Crop rotation in the garden is a useful exercise. It is a change of vegetable crops in one area. If necessary, the allotment is given the opportunity to recover, which is called "leave under steam."
You can alternate plants in different ways, but you need to take into account the rules. The main thing is to observe agrotechnical soundness for all cases. That is, a well-thought-out scheme should turn out, which is a list of categories of plants that need to be planted in turn.
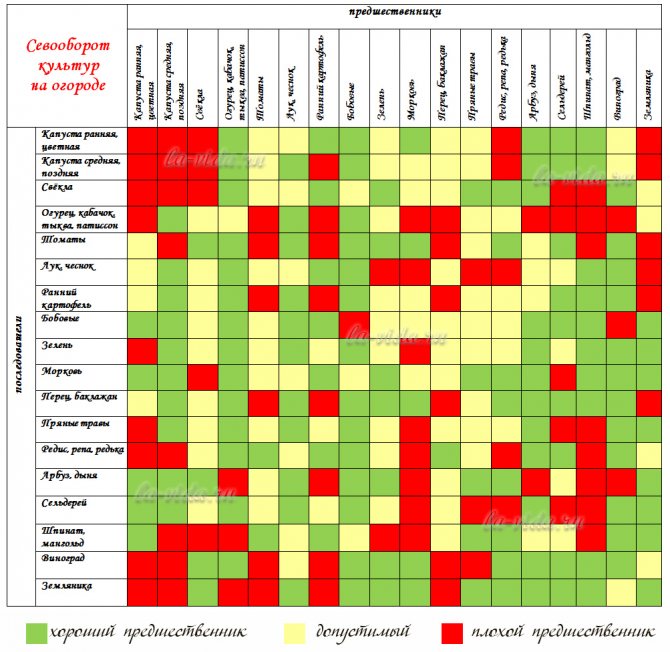
Crop rotation table at their summer cottage
The placement of fruit and berry crops in summer cottages and household plots should also be well planned. Experts have developed a compatibility table for shrubs and trees. Chaotic plantings lead to reduced fruiting and, as a result, poor harvest in subsequent years. Since the specificity of tree planting is such that it can only be clarified after a few years, it becomes difficult to fix this problem. An example of that cherry and sweet cherry. They do not tolerate the close proximity of other fruit trees. Better to plant them away from the main garden. Vegetable crops also do not grow near those places where cherries dominate. Its powerful root system suppresses everything around it. And such a combination as a pear and an apple tree or an apricot and a plum helps each other. The raspberry-peach neighborhood also bears good fruit.
So, here's what to look out for:
Crop rotation rules for the garden
Crop rotation techniques and recommendations allow you to distribute crops on the site with maximum benefit:
- The most fertile beds are allocated for "gluttonous" crops (zucchini, cabbage, cucumbers) with the preliminary introduction of organic matter and mineral fertilizers. After harvesting, to increase fertility, the site is sown with green manure, which, after plowing, improve fertility even better than manure;
- Poorer soils are suitable for tomatoes, peppers, radishes, onions, herbs (unless they are planned to be grown in a greenhouse);
- Carrots, beets, parsley, turnips bear fruit well in poor soils, while clay soils must be diluted with sand to increase air permeability;
- The distribution of crops on the site takes into account the power and length of the roots. Alfalfa and corn have long roots (up to 2 m), the root system of tomatoes is slightly shorter (about a meter), and cabbage, cucumbers and onions take nutrients from the surface layer. This factor is taken into account when alternating crops on the site;
- When drawing up a planting scheme, an alternation of sites for crops that enrich the soil with nitrogen (beans, peas, beans) is performed. As siderates, the greatest benefit in this regard is brought by clover, lupine, alfalfa;
- Perennial crops (rhubarb, lovage, perennial onions, sorrel, tarragon, asparagus) are placed along the edges of the plot, near the fence and buildings;
- Crops with common diseases and pests are not placed not only one after another in time, but also side by side on the ridge, since there is a high probability of mutual infection.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Tomato budenovka characteristics and description of the variety
When organizing plantings in the garden, various factors must be taken into account.
If you plant the same plants on the same site every year and do not change the zones in places, then harmful substances and microorganisms, insect larvae are collected in the soil. They will severely damage crops in subsequent years.
Related plants use similar nutrients. And if they are planted on the site every time without interruption, then then there will not be enough nutrients, which will have a bad effect on the development of crops. The root system will release toxic substances, due to which the quality of the soil for similar plants in the same group will deteriorate sharply.
Such negative moments gradually accumulate. Without proper crop rotation, the soil becomes poorer every year. Even the timely application of appropriate fertilizers will not save such a situation.
Crop rotation is one of the main parts of the competent cultivation of plants in the garden. This measure has the following meaning:
- Economic. Helps fulfill the harvest plan, and even with a surplus. It is imperative to carry out rational planning of the site.
- Organizational. This plan assumes the correct use of equipment and labor to increase yields and reduce financial and labor costs.
- Agrotechnical. Means the correct use of the site and the increase in soil fertility.

Memo: "What to consider when alternating vegetable crops in a crop rotation"
When planning a crop rotation, it is necessary to comply with the condition - vegetables are planted in the former places belonging to the same family with an interval of 3 to 4 years, and the longer this period, the better.
The exceptions are: potatoes, strawberries, beans, which can be planted for years in the same place, provided that there are no specialized pests and a high degree of disease development.
With a small area of \ u200b \ u200bthe garden, most summer residents are forced to plant individual crops in a permanent place, especially for potatoes, which occupies the largest area on the site.
In agricultural technology, the following distribution of the main garden crops is adopted for individual main families:
- onions - all kinds of onions, garlic;
- nightshades - physalis, eggplant, tomatoes, potatoes, peppers;
- legumes - soybeans, beans, peas, beans, peanuts, cowpea, rank;
- umbrella - parsley, carrots, celery, dill, cilantro, cumin;
- cruciferous - radishes, cabbage of all kinds, daikon, radish, turnip, watercress;
- pumpkin - cucumber, zucchini, pumpkin, melon, watermelon, squash;
- haze - chard, spinach, beets;
- aster - sowing lettuce, sunflower, tarragon, Jerusalem artichoke, artichoke;
- labiates - marjoram, savory, hyssop, lemon balm, peppermint, basil;
- buckwheat - rhubarb, sorrel.
To prevent one-sided depletion of the soil, planting plants alternate taking into account what nutrients they require. In a highly simplified form, this is an alternation of tops and roots (for example, after cabbage or tomatoes, carrots are planted).
After garlic and onions, planting of any crops is allowed, but re-sowing them in one place is extremely undesirable.
Memo: What to consider when alternating vegetable crops in a crop rotation (1.9 Mb)
Seed planning
Such an event will help correct the problem with the content of useful components in the soil. Be sure to take into account the following rules:
- It is forbidden to plant the same crop for several years in a row in one place. Moreover, this rule also applies to related plants from the same group. This is due to the fact that they have common pests and a similar reaction to toxic substances.
- Always take a break so that the site has time to rest after the planted plant. The standard period is a couple of years, although many argue that 1 year is enough. But the latter only applies to light crops.For example, celery and salad fall under this definition. For some plants, the rest period should be longer. Cucumbers, parsley and carrots take 4 years, and cabbage takes 7 years.
- Plants not only absorb nutrients from the soil, but also fertilize it due to the composition that is present in their root system initially. Thanks to this, if the crops are rotated correctly, not only will the supply of nutrients in the soil be preserved, but also its composition will improve. For example, legumes help to loosen the earth and add a mineral component to it. Buckwheat and melon saturate with calcium, and datura grass - with phosphorus. If tobacco is planted instead of weeds, then the level of calcium will increase, and if nettle, then the iron will become more.
- It is imperative to apply compost after harvesting. This will keep the soil fresher and healthier.
- Planting plants also helps from pests. For example, garlic and tobacco save from aphids, and thyme from the Colorado potato beetle.
- After heavy crops, lighter crops are supposed to be planted.

If you break these rules, it will lead to the fact that the soil will become depleted.
Recommended alternation considering predecessors
This is the easiest way to compose a crop rotation. But even with its help, you can significantly increase the yield. The table lists the most commonly grown vegetables and gives recommendations for acceptable predecessors.
| Culture | After what crops is it recommended to sow | After what crops it is allowed to sow | After which crops can not be sown |
| Blue eggplants | Siderata are ideal predecessors. Good after melons or early cabbage. It is allowed to sow after carrots, garlic and onions. | Can be sown after harvesting crops of corn, beets and mid-season cabbage. | Tomatoes, bell peppers, potatoes are prohibited as predecessors. Including eggplants of all other types are prohibited. |
| Beans, beans and peas | It is best to choose potatoes or carrots. Not bad onions, pumpkin, garlic. | Do not sow after beets, tomatoes and peppers. Any greens (parsley, dill), eggplants and bell peppers. | Corn, it is forbidden to sow after legumes. |
| Zucchini | Optimum potatoes and all legumes, garlic and onions. After cauliflower. | Allowed after salads, beets and legumes. | Cabbage, eggplant, tomatoes and peppers are prohibited from being predecessors. |
| Common cabbage | Seedlings are planted on potatoes, zucchini and carrots. | Greens, lettuce, tomatoes and eggplants. | Pumpkin, beets, cabbage, radishes, cucumbers. These plants can significantly reduce the yield. |
| Potatoes | Excellent predecessors of cabbage and green manure. It is good to plant after cucumbers, squash, garlic and onions. | Corn and cabbage, beets, greens are strongly discouraged. | All nightshades, cucumbers, eggplants, bell peppers are prohibited. |
| Onion | Optimally: carrots, after cabbage, carrots. | Onions, you can after bell peppers, cabbage. We accept garlic, tomatoes. | It is forbidden to plant after carrots and salads. The choice of crops is very careful. |
| Carrot | Onions, cabbage, salads are allowed. Pumpkin and squash can be. | All legumes, corn, bell peppers and tomatoes can be applied. | Beetroot can not be a predecessor. |
| Cucumbers | Any legumes, parsley and cabbage are great. Garlic, onions, potatoes do not have a harmful effect. | Greens, red beets are allowed. | Cannot be sown after cabbage and eggplant. Tomatoes, bell peppers, plants that use a lot of nitrogen fertilizers are undesirable. |
| Bell pepper | There can be any melons, cucumbers. If the beds are free from under the cucumbers and peas, you can occupy them. | It is possible after radishes, beets. Corn in exceptional cases. | Solanaceae, pumpkin, eggplant are undesirable. |
| Radish | Very unpretentious to its predecessors. Potatoes, legumes, strawberries, garlic will do. | Salads, herbs, tomatoes and beets are allowed. | Carrots and cabbage are highly undesirable. |
| Red beet | Greens, salads, cucumbers and squash are like. Grows well after legumes and green manure. | Good yields after corn, cabbage, garlic and onions. There may be tomatoes, garlic. | Potatoes and tomatoes are not recommended as predecessors. |
| Tomatoes | Ideal bean, can be cucumbers, cabbage. | After garlic and onion, the yield is average. | Bell peppers, nightshades are prohibited as predecessors. |
| Pumpkin | Legumes, potatoes, cabbage are recommended. Good yield after garlic and onions. | Potatoes, salads, herbs, beets are good. | Blue eggplants, carrots, cabbage are not recommended. These include terets and tomatoes. |
| Garlic | Siderates and legumes are ideal precursors. Cucumbers and cabbage are acceptable options. | Eggplants, pumpkin, tomatoes, corn are allowed. | No need to sow after radishes and carrots. |


Due to the fact that potatoes mostly occupy large areas, they can be excluded from the crop rotation. In some areas, it can grow up to 5 years, while you only need to change different varieties.
Causes of soil fatigue
One of the main factors affecting the level of yield in any area is soil fertility. If the same crop is cultivated in one place year after year, the soil condition known as "fatigue" inevitably sets in. Why is there depletion of the soil in a certain area?
- Toxic root secretions, or colins, secreted by plants from year to year, have a particularly detrimental effect on the plants themselves (parsley, beets). Leeks, legumes and corn are immune to colins;
- The fertility of any soil is not infinite, and not all of the trace elements can be renewed with organic matter and mineral additives. Crops of the same family require a similar set of minerals, and growing in the same area of plants, for example, pumpkin or cruciferous, is fraught with the disappearance of certain nutrients from the soil;
- Fungal diseases and pest eggs inherent in the nightshade or umbrella family will appear on the site even after careful treatments, if you do not use the rules of crop rotation.
What after what can not be planted
Remember the incompatible crops that cannot be planted one after the other:
Eggplant, pepper ≠ cucumber; Radish, beets ≠ cabbage; Potatoes ≠ tomato, pepper, eggplant Carrots ≠ onions; Pepper, tomato ≠ eggplant; Carrots ≠ garlic; Beets ≠ carrots, turnips. Cruciferous, nightshade ≠ strawberries Corn ≠ peas, beans
Crop rotation is the key to the success of every gardener. A responsible and correct approach to planning and growing vegetables on a small plot of land is the key to the success of every gardener. As a result, you get a good harvest, organic vegetables, minimum material costs.
Predecessor table
Crop rotation table: followers and predecessors of vegetables when planting (2.5 Mb)
- The best predecessors of tomatoes are cauliflower and early cabbage, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins, greens, carrots and siderates. It is permissible to plant tomatoes after onions, garlic, herbs, beets, cabbage of late and medium varieties. After the rest of the crops, it is no longer worth planting tomatoes in the garden.
- Wonderful precursors of cabbage are cucumber, squash, pumpkin and legumes. But then comes the division. For late and medium varieties, early potatoes and carrots are good, and for early and cauliflower, it is better to sow after siderates and onions with garlic.
- Good precursors of onions and garlic (which you grow not for greens) are cauliflower and early cabbage, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins, early potatoes, peas, beans, beans and green manures.
- The best predecessors of cucumbers, squash, pumpkin, etc. - onions, garlic, legumes, corn, early cabbage and cauliflower.
- Good predecessors of peas - any cabbage, early potatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkins and squash.
- Excellent predecessors of carrots - cabbage, potatoes, herbs and spices, zucchini cucumbers and green manure.
- The best predecessors of pepper and eggplant are cucumbers, onions, carrots, green manure, etc.
- Good predecessors of beets are spices and herbs, potatoes, cucumbers, etc.
- Wonderful predecessors of potatoes - zucchini, garlic, legumes, green manure, etc.
It seems that you managed to figure out how the table works without much difficulty. So, the "hurry-ups" leave us, and we move on.
Each crop uses a certain amount of nutrients to form a crop, while releasing toxic substances into the soil as a waste product. Toxins can build up and inhibit other vegetable plants. With this in mind, each species can be grown after certain crops. The following table provides guidelines for choosing a predecessor.
| Culture for planting | Preceding cultures | ||
| Recommended | Allowed | Ruled out | |
| Potatoes | Pumpkin seeds, legumes, white cabbage and cauliflower | Beets, corn, carrots, onions | Tomatoes, peppers, eggplant |
| Garlic, onion | Tomato, white cabbage and cauliflower, cucumber, zucchini, pumpkin | Pepper, eggplant, corn | Onion garlic |
| Tomatoes | Pumpkin seeds, legumes, cabbage | Beets, onions, garlic | Potatoes, physalis, tobacco, pepper, eggplant |
| Cucumber, pumpkin, squash, zucchini | Peas, beans, early potatoes, early white cabbage and cauliflower | Green, tomatoes | Pumpkin |
| Peas, beans, beans | Cucumber, pumpkin, potatoes, cabbage, tomatoes | Corn | |
| Carrot | White cabbage, tomatoes, legumes, onions, cucumber | Garlic, eggplant, pepper | Root parsley, celery |
| Green and spicy aromatic | Cabbage, pumpkin seeds, legumes | Onions, tomatoes, beets | Parsnips, carrots |
| Eggplant, pepper | Pumpkin seeds, cabbage, legumes | Beets, green | Nightshade |
| Table beet | Early potatoes, cucumber, tomatoes, early white cabbage | Bulb onions | Carrots, beets |
| Cabbage | Beets, cucumber, onions, potatoes, tomatoes | Carrots, peppers | Beetroot, turnip, radish, radish, daikon |
| Vegetable corn | Beets, carrots, green | ||
| Radish and daikon | Undemanding to its predecessor | Cruciferous | |
Ways to increase yields
Vegetable plants of the same species consume the same nutrients from the soil, emit similar toxins, and have the same pests. When cultivating plants in a permanent place, the soil is severely depleted. There is a multiplication of pests, infection with diseases, as well as the growth of weeds. Soil fatigue sets in, its fertility decreases. It accumulates toxins released by plants. We carry out crop rotation of crops according to tables.
To increase the yield of vegetables, the following conditions must be met:
- Alternating the cultivation of crops in the garden.
- Soil enrichment with mineral and organic fertilizers.
- The choice of a place for planting, taking into account the need for lighting and watering.
- Accounting for predecessors in the garden for each crop of farming.
There is no standard and correct crop rotation scheme, since each summer resident grows different crops and in different quantities. Some plant a lot of potatoes, others grow herbs and cucumbers. Therefore, an individual table of crop rotation of vegetables in the beds is compiled. To do this, a diagram of the site and a description of the plants grown by summer residents are entered into the dacha journal. It is desirable to have permanent beds for better crop rotation.
Crop classification and soil interaction


The crops grown in the summer cottage consume various substances from the soil. Therefore, it is necessary to constantly change the beds in places. Plants must be returned to their original growing location after four or six years.To carry out crop rotation, it is necessary to take into account their need for nutrition and soil condition.
How to properly plant tomatoes in the ground
Plants not only extract useful substances from the soil, but also improve its composition. Buckwheat reduces soil acidity, legumes enrich it with nitrogen. Cabbage and potatoes inhibit the growth of weeds. You need to know which family the plants belong to. Crop rotation at the summer cottage takes into account the classes of plants according to the table.
Table 1. Vegetables of botanical families
| View | Vegetables |
| nightshade | tomato, eggplant, potato |
| pumpkin | cucumber, zucchini, pumpkin, lupine, clover |
| bean | peas, beans, soy |
| cabbage | cabbage, radish, horseradish, mustard |
| onion | onion garlic |
| umbrella | carrot, parsley, dill |
| amaranth | beets, spinach |
| aster | salad, sunflower |
| green | lettuce, sorrel, watercress |
| buckwheat | buckwheat, sorrel, rhubarb |
Plants can be divided into four groups according to their nutrient requirements. The following crops require the most fertilized soil: cabbage of all kinds, squash, pumpkin, sunflowers and potatoes. For their growth, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are needed. Plants with average nutritional requirements include tomatoes, eggplants, cucumbers, melons, onions, and corn.
Phosphorus fertilizers, compost, and ash must be added to the soil. Crops such as carrots, beets, spinach, dill and celery are undemanding, but the soil must be mulched with compost and potash preparations must be added. The fourth group includes plants that saturate the earth with nitrogen, loosen it. Legumes: peas and beans. Potatoes and cabbage inhibit weed growth. Cultivation is carried out according to the following principle:
Table 2. Crop rotation in relation to soil
| 1.High demand | 2.Average need |
| 4 legumes | 3 weak need |
Onions for greens: varieties of varieties for planting
The cycle is four years: legumes are moved to the place of plants that require the maximum amount of nutrients and instead of crops with an average need for mineral fertilizers. They move to third place, vegetables with low nutritional requirements take the place of legumes, and legumes take the first place. The relocation takes place annually. This enables the plants to have adequate nutrition.
Changing the place of cultivation of vegetables on the site makes it possible to reduce the use of mineral fertilizers and reduce the number of pests and diseases in the soil. Black steam is best for all plants as it allows the soil to rest. But summer cottages are mostly small, so it is quite difficult to increase soil fertility in this way.
Another way to increase yields is to add nutrients to the soil. The need for plants is different and is divided into groups:
- Manure application. Species required: cabbage, pumpkin and potatoes.
- Phosphate fertilizers and ash. Improves the growth of root crops.
- Introduction of humus, peat, sawdust. Used for onions and herbs.
- Potash fertilizers and ash. Essential for root crops.
When choosing a planting site for vegetable crops, it is necessary to take into account the need for lighting. Light-loving plants include nightshade and pumpkin crops. Partial shade legumes and root crops are taken out. Greens, sorrel and zucchini are shade-loving.
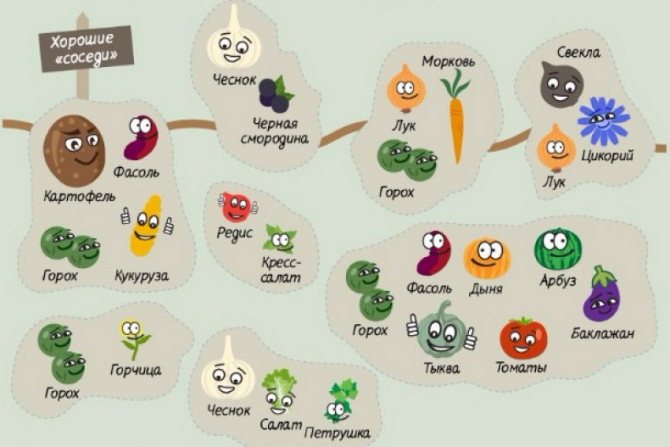
Using mixed landings
You can increase the efficiency of crop rotation by using mixed plantings, while it should be remembered that this term does not mean half a carrot garden and half an onion. Both cultures should sit on the same ridge: a row of carrots, a row of onions. Then onion pests will be scared away by the smell of carrots, and vice versa.
| Need for sunshine | Culture name |
| Photophilous | Tomato, eggplant, pepper, beans, cucumber |
| Moderately photophilous (shading is possible part of the day) | Onions, cabbage, carrots, beans, beets, radishes |
| Shade tolerant | Greens, Chinese cabbage, dill, rhubarb, sorrel, zucchini |
If you want to protect your plantings from pests, plant aromatic herbs-spices and medicinal plants with a strong smell: peppermint, tansy, garlic, catnip, marigold, mustard, coriander. The experience of some farmers suggests that growing a monoculture depletes the soil and pests proliferate.
The bottom line is that a particular vegetable cannot be grown in the same place. This depends on a number of reasons. Any plant absorbs necessary trace elements from the soil. If the crop rotation at the summer cottage is violated or not fully observed, then the land will be depleted, fertility will decrease, which will negatively affect the future harvest.
Another factor affecting the alternation of vegetable crops is the moment that pests and pathogenic bacteria that are dangerous for this particular type of plant, which will destroy crops, may appear on a given area. For example, the onion fly is not afraid of carrots, the root wireworm is not dangerous for the bulbous. Therefore, carrots and onions are good interchangeable plants.
For onions and garlic, cucumbers, cabbage, zucchini, varieties of pumpkin crops, beans, peas, and carrots can be considered good predecessors.
Cucumbers and melons must be planted after cabbage or onions and garlic. It is undesirable for them to allot areas where cabbage or tomatoes grew a year earlier. They, in turn, cannot be planted in the same place for two years in a row.
You should not do so that the predecessors of vegetables when planting are plants of the same family, since they are susceptible to the same diseases, and pests that remain in the soil will continue to infect the garden. For example, a cruciferous flea will destroy a radish if there was a cabbage patch in the area last year.
Neighborhood rules in the country
When planning the planting of vegetables at their summer cottage, you need to know what to grow and after what.
Table 4. Previous crops of agriculture
| Vegetables | Perfect compatibility with | Neutral attitude with | Can't be planted with |
| potatoes | legumes, cabbage | root vegetables, onions | nightshades |
| cabbage | legumes, pumpkin | nightshade, salad | cabbage, beets |
| tomato | cucumbers, legumes | root crops | potatoes, corn |
| cucumbers | cabbage, onions | root vegetables, herbs | potatoes, dill |
| legumes | potatoes, cabbage, cucumbers | Tomatoes, herbs | perennial herbs |
| beet | potatoes, herbs, cucumbers | legumes, nightshade | carrots |
| carrot | cucumbers, herbs | tomatoes, onions | beetroot |
| onion garlic | potatoes, tomatoes | cabbage, beets | carrots, legumes |
| pepper, eggplant | legumes, pumpkin seeds, cabbage | beetroot, basil | nightshades |
| parsley | tomatoes, cucumbers | legumes | carrots, celery |
How deep to plant garlic before winter
We must also remember the rules for the joint arrangement of vegetables in the beds. Usually, plants of the same species do not get along well next to each other, which is important to know when planting plants.
Table 5. Mutual influence of plants
| Plant | Good neighborhood with | Can be planted together with | Neighborhood is not allowed with |
| legumes | eggplant, root vegetables | cucumbers, potatoes, cabbage | onions, tomatoes |
| cabbage | salad, beans, cucumbers | potatoes, beets, mint | parsley, tuberous |
| potatoes | peas, corn, beets | eggplant, garlic, dill | pumpkin, nightshade |
| onion | tomatoes, carrots, beets | potatoes, cucumbers, radishes | legumes, sage |
| beet | cabbage, onions, carrots | carrots, salad | corn, beans |
| carrot | beans, radishes, onions | garlic, tomatoes | dill, parsley |
| cucumbers | cabbage, onions, peas | corn, salad, beans | dill, potatoes, melon |
| tomato | onions, beans, salad, dill | cabbage, peas, cucumbers | potatoes, corn |
Pleasant neighbors - a big harvest
On my garden plot, not only the correct crop rotation, but also the plants have a pleasant neighborhood. I take into account the ability of different cultures to negatively or positively influence the development of each other. I noticed that most often plants of the same family are at enmity with each other, but as an experienced gardener I take into account other factors.
Repelling insects
If the plants are chosen correctly, then their neighborhood will help ward off pests. The point is in biologically active substances - phytoncides, which are released by the green mass of the plant. The smell of onions is not tolerated by a carrot fly, and onion pests are not tolerated by carrot tops. Their beds can be placed side by side.
Another option is to plant in rows on the same bed. Garlic, in addition to the main bed, grows in plantings of strawberries and strawberries, driving away harmful insects of berry crops.
Low-growing velvet and calendula will help ward off pests. 2-3 plants at the edge of the garden will play an important role in allelopathy. Marigolds secrete thiophene, which is disliked not only by harmful insects, but also by weeds. Bindweed does not tolerate such a fragrant neighbor.
Different plant heights
Some plants require light shading, and direct sunlight is contraindicated. Corn can block the wind and sunlight, sometimes pea vines or asparagus beans can cope with this task.


Attracting beneficial insects
Insects help pollinate plants, including fruit trees and shrubs. I plant flowers to attract them to the garden. Perennials and annuals grow not only in the recreation area near the house, but also along the edge of the beds. For example, I occupy 70 centimeters from the edge with gladioli, I plant 1-2 petunias or velvet plants to them.
The use of green manure in crop rotation
Some plants are capable of leaving behind a rich and fertile soil that is suitable for all crops. The point is in the root system, which is equipped with special tubules. Planting oats will rid the soil of a source of fungal diseases. For this, the culture is called the soil orderly.
The siderates include mustard and phacelia. Moreover, we plant phacelia next to the potato plantings so that it does not allow the wireworm and the bear to profit from the tubers.


After digging the onions and garlic, I dig up and plant the green manure. I give preference to legumes, the roots of which emit nitrogen and translate into a digestible state. I think planting legumes three times a day is tantamount to putting in a bucket of manure. In the second half of summer, peas have time to develop and give a small harvest.
Most often I plant wheat and some plants in the fall before winter. In the spring they start to grow, and then I dig it up with them.
The structure of the soil and the content of minerals in it improve, earthworms receive nutrition. Any crops grow well on such beds, but according to the rules of crop rotation, preference should be given to leafy crops - different types of cabbage.
Participants in the process
The composition of the crops that you grow on your site is different.... It depends on:
- Plot area;
- Its importance in providing you with products;
- Keeping productive livestock and poultry (cows, pigs, chickens) on the site.
Agree, it's one thing when you go to the dacha to lie in a hammock and dig deeper into the beds for a change, and quite another if it depends on your harvest how you eat in winter and whether you will live normally until the next season.
The table below will show you how specific crops affect soil health.
| culture | what takes from the soil | positive impact on the soil |
| winter rye | nitrogen, potassium, in the period of ear production - water | after the soil is better processed, the root system is developed |
| spring wheat | nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, water at the beginning of the growing season | same as rye |
| spelled | water | inhibits the growth of weeds (it grows itself like a weed), |
| oats | water and potassium | loosens the earth. If grown as a green manure, then potassium will remain in the soil. |
| potatoes | organic matter | inhibits weed growth |
| peas | organic matter | binds nitrogen |
| beans | organic matter | binds nitrogen |
| clover | organic matter | binds nitrogen |
| cabbage | nitrogen and all minerals. The soil is acidifying | inhibits weed growth |
| radish | minerals | leaves organic |
| tomato | nitrogen and phosphorus | |
| pepper | water | |
| cucumbers | water | |
| zucchini | water | |
| Strawberry | everything | does not acidify the soil |
| beet | magnesium, boron, nitrogen, potassium | |
| carrot | potassium | |
| onion | organic matter |
As you can see, crops have a tendency to pick minerals from the soil, but this process is uneven, and each culture has its own characteristics. So, cereals have a long root system, and are able to take minerals from a depth of more than a meter, while cabbage, for example, takes them from the upper fertile layer.
It is also important to understand that we do not take all parts of the plants to our table, and the same potassium most often goes to the formation of leaves, which can be brought back, processed into mulch (except, again, cabbage). Finally, some of the crops are grown as green manure and are not eaten (although if you are going to grow rye for grain, nothing will hurt you, but you do not eat straw).
Another major reason for the need for crop rotation is plant diseases. Timely change of the landing site serves to prevent their spread.
Practical tips for organizing crop rotation
It is not easy to take into account many factors at the same time, it is even more difficult to remember. Therefore, for the correct distribution of plants, a diary is started, where the following are entered:
- How much and what kind of culture needs to be grown next year;
- Separation of the required crops on a specific basis;
- Breakdown of the garden into plots according to the degree of fertility;
- Distribution of plants by area, taking into account the need for lighting, soil fertility, planting coincidence;
- Accounting for applied fertilizers for each crop.
If possible, allocate a separate area for sowing green manure. If you have 4 parts in the scheme, then this will be the fifth, which will be "under steam". Do not spare space, this scheme will pay off by increasing yields with interest.
After harvesting, note the amount harvested from each area. Thus, you can analyze the success of the selected crop rotation scheme every year and, if necessary, make adjustments.
Tags: vegetable, vegetable garden, usually, crop rotation, table, alternation
About
«Previous post
Practical advice
- You should not rely on your own memory. You can still keep information about how vegetables were planted in the last season. And 2 years ago? Experienced summer residents are advised to keep a diary, where they can draw landing schemes or arrange it in the form of understandable tables. Moreover, to family members. Different things happen in life. Perhaps the next year will turn out so that one of the household will have to take care of planting vegetables in the country.
- When planting perennial vegetables, it is advisable to focus on crops that give an early harvest. For example, asparagus, sorrel, rhubarb.
- In order not to be mistaken in the organization of crop rotation, you can focus on how vegetables grow. In a simplified form, this is expressed as follows: in one season crops are planted that give "tops", the next year (in the same place) - "roots".
- If there is not enough free land, re-planting should be practiced. But this is a somewhat different topic.
The author outlined the essence and all the features of crop rotation. Nothing complicated, as the reader was able to see, this is not. But this applies specifically to the suburban area, when growing vegetables in the open field. With regard to greenhouses (greenhouses), there are slightly different rules, and this must be taken into account.
Have a nice harvest!
Organic farming
Organic farming is clean land that is not contaminated with chemicals commonly used as fertilizers.Due to the correct planning of the seeding order and planting of each crop in a specific place.
This will undoubtedly affect the quality of the future harvest. This task is performed by the crop rotation method. In addition, using this method, you can avoid unnecessary costs and maintain soil fertility. This method of cultivating the land will allow you to collect a large amount of vegetables from each garden bed based on natural fertilizers.