Vegetable growing »Cabbage
0
1164
Article rating
Correct crop rotation can significantly reduce the number of parasites and diseases. It makes it possible to preserve all the useful properties of the land and increase the future harvest, so it is important to know what crops to plant after cabbage.

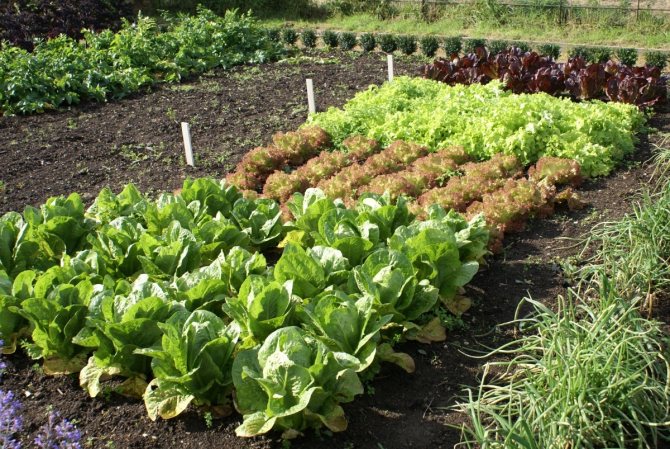
Planting crops in place of cabbage
Basic principles of crop rotation
The plants in the garden should be alternated correctly. There are good and bad predecessors for every plant. They are planted one and a half months before planting the main crop.
How do you know which plants are good and which are bad for cabbage? To understand this, you need to find out what nutrients it takes from the soil. Based on this, it is necessary to alternate it with other crops that require other nutrients.
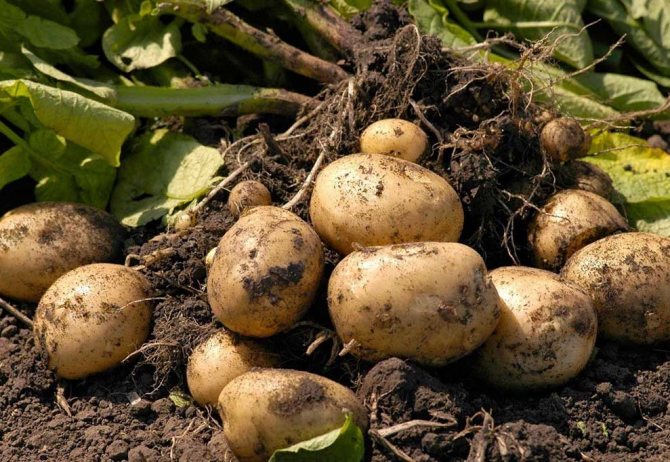
Cabbage is a crop with high nutrient requirementslike pumpkin, potatoes and squash, celery and spinach. Cabbage and potatoes can be grown in one place for 2 years, then they should be replaced with other crops.
These can be crops with an average nutrient requirement:
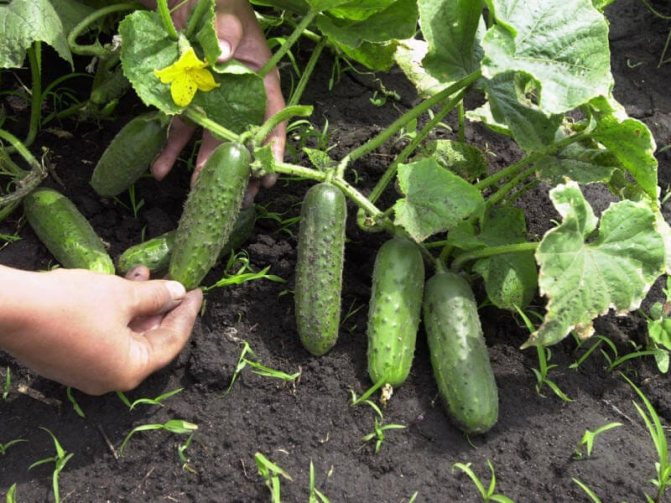
- Cucumber (Latin Cucumis);
- Eggplant (Latin Solanum melongena);
- Carrots (lat.Daucus);
- Polka dots (Latin Pisum);
- Onions (Latin Allium) and herbs.
The presented crops will help restore the nutritional value of the soil. As a result, after them it will be possible to plant the cabbage again.


Cabbage is a crop with high nutrient requirements
Planting cabbage after harvest
The vegetable in question is in great need of high soil nutrition, so it can be planted only after cucumbers or tomatoes. They are the ones who least deplete fertile land.
Among the varieties of greens, parsley, dill or garlic should be distinguished. The best choice of root vegetables would be potatoes, celery, legumes (peas or beans), which do not need a lot of nutrients.
Forbidden predecessors
Not the best version of the predecessor - carrots or zucchini. These crops absorb large amounts of substances from the earth. As a result, cabbage lacks resources for normal development.
The best neighbors for culture: joint planting options
Grows well next to cabbage potatoes (lat.Solanum tuberosum). Good neighbors and crops such as onion, dill (lat.Anethum), beans (lat.Phaseolus). Do not forget about marigolds (lat. Tagetes) are the best flowers for planting with cabbage. They drive away pests from her.
Important! Joint planting with cabbage is justified by those plants that, like her, love abundant watering. This is salad and onions on a feather.
What pests should be protected from cabbage is from fleas. It is she who gnaws through the leaves of the plant, literally making a sieve out of them. So, do it like this, so that the flea passes by, one simple method will help - to plant strong-smelling plants or flowers near the vegetable. These include garlic, coriander, and saffron. If the weather is good and the crop is properly cared for, you can plant eggplants, peppers and legumes next to it. Peking cabbage will also be a good neighbor. Sage, mint, and thyme are also great options. And dill can even scare away aphids from the vegetable.
Marigolds are the best flowers to plant with cabbage
What kind of soil does cabbage like?
The white-headed lady is demanding on the presence of light, high humidity, as well as the composition and quality of the soil, so it is important to choose the right place for planting it.
We take into account the acidity of the soil
Cabbage prefers fertile lands with a neutral or alkaline reaction. The optimum acidity level is 6.7-7.4 pH. Acidic soils are not suitable for white cabbage, increasing the risk of keel disease. Such land can be improved by liming with the help of:
- dolomite flour;
- lime fluff;
- powdered chalk;
- wood ash.
Dolomite flour contains calcium, which reduces acidity, and magnesium, which improves the quality of vegetable products. That is why it is considered the best deoxidizer.
This procedure is carried out in the fall. One of the listed substances is introduced into dry soil at the rate of 1-2 cups per 1 sq. m, the garden is immediately dug up and left until spring.
Choosing and preparing a site for planting
Cabbage grows well on open southern or southeastern slopes, with the possibility of an abundant supply of water. The soil should be characterized by high air and water permeability. With excessive moistening of the earth, the plant suffers from a lack of oxygen, and therefore, it develops poorly and grows slowly.
The best option is loam, which has the ability to retain moisture in its particles. Sandy soils do not retain water and nutrients sufficiently. To improve their properties, it is necessary:
- Remove the top layer of soil from the plot (40-50 cm).
- Lay a 10–15 cm layer of clay on the bottom.
- Mix the initially collected soil with peat, manure and mineral fertilizers and sprinkle on a clay layer.


Loams are ideal for growing vegetables as they provide good drainage and water retention properties.
It is possible to increase the moisture content of the soil if, during the autumn digging, sawdust moistened with urea, peat or sod soil is added. It is recommended to dig the garden bed as deep as possible without breaking large clods. The undulating surface of the site will freeze better in winter and accumulate more moisture.
An important factor when placing cabbage beds in the garden is plant compatibility. When a white cabbage plant is planted next to bad neighbors, the likelihood of their defeat by common diseases or oppression of each other increases.
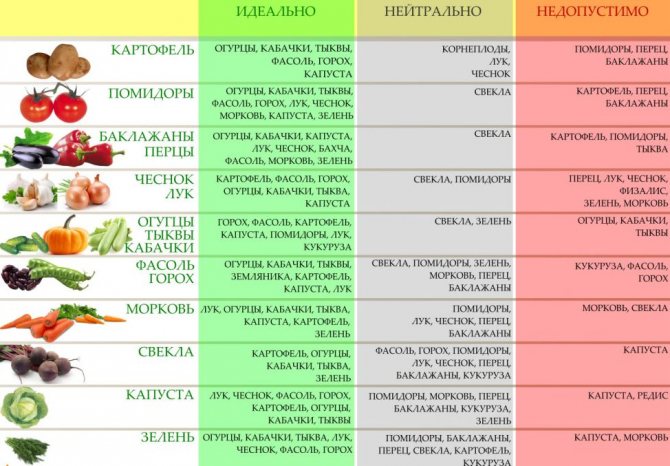
Table: predecessors and neighbors of white cabbage
| Best predecessors |
|
| Bad predecessors |
|
| Ideal neighbors |
|
| Incompatible neighbors |
|


By planting cabbage next to celery, you can ensure the destruction of the earthen flea, and the neighborhood with aromatic herbs will frighten off egg-laying cabbage butterflies.
Do not forget to follow the rules of crop rotation: do not plant cabbage in the same place for more than 2-3 years. This drains the land, increases the risk of disease, and affects yields.
What is better to plant in cabbage beds next year
Many crops can be planted the next year after cabbage, but not crucifers. The latter belong to the same species as cabbage, therefore, they require the presence of the same nutrients in the soil and are affected by the same pests. In the second year after the vegetable, it is better to plant:
- Beetroot (Latin Beta);
- Salad (lat.Lactuca);
- Early potatoes;
- Peas;
- Carrot;
- Cucumbers (Latin Cucumis sativus);
- Parsley (lat.Petroselinum);
- Onions and celery (lat.Apium).
It is permissible to plant peppers, eggplants, tomatoes, strawberries after harvesting cabbage.
You should not plant after the described culture of radish, radish, lettuce, turnip, horseradish, mustard leaf. Otherwise, it will lead to depletion of the soil. Moreover, pests and diseases can remain in the soil, which can be transmitted to planted crops. And this will significantly reduce the harvest.
In order to replenish nutrients in the soil, it is necessary to plant green manure
Agrotechnical cultivation
Seedlings are planted on pre-prepared beds. Early cabbage varieties need to be planted only after the leaves on the birches reach the size of a penny. If planted earlier, then there is a high probability that the plants will suffer from the cold.
Remember that seedlings should have up to 5-8 true leaves. If there are fewer of them, the plant has not yet matured, and will recover for a long time after transplanting. If more - does not form a head of cabbage and will give out an arrow. The seedlings should be a little sluggish so that they do not break when planting.
The cabbage planting scheme depends on the ripening time and variety. Early maturing varieties can be safely planted every 50 cm in the length of the beds and about 30 cm in width. Plants form small heads of cabbage, so that much space is not required for them. Mid-season and late-ripening varieties are giants, and therefore between them you need to leave about 65 cm in length and about 50-70 in width. There is only one way to shorten the distance - if you plant cabbages in your beards. The yield will be great if you shower the plants in a timely manner.
Early varieties of cabbage for consumption at the end of July - August must be planted in the ground with seedlings no later than April 20. For an earlier harvest, you need to take care of planting even earlier and plant the seedlings before April 10. To prevent her from catching cold and dying, each plant can be covered with a cut plastic bottle. Late varieties of cabbage are allowed to be planted until June 10.
When planting, plants are buried to the first true leaf. Remember to cover the puddle of water with dry soil when watering. This must be done to avoid crusting on the soil surface.
Caring for cabbage is simple. It consists of systematic loosening, watering and weed removal. Plants need to be spud 2-3 times per season. Adding soil to the roots will cause additional roots to grow, and the heads of cabbage will turn out to be larger.
As it grows, cabbage requires more and more moisture. The moisture balance in the soil must always be maintained. If there is too much water, the heads of cabbage will begin to crack. We will deliberately not specify the watering rates. The moisture consumption of plants, of course, is the same, but the rate of drying out of the earthen coma depends on the type of soil. In peaty areas, moisture can hold for 5 days, and on sandy areas it will disappear by morning.
To speed up the growth of cabbage, carry out regular plant feeding. For the first time, feed the plants with mineral fertilizers 10 days after planting. After another three weeks, add potassium chloride to the fertilizer.
Sometimes cabbage is fed with a ten-day infusion of mullein. The measure is very effective, it increases productivity, but only a small part of summer residents will be able to find manure.
Harvesting cabbage should be done as the heads ripen. Make sure they don't start cracking. The more carefully and carefully you remove the heads of cabbage, the longer they will be stored. Late varieties of cabbage can be left on the site until the first severe frost. If the varieties are bitter, then a light frost will eliminate this flaw. In this case, the plants themselves will not be affected.
| Tweet |
loading ...
loading ...
Choosing and planting green manure
In order to replenish nutrients in the soil, it is necessary to plant green manure. Oats, mustard and lupine are able to suppress the occurrence of many pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the development of vegetable diseases. Legumes will replace the nitrogen content in the soil. For the winter, siderates are not mowed, only in the spring they are dug deeper into the ground.
Good green manures for cabbage are:
- Daikon;
- Lupine;
- Oats;
- Peas;
- Cereals.
How to grow cabbage (video)
Not every green manure can be planted in autumn. There are winter and spring crops.
- Winter crops Are vetch, rye and rapeseed. They are planted in late autumn. Seeds germinate in spring. You can plant in early autumn, then the slightly overgrown tops will go under the snow.
- Spring - this is phacelia, oats, white mustard, oil radish. They are unable to endure the winter. Both the aboveground part and the roots die off, so in the spring it will be necessary to cut their roots with a flat cutter at a depth of 6 cm in the ground. And then mix them with earth. In order for the green mass to decompose successfully, it is also recommended to spill the soil with a solution of Baikal EM-1.
Many spring green manures are planted before winter.
Many spring green manures are planted before winter. For example, despite the fact that it is customary to plant phacelia in spring, if it is sown in October, nothing bad will happen. It is important to sow 2 times as many phacelia seeds for successful germination. You will have to plant 20 g of a plant per m2. The same can be said for sowing mustard. It is planted denser than usual if planting is carried out before winter.
The positive features of planting siderates before winter are that in the spring they will rise and grow earlier. Accordingly, if you make holes for cabbage next to them, green manure will protect it from freezing. After the vegetable is strong, the herbs can be easily mowed. However, it is not necessary to remove their root system. It will act as mulch.
Features of growing cabbage in the regions
Cabbage is cultivated almost everywhere. Thanks to the centuries-old work of breeders, it became possible to choose zoned varieties: for the northern regions - frost-resistant, for the southern ones - drought-resistant. Planting methods and timing may vary in different climates.
In the Urals, Siberia, Altai
In these regions, cabbage is grown through seedlings. Sowing is carried out in the last days of March - early April.
Fortified seedlings are planted in open ground a little later than in the southern regions:
- early varieties - in the second half of May;
- varieties of medium ripeness, medium late - in early June.
Late varieties in these regions are practically not planted, since in August there are already frosts, and in October the first snow falls.
Table: popular varieties and hybrids of white cabbage for Siberia, the Urals, Altai
| Early ripening |
|
| Mid-season |
|
| Mid late |
|
Another feature of growing vegetables in cold climatic zones is the need to process seedlings with growth activators that stimulate their development:
- Gumat-7,
- Stimulus,
- Epin-extra.
In outskirts of Moscow
The climate of the Moscow region allows sowing cabbage seeds not only for seedlings, but also directly into the ground, provided that they are protected with film coatings, greenhouses or warm beds are used. Sowing time in the middle lane:
- early and mid-early varieties - from April 20 to May 10;
- medium, mid-late and late - from 10 to 30 May.
Seedlings are planted in open ground at the age of 35–40 days.
Table: the best varieties for growing in the Moscow region
| Growing methods | Variety name |
| In the open field |
|
| In the greenhouse |
|
In Ukraine
The mild climate of the country creates comfortable conditions for the growth of the white-headed in all areas. Early varieties are cultivated in greenhouses and in warm beds, mid-season and late ones are sown with seeds in open ground. In the southern regions of Ukraine, even the latest varieties with ripening periods of more than 190 days have time to ripen.
Table: the most common varieties of white cabbage in Ukraine
| Early |
|
| Mid-season |
|
| Late |
|
So, now you are armed with the knowledge of the peculiarities of planting and caring for cabbage. You can boldly get to work and, undoubtedly, the white-headed one will delight you with a rich and crisp harvest.