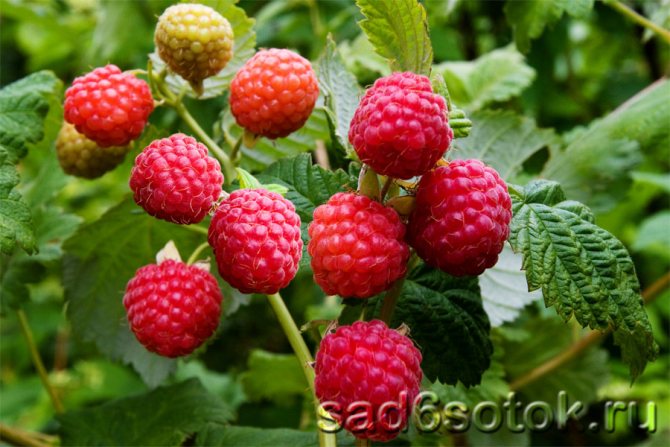
Garden raspberry (or ordinary) is the most common fruit shrub in household plots. It is she who gives early harvests of tasty, ripe and aromatic berries, in contrast to remontant raspberries, which begin to bear fruit only in August.
We already talked about how to grow remontant raspberries in the article: "How to care for remontant raspberries".
Unlike remontant, which gives berries on one-year-old shoots, garden raspberries form a crop on last year's shoots, hence the difference in their agricultural technology.
The most important thing is to keep the fruit buds on the shoots of the current year until next spring in order to get a rich harvest of early berries.
Today, more than a hundred large-fruited, frost-resistant varieties of garden raspberries have been created, which are not afraid of winter frosts and, moreover, are resistant to most fungal raspberry diseases. When properly planted and cared for, these varieties are capable of producing very high yields of sweet, tasty and aromatic berries.
In this article, we will talk about how to properly grow raspberries on your site and recommend the best modern varieties that grow and bear fruit well in almost all regions of the country.
Description
The raspberry bush can grow up to 2 m and has several erect stems with thorny growths. The raspberry root is twisted and twisted, with numerous branches. The leaves are white-bristly below, green above, oblong-ovoid.
Raspberry
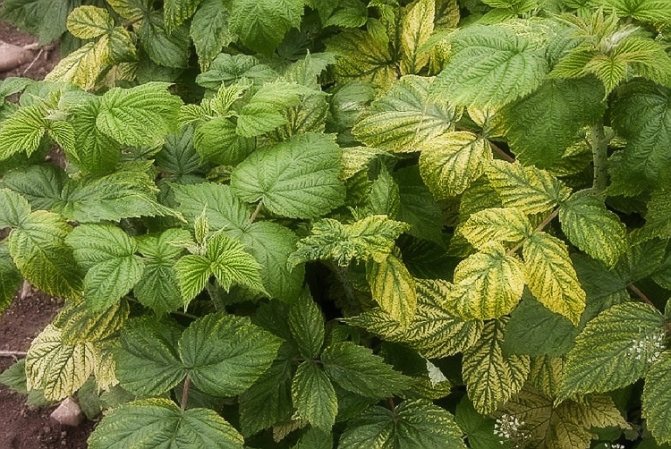
The raspberry fruit is a complex drupe, formed by many accrete fruitlets. The color of the berry ranges from orange, yellow and pink to almost black. Raspberry has a pronounced aroma and contains a whole range of unique nutrients, which made it possible to use it in folk medicine.
The berries are formed on the shoots of raspberries in the second year of life, after which they are removed to make room for young shoots. The exception is remontant raspberry varieties, whose shoots are cut annually. Garden raspberries begin to bear fruit by the end of June, and the fruiting period lasts no more than 2-3 weeks. Repaired varieties of raspberries enter the ripening season later (by the end of July, in August), but this period lasts up to 3 months. And often such raspberries, even under the snow, leave with fruits.

How to tidy up a neglected area
Quite often, in the country for many years, raspberries grow by themselves. Little sense, it's a pity to throw it away ...
Within 1 season, it can be put in order and the next year, you will be surprised at the result.
To do this, at the beginning of the season (May-June), clean up the old raspberry tree.
- Use twine to mark new rows every 70 cm.
- Anything that is not in a row - dig it up.
- In empty places (where there are no raspberries under the twine), plant seedlings that were dug from the row spacing. In a row along the twine, the bushes should be located after about 30 cm.
- Top dressing and watering can enhance the growth of the renewed bushes, and by autumn they will lay flower buds for the next year.


Raspberry bushes: planting
Before planting the raspberry tree, choose a suitable place for the site. Contrary to popular belief that raspberries are shade-loving, they need good lighting and maximum protection from cold winds. Raspberries are usually planted along a fence or structure. The soil for planting raspberries should be low acidity or neutral (if necessary, lime it).
When to plant raspberries
Each raspberry planting period has its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Planting in autumn gives the seedlings time to root, and in spring they start growing earlier. However, with insufficient shelter, raspberry shoots may freeze in winter. An autumn planting (or transplant) is done at least 2 weeks before the arrival of frost. In the middle lane, this is approximately the second half of October;
- Spring planting for raspberry seedlings provides more chances for good adaptation - after all, there are several warm months ahead. Landing is carried out before the buds swell - in the first half of April. The downside of this method is that this season, most likely, you will not see raspberries.
Important! Although it is believed that the plant can bear fruit up to 14 years, however, already by 5-6 years, the fruits of raspberries become smaller, and the yields are reduced. Therefore, for 6-7 years, it is recommended to update the planting of raspberries, replanting young seedlings to a new place.


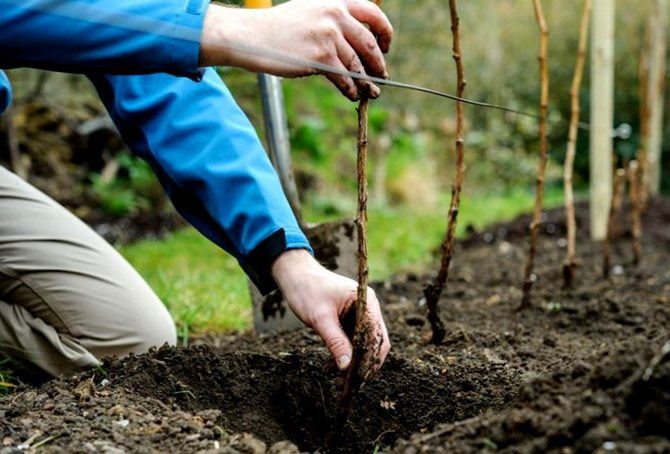
How to plant raspberries
The site for planting raspberry seedlings is prepared in advance: pumpkin or legume crops, siderates are planted. An even better option would be a rested area where nothing grew. The location of the plantings of raspberries is done in 2 ways:
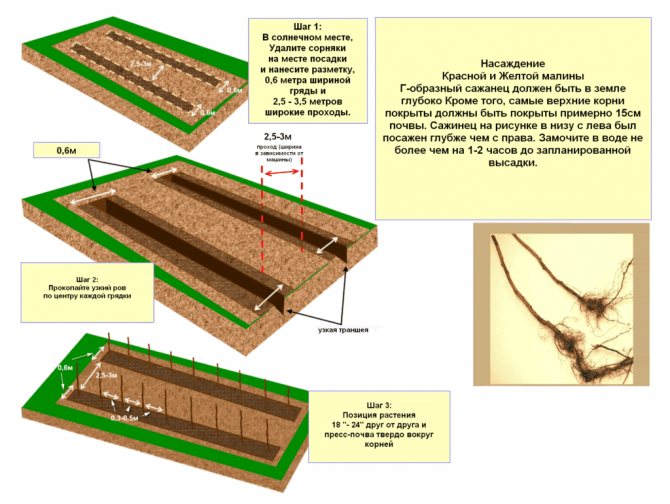
- In trenches: the depth of such a trench is at least 40 cm, and the width is up to 60 cm. The distance between rows of bushes reaches 1.5 m;
- In the holes: the depth and width of the holes are similar to the previous method, and the distance between the seedlings is 0.7 m. The row spacing is 1.5 m.
Soil for planting
The soil from the pits is divided into 2 parts: the upper fertile is diluted with organic matter (for each bucket of humus 1 tbsp. Wood ash) approximately in half and a "pillow" is made of soil for the seedling, leaving about 1/3 of the depth of the hole free. After that, they are planted as follows:
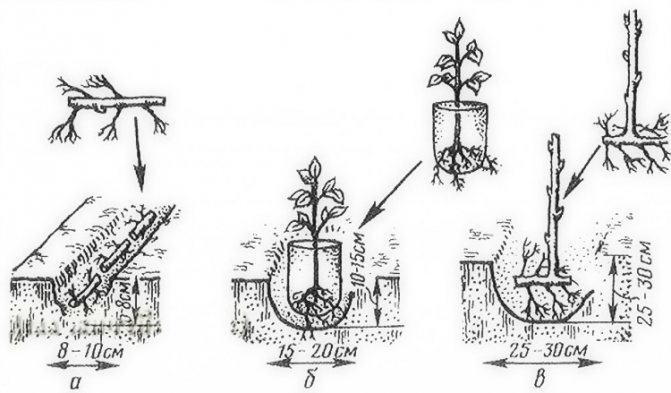
- a prepared bush (stem height up to 40 cm, roots - 25-30 cm) is dipped in a clay chatterbox;
- having straightened the roots, placed in a hole or trench and sprinkled with soil, compacting the earth around the roots;
- at the same time, special attention is paid to the placement of the root collar - it should protrude slightly (2-3 cm) above the soil level;
- at the end of planting raspberry bushes, they are slightly twitched up: if the soil is fed, the bush should be transplanted;
- the last stage of planting raspberries - compacting the soil around the bush, abundant watering (5-7 liters per bush), mulching with rotted straw, sawdust, peat.
Important! The subsequent watering of the bushes depends on the planting time: in the fall it may not be needed at all, and in the spring it is carried out as needed (at least once a week).


What soil does raspberry like
The quality of the raspberry crop depends largely on the planting site. The plant loves good light, so young shoots should be planted in sunny areas.


Recommendations for choosing a place for raspberries:
- flat relief without slopes and hills;
- soils - light fertile, chernozem or loam;
- the best predecessors are legumes and cereals;
- every 9-10 years, raspberries need to be transplanted to another place due to depletion of the land (soil restoration occurs after 6-7 years).
You can not plant raspberries in a place where potatoes, tomatoes or peppers had previously grown, since these plants take from the soil all the nutrients necessary for the normal growth and fertility of the bush.


Features of caring for raspberries
Raspberry care includes basic agricultural techniques: watering, weeding, loosening, mulching, feeding, pruning.
Watering raspberries
Raspberries are among those crops that cannot tolerate drying out of the soil. However, waterlogging can lead to root rot. Therefore, when caring for raspberries, it is important to maintain a balance: abundant rare watering and subsequent mulching allow the raspberries to gain enough moisture. In this case, good drainage of the soil remains a prerequisite.
Important! Garden raspberries need abundant watering during the flowering and fruiting period.
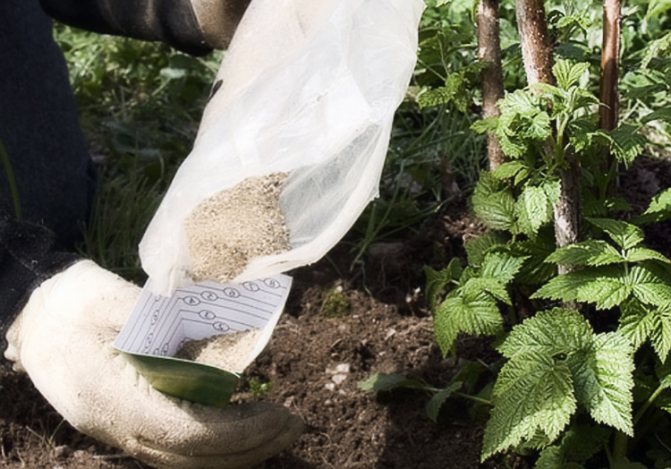
Feeding raspberries
Regular fertilization allows you to achieve higher yields and increase the time of fruiting raspberries without transplanting:
- In the spring, raspberries are fed with mullein diluted in water (1: 10) or chicken droppings (1: 20). Before loosening, nitrogen fertilizers are introduced into the soil under the old raspberry plant: ammonium nitrate (12 g per m²) and urea (10 g per m²);
- In the summer, planting garden raspberries is mulched with bone meal, which contains a number of nutrients;
- After harvesting, the soil between the rows is sprinkled with wood ash, which is an excellent source of potassium for garden raspberries;
- Once every 3-5 years, raspberries are fed with compost or manure, adding it when digging around the bushes after the end of fruiting. A complex fertilizer can serve as a substitute: 200 g per m².
Important! Nitrogen-containing fertilizers for raspberries are applied only in spring, since when applied in autumn, the green mass grows on the bushes, and, on the contrary, dystrophic processes begin in the roots.


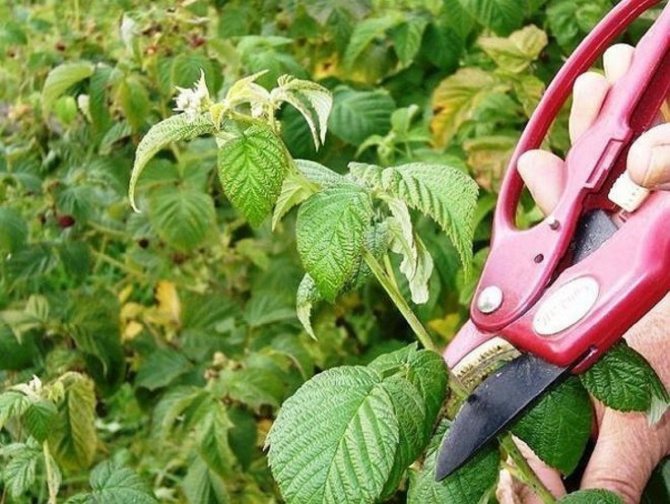
Raspberry pruning
One of the main agricultural practices in caring for raspberries and the main condition for obtaining bountiful harvests is the annual pruning of raspberries. The timing of its implementation depends on the variety of raspberries:
- Garden varieties can be cut off at the end of fruiting, however, most often the operation to remove shoots is carried out with the onset of cold weather: old raspberry shoots are removed with a pruner at the root. 8-10 strongest shoots are left in the bush. After pruning raspberries, the stems are burned or taken out of the site;
- Pruning of remontant raspberries is done in the fall after the leaf is dropped by the bush. In this case, the entire aerial part is removed. Some gardeners practice partial removal of shoots from remontant raspberries, thereby stimulating double fruiting - on the shoots of the first and second year of life. However, this method is not suitable for growing raspberries on an industrial scale, since the ripening of the berries is stretched throughout the summer, and the yield decreases.


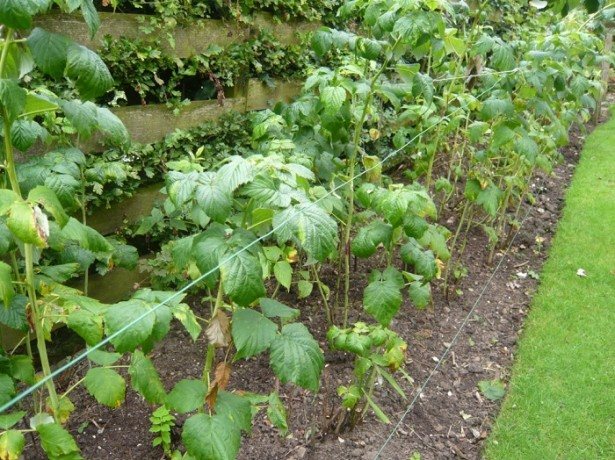
Important! Pruning tall varieties of raspberries provides for the autumn shortening of annual shoots to a height of 1.2-1.5 m. After that, the tall stems are tied in several pieces and attached to a support - a peg or trellis. If the winter in the region is cold, then the raspberries are bent to the ground (no higher than 40 cm) and, if necessary, additional shelter is made from spruce branches, straw, leaves or covering materials.
Requirements for choosing a seat for landing
When choosing a site for planting raspberries, it must be borne in mind that this culture is photophilous and gives a low yield in the shade, but does not tolerate the heat. It prefers areas with moderate moisture, the root system reacts negatively to an excess of moisture in the soil, therefore, when planting, it is necessary that groundwater does not come closer than 1.5 meters to the earth's surface. Otherwise, the root system may freeze in winter.
For growth, flat areas with a large accumulation of snow are preferable. This will give the raspberries a good wintering time. You can also plant this crop on the gentle slopes of the southern and southwestern directions. Excess moisture does not linger here, and there are no cold winds.
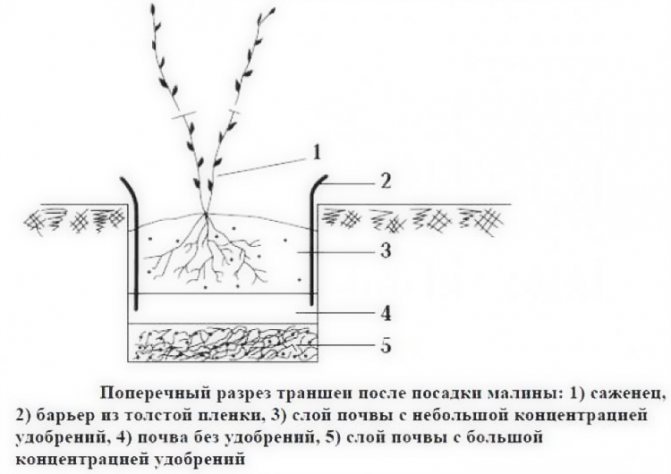

The soil is preferable clay-sandy with good permeability to moisture and air, rich in useful minerals. It can grow on sandy ones only if a large amount of organic fertilizers is applied to the soil.
The soil should not be acidic. To normalize the acidity level, lime or ash is added.
Good precursors to raspberries are:
- carrot;
- beet;
- radish;
- parsley;
- dill.
Reproduction of raspberries
Even one raspberry bush can be the basis for extensive plantings. Reproduction of this unpretentious plant is carried out in several ways:
- lignified offspring: near each bush by the fall, young shoots must necessarily rise, which has its own root system and aerial part. It is enough just to dig up a raspberry seedling and chop off the root that connects it to the mother plant. When planting, be sure to cut off the leaves;
- green root suckers can propagate raspberries in the spring, when young shoots are just rising from the ground. It is necessary to select offspring up to 20 cm high at a distance of about 40 cm from the center of the bush and dig them out with a lump of earth;
- raspberries are propagated by root cuttings if the aerial part is affected by a disease. About 0.5 m from the center of the bush, the earth is dug up and the adventitious roots are removed. Choose roots no thinner than 2 mm and cut them 8-10 cm so that there are 1-2 buds on each cuttings. They are planted immediately, in spring or autumn;
- with green cuttings, raspberry propagation is carried out in the spring (May-June), after thinning the thickened plantings. Cut cuttings (length - 10-15 cm, with 2-3 leaves) are placed in a greenhouse, and after rooting a month later they are planted in open ground;
- dividing the bush can be used to reproduce valuable varieties that give few offspring. In this case, the dug out bush is divided into several full-fledged seedlings with a developed root system, and the aerial part is shortened to improve adaptation.


Important! Since raspberries have a perennial rhizome, they are propagated, as a rule, in ways that use root suckers. Cuttings are taken with a lack of raspberry planting material or poor root formation.
Preparation of planting material
How to grow raspberries healthy and disease-resistant - you need to carefully choose the planting material, then competently prepare the young raspberries for planting on the site.
Instructions for selecting and preparing a garden raspberry seedling:
- there should be more than 2 healthy and strong additional shoots on the trunk;
- it is recommended to choose a seedling with a branched and large root system;
- if the roots have time to dry, then before planting raspberries, properly soak the seedling in plain water;
- the thickness of the branches is allowed from 5 to 8 millimeters.
The best varieties of raspberries
You can choose a more suitable variety in accordance with the climatic conditions of your region and, of course, your capabilities and requests.
Summer (traditional) varieties
This is a common garden raspberry that bears fruit in June-July and requires the removal of two-year-old shoots:
- Meteor. It is characterized by early ripening, resistance to cold and disease. Yields reach 2 kg per bush with a weight of 1 berry 3 g;
- Scarlet Sails. The height of the shoots reaches 2.2 m, and the yield is 1.7 kg per plant. This raspberry variety is resistant to low temperatures even during late spring frosts;
- Tarusa. The variety is characterized by high shoots (up to 1.8 m) and medium ripening times. The yield reaches 6 kg per plant, and the weight of one berry is 5 g. A distinctive feature is the absence of thorns.


Large-fruited varieties
Such varieties of raspberries have many advantages: large fruits weighing up to 12 g, the ability of fruit branches to branch, especially pronounced taste and aroma:
- Giant Ruby. A variety of raspberries with early ripening and medium resistance to frost, has a medium-tall spreading bush and truncated-conical large (up to 11 g) berries of a rich ruby color. High yield - up to 9 kg;
- Patricia. One of the most popular large-fruited raspberries. Yields reach 4-5 kg per plant, and the weight of one berry is 4-12 g. Patricia has good transportability and does not crumble even in a mature state;
- Aboriginal. The variety is characterized by an average ripening period, an average winter hardiness and a shoot height of up to 1.5-2 m.Large (4-7 g) berries have a conical shape, bright red color and delicate sweet-sour pulp. Productivity - 4-7 kg, excellent transportability;
- The golden giant. A raspberry variety with powerful erect shoots and excellent winter hardiness and transportability. The fruits are large (8-14 g), elongated-conical in shape with an unusual dark golden color. The yield from one bush reaches 8 kg.
Repaired varieties
In gardens and on personal plots, remontant varieties of raspberries are increasingly replacing ordinary varieties, since they have a number of advantages:
- early fruiting, which begins in the very first year: they are planted in the fall, and in the summer they are already harvested;
- the absence of pests and diseases, since the fruiting of raspberries is later (the insects have already completed the development cycle), and in the fall all shoots, together with diseases, are cut to zero;
- no need to cover for the winter, since the entire aerial part of the raspberry is removed, and it is enough only to mulch the roots;
- late flowering avoids the threat of late frosts, and this does not affect the yield;
- the minimum number of offspring allows you to almost not thin out the bushes, although if you want to reproduce, this advantage turns into a disadvantage.


The few disadvantages of remontant raspberries also include high demands on good lighting and almost complete absence of a characteristic aroma. However, when fully pruned in autumn, remontant raspberries show high yields with proper care. The most popular varieties are:
- Bryansk miracle. A variety of raspberries with early fruiting dates. With relatively low (up to 1.5 m) shoots, the yield is up to 3 kg of large (11 g) fruits with excellent transportability. Other varieties with early ripening include: Hercules, Diamond, Red Guard;
- Atlant. It belongs to varieties with an average ripening period: fruiting begins at the end of August. The yield from one bush is 2.5 kg. The berries are large (11 g), they hold firmly on the fruit, but they are removed and transported well. Polana, Yaroslavna, Ruby necklace, Orange miracle (yellow) also belong to remontant varieties of medium ripening periods.
Important! Usually, remontant raspberries are chosen for commercial cultivation, since they bear fruit longer than usual, and the safety of fruits is several times higher. Remontant varieties of raspberries with high yields include: Brusvyana (8 kg), Yaroslavna (8-9 kg), Penguin (15 kg), Shugana (9 kg), Yellow giant (12-15 kg).
Pluses of tires when growing berries


The fruit shrub not only does not spread throughout the entire site. The method has other positive aspects:
- The frequency of watering decreases - an impromptu container retains moisture.
- The different varieties do not mix.
- It makes it easier to care for the bushes. It is easier to remove weeds from a single plant.
- All parts are exposed to sunlight.
- After rain, moisture does not stagnate, the likelihood of getting sick with rot of various types and late blight is greatly reduced.
- When harvesting, not a single raspberry will be lost.
Attention! Tires should be changed at least once every 4 years. Constant humidity and the effect of fertilizers corrode the rubber coating, harmful substances enter the soil, which subsequently accumulate the berries.
Harvesting
The earliest varieties of garden raspberries begin to ripen in June, and the late ones ripen only in August. Since the fruits have a very delicate structure, the raspberries are harvested by hand at the beginning of ripening. Therefore, harvesting is the most costly of all processes in the industrial cultivation of raspberries - it takes up to 70% of labor costs. In some countries (Denmark, USA, Scotland, New Zealand), special harvesters are used to collect raspberries, which shake the berries off the stalks.
To maintain high commercial quality, manual collection is used:
- The best time for harvesting raspberries is in the morning before the onset of the sun. However, the berry must always be dry, so early morning is not suitable;
- Raspberry fruits are removed by light scrolling from the fruit tree, without squeezing;
- At a time, only a few berries are taken into the palm so that they do not wrinkle;
- Only ripe raspberries are harvested, and only in some cases is it allowed to remove them together with the fruit;
- If the weather is rainy for a long time, then a preventive collection is carried out, removing overripe and rotten raspberries in order to avoid the spread of infection. These fruits are allowed for processing;
- The collected raspberries are placed in special low boxes in no more than two rows, since under excess weight they can flow.


Preservation requires not only low temperature (0 + 2 ° C), but also a certain humidity - 90-95%, to achieve which special humidifiers and perforated stretch film are used. In this case, raspberries can last up to a week (subject to collection in dry weather), if the conditions are not met, the terms are reduced.
Your actions in the fall - getting ready for winter
- After the summer pruning of the fruit-bearing branches, the raspberries should be fed (see above, fertilizing without nitrogen fertilizers!).
- In the absence of rain, do not forget to water the plantings - by winter, raspberries should gain strength and have time to lay their buds next year.
- Thinning of young branches can be postponed until spring - winter is still ahead.
- Closer to winter, raspberries should be tied in bunches, even if you are not going to bend them to the ground. This will prevent the stems from kinking under the influence of snow and wind.
- Unripe green tops can be cut and dried - the content of acetylsalicylic acid and vitamin C in them is not lower than in berries.


And to see how to grow raspberries in the country, open the video. And then you will know exactly what to do so that there are a lot of raspberries ...
Post Views: 255
Crop rotation rules for raspberries, predecessors and neighbors
The best predecessors vegetable crops, gooseberries, currants, chokeberries will become a berry. Plots near nightshades (potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes, physalis, samberi and others) are not suitable for growing raspberries; crops have common diseases and pests.
Fruit trees (plum, pear, apple, apricot) are not a hindrance for raspberry berries, the roots are at different depths. For raspberries undesirable neighborhood with herbs, marigolds, nasturtium, cherries.
Planting dates in spring and autumn
In climatic zones with harsh winters, it is better to plant raspberries in spring, the approximate planting time is:
- Siberia, Ural, latitude of St. Petersburg - beginning, mid-May, depending on the weather;
- Central Russia - late April or early May;
- Warm regions - late March or early April.
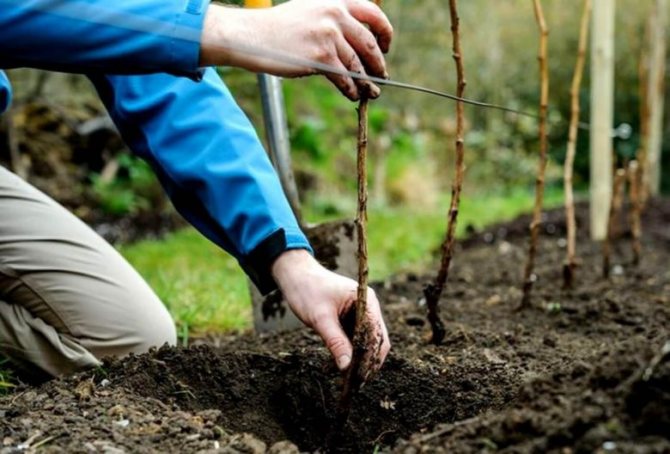


Planting raspberries in the ground
Planting remontant raspberries in autumn is undesirable, the bush will not have time to prepare for winter. In spring, in sunny weather, planting is shaded for the first week.
When planting in autumn the terms are limited by the climatic features of the region, it is worth planting raspberries a month before the onset of cold weather, so that the fibrous root system starts up new shoots. The soil is mulched so that the roots do not freeze too much during the first frost.