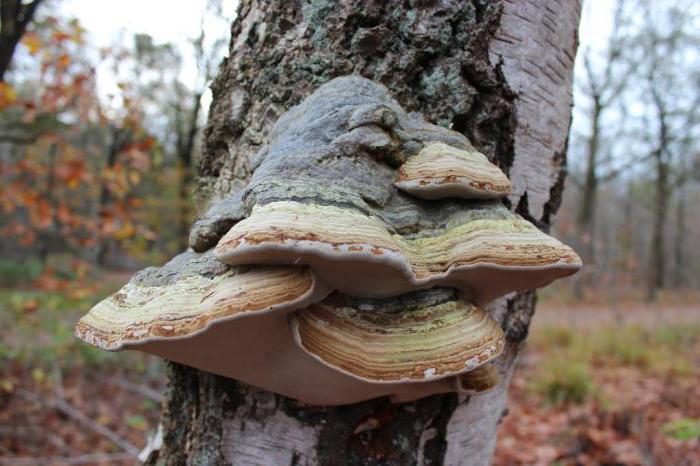
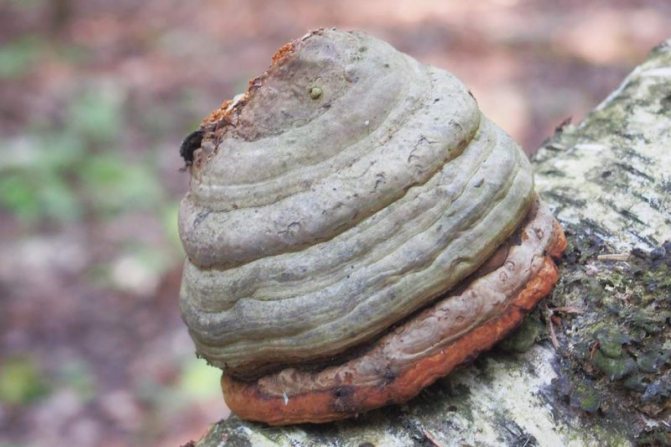
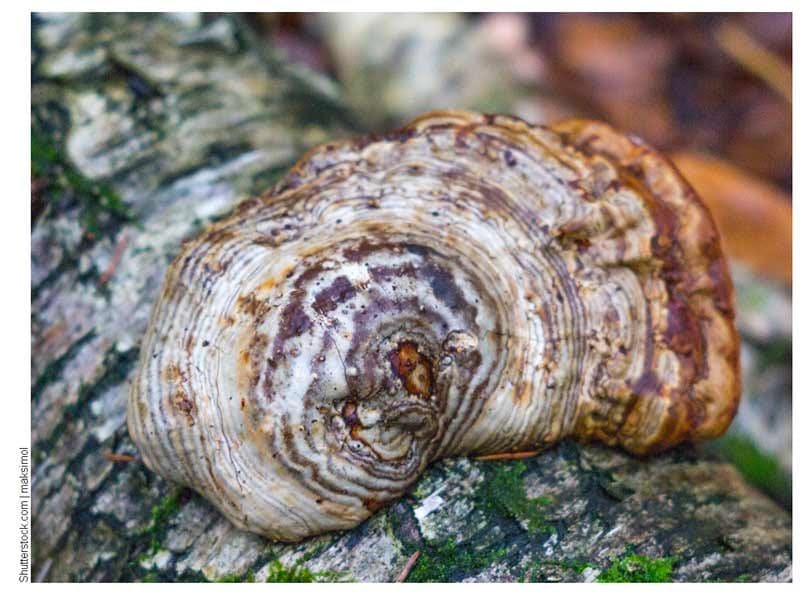
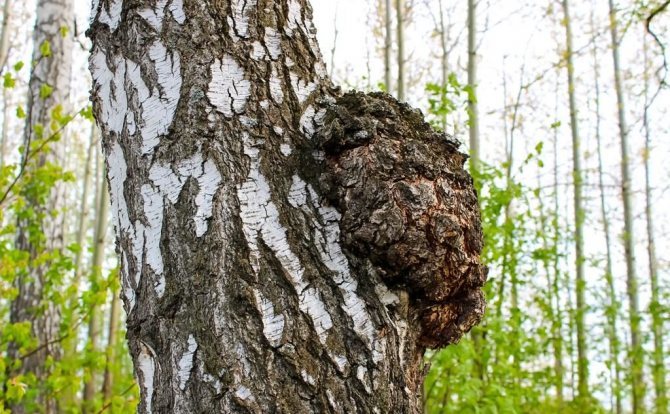
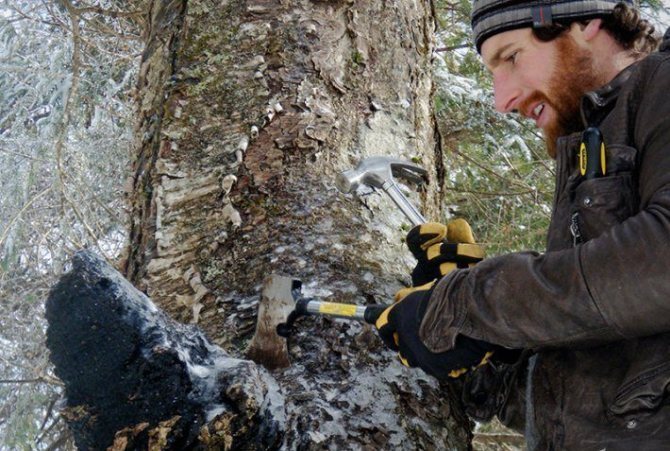
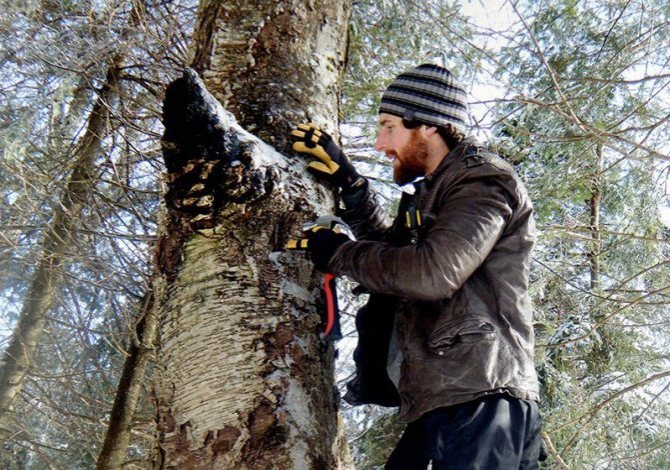
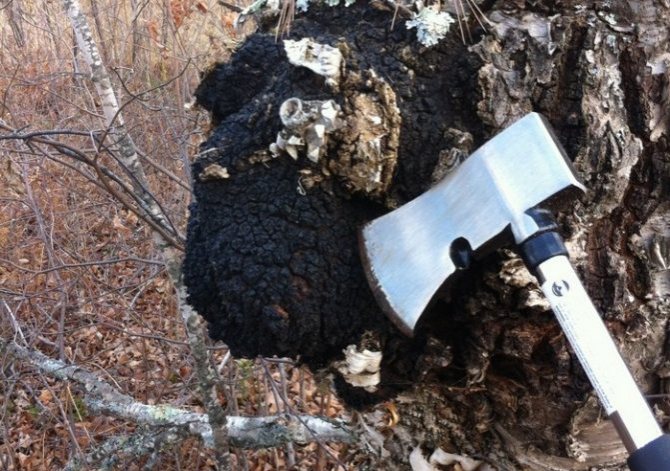
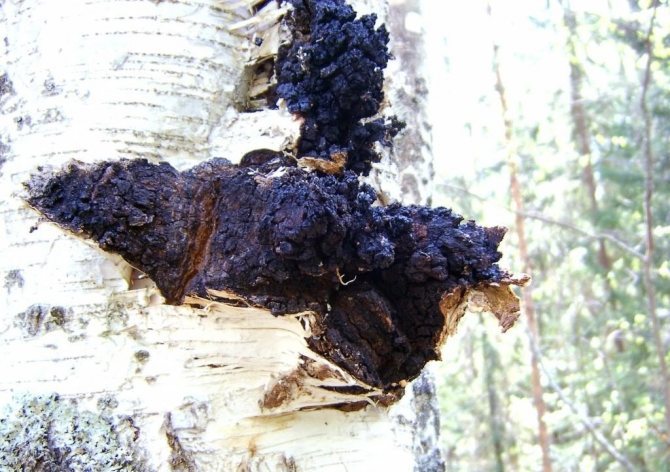
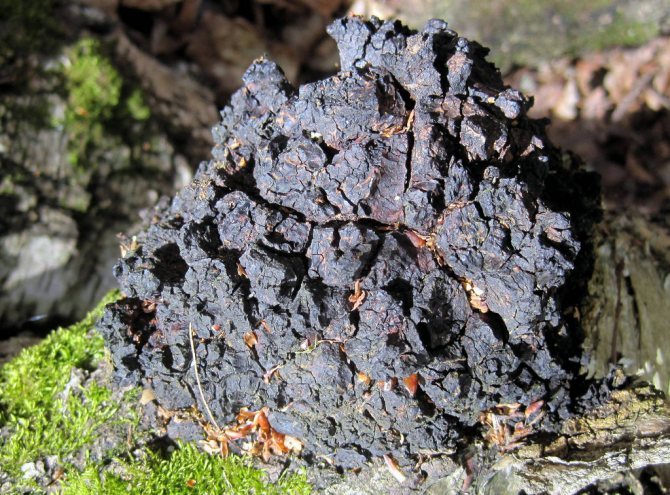
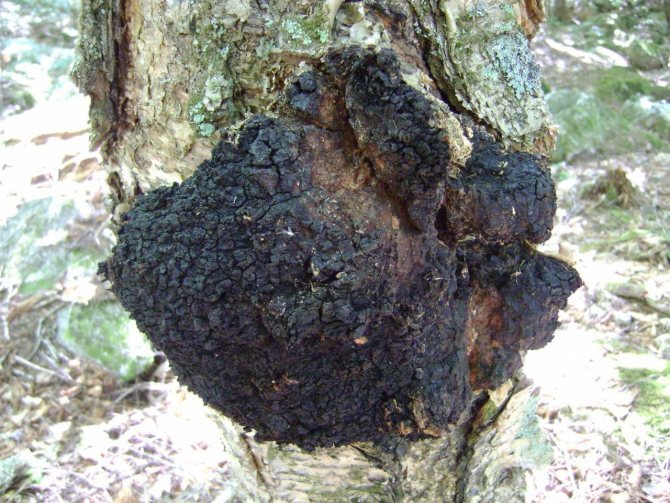
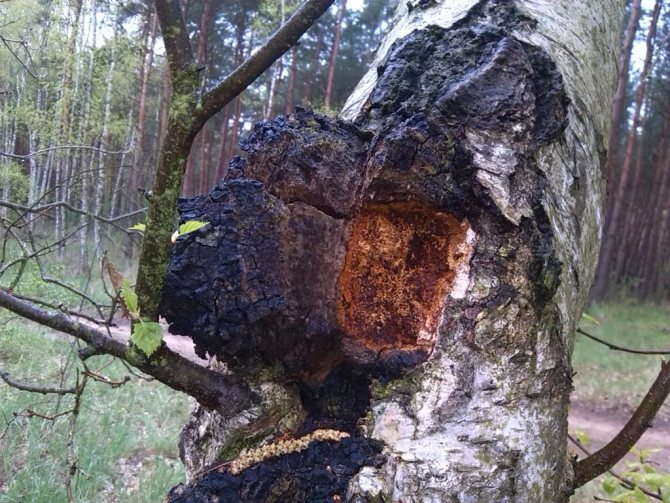
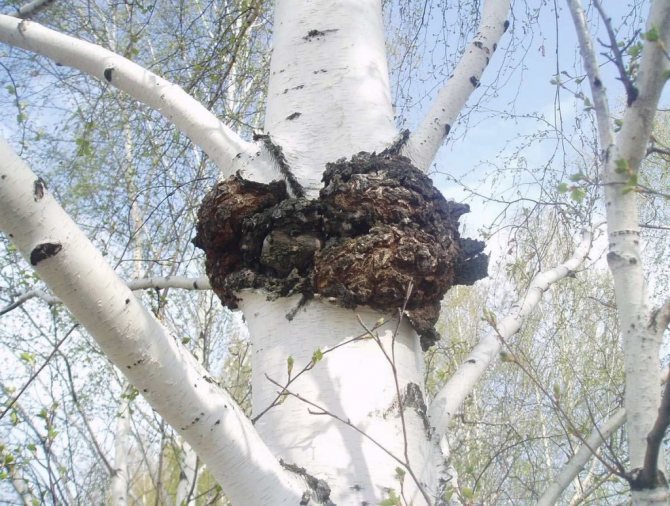
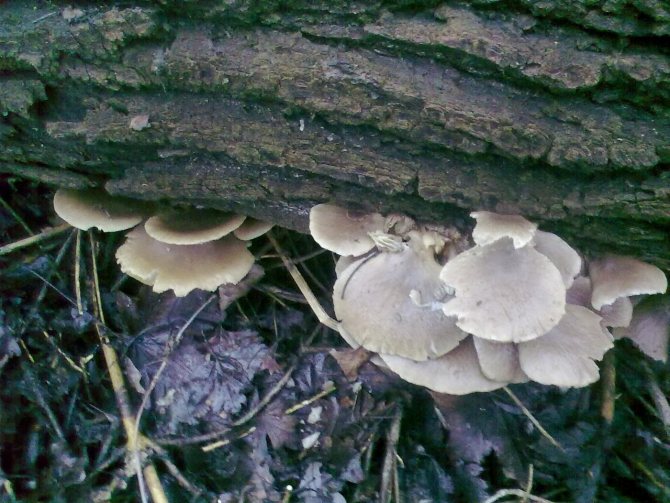
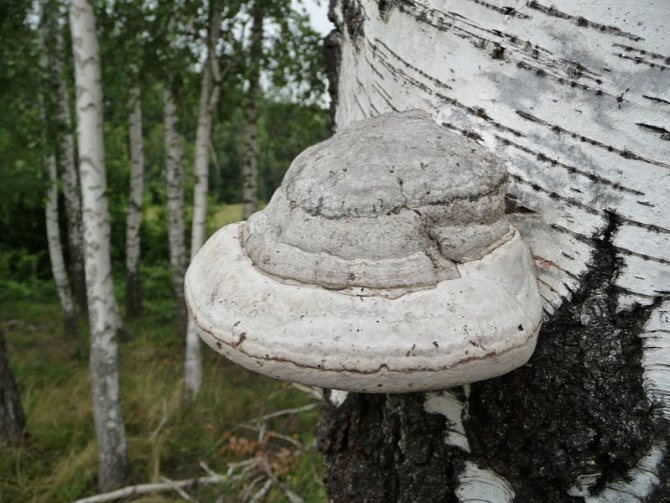
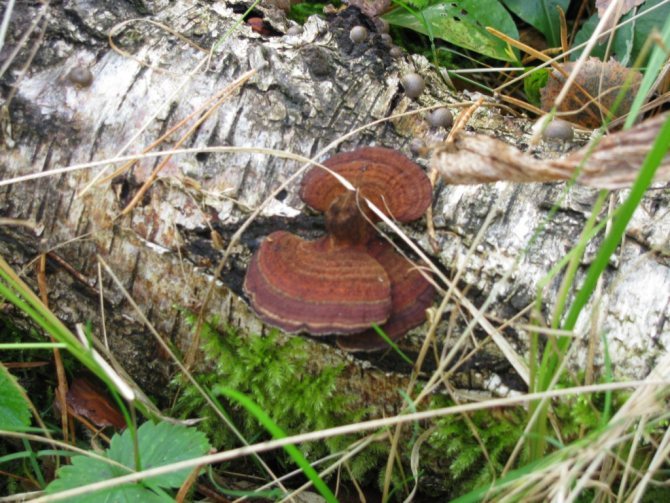
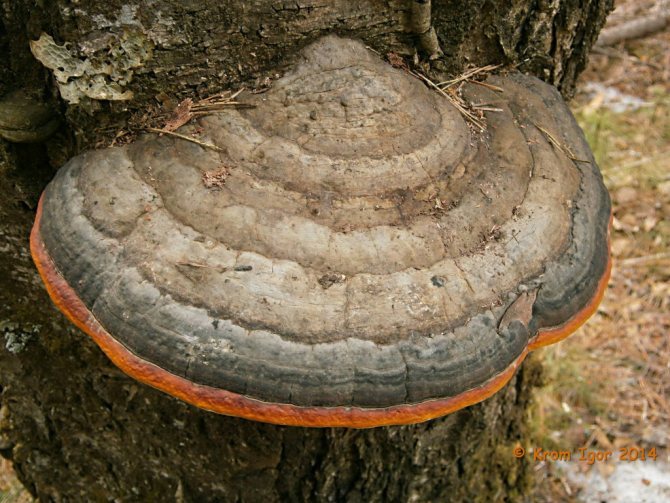
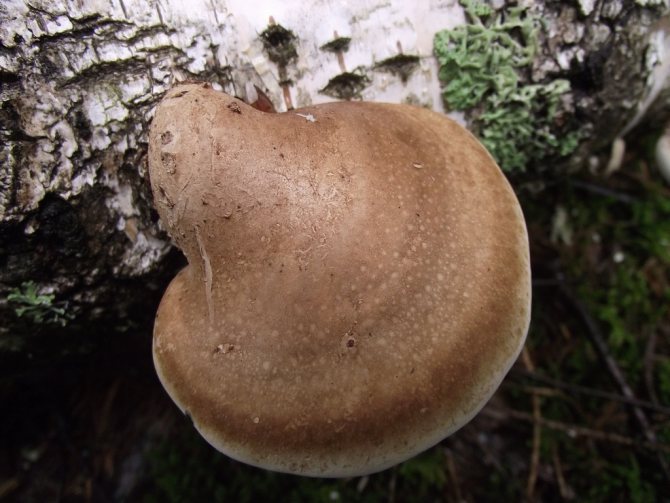
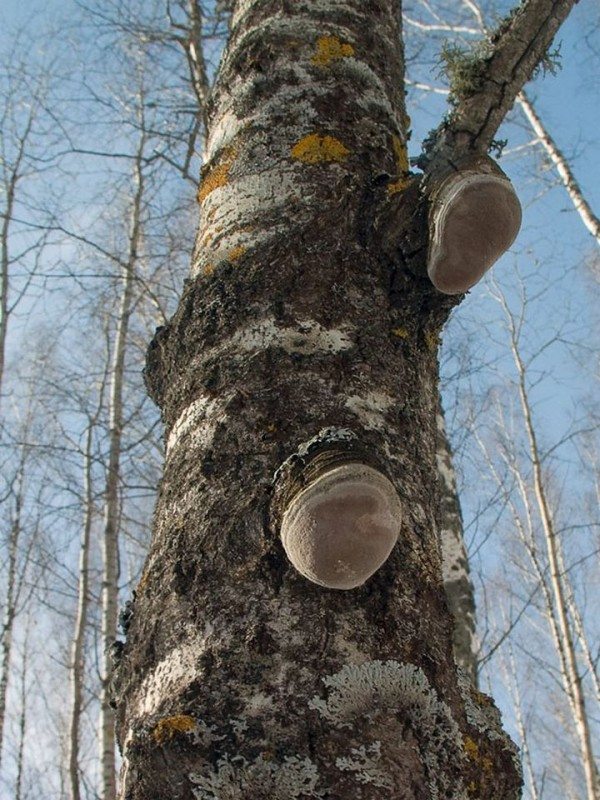
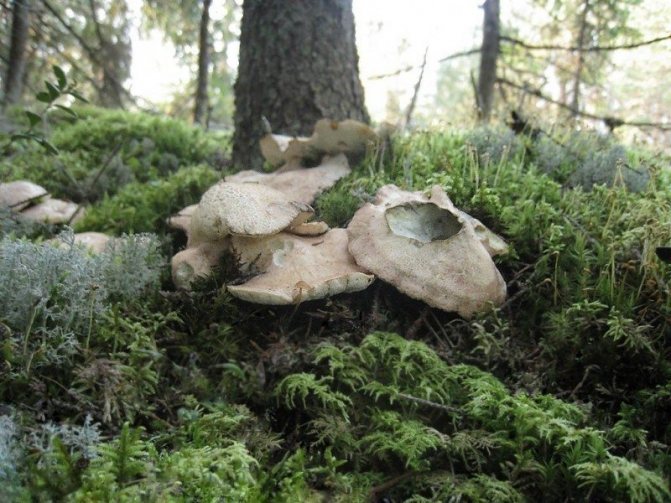
Chaga, or birch mushroom, is a sterile form of mown tinder fungus. Most often it appears on birches, which is why it got its name. In rare cases, you can find it on other trees, for example, on mountain ash, maple or alder.
The sterile form of the fungus is widely used in medicine as an antiblastoma and protivogastritis agent. The chaga mushroom has a peculiar appearance, therefore, after reading the description and looking at its photo, you can easily identify it on the tree.
Characteristics of the birch chaga mushroom
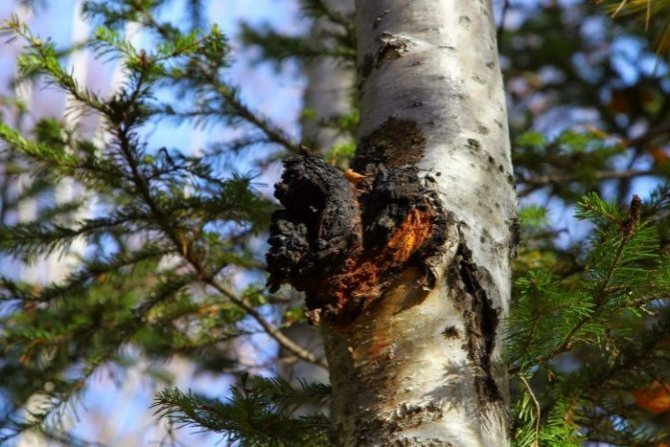

Chaga appears as a result of infection of a tree with a parasitic fungus. Its spores germinate when they fall on damaged areas of tree bark. Infection is accompanied by white heart rot of wood. Initially, light yellow spots and stripes appear in the false nucleus, which gradually expand and merge. A light brown protective zone appears around the rot, black lines are located inside, and rusty-brown inclusions of mycelium are visible on the fracture. The fruiting body of the fungus appears 3-4 years after infection in the form of an irregular growth, after 20-30 years it reaches 40 cm in diameter, and the thickness is 10-15 cm. The shape of the growth depends on the nature of the damage. The surface is black and cracked. Inside, the growth is painted in a dark brown color, closer to the wood in reddish brown, it is penetrated with white veins. The growth of the fungus leads to the death of the host tree. When the tree dies, a spore-bearing fruiting body of the fungus develops around the growth, which consists of comb-like outgrowths. They break through the bark of a tree.
Features and main varieties
There are a huge number of varieties of tinder fungus and most of them are inedible. The following subspecies of the main representative are known:
- reishi mushroom;
- flat;
- umbrella;
- winter;
- birch;
- radiant;
- scaly;
- multicolored.
Of all this variety, umbellate and sulfur-yellow are considered edible.
The umbrella subspecies is similar to oyster mushrooms. They are mainly salted, pickled, dried, sometimes they are also consumed even fresh. Vegetarians do not disdain them either.


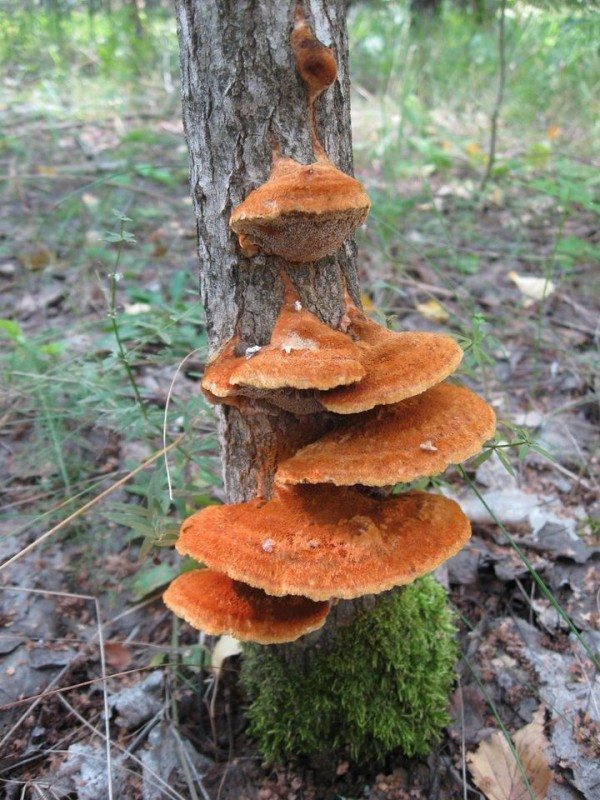
The most common edible subspecies is sulfur-yellow. They eat it only cooked. In terms of its composition, it is quite capable of replacing meat. It grows on tree trunks close to the ground. The flesh of the sulfur-yellow mushroom is white, sourish in taste.
Mushroom pickers often hear the Reishi mushroom, which is also called "varnished". This fruiting body is inedible, but it is often used in cosmetology. Good effect on the growth of nails, had a beneficial effect on the skin. When using cosmetics containing reishi mushroom, the skin is cleansed, acne breakouts disappear.
The Reishi's hat is smooth to the touch, similar to a varnished surface. Hence the name of the mushroom. The color of the cap can be from red to almost black. This fruit body takes all the nutrients from the trunk of the birch, thereby destroying the cells of the tree. Therefore, those trees on which tinder fungi have settled, unfortunately, will certainly die in the end. Gradually, the birches on which this type of fruit body grows turn into dust, since in the place where it grows, the birch becomes infected with red rot.
The use of lacquered tinder fungus in pharmacology
In this way, trees that have turned to dust make room for new, young and healthy trees to grow.But we must note the fact that the tinder fungus settles only on sick or dry birches. Therefore, he can most likely be called a forest orderly.
Spores penetrate into cracks or faults, the tinder fungus begins to grow and the birch is immediately doomed, if not in a hurry, but still death. While this unique organism is still quite young, it has smooth roundish shapes, but as it grows, it takes on a completely different, more intricate shape. The body becomes like an inverted deep plate. His mycelium is inside the tree.
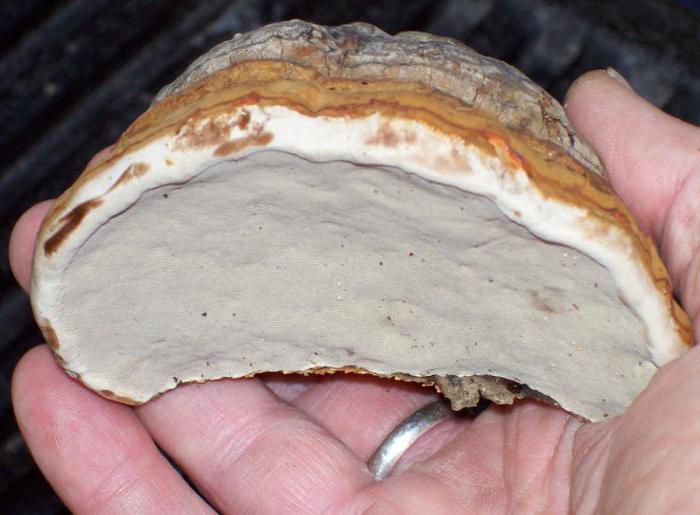
The color of the mushroom also changes as it matures. At first it is light, almost white, but over time it turns brownish. The body of the fungus itself consists of several layers. The top layer is hard, dark brown colored, the surface is uneven: convex in places, concave in places. Over time, the top surface of the mushroom can crack. The middle layer is porous and resembles a sponge. Initially, it is light and soft, but very quickly darkens and hardens, resembling a cork. The inner layer is reddish brown with light veins.
When chaga birch appears
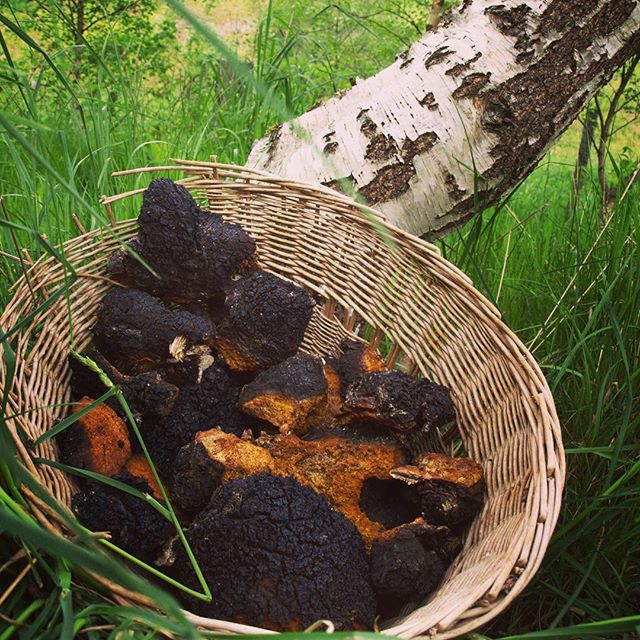
As a medicinal raw material, fruit outgrowths and spore-bearing bodies of birch chaga are harvested throughout the year, but most actively in late autumn, winter or early spring, when there are no leaves on the trees and the fungus is easier to notice. Chaga is chopped down with an ax near the tree trunk, the loose, light-colored part that is not suitable for use is cleaned, the remains of bark and wood are removed, and the mushroom is divided into pieces. Chaga is dried in air or at a temperature not exceeding 60 ° C in dryers. The dried mushroom is stored in a glass, tightly sealed container, protected from light for up to 2 years.
Oyster mushroom varieties: oyster, horn-shaped, pulmonary, late
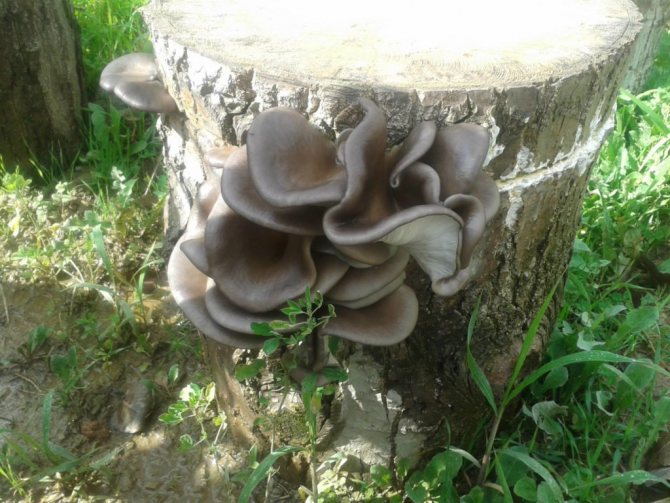
Connoisseurs confidently fill the baskets with yet another tasty trophy. These are mushrooms on a stump, the name of which is oyster mushrooms, and they are very popular with mushroom pickers. Oyster mushrooms can be grown in the forest or grown on an industrial scale. These mushrooms are subdivided into several types:
- Oyster mushroom, common. Their fruiting bodies are in close contact with each other and line up in several floors. The legs are very short, and the caps are usually dark gray or brown. There are colonies of light beige mushrooms. The name hints at the similarity of the mushroom family to a large oyster colony. The fungus is resistant to cold weather.
- Oyster mushroom horn-shaped. These mushrooms grow on stumps in large colonies, like honey mushrooms. They are distinguished by a long leg, located off the center of the cap. The color is always light, golden or beige. The plates under the cap go over to the leg and look like jumpers. The species is not often used for cultivation. The fungus does not tolerate cold well, and the fruiting period is shorter.
- Oyster mushroom. The family forms a large cluster of fruit bodies. The legs of these edible mushrooms growing on stumps are short, located closer to the edge of the cap. Oyster mushroom has the most delicate pulp, and besides, it is quite elastic.
- Oyster mushroom late. This mushroom is very different from other types of oyster mushrooms. It has a layer under the cap that is soft, like gelatin. Color - greenish brown or light brown. The plates are only under the cap, they do not go to the leg. But the taste of the mushroom is not very pleasant. It leaves a bitter aftertaste and a rubbery pulp. But even these oyster mushrooms have their own lovers.
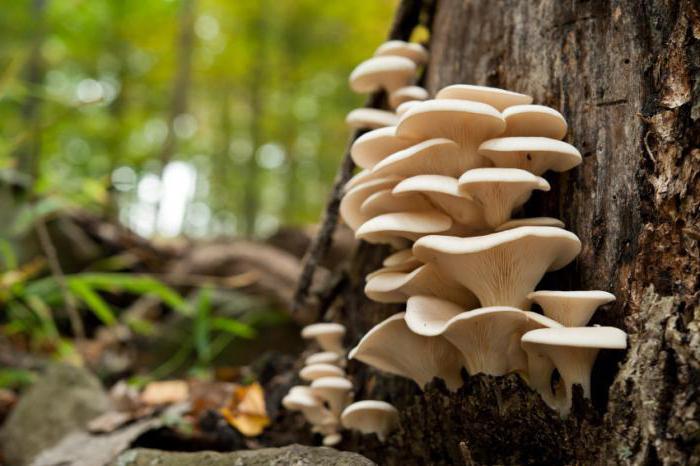


On special farms and even in summer cottages, oyster mushrooms on stumps give a stable harvest until the onset of frost. In the cold season, stumps can be moved to equipped rooms. And on an industrial scale, oyster mushrooms are grown in a special substrate.
Contraindications and possible harm
Chaga has practically no contraindications. The composition of this mushroom does not contain substances that pose a serious threat to human health. But in some cases, after taking chaga, you may experience:
- bowel disorder (mushroom-based medicines act as a laxative);
- overload and excessive excitement of the nervous system (with prolonged use of decoctions and tinctures);
- individual allergic reaction (if a person is sick with hay fever and atopic dermatitis).
Medicines containing chaga are not recommended for use when:
- problems with the nervous system;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- the use of antibacterial drugs;
- internal administration of glucose;
- chronic colitis and dysentery;
- drinking and smoking.
When treating chaga, one should minimize the amount of fried and fatty foods in the diet.
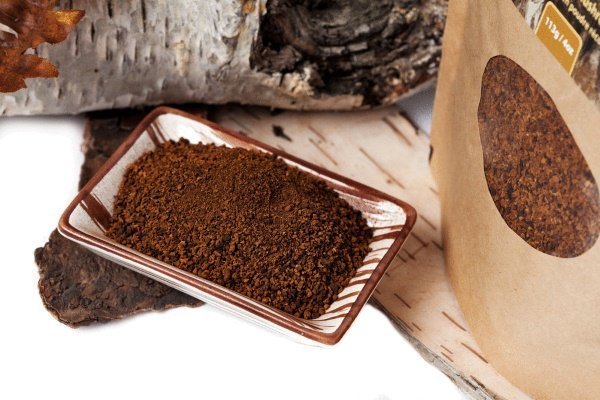


Chaga is a mushroom with a large number of beneficial substances for human health. But if used incorrectly, the effect of its reception will be minimal. Therefore, before using chaga for treatment, it is necessary to study in detail the instructions for preparing medicines based on it, and consult with specialists.
0
Food in the forest. 1.1.3. Tree mushrooms - polypores


Table of contents:
General characteristics of wood-destroying fungi
Oyster mushrooms Other types of woody fungi Lamellar parasitic mushrooms - mushrooms Wood-destroying fungi of the genus scale scales and hyphalomas, false (poisonous) mushrooms Real wood polypores Growth characteristics and age-related changes in polypores
General characteristics of wood-destroying fungi
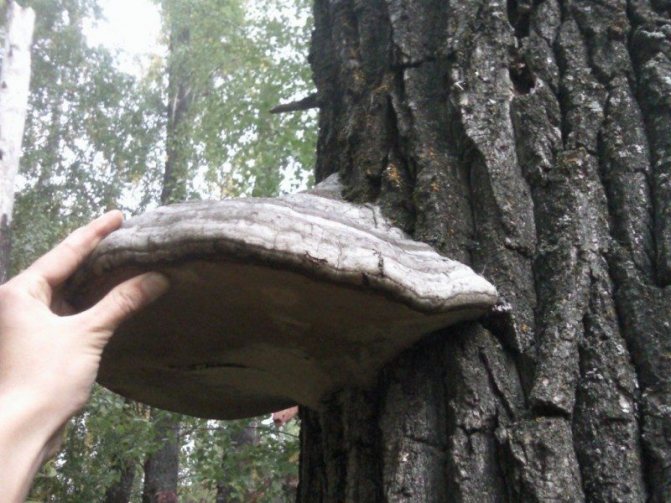


Polypores are macromycete fungi that grow on trees and often kill the host tree. With this word, a stereotype immediately pops up: a kind of a canopy on a tree. In fact, tinder fungi are very diverse, there are more than 600 species. This is not a taxonomic group - this includes members of different families of the class basidiomycetesthat have a different appearance and are united by only one common ecological feature: they are all wood-destroying xylotrophs, feeding on dead or living wood, in the latter case, parasitizing on the tree and eating its owner.
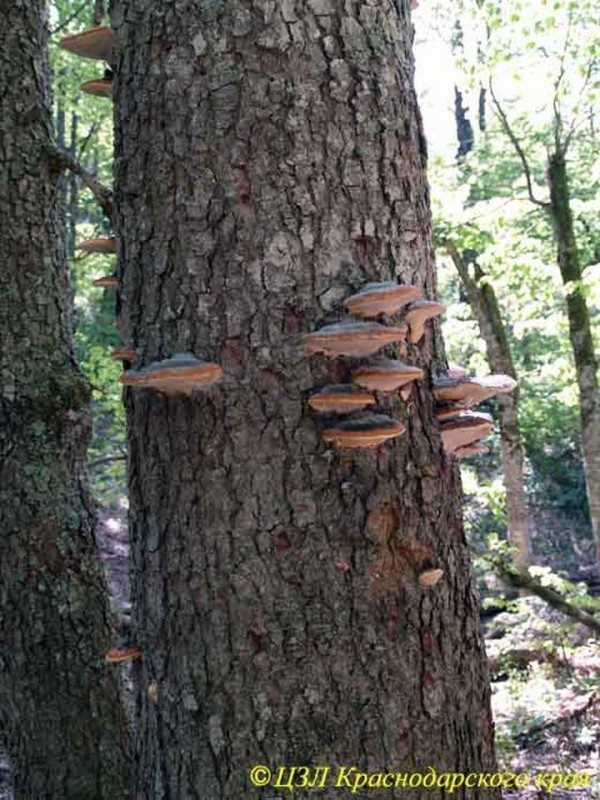


1. Typical multi-tiered groups of canopy-shaped basidiomas (fruiting bodies) of tinder fungus bordered by Fomitopsis pinicola on a living Caucasian fir tree. This tinder fungus settles on different breeds, both on conifers and deciduous
Occupying isolated ecological niches of tree parasites, tinder fungixylophages (from the word "phagos" - "to devour", Greek.) They usually settle on old and weakened trunks, gradually destroying them and making room for new forest generations (although there are "aggressors" fatally and quickly affecting young and healthy trees ). Others are saprophages (saprotrophs), feeding on the already dead wood of dead wood trunks, stumps or dead wood, half-rotted branch decay and roots. Usually, fungi belonging to these subgroups successively replace each other on a woody substrate: xylophagous parasites "prepare the ground" for saprophages and saprotrophs. And all together they participate in the eternal cycle of substances in the forest ecosystem, decomposing wood and processing lignin and cellulose to simpler and more easily digestible organic compounds (cellulose, for example, is decomposed to simple sugars such as glucose).
Many tinder fungi cause significant damage to the forestry and woodworking industries. But at the same time, almost all tinder fungi have properties useful for humans as sources antibiotics, antioxidants and many other valuable medicinal substances. Polypores have also played an important role in human history as suppliers of tinder (and this is not only a campfire, but also the first firearm).
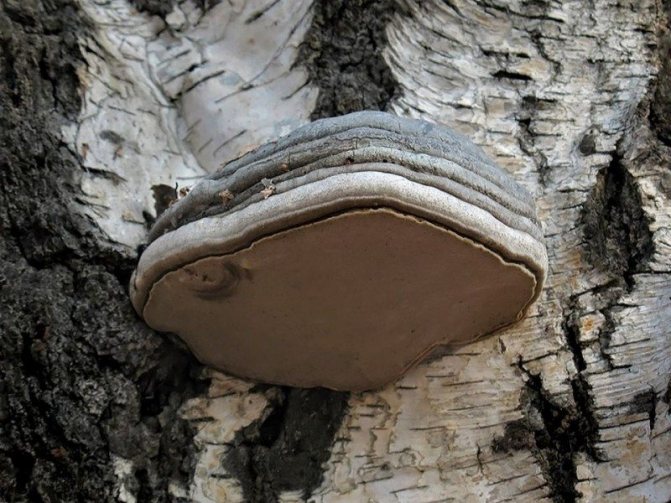
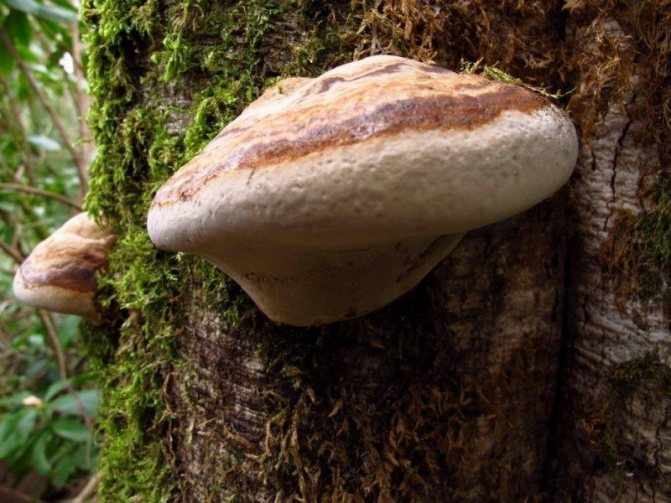
Usually tinder fungi show a certain selectivity towards tree species, although narrow specialization is not common in them. For example, the false aspen tinder fungus Phellinus tremulae obligate xylophagous parasite aspen (narrow specialization).The edible birch sponge, or birch piptoporus Piptoporus betulinus, too, like the aspen tinder fungus, is a "monogamous", settling on birch, but only on already dead trunks (that is, it is an obligate saprophage of birch). Another aspen lover, the fox tinder fungus Inonotus rheades, only prefers aspen, but also parasitizes other species. At the same time, it lives on both dead and living trunks. Its relative is the tinder fungus Inonotus obliquus, widely known as the famous birch chaga , also prefers one tree species - birch, although it is found on aspen, alder, and mountain ash. This tinder fungus, like the fox tinder fungus, lives both on living trees and on dead ones, but at the same time it itself undergoes two stages of development. Chaga is a sterile (non-spore-bearing) growth of a fungus on a living trunk. And only after the fungus kills the tree, it passes into the second stage of development - spore-bearing. Bordered polypore, or pine Fomitopsis pinicola, despite its species-specific name, settles on dead and living trees of all kinds - both coniferous and deciduous. Tinder fungus Letiporus sulfur-yellow Laetiporus sulphureus also parasitizes almost all trees indiscriminately, but those Letiporus that settle on conifers cause poisoning in people (therefore mycologists recently, this species has been divided into 2-3 independent species, separately distinguishing pine and spruce sulfur-yellow tinder fungi).


2. False aspen tinder fungus Phellinus tremulae = obligate aspen parasite, infects live aspen trunks over 40 years old and does not inhabit any other trees


2a. Piptoporus birch Piptoporus betulinus is an obligate birch saprophage. He feeds only on her wood, but already dead


2b. The inedible tinder fungus, Inonotus rheades, only prefers aspen, but also parasitizes some other species. Inhabits dead trees, but can also attack living ones


2c. Bordered polypore, or pine Fomitopsis pinicola on a tree stump. Barnaul belt forest
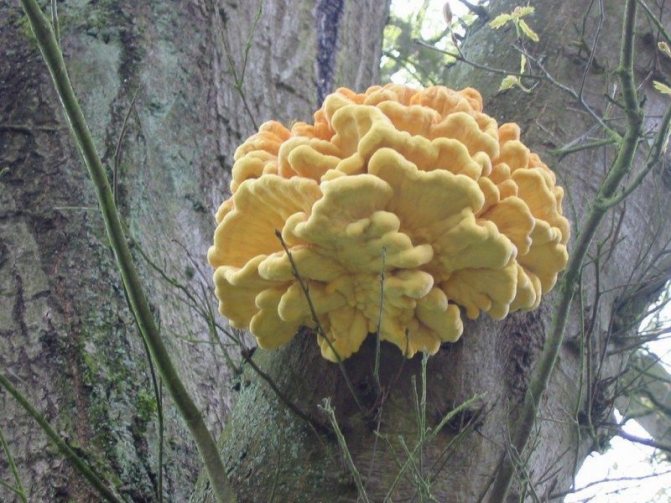


2d. Sulfur-yellow polypore Laetiporus sulphureus
Substrate - a nutrient medium for polypores
With respect to the substrate (living trunks or dead organic matter), on which tinder fungi settle, we also observe a strong spread. Some species of tinder fungus - xylophages are capable of developing only on living trees (for example, false oak tinder fungus - photo 3), which is due to their species-specific need for vitamins produced by this particular tree species. Others - saprotrophic - grow only on dead wood prepared by previous xylophages. And, for example, the edible tinder fungus Albatrellus ovinus generally grows on the ground - not even on deadwood or stumps, feeding on the almost decomposed wood of branch decay. And there are many forms of "omnivores", feeding on both dead organic matter on the ground, and drinking the juices of living trees, sitting on trunks and branches. In this case, it is advisable to talk not about species or population consortia (as is the case with the previously described fistulin), but about an ecosystem consortium, referring to the entire type of forest as a whole (for example, oak forests, complex forests), or even more broadly - deciduous or coniferous forests.


3. Xylophagus false oak tinder fungus Phellinus robustus is found only in oak forests, parasitizing precisely on live oaks, although sometimes it also settles on the trunks of other accompanying deciduous species, but also only living


3a. Trametes versicolor saprophage settles on dead hardwood trunks and even on log walls


3b. Antrodiella pallid Antrodiella pallescens is a saprophage growing on dead and fallen birches killed by the real polypore Fomes fomentarius (it is in the upper part of the frame). Sometimes it grows on the tinder fungus itself


3c. The edible saprotroph of the sheep polypore Albatrellus ovinus grows on the soil in clearings and edges in coniferous forests, feeding on already semi-decomposed branch litter
Tinder fungus - pasture or a source of tinder?
By and large, the ecological group of tinder fungi should also include liver mushroom fistulin... However, the classic tinder fungi have one more property, which is not very typical for fistulin - as they ripen, they stiffen and turn into "plywood" or "cork". From a consumer point of view, this property is much more important than appearance or type of food: the life of an edible tinder fungus as our "pasture" is very short.
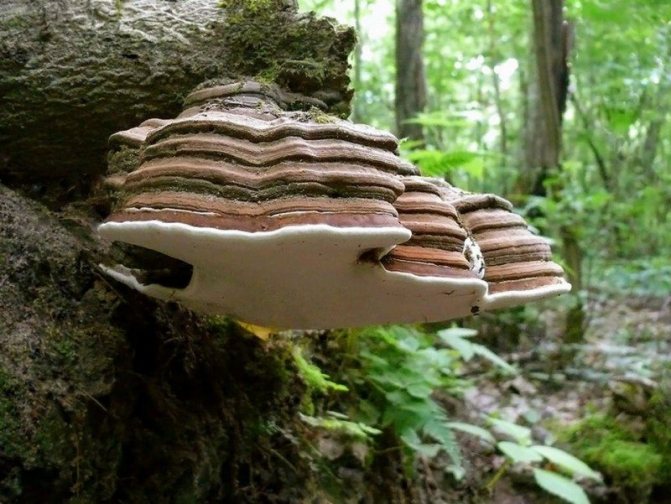
Among the tinder fungi there are few poisonous, but almost all of these mushrooms are inedible due to the rigidity and woodiness of the fruit bodies. Those that are edible are suitable for food only at a young and young age. It should also be noted that among the edible tinder fungi, the absolute majority give a short-lived fruiting body (basidioma), while many inedibles form perennial woody fruiting bodies, sometimes even living for 20-30 years. It is these perennials with a characteristic tinder-like shape in the form of a visor that give us real tinder.


4. "Classic" perennial and inedible (edible only at an early young age) tinder fungus Fomes fomentarius on dead birch. The "annual rings" are clearly visible. "Fomes" in Latin means "tinder", that is, the mushroom is named so: "tinder tinder"


4a. Also "classic perennial" tinder fungus Ganoderma applanatum on an oak stump
Oyster mushrooms
In appearance and lifestyle, oyster mushrooms are close to tinder fungi (in particular, oak mushrooms live on oak - photo 5), however, these mushrooms belong to lamellar basidiomycetes... Tinderpots are traditionally considered tubular, or spongy basidiomycetes .
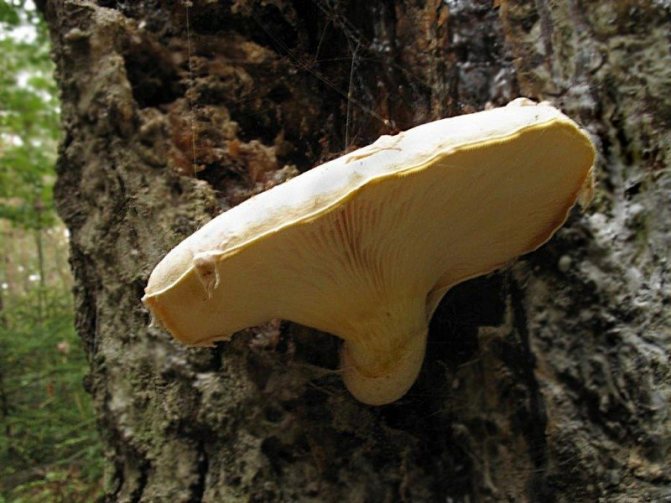


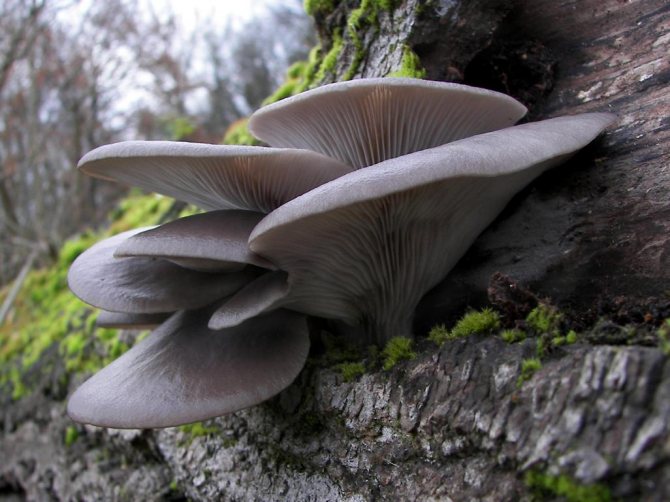
5. Oyster mushroom Pleurotus dryinus has a lamellar hymenophore
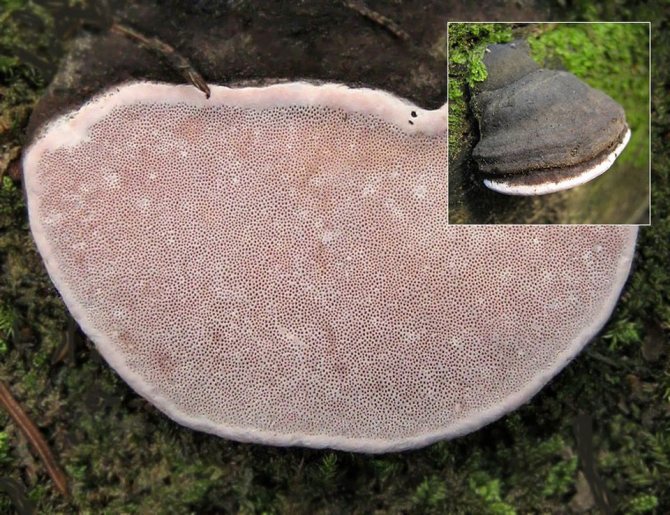


5a. Tubular (spongy) hymenophore of the "classic" pink tinder fungus Fomitopsis rosea close-up
Other types of woody mushrooms
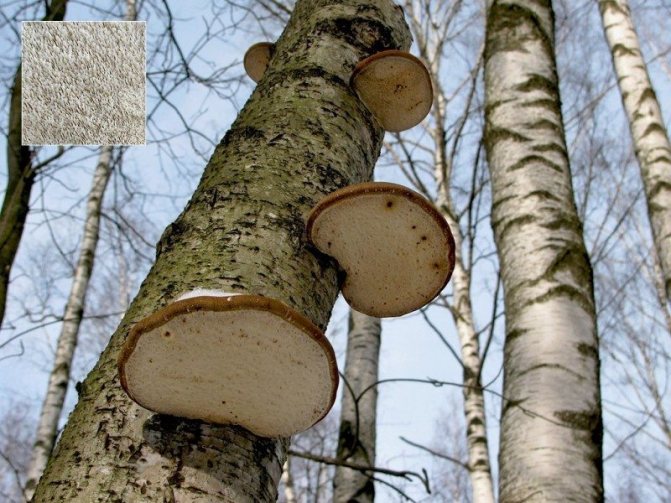
In addition, there are many species of other woody mushrooms occupying niches similar to tinder fungi, oyster mushrooms, liverwort, but very diverse in appearance and not at all similar to tinder fungi (however, they often do not look like mushrooms at all in our usual view - photo 6, 6a, 6b, 6c, 6d). Unlike real tinder fungi, these do not grow stiff with age, like oyster mushrooms. Among them there are also edible and poisonous, which will be described in the corresponding paragraphs. And the above-mentioned real tinder mushroom, birch chaga, does not look like anything mushroom at all. And this is the only mushroom that is edible in a state of complete numbness - it is brewed like tea.
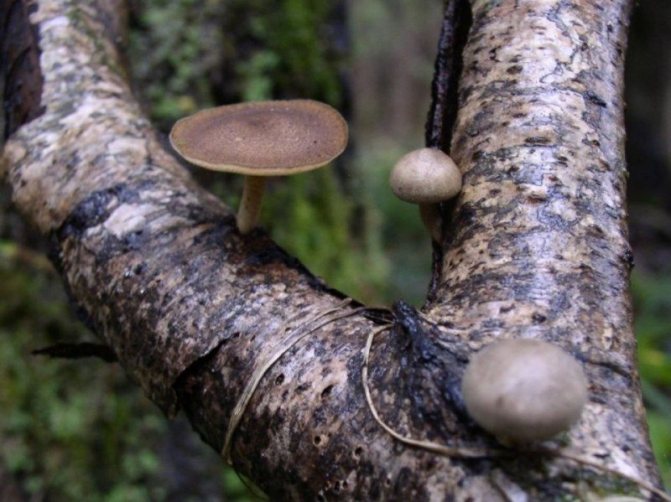


6. Edible winter tinder fungus Polyporus brumalis from the Polyporovye family - stands on a stem like a "classic" land mushroom. Saprotroph. Occurs on deciduous species (birch, alder, linden, mountain ash, willow) or rotting wood immersed in the soil
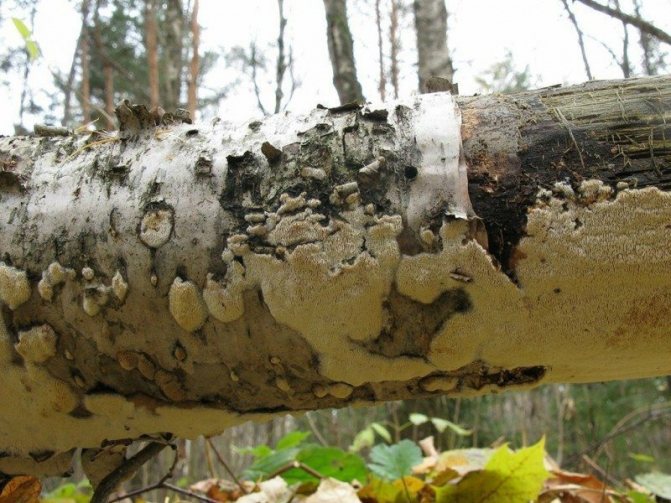


6a. Paradoxical schizopora Schizopora paradoxa - found on woodwood and dry wood of various deciduous species (here - on birch). A widespread species of tinder fungus, but in Latvia it was included in the Red Book
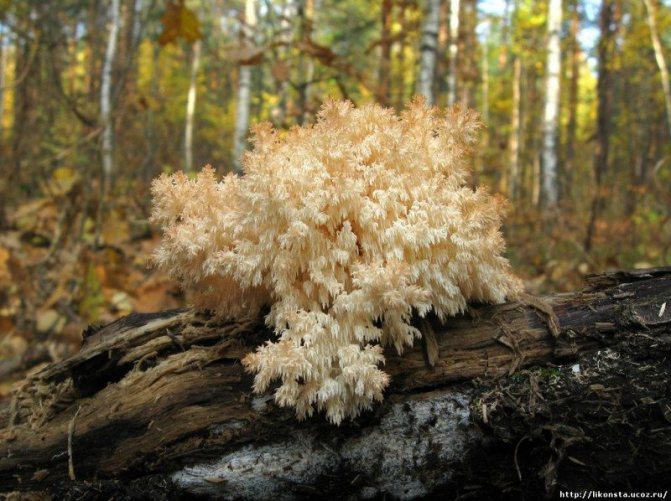


6b. Hericium coralloides is an edible tinder fungus from the Hericiaceae family. It grows on stumps and valezh of deciduous species - aspen, oak, but more often birch
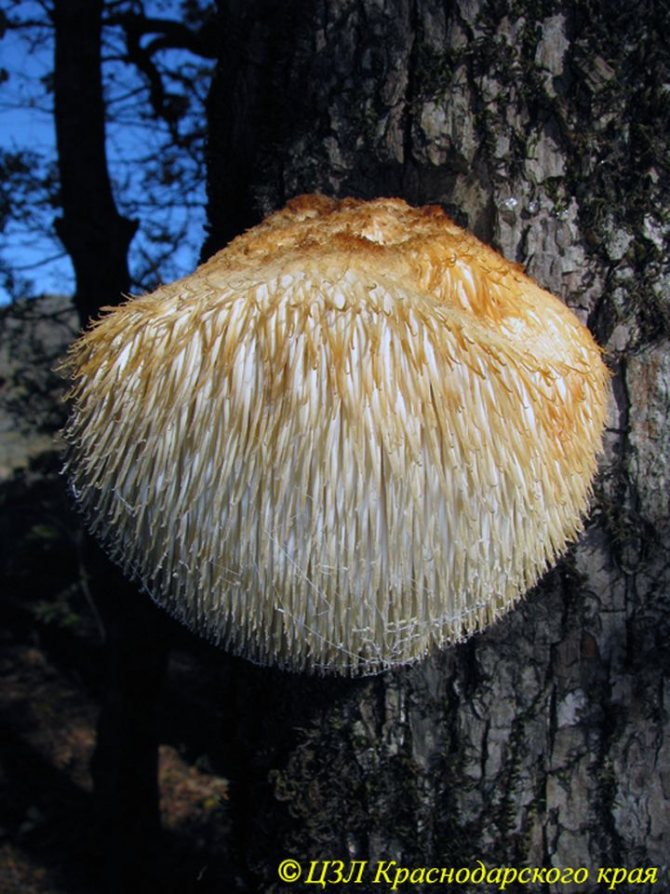


6c. Annual fruiting body of Hericium erinaceum tinder fungus Hericium erinaceum on the trunk of a sessile oak. Gelendzhik TLV, September – October 2009


6d. On the decaying wood, especially often on the deadwood and branch decay of elderberry, the quite edible mushroom Auricularia auricola judae from the class of heterobasidiomycetes grows, which is named in Latin "Judas ear"
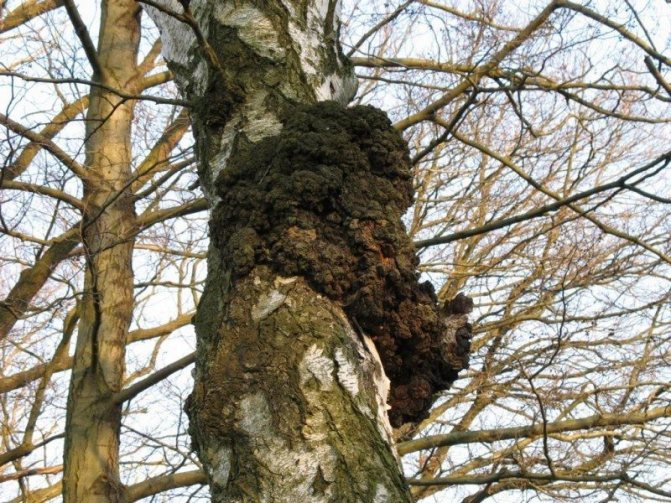


6d. The edible tea and medicinal mushroom Tinder fungus Inonotus obliquus, better known under the name of the famous birch chaga, looks like a cancerous growth of wood rather than a mushroom. It parasitizes living trees. But its spore-bearing stage appears only when the tree dies.
Lamellar parasitic fungi - honey agarics
Many lamellar fungi (along with oyster mushrooms) also belong to parasitic fungi that settle on living wood and very quickly destroy it. For example, the famous autumn honeydew Armillariella mellea, its close relative, the thick-legged honeydew Armillaria gallica, their distant relative from the family of stropharia honeydews, summer Kuehneromyces mutabilis, and the winter honeydew of Flammulina velutipes, which are completely unrelated to them. However, these mushrooms, well-known to the population, are not considered in our reference book, but will only be mentioned as consorts of the corresponding tree species.
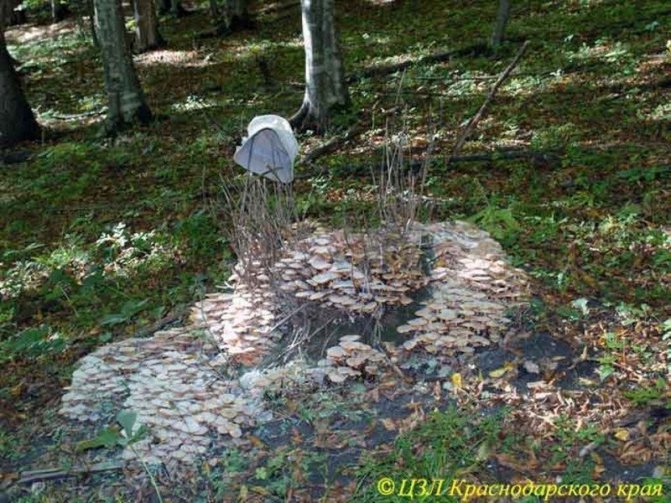


7. Fruiting bodies of autumn honeydew Armillariella (Armillaria) mellea on stump of pedunculate oak, September – October 2009. This fungus infects about 200 species of trees and shrubs, and even parasitizes herbaceous plants such as potatoes


7a. Armillaria gallica, a thick-legged honey fungus, settles both on dead wood and on forest litter.


7b. The summer honey agaric Kuehneromyces mutabilis from the stropharia family is a twin of the real armilaria honey agarics. Also an edible and tasty mushroom that grows in large groups on half-decayed stumps


7c. "Winter honey mushroom", it is also a winter mushroom of flammulina Flammulina velutipes is completely unrelated to other mushrooms (it is from the family of ordinary mushrooms), but just as aggressively destroys living trees, although it does not disdain dead stumps
Wood-destroying fungi of the genus scaly and hyphaloma, false (poisonous) mushrooms
Wood-destroying fungi of the scaly genus Pholiota and hypholoma Hypholoma from the stropharia family are also widespread. These are by no means known to everyone, but some of the scales and hypholus are often confused by the population with real mushrooms - they are so similar. Therefore, even their scientific Russian names often begin with the words "honey mushroom" or "false hair". Edible scales and hyphalomas will be discussed in detail in the relevant paragraphs.


8. Scaly destructive Pholiota destruens - inedible because of the bitter taste with an unpleasant odor. Interestingly, old mushrooms lose their bitterness and become sweetish, but by this time they have hardened strongly.


8a. Pholiota tuberculosa, bitter and slightly edible scale, tuberous


8b. Edible golden scaly Pholiota aurivella looks like summer honey


8c. Brick-red pseudo-foam Hypholoma lateritium - poisonous twin of real honey agarics, settles on oak stumps


8d. The sulfur-yellow pseudo-foam Hypholoma fasciculare is the deadly poisonous counterpart of the real honey mushrooms. It grows in the same place and in the same way as autumn honey
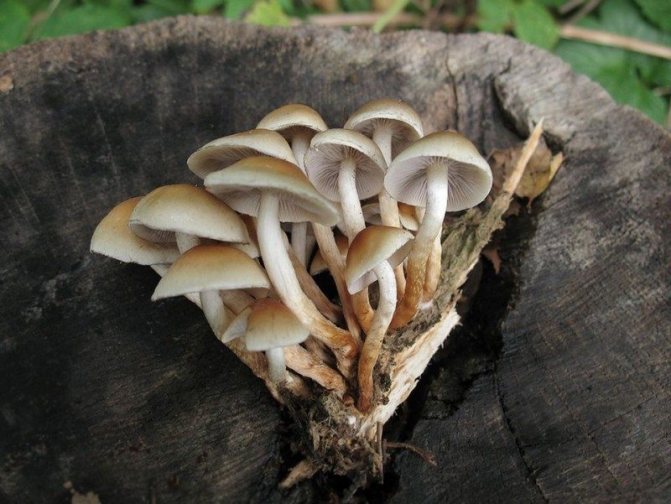


8d. Hypholoma capnoides is the edible counterpart of the summer honey fungus. It grows, supposedly on the soil, but in fact - on branches and pieces of wood buried in the soil
Real tree polypores
It has already been said above that tinder fungi are not a taxonomic group, but an ecological group in which mushroom pickers unite representatives of different families of the class basidiomycetes... Not all mushrooms found on trees, stumps and deadwood are popularly called tinder fungi - but only those that have a "classic" canopy shape on a tree or stump, tubular (spongy) hymenophore and become lignified with age. In our review, they will also be considered from the standpoint of not a scientific taxonomy, but from a consumer taxonomy, where the main factor is not kinship, but edibility and habitat. From this point of view, according to morpho-ecological characteristics, we will divide them into tinder fungi "Real" (classics of the genre), "Polyporus" (with legs) and lamellar (oyster mushrooms).
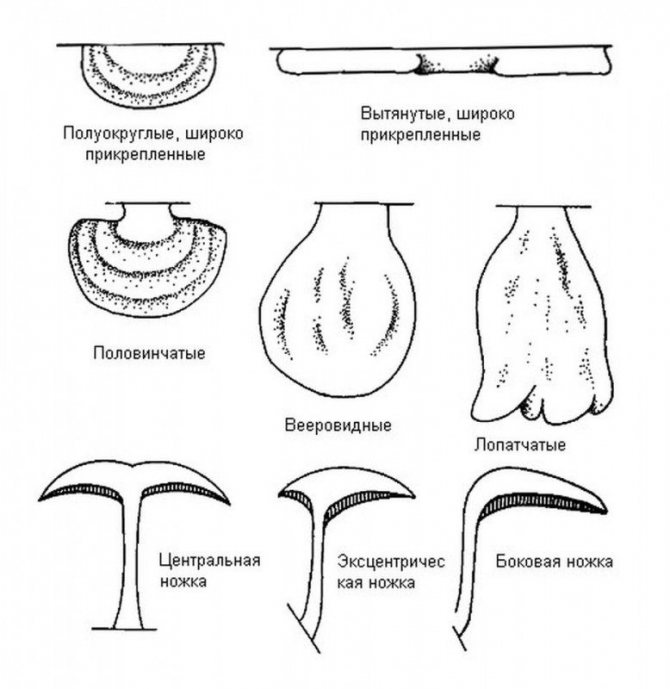

9. Morphological types of fruiting bodies and methods of stalk attachment in woody fungi according to the classification of L. Ryvarden and R.L. Gilbertson (1993). The scheme is based on the monograph by T.V. Svetlova and I.V. Zmitrovich "Polypores and other wood-dwelling aphyllophoric fungi" on the mycoweb site.
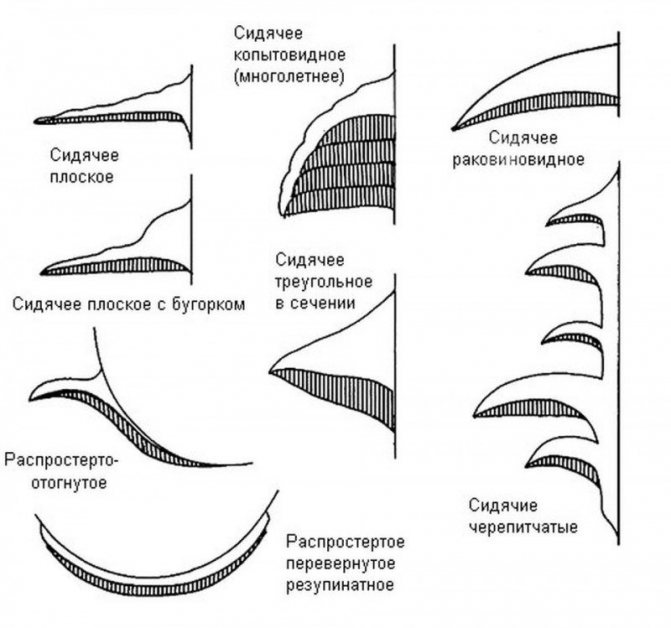

9a. Types of fruiting bodies of "real" tinder fungi without a stem according to the classification of L. Ryvarden (1976). Same source
When determining tinder fungi, an important role is played by the lower spore-bearing surface of the fruiting body - the hymenophore. Here, attention is paid to its color, as well as the shape, structure and size of pores (tubes) or plates. There are three main types of hymenophores: tubular, labyrinthine and lamellar..
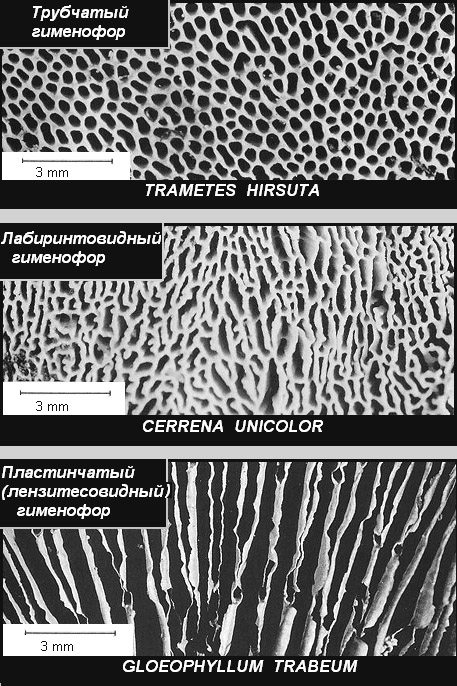

9b. Types of hymenophores according to T.V. Svetlova and I.V. Zmitrovich. Same source
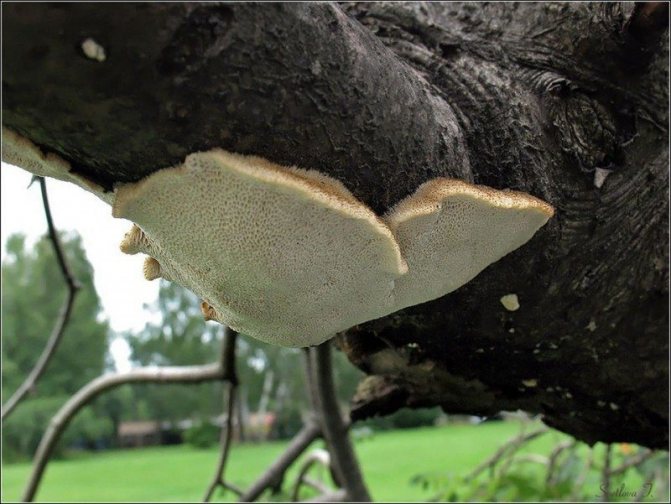
The most common type of polypore hymenophore is tubular. It is available in all, without exception, real and most polyporus tinder fungi.
Growth features and age-related changes in tinder fungi
The mycelium of polypore fungi lives inside a woody substrate (a living trunk or branch of a tree, stump or deadwood, half-decomposed branch waste and pieces of wood on the soil), on the surface of which fruiting bodies - basidiomas are then formed. From the moment the mycelium begins to develop to the formation of the first fruiting bodies, it takes a long time. At the same time, as you already know with the example of the hepatic fungus fistulins, as they grow and "mature", the basidiomas greatly change externally. Fruiting bodies appear on the surface more often in the form of tubercles or flat spots and gradually acquire the volume and shape of a ripe mushroom. Moreover, even in "adult" fruiting bodies, the shape can vary greatly depending on the nature of the substrate (hard living wood, hollow or crack in the trunk, mossy stump, buried branch decay) and its orientation in space (vertical trunk, horizontal branch, crack) ... If cap mushrooms are quite easily identified at a very early age, then woody polypores at the initial stages of development are often impossible to determine without resorting to special research. The only thing that saves from poisoning is that there are very few poisonous among tinder fungi.
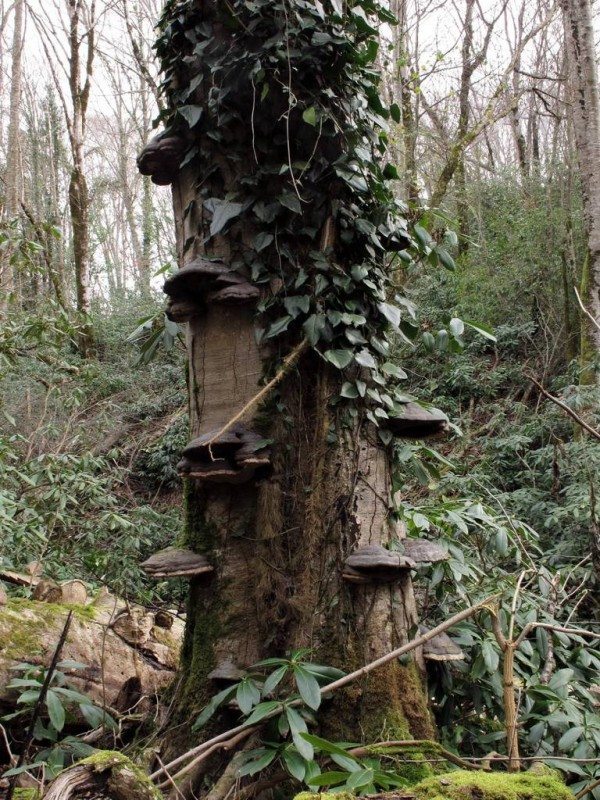


10. Classics of the genre = true tinder fungus Fomes fomentarius on a vertical beech trunk. An edible mushroom and a major source of tinder. Adler, February 16, 2015
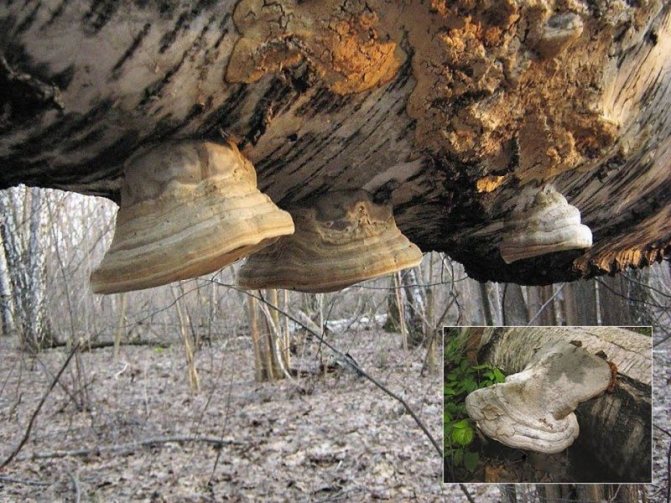


10a. And this Fomes fomentarius, which has grown from below on a horizontally located branch, does not at all resemble its classic hoof-like shape. For comparison - the inset in the lower right corner of the photo. Moscow suburbs


10b. Inedible tinder fungus Ganoderma southern Ganoderma australe. Adler, February 16, 2015


10c. And this Ganoderma (presumably also southern - australe; photographed there and at the same time as in the previous photo) the author of the photo could not identify


10g. Inedible tinder fungus, harsh-haired Trametes hirsuta on a dead mountain ash trunk. Zailiyskiy Alatau, Kazakhstan


10d. And this harsh-haired tramesto - also on a horizontal branch - "stuck" to it with the upper surface of the fruiting body. Moscow suburbs
It should be said that not all "real" tinder fungi are suppliers of real tinder. There are several families of false tinder fungi (but of a classic appearance) that woody and harden with age. Tinder fungi that give tinder do not stiffen, but cork: their fruit body inside contains a spongy cork-fibrous tissue, which is used to make tinder using a rather complicated and time-consuming technology in the field (at home, it is enough to just soak it with nitrate). Tinder fungi include fungi, in which the upper surface of the fruiting body is always smooth or rough, but not cracked. Of the widespread are representatives of the genera Fomes (the only species of Fomes fomentarius, it is also the main supplier of tinder), Fomitopsis and Ganoderma.
Anatoly Levin
Composition and medicinal properties
Chaga contains elements that, in combination, provide a healing effect. The list of biologically active substances contained in a birch mushroom consists of:
- flavonoids;
- alkaloids;
- tannins;
- groups of organic acids.
Each of the elements in chaga has an individual therapeutic effect:
- organic acids control and normalize the acid-base balance of the human body;
- flavonoids have anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, diuretic and choleretic effect;
- phytoncides provide antimicrobial effect;
- alkaloids have a beneficial effect on the heart muscle;
- tannins strengthen and restore the mucous membrane and skin (used for bleeding and inflammation);
- melanin stimulates metabolic processes and restores the body.
Additionally, chaga contains minerals and trace elements. Of these, the most beneficial to human health are:
- magnesium - effective for diseases of bones, joints, teeth, heart, gastrointestinal tract, nerve tissues;
- potassium - helps to treat diseases of the blood, heart, kidneys, and has an antitoxic effect;
- iron - normalizes blood formation and tissue respiration, liver and spleen function, prevents anemia;
- manganese - strengthens bone tissue, improves the absorption of vitamins, relieves inflammation;
- copper - has a beneficial effect on hemoglobin, skin, hair, cellular respiration, oxygen supply, the construction of bone tissue, the work of the nervous system.
Also, the composition of chaga is filled with zinc, cobalt, nickel, silver and aluminum. Most of the elements contained in birch mushrooms are beneficial to human health. Therefore, chaga is used not only in medicine, but also in cosmetology.
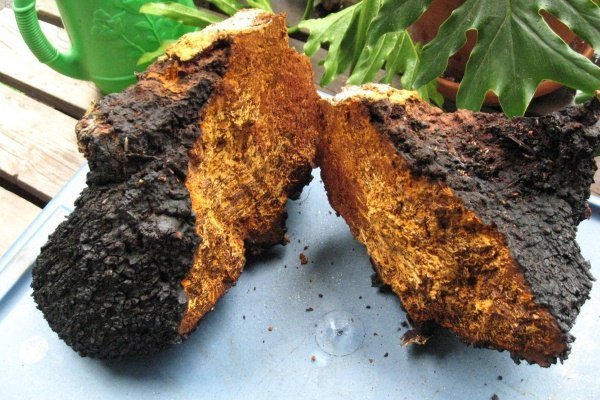


The effect of fungi on the bark of a tree
Mushrooms that grow on trees are the same parasites... They not only destroy tree bark, but also have a detrimental effect on the root system. Most often, they appear on old trees, the bark of which has already been infected by birds or insects. Not only forest, but also garden trees fall under the influence of mushrooms. Quite often, mushrooms act as provocateurs of the appearance of various rot or diseases and can completely destroy a tree.
But these mushroomslike tinder fungi, on the contrary, bring a lot of benefits. They contribute to the decomposition of old wood and enrich the soil with nutrients.
Mushroom pickers are accustomed to the fact that mushrooms grow underfoot, and when they come to the forest, they don't even raise their heads. And most likely, they pass by tasty and fragrant mushrooms that are located in the trees. But some do not have the opportunity to go to the forest and enjoy its beauty, collect gifts. In this case, you can grow mushrooms yourself using just a few stumps.
Published on 03/16/2018 by samsonmain and was posted under Edible. Bookmark the permalink.
Mushrooms and mushroom places of the Samara region
Deadly mushrooms: description of types and measures for their use
Types of birch chaga
Related species of birch chaga are radiant and bristly-haired tinder fungi.
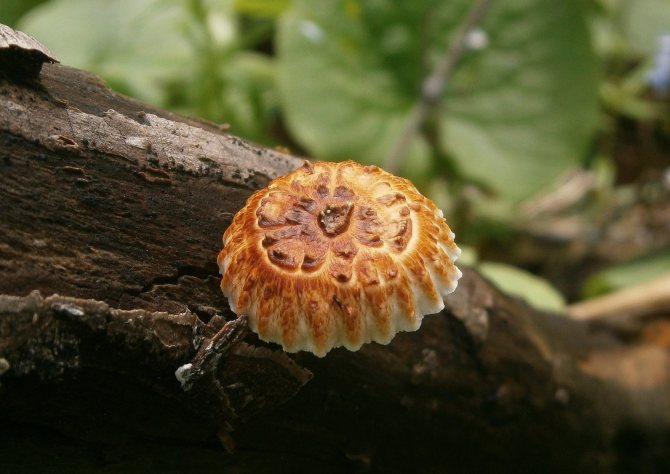
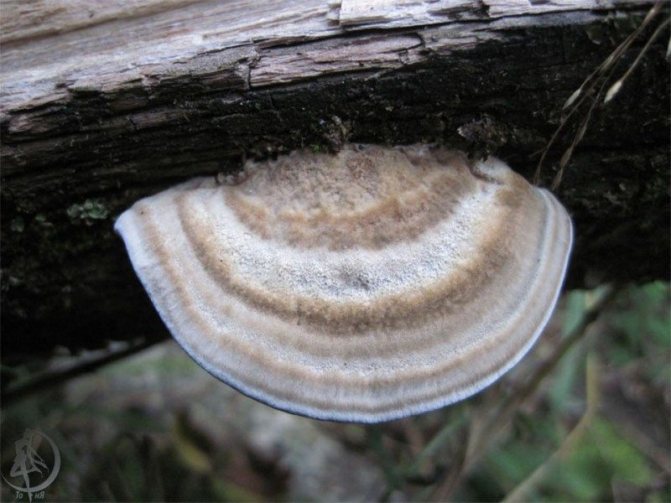
Radiant polypore, or inonotus radiant (Xanthopória radiáta)
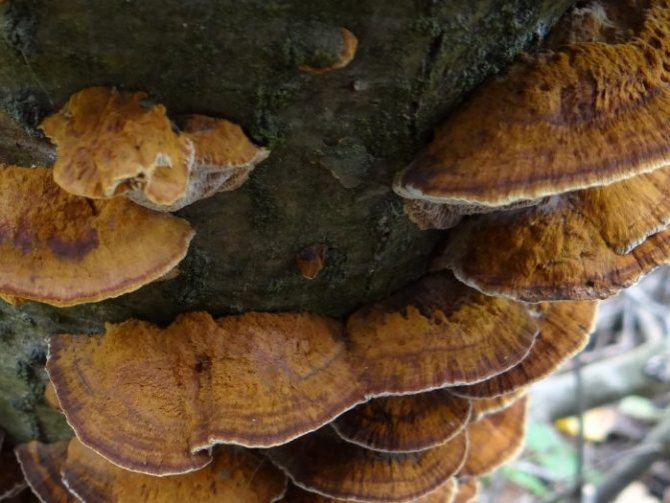


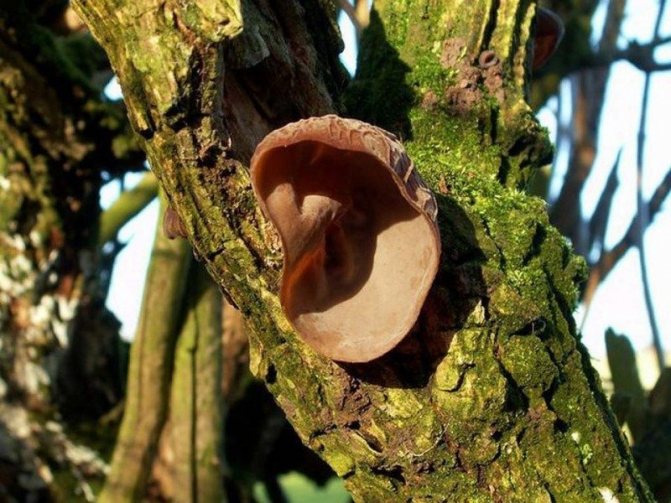
The fruiting body is annual, looks like a sessile, widely grown lateral cap, if there are several of them, then they form a kind of "tile". The length of the caps is about 5 cm, the width is 6-8 cm, and the thickness is 5-20 mm. The caps are flattened, the edge is sharp, in young mushrooms the surface is velvety, from yellow to reddish-brown, later becomes naked, shiny, rusty or dark brown, wrinkled. The pulp is shiny, fibrous, light brown or red-brown in color. The fungus infects the wood of deciduous trees, grows mainly on alder, rarely on birches. Found in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, in the Himalayas.
Bristly-haired polypore (Inonotus hispidus)
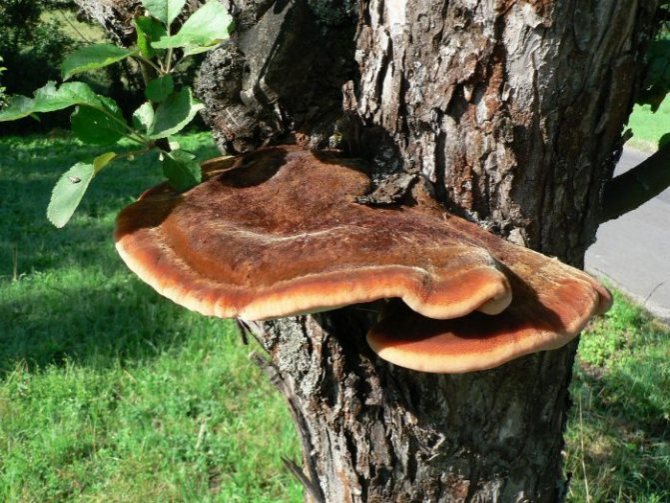


The fruiting body is annual, capped, sessile, solitary, or 2-3 caps form a "tile", widely growing to the substrate. The size of the cap is 10 × 16 × 8 cm. The surface of young mushrooms is colored red-orange, later red-brown or blackish, velvety-hairy. The pulp is brownish, light at the edge and surface of the caps, radially fibrous. The fungus is widespread in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, grows on broad-leaved trees, oaks, ash and apple trees, less often found on fir, maple, horse chestnut, alder, birch, hawthorn, beech, walnut, mulberry, pear, sycamore, poplar, plum.
Edible mushrooms growing on a birch
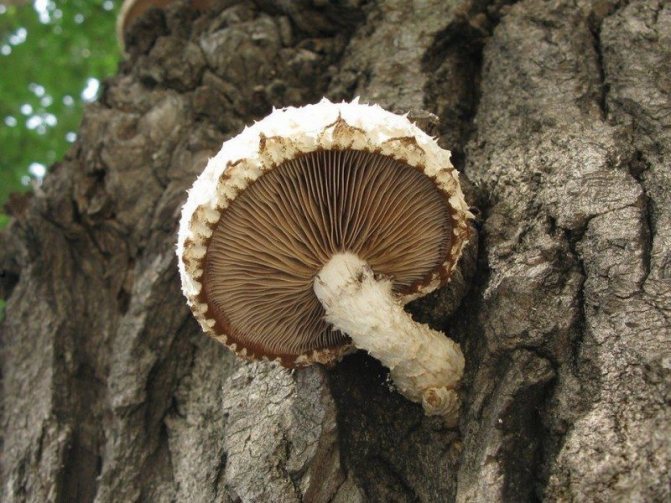
In addition to Chaga, there are many birch mushrooms that also grow directly on the trunk. Oyster mushrooms and honey mushrooms are widely known, which are often used in cooking for the preparation of various dishes.Among oyster mushrooms there are no inedible and poisonous species, but the photo and description of the mushroom, for example, must be studied carefully in order to be able to distinguish it from a false one.
Oyster mushroom
Oyster mushrooms got their name because the fruit bodies hang from the trunks of birches. They are not only tasty, but also healthy, because they are often used by housewives to prepare various dishes. There are many varieties of oyster mushrooms, and the most popular are common, horn-shaped, pulmonary and orange.
Oyster mushroom or oyster is a large mushroom, the diameter of the cap reaches 30 cm. It is shell-shaped in shape, with inward-directed edges and a smooth surface. It later becomes flat.
The color is changeable, it can be dark gray with a brown tint, ashy with a slight purple tint. The leg is short, curved, light. The pulp of the fruit part is light and soft, and becomes more rigid with age. You can meet the common oyster mushroom from the beginning of autumn to the beginning of winter.


You may be interested in:
How to distinguish real mushrooms from false mushrooms (28 photos)? Ryzhiki is a popular forest delicacy in our country with an exquisite taste. They are not inferior in their gustatory qualities ... Read more ...


Oyster mushroom
Oyster mushroom differs from the previous one in that it has a smaller and funnel-shaped cap. The color is almost always light, with a grayish tint. The pulp is white and fleshy, odorless and tasteless.


Oyster mushroom
Oyster mushroom has a thin tongue-shaped cap, with cracked edges, beige in color, the diameter of which reaches 8-9 cm. The lamellar part is descending. The pulp is always thin and firm. The leg is almost invisible, it has a slight pubescence.
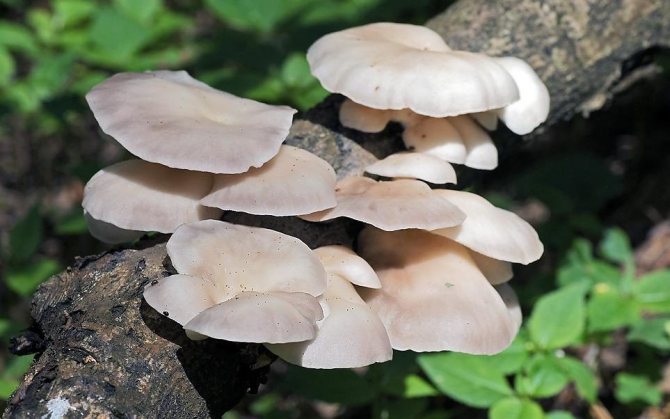


A distinctive feature of orange oyster mushroom is the bright orange color of its fruit part. The hat adheres to the tree with its lateral part, therefore it most often has an irregular shape with wavy edges. The surface of the cap is pubescent.
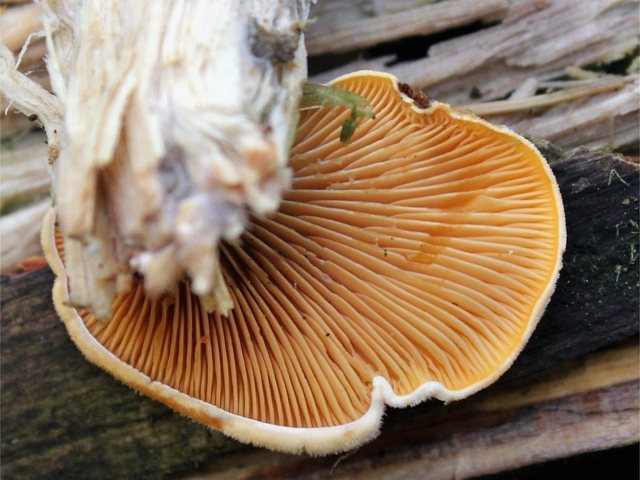


In this variety, the leg is completely absent, and the plates are large, wide, orange. Faint putrid taste and smell. The mushroom is considered inedible due to the fact that it is quite hard and has a specific taste and smell. Despite this, young fruits are still eaten.


You may be interested in:
What is the name of a mushroom with a red cap and its description (24 photos) Very often mushroom pickers meet in the forest many different mushrooms with a red cap. They usually look very ... Read more ...
Edible mushrooms
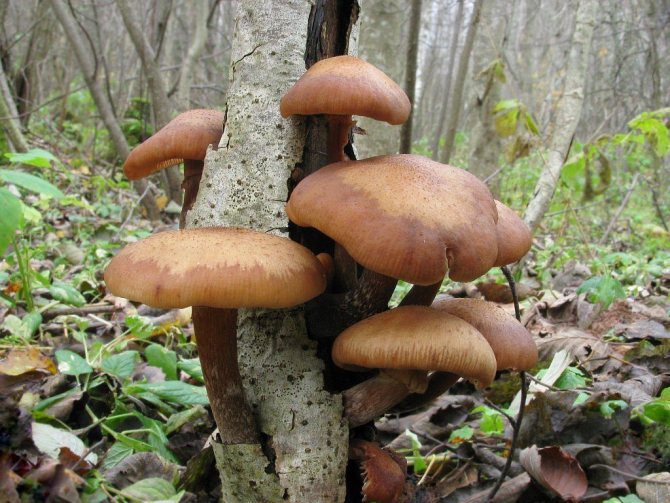
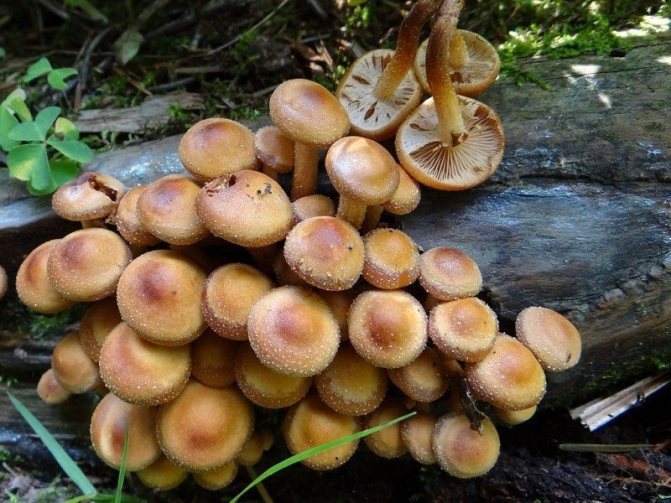
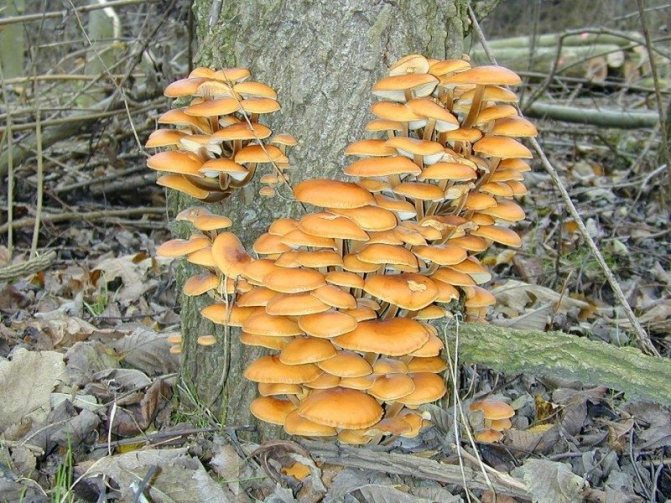
Honey mushrooms are no less common. They are often used in cooking and are prized for their taste. They are divided into summer, autumn and winter, depending on the peak yield.
Summer mushrooms have a thin hat with edges wrapped inward, which straighten out with age. The hat is painted yellow with a brown tint. The diameter of the cap does not exceed 8 cm, and centric water circles can appear over its entire surface. Over time, the circles disappear.
On the inside of the cap there is a lamellar system, which becomes darker over time. The leg is high, brown and thin, has a ring and scales located below it. You can meet summer mushrooms from July until the first snow.
Autumn mushrooms are distinguished by a flat cap with wavy edges, painted green-brown. The pulp of autumn mushrooms is soft, dense and white. The leg is high, widened at the base, covered with scales. You can meet autumn mushrooms from late August to late autumn.
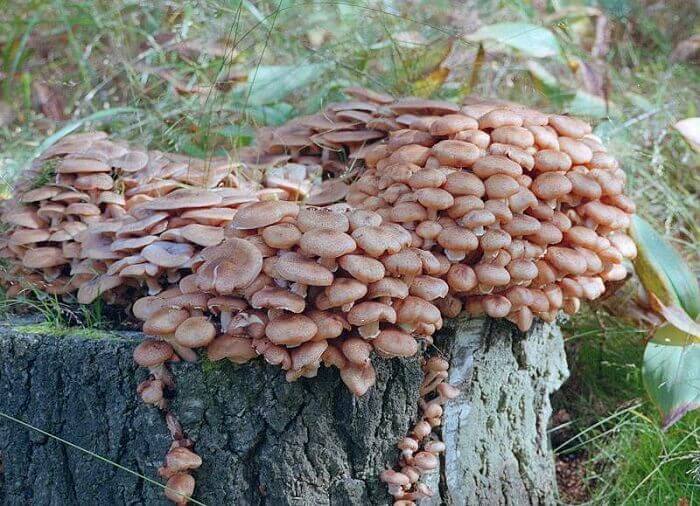


Winter mushrooms cannot be confused with anything, since the surface of their cap is glossy, light brown in color with a reddish tint. It is convex in shape. The flesh is thin and tough, mostly white. The leg is cylindrical, 8 cm high, light brown in color. You can meet this variety from the onset of cold weather until the beginning of spring.
Education
Birch chaga penetrates into wood through cracks in the bark damaged by the sun, frost, insects, and inhabits only sufficiently mature trees. Having settled inside, the spores germinate and develop within 4 years.Then a characteristic dark growth appears on the surface of the trunk, which grows for a long time, increasing in size. Hyphae penetrate 0.5-1 m deep into the wood, depriving the tree of food.
This parasitic tinder fungus also grows on aspen, linden, alder, mountain ash, beech, elm, maple, but only the chaga birch mushroom has medicinal properties.
Peculiarities of chaga collection
For medicinal purposes, only those fruiting bodies of birch chaga that have grown on living trees and are not old are used. Old chaga is crumbling.
All mushrooms are capable of concentrating harmful substances from the environment. Birch tinder fungus is no exception. Therefore, you should not prepare chaga in ecologically unfavorable places.
The ideal time to harvest birch mushrooms is from early August to late October. At this time, it is maximally saturated with useful substances.
Indications and restrictions for use
Healing wood sponge is recommended for various diseases. The list of indications for internal use is quite long and includes diseases of many body systems. These include:
- oncology;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- leukopenia;
- viral diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- diabetes mellitus and other disorders of the endocrine system;
- damage to the mucous membrane of the duodenum;
- gastritis;
- the transferred operation;
- insomnia, depression and other nervous disorders;
- obesity;
- cramping;
- tachycardia and hypertension.


Chaga birch mushroom In addition, the mushroom is used for general strengthening of the body and increasing immunity, to stimulate brain activity. Chaga is also used externally to treat diseases such as:
- dermatosis;
- rash;
- colds on the lips;
- keratinization of the integumentary epithelium;
- abscesses;
- burns;
- frostbite;
- scuffs, abrasions and wounds;
- acne;
- peeling of the skin;
- insect bites.


The use of the fungus for the treatment of diseases In dentistry it is used as an anti-inflammatory and analgesic agent for:
- deep damage to the periodontal tissue;
- inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues;
- damage to the oral mucosa;
- toothache.
However, it is not always possible to use tinder fungus for medicinal purposes. Contraindications to the use of the mushroom are:
- taking penicillin drugs;
- intravenous administration of glucose solution;
- insufficient bowel movements;
- inflammatory disease of the colon mucosa;
- shigellosis;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- individual intolerance.
Advice!
During the treatment period, it is recommended to replace meat with vegetable and dairy sources of protein. You should not eat canned and smoked foods, spicy foods. In addition, you should give up bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse.
Tinder
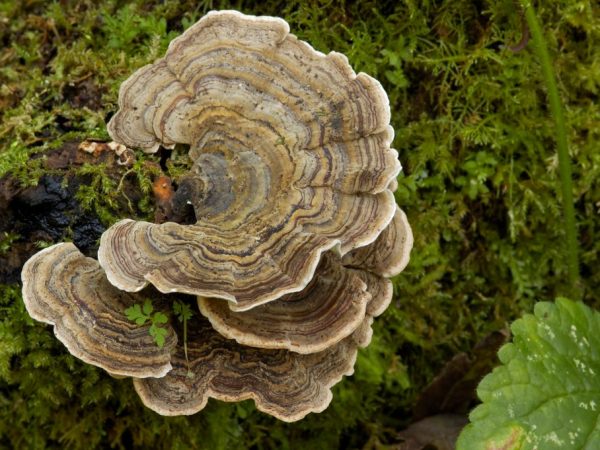


Tinder shape resembles an ear
The fruiting body is characterized by its external variability. Different species can be very different in structure from ordinary mushrooms. For example, the type of changeable tinder fungus resembles a saw-leaf in structure, and the smoky one looks like a washer. One name unites completely different species.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
Polypores, like honey mushrooms, are a non-systematic group of mushrooms. Usually, tinder fungi are called all mushrooms that develop on wood and very rarely on soil and are characterized by the following features in the external structure:
- fruiting body: prostrate, sessile or cap-pectoral;
- hymenophore: tubular;
- pulp: can be both fleshy and tough in consistency (leathery, corky, woody).
Already at the end of the 19th century, the group, which was considered systematic and the fungi were separated into a separate family Polyporaceae, was recognized as artificial. But until the middle of the 20th century, it was preserved in systematics.
The edible species is sulfur-yellow tinder fungus. It is attached by the fruiting body to the bark of a tree or stump, the body and leg are not distinguished. The mushroom bodies are shaped like ears or wavy petals. Young mushrooms are eaten after boiling.Individuals on conifers are bypassed, they are poisonous to humans. The species affects the following trees:
Also, representatives of this species are used in Russia and China for medicinal purposes for the preparation of tinctures, ointments, powders.
Chaga recipes
Chaga has a strong effect, before starting treatment, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
You can make vitamin tea: put chopped chaga and aromatic herbs (black / green tea, mint, lemon balm, etc.) in a thermos in equal proportions, pour boiling water for 8-10 hours (1 to 5). Add honey before use.
For bleeding gums, prepare an infusion of chaga (1 teaspoon) and chamomile (1 teaspoon). Pour 0.4 liters of boiling water, leave for 4 hours in a sealed container, strain, use for rinsing.
The use of chaga in medicine
In official medicine, the following chaga medicines are used:
- Chaga, shredded dried raw material - for the preparation of decoctions, infusions and tinctures.
- Alcohol tincture - as a general tonic for the treatment of depression, juvenile acne, spasms of internal organs.
- Decoction - with diabetes mellitus to lower sugar levels, with chronic gastritis, intestinal atony. For a long time, the broth is used as an auxiliary therapy in the treatment of cancer.
- Infusion - in case of gastric diseases, to restore the body after infectious diseases and operations. Outwardly, the infusion is used for rinsing the mouth with tonsillitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease. Inhalations with infusion help to eliminate hoarseness, relieve inflammation in the airways.
- Befungin - chaga extract in combination with cobalt chloride. It is used to treat psoriasis, gastritis, gastrointestinal dyskinesia, intestinal atony, tumor pathologies.
Porcini mushrooms on a birch. Mushrooms of Russian forests. White birch mushroom. The dream of any mushroom picker.
White birch mushroom (spikelet) (Latin Boletus betulicolus). This mushroom is a separate species or form of porcini mushroom. In some Russian regions, it acquired the local name spikelet. This was due to the fact that the first appearance of fruit bodies coincides with the earing of rye.
In the early summer time, I had to collect birch whites in the forests of various regions of Russia. And, almost always, I found them somewhere on hillocks, embankments, near old ditches, on abandoned roads and paths, lawns with dry white grass….
There is a peculiar belief that the first porcini mushrooms can be found directly in the period when rye begins to spike in the fields. It is due to this feature that it is customary to call it "spikelet".
WHAT IT LOOKS LIKE:
Hat: up to 20 cm or more in diameter, up to 9 cm in thickness. At first, it is almost spherical, then hemispherical to cushion, smooth or somewhat wrinkled.
In dry weather, sometimes fissured, naked, dry, in wet weather, somewhat slimy, dull or shiny when dry. The color is whitish, sometimes buffy-yellowish or light brownish.
The tubular layer near the stem is deeply notched, easily separated from the pulp, white in youth, then turns yellow, then becomes olive green.
Leg: up to 15 cm in height, up to 6 cm or more in diameter. At a young age, usually tuberous or ovoid, then elongates, remaining more thickened downward.
It is solid, with a thin mesh pattern in the upper part of the leg, whitish, light brownish, often with the same shade as the cap, but more often lighter than the latter, especially at the top and at the very base.
The pulp is fleshy, strong, juicy, white. At a break or cut, the color does not change. The smell is pleasant, mushroom. Has no particular taste.
The birch cep is found both singly and in rather large families.
This mushroom grows exclusively under birch trees, it is found throughout the habitat, where there are birch forests and groves, as well as in forests mixed with birch. Fruiting from June to October. It often grows throughout Russia, as well as in Western Europe.
Preference is given to exclusively open spaces, for example, it can be easily found in small forest clearings, along roads and on the edges, at the very edge of forest paths.
The pronounced taste and bright aroma of porcini mushrooms makes them an ideal product both for preparing independent dishes and for using as an additional ingredient in dishes with a complex composition.
What is not prepared from porcini mushrooms! Appetizers and salads, soups and main courses, pies and marinades. Porcini mushrooms are boiled, fried, stewed and baked, dried, pickled and salted ...
Hemp mushrooms are edible. Features of growing mushrooms on stumps
The types of mushrooms that grow on stumps can be bred at home, creating for them as close to natural conditions as possible. The best option is to grow wood mushrooms in a summer cottage.
For stumps, you need to use cuts from deciduous trees, or use real stumps left over from recently cut trees.
Most often, oyster mushrooms are grown on the site. To ensure their growth and normal development, you need to take poplar, birch, maple wood. Conifers should not be used, as they contain a large amount of caustic resins that can destroy the mycelium.
If fresh wood is used, then it is not necessary to soak or moisten it first. If the stumps are old, then they need to be kept in a container of cold water for several days.
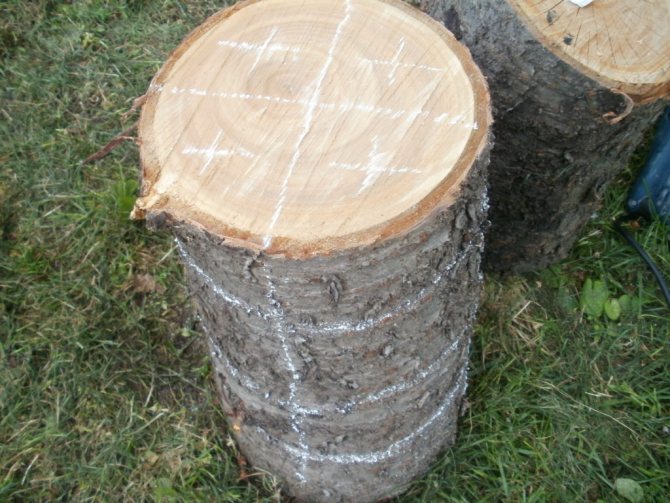
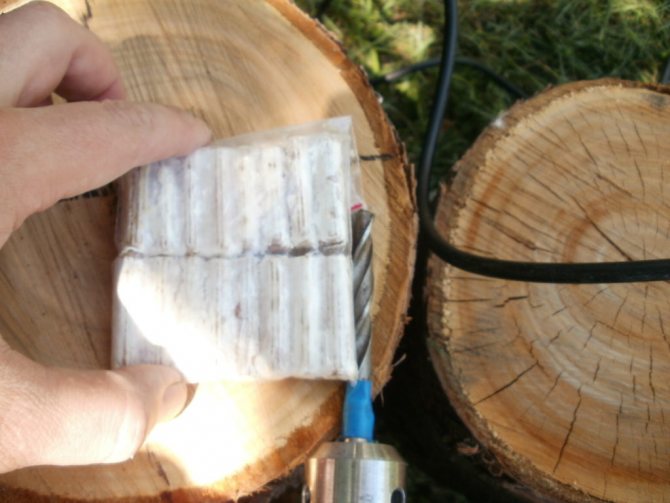
After the logs are ready, you can add the mycelium of the selected type of woody mushroom. To do this, you can make holes in the hemp in a checkerboard pattern. Their depth should not be more than 6 cm, and their diameter should be 1 cm.
The mycelium should be poured into these holes. After that, they need to be covered with moss or closed with adhesive tape.
The logs with mycelium must be placed in the basement. They should be folded in a pyramid shape and covered with burlap.
The stumps should remain indoors until the mycelium sprouts. Then they can be placed in the ground. It is recommended to do this in May, when the normal temperature regime is established.
For planting hemp, you should choose a shaded place. You need to dig a hole no more than 15 cm deep, cover the bottom with wet leaves or sawdust. You need to place a stump in the hole. The distance between each of them should be at least 35 cm. Stumps should be watered if necessary.
Another way is to grow woody mushrooms in a trench. You can do it this way:
- Dig a trench up to 15 cm deep.
- Pour dry barley at the bottom, which will provide the mycelium with good nutrition.
- Put the disinfected mycelium on top. Each stump should have 300 g of seed.
- Place the moistened stumps on the mycelium and lightly sprinkle with soil.
After planting woody mushrooms, you need to water the soil. This should be done carefully, as excess moisture does not benefit the growing mushrooms. It is best to use a spray bottle for watering. Watering should be done during dry periods.
For the winter, the mushroom plantation should be covered with a layer of straw or foliage. It is necessary to cover the stumps with material so that the mushrooms do not freeze.
The first crop, if everything was done correctly, can be harvested within a month after planting the mycelium.
How to use chaga fruits for oncology
Our great-grandmothers were also convinced that a decoction of the plant we are considering reduces the risk of developing malignant neoplasms by half - for prevention, you just need to periodically add raw materials to tea. Also, the remedy is effective for people who are already sick.
The birch mushroom is effective both in complex measures and as an independent medicine. The results of clinical studies made it possible to reveal that there is a result of the treatment with chaga and it is undeniable, after which, on the basis of the plant, official pharmaceutical preparations began to be created.
After using chaga in the initial stages of the disease, the condition of cancer patients improves significantly - the tumor grows much more slowly, the pain subsides, and the general well-being becomes much better.The choice of the remedy and its dosage depends on each individual case - the stage of the disease, the measures taken to improve the health, the duration of treatment.
We present to your attention a recipe for a remedy that helps with tumor diseases. Required Ingredients:
- 300 grams of chaga mushroom;
- 150 grams of pine buds;
- 30 grams of St. John's wort;
- 375 ml. cognac;
- 7 gr. wormwood herbs;
- 150 grams of rose hips;
- Aloe "arrows";
- 750 ml. honey without added sugar;
- 15 gr. licorice (root).
The mushroom is crushed in a blender or on a grater, the resulting raw material is poured into a bowl or large saucepan. Following the chaga, pine buds, wormwood, St. John's wort, rose hips and licorice are added to the container (the number of components must strictly correspond to the recipe).


After that, the entire mass is filled with 4.5 liters of ice water (it is better if the water is taken from a natural spring or well), set aside for 120 minutes.
After the specified time, you need to put the pan on the fire, bring to a boil and cook the "medicine" for two hours. At the end of the first stage, the broth is carefully covered with a warm blanket or bedspread - the liquid should cool and infuse for 24 hours.
Let's proceed to the second stage of preparation:
- Strain the cooled broth from berries and herbs, the latter can already be thrown away.
- Add honey and cognac to the liquid, mix thoroughly.
- Cut off several dozen leaves from the aloe (it is important that the plant is not watered for several days, and its age is from 3 to 5 years). Squeeze out the juice, it needs exactly 300 ml.
- Add the gummy mass to the almost finished medicine, mix again until smooth.
After 4 hours, the product can be taken in a strict dosage:
- 1 teaspoon two hours before meals, three times a day for the first 6 days.
- 1 tbsp. spoon one hour before meals, three times a day - the rest of the days.
The course is calculated individually and can last from two to 15 weeks.
We looked at how to make a decoction of chaga, but the plant can also be infused on an alcohol basis. For this you only need vodka and chaga mushroom. Raw materials are crushed on a grater (you need half a 250 g. Glass), after which 1 liter of vodka is poured. It is infused for 14 days in a basement or other dark, cold room, filtered. Method of administration - 1.5 teaspoons three times a day for an hour and a half before meals. The recommended duration of treatment is 10-14 days.
Remember, the use of any medication must be agreed with your doctor.
Can you eat woody mushrooms?
Mushrooms that grow on trees and are considered conditionally edible can be used for food, but on one condition - they must be young. In addition, they must undergo the necessary heat treatment.
You can make curly griffola soup (ram mushroom). A fungus of this type has a positive effect on the state of health: it stimulates the process of removing toxins from the body, allows you to suppress headaches, even migraines.
To prepare the first course from wood mushroom you will need:
- 300 g of mushroom ram;
- 7 potatoes;
- one onion and one carrot;
- a glass of wheat flour;
- 2 chicken eggs;
- salt;
- black peppercorns;
- dill and parsley to taste.
Vegetables need to be washed, peeled.
Use flour and water to make homemade soup noodles. To do this, add 0.5 teaspoon of salt to 0.5 cups of flour and beat in two eggs. The dough needs to be rubbed with your hands, making crumbs. Gradually add all the remaining flour to the flour mass. Leave the noodles to dry.
Mushrooms need to be washed and cut, placed in water, which should be salted after boiling. Cooking time - at least an hour.
Peel and chop potatoes and carrots. The onion must also be peeled and finely chopped.
Add black pepper and chopped vegetables to the prepared mushrooms. You can also add 2-3 bay leaves. Boil everything together for another half hour. Add homemade noodles, simmer for 10 minutes and turn off heat. At the end, put finely chopped greens.
It is good to add sour cream to any mushroom soup. It must be placed separately on each plate.
When preparing edible wood mushrooms, it must be borne in mind that they do not have a pronounced taste. Some of them, quite suitable for food, emit an unpleasant aroma during cooking.
Mushrooms growing on trees and stumps are both edible and inedible. They can be grown in their own summer cottage. On their basis, you can cook dishes, but more often wood mushrooms are used to prepare medicinal compositions.
«>
Use of tinder fungus
Some varieties of this class are also used in traditional medicine. For example, bordered tinder fungus is used to treat liver, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Other diseases curable with tinder fungus:
- incoagulability of blood;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- gout;
- insomnia;
- obesity.
Unlike the canted inonotus, this Basidiomycete is also used in everyday life. The dried fruit body of the saprophyte is useful for lighting stoves and fireplaces. If you set fire to a dry piece of pulp and leave it to smolder, you can get rid of annoying insects in the room for a long time.
Cultivating at home
Growing mushrooms at home on stumps is carried out with two goals:
- Utilitarian: edible is used for eating. This is how whole mushroom plantations are bred in the basement or in the garden.
- Decorative: decorating fruit trees or gardens. People decorate the dacha with bright fruit bodies: some types of tinder fungus are suitable for such purposes.
The search for suitable stumps is carried out in the forest or dried trees are cut. Some species take root equally well on all types of wood, while others are more demanding on the substrate. Growing on a large scale requires the following:
- Suitable place for sowing, high quality mycelium.
- Temperature and light conditions.
- Regular treatment and replacement of stumps or other substrate. Fruit bodies completely destroy wood in 6-8 years.
If the mushrooms have grown on their own plot, then they will be tasty, environmentally friendly, with healing properties.
Mushrooms growing on trees and stumps are edible or unsuitable for food. They use wood as a nutritious substrate. Some types of such fungi parasitize, disrupting the integrity of living tissues; others process dead wood and become food for birds and animals. Medicinal compositions are prepared from some types of woody mushrooms.
Chaga - beneficial properties
Recent research has found that this mushroom has many benefits. Chaga, whose medicinal properties have already been proven, affects the body as follows:
- provides an antispasmodic effect;
- improves the functioning of the heart and brain;
- has a mild hypotensive effect;
- strengthens the body's defense system;
- participates in hematopoiesis;
- accelerates the process of scarring and subsequent restoration of injured tissues;
- relieves intoxication;
- normalizes blood glucose;
- prevents hyperpigmentation;
- enhances the work of anticancer drugs.
Interesting facts about the mushroom
The drug Brefulgin is made from chaga, which is indicated for peptic ulcer disease, chronic gastritis and oncological diseases. No wonder. The fungus has a positive effect on the human body, preventing the development of many diseases and eliminating existing ones.
This mushroom is also mentioned in Solzhenitsyn's novel Cancer Ward. In the work, he is presented in the form of a drug that treats cancer.
Another interesting fact that everyone should know. The best mushroom, which will be rich in vitamins and minerals, is in the highest place. The higher the chaga, the more beneficial properties.
All useful properties are preserved only during natural drying without the help of an oven. Of course, this requires more time, but all trace elements and substances will have a positive effect on the treatment and prevention of diseases.
The shelf life is approximately 2 years if stored correctly. It is recommended to grind chaga into powder only before use.
Preparation of medicinal drinks
It is absolutely safe and even very useful to consume tea made from birch tinder fungus. There are many ways to make it - and put chaga, and boil it for infusion, and make it from a mushroom that was ground into powder beforehand. The recipes can be different, but they are all quite simple and do not require a lot of effort and time to wait for preparation. Here are some ways you can benefit from the fruiting body.
Healing tea prepared in several steps:
- dried mushroom powder is poured with hot water;
- placed in a dark place at room temperature for several days;
- the resulting brewed tea is thoroughly filtered;
- the resulting concentrate is diluted with hot water to its original volume.
Psilocybin Mushroom: How to Eat Different Types of Psilocybe
After that, the medicinal drink can be consumed. Store in the refrigerator for no more than three days, after which it will lose its beneficial properties.
Infusion from birch tinder fungus is prepared according to the same principle, but it does not need to be refilled with hot water to its original volume. This makes the infusion more concentrated. Rinsing your mouth with this infusion helps with gum disease.
However, not everyone can use infusions, teas, tinctures from birch tinder fungus. In no case should this be done to pregnant and lactating women, as well as people with diarrhea or colitis. With such diseases, useful substances will not be absorbed and there will be no benefit from the use of birch tinder fungus. The same is the case when a person uses antibiotics. It is also impossible to combine the consumption of glucose and birch mushroom at the same time.
Chemical composition
To understand the benefits and harms of the chaga mushroom, you need to familiarize yourself with its composition. The main active ingredients of chaga are water-soluble pigments. In addition to them, sterols, triterpenoids, agaricic acid, resins, micro- and macroelements, in large quantities - magnesium and potassium are found in the mushroom. Various acids were also found: formic, acetic, oxalic, vanillic. Lignin, polysaccharides, fiber are present. The proven antitumor effect of chaga depends on the presence of agaricic acid and sterols.










































