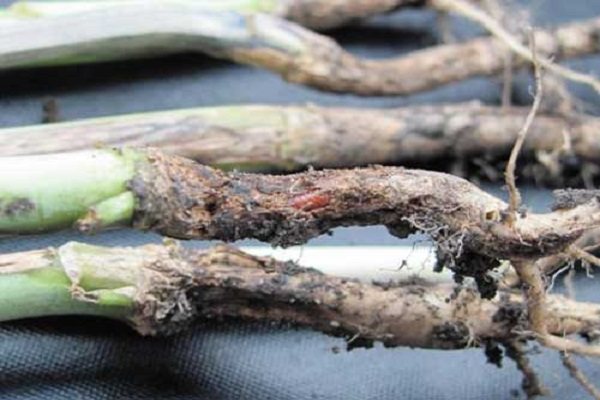


In fact, there are two reasons for the appearance of the "black leg", since in this case two pathogens with similar symptoms act at once:
The symptoms of exposure to both fungi and bacteria are very similar, which makes it difficult to establish the correct diagnosis and, accordingly, further affects the effectiveness of plant treatment. Therefore, as a rule, a misdiagnosis leads to erroneous actions, as a result of which crops can die.
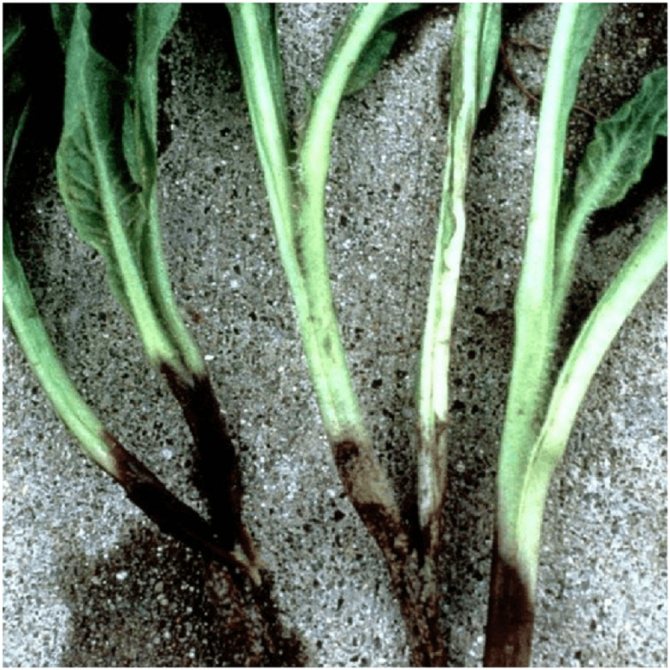


Fungal type of disease
The surface layer of the soil, as a rule, contains a huge number of various pathogenic fungi (saprophytes
), which mainly feed on plant residues, but in case of their lack, they do not disdain living organic matter.
Representatives of saprophytes include such varieties of mushrooms as: Phytium, Olpidium, Phoma, Rhizoctonia, Aphanomyces
and others. They multiply en masse and can be most abundantly observed in the soils of greenhouses, greenhouses and greenhouses, where they attack the root system of young shoots and seedlings.
Representatives of these saprophytes primarily affect plants that have slight damage to the root system. The course of the infection, in this case, has a sluggish appearance, and the lesion itself is small in size, since first of all small wounds on small roots are infected. In this case, the stems of the affected plants may not acquire a rich black tint, but have a gray, whitish or dark greenish color.
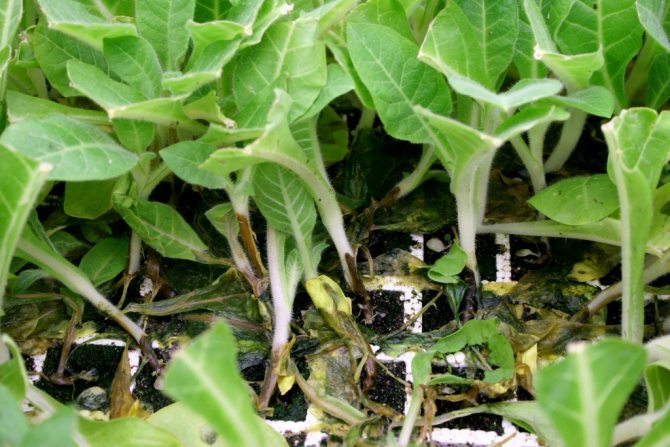


Especially often, plants that have passed the pick of seedlings are exposed to this disease, as a result of which small wounds can form on their root processes. This situation is used by harmful fungi, attacking areas of the root system damaged during transplantation, and then gradually more and more, expanding the zone and focus of the lesion.
You can often observe how when extracting infected shoots from the soil, they turn out to be practically rootless. For this property to completely destroy the root, this disease is popularly called "root-eater
».
As a rule, small and not yet developed seedlings fall into a special risk zone of infection, since adult plants with a strong stem and hard cuttings cannot be overcome by these mushrooms.
To avoid infection with saprophytes, the picking of seedlings should be carried out in separate pots with fresh soil not infected with infection. This method allows you to almost completely level the problem.


As for the classic "black leg", it is usually carried by aggressive and dangerous fungal pathogens from the genus Fusarium (Fusarium
). Representatives of these fungi can infect both animals and humans, causing diseases such as
mycosis, mycotoxicosis, dermatitis
and other dangerous diseases. Alas, this variety of Fusariums can also exist in the form of saprophytes, affecting living plants, and this type of fungi does not penetrate into the root system, but strives to break through as high as possible, that is, into the juicy tissues of the stems, getting into the crops through the hypocotal knee.
When plants are damaged, Fusarium releases a powerful dose of a special toxin, as a result of which the stem twists and darkens, acquiring a black tint, due to which the infection is called "black leg". At the same time, the infection process occurs quite quickly, within only a few days, and the infection itself spreads in all directions at once. Fusarium, for the swiftness of its infection is often called "haymaker
».
Unfortunately, this infection can also be found in the seed coat. In this case, the harmful spores of Fusarium affect almost all seedlings. Therefore, in order to avoid mass infection of plants, it is recommended to treat prepared seeds with fungicides and warm them at a high temperature before planting. It is also advisable to pre-disinfect the soil.
The most susceptible to infection are young, and only emerging seedlings (with one or two leaves), which die very quickly. If you pull the infected sprout by the infected stem, it does not immediately yield, since the root system of such a plant is usually intact, and the immediate focus of infection or the mycelium of Fusarium can be seen by the dark ring that fills the internal tissues of the culture.


It is noteworthy that there is a variety of Fusarium, which is capable of forming symbiosis with plants, forming mycorrhiza or fungus root. A symbiotic association of fungal mycelium with the root system of some cereals can often be observed.This fact brings tangible benefits, contributing to the growth of the vitality of cereals (for example, wheat and rye). However, this symbiosis can be detrimental to flowering plants such as pelargonium.
Another feature of Fusarium is that this harmful fungus is capable of infecting sufficiently mature crops. At the same time, the process of infection in mature plants occurs secretly and the symptoms of infection are quite difficult to determine, since in this case the stems of the shoots die off gradually, one after the other. As a rule, the flowering process in plants slows down, and the culture itself looks underdeveloped and oppressed. On a cut of infected stems, fungal hyphae can be found, which look like dark dots.
Fusarium control methods
Among the biological methods of dealing with the "black leg", the drug "Trichodermin" has gained particular popularity, which can be used at all stages of the development of the disease. Moreover, this biological product is both an effective means of preventing many root infections and contributes to the elimination of directly foci of infection. Moreover, when introduced into the soil, it suppresses about 60 types of soil infections, which, among other things, cause root rot, while infecting the fertile layer of the earth.


Bacterial disease
Plants infected with bacterial rot have similar symptoms of the "black leg" manifestation. This type of bacteria is called Erwinia (Erwinia
) and they usually live in the upper layers of fertile soil, since it is there that there is enough oxygen and decomposed plant organic matter, which the parasites feed on.
Bacteria, unlike the Fusarium fungus, in order to cause serious damage to plants, must have a large colony, therefore the infection process in this case is much slower. The disease, as a rule, manifests itself already at a fairly mature stage of plant growth and development.
The most typical representatives of these infections are:
· Bacteria (subspecies E. c. Subsp. Carotovora). They look like black ink, which form the so-called "black leg" on the plant
Bacteria (subspecies E. c. Subsp. Atroseptica). They look like soft rot with a disgusting odor.


As a rule, bacterial rot most often affects the lower part of the stem, but can develop both on the leaves and on the buds of plants. In this case, the infection is transmitted from one culture to another, especially in places with thickened plantings, where there is no normal air circulation, there is a lack of sunlight and there is high humidity.
First of all, representatives of bulbous cultures are infected with a bacterial infection. At the same time, the juicy and dense stem at the base softens and the plant breaks. If an infected bulb is pulled upward, it easily breaks off and a liquid similar to mucus flows out of the lower part of the stem (at the very base). In this case, the lesion may have a brown, dark greenish or almost black tint.
It should be remembered that the appearance of mucus, as a rule, is the first symptom of a bacterial, not fungal infection of plants (!).


Methods for dealing with bacterial rot
To combat bacterial infection, it is recommended to treat foci of infection with a solution of potassium permanganate (0.2 grams per 1 liter of water), a solution of copper sulphate (0.2 grams per 1 liter of water), a one-percent "Bordeaux" mixture.
It is advisable to sprinkle the surface of the soil with river sand, which is pre-mixed with dolomite flour and ash. At the same time, the task of sand is to absorb excess moisture, ash will help to reduce the acidity of the soil, and dolomite flour will strengthen the vitality and immunity of weakened seedlings.
For the prevention of "black leg", you can also use the drug "Fitosporin
»(Based on 100 milliliters of the drug per 10 liters of water), pre-soaking the seeds in the prepared solution.
As for planting seedlings, it is recommended to pour 5 milligrams of the finished solution into each prepared hole immediately before planting the plants in the ground.


Preventive measures to combat the "black leg"
First of all, you should take care of preventive measures, which should include:
· Treatment of seed material with fungicides ("Maxim", "Fitosporin-M", "Vitaros" and similar preparations)
Disinfection of the soil prepared for seedling with a solution of potassium permanganate (3 grams per 10 liters of water)
Elimination of excessive acidity by introducing wood ash into the soil
Targeted thinning of thickened areas
Availability of an effective drainage system
Timely airing and loosening of the soil
Compliance with the application of fertilizers (especially nitrogen)
Replacement of the top contaminated soil in greenhouses and greenhouses, which must be done once every two or three years


Since the infection primarily affects weakened and underdeveloped seedlings, you should follow the rules of crop rotation and do not sow crops too early, thus disrupting the natural and natural biorhythm of plants.
It is also important to remove all plants infected with the blackleg from the site at the first signs of infection.
Folk methods of struggle
A strong infusion of onion husks (20 grams per 1 liter of water) is used to combat the "black leg". This method is especially effective at the initial stage of the development of the disease. Instead of onions, you can also insist marigolds (in the same proportion).
Helps to resist the disease and the usual shell of chicken eggs, which is pre-dried and crushed into powder, and then sprinkled with infected plants.


Seeds intended for sowing (purchased from hands or collected independently) should be treated with a solution of potassium permanganate for half an hour.
"Black leg" is a concept familiar to almost everyone who is engaged in agriculture. They designate in a simple way a group of diseases that have some similar symptoms. In fact, these are different diseases - either fungal, or bacterial, sometimes viral, caused by a variety of pathogens.
Plants are most vulnerable in the initial period of their vegetative development. Therefore, it is the seedlings of tomatoes, peppers, flower crops, etc. that need special attention in order to timely prevent the "black leg". It is better to insure against such a misfortune in advance - it is better to prevent than to fight.
I will tell you how to correctly diagnose the disease and ensure a competent selection of methods and means - either early preventive protection, or the fight against an illness that has already hit the seedlings.
Folk ways of dealing with a black leg
You can fight this disease without resorting to chemistry. Here are some simple tips for growing healthy seedlings:
- Sprinkle wood ash around the plants.
- Do not overmoisten the soil, moderately water the seedlings using a watering can or a spray bottle.
- Timely thin out overly dense plantings.
- Be sure to dive seedlings. Some gardeners believe that picking plants is optional. But it is needed, as it promotes the branching of the root system, which means that the roots will provide the plant with good nutrition. From this, the seedlings will become strong and grow well.
- Fertilize the plants correctly, do not allow an excess of nitrogen fertilizers, as this leads to the disease of the seedlings with a black leg.
- When growing seedlings, manure or humus should not be applied, there is a fungus in large quantities.
- Water the seedlings with onion peel infusion. Such watering will have a beneficial effect on diseased plants.
Blackleg protection measures - prevention and control
It is advisable to use comprehensive protection measures aimed at both phytopathogens (both fungal and bacterial)
Prevention measures
1.Use only clean, disinfected containers (pots, pallets, boxes) for growing seedlings.
2. It is imperative to treat seed material with fungicides.
3. Avoid excessive soil moisture - reduce the number of seedlings irrigated, ensure the availability of drainage, etc.
4. Avoid soil acidification by regular loosening and / or adding agrovermiculite to the seedling soil.
5. Observe the optimal time for sowing seeds, taking into account the grade, geographic location, etc.
6. Pale, elongated seedlings are most often damaged by the "black leg", therefore it is recommended to use root stimulants "Kornevin", "Root-Super", "Kornestim", etc., providing improved rooting and painless transplantation / picking of seedlings.
7. It is best to use special "clean" peat-manure or vermicompost seedling soils tested, "North-West peat, etc.), which contain all the components and trace elements in the required proportions. It is strictly forbidden to use forest, greenhouse or other untreated soil. Beware of buying primer from an unknown manufacturer in cheap stores. No need to engage in "amateur performance" - mix something, or add something.
8. If you cannot get rid of the desire to add something or mix, then it is recommended to use only humus aged for at least 2 years, and when adding peat to the seedling soil, observe the exact dosage, excessive peat content is not permissible.
9. Avoid thickening of plantings, timely thin out the seedlings and dive seedlings.
10. When the first signs of wilting appear, as well as fortifying agents, use drugs - stimulants "Epin", "Krepysh", "Zircon", "Immunocytofit", Previkur Energy etc.
11. Excessive acidity of the soil can be neutralized by adding ash.
12. To carry out preventive treatments with biological products - "Trichodermin", Fitosporin, "Fitolavin" or others. They contain bacteria or fungal spores that destroy pathogens at their level. Biological fungicides are used as a prophylactic agent, as well as for direct control of the "black foot".
13. To use the latest varieties and hybrids of plants, resistant to fungal, bacterial and viral infections, the science of breeding and biology does not stand still.
Gardener Tips
Gardeners warn that if the seedlings are infected with rot by more than 50%, it is better to completely destroy the seedlings. The threat to grow weak plants that will yield negligible yields is very high. It is better to change the contaminated soil or apply several methods for disinfection.
For high-quality seedlings, it is better to use store-bought seeds and soil. In home components, there is a high probability of developing fungi.
It is also worth paying more attention to examining the seedlings, especially during periods of their weakening, in order to immediately notice the symptoms of the disease.


Experts do not advise to use cold water for irrigation, to allow excessive amounts of fertilizers, so as not to create comfortable conditions for black rot.
Gardeners warn: in the absence of preventive measures, the risk of developing a fungal infection is high, then it is almost impossible to get a good harvest.
What to do if the cabbage has undergone re-infection
If the disease develops again, the plants can be helped by the following measures:
- dig in a gliclazide tablet at a depth of 1 cm;
- regularly loosen the soil and huddle bushes;
- watering at the root with a weak solution of manganese;
- tame the soil with ash;
- treat the plants with a solution of "Trichodermina", prepare it from 100 ml of the substance and 10 liters of settled water, the treatment is carried out in cloudy cool weather; with a large area of infection, the treatment is carried out at least 5 times;
Important! Trichodermine is non-toxic and does not accumulate in the plant.
Causative agents of the disease
The causative agents of the black leg have the ability to penetrate into the most distant parts of the plant through the vessels, while outstripping the manifestation of the external symptoms of the disease.
The following pathogens are known to modern science:
- Phoma betae;
- Aphanomyces cochlioides;
- Pythium ultimum;
- Rhizoctonia solani;
- Pectobacterium;
- Fusarium.
Phoma betae, otherwise Thomas, promotes the development of phoma root rot, especially carrots, beets and cabbage are susceptible to this pathogen. The fungus appears along with the seeds, since it is a saprophyte or parasite on the aerial parts of sugar beet seeds. When it gets on seeds in wet weather conditions, it attacks the sprouts.
In most cases, it is difficult to identify the pathogen based on symptoms alone, unless the infection is caused by Aphanomyces. Under their influence, the upper part of the hypocotyl becomes much smaller and blacker, while the base of the cotyledon is also affected by the disease.
Aphanomyces, Pythium and Rhizoctonia were not seen in the aerial portions of the beets, thus allowing them to thrive in the soil.
Rhizoctonia solani, or Rhizoctonia, is also a mushroom. As a parasite of underground parts of plants and roots, it is more often found on potatoes, affecting the tubers themselves. And in this case it is called black scab.


When summer temperatures are very high and there is little rainfall, the infection is latent, and the plants do not show any external signs of damage. Therefore, in the field, the tuberous form of potato disease usually reveals itself in the second half of the growing season, it is called wet rot, and its causative agent is all species of the genus Pectobacterium.
Fusarium has also been identified, but as a secondary infection.
How is it developing and why is it dangerous?
The causative agents of the disease are found in the soil. As soon as conditions are suitable for them, they immediately settle on seedlings. Saprophytic molds feed on organic debris. In greenhouses or seedling cups where space is limited, nutrient deficiencies occur. Therefore, pathogens attack the roots of plants through mechanical trauma when diving.
Bacterial origins are especially contagious. The defeat passes from diseased plants to healthy ones with air currents, when leaves come into contact, through insects or improvised means.
The main symptom of the bacterial form of the disease is mucus, which is located in the damaged stem. Inaction leads to the death of mature plants and loss of yield.
Basic prevention: what to do
What to do to prevent the black leg from appearing on the plants? The only specific measure against blackleg is disinfection and proper preparation of the soil. For seedlings, it is better to purchase high-quality soil mixtures from well-known manufacturers, which are completely processed from all pathogens. Planting in peat tablets also eliminates infection.
Seedling soil
Substrates for seedlings using garden soil must be disinfected. The highest guarantee is given only by severe heat treatment.
To warm the soil, it is poured onto a baking sheet with a layer of 1.5-2 cm and kept at a temperature of 120-125 ° C for 45 minutes. You cannot increase the degrees. When heated to more than 130 ° C, soil organic matter is carbonized, forming toxic compounds.
After disinfection, the soil remains sterile for a short time. Therefore, it immediately needs to be populated with beneficial microorganisms that will displace pathogens. To do this, add 1 liter of vermicompost or 2 glasses of Piksa supercompost to 10 liters of soil mixture. Spill with Fitosporin solution.


Seedling containers are washed with hot water and laundry soap. Immerse in a 1.5% potassium permanganate solution for 20 minutes and rinse with running water.
An easier disinfection method is freezing, but it does not work against all blackleg pathogens.
Soil in greenhouses and greenhouses
In autumn, after harvesting, the soil is treated with bleach. The product is applied dry at the rate of 200 g per 1 m², covered with a rake.
The most effective substance against the causative agents of the black leg is 40% formalin. 4 weeks before planting the seedlings, the soil is dug up several times, removing the plant debris left over from the fall.
In 100 liters of water, 1 liter of formalin is diluted. The soil is poured with a solution at a rate of 20 liters per 1 m².
The same treatment is carried out in the open field without observing crop rotation or in the presence of infection in the previous season.
Subsequently, the soil and tomato plants are treated with biological preparations up to 2 times per season.
In order for the seedlings to take root well and begin to build up a powerful root system, mineral fertilizers are applied 3-4 weeks before planting. The norm per 1 m²: wood ash - 200-300 g, potassium sulfate - 30 g, superphosphate - 50 g. In a week, ammonium nitrate is added - 25 g. After the fertilizer has been distributed, the soil is dug up and spilled with water.
Treatment
"Fitosporin-M"
Six grams of powder is dissolved in a bucket of water at room temperature, infused for 1-2 hours, stirring occasionally. The resulting liquid is sprayed on the ground part of the plants in the morning or evening.
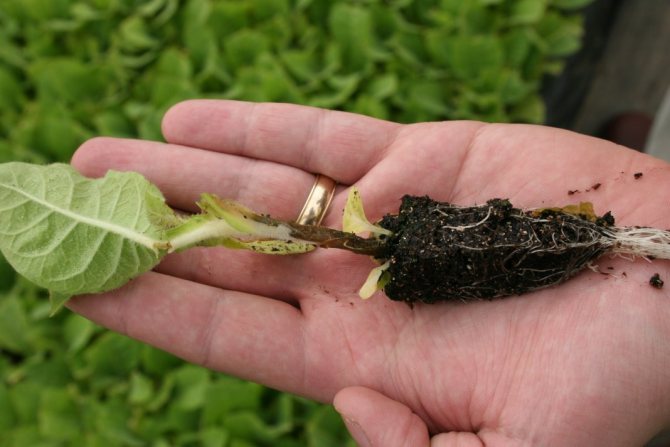


Previkur Energy
25 ml of the concentrated substance is diluted in 10 liters of settled water. The solution is used to treat the leaves of young plants. The treatment is carried out 3-4 times, depending on the degree of damage.
Also, seedlings can be watered with a 0.5% manganese solution, soda or 1% Bordeaux liquid.
The grown seedlings are subject to treatment, they do not need to be destroyed. However, this cabbage is not suitable for storage. At the first symptoms, the bushes are watered with potassium permanganate and the soil is sprinkled with wood ash. Some gardeners recommend to bury a tablet "Glyocardin" under the root.
Interesting!
The most effective drugs for combating the disease are those that contain mancozeb or copper oxychloride.
Prevention in the pre-sowing period
It is preferable to use purchased soil mixtures in sealed bags for sowing seeds. Seedling containers should be cleared of last year's soil, thoroughly rinsed and disinfected.
If soil from a summer cottage is used, it should be pre-calcined in the oven or on the burner. For disinfection, the soil can be treated with formalin or a dark solution of potassium permanganate.
Advice. A week before use, the calcined and disinfected soil should be fed with biofertilizer to saturate with microorganisms.
In the case of massive planting of seeds, for example in a greenhouse, it is necessary to carry out preliminary liming of the soil by adding wood ash in the amount of 100g / m². Agronomists also advise to disinfect the soil in the greenhouse by adding colloidal sulfur at the rate of 5-8 g / m². The soil should be loose and light.
For reference. The addition of sesame, flax or milk thistle fiber to the soil shifts its pH to the alkaline side.
Also, a way to protect against fungal infections is to dress the seeds before sowing with one of the following means:
- biological product "Planriz" - treat with 1% solution one day before sowing;
- "Fitosporin-M" in bottles - dissolve 4 drops in a glass of water, soak for 2 hours.
After planting, the soil should be watered so that it is moderately moist, do not overcool the container with seeds.
You may be interested in:
What is the causative agent of the disease?
It is a kind of bacteria that is shaped like a stick. If the conditions suit them, they multiply very quickly. Uniting in colonies, they begin to infect plants.Many cultures are susceptible to this disease, so it does not experience a lack of nutrition.
The bacterium cannot overwinter in the soil on its own, so it looks for plant residues, tubers. Will survive the winter in the stem or root of weeds. With the onset of warmth, it continues to reproduce. That is why it is recommended to remove all plant residues from the fields.
Why are chemicals often used?
Biological products are living organisms, so they must be constantly injected into the soil. This is about 5-7 days. When using the drug as a prophylaxis, it can be watered with a solution every two weeks. What is chemistry? This is heavy artillery, because no pathogenic bacteria remain in the soil, and even beneficial bacteria are not present.
Therefore, after chemistry, it is necessary to restore the soil again, reapply biological products. Sometimes it is impossible to cope with the disease without chemicals. From chemicals you can use:
Maxim Dachnik
Etching should be carried out directly before disembarkation. The main element is fludioxonil, which destroys fungus at the cellular level. As a result, the immunity of plants to fungal diseases increases during the growing season. The tool is sold in ampoules, bottles from 2 to 100 milliliters. To process a large number of planting material, the product is purchased in containers from 5 to 20 liters. The drug has a type of suspension without aroma, it is simply diluted with water. The concentrate is supplemented with bright scarlet pigments, which makes it possible to control the etching quality.


Vitaros
It is a drug for contact and systemic exposure. The main purpose is dressing tubers, bulbs, rhizomes and seeds. The drug destroys pathogens of various diseases, on the plane of the planting material, and from the inside. The agent acts in such a way that it sticks to the seed, falls into the middle of the seed. The product can be from 2 ml to 50 ml, and also in 100 ml bottles.
Popular: The main pests of cabbage and methods of dealing with them
Top dressing of seedlings
With the threat of the spread of a fungal disease, it is necessary to increase the immunity of young plants. For this reason, it is necessary to avoid feeding seedlings only with nitrogen fertilizers.
In the soil mixture for seedlings, there must be a large amount of phosphorus, potassium and calcium, its reaction must be neutral. In addition, plants are fed with soluble phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, similar to potassium sulfate and monopotassium phosphate, as well as complex fertilizers with a high content of these nutritional components, similar to the Master.
Blackleg seedlings are a disease that is easy to prevent, but difficult to stop. For this reason, disinfection of implements and soil, prompt preventive treatment of young plants and, most importantly, the fulfillment of optimal conditions for growing seedlings, is the best method to eliminate annoying losses when growing seedlings of vegetables and flowers on your own.
How to prevent black leg infection?
So that a black leg does not appear in cabbage seedlings, how to fight? It is already clear that it is necessary to prevent waterlogging and increased acidity of the soil, thickening of crops and the formation of an earthen crust.
It is possible to save plants from disease. Prevention consists of the following measures:
- Conduct steam disinfection of the soil before sowing.
- Disinfect the prepared soil using a manganese solution (weak).
If a lot of seeds are sown, a drug called trichodermine should be added to the soil, following the rules in the instructions. Trichodermine is a biological substance used in the treatment or prevention of plant diseases. Once in the soil, it destroys many pathogens.
- To deal with the processing of seeds intended for sowing.To do this, they must be put in gauze and held in any fungicidal agent, adhering to the recipe standards. Soaking in water with manganese is also good. The seeds must be kept for at least 20 minutes, and then rinsed under running water without removing them from the gauze;
- To process seeds with agents that stimulate the plant's immunity. The most popular among them:
- Epin - Extra;
- Immunocytophyte;
- Agate 25 K;
- Sodium humate.
- Pour the calcined river sand onto the soil. It is recommended to do this immediately from the moment of sowing or diving;
- Avoid accumulation of liquid in the ground. Watering should be regular, but at the same time moderate. It is advisable to make drainage holes in containers under the seedlings;
- Periodically open windows and doors in the room with seedlings;
- Monitor the temperature indicator. It is undesirable to expose the plants to a sharp decrease in temperature, since the development of a black leg is possible;
- If the cabbage is still struck by the disease, you need to get rid of all infected sprouts. Then irrigate the rest of the seedlings using Bordeaux liquid or the same manganese solution.
Have a nice harvest!
What conditions are necessary for a virus to develop favorably?
No disease will begin to actively develop if the environment is opposed to it. Conditions that bacteria need for their active reproduction and progression:
- The presence of a virus in the soil. Finding the remains of infected plants in it.
- Planting contaminated seed.
- The potatoes were damaged during harvesting.
- The conditions for proper transportation and preservation of the vegetable were not met.
- The disease is transmitted by insect pests.
- Lack of nutrients in the soil.
The disease progresses best in rainy weather and damp summers.
The breeders have not developed a blackleg resistant potato variety. But there are species that are more resistant to this disease.
Causes of the disease in tomatoes
Infection is caused by contaminated soil and seeds. In the future, the development of the black leg is facilitated by gross violations of tomato agrotechnology:
- sowing seeds in non-disinfected containers and soil mixtures;
- no seed dressing;
- high acidity, compaction of the substrate;
- thickening of landings, no picking;
- sudden changes in air temperature;
- increased soil moisture;
- low temperature combined with high air humidity;
- poor lighting, lack of ventilation;
- excess nitrogen in the soil.
Infection of plants accelerates root damage by the larvae of sprout flies.
The author of the video shows tomato seedlings, which are affected by bacteria and protozoa fungi.
Summer residents advice
Black leg disease is very progressive. In order to prevent most of the harvested crop from rotting, summer residents are advised to pay more attention to the prevention of the disease. Since treatment is a laborious process. The presence of blackening stems indicates the active development of the disease. To prevent development will help:
- Weeding three times. Remove diseased plants at least three times. With subsequent disinfection of germination sites.
- Treatment with preparations of the seed and the site itself after germination.
- Regular inspection of the bushes, at least once a week.
It is important to remember that any business is taken seriously. Observing the measures, rules and requirements, they get an excellent harvest. Everything is in the hands of the gardener.
Sources:
Signs


Main signs:
- Blackening of the stem.
- The stem color is gray, brown or dark green.
- Decay of the bottom.
- Partial or complete absence of roots.
- The lower leaves turn yellow and fall off.
- Internal tissues are soft and tear.
It is worth knowing that similar symptoms may be due to another disease. Fusarium is a parasite that attacks the stem of tomatoes without touching the roots.
By spreading toxins throughout the plant, it, just like the "black leg", contributes to curling and blackening of the lower part of the stem and its thinning. Only the base of the stem does not break, as in the case of the "black leg", but has a solid, durable character. To recognize it, you should pull out one bush a little and see if the roots are intact.
Preventive protection measures
If no black leg disease has been detected on the site, but there is a danger of its appearance due to favorable conditions for the reproduction of bacteria, then it is recommended to immediately start taking preventive measures.
Biological agents
Biological methods of protecting potatoes from blackleg are considered the safest and do not harm the human body and the environment. These include:
- Compliance with the recommended rules for storing the crop, carrying out treatments in the storage, maintaining the temperature and humidity at the proper level.
- Growing varieties of potatoes with high blackleg resistance (for example, Viliya, Karnea, Ulyanovskiy, Skorospelka 1).
- Drying the soil on the site, timely removal and burning of vegetation residues.
- Diseased tops or other vegetation cannot be used as compost, it must be burned, and the ash must be buried at a depth of at least 15 cm.
- Apply dolomite flour on the site to reduce acidity and prevent massive growth of bacteria.
- The harvested crop of potatoes should be carefully sorted out and dried.
- Tubers with mechanical damage are subject to rejection and are not allowed for planting, since it is such material that is most susceptible to diseases.
Chemicals
If the risk of damage to the potato with a black leg is very high or signs of the onset of the disease were noticed on the site, then you will have to resort to using drugs of chemical origin. Reviews of gardeners indicate that the greatest efficiency is brought by:
- Spraying potato tubers before planting with means.
- The area where potatoes are planned to be planted is watered not only with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, but also with preparations designed to combat fusarium (for example, "Previkur", "Fundazol", "Topsin-M" and others).
- Preventive measure is watering with the addition of "Effecton", which is diluted in a ratio of 3 tbsp. l. 10 liters of water. Under each potato bush, 0.5 liters of solution is applied.
- Before being sent to the storage, potato tubers are treated with Maxim.
Timely preventive measures will help protect and preserve the potato crop and prevent the appearance of such a dangerous disease as black leg on the garden plot.
Plant care rules
Seeds should not be placed very close to each other: do not scatter them randomly over the surface of the substrate. If this rule is neglected, the seedlings will press against each other, the earth will cease to "breathe", which will lead to acidification, the appearance of a fungus, the seedlings will weaken and be amazed by the black leg. After infection of one plant, the disease will be picked up by the "neighbors": there is a risk of losing all the seedlings. To avoid this, plant the seeds at some distance from each other or in different containers. Subsequently, the care is as follows:
- It is necessary to regularly inspect seedlings for the presence of disease lesions: timely detection of the disease will help to avoid the death of crops.
- Water the seedlings carefully: use a medical syringe or pipette. Remember that moisture should not stagnate in the soil, do not flood the seedlings - an excess of moisture will lead to acidification of the soil. Water should not get on the seedlings. To avoid this, pour water into the pan.
- Loosen the soil after each watering, make hilling.
- The seedlings must "breathe". Good air exchange can be created by regular ventilation.
- Choose conditions that are comfortable for growing - there should be no changes in air temperature in the room, greenhouse or greenhouse.
- It is advisable that the soil does not cool down - protect the seedlings from drafts, if necessary, remove them from windows and sills.
- Timely thin out the thickened sowing, dive the plants. Remember that with densely planted plants, the earth becomes acidic, fungus develops in it. Plant seeds in small pots initially. If the seedlings are in one container, then after the formation of three leaves, transplant them into separate containers.
- Do not feed the seedlings before picking - nitrogen fertilizers are often applied, which provokes the formation of a black leg.
- Choose well-lit areas. If they are not there, then arrange additional artificial lighting - this will prevent the seedlings from pulling out.


Resistant varieties
- Vologda F1. Greenhouse, mid-season hybrid. It tolerates all types of diseases and viruses well.
- Ural F1. Mid-season cultivar for indoor cultivation. The harvest begins to ripen on day 120. The fruits are large, round and red, the weight of one tomato is 350 grams.
- Firebird F1. An early ripe, lettuce hybrid for indoor use, but it can also bear fruit well in an open area in the southern regions of the country. The hybrid not only staunchly resists various diseases, but is also capable of yielding at low temperatures and lack of sunlight.
- Bohemia F1. A hybrid with a determinate type of bush. The variety is bred with persistent resistance to all types of diseases.
How do you know if a plant is infected?
Observing the appearance of the plant will help to timely identify the disease in potatoes and take measures to eliminate it. A characteristic sign of the disease is the presence of blackening bases of the stems about 10 cm up. Hence the name.
The main symptoms of the onset of the disease:
- The first sign is yellowing of the leaves, curling and drying. Revealed in the period 3-4 weeks after germination.
- The stems and roots of the plant begin to blacken. And they easily come off at the site of defeat.
- During flowering, diseased bushes lag behind others in terms of development. The active development of the disease occurs precisely during this period.
- If the disease is at an advanced stage, then the bacteria move from the stem to the tubers.
- The joints of stolons with root crops become rotten and give off an unpleasant odor.
- In a rainy summer, the stem of a faded plant begins to deteriorate, the color turns dark green. If you squeeze it, there is an emptiness in this place.
- Bulba can become infected from the soil or from a nearby infected fruit. First, the potato becomes covered with brown spots, then the tuber tissue turns black and begins to rot.
- If the conditions are unfavorable for the development of the disease, it still develops, but in a slow form. It will begin to progress only next year.
Related article: Planting potatoes for the winter: instructions, pros and cons
A careful examination of potato bushes will help to identify diseases in time and take the necessary preventive measures. After all, those bushes that were struck by a black leg do not form tubers.