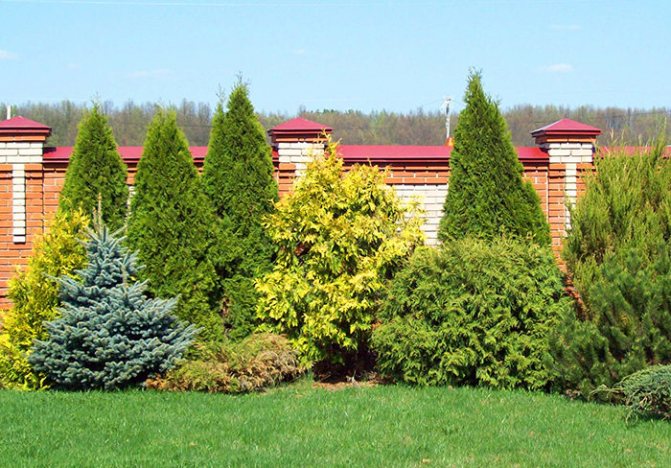
Many gardeners call the reproduction of conifers their hobby, which they do not for profit, but for their own pleasure. And it is not surprising, because this process, although it requires full dedication, in itself is very exciting and interesting. Evergreen trees and shrubs serve as a decorative decoration for any garden plot. In addition, they bring undoubted benefits due to the ability to purify the air, therefore they are always very popular. The propagation of conifers is possible by several methods, which are discussed in detail in the article.

Pros and cons of breeding coniferous cuttings at home
To grow conifers, one of the selected schemes is used: they can reproduce by division, seeds, and also cuttings. Experts consider cuttings to be one of the most effective methods of culture propagation. The advantages of self-breeding by cuttings:
- the ability to get a copy of the selected mother plant;
- ease of procedure;
- the ability to fully control the process.
The disadvantage of grafting may be the specific feature of the selected tree.
Thuja is an evergreen shrub that takes root well after cuttings. Young shoots completely repeat the varietal characteristics of the mother plant, therefore, the thuja is considered especially suitable for propagation by cuttings.
Juniper is one of the representatives of Cypress, which are undemanding and grow in different climatic conditions. Cuttings are suitable for tall varieties. Junipers spreading along the ground are propagated by layering.
Cypress is an evergreen ephedra that is propagated by cuttings and layering. It takes root well in the soil, it is almost never sent for growing, during the winter the shoots are able to develop a strong root system.
Fir, varietal species of pine and sequoia are almost impossible to root on their own. For breeding in nurseries, grafting and layering are used.
Information! For grafting, adult plants are chosen, the age of which does not exceed 10 years. Old trees form shoots with low germination rates.
When is it better to propagate conifers by cuttings
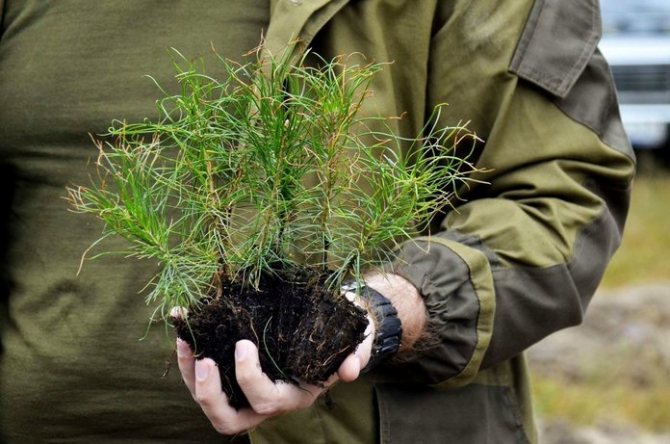
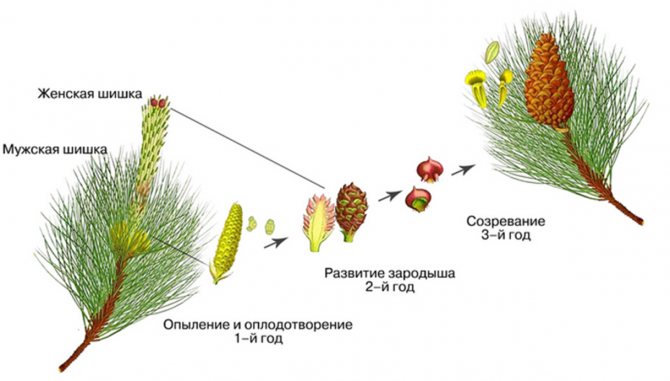
Cutting of shoots from the mother tree is permissible at any time of the year. The preservation of the genetic material does not depend on the timing of cuttings. Experts are of the opinion that the best time for cuttings is winter. In the first decade, the processes of sap flow are activated in trees.


During the period that passes from the moment of harvesting before winter to the beginning of planting, conifers have time to take root well. In summer, strong lignified seedlings are planted on the site.
Reproduction of conifers by cuttings before winter
Harvesting of conifers is carried out before the onset of winter. This increases the plant's chances of a successful spring-summer planting.
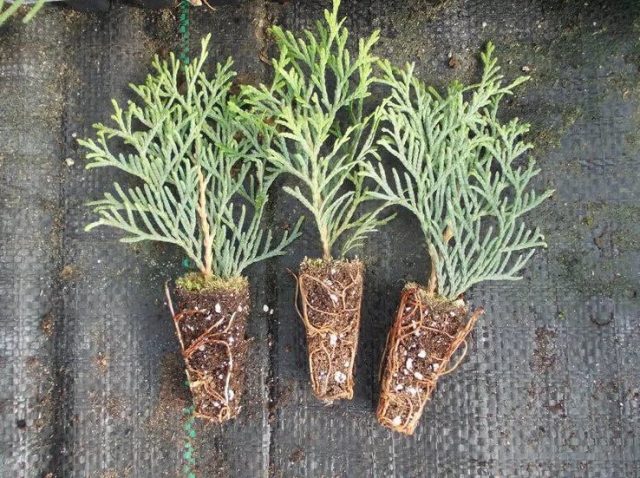
To carry out cuttings of conifers before winter, choose the upper shoots or tops. The length should not exceed 20 cm. After cutting, the cuttings are cleaned of needles, leaving only a part of the bark. If in some places the bark is separated, then it is completely removed.
Rooting of conifers by cuttings before winter is possible in several ways or by mixing them:
- with water;
- on the sand;
- under the film.
The simplest and most effective way is considered to be rooting conifers with water.It is not suitable for all types of plants. Shoots of pines, fir, cypress trees take root poorly by water. Thuja and juniper sprout quickly enough.
Reproduction of conifers by cuttings in autumn
It is possible to grow conifers by cuttings in the fall. Autumn cuttings differ little from winter ones. When using the soil, the shoots are left on the terrace or veranda, before the onset of winter they are brought into a warmer room.
Reproduction of conifers by cuttings in summer
For summer grafting of conifers, the method of rooting in boxes is suitable. In summer, shoots need to be watered frequently due to the hot weather. In the fall, they are transferred to the garden bed or taken indoors for the winter to be planted next season.
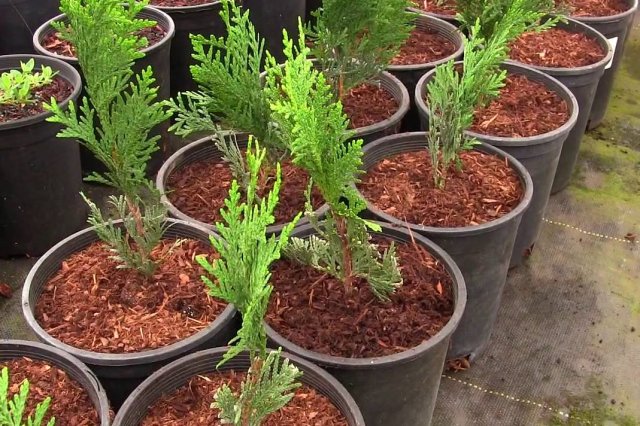


Reproduction of conifers by cuttings in spring
Spring cuttings of conifers are very rare. Experts believe that this period is not suitable for rooting. Shoots spend the summer outdoors, in winter they need room heat.
Rules for harvesting coniferous cuttings
The result of breeding conifers by cuttings in winter depends on the choice of material. When examining the ephedra, suitable branches are selected based on the following characteristics.
- Shoots should not be younger than 1 year, while branches of 3 years of age are considered the best option for breeding before winter.
- Shoots should be outwardly developed, look strong, not have any flaws.
- The length of the shoots for junipers, cypresses, thujas should not exceed 15 cm, the length for spruce and fir - up to 10 cm.
A cloudy day is chosen for grafting, the cut is carried out in the morning. In order to have a good idea of the sequence of actions during the propagation of conifers by cuttings, many breeders watch videos with master classes of specialists. This is justified for the reason that the success of further rooting depends on the quality of the cuttings and the choice of the shoot.
Norway spruce: description
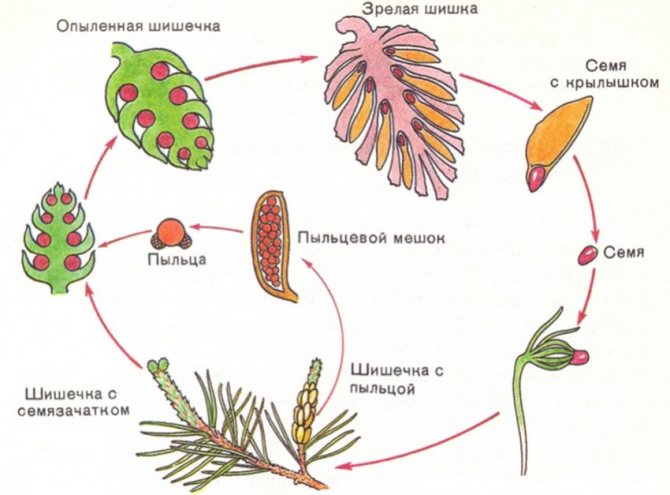
Also common spruce (lat. Pícea ábies) is also called European spruce. Plants of this species belong to the Spruce genus, the Pine family. This is the only species considered indigenous in Central Russia. The homeland of the coniferous tree is considered to be European countries, the Western European mountains, a forest zone located in the European part of Russia (extending to the Urals). It forms spruce or mixed forests protected by nature reserves.
In the description of the common spruce it is noted:
- How fast the spruce grows, reaching a height of 30 to 35 meters after 15 years of slow growth. In some cases, it can grow up to 50 meters.
- The trunk is 1.2-2.0 m in diameter.
- The plant is pointed, broadly conical in shape. The diameter of the crown of the common spruce is from 6 to 15 meters.
- The young bark of the plant is smooth and brownish. At a later age, it becomes rough and scaly, acquiring a reddish-brown tint.
- The shelf life of dark green needles on the branches reaches 6-12 years. Its thickness is 0.1 cm, and the length of the tetrahedral coniferous needles grows from 1 to 2 cm.
Common green spruce blooms by May. Female flowers are in the form of green or purple bumps. Male ones look like yellow-red spikelets. Unripe buds are light green or purple in color. In a mature state, they are cylindrical, reddish-brown, hanging down. Their length is 10-15 cm, width - 3-4 cm.
The good news is that the common spruce lives for how long:
- This frost-hardy plant has a lifespan of 250 to 500 years.
- But at the initial stage (up to 10-15 years), ordinary spruce has a very low growth rate.
- Then the spruce tree begins to grow very quickly. Its annual growth is 15 cm wide and 50 cm high.
In order for the tree to develop and grow well, it is necessary to fight pests and diseases. The plant is dangerous:
- spruce bast beetle roll;
- spruce-larch hermes;
- Schütte's disease.
The plant must be protected from their harmful effects, since it can suffer greatly, even die.
Norway spruce photo is very decorative. It has an excellent color and crown shape. The plant has many varieties, which are distinguished by the type of branching. His tree is inherited. The most ornamental plants are actively used in landscape design in the form of alleys, hedges, in single plantings or compositions.


How to root ephedra from a cutting
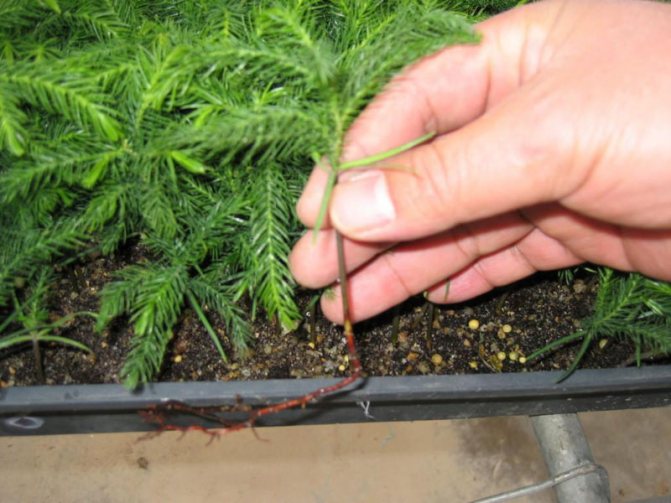
Rooting, which is carried out before winter, consists of several successive stages.
- First, the stalk is cut or broken off. In this case, a piece of wood with remnants of bark should remain at the base.
- A fresh cut is powdered with a root-type biostimulant. This will help the cuttings take root faster.
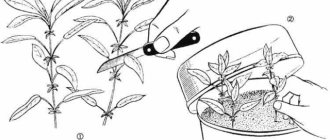
- A suitable container with high sides is chosen for the seedling, then it is filled with wet sand. Before planting, it is spilled with a weak solution of manganese.
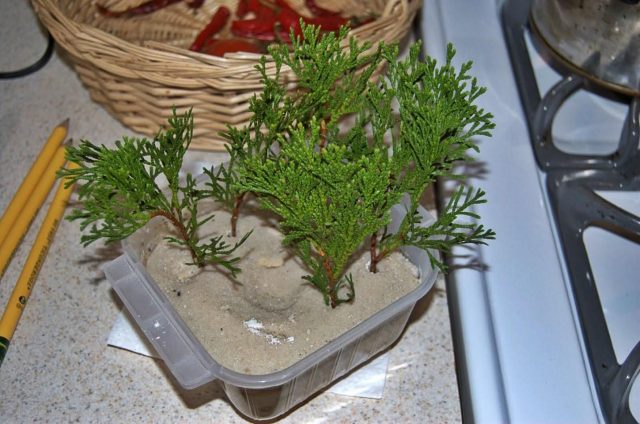


- A depression is made in the sand. It is convenient to use a wooden stick with a diameter of at least 6 - 8 cm.
- Shoots are buried in holes at a distance of 3 - 5 cm from each other.
- The soil is compacted so that no voids remain inside.
- The container is covered with plastic wrap or plastic cap. This helps create a greenhouse effect inside the container. Thanks to this, the soil will be timely moistened.
Landings are removed in shaded areas, where they constantly maintain a temperature regime of at least +22 ° C.
Many people use rooting cuttings in the water before winter.
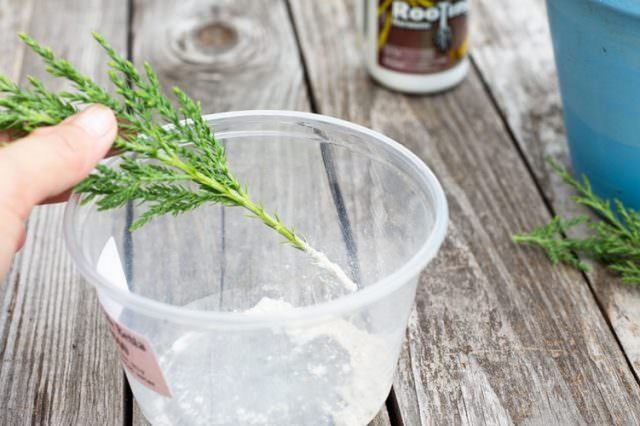


- The prepared material is released into the root growth biostimulator solution for 12 hours.
- At the same time, sphagnum moss is being prepared. It is soaked in water, then the excess water is squeezed out.
- Moss is laid out on plastic wrap up to 10 cm wide and up to 1 m long.
- Cuttings are placed on the moss so that the tip of the scion is visible above the tape.
- The film with moss is rolled up with a snail, pressing it tightly to the surface.
- The prepared snail is tied with a tourniquet and placed in a bag with a little water.
This structure can be hung from the window like a flowerpot. After rooting, the seedlings are planted in prepared soil.
Information! For summer and spring cuttings, the biostimulator is not used.


Soil preparation
Conifers thrive on sandy or sandy loamy soils. The land should be loose, light and fertile.
You will be interested to know how to properly plant a pine tree in your summer cottage.
An ideal mixture consists of components taken in equal proportions:
- peat;
- coarse sand;
- fallen needles.
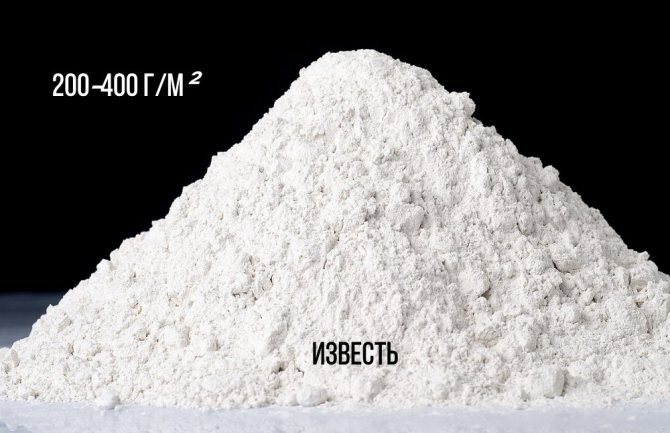
The acidity of the soil is desirable neutral... If it is increased on the site, you need to add lime during planting - 200-400 g / m². If seedlings are planted rather than seeds, nitrogen is added (more details below). For young trees, drainage from fragments of brick or expanded clay must be placed on the bottom of the pit.


No matter how the planting is carried out, in a pot at home or immediately in open ground, the peat substrate must be disinfected. It is either ignited or spilled with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
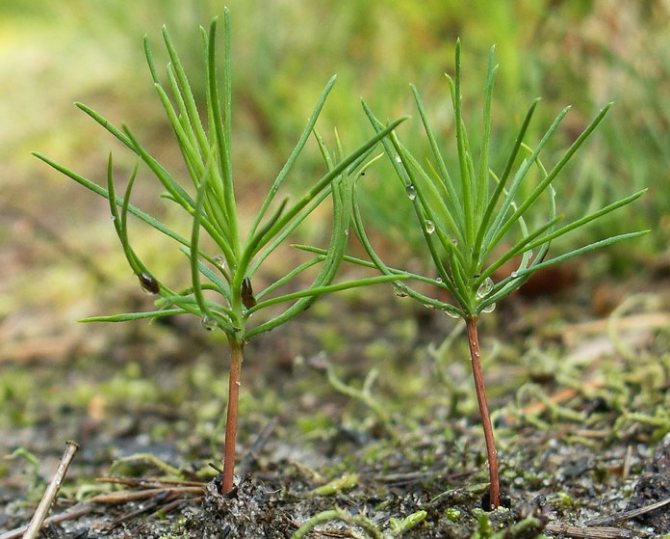
Growing conifers from cuttings
Further care for conifers includes several rules:
- After planting for rooting, the shoots need regular moisture. They are sprayed with warm water once a week. The land should not be waterlogged or dry.
- For the full development of the culture, a temperature regime at the borders of +18 to +22 ° is necessary. Frost-resistant species will feel comfortable at temperatures from +16 ° C.
- Shoots need regular ventilation. To do this, the boxes are opened for several hours daily, gradually increasing the length of time.
- Plants are fed with special preparations for conifers 1 - 2 times per winter.
- To saturate the soil with air, the soil is regularly loosened.
Information! Daylight hours for the growth of conifers should not be less than 10 - 12 hours.
Many breeders plant conifers after rooting in closed greenhouses. It should be borne in mind that young plants at this stage need warmed up soil. The soil index should not be lower than +25 ° C, the air temperature inside the room can fluctuate from +18 to +20 ° C. In addition, it is necessary to monitor the humidity: at this stage, its indicator should be higher than usual.
There are several signs by which you can determine that mistakes have been made in caring for conifers:
- Redness or fluttering of the needles indicates the presence of a fungal infection (this can be caused by an excess of moisture or planting in soil that has not been disinfected);
- Scattering of formed young needles is a signal of a lack of nutrients, possible acidification of the soil.
Common spruce varieties
The most popular low-growing varieties of common spruce include varieties with a spherical or nest-like shape. A tiny shrub Picea abies "Nidiformis" is used:
- for the design of rockeries;
- the formation of low curbs.
At him, to an adult state, the height reaches 40 cm, and the spreading crown is 1 m wide. Graceful, thin branches, arranged in the form of a fan, are covered with short soft needles of an emerald, delicate shade.
Little Gemm looks charming:
- Shoots depart from the middle of the tree.
- The branches are framed with thin dark green soft needles.
- The plant gives the impression of a hemispherical pillow.
Its most attractive plant form, planted in a flowerpot or floor container. The crown of Picea abies "Will's Zwerg" has a dense narrow-conical shape with young shoots of a pale green color. She acts as a tapeworm in compositions.
Glauka Globoza obtained by selection differs in:
- the presence of a clearly defined trunk;
- spreading shoots are strewn with a huge number of thin needles, silvery with a blue tint;
- the tree has a spherical crown;
- fruits in the form of cones resemble New Year's toys.
The tree adorns urban compositions in parks and squares and alleys.
Very decorative miniature creeping "Nana" in the form of a soft pillow. And "Echiniformis" is associated with a kolobok. Due to its round shape, paths are adorned with the plant. A feature of dwarf varieties of common spruce is their sensitivity to insufficient light.
In park design, medium-sized spruce varieties are widely used, reaching 15 m with a crown width of up to 2-3 m. They are used in the form of lonely plants against the background of lawns or walls of houses. Such compositions are complemented with white stones or driftwood. Spruce trees with weeping branches, used on the banks of reservoirs, are considered popular. Tall trees will not spoil any landscape, playing the role of tapeworms, compact varieties look good in group compositions.


Planting conifers by cuttings in open ground
Despite the fact that when conifers are propagated by cuttings for the winter, the shoots have time to harden enough, some of them need growing. This is the name for planting on open ground for a period of time that passes before planting in a permanent place of growth.
Sometimes young conifers can be growing for 2 - 3 years. To do this, they choose protected areas that can be additionally covered in winter, during frosts.
There is another way to grow coniferous seedlings - in a school. It is suitable for growing conifers from cuttings that have been obtained in large quantities before winter.
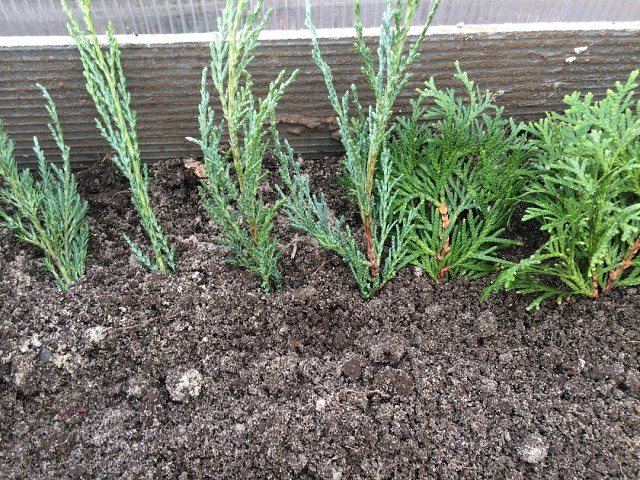


On the site of a school with dimensions of 1.5 by 1.5 m, up to 100 copies can be planted. About 30 - 35 pieces will be ready for planting in a permanent place of growth.
Young coniferous plants are transplanted to the school by the transshipment method.If they were rooted with moss, then it will be enough to separate part of the moss and bury it in the prepared hole.
After disembarkation, arcs are pulled over the shoots, covered with a special industrial material. This is necessary to protect from direct sun rays, which can provoke burns during the adaptation stage, as well as to protect against through winds.
For planting in a permanent place, strong coniferous seedlings with a developed root system are chosen. Before that, 2 - 3 winters may pass after grafting. This is not surprising, because we are talking about growing trees that will exist for about 30-40 years or more. After planting in an area where trees will grow constantly, control over growth and development is noticeably reduced. Trees need regular, but not frequent watering, as well as 2-3 additional fertilizing per year.


Low-growing spruce
So that the spruce does not cover the living space of smaller plants, it is planted along the fences, where it quickly grows into a dense, solid “living” wall. " More than 20 varieties of spruce are used in park design. When choosing a plant, you need to pay attention to the configuration of its crown and what it will become when it grows. Norway spruce varieties are presented here in 50 garden forms:
- Ate are large-sized, medium-sized and dwarf. The most popular for landscape design are low-growing ordinary spruce and creeping varieties.
- In nature, Picea abies, common spruce, has a height of 50 m, and the diameter of the crown of common spruce is 8-15 meters.
- In medium-sized ones, the height is up to 3 m.
- Low-growing ordinary spruces reach a height of up to 1.2 m. They have a varied range of shades (from rich green to golden).
In undersized spruce trees of this species, which have reached the state of adults, the size is much smaller than that of the original species. Common dwarf spruces reach a height of up to 2 m. They are known as cushion trees and are called Picea abies "Nidiformis". The width of their crown reaches 2-3 m. The main advantage of the dwarf spruce is that the common spruce variety has a growth rate of only 10-15 cm throughout the year. The beauty of their crown of a pillow-shaped or pyramidal fir tree can decorate any part of a garden, square or park.