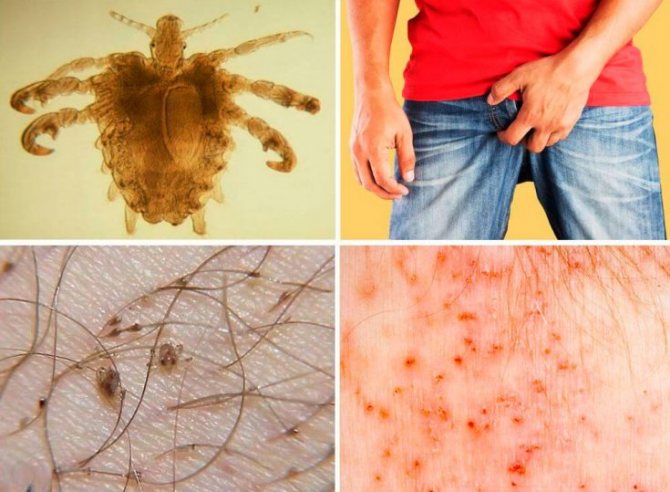
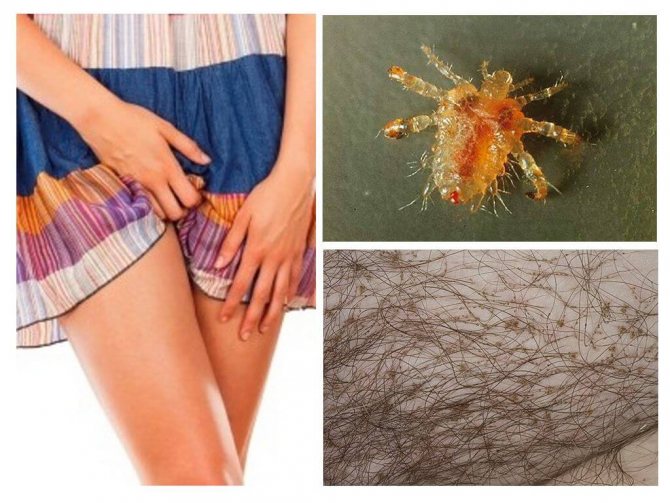
Pubic lice in humans are ectoparasites, which are the causative agents of phthiriasis (pubic lice). Insects live mainly on the pubis in the groin area, they can climb over the hairline of the abdomen, as well as the area of the armpits. Sometimes parasites affect the scalp of the face: eyelashes, eyebrows, mustache or beard. Parasites, like other types of lice, feed exclusively on human blood, which gives him great discomfort. Pubic lice are not adapted to other habitats.
Phthiriasis in men
How lice look and are transmitted - their types, structure and life cycle, how they are transmitted and reproduced
The louse is a parasitic insect, ranging in size from 1.5 to 4 mm. Habitat scalp, pubic hair, and bedding or underwear. The habitat and reproduction of the parasite affects its subspecies. This is due to the structure of the legs of the lice. One species has adapted to exist on the scalp, the other on the scalp of the pubic zone. At the same time, body lice and hair lice are morphologically very similar in structure. In fact, this is one and the same subspecies, which split over time.
Lice are longtime human companions. The earliest chronicle mentions of this parasite can be found in Aristotle. Dried lice have been found in tombs almost all over the world. Scientists believe this parasite appeared between 170,000 and 80,000 BC.

REFERENCE: Almost 500 BC. e. the famous ancient Greek historian Herodotus wrote that the Egyptian priests and scribes always had their heads carefully shaved, "... so that no louse or other unclean creature could cling to them when they serve the gods ..." For the same purpose, the pharaohs and kings shaved their heads and chins and nobles in ancient Egypt.
The life cycle of a lice is divided into several stages:
- Egg (nit)... The egg can ripen from several hours to several days, depending on the type of parasite, as well as the ambient temperature. The higher it is, the faster the larva will hatch. If the temperature drops below + 22C⁰, the development of the embryo in the egg is suspended.
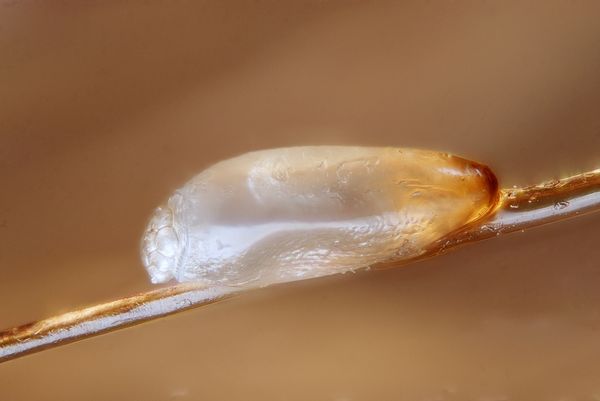


- Nymph or the stage of the larva. At this stage, the parasite undergoes 3 molts. The duration of nymph development at the first stage is 3-5 days, at the second - 5 days, and at the third - 4 days.


- Imago, the stage of an adult insect. During this period, the parasite is able to continue its appearance. Under optimal conditions, it lasts about a month. During this time, female lice lay several eggs each day.


Considering that any subspecies of lice is essentially the same insect, we will consider in detail exactly the hair type, as the most common. The description of pubic and body lice will contain only their specific differences from the hair morphotype of the insect.
Head louse
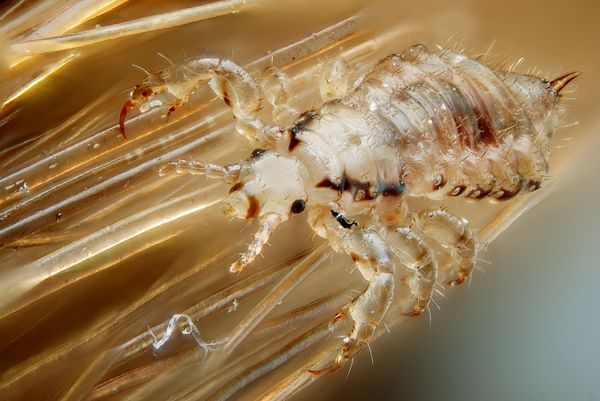
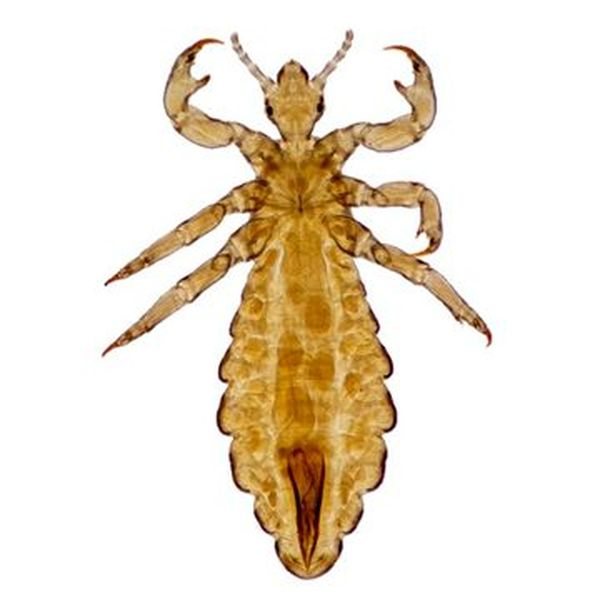
(lat.Pediculus humanus capitis) is one of two morphotypes of the human louse. This parasite lives on the scalp, in the hair growth zone, as well as on the beard and mustache. The body of a louse in length can be from 2 to 4 mm, depending on the sex of the insect, as well as its age. His body consists of:
- one pair of antennae;
- piercing-sucking apparatus;
- three pairs of walking limbs;
- breasts;
- abdomen.


The head of a louse consists of several parts: the upper lip, forehead, occiput and crown, as well as the clypeus. They are all separated by seams. In some cases, you can observe the division of the head by a seam into two parts: left and right. These areas are called the eye lobes. On the side of the head, closer to the center, there are filiform antennae. They consist of 3-5 independent segments. Sensitive receptors are located at the ends of the last two segments. In males, the third segment of the antenna has a projection (appendage) bearing a spine or bristle, and the first segment is noticeably larger than in females.
Lice also have reduced single-lens eyes. They are conical or hemispherical, with or without a pigment spot. The optic organ is located behind the antennae, at the back of the head, and is considered a vestigial organ. The insect moves mainly by smell, which is captured by the antennae on the head.


On the abdominal part of the body of a louse, its mouth opening is located. It is located on an annular fold that extends from the anterior edge of the parasite's head. On the mouth opening, you can see many small processes - chitinous hooks. With these hooks, the parasite holds onto the victim's skin during the bite. The mouth apparatus itself is located inside a special capsule located inside the insect's head. It moves out of the capsule with the help of special muscles when the insect drinks blood, and retracts back when the parasite finishes feeding. The oral apparatus itself consists of three stylets:
- The upper stylet is a double groove with a central passage. It works on the principle of a suction-pressure pump that drives a specific muscle group.
- The middle stylet looks like a salivary tube. Its task is to transfer salivary enzymes to the victim's wound.
- The lower stylet is spiny. It consists of a toothed apex and a groove where the first two stylets lie.
The insect's chest can be divided into three parts: the prothorax, the mesothorax, and the metathorax. The size of this part of the parasite can be much shorter than the head. The shape ranges from hexagonal to elongated oval. On the chest there are a pair of mid-thoracic spiracles (stigmas), as well as the legs of an insect. Three pairs of legs are not equally developed and differ in length in males and females.
Lice legs are very strong and tenacious... They consist of a coxa (or coke), trochanter, femur, tibia and tarsus, which has 1 or 2 segments. The first legs are smaller than the middle and hind legs. Sometimes on the last segments you can see the accrete tibia and tarsus. The widened tibia has spines, projections, and bristles. At the end of the lice's paw, there is a furrowed claw in the shape of a sickle. With the help of it, the insect firmly holds both the skin and the hair of a person.
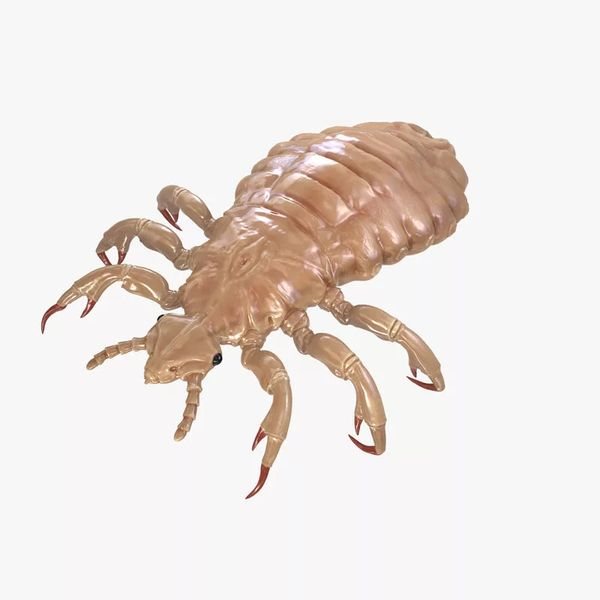


The abdomen of the parasite has a different shape. It consists of nine segments and can take a broad-ovate or narrowly oblong shape, depending on the maturity of the insect, its morphotype, sex, and also its saturation with human blood. At the ends of the segments of the abdomen, spiracles are located, as well as appendages in the form of hairs, bristles and hairs. All this "bristle" helps the parasite to move in the hairline with minimal risk.
The hair louse has a gray tint, in some places the insect may have brown, brown or red spots.
The life cycle of an insect can reach one and a half months. During this time, an adult female lays up to 5 eggs (nits) per day. Young individuals emerge from them. By the way, young lice have a more brown color in contrast to adult insects.
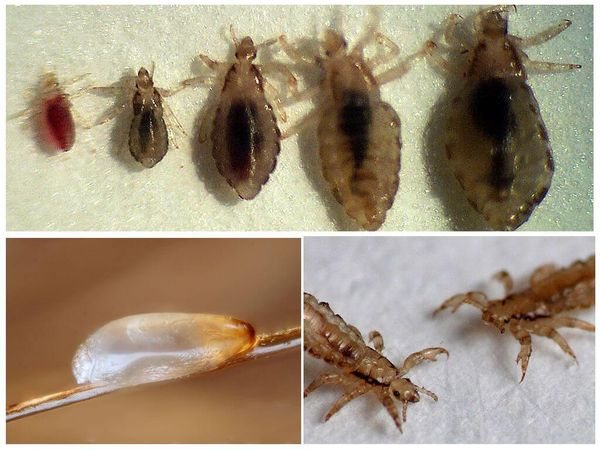


Hair lice are transmitted through direct contact of an infected person with healthy people. The invasion often occurs in crowded places. For example, in educational institutions, large offices, kindergartens and other places.Often, the louse passes between family members, crawling over clothes or bedding, as well as through combs. The head louse is a carrier of dangerous diseases, and the infestation by this parasite is called head lice disease.
Any morphotype of lice is formed, among other things, due to the temperature environment. This is how the hair louse lives and reproduces at a temperature of 28C⁰. These conditions are just right for the scalp. When the body temperature reaches 10C⁰, which is equal to the temperature of the corpse, the hair louse leaves its owner in search of a new food base. When the temperature reaches 44C⁰, the insect quickly dies.
INTERESTING: In nature, different morphotypes of the parasite do not interbreed, but under laboratory conditions they can produce fertile offspring. Moreover, one type of lice can quickly turn into another and vice versa. So, if the head louse is kept on the human body, then after several generations its offspring will begin to acquire the characteristics of a body louse, and vice versa.
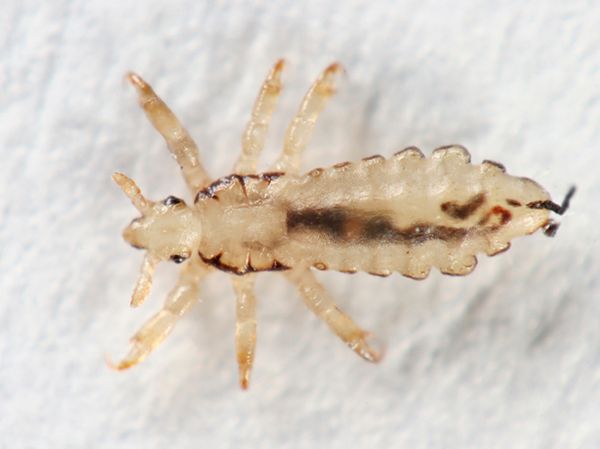
Body or body louse
(Latin pediculus corporis) - also a parasite, head lice morphotype. It is believed that this subspecies is evolutionarily younger than hair and pubic lice, since wearing clothing has become mandatory for people relatively recently.
The structure of a body louse is not very different from a hair lice. They are distinguished by their size, the body louse is larger than its relative, on average by 1-1.5 mm. They also differ in color. The body louse has a lighter, almost white color.
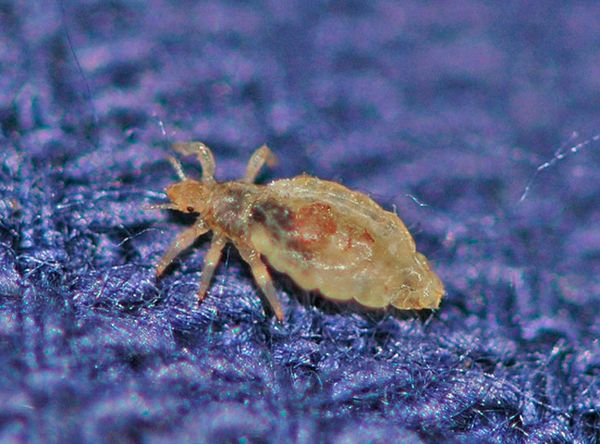


This subspecies parasitizes mainly on human clothing, attaching eggs to the pile of underwear or bedding. The insect feeds on it by running from clothing to human skin. The louse is transmitted through the common bed, as well as through clothing. The life cycle is about 48 days.
IMPORTANT: The body louse can be a carrier of dangerous diseases. So in 1909, Charles Nicole, in experiments on infecting body lice on sick monkeys, first established that lice are a carrier of typhus.
Carp or pubic louse
(Latin Phthirus pubis) - is also a human parasite and belongs to the subspecies of lice. Some doctors consider the infestation by the venereal disease.
Pubic louse has a similar structure to head and head lice, but the body of the parasite has a shorter appearance. His chest and abdomen are a single whole and do not have a clear differentiation. Adults do not grow more than 3 mm, their body has a rounded shape, the color is dark brown or yellow.
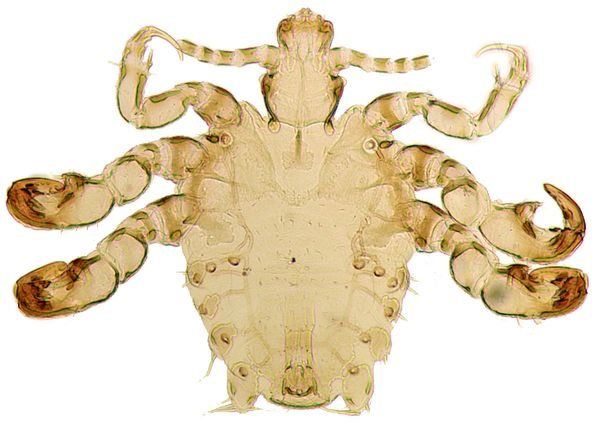


The carrion grows up to 3 weeks, after which it dies... An adult female of the parasite lays up to 3 eggs per day. The insect lives and feeds mainly in the pubic area, in the genital area, around the anus, sometimes in other areas covered with hair: in the armpits, on the chest and in the abdomen. The insect occasionally rises to the head of a person. This is due to the special structure of the legs of the insect. They are designed to grip hair that is triangular rather than circular.
Pubic louse is transmitted through sexual contact. Less commonly, through the use of personal belongings, as well as towels.
What is this disease
Pediculosis is usually called a disease of the skin and hair, which is caused by ectoparasites - lice. These small insects feed from twice a day thanks to their sharp proboscis and suck several mg of blood per day. After that, the color of the parasite changes from gray to red.
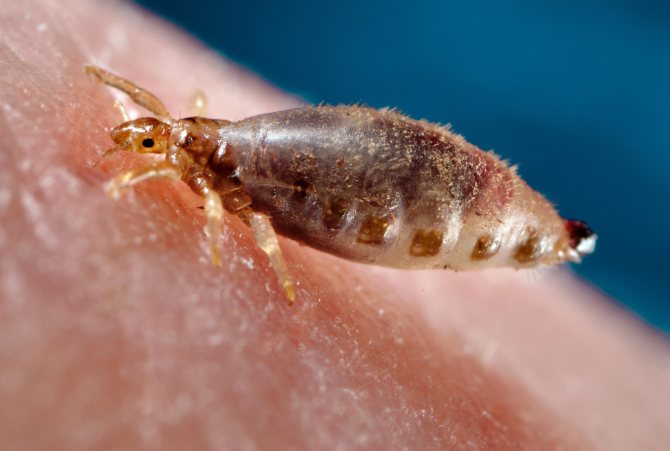


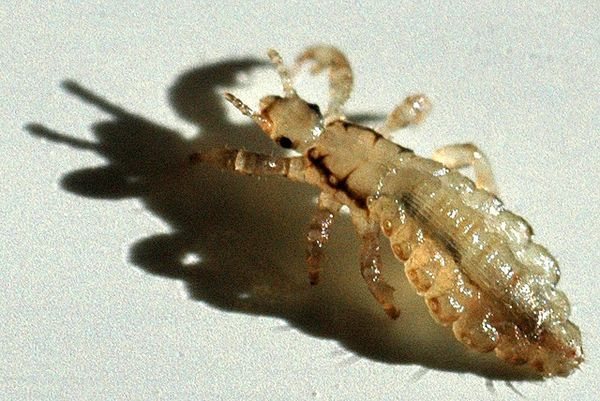
Human louse
Lice are able to crawl quickly, they cannot fly or jump. Parasites die at rather high or low temperatures, as well as without human blood.
The ideal temperature for lice breeding is 28 degrees.


The disease is caused by three types of parasites:
- Head. Found on the beard, eyelashes, head, eyebrows.
- Wardrobes. Lice are found in the folds of the skin.
- Pubic. Habitat - pubic hair.
Having reached the hair, the lice reproduce quickly by laying eggs - nits. One individual can reproduce up to 10 eggs in 24 hours, which mature within a week.


What do lice nits look like?
Lice nits, they are also eggs, are dense formations of an elongated shape. The length of the nits reaches 0.5-1.5 mm, the width is 0.2-0.7 mm. Lice attach eggs to the base of the hair, or to the pile of clothing, depending on the subspecies of the insect. Eggs are usually white, pale yellow, rarely pearlescent.
Lice eggs may vary slightly in shape and size:
- Head lice nits are often elongated., can be up to 1 mm in length. The color is white, whitish with a yellowish tinge.
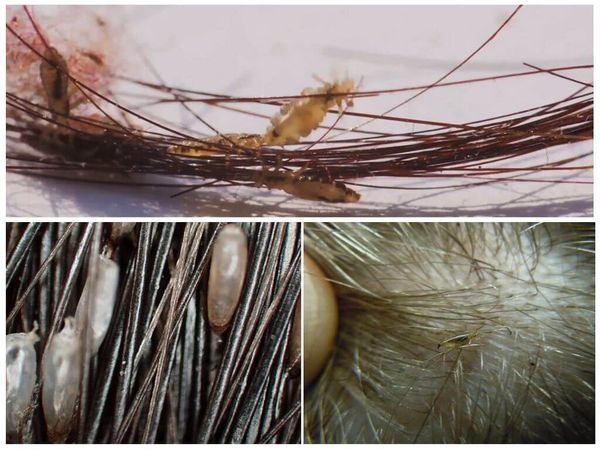


- Body lice nits also have an oblong shape. In length, they can reach about 1.5 mm. The color is white, brown.


- Pubic louse lays round or pear-shaped eggs. Nits do not exceed 0.5-0.8 mm in length and have a bright brown or yellow color.
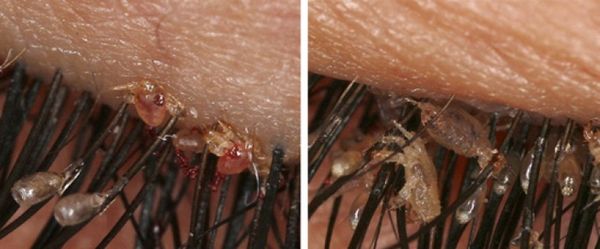

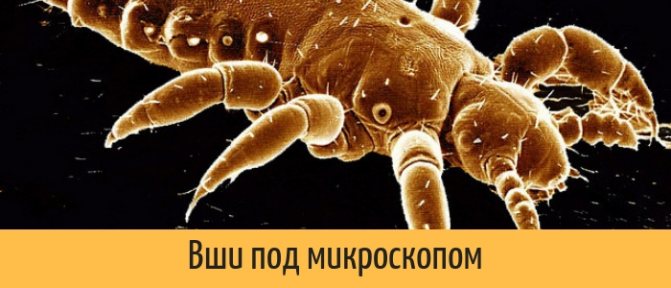
Lice under the microscope
Under the microscope, you can see the complete structure of the lice. It is noteworthy that body lice and hair lice can often have a translucent structure, which allows you to fully consider the location of their internal organs.


Do not take a drunk brown or red individual for research. The blood will not allow the test insect to be seen properly.
INTERESTING: It will be quite difficult for an inexperienced researcher to distinguish lice from lice without a microscope. But you can be sure of one thing: if an insect was removed from a person for study, then it is a louse.
What color are lice in humans and in nature
Only the studied subspecies of lice are about 150 pieces. And they all can vary in shape, structure and color. For example, a human louse can be white, whitish, yellow, brown, or red.


In nature, you can find insects with a black or dark color. But most often insects are whitish, brown or yellow.
Frequently asked Questions
Consider the most frequently asked questions regarding the topic of lice:
Expert opinion
Alexandra Valerievna
Doctor Trichologist
What do live nits look like?
Live nits are eggs attached to the base of the hair, nap of clothing or underwear. You need to understand that eggs by themselves do not show any action. They are a cocoon for the larva.
What do newly hatched lice look like?
The larvae that have just hatched from the egg appear as a tightly compressed adult with a darker color. Their size does not exceed 0.5-1.5 mm, depending on the subspecies of the insect.
How many legs do lice have?
Lice have three pairs of walking limbs.
What is the difference between male and female lice?
Males are usually smaller than females. They also differ in the structure of the abdomen. In males, it is more rounded, conical and narrowed. The genital opening is located behind the anus. In females, the end of the abdomen is two-lobed.
Do lice have wings?
Officially, lice belong to the subclass of winged insects, but they do not even have wing buds. In the course of evolution, these parasites have lost the ability to fly.
Could there be lice on the eyebrows and eyelashes?
Yes they can. Some subspecies of lice actively reproduce on the eyelashes.
Useful videos
Why do lice appear on the head?


With the problem of head lice, a larger number of the population is faced. At the same time, many people did not even wonder what the lice look like, what are the features of different types of parasites. For effective pest control, you need to use useful information about the characteristics of insect life.
Symptoms of infection and treatment methods for head lice
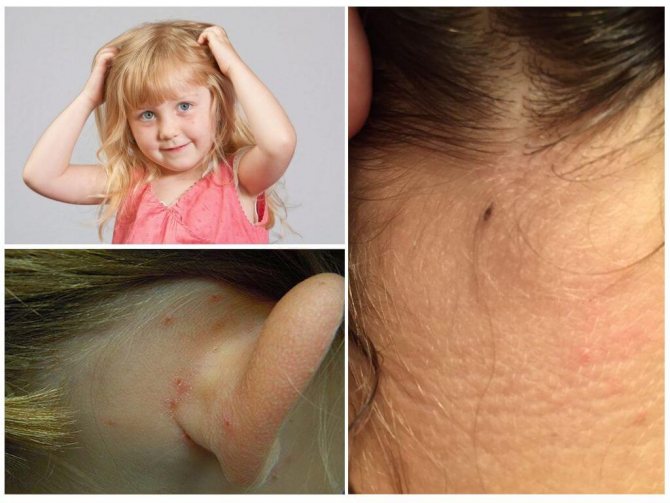
Pediculosis is manifested by one striking symptom - acute itching. The bite site itches a lot. Often, sufferers will comb the affected areas until they have blood and ulcers. However, they become inflamed and redden. The localization of the affected areas of the body may be different, but most often the places of the hair growth line, as well as the hair areas themselves, suffer.
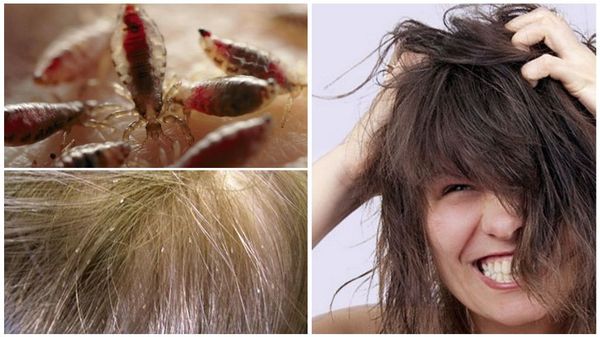

Lice are easy to spot. It is enough to carefully examine the hair near the bite sites. Usually nits can be found on them, as well as the parasites themselves. It is better to examine wet hair... Thus, the chances of finding the causative agent of head lice are much higher.
For the treatment of the disease, standard therapy is used, as well as alternative methods of treatment. Let's consider some of them.
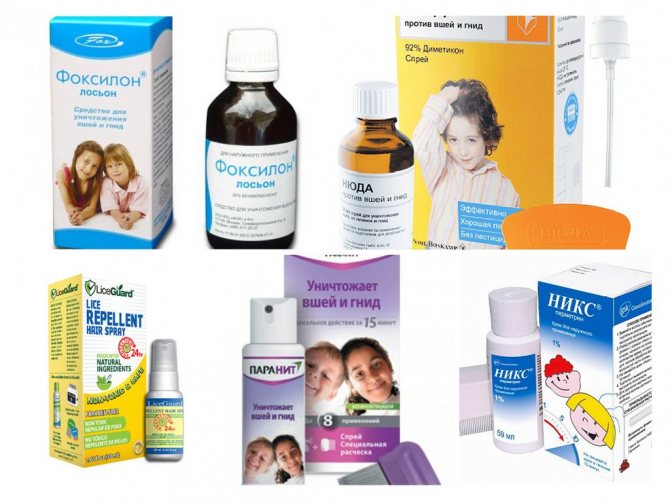
Pharmacy and cosmetics
For the treatment of head lice use:
- drugs with the active substance malathion (means "Medilis Malathion" average cost 200 - 250 rubles);


- drugs based on permethrin (means "Pedikulen ultra" average cost 500-550 rub.);


- preparations based on dimethicone (means "Nuda" average cost 580-650 rub.).


Pharmaceutical effects can be enhanced by traditional medicine
Folk remedies
Among the folk remedies there are completely radical methods of combating the parasite, for example, shaving baldly. But within the framework of this article, we will only get acquainted with the gentle options:
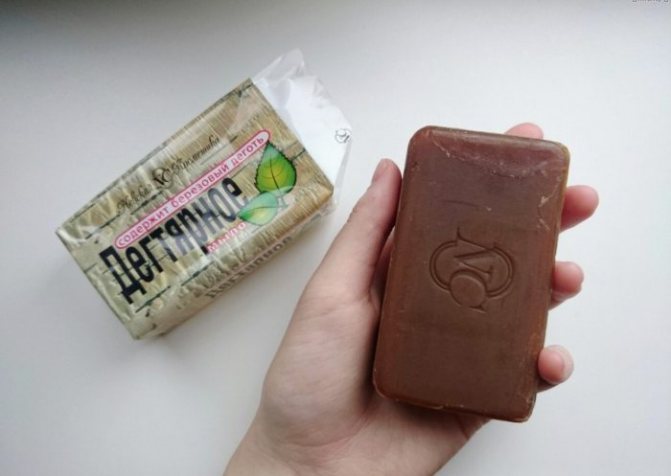
- Tar soap. Good support for the fight against parasites due to the high concentration of alkali.
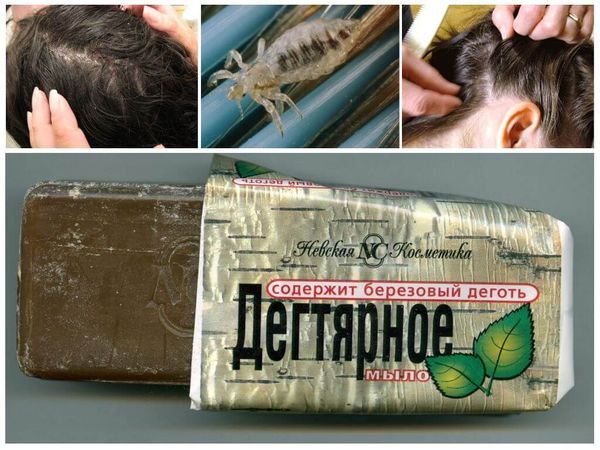

- Vegetable oil mixed with kerosene... Kerosene kills adults, oil softens its effect on the skin.


- Cranberry juice... Acts mainly on nits, dissolving the shell of eggs.


In order not to subject your hair to a global revision for the presence of parasites in it, it is worth observing preventive measures.
Description
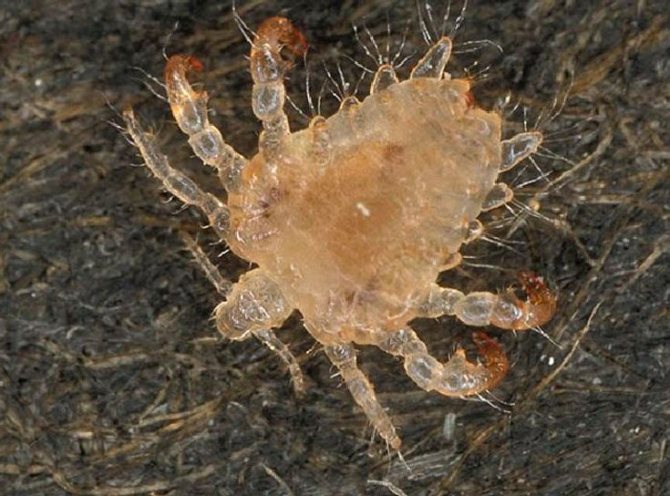


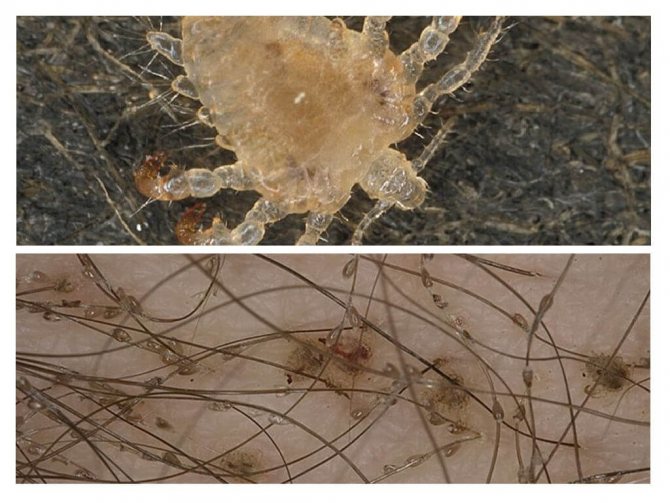
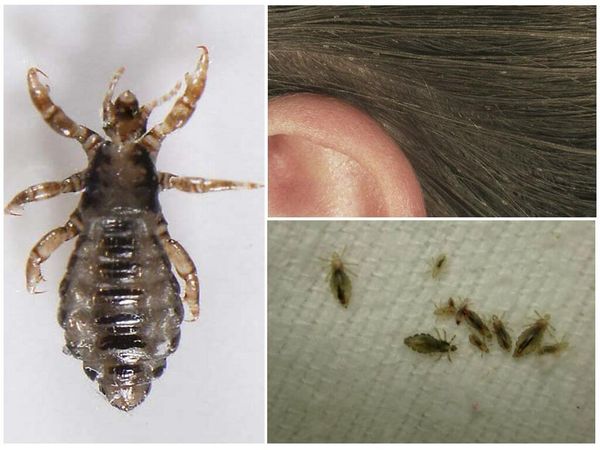
To make a diagnosis, you need to know what these parasites look like. In the people they are also called ploshchits, because they stick to the skin of a person so that it is rather difficult to notice them. In appearance, the ploshchit resembles a speck adhering to human skin.
Pubic lice are small enough individuals, no more than 2 millimeters long. The shape of the body is rounded and relatively wide, and its color resembles the color of human skin, which allows the parasite to perfectly disguise itself among the hair. If you look at the parasite through a magnifying glass, then in appearance, the shape of the body of the plane resembles a crab. The body of the parasite has a trapezoidal body shape, tapering towards the back of the parasite. In this case, it is possible to clearly separate the pectoral element, in relation to the rest of the body. Hind legs (and there are 4 of them) are somewhat thicker than the rest. At the same time, they are armed with peculiar hooks, which allows them to be securely held on the hair. Below are photos of pubic lice.
Disease prevention
Statistics show that children are most often susceptible to head lice disease. Therefore, it is so important to explain the precautions to your child. These include:
- Shampooing at least 2 times a week.
- Using personal hair hygiene products... A child and an adult should use an individual comb.
- You should not measure and even more so wear someone else's hat... As a last resort, it must be turned out with the seams.
- Change bed linen at least once a week.
- Thoroughly iron all underwear and bedding, especially the seams.


It is possible and necessary to observe these precautions not only after an illness, but also at any time. This will minimize the risk of infection.
- about the author
- VK profile
Do I need to go to the doctor
What to do if a child has lice? Pediatricians are involved in the treatment of head lice. But you don't have to seek medical attention.
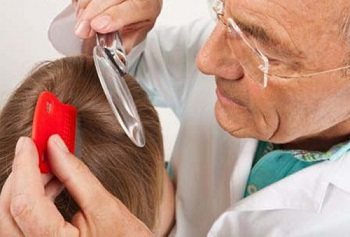

The main thing is to isolate the child and not allow him to be in groups in order to prevent infection of others. How to get rid of lice from a child? To do this, you can use any of the available pharmaceutical pesticide products, such as dust shampoo or soap.
In just 1-2 shampoos, you can completely get rid of head lice, but in the next 5-7 days prophylaxis and daily visual examination of the scalp are introduced (this can also be done independently).
If the child also develops inflammation and peeling, then you should still consult a doctor. You need to make sure that there is no allergic reaction or infection.
In this video clip, the famous doctor Komarovsky will tell you what to do if a child has lice and nits - about effective treatment measures: