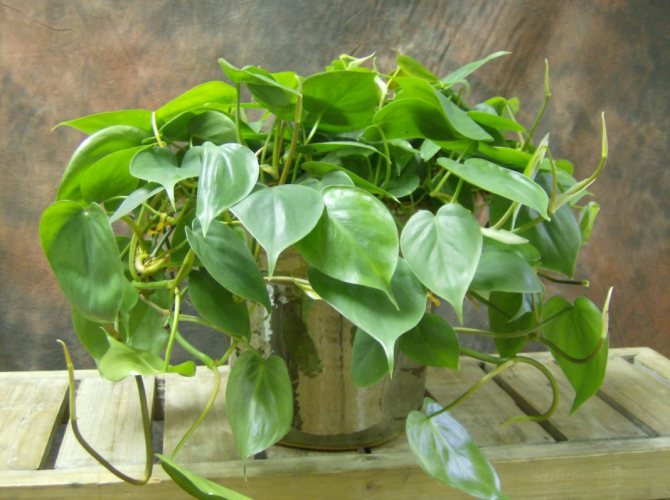
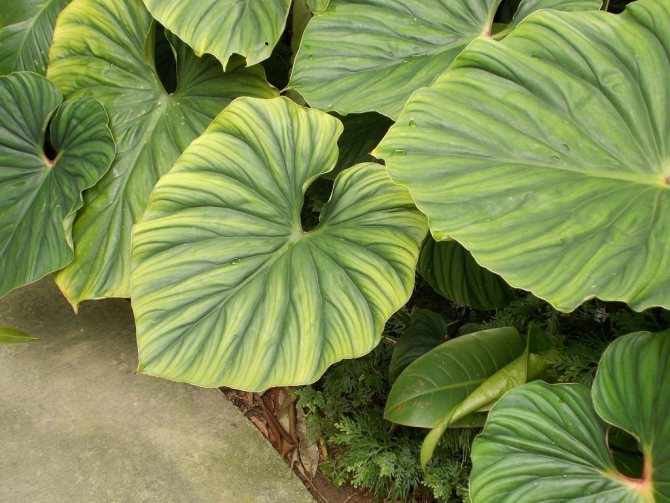
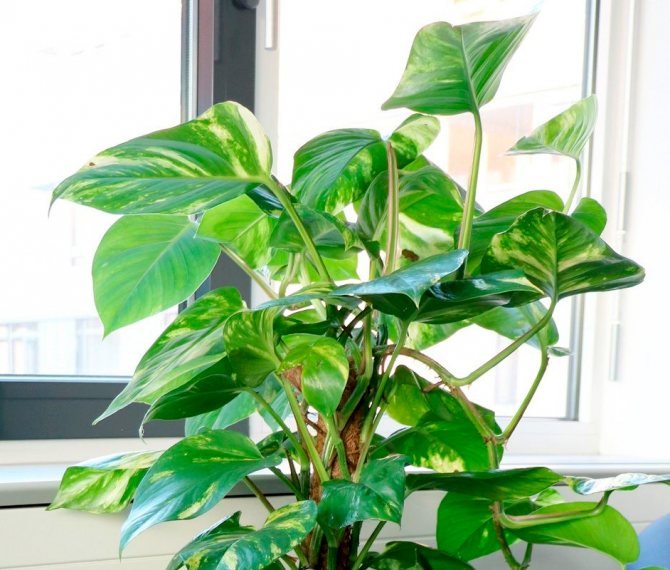
Scientists have discovered a huge variety of species of this plant - about nine hundred.
Philodendron is ideal for growing in an apartment, as it is very unpretentious. Undoubtedly, it is precisely the fact that it does not require much maintenance for itself that is the most significant plus in favor of introducing this plant in your home.
In their natural environment, these plants grow in warm, tropical climates, in places such as Central and South America, Australia, and the Pacific Islands.
They can be found in swamps, warm jungles, along river banks. They need support on another tree, even the very name of this plant from Greek means “I love the tree”. Philodendrons love warmth and quickly become accustomed to hot temperatures while maintaining the right humidity. For the plant to be lush and beautiful, it is worth taking care of lighting - philodendrons do not like direct sunlight, for favorable growth and development they need diffused sunlight and moisture.
Philodendrons include shrubs, epiphytic, terrestrial forms, as well as lianas. The root system is branched, as a rule, air roots appear to absorb moisture and nutrients from the air. The peculiarity of these plants is the change in leaf shape with age.
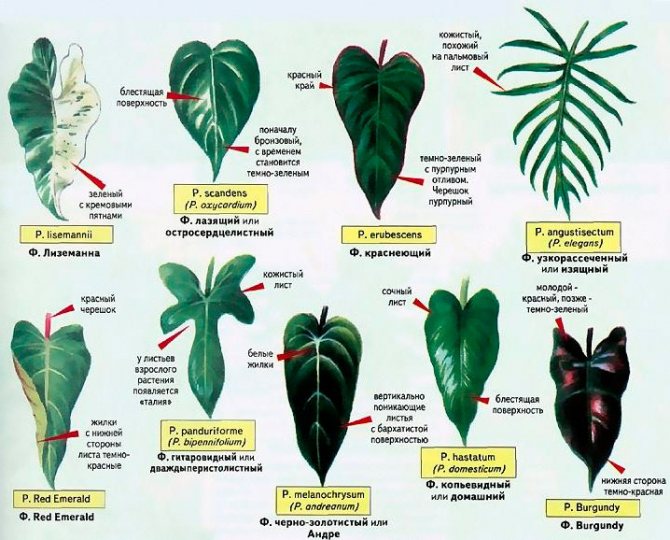
3.Types of Philodendron:
3.1. Philodendron elegant - Philodendron elegans
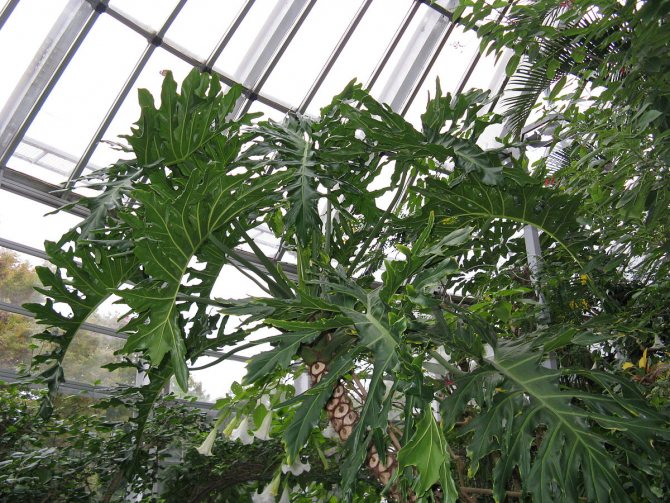
A large, powerful liana with a flexible stem that rarely gives off lateral shoots. Differs in large, glossy, green, pinnately dissected leaves up to 45 cm long. Very airy plant.
↑ Up,
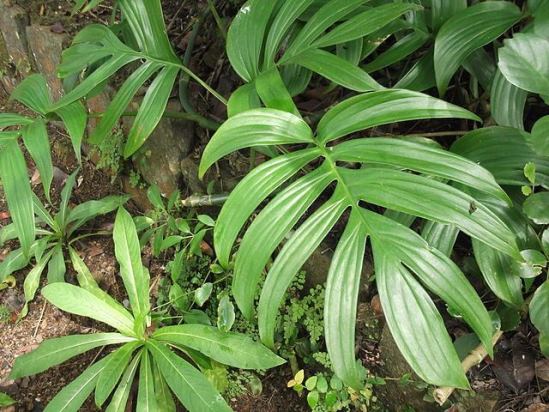

3.2.Philodendron guitar-shaped - Philodendron panduriforme
Leaves of this species are able to change shape with age. Young leaves are simple, heart-shaped, large and have a beautiful shape, reminiscent of a guitar.
↑ Up,
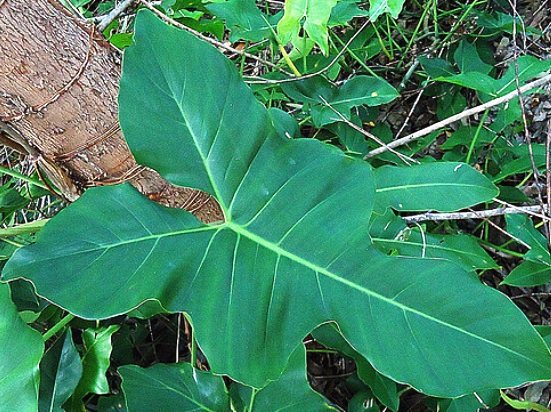


3.3 Philodendron climbing or scandens - Philodendron scandens
A graceful liana with thin, non-branching shoots. The leaves are cordate. There are varieties with variegated leaves with contrasting stripes.
↑ Up,
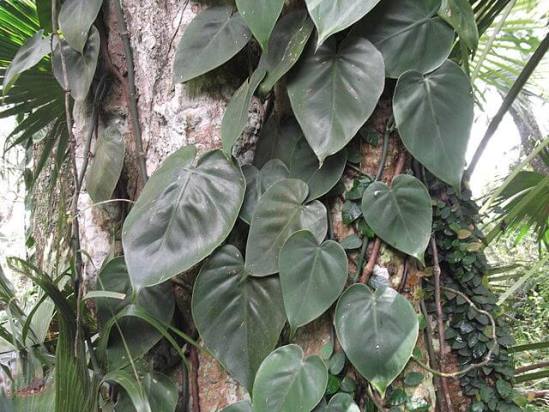


3.4 Phylodendron Brasil - Pfilodendron Scandens Brasil
Decorative-leaved vine with heart-shaped glossy leaves on short stalks, colored green with yellow stripes of varying thickness.
↑ Up,
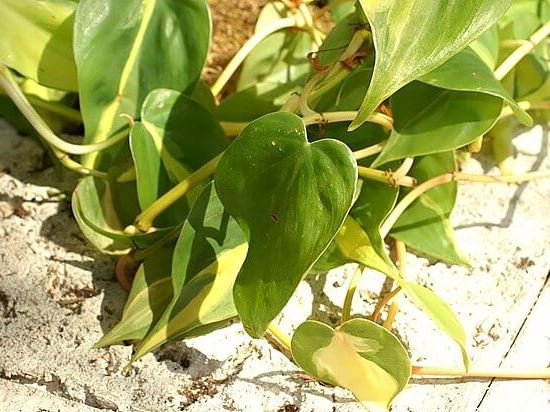


3.5 Philodendron blushing - Philodendron erubescens
Liana, which has young leaves, leaf petioles have a red tint. One of the few species that bloom indoors. The flowering resembles a calla - a thin cylindrical spike consisting of small white flowers surrounded by a large bright red blanket.
↑ Up,
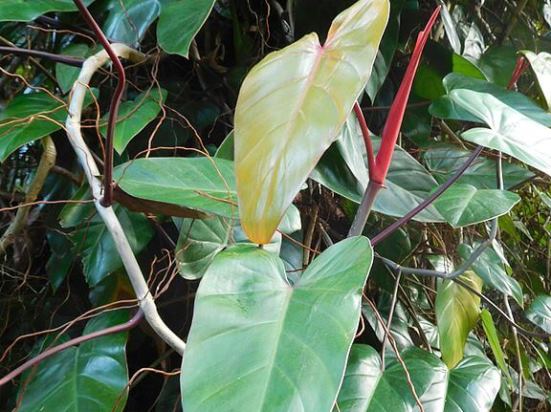


3.6. Philodendron Sello or bipinnate - Philodendron selloum
A large openwork plant with large carved leaves, somewhat reminiscent of a monster. With age, this species forms a trunk and reaches 3 m in height, so a spacious room is required for its cultivation.
↑ Up,
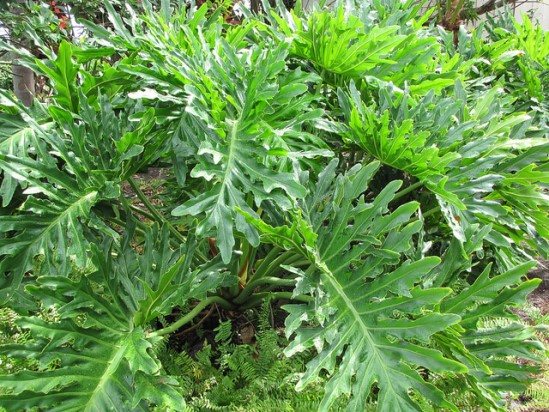


3.7 Philodendron Xanadu
Despite the external resemblance to the philodendron, Sello differs in more compact size - it does not exceed a height of 1.2 m and a width of 1.5 m. The leaves are glossy, dark green, deeply cut, each can consist of 15 - 20 "fingers". An interesting feature of the plant is that the base of the petiole of each leaf is wrapped in another hard, light green, belt-like leaf about 10 cm long, which falls off over time. When damaged, the leaves of this philodendron give off a pleasant coniferous aroma.
↑ Up,
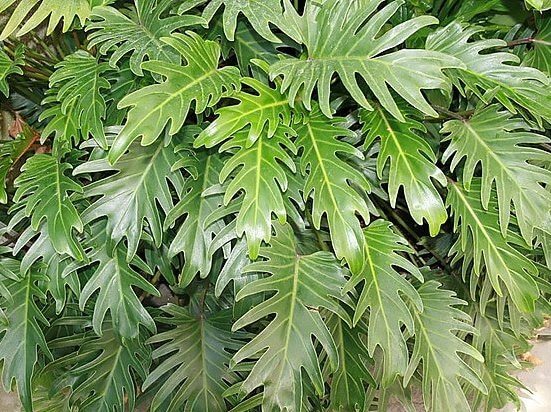


3.8.Philodendron ivy - Philodendron hederaceum
A rather compact climbing plant with dark green, glossy, cordate leaves on short petioles. In length, the stems of plants reach 3 - 6 m. Young leaves often have a bronze or brown tint.
↑ Up,
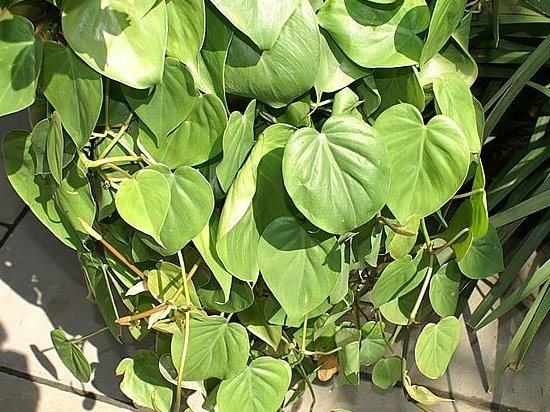


3.9. Phylodendron cordate - Philodendron сordatum
An evergreen vine with long, powerful shoots and heart-shaped glossy green leaves.
↑ Up,
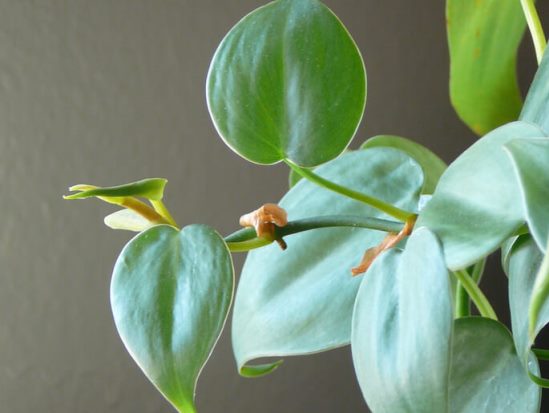


3.10 Philodendron Princess pink
A unique decorative leafy plant with large glossy, dark green leaves, which darken with age and are covered with spots and pink stripes of various shapes. Young leaves are brown. Plants form a small, thick trunk with age.
↑ Up,
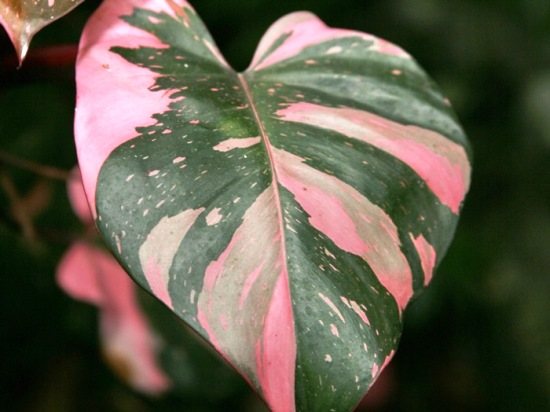


3.11 Philodendron brilliant or mix - Philodendron micans
A beautiful liana with green leaves that are velvety to the touch. Young leaves of a bronze shade with light green veins. A gorgeous plant for hanging baskets.
3.12. Phylodendron warty - Philodendron verrucosum
A large vine with large, dark green, spear-shaped, glossy leaves. An interesting feature of the species is that the leafy branched veins are highlighted in a light green tint. Young leaves are tightly rolled into tubes and have a burgundy-brown tint.
↑ Up,
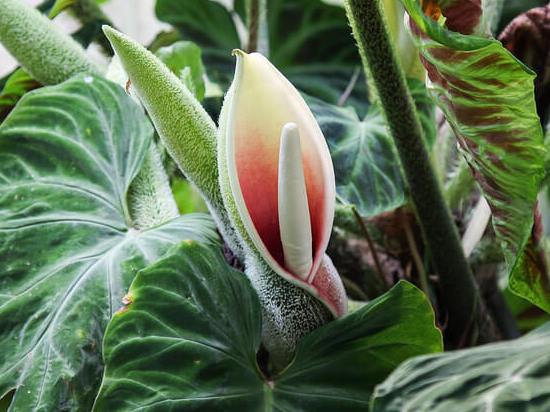


3.13. Phylodendron spear - Philodendron hastatum
A large evergreen vine with bluish green, green, or silvery green leaves in the shape of an elongated spear.
↑ Up,
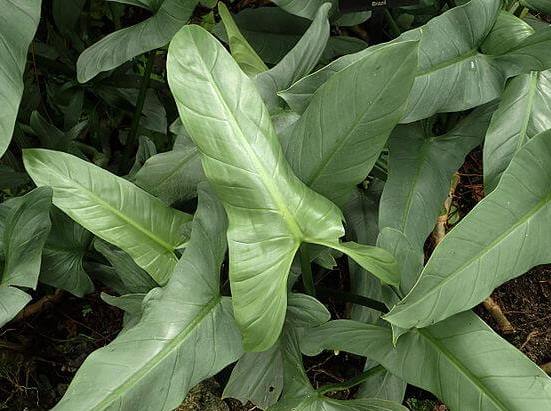


3.14 Philodendron Red Emerald
A valuable evergreen ornamental-leaved plant is a liana with large blue-green leaves. There are variegated varieties with leaves that have white or pink spots and stripes. The leaf petioles are long, ribbed, burgundy. Young leaves are also burgundy.
↑ Up,
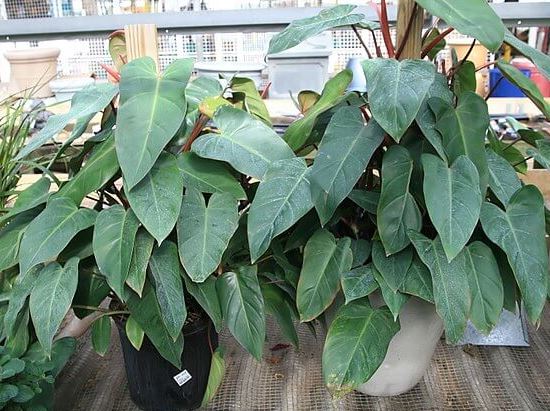


3.15 Philodendron Ornatum - Philodendron ornatum
Ornamental-leaved plant with large heart-shaped dark green leaves on long petioles. Plants with silvery-green or blue-green leaves are often found.
↑ Up,
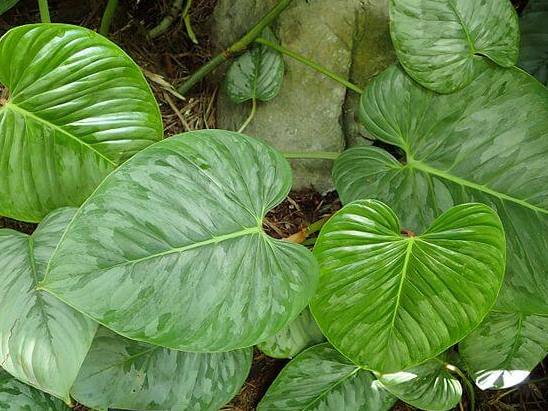


3.16. Philodendron squamiferous - Philodendron squamiferum
An evergreen vine with large, deeply divided, dark green, glossy leaves. Young leaves are simple, whole-edged, and beautiful deep cuts form only with age. The leaf petioles are long, often covered with yellowish or pink scales. With age, the plants form a powerful trunk.
↑ Up,


Description of the plant
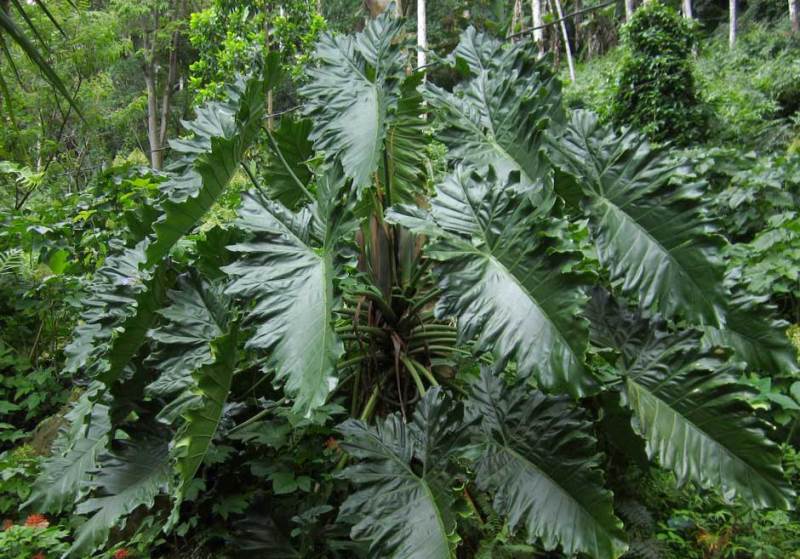


This flower belongs to the Aroid family - an evergreen perennial plant. The genus Philodendrons is large (about 900 plant species, many of which have not yet been fully studied by botanists) and incredibly diverse. In it there are small bushes and real giants, differing in forms, ways of feeding, preferences for living conditions. Most often, in their natural environment, Philodendrons climb up the nearby trees, but there are also epiphytic and semi-epiphytic species that extract moisture and food from the surrounding world (air, dew, sun). If the seeds of Philodendron have sprouted away from trees and other supports, then the shoots will creep along the ground, guided by the shadow, towards the nearest support: to a tree, wall or fence. In natural conditions, the length of the Philodendron vine can reach 200 m.
Philodendrons have both underground and aerial roots. Numerous aerial roots, small and hairy, are used to attach to supports. With long and thick roots, plants absorb moisture and feed themselves.Sometimes such roots make their way under the soil and play the role of a root system there. It is very convenient, especially if the root system is damaged or died.
Appearance
Philodendron's stems are fleshy, woody at the base. There are species that have a rather powerful stem, which allows plants to rise to great heights without support.
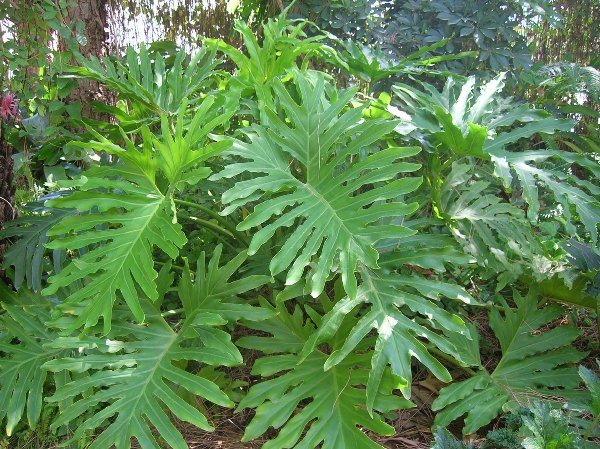


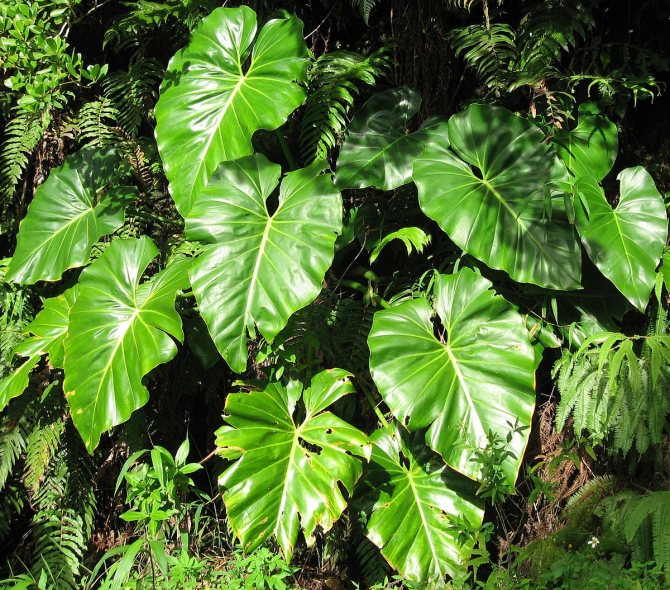
The leaves of the flower are large, shiny, very often carved. One plant may have leaves that are different in shape and size. Scaly leaves (cataphylls) protect the vegetative buds. The main leaves are alternate, petiolate. The length of one such leaf, in some species, reaches two meters, and the width is 90 cm.But other types of Philodendron have more modest leaves in size - only 11 cm.The leaf plates are ovoid, heart-shaped, oval, pinnately dissected or arrow-shaped.
It might be interesting: Syngonium - home care
Young leaves at first look like hearts, and as they grow, they change their shape and size. In addition, as a rule, the color of the upper leaves of the flower is darker than the lower. The color of the leaves is mainly dark green, with the upper side being more intensely colored than the lower. There are species with crimson leaves, but rarely.
Bloom


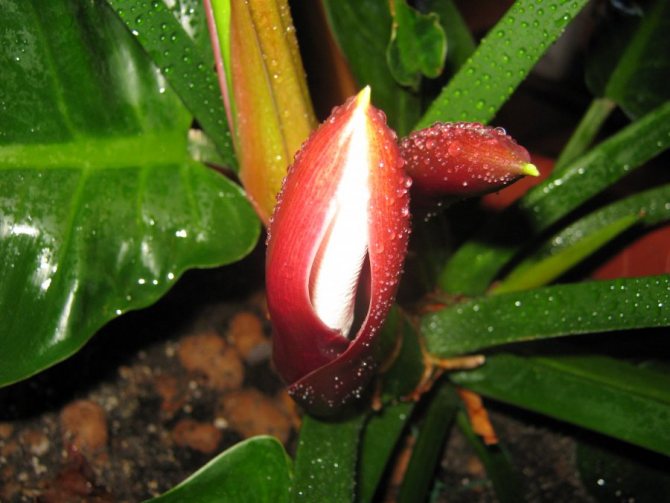
In nature, Philodendrons are flowering plants. They form flowers in the form of cobs with waxy two-colored bedspreads in the form of a hood. The bedspreads are painted in shades of pink, pale green, red and purple. The flowers are bisexual. The fruits are small berries that ripen at different times, depending on the species. Unfortunately, at home, even with extremely comfortable content, Philodendrons rarely bloom.
Philodendron juice is toxic and gloves should be worn when handling it. At the same time, Philodendron belongs to useful plants that have a beneficial effect on the microclimate of the room in which it grows. It releases phytoncides that kill microbes dangerous to humans. NASA has added this flower to the list of air purifying plants.
Diseases and pests
This indoor flower, like most aroids, rarely gets sick and is affected by pests. Weakened plants can be attacked by aphids, scale insects and other sucking insects.
Table: Aroid pest control
| Pest | Signs | Control methods |
| Aphid | Green or black rounded insects. The plant stops growing. |
|
| Shields | On stems and leaves, oval convex tubercles of brown color. In severe cases, they merge into a solid crust, the plant seems to rust. | The treatment of the scale insect on the philodendron is the same as for the defeat by aphids. In combination with Aktara, washing with soapy water is required. |
| Thrips | Oblong winged insects 1–1.5 mm long. On the leaves there are black dots, a sticky coating. |
|
| Spider mite | On the stems and leaves there are thin threads of cobweb. |
|
Reproduction methods
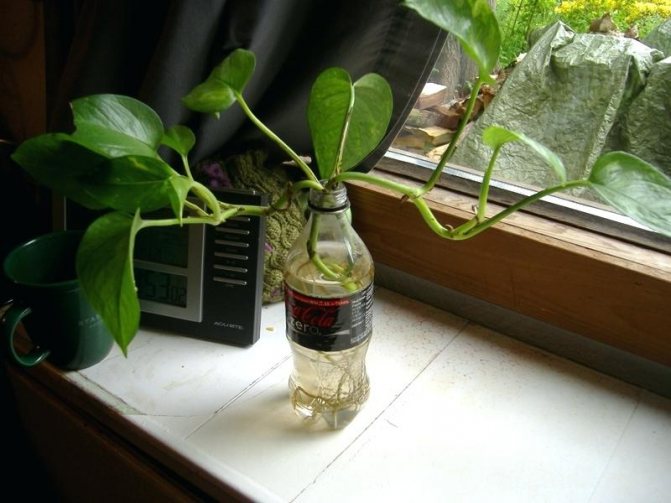
Philodendron propagates very easily by apical or stem shoots, cuttings, air layers. Using an aerial rooted area is the easiest way to root a plant. You can try to propagate by seeds, but this method is more suitable for greenhouse farming.
The best time for philodendron breeding is spring.
Propagation by cuttings and leaves
- Carefully cut off the selected apical or stem shoot with two or more leaves with a sharp knife.
- Sprinkle the sections with crushed activated carbon and leave to dry for several hours.
- Fill small pots with a mixture of peat and sand (instead of sand, you can use perlite) in equal proportions or sphagnum moss and moisten well.
- Press the dried cuttings into the mixture by 3 cm or lay them on top so that the growing point is on top.
- Make a greenhouse out of a plastic bag or glass jar and place in a bright spot. Temperature from 25 ° С to 30 ° С.
- Ventilate the greenhouse briefly and moisten the soil every 2–3 days.
- After a month, you can remove the shelter.
- When the cuttings have roots and 2 young leaves grow, they are transplanted into slightly larger pots and looked after like an adult plant.
Using the same method, you can root a leaf with aerial roots or a piece of heel. If you just cut a leaf, then it will not be possible to root it.
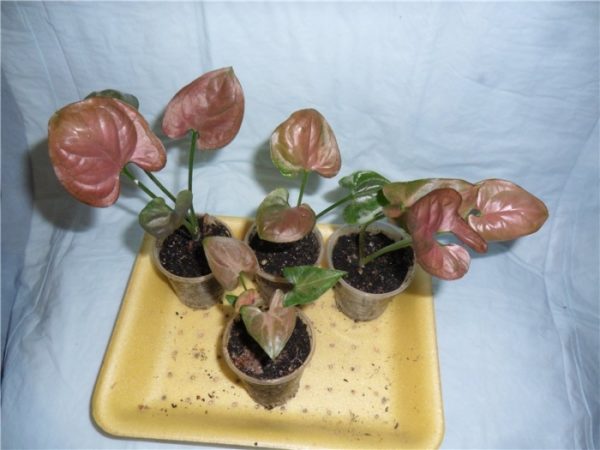


Rooted cuttings of philodendron
A philodendron from which cuttings were cut rejuvenates and gives many new shoots.
Rooting of air layers
It is very easy to propagate a philodendron with air layers. For this climbing philodendron, you need to choose a shoot and lay it on a moistened peat substrate or sphagnum moss in a small pot. You can fix the shoot with a piece of bent wire, or by slightly burying it in the ground. After a month, the cuttings will take root and can be cut off from the mother plant.


You just need to put the shoot on moistened soil and fix
Planting a woody stem
A large plant with a woody trunk is propagated as follows:
- Make small cuts on the stem and sprinkle them with Kornevin.
- Moss the moss and attach to the incisions, wrap cellophane on top and tie.
- The moss must be sealed on all sides. If this has not been achieved, it is sometimes necessary to add water to it to keep it moist.
- When the roots appear (they will be clearly visible through cellophane), the top is cut off and planted in a pot, after removing the bag with peat.
- New shoots will soon appear on the remaining stem.
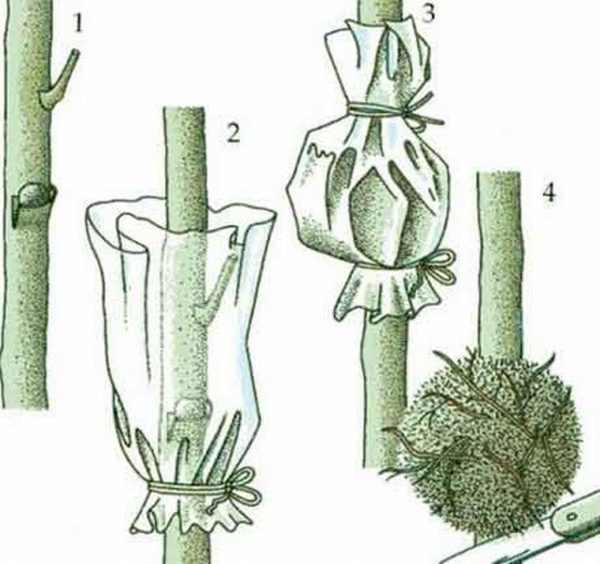

Rooting a woody stem - a method suitable for adult philodendrons
We recommend: Caring for eucharis at home - simple secrets of abundant flowering
Growing from seeds
Treelike forms propagate using seeds. Use only fresh seeds - it is best to purchase them in specialized stores, checking the expiration date.
- The seeds are soaked overnight in distilled water, then planted in a prepared mixture of peat and sand. The seeds must not be covered with soil, they must be on the surface!
- The container with seeds is covered with a bag and placed in a bright place, avoiding direct sunlight. The ideal temperature is not lower than 28 ° C.
- The container is opened when 2-3 leaves appear on the seedlings - after about 7 weeks.
- When the seedlings are 10 weeks old, they can be transplanted into separate pots.
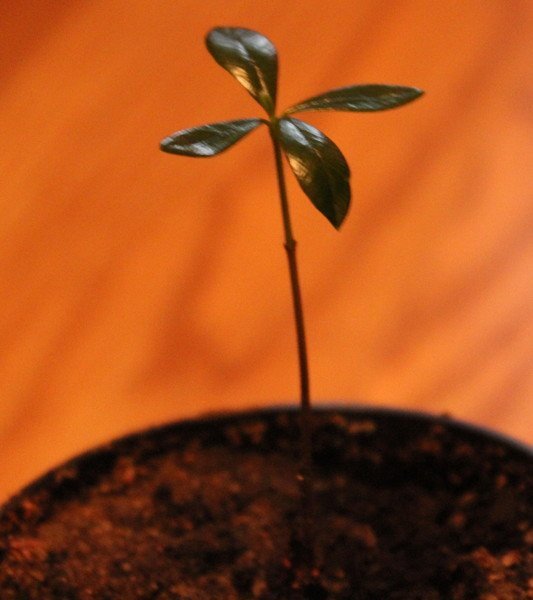


Seed-grown philodendron - rare for home breeding
Almost all types of philodendron root easily in water. But this method is not entirely suitable for a plant, since its root system must adapt to new conditions - the soil substrate.
Table: in what conditions is it better to keep a flower at home
| Period | Temperature | Watering | Humidity | Illumination |
| Autumn winter |
| Moderate, as the earthen coma dries |
| Diffused bright light |
| Spring Summer |
| Abundant and regular | Regular spraying of leaves |
Most types of philodendron tolerate ordinary indoor conditions well, but if you want the plants to show themselves in all their glory, you must adhere to these recommendations.
Care
Despite its unpretentiousness, a tropical guest will delight you with lush greenery and active growth only with proper care. It is uncomplicated.
Watering and humidity
Philodendron grows well in high humidity conditions. Therefore, regular abundant watering is essential, especially in the hot summer period. In winter, the amount of water is reduced by keeping the earthen lump moist, but not flooding.
At any time of the year, the philodendron requires daily spraying. During the heating season and on hot summer days, the pots are additionally placed on pallets with wet expanded clay or moss to prevent dry air.
When and how you can feed a flower
The philodendron does not have a pronounced dormant period, so feeding can be done all year round. In spring and summer, when the rapid growth of young leaves and shoots begins, fertilizers are applied every two weeks. In winter, they are limited to one top dressing per month.
The plant responds best to complex fertilizers with an equal content of the main nutrients - nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. From organic feedings, it is worth giving preference to the infusion of bird droppings or mullein. It is prepared by soaking dry droppings in an equal amount of water by weight for a week. The fermented mixture is diluted with clean water in a ratio of 1:10. Fertilizers are applied only in liquid form and after watering, so as not to burn the delicate roots.
Do not abuse drugs with a high nitrogen content, otherwise philodendrons will begin to develop rapidly, and the windowsill will simply become cramped for them.
Table: Home Care Mistakes and Ways to Overcome Them
| Problem | Cause | Decision |
| Leaves turn yellow and fall |
|
|
| Philodendron does not grow |
|
|
| The tips of the leaves dry | The room humidity is too low. |
|
| Black or brown spots on the leaves |
|
|
| Drooping foliage | The flower does not have enough moisture. | Adjust the frequency and volume of watering. The soil in the pot must be kept moist at all times. |
| Quite large transparent drops appear on the leaves | This is a natural process for removing excess moisture. Philodendrons "cry" in high humidity indoors, as well as when the weather changes before rain. | You don't need to do anything.Drops on the leaves do not harm the plant in any way. |
| Stalks rot | A combination of abundant watering and low temperatures, usually in winter. |
|