Climbing roses are the most popular flowers used for vertical landscaping of gardens. These plants have a wide variety of heights and colors, which allows you to create unique flower arrangements.
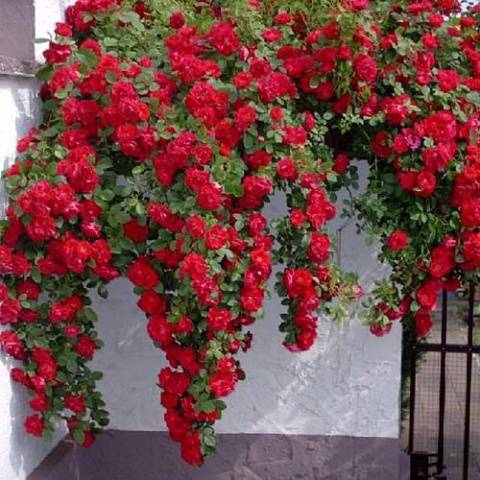

But it often happens that the grower is waiting for the buds to bloom, but the climbing rose does not bloom. It's a shame, isn't it? Let's try to figure out what was done wrong.
Why roses do not bloom but bush


There can be several reasons for the poor flowering of the bush. By denying and analyzing each of them, one can find the answer to the question being asked.
The reasons why roses do not bloom but bush can be of the following nature:
- wrong landing site;
- improper feeding (not so, and not how much);
- landing site - shade, partial shade
If it is decided to equip an old garden with a rose garden, where there are huge trees, wattle fences and vines, and you really want to bring some of the world into it, then preference should be given only varieties of roses the latest selections. If a rose is planted, but it was bred in the last century, then no matter how beautiful it is, it will not bloom in a sunny area, in partial shade.
Very often compatriots, visiting Europe, do not even think that the rose gardens created there, with a play of light and shadows, lovely aromas and a breathtaking look, are a finely selected varietal assortment. Trying to embody what he saw, the plantings are followed by disappointment, because in the shade the rose "drives" abundant foliage, and flowering is either absent or very scarce.
How to choose a place to plant roses
The answer to the question why roses do not bloom, but bush, also depends on the place of planting of the bush. When planting a rose bush, it is necessary to be guided exclusively by the agrotechnical characteristics of the variety. If a rose is chosen for partial shade, then the description of the variety must necessarily indicate "The variety is tolerant to shade" or simply "Partial shade is allowed." Otherwise, flowering will be poor.
How to be? Several options are possible:
- cut off huge tree branches (at least provide eastern lighting);
- transplant the bush to a well-lit place.
Also roses can and should decorate the northern walls of our houses. But, again, preference should be given to the newest varieties, which are adapted for flowering from the north side.
If the rose is of unknown origin and is planted at random, from the north side, it is unnecessary to wait for flowering.
Moreover, return frosts can destroy tender young shoots, and flowering will also be absent.
Other reasons
Diseases affect the ability to bloom
If you decide to find out why the climbing rose does not bloom, check if the plant is sick. Most often, flowers are affected by powdery mildew or bark cancer. What if the disease is present?
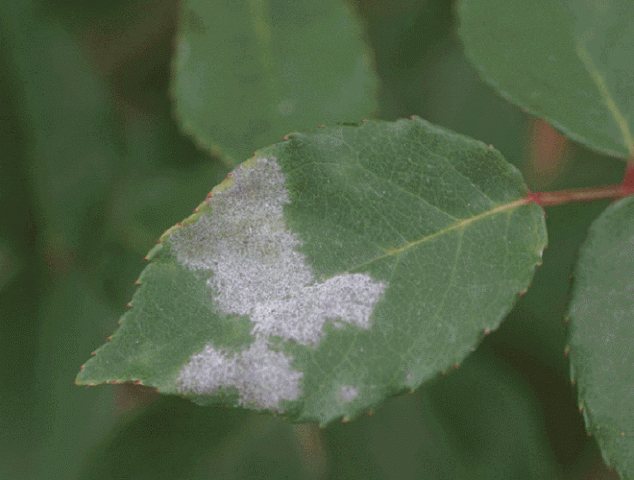


Consider the necessary activities:
- from powdery mildew, the buds and shoots are sprayed twice in early spring with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid, the same measures can be carried out as preventive measures. There will be no harm;
- for the prevention of cancer, timely feeding of climbing roses with fertilizers containing potassium, the correct shelter of plants for the winter is necessary.
Among the reasons is the wrong landing site.
The queen of the garden does not form buds and does not bloom if she lacks light. In addition, shoots develop incorrectly in the shade.Due to the strong stretching, they do not have time to ripen, in winter they can freeze out. The detached plants will be weak, they are unlikely to bloom.
A large amount of light also has a detrimental effect on the ability of climbing roses to bloom. Many buds can form, but the hot sun burns them.
What rules for planting roses you need to follow:
- A well-lit place is selected for the queen of flowers, but at noon direct sunlight should not fall on the plant.
- Climbing roses need to be protected from the north wind. Cold can cause the plant to not flower.
- Trees on the site should be kept clear of roses. As a real queen, she doesn't like to share space with anyone. Moreover, trees have a powerful root system, no matter how you feed the flowers, they will always lack nutrients.
Advice! If you are a novice florist, do not neglect the advice and recommendations of knowledgeable people at the time of planting rose bushes.
Plants wintered badly


Autumn work is an important event. If they are carried out poorly, in the spring you will involuntarily ask a question, last summer the rose bush bloomed violently, but now it does not please with flowers.
In the fall, wild shoots are cut, weeds are removed. While the vine is not frozen, it is bent to the ground. To prevent the shoots from rising, they are carefully pinned. To save the plants from a drop in temperatures and excess moisture, a shelter is made over the roses. It can be made of plastic wrap, boards.
Important! The shelter should allow for the possibility of an air gap.
If it is not there, climbing roses can snuff. Then there can be no talk of any flowering in the summer.
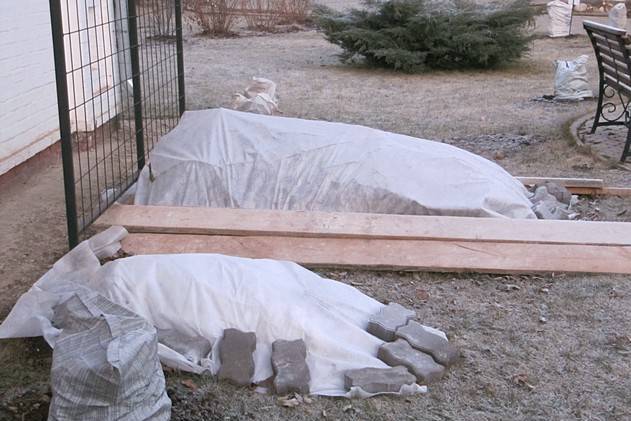


How to feed roses
Having planted a rose bush, flower growers are in such a hurry to get a lush flowering that zeal in feeding leads to the opposite result. As a result of the application mineral fertilizers, especially nitrogenous, fattening of the bush occurs when it grows annual shoots that exceed the characteristics of the variety in thickness and length. In this case, the question arises - Why the roses do not bloom but bush.
The main mineral fertilizer for roses is nitrogen (ammonium nitrate, urea). It is they who will give strength to the growth of shoots, provide foliage. However, a high dose of these fertilizers:
- in spring and in the first half of summer - it will delay flowering, or even stop it altogether;
- in the second half of summer - it will prevent the ripening of the shoots;
- the resulting buds will rot without entering the flowering phase;
- will promote the growth of fatty shoots and attract aphids to young and juicy pink branches.
Rosebushes overfed with nitrogen have oily shoots with little branching and no flowering. Ate the bush by mid-July did not lay buds, it is cut off by a third.
What fertilizers do roses like
Phosphate fertilizers for roses
If a rose bush is planted in soils of light granulometric composition with an acid reaction, then this element is in an inaccessible form. In order for the plant to be able to use the element for the formation of buds and flowers, it is necessary either:
- add organic matter (microflora will process inorganic phosphorus into organic, available, assimilable - but for a long time);
- apply water-soluble phosphorus fertilizers in the form of, for example, superphosphate.
To contribute superphosphate it is necessary only in a dissolved form so that the element reaches the level of occurrence of the root system. It is also necessary to take into account the fact that as soon as the soil dries up, the assimilation of the element stops.
Potash fertilizers for roses
No optimal amount potash fertilizers bud formation is also not possible. Moreover, potassium helps to increase the immunity of the rose bush, resistance to both adverse weather conditions and infectious diseases.
Among the potassium fertilizers for roses, potassium sulfate is the most acceptable. Rose growers prefer this drug because:
- fertilizer does not cake;
- applicable on any soil;
- well soluble in water.
Complex fertilizers for roses
Agrochemistry is a rather complicated science and it is not always possible to create the composition you need for roses yourself. That is why the scientists went to a meeting and put into production ready-made, complex preparations specifically for roses.
It is not at all difficult to acquire them now, and using the instructions, you can carry out high-quality feeding, both under the root and foliar.
In places of sale, especially in large flower-growing centers, sales managers can give comprehensive advice on the timing and doses, as well as help to decide on the choice of mineral fertilizer specifically for roses. Make full use of their knowledge and experience.
How not to overdo it with fertilizers
The use of complex feeding of organic fertilizers together with mineral fertilizers contributes to the best assimilation of all nutrients.
Using a scheme proven by rose growers, you can avoid fattening and achieve abundant flowering.
If, when planting, the root hole is abundantly filled compost with fertilizers, then no feeding is carried out in the first year. For the next year, the schedule is approximately as follows:
- the first feeding is carried out during the period as soon as the roses start to grow intensively. In different regions it is different, but about 2-3 weeks after the spring opening. 1 tablespoon of ammonium nitrate is dissolved in a bucket of water;
- the second feeding during the period of intensive growth of shoots. On a bucket of water take 1 kg of cow dung, 10 g of ammonium nitrate, 20 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate;
- the third top dressing in early July is carried out with the same components, but without ammonium nitrate, and we increase the dose of potassium sulfate to 30 g.
Preventive actions
Any problem is easier to prevent than to get negative consequences. The garden will be filled with the fragrance of climbing roses, if the following rules are observed:
- Spring anti-aging pruning.
- Preventive spraying of bushes with fungicides.
- Compliance with the intervals between the bushes when planting.
- Competent agricultural technology.
- The rose variety must be adapted to the growing region.
- Do not plant roses in the shade of other plants and buildings.
- Stagnation of moisture at the roots of the plant is unacceptable; drainage from expanded clay is installed at the bottom of the planting pit.
- Shrubs are covered with additional devices for the winter, even if the variety is winter-hardy.
- Provide the plant with rational watering and complex fertilizing.
With the systematic care of the flower, the correctly chosen planting site, the observance of agricultural technology, the garden will be filled with the fragrance of fragrant beauties. Climbing roses are a noble decoration of the suburban area.
Features of soil and climatic conditions for roses
When planting a rose bush and especially dressing, it must be borne in mind that clay soils retain nutrients for a long time, so the amount of nutrient supply should be limited.
If the soils are sandy, then leaching occurs quickly, and the soils become "fresh", therefore, fertilizing should be carried out more often, but in small doses.
If the summer is rainy, then nutrients are quickly washed out from the root zone of the plant, and they must be renewed in a timely manner.
In a hot summer, feeding is reduced, and watering is increased.
When roses are not fed
The rose bush blooms in waves. After feeding the plant and waiting for the first wave, you need to:
- fully enjoy the bloom;
- cut off what has faded;
- give the opportunity to "rest" for 1.5-2 weeks, during this period complex biochemical processes take place, in which there is no point in interfering;
- promptly delete weeds, it is easy to loosen and water the root zone regularly.
It is necessary to wait with feeding until new points of growth appear and at this moment give the next feeding.
Considering the question "Why roses do not bloom but bush", having weighed all the features of your pink kingdom, you can easily identify the causes and try to eliminate them. This does not always work out in the current flower season, but next year roses will certainly delight you with an abundance of fragrant and beautiful flowers.
How to help the plant?
To help the rose bloom, determine the cause that influenced the decrease in flowering. Do not forget that thorny beauties are demanding on the fertility of the soil, the presence of sunlight.
Rejuvenating pruning stimulates shrubs to grow buds, even if the flower stands are already old. In the spring, during the budding period, the bushes are necessarily sprayed with insecticides and fungicides. Plants are not allowed to start, young shoots thickening the bush are removed in time.
The modern floriculture industry offers a wide range of complex, balanced dressings for roses and growth and flowering stimulants.


Wild growth
Very often, a weaving wild growth is formed on the base of the bush, which absorbs nutrients, which does not allow the rose to bloom fully. Therefore, it is necessary to cut off all wild spiked shoots in a timely manner to their very base. Places of cuts should be treated with powdered coal.
In addition, you should cut off weak shoots on which buds do not form, remove dried and wilted flowers until the petals completely fall off on them. In the spring, after the last frost, it is worth carrying out sanitary pruning and thinning out very dense bushes. It is worth remembering that the cutting tool must be sharp and disinfected.
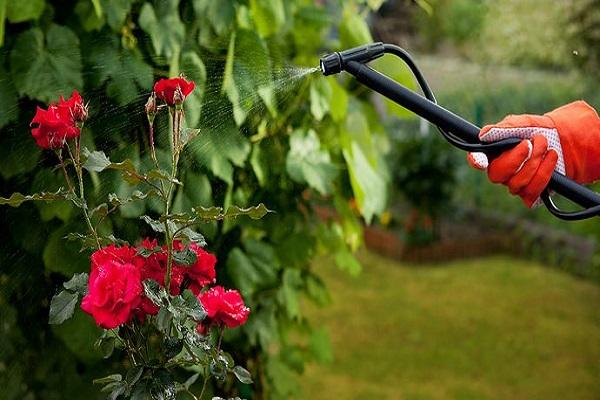
Protecting roses from diseases and pests in summer
Aphids, caterpillars, sawfly larvae, leafhoppers and pennybill slobber - many insects do not mind eating a rose. And if you do not want to deal with the consequences of their appetite, it is advisable to think in advance about preventing the appearance of pests in your rose garden.
You can regularly (every 7-10 days and after each rain) dust the rose with a mixture of ash and tobacco dust or spray it with garlic infusion in combination with soap, but if you do not believe in folk remedies, give preference to professional preparations. After all, you won't have to eat a rose, which means you can use insecticides.
Usually, two preventive sprays with bioinsecticides (Aktofit, Fitoverm, etc.) are enough to prevent insects from appearing in your flower garden. There is another way - you can not engage in prevention, but solve problems as they arise, i.e. first detect the pest, and then fight it. However, in this case, in order not to be too late, all the bushes must be carefully examined at least once a week.
The most common rose diseases are rust, powdery mildew, black spot and chlorosis. To prevent their appearance, it is necessary to carry out preventive plant treatments. At the first sign of illness, remove and burn all affected leaves, buds and shoots from the bushes, and then spray. Such drugs as Ridomil Gold, Profit or a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid help well. Processing should be done twice with an interval of 10-14 days.
Reasons for the lack of flowering and their elimination


The climbing rose does not bloom in the first year. When growing on a personal plot, this must be taken into account. You should also take into account what kind of roses they are: climbers or ramblers. The latter in the first year will also not please with flowering, in addition, they are very demanding to care, especially to prepare for the cold weather.
Unsuitable soil


The soil for climbing roses should be nutritious and loose.Depleted soil cannot give anything to the plant, it will not bloom. Sandy and clay areas are also not the best option for a climbing rose. The first type of soil is too dry, and the second is heavy, dries out slowly and does not allow oxygen to pass to the roots.
Top dressing will help to enrich the composition of the soil. In the first year, fertilizers are not applied or they only manage with organic fertilizing. Infusions are made from chicken manure (concentration 1:20) or mullein (1:10). One bush goes from 3 to 5 liters of solution. Ammonia (30 g / m 2) should be added in the spring. The procedure is repeated every two weeks. When the buds begin to set, the plant needs nitrogen.
A lot of overgrowth


Nutrients stimulate the growth of new shoots and stems of the climbing rose. However, in parallel, root shoots develop near the bushes. Excessive branches must be cut off immediately. If this is not done, the bush will become untidy and shapeless, and the varietal climbing rose will gradually turn into a wild one. The plant will give all its strength to the formation of green mass, but it will not bloom.
Getting rid of root scions is easy. You need to cut them off with a sharp blade at the very surface of the earth. Small twigs with thorns and leaves are also cut. A neatly formed climbing rose bush is more resistant to pests and blooms profusely.
Incorrect cropping


When forming a bush, you need to follow some rules, otherwise it will not bloom:
- Consider the variety of climbing roses. In some, flowers are tied on last year's shoots. In the summer, they are pruned, since they will no longer give buds. The shoot is pruned to the very base, from 3 to 10 new ones will grow in its place. Re-flowering varieties form differently. The main shoots are harvested in the fourth year, when they are completely weakened and turn into ugly hanging lashes.
- If young shoots have grown too much and do not let light into the inside of the bush, they are removed.
- Last year's shoots are cut very carefully, capturing only the upper part, where there are no formed buds.
- Too thick stems with coarse bark are best cut with a hacksaw.
- The cut is usually made over the outer kidney, holding the scissors at an angle. So there will be no accumulation of excess moisture on it. Immediately after pruning, the branches are treated with disinfectants.
- Rejuvenating pruning is carried out in the spring, it is it that stimulates the appearance of buds. First of all, they get rid of the branches that grow inside the bush, as well as from diseased and thin stems.
It is worth remembering that with too much pruning of a climbing rose, the bush begins to develop incorrectly.
Lack or excess of fertilizer


If you overdo it, climbing roses won't bloom either. Nitrogen fertilizers are especially insidious. Their excess leads to the rapid growth of shoots to the detriment of budding. Shoots become thick and densely overgrown with leaves, roses do not bloom. Top dressing with superphosphate, wood ash and potassium nitrate will help restore the balance of minerals in the soil. These fertilizers are much safer for climbing roses.
With a lack of minerals, problems arise not only with flowering. At the same time, the stems are deformed, the root system suffers, and the leaves change their usual color. To make the dressing harmonious, you can use complex fertilizers for climbing roses, strictly following the recommendations on the label.
Damage by pests and diseases
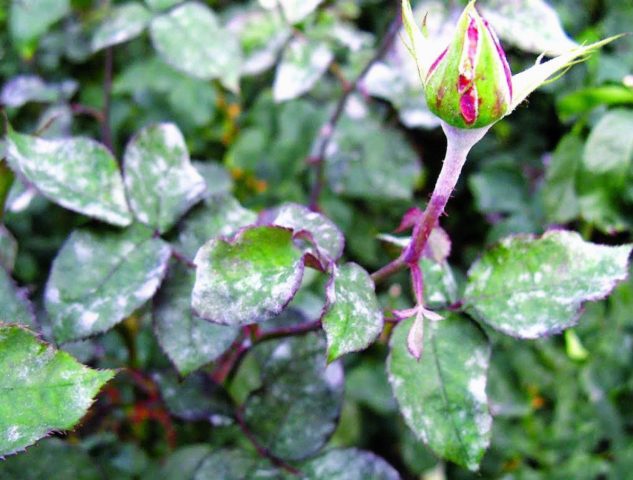


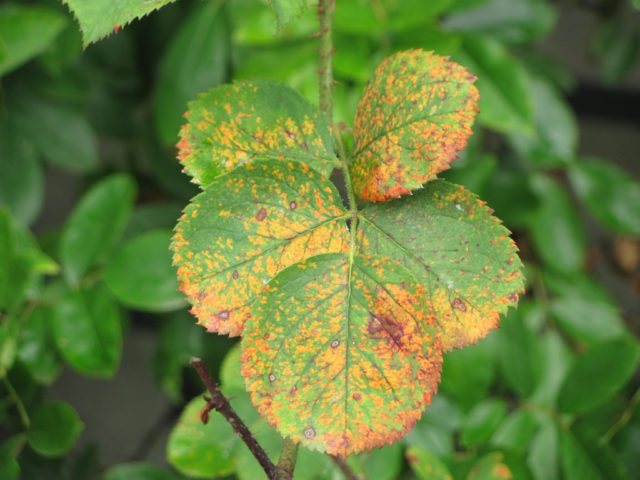
The most dangerous diseases of climbing roses include:
- Rust. This disease manifests itself in warm, humid weather, its causative agent is the fungus phragmidium. The danger is that spores get on the plant from clothing, skin or garden tools. The stems and leaves of a climbing rose are covered with orange spots, it does not bloom, over time the green mass dries up and falls off. All the leaves will have to be cut off, the bushes will have to be sprayed with Bordeaux mixture and 3% iron vitriol, and the soil will have to be dug up.


- Powdery mildew. Another fungal disease.It manifests itself as a gray bloom on the buds, branches and leaves. Plants are treated with various preparations: vitriol and potassium, colloidal sulfur, as well as a folk remedy - soap and soda.
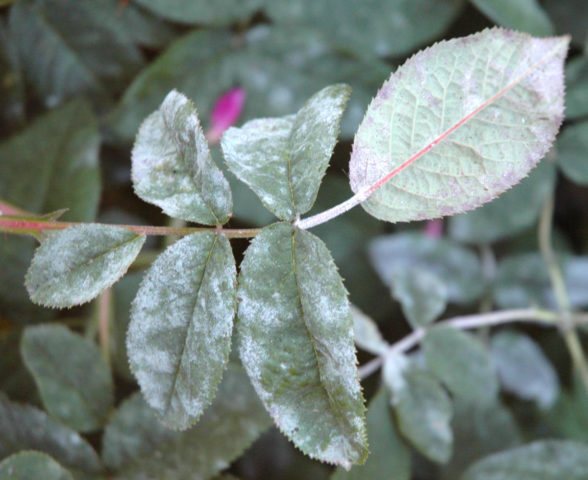


- Chlorosis. Appears from a lack of minerals in the soil. Leaves turn white or yellow. At this time, it is very important to feed the bushes with the necessary fertilizers.


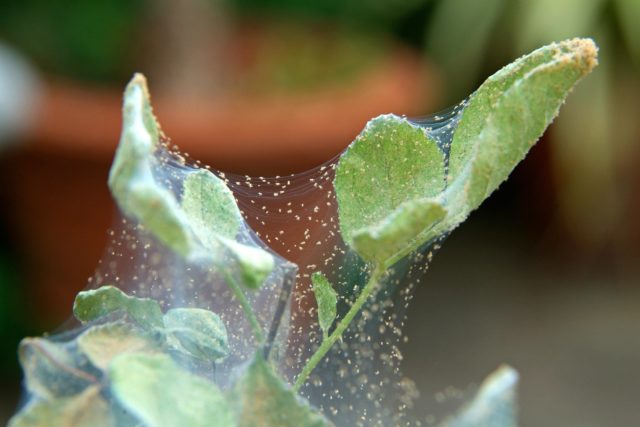
- Spider mite. Insects live on the back of the leaves and feed on their sap, while they wrap a transparent cobweb around them. An effective way to combat is tincture based on tobacco, yarrow or wormwood.


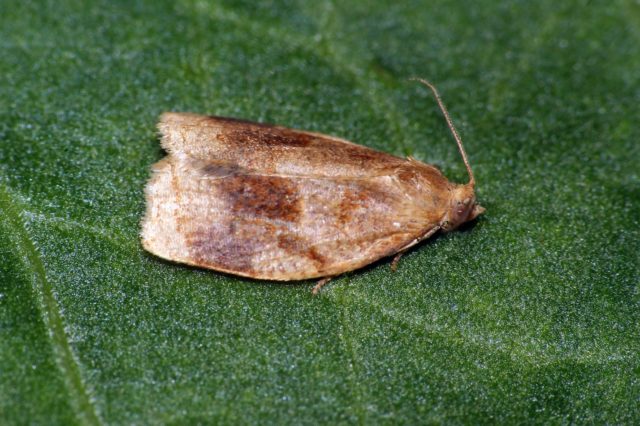
- Rose leaf roll. Insects lay eggs on leaf plates, from which white larvae emerge. The leaves are rolled up in tubes. You need to get rid of them. Plants are sprayed with Intavir, Karbofos or Iskra.


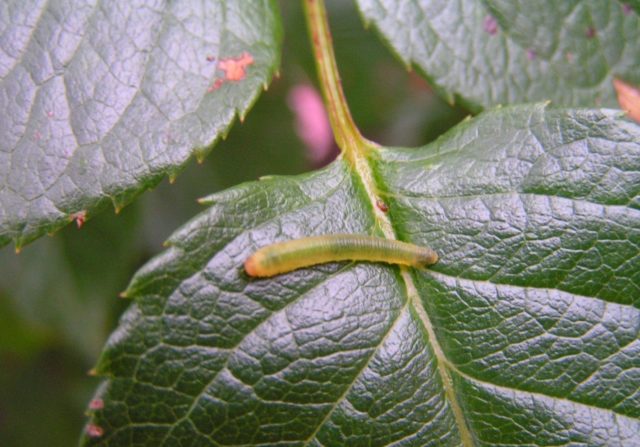
- Rose sawfly. The body of the insect is black, with a glossy sheen. Eggs are laid in the leaf axils, the larvae penetrate the stems and harm it, the climbing rose does not bloom. In the fight against this pest, Fufanon and Intavir help.


Category: "Questions and Answers"
Question number 1. What fertilizers are needed to improve the flowering of a rose?
It is best to add NPK complex mineral mixtures. Superphosphate and potassium salt are used separately. This mixture is successfully replaced by ash, which is rich in phosphorus and potassium, it is these macronutrients that provide abundant flowering, large flowers and bright colors.
Question number 2. Roses grow in the sun, the land is fertile, watering is good, and roses bloom poorly. Why?
Check the acidity of the soil. No matter how rich the soil is at values less than pH - 6, nutrients are inaccessible to plants, since insoluble compounds are formed in an acidic environment. For neutralization, you can use calcium nitrate, it will also enrich the soil with calcium.
Folk ways to improve the flowering of roses


Following the example of the leading European rose nurseries, domestic gardeners use mullein 4 - 5 kg / m2. It is applied to the soil for the main top dressing and as a dry mulch, as an MLU (slow acting fertilizer)
Not always, gardeners have the opportunity to purchase mineral fertilizers. Many people prefer organic matter. Good for roses bird droppings, but use it only in spring, due to the high nitrogen content.
- Fresh droppings are infused in a solution of 1:20,
- Dry, mix with soil 1 - 2 kg for each bush.
Twice a year, in spring and autumn, they bring well-rotted humus - 3 - 4 kg / m2.
It is often mixed with ash - 200 - 300 g (1 - 1.5 cups) for each bush.
The most affordable organic fertilizer - compost... It can be prepared by every gardener. To do this, plant residues are put in a pit or well-ventilated box:
- Mown lawn grass,
- Weeds cut down (no seeds),
- Shredded branches.
Compost is supplemented with food waste, with the exception of meat and dairy products. They cause unfavorable rotting. Natural synthesis of compost from six months to two years. With the use of EM - drugs, the process is accelerated at times.
Climbing rose: care, pruning work in spring
- With the onset of warm days (early-mid-March), cover the bare surface of the winter frame shelter from the frame and the rose bush itself with snow. This will help protect the flowers from the spring temperature drops during the day and night.
- After 2 weeks, remove the remaining snow, run a groove to remove the melted water
- Ventilate for 20-30 minutes daily, opening the shelter from both sides
- When it gets significantly warmer and there is almost no snow left, start preparing for the full opening of the plant. To do this, open one or two sides of the shelter for ventilation. Next, sketch in the covering material, leaving a small vent for the flowers to breathe.
- After a week, free the roses from the protective material from the east or north, at your discretion.
- After a couple of days, you can fully open the bushes and remove the leaves from the soil.
- Now we do cosmetic pruning, removing broken, dried or crippled branches to a whole part
- Next, we irrigate from infections with copper chloride or copper sulfate
- We huddle and cover with spruce or thin agrofibre, lutrasil or cloth
- With the onset of a stable above-zero temperature, in the absence of the risk of night frosts, we do the main pruning, giving the desired shape to the bush and removing weak shoots
- We immediately treat diseases and pests with the same copper sulfate
- We make top dressing from warm infusion of mullein 1:10, at the rate of 10-15 liters per bush
Shelter for rose cuttings


In a day or two, when the soil "shakes out", over the groove I install a greenhouse 30 cm high with a slope to the south - roses love warmth and light. I close the sides with a thick plastic wrap, the top with a removable frame. I also cover the frame with plastic wrap on top, securing it with slats. The lower part of the frame is upholstered with sacking. Burlap plays a special role in growing roses from cuttings: once a day I moisten it well with water so that the air inside the greenhouse is constantly humid.
I cut the cuttings of roses from the shoots that I prepared last fall. Each cutting should have 2-3 buds. I make the lower cut oblique (under the kidney), the upper cut - straight, above the kidney. Roses take root well from cuttings cut with a sharp razor: the cuts are even, without chipping.
Weak ground


Rose prefers fertile, loamy, loose soil. Lack of flowers may indicate depletion of the soil. Clay and sandy soil is heavy for a rose bush.
To obtain a light substrate, sand is poured under the bush, the earth is carefully loosened. A little lime will help make the earth crumbly. To enrich the soil, top dressing is applied:
- in the spring they are fed with ammonium nitrate, 30 g of the substance per square of earth, repeat after 15 days;
- organics - manure infusion 1:10, 4 liters of solution are consumed per plant;
- during the period of bud development, the bushes are fertilized with nitrogen.
Before planting seedlings, the soil is loosened to a depth of 70 cm. The quality of the soil and the cultivation of the land affect the formation of buds.
Launched a bush
The reason why the climbing rose does not bloom is the growth in the root zone. In the absence of normalizing pruning, a huge number of shoots grow, they eventually lose their cultural properties, turn into an ordinary game, take most of the nutrients.
Important! Cut off excess shoots at soil level. Use clean, sharp pruning shears.
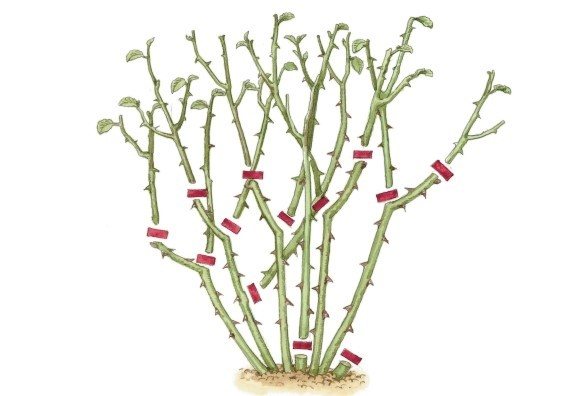

In order not to run the bush, pruning is carried out in the spring. You should not delay with her, the first warm days are a good time to work. First of all, you need to cut out all frozen and damaged shoots, and secondly, those that grow inside the bush.
Shrub pruning can be done in spring, summer and fall. Below are expert tips on how to get the climbing rose to bloom with the right pruning. Additional conditions that guarantee good quality of the bush: use of high-quality garden tools, removal of all buds directed to the center of the bush, oblique cuts, no hemp.
A lot of overgrowth
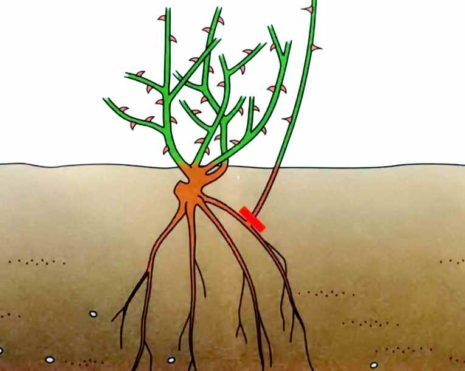

Nutrition is necessary for the growth of stems and new shoots. New root growth begins to develop next to the bush. If you do not cut off all unnecessary branches in time, the plant will turn into a shapeless bush and will start to run wild. The forces will go to the development of greenery, the buds will stop appearing.
Cut off the root shoots near the ground with sharp garden shears. Small branches with thorns and leaves are removed. The formation of a neat bush will help to throw all the resources for flowering.
Pruning the bush in the spring rejuvenates the plant and allows you to increase the number of flowers.Weak, sick, unproductive, as well as the stems growing inside the bush are cut off. Thanks to pruning, the inside of the rose is aired.
Important!
Excessive pruning of the bush leads to improper plant development.
Professional advice


A few simple guidelines will help make your garden beautiful and blooming:
- the difference between a climbing rose and other varieties is that it blooms on last year's shoots, therefore, they must cover the growth for the winter;
- in the second year, many lateral shoots grow, if they are not removed, then in the third year of life the rose will give few flowers;
- the remaining shoots are cut by a third, this procedure awakens the lower buds;
- it is better to lubricate the sections with brilliant green or iodine;
- the formation of the bush is done only after flowering;
- rose loves horse manure, flowering will be abundant;
- if you need to plant bushes against the wall, then this should be the south side;
- in autumn, when pruning, about 5 strong annual shoots are left;
- it is impossible to allow the rose to spread on the ground, if it does not braid the arch, arbor, then it is necessary to make supports for it;
- while working in the garden, when pruning branches, use a sterile tool;
- shoots or buds cannot be broken off, only cut with sharp scissors or pruning shears;
- a plant transplant is done as a last resort, if an unsuccessful place is chosen and the rose does not bloom, it is transplanted in the spring, before the buds awaken, or in September.
In the spring, when the temperature rises to 10 degrees, the shelter is removed. Without fresh air, fungi can develop and the plant becomes sick. Airing on winter days, when the thaw comes, is a must for a climbing rose.
Incorrect cropping
The next possible reason for the lack of flowering is wrong cropping... In the spring, some groups of roses (shrubs, English roses, klaimings) should never be heavily pruned. For them, only a sanitary and light shaping haircut is used, when the tops are shortened to a strong kidney. This is done to encourage branching.
It is not worth trying to form a small bush rose from a tall shrub. By cutting its stems in half (as is sometimes advised), you will significantly postpone the flowering time, since the plant will recover for a long time after this procedure, growing new shoots. But, interestingly, the nature of her growth will remain the same, that is, all the sacrifices will be in vain.
In the summer, in order to force the rose to release new flowering shoots, it is necessary in a timely manner remove wilted flowers... If you live in a country house, it is advisable to do this every day, going out into the garden with a pruner. By neglecting this rule, you will not wait for re-flowering.
Faded buds are cut off immediately. Photo by the author
In addition, all the so-called "blind" shoots that have not released buds must be shortened (certainly by a strong bud) by about half, thereby prompting the rose to branch. This technique allows you to achieve flowering. But this is all provided that the plant is healthy and receives enough sunlight and nutrition.
Another nuance: if for some reason in the spring you (did not know, did not notice or were simply too lazy) did not remove thin and unproductive shoots growing inside the bush or close to the ground, which will never bloom, remove them in the summer. An important rule of English flower growers applies here: there should not be shoots thinner than an ordinary pencil on a rose bush. The rose, freed from them, will concentrate on the flowering of the main ones.
Removed unproductive shoots. Photo of the author You can find out about all the intricacies of pruning roses of different types in the Pruning Academy of our website. Take a look at Lesson 7. Pruning roses.
Climbing roses in landscape design: photo
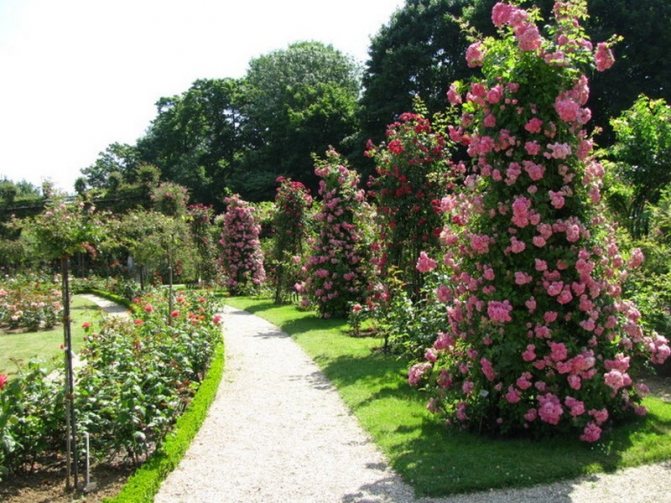


Flower pyramids along the garden alley
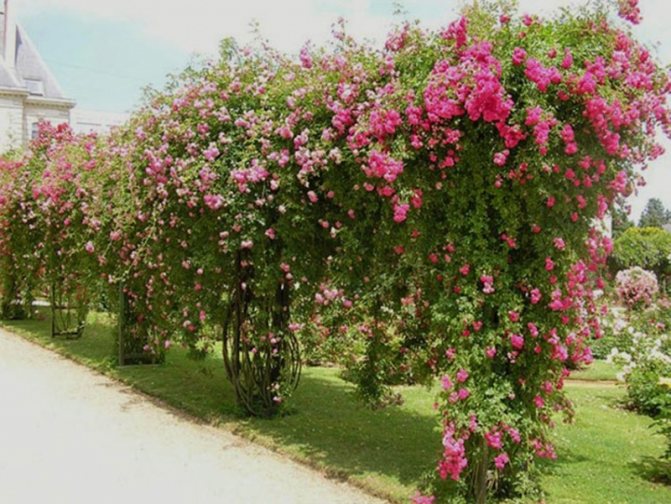


Living vases
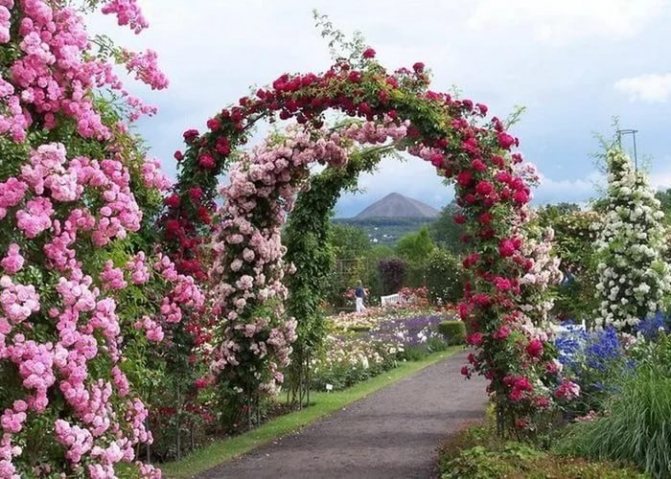


High arch made of climbing roses
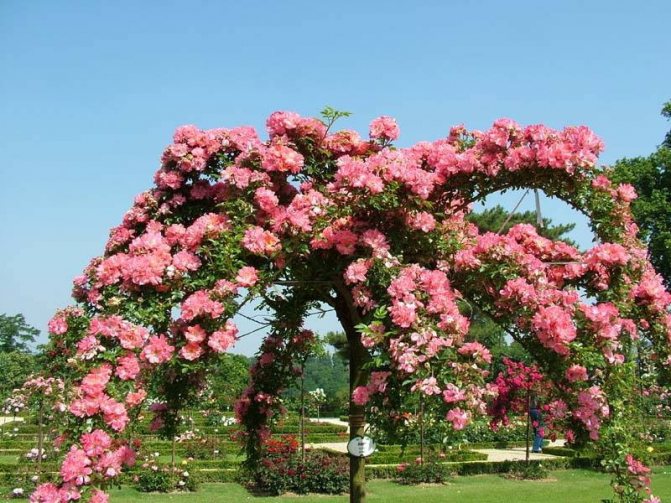


Extraordinary beauty design
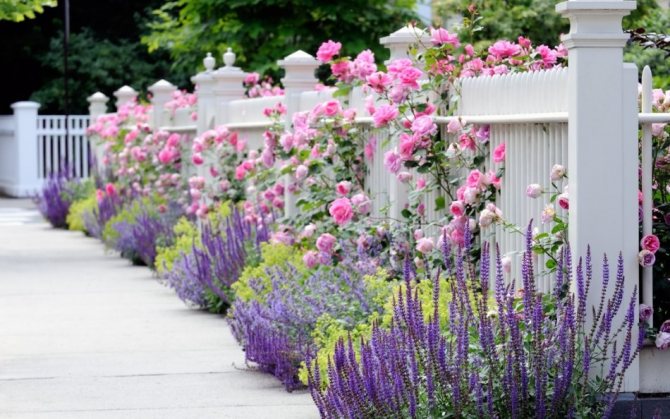


Gentle Polka in the interior of the site
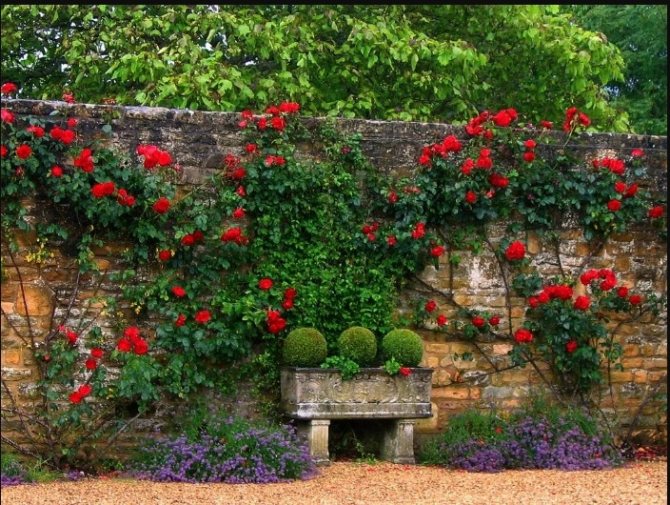


Unusual design of a garden wall with fresh flowers
Thanks to the huge assortment of climbing rose varieties, having organized the appropriate care, you can change the decorative decoration of your site beyond recognition until late autumn.
When will the roses bloom?


Cuttings of roses will take root securely when about 2 months have passed. I transplant them to an open bed protected from the wind and bright sun, but already open (in the "school"). They are still small to plant them in a flower garden: there is no special beauty yet, and other plants, larger ones, will interfere with their development.
The grown roses from cuttings will bloom at the end of August. True, there will be a little color, but still there is reason to rejoice. Important: cuttings of roses need to be planted in April, since May roses can bloom in autumn, and before wintering, the bushes will be weakened, and this is the risk that they will not survive the winter.
Roses from cuttings, planted in April, also not all survive. About 1/3 of all cuttings are rooted in me. But these are cuttings - you can plant more of them.






















