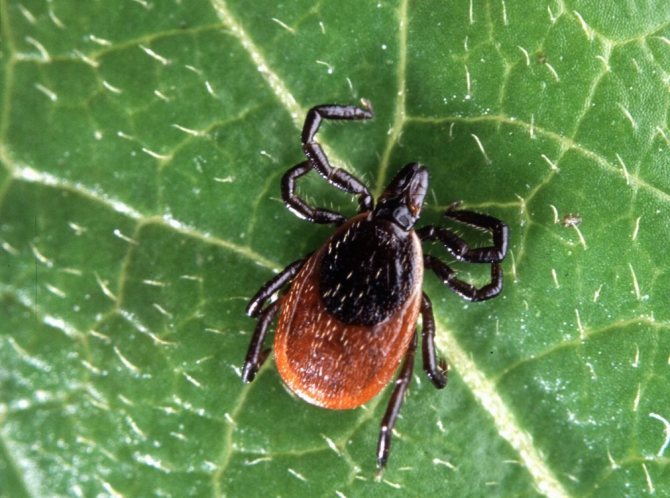
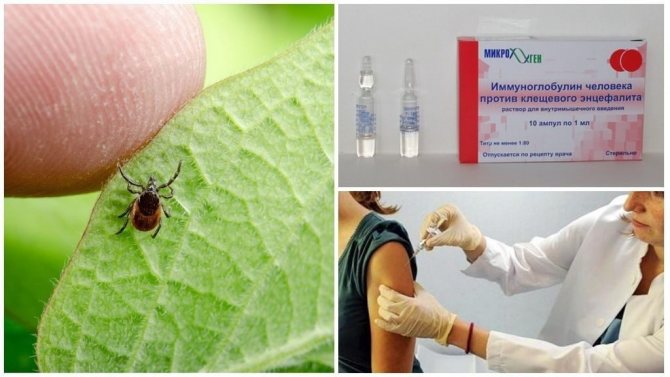
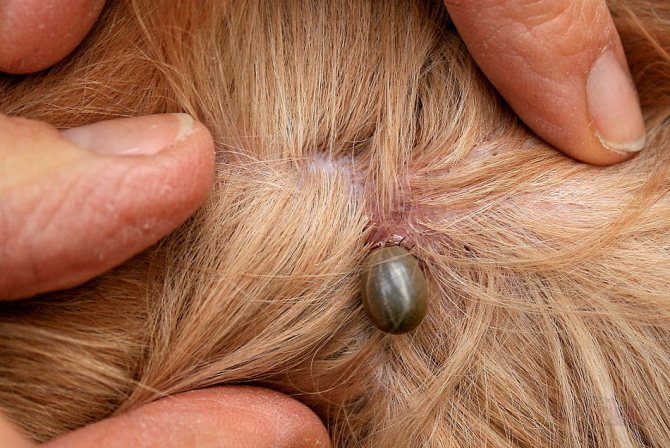
Every year in May is the season of summer cottages and picnics. But along with this comes an active breeding season for ticks, which are not only very hungry, but also dangerous. These bloodsuckers, at best, cause severe skin redness and an allergic reaction. In addition, ixodid ticks are carriers of many diseases, some of which lead to irreversible consequences. Therefore, you must definitely be able to protect yourself from a dangerous bloodsucker and know how to act in the event of a bite. However, it is worth remembering that even antibiotics for a tick bite are not always able to help, since there are several types of these bloodsuckers and each of them uses its own means of treatment.

Properties and indications
Doxycycline belongs to the antibacterial agents of the tetracycline series - it is an improved form of tetracycline with a wider spectrum of action. The drug is made in a semi-synthetic way and goes through several stages of purification, due to which well tolerated by the body and effectively destroys pathogenic microorganisms. Gram-negative and positive bacteria, including the causative agents of Lyme borrelia disease, are susceptible to the effects of doxycycline.
Borrelia enter the human body along with the saliva and body fluids of infected ixodid ticks. Doxytsklin does not destroy foreign agents, but prevents their reproduction and controls the population, due to which bacteria die out and the pathological process is stopped.
The active substance of the drug is almost completely absorbed into the bloodstream and quickly reaches the required concentration, therefore, the fight against pathogenic microorganisms begins almost immediately after it enters the body. In addition, Doxycycline has no toxic effect and practically does not have a negative effect on the intestinal microflora.

Doxycycline cannot be taken on your own, since this can cause unpleasant consequences - with tick-borne borreliosis, an antibiotic is prescribed by a doctor if there are certain indications.
- Proven contact with ticks. If a person has found a tick adhering to the skin, and the area of his residence is included in the list of endemic (places where there is an increased risk of infection with borreliosis) preventive treatment is recommended to start no later than 3-5 days after contact, ideally in the first 72 hours.
- Confirmed being infected with Lyme disease. If borrelia were detected in the tissues and biological fluids of the tick or the victim, Doxycycline therapy is prescribed immediately.
- The disease is in the second or third stage. Doxycycline is part of complex therapy in the second and third stages of Lyme disease, when the patient has the corresponding symptoms, and the diagnosis is confirmed using laboratory methods.
IMPORTANT! Doxycycline is effective only in the fight against borreliosis - if you suspect other diseases that are transmitted by the tick (for example, tick-borne encephalitis), other drugs are needed.
Droppers and injections
As a treatment for serious diseases and relieving exacerbation of symptoms, droppers can be prescribed through which the necessary medicine will penetrate into the blood.Antibiotics are given in this way: Ceftriaxone, Claforan, or Doxycycline. For a child, the doctor may recommend Sumamed, if for some reason this drug did not fit the baby, it can be replaced with Azithromycin - 5 intravenous droppers every day.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to take tetracyclines and cephalosporins together, the interval between courses of treatment should be ten days.
For the treatment of viral diseases, immunomodulators are prescribed. A good remedy from a domestic manufacturer is Allokin-Alpha. To improve the patient's condition, three injections are enough, however, in case of infection with tick-borne encephalitis, the administration of the drug will be ineffective. Immunoglobulin Octagam may be recommended for a child.
If a person goes to the clinic on the day he was bitten by a tick, most likely, he will be prescribed the introduction of 3 million IU of Realdiron. If an animal bite is detected on the second or third day, the patient will be prescribed the introduction of 3 million IU of the drug into the damaged area and from three to five injections of 3 million IU intramuscularly every day, the course of treatment is usually 21 days. In case of serious complications and mental disorders, up to 20 million IU of Bicillin-5 is put in inpatient conditions.
In some cases, the disease borreliosis can be cured only with repeated undergoing treatment, in which antibiotics and immunomodulatory agents are administered intravenously. The tablets are ineffective in this situation.
Read also:
Scabies mite in humans: symptoms and treatment
Treatment regimen
The dosage and features of taking Doxycycline with a tick bite or confirmed borreliosis are prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the clinical picture, age, general condition of the patient and other factors.
The drug is available in several forms:
- capsules;
- pills;
- powder, which is diluted with sterile water for the preparation of intramuscular injections or intravenous administration.

To prevent the development of tick-borne borreliosis after being bitten by an infected tick, Doxycycline is usually taken orally, but in difficult cases, when it is necessary to create a high concentration of the active substance dosage in the blood as soon as possible, the intramuscular or intravenous route of administration is chosen.
- For prophylactic purposes, Doxycycline is taken for 5-10 days, the standard dosage is 100-200 mg per day (as a rule, 200 mg is taken on the first day, and 100 mg on all other days). It can be taken once a day or divided into two doses after meals with clean water. For children under 14 years of age, the dosage is calculated based on physiological characteristics - on the first day, 4 mg of active substance per kilogram of body weight, on the following days, 2 mg.
- For the treatment of mild stages of borreliosis, adults are prescribed 200 mg of Doxycycline per day, children - 4 mg per kilogram of weight, the course of treatment is 20-30 days.
- In severe cases and in the chronic form of the disease, Doxycycline is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The powder is diluted with sterile water for injection, dextrose is added, mixed until completely dissolved, after which a solution for injections or droppers is used. The dosage is 200 mg of the active substance per day, injections are given once a day, the dropper is placed for 1-3 hours at a rate of 0.5 mg / ml per hour.
For children under 3 years of age and infants, Azithromycin or Augmentin in the form of a suspension is often prescribed instead of Doxycycline, but the drugs can be changed only after consulting a doctor. Treatment is carried out under medical supervision, and it is strictly forbidden to interrupt the intake of antibiotics on your own - if you do not complete the full course of treatment, live borrelia may remain in the body, which will cause a relapse of the disease.
REFERENCE! Most drugs contain doxycycline hydrochloride, which creates an acidic environment in the esophagus and can lead to ulcerative lesions. In the presence of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or a tendency to them, it is better to take drugs based on doxycycline monohydrate, a substance relatively safe for the esophageal mucosa.
Antibiotics for children with a bite
Antibiotics for children with a tick bite are also necessarily prescribed. For a small patient, suffering from borreliosis can often be tantamount to death. Therefore, if you find a bite on a child, then you should not delay visiting a doctor and then taking medications.
The dosage of the drug for the child requires a calculation by weight. This means that the amount of the drug will depend on how heavy the baby is. The calculation is based on the principle of 4 mg of the drug per 1 kg of body weight. The child takes this dose for one day, after which, starting from the second day, in case of prophylaxis, the dosage should be halved.
If a child undergoes treatment with a confirmed diagnosis, then the dosage and duration of the course should be strictly determined only by the doctor!
Remember, the main way to avoid health problems is to take safety measures to prevent the bites themselves. To do this, in the spring and summer period, you need to observe special precautions, which include:
- Use of special protective equipment against ticks;
- Choosing the right clothes for going outdoors (clothes should cover the largest possible surface of the body and prevent the tick from accessing the skin);
- Choice of places with the minimum possibility of contact with these parasites.
It is the observance of these precautions that will best protect your family, including children and pets, from ticks.
Contraindications

The following diseases are among the contraindications for taking Doxycycline:
- individual intolerance to tetracycline antibiotics and other components of the drug;
- severe liver and kidney dysfunction;
- myasthenia gravis;
- porphyria;
- a decrease in the concentration of leukocytes in the blood.
Doxycycline is not recommended for children under the age of 8, and for any chronic diseases it should be used with caution, under the supervision of a physician.
FLYING ERYTHEMA
Treatment of borreliosis, accompanied by erythema migrans without complications from the cardiovascular and nervous systems, involves the following measures:
- Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime - 14-21 days. Doxycycline - 10-21 days
- Doxycycline is contraindicated for pregnant women or while feeding; Amoxicillin or Cefuroxime is prescribed for 14-21 days
- If the patient cannot tolerate all three first-line antibiotic drugs, macrolides are prescribed. Note that macrolides are not recommended as first-line therapy for borreliosis.
- If it is impossible to carry out the differential diagnosis of erythema migrans with community-acquired cellulitis (phlegmon of subcutaneous fat), antibiotics are prescribed that are effective in both conditions - Cefuroxime or Amoxicillin Clavunate (Amoxicillin Clavulanic acid)
Combination with other drugs
Doxycycline is often part of complex therapy, but in combination with some drugs, reactions that are undesirable for the body are possible:
- antibiotics of the cephalosporin, penicillin and tetracycline groups reduce the effectiveness of the drug;
- anticoagulants in combination with Doxycycline can provoke dangerous changes in the composition of the blood;
- antacids and laxatives reduce the absorption of the antibiotic;
- mineral complexes and bioactive supplements containing calcium or iron block the active components of Doxycycline and significantly reduce its effectiveness;
- oral contraceptives and estrogen-containing drugs in combination with the drug lose their therapeutic effect, and the woman has an increased risk of uterine bleeding.
REFERENCE! When taking Doxycycline, it is recommended to minimize the consumption of milk and fermented milk products, to give up smoking and food that can irritate the gastric mucosa (onions, garlic, spices, smoked and salty foods) - this will increase the effectiveness of the drug and reduce the likelihood of developing ulcerative lesions.
Pharmodynamics
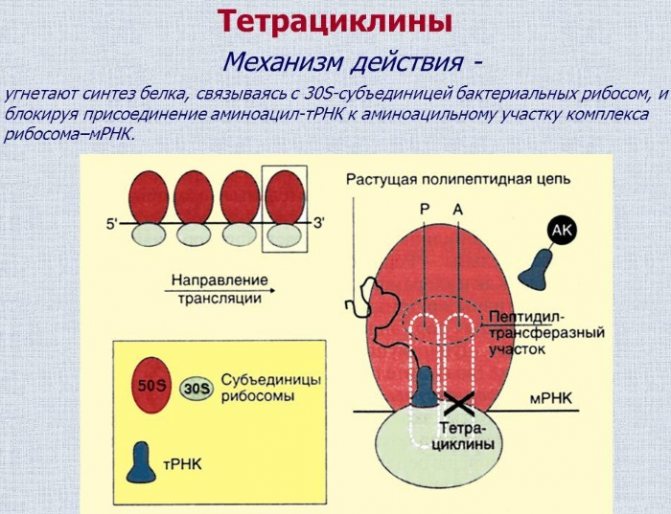
The bacteriostatic properties of Doxycycline are due to the fact that its active substance inhibits protein synthesis of infectious agents. The drug disrupts the bonds of RNA molecules that carry out a transport function with informational ribosomes.
As a result of this process, pathogenic microorganisms lose their functional ability to divide and increase their population.
The main pharmacodynamic property of Doxycycline is its high activity against bacteria of the following strains:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- streptococcus;
- clostridium;
- gonococcus;
- Escherichia koli;
- shigella;
- salmonella;
- enterobacter;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- rickettsia.

The appointment of Doxycycline is carried out only after a specific strain of an infectious microorganism has been identified, which is sensitive to the active substance of the drug.
Side effects


Doxycycline is a potent antibiotic, and in some cases it can cause unpleasant reactions of the body from different organs and systems:
- loss of appetite, nausea, diarrhea, dryness and bad taste in the mouth;
- allergic manifestations - itching, rashes, edema, bronchospasm;
- deterioration of vision and hearing;
- surges in blood pressure, increased heart rate;
- muscle and joint pain;
- changes in blood tests.
Alcohol while taking tetracycline antibiotics is unacceptable - this combination can cause serious intoxication of the body.
As a rule, side effects when taking Doxycycline are not very pronounced and go away on their own after a while, but if they worsen or are observed for a long time, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Oral antibiotic therapy
To prevent the development of disease after a tick bite, time is of the essence. Action should be taken immediately. It has been proven that it is necessary to take an antibiotic in the first 3 days after a tick bite. Otherwise, the disease can not only develop, but also take on a chronic form.
Having found a tick on the body, it is important to immediately go to the hospital. You cannot try to remove the parasite yourself, so as not to leave its proboscis under the skin. Specialists will remove the tick and send it for examination. Without waiting for the result, prophylactic treatment with Doxycycline will be prescribed.
If a patient seeks help at a medical facility more than 10 days after the bite, there is very little chance of a complete cure. Moreover, even the very introduction of Doxycycline against the background of developing borreliosis can cause complications.
- Oral administration of antibacterial drugs is indicated for patients with borreliosis (local or disseminated infection) with erythema migrans, provided there are no signs of complications from the cardiovascular and nervous systems
- Doxycycline is contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, pregnant or breastfeeding (in the UK, doxycycline is not recommended for children under 12 years of age). This group of patients is prescribed Amoxicillin and Cefuroxime.
- Macrolides (eg, erythromycin or azithromycin) are not used as first-line treatment for borreliosis.These drugs are prescribed to patients with intolerance or allergy to first-line drugs (in this case, the condition of the patients must be monitored)
- 1st generation cephalosporins are ineffective in the treatment of borreliosis
- In different studies, borreliosis was treated for 10 to 21 days. Experts never came to a consensus on the duration of treatment, but in most cases, it took 14 days for successful treatment. A study conducted in Slovenia demonstrated the effectiveness of treatment between 10-day and 15-day courses of Doxycycline in patients with typical solitary elements of erythema migrans. The course of treatment with Azithromycin is 7-10 days.
- If erythema migrans resembles cellulite, use Cefuroxime or Amoxicillin Clavulanate
- Oral antibiotic therapy is indicated for patients with cardiac complications of borreliosis if they are not accompanied by chest pain, syncope, dyspnea, degree I and II atrioventricular block with a PR interval of ≥ 300 milliseconds (patients with the listed pathologies are prescribed infusion a / b therapy)
- The studies used a course of treatment lasting from 10 to 21 days, but the effectiveness of these courses was not compared; in most cases, a 14-day course of treatment allows you to achieve an effective result, but there is currently no consensus on this issue
- Lyme arthritis is treated in the same way as uncomplicated borreliosis for an extended period of time (28 days). Chronization and relapses of pathology also require appropriate therapy.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve Lyme arthritis pain (along with antibiotics)
- Chronic or recurrent arthritis caused by borreliosis requires a repeated course of treatment (28 days with oral antibiotics or 14-28 days of infusion of Ceftriaxone). Note that in this case, preference is given to oral treatment (except for cases when in the first cycle of treatment oral therapy did not give any response)
- Arthroscopic synovectomy is indicated for patients who do not respond to antibiotic therapy (antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis)
- In some cases, intra-articular injections of corticosteroids are used, systemic administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antirheumatic drugs that can modify the pathology (for example, hydroxychloroquine) (with antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis)
- The decision on the appointment of treatment for patients with neurological complications and joint damage is made depending on the individual characteristics of a particular patient and under the supervision of a doctor.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR BORRELIOSIS
| Basic treatment | Alternative treatment |
| Classic start | |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day - OR - Amoxicillin: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 3 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 3 times a day - OR - Cefuroxime: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day | Azithromycin: children - 10 mg / kg per day orally, once; adults - 50 mg orally once - OR - Erythromycin: children - 30-50 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 4 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 4 times a day - OR - Clarithromycin: children - 15 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day |
| Cellulite-like erythema migrans | |
| Cefuroxime: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day - OR - Amoxicillin Clavulanate: adults - 500 mg orally 3 times a day; DOSAGE IS DETERMINED BY AMOXICILLIN CONTENT | |
| Cardiac complications | |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day - OR - Amoxicillin: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 3 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 3 times a day - OR - Cefuroxime: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day | |
| Arthritis with borreliosis | |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) - OR - Amoxicillin: children - 20-50 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 3 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 3 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) - OR - Cefuroxime: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) | Erythromycin: children - 30-50 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 4 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 4 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) - OR - Clarithromycin: children - 15 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) |
| Chronic or recurrent arthritis | |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) - OR - Amoxicillin: children - 20-50 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 3 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 3 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) - OR - Cefuroxime: children - 15-30 mg / kg per day orally, dividing the total daily dose into 2 doses; adults - 500 mg orally 2 times a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) | Ceftriaxone: children - 50-100 mg / kg per day intravenously 1 time per day; adults - 2 g intravenously once a day – – Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Ibuprofen: children - 10-15 mg kg orally every 4-6 hours (according to indications) (maximum daily dose in children - 40 mg / kg), adults - 300-400 mg orally every 6-8 hours (by indications) (maximum daily dose in adults - 2400 mg / kg) OR Diclofenac: adults - 50 mg orally 3 times a day (according to indications) |
Analogs
Almost all drugs of the tetracycline group, as well as cephalosporins, which have a similar spectrum of action, are analogs of Doxycycline:
- Vibramycin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Unidox Solutab;
- Amikacin;
- Tetracycline
Despite the fact that Doxycycline analogs have a similar therapeutic effect, the indications, contraindications and features of the effect are different for them, therefore, it is impossible to independently make adjustments to the treatment regimen.
NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS (NEUROBORRELIOSIS)
Despite the fact that parenteral antibiotic therapy is successfully used for neurological complications of borreliosis, oral administration of Doxycycline does not demonstrate the expected effect.
Patients with early neurological symptoms of borreliosis, characterized by limited lesions of the meninges, cranial nerves, nerve roots, or peripheral nerves (Bannwart syndrome), are prescribed a 14-day course of oral (Doxycycline) or infusion antibiotic therapy (Cefotaxime, Ceftriaxone, or Benzylinenzyl).
The European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS; European Federation of Neurological Societies) recommends in the late stages of borreliosis with peripheral neuropathy and atrophic acrodermatitis, oral doxycycline and intravenous ceftriaxone. However, for any manifestations of complications of borreliosis from the central nervous system (myelitis, vasculitis, encephalitis), intravenous administration of Ceftriaxone should be prescribed.
With regard to the treatment of facial paralysis (also see the article "Cranial Nerves. General Information"), as complications of borreliosis, the recommendations are contradictory, due to the lack of accurate data confirming the fact that these complications are related to neurological complications of borreliosis or acute borreliosis without signs of central nervous pathology. systems (in this case, experts considered isolated facial paralysis in patients with borreliosis as early neuroborreliosis with damage to the cranial nerves).
The decision to treat patients with borreliosis with complications from the musculoskeletal system and the nervous system is made depending on the condition of a particular patient and the recommendations of the relevant specialists.
TREATMENT OF BORRELIOSIS
BASIC PRINCIPLES FOR PREVENTING BORRELIOSIS
| Patient group | Treatment |
| Tick infestation bulletin | One prophylactic dose of antibiotic (Doxycycline) Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years - 4 mg / kg per day orally, single dose; adults - 200 mg orally once |
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT OF ACUTE BORRELIOSIS
| Classical development of pathology | Oral antibiotic therapy |
| The clinical picture of cellulite (phlegmon PZhK) | Oral antibiotic therapy |
| Cardiac complications without high blockade | Oral antibiotic therapy |
| Cardiac complications with high blockade | Infusion antibiotic therapy Additionally: Temporary pacing |
| Early symptoms limited to peripheral nervous system involvement | Depending on the indication, oral or infusion antibiotic therapy is prescribed |
| Lesions of the central nervous system | Intravenous Ceftriaxone |
| Arthritis | Oral antibiotic therapy Additionally: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| Recurrent or chronic arthritis | Oral or infusion antibiotic therapy Additionally: Arthroscopic synovectomy Pharmacotherapy |
- Patients with borreliosis and early neurological complications, limited lining of the brain (including meningitis), cranial nerves, nerve roots, or peripheral nerves (Bannwart syndrome) are prescribed a 14-day course of oral (Doxycycline) or infusion antibacterial therapy (Cefotaximex or Benzylpenicillin)
- For borreliosis with neurological complications such as peripheral neuropathy and atrophic chronic acrodermatitis, oral doxycycline and intravenous ceftriaxone are recommended
- With myelitis, vasculitis, encephalitis, intravenous administration of Ceftriaxone is prescribed, the duration of the course is from 14 (with early symptoms) to 21 (with late symptoms) days
- With regard to the treatment of paralysis of the facial muscles caused by borreliosis, there is no consensus, since there is no precise data confirming whether these paralysis are a neurological complication or an infectious complication without disturbances from the central nervous system (experts consider isolated facial paralysis in patients with borreliosis as early neuroborreliosis with damage to the cranial nerves)
- The decision on the appointment of treatment for patients with neurological complications and joint damage is made depending on the individual characteristics of a particular patient and under the supervision of a doctor.
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR BORRELIOSIS
| Early neurological symptoms |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day - OR - Ceftriaxone: children - 50-100 mg / kg per day intravenously 1 time per day; adults - 2 g intravenously once a day - OR - Cefotaxime: children - 150-200 mg / kg per day intravenously, dividing the total daily dose into 3 injections; adults - 2 g IV every 8 hours - OR - Benzylpenicillin: children - 25-50 mg / kg intramuscularly or intravenously every 4-6 hours, the maximum dose is 2.4 g every 4 hours; adults - 2.4 g intramuscularly or intravenously every 4-6 hours |
| Late neurological symptoms |
| Doxycycline: children {amp} gt; 8 years old - 2 mg / kg orally 2 times a day; adults - 100 mg orally 2 times a day - OR - Ceftriaxone: children - 50-100 mg / kg per day intravenously 1 time per day; adults - 2 g intravenously once a day |
| Complications from the central nervous system |
| Ceftriaxone: children - 50-100 mg / kg per day intravenously 1 time per day; adults - 2 g intravenously once a day |
Useful video
Check out the video about the treatment of borreliosis with the drug "Doxycycline" in detail:
Doxycycline effectively destroys the pathogens of borreliosis and can prevent many of the complications that this disease entails, but requires caution when taken. The drug should be taken exclusively under the supervision of a physician, carefully following his recommendations and monitoring the patient's condition.
Doxycycline is one of the most popular medicines for treating many infections, including tick-borne borreliosis. But the drug requires careful selection of the dosage. Treatment methods should be selected only by an infectious disease doctor.And the task of a patient bitten by a tick is to contact a medical institution in time.
Timing of therapy
To prevent the development of disease after a tick bite, time is of the essence. Action should be taken immediately. It has been proven that it is necessary to take an antibiotic in the first 3 days after a tick bite. Otherwise, the disease can not only develop, but also take on a chronic form.
Having found a tick on the body, it is important to immediately go to the hospital. You cannot try to remove the parasite yourself, so as not to leave its proboscis under the skin. Specialists will remove the tick and send it for examination. Without waiting for the result, prophylactic treatment with Doxycycline will be prescribed.
If a patient seeks help at a medical facility more than 10 days after the bite, there is very little chance of a complete cure. Moreover, even the very introduction of Doxycycline against the background of developing borreliosis can cause complications.
What is doxycycline
Doxycycline is a semi-synthetic antibiotic. It is known for its broad spectrum of action and belongs to the group of tetracyclines. The essence of its work is to inhibit the synthesis of protein, which is the basis of the cells of microorganisms. The drug stops the multiplication of pathogens and causes their death.
It exists in several dosage forms:
- pills;
- capsules;
- lyophilisate for solution preparation;
- solution for direct intravenous injection.
Application features
After the drug enters the body, it is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. Simultaneous food intake slightly affects the absorption of the drug.
Doxycycline is effective at the initial stage of Lyme disease (tick-borne borreliosis), as well as in other infectious and inflammatory diseases of the respiratory and genitourinary system.
Side effects and contraindications
The drug also has side effects, which can manifest themselves in the form of:
- allergic reactions;
- nausea;
- stomach ache;
- candidiasis;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
It is undesirable to use doxycycline in the following cases:
- hypersensitivity to tetracyclines;
- severe liver failure;
- during lactation;
- during pregnancy;
- in children under 8 years of age.
The warning is related to the properties of tetracyclines to influence the formation and growth of a child's teeth. The drug is able to slow down their development and change color. For this reason, starting from the fourth month of pregnancy, during breastfeeding, as well as in young childhood, the drug is given only if its benefits obviously outweigh the possible harm.
Combination with other medicines
When Doxycycline interacts with other medicinal substances, it is important to take into account that its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract is reduced by medications containing magnesium and iron. For this reason, their simultaneous use is separated by a three-hour interval.
What can you drink if you are allergic to a bite
Redness (with borreliosis will appear only after a week) and edema are a common reaction of the body to a bite.
Antihistamines that can be used to reduce allergic reactions:
- Suprastin;
- Diazolin;


The drug Diazolin is a fairly effective drug with a pronounced antihistamine effect. - Tavegil;
- Loratadin.
The usual redness will disappear within a few days, and if you take anti-allergy medications, it will happen faster.
Doxycycline from tick-borne borreliosis
The drug is used after a tick bite as a prophylaxis for the most dangerous disease - tick-borne borreliosis (or Lyme disease). This infection is caused by borrelia, which are carried by ticks common in Russia. The causative agent of the disease Borrelia Miyamotoi was discovered by Japanese scientists relatively recently, in 1995.
Borreliosis is common throughout the Northern Hemisphere.The risk group consists of residents of areas with mixed deciduous forests.
This is a natural focal infection. This is not the case when a microorganism is introduced from a new territory or when a non-pathogenic mutates and turns into a pathogenic one. This one was on the territory of Russia and in the same way on the territory of Europe and North America, always.
Alexander Platonov, Head of the Laboratory of Natural Focal Infections of the Federal Budgetary Scientific Institution of the Central Research Institute of Epidemiology of Rospotrebnadzor
Infection begins when the tick's saliva is injected under the human skin. The incubation period lasts approximately three days to a month. Due to the resistance of Borrelia and their ability to instantly reproduce, human immunity cannot overcome the disease without the help of drugs. Lack of timely therapy leads to complications: the nervous system, brain, heart and joints are often affected. About a quarter of people affected by infected tick bites remain disabled. That is why doctors advise starting prophylactic treatment, even if an infection test has not been performed.
Video: incubation period and manifestations of borreliosis
When antibiotics are required
Antibiotic therapy is needed for people who have been bitten by a borrelia-infected tick. Not every ixodid tick carries a bacterial infection. It is believed that in Russia only 30-40% of all ticks contain spirochetes. Every year, 6-8 thousand new cases of tick-borne borreliosis are detected in the country.
If a tick has bitten, then, first of all, you need to remove it yourself using tweezers or go to the emergency room, where doctors will remove it. To find out whether an insect is infected with borreliosis, it must be sent for research to a sanitary and epidemiological laboratory. A specialized institution will conduct a rapid test for Borrelia using temporal microscopy. And also the bloodsucker will be examined for viral encephalitis.
It is not recommended to routinely examine a tick bite for the presence of tick-borne infections for several reasons:
- In Europe, almost a quarter of ticks are infected with bacteria, but infection develops only in 1–5% of suction. A positive result means that the insect is infected, but does not predict the likelihood of transmission of the pathogen.
- Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for borreliosis is justified only in the next three days after tick sucking, and the results of insect research are often obtained much later.
- Often, the disease develops with a negative test result of the bloodsucker. If no infection is found in the tick, then this creates a feeling of safety in the patient, and he does not go to the hospital even if a characteristic clinical picture of the disease occurs.
That is why, when a tick sucks, regardless of the results of the study, it is imperative to take a prophylactic dose of an antibiotic. If a tick bite was not detected or it was not possible to take a medication within 3 days, then it is necessary to contact an infectious disease specialist if erythema migrans or other characteristic signs occur.
If there is erythema and a history of a parasite bite, then this is confirmation of Lyme disease and etiotropic antibiotic therapy is required. If, after a tick bite, symptoms such as headaches and muscle pains, decreased performance, cognitive impairment, neck and back pain, weakness, fatigue appear, then laboratory diagnostics are required.
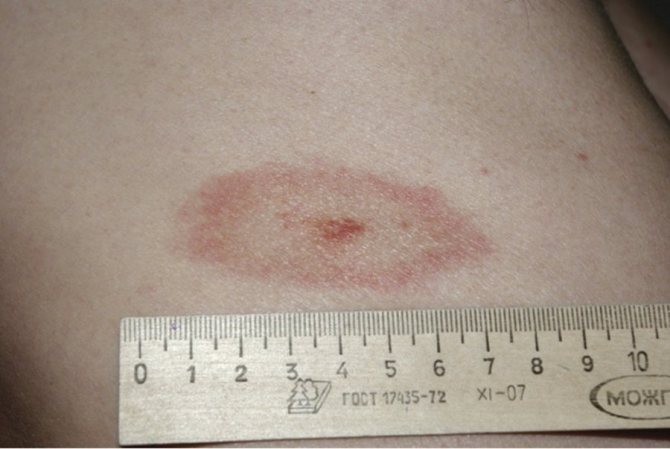

A bitten person must observe the bite site for a month (erythema migrans in the photo)
To detect Lyme borreliosis, a serological diagnostic method is used (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), indirect immunofluorescence reaction (RNIF), immunoblotting (IB)).The first antibodies LgM appear only 3 weeks after infection, and immunoglobulin LgG is synthesized after another 1-3 weeks.
It is inappropriate to examine the patient at an early stage of the disease, even if he has erythema migrans, since there is a high risk of getting false negative results. In addition, early antibiotic administration can lengthen the duration of the immune response.
If the patient has erythema migrans, then antibiotic therapy begins without further examination. In a situation where, after a tick bite, symptoms characteristic of Lyme borreliosis developed within 30 days, but there is no migratory erythema, laboratory diagnostics are carried out to detect an immune response.
If immunoglobulins of class M and G are absent, then after 2-4 weeks the tests are repeated. If immunoglobulins are present, then an antibiotic is prescribed. But if more than a month has passed after the bite and the analysis shows the presence or absence of immunoglobulin M and the absence of immunoglobulin G, then treatment is not required (if LgG is detected, therapy is indicated).
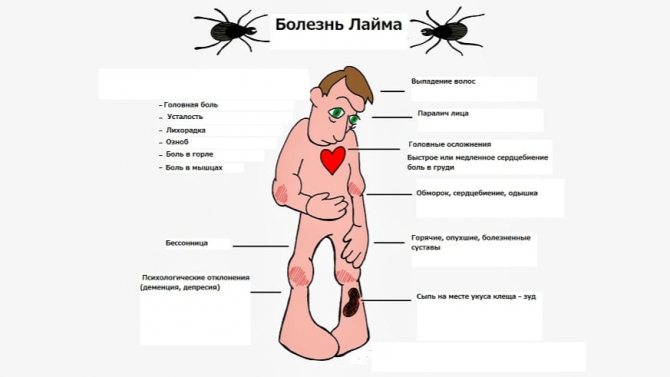
Borreliosis symptoms
The symptoms of the disease appear gradually. At the first stage, they look like this:
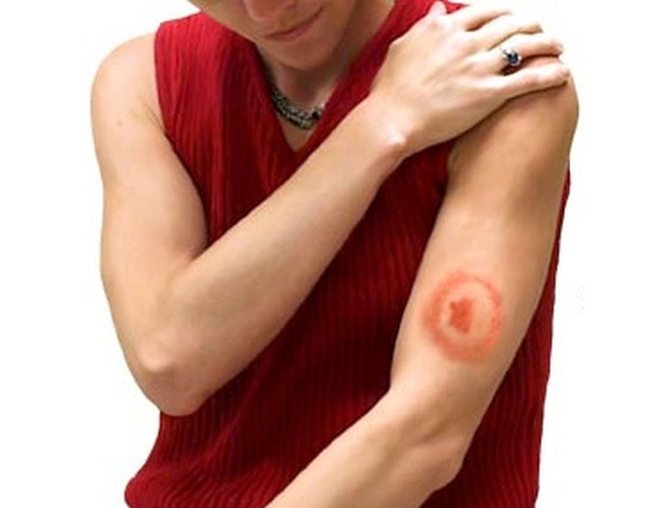
- The bite site becomes noticeably inflamed and reddened.
- The spot increases in size, its edges swell.
- The body temperature rises, muscle pains appear.
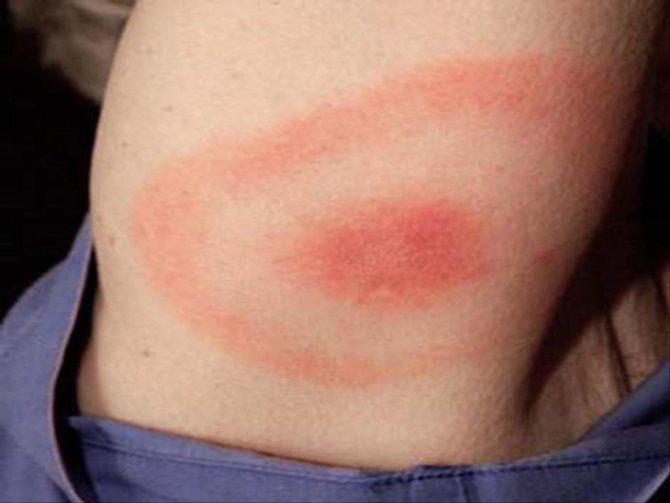
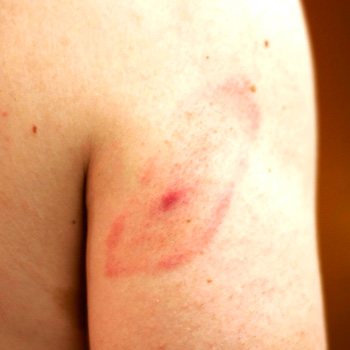
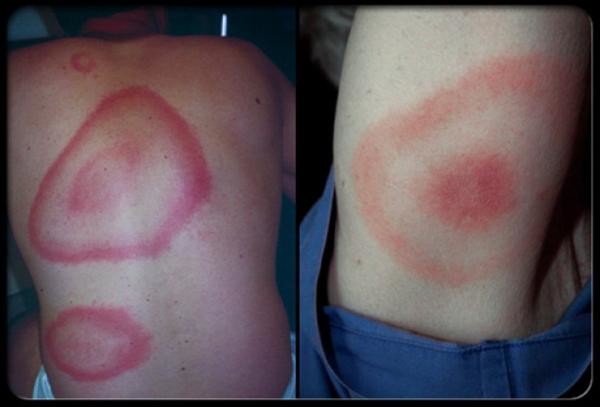
It is necessary to carefully examine the site of the bite, around which the so-called annular erythema appears - the main symptom of borreliosis. The inflamed dense formation grows and becomes like a ring. The central part of the patch around the bite point is lighter, and the edges appear inflamed red.
It is not uncommon for the infection to diminish slightly after a few days. But if the patient misses the first signs of the disease, then after a month his condition worsens. He has more severe symptoms:
- Inflammation of the joints.
- Signs of damage to the nervous system and heart.
- Severe sore throat, facial paralysis.
- Insomnia, speech impairment.
Bitten by a tick: what pills to drink?
Together with the awakening of nature, those with whom they would not meet at all - ticks, awaken. The peak of activity of these blood-sucking arachnids, dangerous for humans, begins closer to April. Ticks become especially aggressive in September and October, on the eve of a cold snap.
If the winter turned out to be warm, and the spring is early, this is exactly what is needed for the hordes of ticks to feel great.
Going to the forest, park or dacha, especially with children, you need to be careful: protect open areas of the body, wear a hat and have in your arsenal pharmaceutical preparations that you can take if the tick still managed to penetrate the skin. What means, when and how should be used?
In addition to first aid measures, which consist in the quick and correct extraction of the tick from the skin, it is necessary to take care of the prevention of dangerous diseases, the likelihood of which arises after contact with an unsafe arthropod.
This can be done with the help of special medications. However, even timely prevention is not a guarantee that a person will not develop one of the diseases carried by these blood-sucking diseases.
It is not always possible to notice a tick on the skin on your own, especially if it is attached to the scalp
Attention! None of the existing tools are capable of giving one hundred percent results. However, it can increase the body's resistance by reducing the severity of bacteria and viruses, and this will increase the chances of staying healthy.
Medicines after contact with a tick are taken for prophylaxis.
Preventive treatment is very important, as it can prevent the occurrence of consequences in 80–85%.
Fortunately, a tick bite does not always mean infection with dangerous viral or bacterial diseases, since not all specimens found are carriers of pathogens.
In addition, how long the tick has spent on human skin is of great importance. The later it was noticed and removed, the higher the risk of infection.
Ticks, practically blind, can smell an approaching living creature from a distance of 10 meters: they catch on passing animals and people, sitting on the branches of low trees or bushes
If the ixodid tick has sat on the skin for a long time and fed, it is advisable to examine it for the presence of viruses and bacteria in the sanitary-epidemiological station, hygiene and epidemiological centers or other microbiological laboratories that are available in the settlement.
It is necessary to test the caught specimen as soon as possible: if the pathogen is detected later than three days after interacting with the tick, preventive treatment may already be ineffective.
It is not necessary to wait for the results of the analysis, it is possible and necessary to carry out prevention in order to prevent the occurrence of tick-borne encephalitis and borreliosis. Timely therapy can also prevent the appearance of hemorrhagic fever, severe allergic reactions resulting from a bite.
Tick-borne encephalitis
The disease, otherwise called spring-summer tick-borne meningoencephalitis, is a viral infection that manifests itself as:
- fever;
- toxicosis;
- lesions of the gray matter of the brain (encephalitis), the membranes of the brain and spinal cord (meningitis and meningoencephalitis).
The encephalitic form of tick-borne encephalitis is characterized by brain damage with impaired consciousness, seizures, decreased muscle tone, rhythmic twitching of individual muscles of the feet
The disease has a very severe clinical course and can be fatal.
Tick-borne borreliosis
The disease is also called Lyme disease, or Lyme borreliosis. It is infectious and associated with the bite of ixodid ticks. A serious illness affects the skin, nervous system, heart, joints.
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia, which multiplies in the intestines of ixodid ticks and is excreted in their feces. You can get infected not only from an arachnid bite, but also by crushing it on your skin.
The greatest risk of infection is observed in summer at temperatures above 20 degrees, when the activity of ticks is increased.
With Lyme borreliosis, severe intoxication occurs, which manifests itself:
- headache;
- weakness;
- an increase in body temperature;
- wave-like muscle pain;
- aching joints.
In addition, disorders of the respiratory system appear in the form of dry cough, sore throat, and an increase in the lymph nodes closest to the site of the bite occurs. The patient may experience nausea and vomiting.
If the disease is left untreated, the infection eventually enters the bloodstream and causes damage to the nervous system, which manifests itself:
- violation of sensitivity;
- loss of reflexes;
- weakening of voluntary movements (difficulty walking, running).
The victim may be impaired in color perception, smell, touch, problems with chewing, swallowing, a tendency to faintness, head movements are difficult, sleep and concentration of attention worsen.
After a few months (up to a year), the disease becomes chronic with damage to a specific organ or system with periodic exacerbations.
Tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease, which can lead to fatal consequences, are successfully cured, the main thing is not to waste time.
To prevent diseases that can be triggered by a tick bite, the following groups of funds are used:
- antiviral;
- antibiotics;
- immunoglobulin.
Antibacterial drugs have a bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect on the body, suppressing the growth of bacteria, as well as killing them.
At the same time, antibiotics contribute to the elimination of dead bacteria and their waste products from the body.
The agents can be active against both a narrow spectrum of bacterial agents and have a wide range of effects, which is used when choosing a drug for the prevention of tick-borne diseases.
The range of antiviral drugs is very wide. They can be divided into 2 groups:
- immunostimulants. Dramatically increase the production of interferons;
- antiviral. They have a direct inhibitory effect on the virus and block its reproduction.
Note! Self-medication can be a waste of valuable time and can be life-threatening.
In cases where the tick bite does not pass, it is necessary to consult a doctor so that he prescribes the necessary medications and preparations. Ticks are carriers of various diseases. The causative agents of infection are found in arachnids in the intestines or in the salivary glands.
They enter the human body during the act of sucking. Immediately after a tick attack, a person does not experience unpleasant sensations. Therefore, some patients do not associate their illness with the bite.
However, if the wound becomes red or inflamed, it could be a sign of infection.
Redness of the site after a tick bite can be a symptom of ixodic tick-borne borreliosis. The disease is widespread in Europe, USA, Canada and Russia. Tick-borne borreliosis is called Lyme disease or tick-borne erythema (redness). The disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic ring-shaped red spots.
The incubation period lasts from 1 to 35 days, averaging 7-10 days. When the disease intensifies, a red speck appears in the place where the tick bitten left the wound.
It has a round or oval shape. Sometimes its edges are uneven. The stain intensely itches, causes pain and burning.
Some patients complain of a tightening sensation in the skin and a lack of sensitivity in the affected area.
Within a few days, erythema rapidly increases in size, expanding in all directions. The diameter of redness can reach 7-10 cm or more. The outer edge of the spot is colored brighter. It rises slightly above the skin level.
Over time, the central portion of the redness may fade or become cyanotic, making it look like a ring. In some people, a uniform color of the affected area remains.
In the area of erythema there are vesicles (vesicles with fluid) and areas of necrosis.
Infected people experience drowsiness, fatigue, chills, and mild headache. They may have swollen lymph nodes, pain in joints and muscles. Sometimes nausea and vomiting are observed.
A few days after the tick bite, other redness may appear on the body. Their size is slightly smaller than that of primary erythema. Most often, spots are localized in the armpits, groin and neck.
However, the absence of symptoms should not be soothing.
The disease continues to develop. The causative agents of Lyme disease (borrelia), spreading through the bloodstream throughout the body, settle in the brain, heart, joints and liver, causing inflammatory changes.
If symptoms of Lyme disease are found, an urgent need to consult an infectious disease doctor. He examines the patient, diagnoses and prescribes treatment.
At the first stage of the disease, tetracycline antibiotics are prescribed. The patient takes Tetracycline or Doxycycline (Vibramycin) several times a day for two weeks.
For children under 8 years old, the doctor will prescribe Amoxicillin (Flemoxin, Amoxil) in tablets or in the form of injections.
During treatment, you must strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.It is forbidden to reduce the dosage and prematurely stop taking medications. To achieve the destruction of pathogens, the body must maintain the required concentration of the antibiotic. You cannot prescribe and take pills on your own. They can change the picture of the disease and make the diagnosis difficult.

Doxycycline after a tick bite
Where to go and how to take Doxycycline
If you find the primary symptoms of tick-borne borreliosis in yourself, you do not need to try to fight them yourself. It is wiser to urgently contact an infectious disease specialist. It is desirable that this happens within 96 hours of the bite.
It is not recommended to remove the insect on your own, but if this does happen, the tick or its fragments should be brought with you for research. This procedure will help the patient bypass the stage of additional testing.
The dosage form and dosage of doxycycline are prescribed by a medical professional, you cannot set the dose yourself. One of the most common forms is tablets containing 100 mg of the active ingredient. They are used to prevent the development of the disease.
In order to prevent Lyme disease after being bitten by an infected tick, it is recommended to take doxycycline 1 tablet (0.1 g) 2 times a day for 5 days.
Methodical recommendations / ed. Academician of the RAMS Yu.V. Lobzin.
In addition, for prophylaxis, the drug is also used in the form of an injection, which is important to do no later than three days (72 hours), after this time the injections will not help.
However, only the attending physician prescribes a specific treatment regimen. He will choose the optimal dosage, taking into account the entire clinical picture, including additional diseases and individual characteristics of the body. The sooner treatment begins, the more realistic the chances of a complete cure for the disease.
After completing the course of using the drug, you will need to pass urine and blood tests.
How do ticks attack?
The greatest activity of dangerous bloodsuckers occurs in late spring and early summer. But in some regions, ticks can be found easily even in autumn. Bloodsuckers hide in the grass or sit on the branches of low bushes and wait until a potential victim passes by. These insects do not know how to jump and fly, but upon contact with skin and clothing they will immediately catch on. On the paws of the tick there are special villi that allow them to linger on any rough surface. If a tick clung to a person's clothes, then he will immediately start looking for a suitable place for a bite. Initially, his task will be to get under a jacket or pants. Ticks can climb over collars, legs and sleeves, so these parts of clothing must be especially well protected and carefully buttoned.
Once the mite is on the skin, it will not attack immediately. Initially, he will try to choose the most suitable place for his meal.
There are certain areas of the body that these parasites especially like. These are the neck, armpits, groin, head, abdomen and back. Here it is worth looking for a tick first.
If you find a bloodsucker on your body, you should not immediately drink handfuls of antibiotics. This will only harm, since drugs of this type must be used as carefully as possible. It is advisable to consult a doctor before using antibiotics. Moreover, not in every case is infection with a dangerous ailment, therefore, such drugs may simply not be necessary. Of all existing ticks, only 25% are carriers of dangerous ailments. Therefore, in any case, you will have to consult a doctor, take a test in a laboratory to determine the degree of danger, and after that the specialist will decide what drugs are needed and how to take them to the patient.
The most common problems caused by a tick bite are: allergic reaction, encephalitis, borreliosis, anaplasmosis and ehrlichiosis. All these diseases require specific treatment and antibiotics will not be relevant in every case. In some situations, everything goes without complications, if you just remove the tick correctly and lubricate the bite with brilliant green.
Doxycycline analogs and their differences
Doxycycline has been in demand for a long time, so it is not surprising that during this time many analogs have appeared that differ little from the well-known drug.
Doxycycline analogs include:
- Vibramycin,
- Bassado,
- Unidox Solutab,
- Doksal,
- Dovitsin,
- Monoclin,
- Xedocin.
Some of them have small peculiarities.
Unidox Solutab has the most sparing effect on the intestinal microflora among Doxycycline analogues
Table: differences between drugs analogs of Doxycycline
| Doxycycline analogs | Features of the |
| Vibramycin | Retains many of the side effects of doxycycline. It is best not to use it during pregnancy and during breastfeeding. |
| Bassado | Not recommended for kidney and liver problems. |
| Unidox Solutab | The most modern analogue of doxycycline, preserving the beneficial intestinal microflora. |
Precautions while using the drug
The tetracycline antibiotic is capable of affecting numerous processes within the human body. That is why you should carefully study the instructions for use and strictly follow the doctor's recommendations.
Features of the use of Doxycycline after a tick bite:
- The drug is capable of destroying the effect of estrogen-based oral contraceptives. The risk of uterine bleeding increases.
- Reduces the effectiveness of lactam antibiotics against microbes.
- Combining the use of the product with alcohol is strictly not allowed. Alcohols reduce the rate of excretion of the active substances of the drug and as a result there are problems with the kidneys and liver.
- Combined use with retinol increases intracranial pressure.
Important!
Taking the drug together with anticoagulants requires special control. In this case, regular monitoring of prothrombin markers is required. It is also recommended to minimize exposure to direct sunlight due to the high risk of photosensitivity.
Testimonials
I consulted with our infectious disease specialist, and he unequivocally said: I was bitten by a tick - you need to take antibiotics for 2 weeks. The fact is that to confirm borreliosis, blood is donated for antibodies, but only they appear three weeks after the bite (it was checked on myself - there were no antibodies in two weeks), and you cannot lose these three weeks, antibiotics must be taken as early as possible. Prophylaxis is carried out with DOXICYCLINE 0.1 g 2 times a day. Our infectious disease specialist said that it was necessary to take 2 weeks, on the Internet there are different recommendations - both 5 days and once 0.2 g, but I trust the "live" patented specialist more. I drank doxycycline for 3 weeks because there was a confirmed borreliosis, by the way, without any negative consequences for the body ...
I had a double opinion about the drug. On the one hand, after reading on the Internet, I found that basically only it is prescribed for tick bites for the prevention of infectious diseases such as encephalitis and borreliosis. But on the other hand, he has so many restrictions that it is time to think about developing a drug that is more gentle for the body. Now it is already difficult to figure out whether there was an infection, since the course of the antibiotic has been drunk. It is useless to donate blood, the tick is not available. But, what is very important, and what I learned later, the drug should have been injected within 72 hours after the bite. I definitely recommend the drug, but I hope it won't come in handy.
Antanel
And this DOXYCYCLINE, I looked, costs only 10–20 rubles per package and is valid for 5 years, so they bought everything quick and put it in the first-aid kit. This is so as not to rush somewhere in the holidays around the Moscow region in search.
Nyura
Doxycycline, like any antibiotic, requires careful attention when choosing a dose and determining an individual treatment regimen. If you have been bitten by a tick, you need to seek help from an infectious disease specialist as soon as possible, who will prescribe this drug and explain how to use it correctly.

If a doctor prescribes Doxycycline for a tick bite, how should I take this drug? First of all, if you are taking any other medications in parallel, you need to inform the doctor about this, because Doxycycline tends to interact with some of them. Some combinations lead to a decrease in the bioavailability of Doxycycline, because its components are poorly degraded and absorbed in an alkaline environment.
Vitamins, which contain calcium or iron, block the active active ingredients of Doxycycline, which makes it impossible to obtain any benefit from taking the drug.


Doxycycline has a stabilizing effect on the entire microflora of the body, that is, it prevents the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, but does not kill any of their specific species. It is useless to take antibiotics, for example, Tetracycline or Penicillin and all drugs based on them at the same time, because antibiotics destroy specific bacteria, while Doxycycline controls their population. Doxycycline has a depressing effect on the reproduction of opportunistic microflora in the intestine. Therefore, it can enhance the action of certain medicines, such as medicines that thin the blood and prevent it from clotting. Interaction studies have shown that doxycycline reduces the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives when they contain estrogen. The most popular drugs that do not need to be combined with Doxycycline:
- Erythromycin, Hydrocortisone, Aminophylline;
- Phenytoin, Rifampicillin, Carbamazepine;
- Penicillin, tetracycline, and other antibiotics;
- Cholestyramine, Cholestipol;
- Warfarin, Phenilin;
- Retinol.
If a drug contains iron, calcium, magnesium or hormones, is an antibiotic, affects the circulatory system and the production of enzymes, you should not use it simultaneously with Doxycycline without first consulting your doctor.
The effectiveness of the course of antibiotics - the result is not 100%
Many compatriots are already aware of this problem and are actively interested in what antibiotics are best used for a tick bite. It is worth giving the answer right away - today there is no uniquely effective protocol for curing Lyme disease at different stages of the disease, based only on antibiotics.
All schemes of preventive courses based on antibiotics do not give an unambiguous result. In this case, a cure is possible, but only with the control of serological blood samples - IgM, IgG antibodies, assessed by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Diseases arising from a tick bite Antibiotics after a tick bite Sumamed with a tick bite Tetracycline with a tick bite Doxycycline for the treatment of a tick bite
A tick bite is a danger that many people face when relaxing in a forest, park or in the country.
Moreover, parasites can bite not only adults, but also children. The situation is further exacerbated by the fact that bloodsuckers are carriers of diseases that can not only seriously undermine human health, but also lead to death.
Antibiotics with a tick bite can prevent the development of complications and severe consequences.
If symptoms of a tick bite or the bloodsucker itself are detected, first aid is provided to the victim, which consists in removing the parasite and processing the affected area.
After that, it is necessary to take the removed animal to the clinic, as well as pass an analysis, according to the results of which, if necessary, the doctor will prescribe certain pharmaceutical preparations.
In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed to patients after a tick bite.
On a note!
Not every tick carries disease. Most infections, thanks to a strong immune system, do not cause infection.
The bite is not accompanied by pain, which is why a sucked pest can go unnoticed for a long time.
Symptoms of pathology appear after some time and directly depend on the individual characteristics of the human body, as well as the number of sucked parasites.
However, ticks are often found that can be carriers or intermediate hosts of the following types of infections:
- tick-borne viral encephalitis;
- borreliosis;
- anaplasmosis;
- rickettsiosis;
- ehrlichiosis, etc.
Borreliosis is especially dangerous - a disease that affects not only the skin and joints of a person, but also the cardiovascular and nervous systems.
And if you can be vaccinated to protect against tick-borne encephalitis, then it will be powerless against other diseases caused by the parasite, including borreliosis.
Therefore, the sooner a person takes an antibiotic after a tick bite, the more likely it is to avoid irreversible consequences that can lead to death.
Most often, signs of infection with an infection after a tick bite begin to appear already after an hour from the moment the parasite is affected by the skin.
In the lesion, there is swelling and redness with clear boundaries (erythema). Such signs are evidence of Lyme spirochete infection.
Moreover, erythema is migratory, and therefore, it can manifest itself in other parts of the body.
Diseases arising from a tick bite
Important!
Taking antibacterial drugs is aimed at stopping the infection and symptoms of an infectious disease.
Since therapy for the specific development of the disease can differ both in the use of drugs and in the duration of the period. Usually, drug treatment is prescribed from 10 to 20 days after the onset of signs of the disease.
Self-medication can weaken the immune system, disrupt the functioning of the liver and kidneys, causing a strong allergic reaction of the skin.
The antibiotic for ticks can come in various forms. In the first stage of treatment, the doctor usually prescribes oral preparations in capsule, tablet or liquid form, which are highly absorbable.
When confirming the presence of a tick-borne infection, intramuscular and intravenous injections are prescribed. Antibiotics of this category can also be in the form of powders, from which injectable solutions are prepared.
An antibiotic for prophylaxis prevents infectious complications. Below is a list of the most popular drugs.
Clarithromycin
It is an antimicrobial agent, in which clarithromycin acts as an active ingredient (250 or 500 mg per tablet). Corn starch, lactose, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide are used as auxiliary substances.
- The drug is intended for the treatment of infections caused by various microorganisms sensitive to the drug. The composition is also prescribed for respiratory diseases, for the treatment of infected wounds, furunculosis and folliculitis.
- An antibiotic for a tick bite for adults and children over 12 years old is prescribed in a dose of 250 mg, in the presence of severe infections, the dose is increased to 500 mg 2 times a day. The drug is taken regardless of food 2 times a day.
- The duration of treatment depends on the degree of the disease and varies within 1-2 weeks.
When using the drug, side effects are possible, which manifest themselves in the form of an allergic reaction, tachycardia, disturbances in taste, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Important!
It is not recommended to use the antibiotic for children under 12 years of age, for people with hypersensitivity to the drug's components, as well as for women during pregnancy. The cost of a blister of 10 tablets with a dosage of 250 mg within 130 rubles.
Azithromycin
Antimicrobial drug of the macrolide group with a wide spectrum of action. It is used for the treatment of intracellular and bacterial infections of different localization, for the treatment of skin, respiratory and ENT infections, chlamydia and Lyme disease, as well as uncomplicated diseases of the genitourinary system.
Azithromycin is taken one hour before meals or 2 hours after meals. The daily dose and duration of treatment is prescribed by the attending physician, based on the individual characteristics of the organism. Usually the daily dose does not exceed 250-500 mg.
- For the treatment of infection caused by a tick bite, the drug is taken 2 times on the 1st day, 500 mg, 250 mg from the 2nd to the 5th day of therapy.
- For children over the age of five, the dose is prescribed taking into account the weight of the child. On the first day of therapy, it is used at the rate of 10 mg / kg of body weight, on the following days, 5 mg / kg of body weight.
Taking an antibacterial agent is contraindicated in lactating and pregnant women, children under 5 years old, people with severe liver (kidney) pathology and intolerance to this group of antibiotics.
Important!
Taking an antibiotic can cause side effects in the form of frequent headaches, indigestion and loss of appetite, increased bilirubin and urea.
The cost of the drug varies depending on the dosage and the number of tablets (capsules) in the range of 65-110 rubles.
Azithromycin was prescribed to his son after a tick bite even before the test results were obtained. We drank the antibiotic as prescribed by the doctor, passed the analysis - everything is normal.
Olesya, Uman
Sumamed
Another antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action from the group of macrolides, based on azithromycin. Presented in the form of hard gelatin capsules containing a yellowish crystalline powder. The composition has bactericidal properties, making it effective:
- with tick-borne infections (Lyme disease);
- infected dermatoses;
- in the treatment of ENT organs and inflammation of the genitourinary system.
Available in the form of tablets and powder for the preparation of suspensions.
The drug is recommended for use in adults and children weighing more than 45 kg. With a tick bite and erythema migrans, the total dose should not exceed 3 g. On the 1st day, 4 capsules are taken at a time (1 g), then 2 capsules at a time (500 mg every day).
Important!
When using an antibacterial agent, side effects are possible, which are expressed in the form of nausea, vomiting, flatulence, an allergic reaction and an increase in the activity of liver enzymes.
The composition is contraindicated in pregnancy, lactation, hypersensitivity to azithromycin, erythromycin and other macrolide components of the drug.
The cost of a package of 6 capsules of 250 mg is within 460 rubles.
Tetracycline
Tetracycline for tick bites
Antibiotic of the tetracyclines group with bacteriostatic action.
The drug based on tetracycline hydrochloride is effective against various gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, rickettsia, spirochetes, leptospira and other viruses.
Tetracycline can be purchased in the form of tablets, dragees, granules from which syrup is made, and suspensions for oral administration.
For better absorption, the medicine is taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal with plenty of water.For adult patients and children from 12 years of age, the daily dose of Tetracycline is 2 tablets (2 g).
Important!
As side reactions, allergic reactions, dyspeptic symptoms, kidney and liver damage, dysbiosis, skin pigmentation and changes in mucous membranes are possible.
The price of 20 tablets Tetracycline (100 mg) is about 60 rubles.
I decided to drink the antibiotic on my own, after I discovered a tick bite. However, Tetracycline caused severe digestive upset in me. Then I struggled with this problem for a long time. Therefore, it is better to consult a doctor about what and how to take in such situations.
What is the ideal dose of Doxycycline?
When bitten by a tick, there is a danger of contracting borreliosis, or Lyme disease. This is a disease that poses a real danger to human life and health. In developed countries, after a bite mark or a tick itself is found on their skin, a person seeks medical help. The tick is removed, a sample is taken from the site of the bite, which is examined for borrelia. If a person has managed to save the tick itself or large fragments of its body, the tick itself will be examined. This will help the patient avoid unpleasant tests.


The drug is dispensed by prescription
In the event that the victim has any signs of the disease, a blood test, a study of the intra-articular fluid, and a puncture of the spinal cord are done.
It is on the basis of these tests that the doctor can find out if it is necessary to prescribe Doxycycline. Some ticks do not infect a bitten person with anything dangerous, some of them do not belong to the species that transmits borreliosis. What's going on in Russia? Some citizens simply do not seek help, remove ticks using folk methods and do not carry out the prevention of Lyme disease. Another part goes to a medical institution, where it is faced with the incompetence of medical personnel. Doctors prescribe such a powerful agent as Doxycycline, without any preliminary research, no one is going to investigate the patient or the potentially infected tick.
Doxycycline has a very wide range of applications, it affects many microorganisms. The unfounded use of Doxycycline has a bad effect on the gastrointestinal microflora, especially in children, especially if there is a tendency to intestinal dysbiosis. In the international medical community, it is customary to start prophylactic doxycycline intake within the first 72 hours after a potential infection, that is, the patient has three days to take care of his health. After this period, the appointment of other drugs is required. In Russian practice, there is a typical situation when victims go to the doctor a week, 2 weeks and even a month after the bite. And the doctor prescribes Doxycycline, as if this drug is capable of performing a miracle. In fact, the main purpose of Doxycycline is to prevent the development of the disease, and not to eliminate the full-scale damage to the nervous system, joints and heart.
Pharmacy preparations for tick bites
Medicines for a tick bite are divided into several areas:
- Detoxification. These are medicines that help to eliminate toxins and restore damaged cells, as well as prevent the entry of harmful substances into the blood. As a treatment, it is necessary to take Atoxil, Albumin and drink more fluids.
- Antibacterial. If human skin is affected by a tick bite, antibiotics Tetracycline, Doxycycline or Amoxicillin are prescribed. Penicillin, Ampicillin, or Ceftriaxone may be prescribed for mental disorders, heart problems, and joint diseases.If there is an individual intolerance to all of the listed medicines, macrolides are selected - one of the most common is Erythromycin.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce body temperature, relieve pain and suppress inflammation. These are Indomethacin, Naproxen, Nurofen can be recommended for children.
- Immunostimulating, improving the state of the body's natural defenses. This includes funds such as Immunal, Timogen or Imudon. Also, for general health improvement, it is necessary that patients drink vitamins A, B, E. To normalize the emotional state, the doctor may advise taking tranquilizers.
- Antiallergic medicines, if an irritable reaction to the bite occurs: Suprastin, Allergodil or Claritin.
Read also:
Treatment of tick bites with doxycycline, important points
To suppress inflammatory processes in the joints and stimulate blood circulation, physiotherapy is recommended, this includes electrophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation, magnetic field treatment, professional therapeutic massage and paraffin therapy.


Most often, doxycycline is prescribed as an antibiotic for a tick bite.
How to take Doxycycline correctly?
In order to get the best effect, you need to take the average daily dose at a time or divide it by 2 times with an interval of 12 hours between doses. Smaller portions do not give the desired effect. To minimize harm to the intestinal microflora, it is best to use Doxycycline after a meal. During preventive therapy, you need to drink plenty of fluids. You need to drink the drug only with drinking water, do not use soup, jelly, fruit drink, juice, alcohol or other drinks for these purposes. Since Doxycycline interacts with calcium, in order to get the benefits of taking it, you can not drink the tablets with milk, kefir, fermented baked milk and other dairy products. What can be done to protect the intestines from the negative effects of Doxycycline:
- do not take alcohol in any form during the course of the antibiotic;
- temporarily exclude from the diet all foods that irritate the intestinal mucosa, namely sour fruits, spices, spices, ginger, garlic and onions, sour sauces and tomato paste;
- do not use at the same time Doxycycline and drugs with which it enters into active interaction, including vitamin complexes;
- take probiotics or prebiotics at the end of the course;
- introduce real live yogurt into the diet after the end of the intake.


It is forbidden to drink alcohol during the course of antibiotics
Since it is physically very difficult for some people to abstain from alcohol even for 10 days, one should take into account the fact that the simultaneous use of alcohol and bacteriostatics, which include Doxycycline, almost completely destroys the positive effect of taking drugs. The toxic effect of alcohol on a person increases, as a result of which intoxication occurs faster, lasts longer, and then ends in a painful and painful hangover. Often, while taking alcoholic beverages and Doxycycline, the following manifestations are observed:
- vomits a person uncontrollably;
- there is a sudden and uncontrolled stool disorder, diarrhea;
- coordination of movements and control over the position of the body in space are disturbed;
- there is a spasmodic headache of great intensity.
Severe alcohol intoxication during the course of Doxycycline increases the likelihood of pathological liver damage, and reactive hepatitis may develop. If a person does not have a desire to abstain from alcohol, then to reduce the risk of adverse effects, it can be consumed no earlier than 35 hours after the last dose of Doxycycline.People who smoke on a regular basis have a change in metabolism compared to a person without chemical addiction. This must be taken into account when choosing a dosage. Usually, smokers are prescribed an increased dose of Doxycycline to achieve a preventive effect from taking it.
LESIONS OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
Patients with borreliosis and complications of the cardiovascular system, but without high-grade heart block, are prescribed oral antibiotics. Hospitalization, continuous monitoring of the condition and the appointment of infusion antibiotic therapy is indicated for patients with joint pain, syncope, dyspnea, atrioventricular block II or III degree, or AV block I degree with an interval of PR ≥ 300 milliseconds. If the degree of AV block is high, a temporary pacemaker is recommended.
Treatment for arthritis associated with borreliosis depends on the type and extent of the infection:
- People with Lyme arthritis are given oral antibiotics, including doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime for 28 days, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as adjuvants to relieve the condition
- For recurrent or chronic joint edema, an additional 4 weeks of oral (preferably) or 2-4 weeks of parenteral antibiotic therapy is prescribed
For antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis, arthroscopic synovectomy has been successfully used. There are also reports of the successful use of single intra-articular injections of corticosteroids, systemic administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antirheumatic drugs (for example, hydroxychloroquine) in patients with antibiotic-refractory Lyme arthritis (such treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of appropriate specialists).
What is Lyme disease?
How dangerous is the disease from the development of which Doxycycline helps? It is imperative to take the drug, observing the dosage and maintaining the full course. You should not stop taking it on your own until the moment as recommended by the attending physician. Lyme disease has the following picture:
- a person is bitten by a tick or other carrier of disease-causing borrelia;
- microorganisms enter the body through the bite site;
- a red spot forms on the skin around the bite, which increases in size;
- Borrelia are ubiquitous throughout the body, affecting the central nervous system, brain, heart and other organs;
- the immune system begins to react strongly to the invasion of foreign agents;
- the person receives serious damage to the joints, the normal functioning of the heart is disrupted, the nervous system suffers.

As a result, the victim receives either disability or death. With poor-quality treatment or in the absence of medical care, Borrelia can firmly settle in the body and exist in the lymphatic system for more than 10 years, periodically provoking an exacerbation of Lyme disease.
Tick-borne diseases
Tick-borne infections belong to a special group of tick-borne infections. These insects can be carriers or intermediate hosts of tick-borne viral encephalitis, borrelia, rickettsia, some parasites, as well as a number of other viruses and protozoa.
Lyme disease
Most infections that can be transmitted by insects usually do not cause infection due to the immune system. However, part of the pathogens in almost 100% of cases enter the body, let's figure out which are the most dangerous.
It should be noted that not every tick is infected with tick-borne encephalitis, this is more typical for forest areas where insects encounter natural representatives of the fauna. Also, not every case can cause Lyme disease.
What diseases are tick-borne infections:
- typhus and relapsing tick-borne typhus;
- tularemia;
- babesiosis;
- ehrlichiosis;
- hemorrhagic fever;
- Tsutsugamushi disease;
- rickettsiosis;
- spotted fever;
- Marseilles fever and others.
Drug interactions
It is recommended to avoid the simultaneous administration of Doxycycline with drugs of the following categories and types:
- containing in their composition calcium, potassium, magnesium, iron compounds and other minerals in order to avoid the formation of inactive chelates;
- barbiturates (with joint therapy, the level of Doxycycline decreases in the patient's blood);
- medicines of the penicillin and cephalosporin series, since they are antagonists of the bacteriostatic Doxycycline;
- containing retinol (there is a risk of increased intracranial pressure);
- oral contraceptives (Doxycycline reduces the effect of these drugs).


Patients who are prescribed antibiotic therapy should inform their doctor that they are taking other medications in parallel.
Pharmacokinetics
Doxycycline for a tick bite is most effective if it is taken in the first 1-2 days after an attack by a blood-sucking parasite. This minimizes the risk of contracting the body with dangerous infections. After taking the Doxycycline capsule and dissolving its protective shell, the active substance of the drug is released.
The drug is rapidly absorbed into the intestinal wall, saturating the bloodstream. Doxycycline is characterized by rapid absorption and a slow elimination process. This is a distinctive feature of this medication among all tetracycline antibiotics.
The active substance Doxycycline binds 80-90% to serum proteins and is quickly distributed among all body fluids. The simultaneous intake of food or drinking of various drinks does not affect the degree of absorption of the drug.
Depending on the dosage of the drug, its therapeutic concentration remains in the blood for 18-24 hours. The concentration of Doxycycline in the cerebrospinal fluid is 10-25%. The metabolism of the drug occurs in the liver tissues.
The half-life of the active and auxiliary substances of the drug varies from 12 to 22 hours, depending on the therapeutic dose that was taken the day before. About 60% of the drug is utilized from the body as part of the feces.
Another 40% of the constituents of Doxycycline are excreted by the kidneys along with urine. During the half-life of the antibiotic, an additional load on the liver and kidney tissues is created on metabolites. This pharmacokinetic feature of Doxycycline should be taken into account in people who suffer from chronic diseases of these organs.
Overdose
During an overdose with Doxycycline, signs of acute intoxication of the body develop.
The patient may have the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- Strong headache;
- an upset bowel movement, which is most often accompanied by diarrhea;
- physical weakness;
- pain in the stomach and right hypochondrium;
- yellowness of the skin (develops as a result of a critical load on the liver tissue);
- loss of consciousness, if a large amount of the drug was deliberately used and the patient has severe drug poisoning of the body;
- manifestation of various kinds of allergic reactions.
Doxycycline overdose therapy is symptomatic. Blood purification by hemodialysis is ineffective. The patient is prescribed sorbents for taking medications, the stomach is washed, and droppers with glucose and saline are prescribed to replenish the lost fluid.