Almost every person living in central Russia or in its European part has at least once faced such a phenomenon as the invasion of May beetles. Usually for children, this event is of an amusement nature. Large and loud buzzing insects tend to fly around a street lamp at dusk. Knocking on the glass and getting burned, they fall down and fall into the hands of young naturalists. But few people thought about what the May beetles eat.
Important!
In addition to being fun for children, these insects are tree crown pests. Sometimes their invasion leaves behind serious and irreparable consequences. Trees lose part of the crown, which is why the processes of photosynthesis are disrupted, and the plant cannot receive adequate nutrition. This factor leads to a decrease in yield or even to the death of a representative of the flora.
Description of the beetle and its larva

Chafer
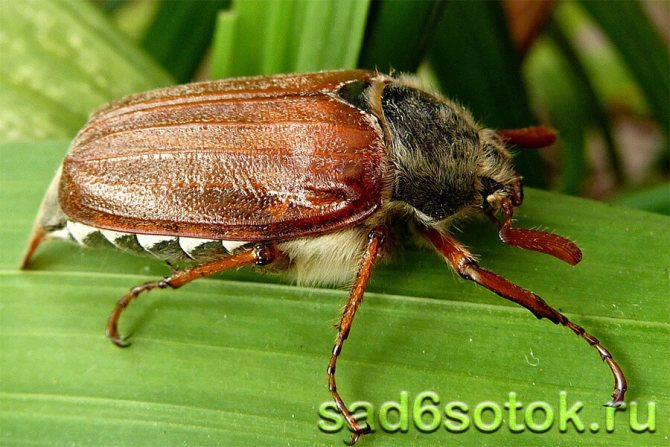
Adults large, reaching 3.5–4 mm in length and painted black or reddish-brown. The body is soft, barrel-shaped, covered with thick hairs. It is elongated and passes into a process from the back.
The body consists of 3 sections: head, chest and abdomen. On the head is a mouth, a pair of compound eyes, consisting of many simple eyes. Antennae with widened plates at the end are located in front of the eyes. These are insect olfactory organs, in males they are more developed.
On the chest of beetles, 3 pairs of legs are visible, and on the back the wings are protected by rigid elongated elytra. Insects have sharp jaws, they gnaw off pieces of leaves with the ends of the upper jaw, and grind them with the lower ones.
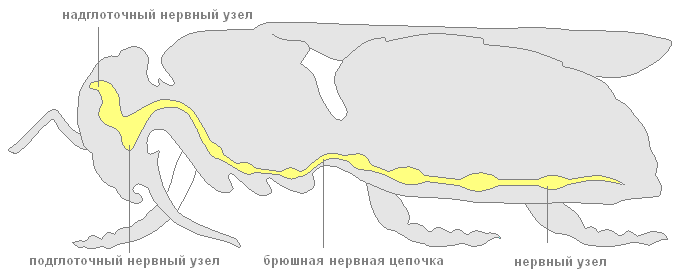
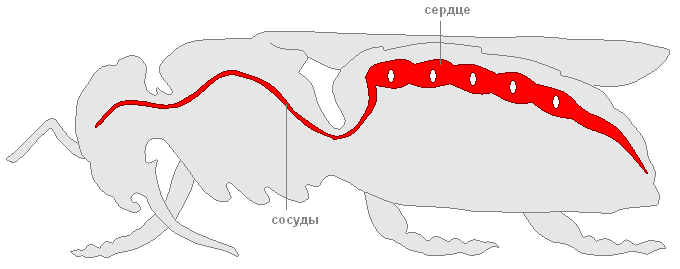
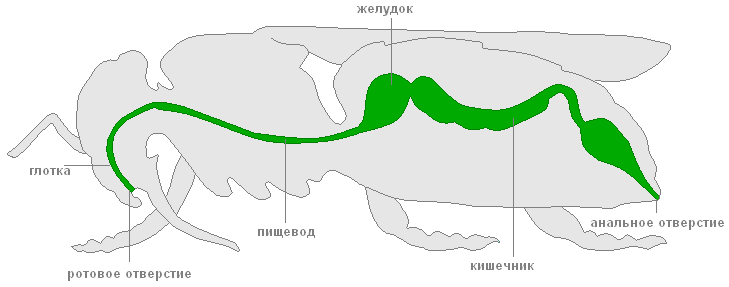
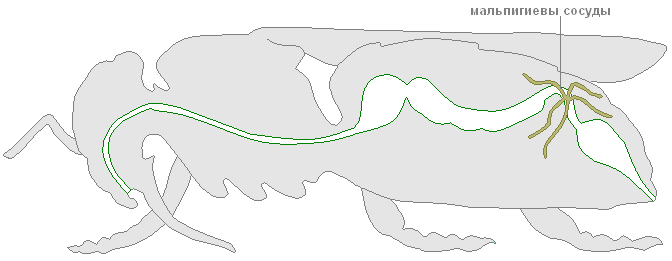
In addition to the digestive organs, the May beetles, like other arthropods, have a developed circulatory, respiratory, excretory, nervous and reproductive systems. Outwardly, males differ from females in the size of the antennae, they are longer and curved in shape.
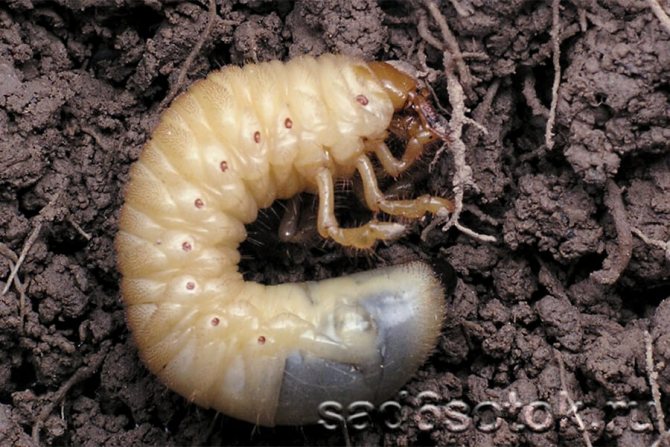
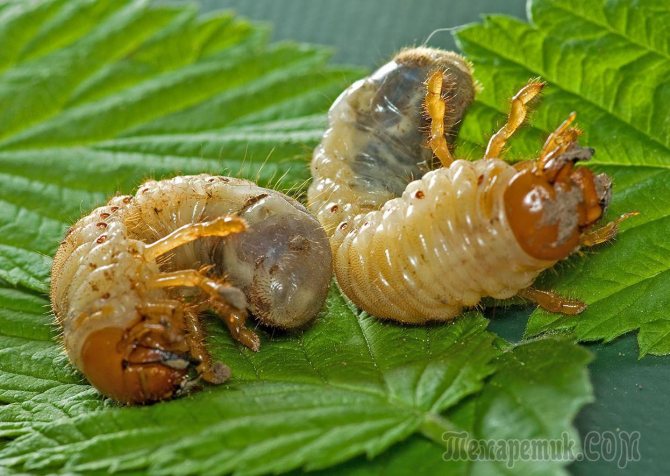
Larvae do not look like adult beetles. They have a thick, soft and arched, whitish body 3-5 cm long. The large head and three pairs of legs are yellow-brown in color. The wings are not developed, but there are spiracles on the sides of the body.
From a larva, the pest turns into a pupa, which in appearance is already similar to an adult May beetle. The pupa has a head with antennae, compound eyes and legs. The wings are shorter than that of an adult insect, the chitinous cover is dense and without a characteristic color. The pupa moves slightly, but cannot move and absorb food.
In our country, there are 6 species of the May beetle. The most common are the western and eastern types. They are similar to each other and differ only in the structure of the abdomen.
Cabbage worms
Medvedka is one of the most serious pests in the planting area. Among the people, she was nicknamed "earthen cancer". She got this name because of the elastic front back. It looks like the shell of an ordinary crayfish. She flies and swims beautifully in the water. Confidently makes earthen passages and quickly moves on its surface. Crawls out only at nightfall.
The bear is characterized by sharp sounds that create a rather frightening sensation at night. That is why it has another name among the people - the spinning top.
The bear larva is unpretentious in food.Eats eggplant roots, onions, cucumber leaves and sometimes the vegetables themselves, cabbage, potato tubers. She prefers to live in soil where there is a good supply of sunlight. Therefore, if a plant interferes with the penetration of sunlight and restrains its burrow, it is threatened with complete destruction. After all, the insect's mink is very small - the size is no larger than a chicken egg, and its depth is 10-15 cm.
How to get rid of an insect?


If, after rain, around the end of May and the beginning of the first summer month, you notice the appearance of dug wavy patches of land or plants cut off at the base of the territory, or the exit to the surface looks like a small hole, then you are at the mercy of a pest.
The insect's nest looks out a little from the ground. You may not notice it right away. It resembles an ordinary hummock. You can understand that a bear has started up in your possessions by the absence of vegetation around this hummock within a radius of 20 cm.
A clutch with eggs, which are equal in size to a pea, the bear visits quite often, making sure that everything is in order with the offspring.
Pest control
- The consequences after the presence of pests in your garden are enormous. When the entire crop is harvested, it is better to do this in early spring, loosen the ground, or better dig it up as deep as possible. So you will violate the underground possessions of the bear and destroy her egg clutches. Burrows in the garden are unique structures with a large number of moves and exits.
- Plant special plants where the pest lives. Medvedka is frightened by the smell of marigold. For her, it is harsh and has a poisonous pollen. Also, the infected area can be planted with lupines, which are considered perennial. After that, next to these flowers, which will bloom for more than one year, other weeds will no longer grow, and the larvae will have to feed on their roots, and they are poisonous for the future generation of beetles.
- A good way when watering a plot is to use a special infusion of onion husks (for 10 liters of warm water, take 1 kg of husks, leave for 5 days) or their waste. An infusion of chicken manure diluted with water 1: 3 will also help you. You can water the plants abundantly, or spray them daily. Irrigation will allow it to be evenly distributed throughout the plant. And if you combine these two methods together, the effect will be significant.
- The capture of adults is carried out by enticing the insect to smell of vegetable oil. Pour a couple of drops of oil into the bear's mink, wait a little and pour a glass of water. This will give a characteristic odor that the insect senses from a distance. The specimen will creep in and die.
Description
From May to July, insects end the mating season, it is after this that the bear begins to lay eggs in its nest. At a time, there are from 50 to 500 eggs of future insects. From the outside, they look like millet grains. Dark brown in color, 3.5 mm long.
If the habitat is favorable, then after 9-18 days the first larvae will begin to appear from the eggs. The food for which, at the initial stage of life, will be the remains of the shell and the salivary secretions of the mother on the walls of the nest.
After a few days, they will turn into a nymph, which in appearance looks like a full-fledged bear. The transformation into a full-fledged individual goes through a dangerous, lengthy process. Not everyone can cope with it. The weak are at risk of death.
Their full maturation occurs only after a year. From the moment of birth and through the fourth stage of growth, the larva of the bear grows from 15 to 33 mm. The diet includes earthworms and small insects, or the fruits of plants left over from the fall.
An interesting fact: the fertility of an insect is noticeably reduced if there are no cereals in the diet.
Pest life cycle
The insect goes through 4 stages of development: egg, larva, pupa, imago (adult).With the arrival of spring after the blooming of the leaves, the years of the May beetles, emerging from the shelter, begin. It lasts 1–1.5 months. At this time, mating occurs and in June females lay eggs in the soil to a depth of 10–20 cm. Ovipositions can be found not only in the ground, but also in the hollows of old trees. Each female lays up to 70–80 pieces, and then dies.
After 4–6 weeks, thick yellow-white larvae emerge from the eggs. This stage is the longest, it goes underground for 3-4 years. The larvae have 4 stages of maturation, accompanied by summer molts. In the first year, when the oral organ is not formed, young larvae feed on humus and small roots, from the next year their appetites grow and the larvae switch to feeding on the roots of trees, vegetables, shrubs.
In warm weather, the larvae rise to the soil surface into the root layer, with the arrival of winter they go 50–70 cm deep. As they grow older, they become more dangerous. The pest grows and needs more food.
The larvae turn into motionless pupae at the end of the cycle - at the end of summer or at the beginning of autumn. After 1.5 months, the chitinous cover of the pupa bursts and adult insects appear. They will remain deep underground until spring arrives.
Adult beetles live for 1 year. It was noticed that after 25-30 years there is a sharp increase in the number of pests. This is preceded by 3-4 years of decrease in insect activity.
Habitat
May beetle lives almost everywhere, except for those places where permafrost. In Russia, it is widespread everywhere, including Yakutia.


The eastern species likes to settle in high crowns of trees, and the western one chooses hills and hills for living.
Before the hatching of an adult, the larva is underground: in the spring it gets closer to the roots, and in the winter it goes to a depth of 1 m.
Signs of plant infection
Adults feed mainly on leaves. They eat or perforate leaf blades, damage buds, ovaries and flowers. Because of this, the process of photosynthesis is disrupted in plants, they weaken and wither.
There is more harm from the larvae, they are gluttonous and damage plant roots, 3-5 pieces can completely destroy the root system of a young tree. Even minor damage makes the plant vulnerable to pathogens. Young plants wither and are easily removed from the ground, and adult specimens, possessing a reserve of vitality, do not die, but slow down their development. The yields of vegetables and fruits are decreasing, lateral shoots on trees do not ripen well.
Adult insects and larvae are easy to spot in aerial areas and in the soil and be sure they are the cause of crop damage.
Bear larvae: what are the features
The larvae of the bear begin active life with the arrival of real spring heat. They hibernate, buried to a depth of about 2 meters or in dung heaps. The closer the warmth, the higher the larvae rise to the surface of the earth. At a soil temperature of about +12 degrees, they already feel very comfortable.
In the month of May, the process of laying eggs begins. It is characterized by the fact that sexually mature individuals get out of their hiding places at night on the surface of the earth and go in search of sexual partners. After mating, the female is busy arranging a nest for herself. At a depth of about 5 centimeters below the surface of the ground, she digs many underground passages. The main nest is at a depth of no more than 20 cm.
The female lays at least 400 eggs, which ensures the required level of survival of the species. The development of eggs and the birth of bear larvae occurs under certain conditions. This requires high humidity, high temperature and air access.
The reasons for the appearance of the pest on the site
May beetles prefer sandy soils, in heavy clay areas are less common.It is more convenient for females to lay eggs in unconsolidated soil. They love well-groomed and cultivated gardens and vegetable gardens., here are favorable conditions for them - nutritious soil, many plants, compost and humus heaps.
The life of the larvae is affected by temperature and humidity. High humidity is detrimental to them, and when the temperature rises above 25 ° C, they sink to greater depths. During spring cold snap and return frosts, May beetles freeze and may die.
The number of pests is reduced by the influence of fungi, bacteria and parasitic nematodes.
How to determine the presence of a bear in your garden
To find out about the presence of bear larvae in a summer cottage is often obtained already with a superficial examination of the territory. Insect nests are small bumps; a distinctive feature is the absence of vegetation around them. When organizing a nest, the female takes care of sufficient heating of the soil, for which she removes all plants that can create a shadow over the mink. Bears are very caring mothers, they often check the condition of their burrows with egg clutches, and, if necessary, move them to another place.
If you notice a bump on the land, try pouring water over it. Quite often, this method helps to bring the pest to the outside, where it can be destroyed mechanically, but do not get carried away by excessive watering of the entire territory, since the high level of moisture weakens the root system of plants, which, in turn, simplifies the process of spoiling rhizomes for the bears.


What crops are affected by the pest?
May beetles are polyphagous, damage many crops. Adult insects gnaw leaves and ovaries poplar, oak, maple, birch, aspen, alder, walnut, linden, willow, elderberry, acacia, elm, honeysuckle, alder, mountain ash, dog rose.
The insect can be seen on fruit trees and bushes: apple, plum, cherry, grape, sea buckthorn, black currant, gooseberry... Beetles love pine needles pines, spruce, larch, cedar... Lucky only ash, its pest bypasses.
The larvae feed on the roots of these trees, roots and roots of vegetable crops: potatoes, onions, beets, corn, sunflower... Larvae bring great damage to plantations strawberry.
Food
May beetle inflicts great harm on deciduous and mixed forests, fruit and berry crops. It feeds on leaves, flowers, and damages the ovaries.
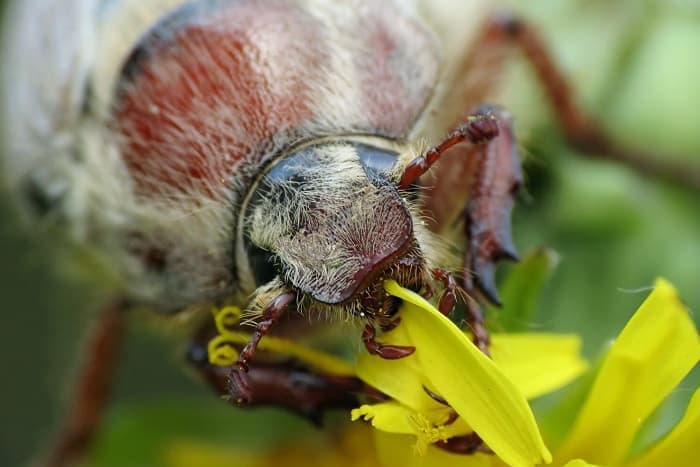


His favorite delicacies are plum, apple, cherry, hazelnuts and walnuts, he loves oak and birch. Also, the foliage of shrubs serves as food for the beetle, and needles are also suitable for the oriental species. He eats everything suitable for food in one area, then flies to another.
Nurseries are especially affected by the invasion of beetles, since they can completely gnaw on young seedlings. The only plants that the insect does not eat are lilac and ash.
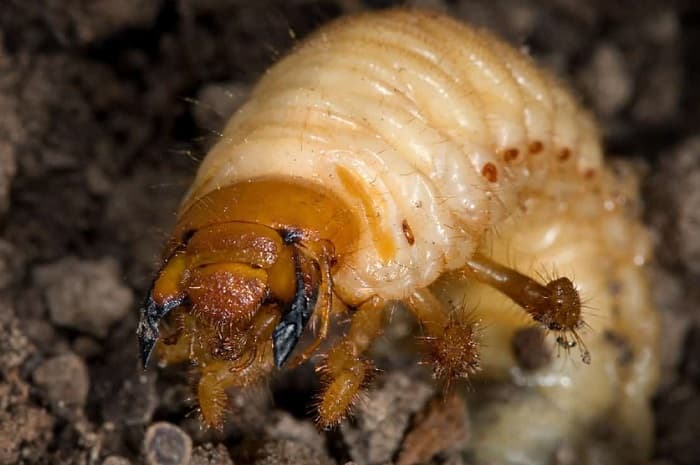


The larvae damage the roots of young trees, cereals and vegetables, as a result of which the plants die. These disgusting-looking, translucent worms (popularly called "hrobak" or "furrow") are well known to gardeners. If measures are not taken in time against them, they can destroy all seedlings.
Means of struggle
Chemical and biological products
Antikhrusch
Insectoacaricide affects the nervous system of the pest, paralyzes it and the larvae quickly die. Indirectly, the drug reduces the risk of viral and fungal diseases.
Before planting potatoes, the soil is sprayed with a working solution at the rate of 10 ml of the product per 5-10 liters of water. This volume is designed to process 1 weave.
To soak the roots of vegetable seedlings and seedlings of fruit trees, dilute 10 ml in 3 liters of water.
The soil around strawberries, berry bushes and fruit trees is watered with a solution of 10 ml of the drug and 5 liters of water.
Vallard
According to summer residents, this new drug is one of the most reliable in the fight against May beetle larvae.5-6 granules are scattered around the plants in the root zone and embedded in the soil to a depth of 5-10 cm.
Before planting, for the treatment of the roots of seedlings of fruit and ornamental plants, a mixture is prepared from a solution of an insecticide with the ground. 3 tsp of the product is added to 200 ml of water and stirred. Earth is poured into the container, the solution is added and more water is poured, bringing the volume of the "talker" to 1 liter. Roots are dipped into this mass before planting.
Zemlin
Once in the pest's body, the insecticide blocks the basic functions of life. The larvae cannot move, absorb food and soon die. The granules of the drug are applied to the ground when planting plants in the holes or during the growing season at the rate of 30 g per 20 sq. m.
Bazudin
An intestinal contact insecticide based on diazinon. The consumption rate of the drug is 30 g of granules per 20 sq. m. landings. Pre-mix them with dry sand or sawdust, loosen the soil and spread the mixture evenly.
Initiative
An effective preparation for contact action. Shows protective properties during the first days after application. 30 g of microgranules are poured into a container with dry sand with a volume of 1 liter, mixed and evenly scattered around the root zone.
Nemabakt
A unique biological product from pest larvae based on useful nematodes. The contents of the package (foam crumbs) are poured into a colander, which is placed on a bucket and washed with water (10 l), periodically squeezing out the crumbs. The resulting solution is stirred and used for watering the soil.
Folk methods
- Plants under the root are watered with a strong infusion of onion peels. Half of the bucket is filled with onion peels, hot water is added to the brim and left for a day. The infusion is filtered, but not diluted before use.
- Ammonia will drive the larvae off the site. Dissolve 20-30 ml in 10 liters of water and water the soil. This treatment is also good as a prophylaxis for strawberry bushes.
- From the pest, shoots of potatoes, vegetable seedlings are watered with a solution of potassium permanganate (3-5 g per 10 liters of water). The soil is spilled with the indicated solutions since May, when the pest has already risen into the root layer.
- The area is cleared of the larvae by mustard, they do not like the smell of this plant. Beginning in spring, the aisles and the soil around the trees are planted with mustard or other cruciferous crops. When the green mass grows back, it is embedded in the soil.
- Planting leguminous plants similarly affects the pest: lupine, beans, peas, beans. The soil under trees and shrubs can be covered with white clover. On the roots of this plant, as well as on legumes, bacteria are formed that participate in the accumulation of nitrogen in the soil. May beetle larvae do not tolerate this.
- In May, adults are harvested by hand. In the morning, insects are inactive, therefore, having noticed them, the branches of trees and shrubs are carefully shaken off, beetles are collected and destroyed.
- Traps are built to catch insects. Plastic bottles with a cut-off neck are hung on the trees. Sweet fermented liquid (compote, diluted jam, kvass, beer) is poured into the container.
- The May beetle is attracted by any light source at night. Therefore, the trap is installed next to a switched on flashlight or light bulb. The bait can be a wide container with water: a basin, a bucket, a bowl.
- For another option, the inner walls of the empty container are coated with any viscous and sticky substance. The insects that have flown into the world will fall into a trap, in the morning it will only be necessary to collect and destroy them.
Drugs that help fight crustaceans
Today, there are many products on the market, the use of which allows you to largely cleanse a heavily infested area from pests.
Common means of multidirectional action
Most often, summer residents use:
- contact-intestinal insecticides, acting mainly on the larvae of the first year of life - "Zemlin", "Pochin" ("Pochin").Produced in the form of powder or microgranules, which are embedded in the topsoil during spring digging, approximately 15-20 g per 10 sq. m. Young pests absorb the poison along with humus and die within 3 days;
- preparations of contact-intestinal action ("Vallar", "Bazudin", "Aktara"), which are active not only against crustaceans, but also against other soil pests - wireworm, bear, etc. Produced in both dry and liquid versions. They can also be applied to the surface layer of the soil, or used to treat plant roots before planting. For example, they do this when they want to get rid of the beetle larvae on strawberries as much as possible. Prepare a solution of the drug according to the instructions on the package, and etch the roots of young bushes with it, intended for planting on a new bed;
- means of long-term influence (for example, "Antikhrushch"). It is sold in the form of a suspension, which must be diluted with water (the norm of the drug content in the solution for each culture is indicated on the package). The resulting liquid is treated with the roots of the seedlings, and the plants already on the site are shed under the root;
- "Ammonia water"; the working solution is prepared from ammonium nitrate (200 g per 10 l of water). This amount is enough for 1 sq. m. of the future garden. 3-4 months before planting the plants, the soil is thoroughly dug up and spilled with the preparation. The method is very effective. It allows you to get rid of the May beetle larvae in the ground for several years, but in the middle lane it is suitable only for summer-autumn plantings.
The procedure for applying insecticides:
- Read the instructions on the packaging carefully.
- Take the necessary safety measures - put on gloves, a respirator, protect pets and children from access to pesticides.
- Dilute the drug as directed and use as directed.
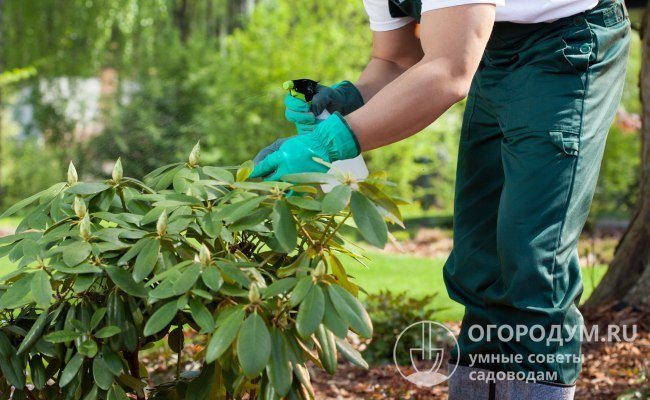


If folk remedies are ineffective, use insecticides. When working with pesticides, strictly follow the instructions on the package and observe safety measures
Biologicals
In addition, there are popular biological products ("Nemabakt", "Fitoverm", "Boverin", "Aktofit"), which can be used if the number of crustacean larvae in the soil is not very large. The composition of such funds includes natural enemies of the pest: microscopic nematode worms, pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria or fungi).
The use of biological products in the recommended concentrations does not pose a danger to people, domestic animals and beneficial insects, and does not have a negative impact on the ecosystem of the garden as a whole.
Prophylaxis
- The simplest agrotechnical pest control is spring digging of soil in the beds and in tree-trunk circles... During this time, the larvae are easy to spot. Tillage is mandatory for virgin areas. On such lands there is always a large accumulation of pests.
- The vegetable garden and garden are kept clean throughout the season, on time destroy weeds, especially wheatgrass... It attracts not only the wireworm, but also the beetle larvae.
- Useful soil mulching... A loose layer of chopped straw and wood shavings prevents females from laying eggs.
- At the pest many natural enemies, among them are various birds, hedgehogs, ground beetles, moles. To attract birds, you can install several birdhouses on the site. They will save plants from damage by both adult beetles and larvae.
If you do not hesitate and use the whole range of measures, then all attacks of the May beetle and larvae can be successfully repelled and make your site unattractive to the pest.
You will learn more about how to deal with beetle larvae from the video.
Other differences
These pests are distinguished not only by size, but also by developmental features. The “baby” of the May beetle differs from the bear in that it is practically harmless for the first two years of life, while the cabbage larva begins to actively feed on plant roots from the first days of life.But to say that it is more dangerous than a beetle, one cannot turn his tongue: the three-year-old faces of the May beetle destroy the root system of a young pine in 24 hours. Therefore, the fight against the pest should begin immediately after the detection of the insect at any stage of development.
The May beetle caterpillar is more difficult to detect due to the fact that the female lays eggs at great depths, and they are rarely found during spring field work - digging or plowing. The nest of the bear is located higher to the surface, it can be excavated, which facilitates the destruction of the pest at an early stage. By the way, insects differ in the number of eggs laid in the nests. In the May beetle, this number does not exceed 70, and the bear can postpone up to half a thousand.
Matured May beetle larvae like to settle in manure or a pile of compost, fallen leaves, old rotten stumps and thickets of grass. Medvedka, on the other hand, is buried in a dung heap when cold weather sets in, so that it can calmly overwinter and lay eggs there. This feature is used to destroy the pest: they create a manure pit about 30 cm deep with a layer of manure of at least 15 cm, throw earth on top of it, so that when the snap gets cold, the insect goes to the heat of the fertilizer. And when frosts come, the manure heap is scattered, and insects die, because they cannot stand low temperatures. But in the absence of a shallow warm bed, a bear in search of a cozy rookery can justify a nest, a breakthrough course up to 2 m deep. This is more common in regions with a sharply continental climate, where winter comes quickly and with severe frosts. At this depth, the larvae will be safe.
The difference between the larvae of the bear and the May beetle is also found in culinary preferences. Presumably indicate the presence of beetle larvae in the garden damage to apple and pear trees, apricot. He eats strawberry beds and berry bushes (currants, raspberries). Can occasionally gnaw potato tubers. The defeat of the beetle leads to wilting, the subsequent loss of leaves and the rapid death of the plant.
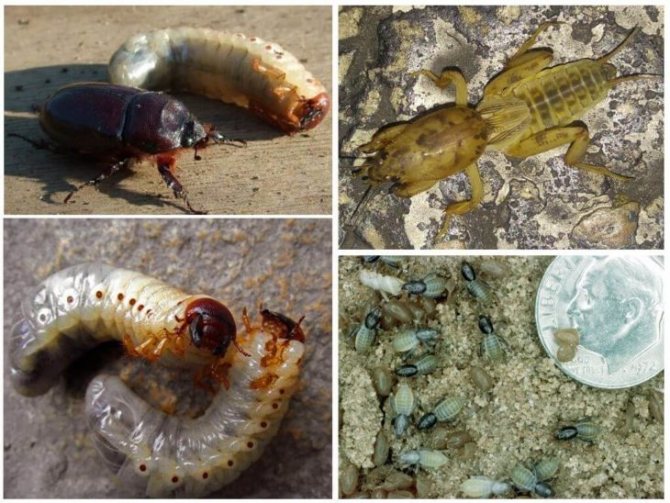


The larvae of the bear are gluttonous from the first days of life, while they do not particularly touch and eat everything that comes along. Preference is given to vegetables, especially nightshade - potatoes, tomatoes, eggplants. They willingly eat the roots of cucumbers and onions, but cabbage is beyond competition, this is the bear's favorite dish. The omnivorous nature of the growing bear knows no bounds. Not only can they eat autumn carrion, in which case the roots of fruit trees - apple trees, plums, peaches and apricots, and even barren ones, such as willows and poplars, oaks and ephedra, are suitable. The bear also feeds on the roots of flowers, especially loves bulbous plants - gladioli, tulips, etc. And if there is little plant food, they will eat insects found in the ground, smaller than themselves, earthworms and even younger larvae of their own kind.
May beetle and bear larvae prefer different types of soil. More precisely, almost any soil is suitable for the May beetle, and the cabbage loves acidified loose soils with a high level of groundwater. Therefore, in areas located in the lowlands, in the floodplains of rivers and lakes, on the banks of streams, in meadows and wetlands, bear larvae are found much more often than in dry, dense soil on elevations.
To top it off, we can say that the larvae of the May beetle are engaged in land reclamation - they enrich the soil, loosening it and saturating it with oxygen, facilitating the access of moisture. Another practical application of crustaceans is feeding them to poultry and using them as bait when fishing for large fish (ide, big chub and other carp). The bear larva, and even adults, are considered good bait when catching catfish. The reason is that they can make a noise that attracts this fish. The larvae of both of these insect pests are eaten not only by fish and birds, but also by moles, shrews, starlings and other birds.
What does a bear look like (cabbage)
The common bear lives throughout the European part of our country. Most of all, she loves to settle in loose, moist soils near rivers and streams. On her backyard, she most often chooses places intended for planting cabbage, compost and manure heaps.
A sign that a bear has started up on your site is the appearance after rain in May - early June of winding exploded areas of land and plants cut under the base.
The bear's nest looks like a hummock towering above the ground. It is easy to distinguish such a bump - nothing grows around it within a radius of 30 cm. In the nest, the insect lays eggs of a gray-yellow color the size of a pea.
Medvedka is one of the most harmful pests of vegetable gardens and orchards. Popularly referred to as "green cancer" because of its back-armor, it looks somewhat like a cancer. With the help of her strong forelimbs, she digs her passages underground like a mole.
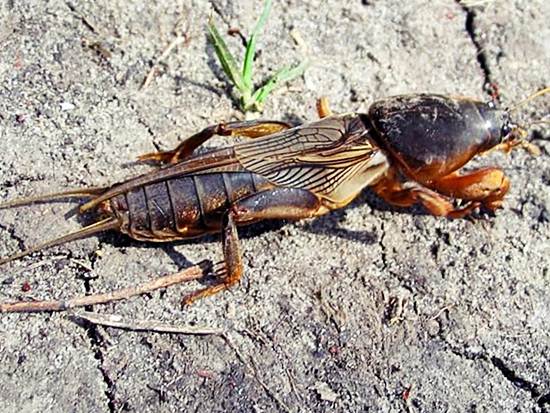


In the photo: Medvedka
Medvedka perfectly both swims and flies, and moves on the ground, although it spends most of its life underground, getting to the surface at night, while making a rather sharp sound. That is why the people gave her another nickname "spinning top".
Medvedka digs holes for itself 10-15 cm deep and straightens out equally well with any plants that darken its hole from the sun, be it potatoes, cucumbers, cabbage, eggplants or even onions. Many gardeners, digging up the soil in early spring and autumn, hope that in this way they will deal with the pest, but not everything is so simple.
Larva of a bear (cabbage)
As we wrote earlier, in the period from May to June (when the mating season ends), the bear lays 50-100 eggs in its nest, from which larvae will develop later.
Larvae in a favorable environment, especially in the presence of moisture, hatch from eggs in 10-18 days.


It looks like a bear larva
The bear larva looks like an adult insect, but it has no wings. First, the larva feeds on the eggshell and saliva left in the nest. And then during the year, until the larva matures, it will happily eat your plants.
It has been noticed that the bear loses fertility if there are no grains in her diet.
Common types
On the territory of Russia there are 9 types of beetles. The most common and harmful are two of them.
Khrushch or western May beetle
This is a rather thermophilic species, it lives in the forest zone and forest-steppe of the European part of the continent, does not climb north of Smolensk and the Moscow region, east of Kursk and Voronezh, you will not find it either. A distinctive feature of the insect is a black head and pronotum, elytra, light brown to red. This beetle prefers to feast on deciduous plantings, does not touch coniferous plantings. Nearby fruit crops are also affected.
East May Khrushch - a close brother of the western species
The insect is found both in the European part and throughout Asia. It can withstand the cold climate of the northern regions (it reaches Arkhangelsk), the Urals, Siberia, and Transbaikalia. This type of beetle can be recognized by the points on the head and pronotum, which are also lighter than in the western species, covered with long yellowish hairs. It is smaller - 20–29 mm. A favorite delicacy is young inflorescences of coniferous trees (pine, larch, spruce), in the absence of such, he does not disdain deciduous plantings, garden crops.
Note! The four to five year development cycle of May beetles is manifested in the frequency of insect infestations. In summer, they creep out of the soil in clouds and literally hang in clusters on trees. After another 4–5 years of calm, the beetles' raids are repeated.