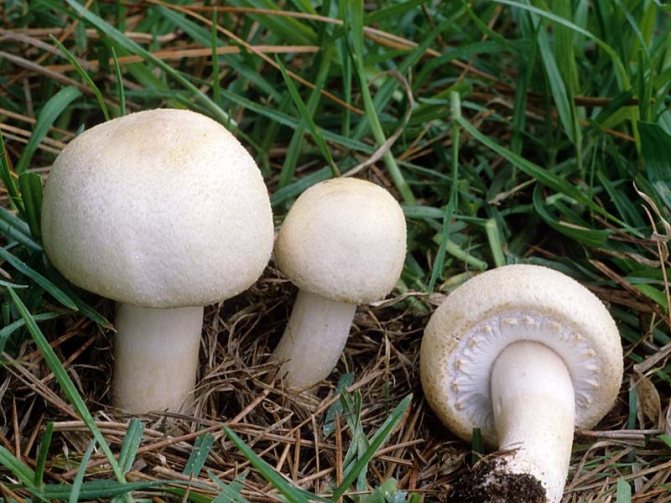
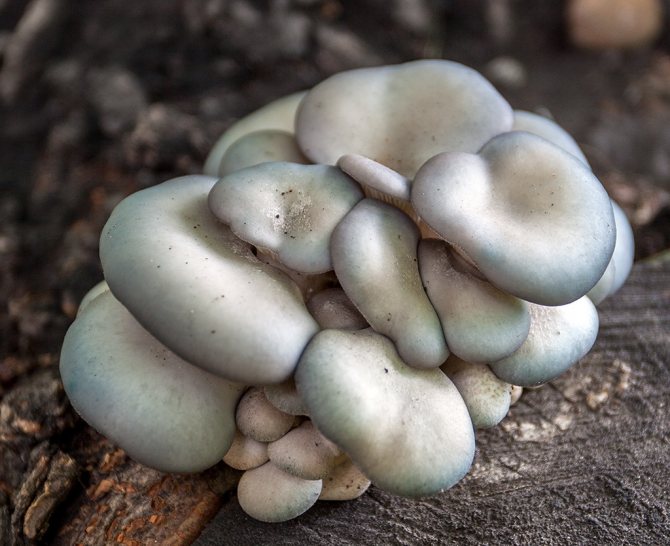
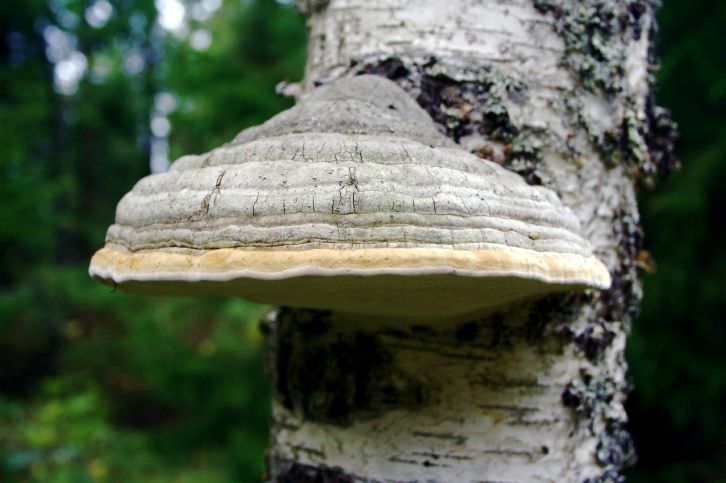
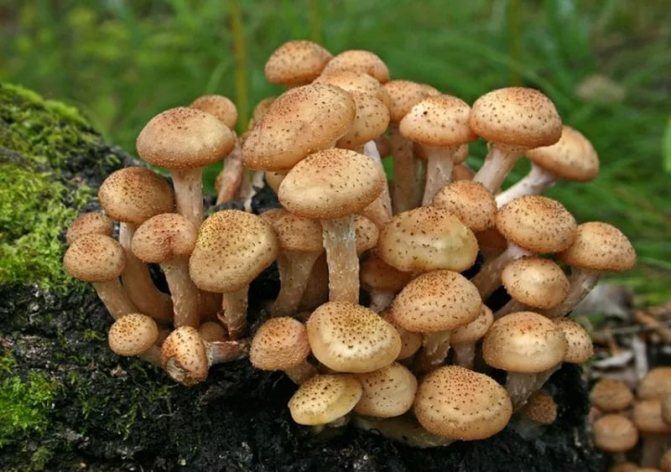
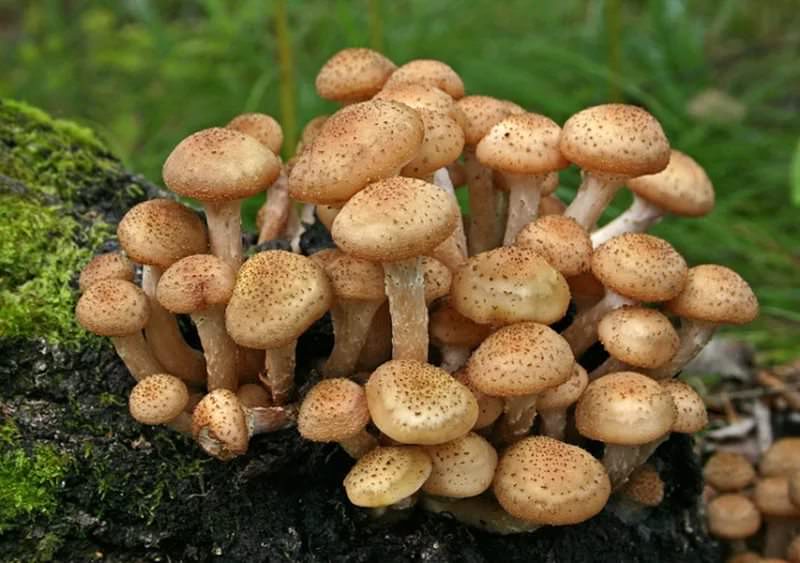
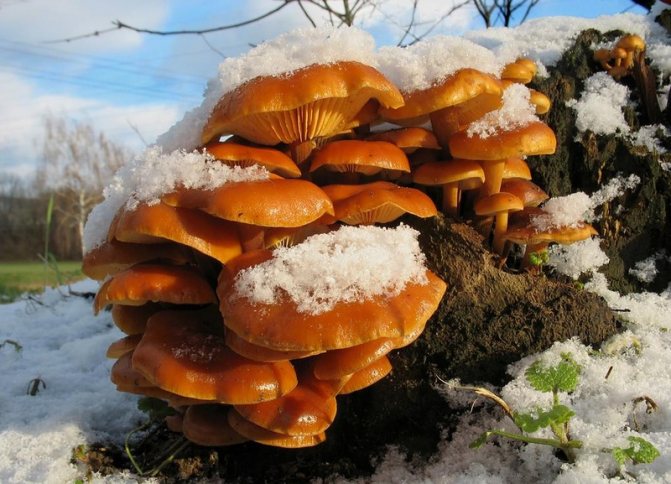
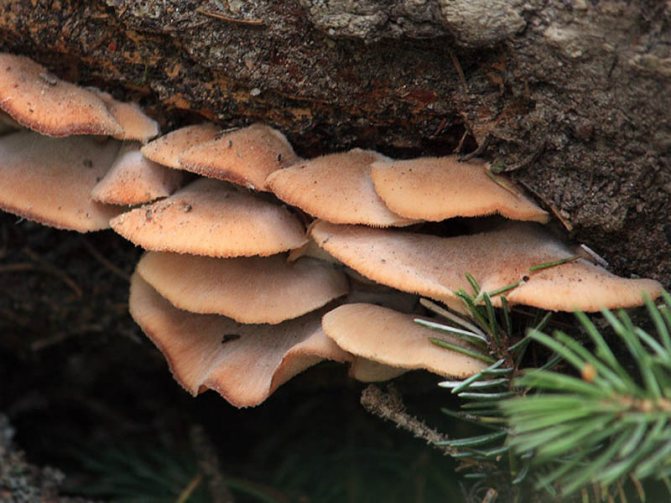
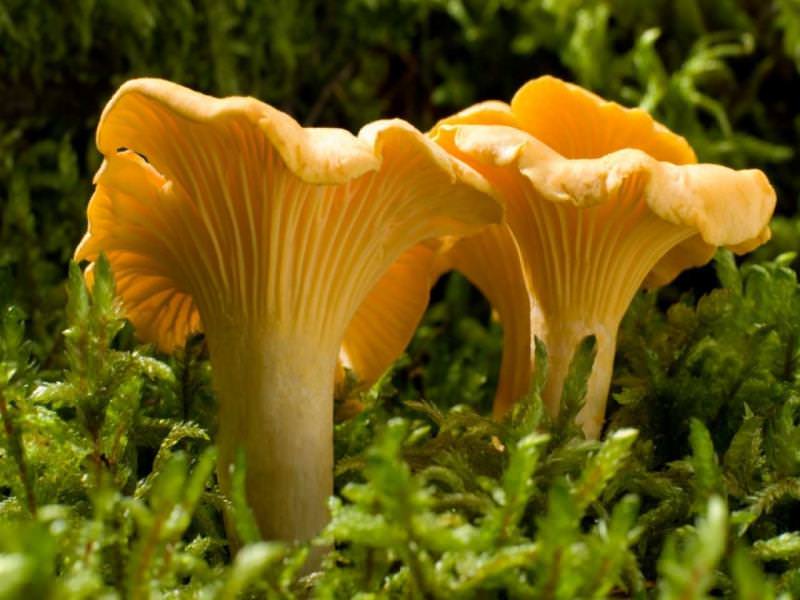
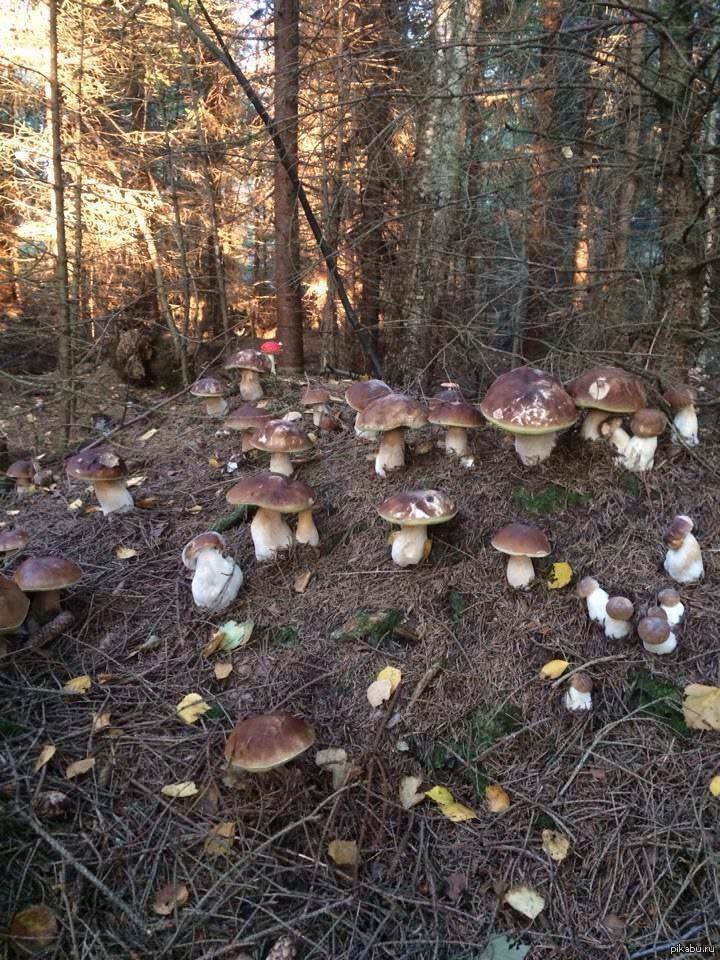
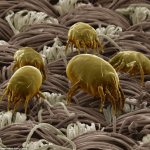
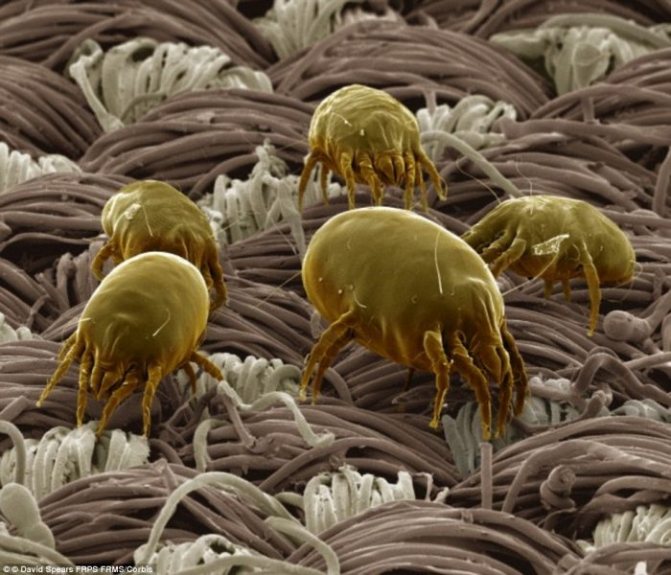
Differences between saprophytes and parasitic microorganisms
In life, parasitic and saprophytic bacteria are very difficult to distinguish, even when using a large knowledge base and special equipment. This is due to the fact that parasites often lead a semi-prophytic lifestyle, that is, they adapt to the environment, and begin to consume half-life products. Usually, they are distinguished by their external characteristics (look at the photo, how saprophytes differ from parasitic bacteria).
Hence the need for subclassing:
- Optional parasitic bacteria. They are also referred to as semi-saprophytes, or parasites of conditional origin. Usually they lead a parasitic life, but, if necessary, attack still painful plants.
- Optional saprophytes (conditional saprophytes / semi-parasites). They are characterized by behavior similar to the vital activity of facultative parasites, only they refuse live food.
Consequently, some saprophytes do not feed exclusively on carrion and rot, which makes them similar to parasites that do not consume a purely living substrate, but the main thing is that they do not harm healthy plants and environments.
Saprophytic and pathogenic microbes
By the nature of their relationship with the flora and fauna, microbes are divided into two groups: saprophytes and parasites.
Saprophytic microorganisms mainly live on dead substrates. They do not cause diseases in humans, animals and plants. Saprophytes are widespread in nature. Many microbes have adapted to a parasitic lifestyle and have the ability to cause infectious diseases in animals and plants. These pathogenic microbes are called pathogenic.
Pathogenicity is a specific feature of pathogenic microbes. Each type of microbe is capable of causing a certain infectious disease. For example, tubercle bacillus causes tuberculosis, anthrax - anthrax. However, individual strains of the same pathogenic type of microbes have different pathogenic effects in strength.
The degree of pathogenicity of the microbe, the activity of its introduction into the body, the intensity of reproduction, the ability to produce various toxic substances that suppress the body's defenses are called virulence. A measure of virulence is the minimum number of microbial cells, when introduced into the body, a fatal disease occurs.
At the same time, they speak of high and low virulence and avirulence of certain representatives of the same species. And depending on the environmental conditions, the virulence of pathogenic microbes can increase, decrease and completely disappear.
It is possible to artificially change the virulent properties of microbes in the desired direction, which is of great practical importance. This is the basis for obtaining live microbes with weakened virulence or live vaccines, which are successfully used to prevent infectious diseases.
Along with pathogens, there is a relatively large group of microorganisms called conditionally pathogenic. Under normal living conditions of the animal, these microbes do not cause disease, that is, they are saprophytes; however, with the weakening of the body due to malnutrition, overwork, overheating, hypothermia, intoxication, they become capable of causing disease and acquire high virulence. So, conditionally pathogenic E. coli can cause a severe disease of white diarrhea in newborn young animals.
SAPROPHIES (Greek.sapros rotten phyton plant) - microorganisms that feed on decaying organic matter.
S. are widespread in nature - in the soil, various reservoirs, and the air. Representatives of the normal microflora of the open cavities of the human and animal body are also considered C. However, the data of gnotobiological studies have shown that the relationship of the normal microflora with the host organism is more complex and should be considered as symbiotic (see.
Human microflora). The works of S. N. Vinogradskiy and M. Beyerinck discovered the great role of S. in the cycle of substances in nature. S. (especially soil bacteria and fungi) participate in the mineralization of organic substances (ammonification, nitrification, denitrification), as well as in the nitrogen fixation process, which is important for the maintenance of life on Earth (see).
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Castor oil from worms and parasites
Nitrogen fixation is carried out both by microorganisms living freely in the soil, such as Clostridium pasteurianum, Azotobacter chroococcum, Azotobacter agilis, and by plant symbionts (Rhizobium). S. participate in the cycle of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and iron; due to their high catalytic activity, they break down cellulose, chitin, keratin, oxidize hydrocarbons - methane, propane, etc.
Industrial waste has led to environmental pollution (see). It seems possible to use the appropriate S. strains for the removal of hazardous waste, in particular for wastewater treatment. However, the proliferation of synthetic organic substances (plastics, detergents, insecticides, fungicides, herbicides), often resistant to the action of microorganisms, raises the question of the need to design materials that could be destroyed by the corresponding microorganisms.
In medical microbiology (see) S. are usually opposed to parasites (see), causative agents of diseases of humans and animals. The relativity of this opposition is obvious. With a decrease in the natural resistance of the macroorganism, infections may occur, caused even by obligate representatives of the normal microflora - bacteroids (see.
), lactobacilli (see. Lactic acid bacteria), etc. It can be assumed that representatives of normal microflora are transitional forms in the evolution of saprophytes into parasites. The relationship between a number of pathogenic bacteria (see) and the corresponding inhabitants of soil and water (acid-resistant mycobacteria, diphtheroids, water vibrios) is shown.
Bibliography: Petrovskaya V.G. and Marko O. P. Microflora of the person in norm and pathology, M., 1976; Stay-n and er R., Edel berg E. and In g-r e m J. The world of microbes, trans. from English, t. 1 - 3, M., 1979; Cha ahav and OV, Gorskaya EM and Ruban S. 3. Microbiological and immunological bases of gnotobiology, M., 1982.
Symbiont mushrooms
Symbiosis is the cohabitation of different organisms in which both benefit. Symbiont mushrooms are involved in the formation of two symbioses:
- lichens formed as a result of interaction with algae and bacteria;
- mycorrhiza - with the root system of plants.
Power features
Mushrooms, braiding the small roots of plant organisms, feed on organic substances that make up their composition. Such actions do not harm plants, but contribute to the absorption of nutrients from the soil (nitrogen, phosphorus, trace elements) and water.
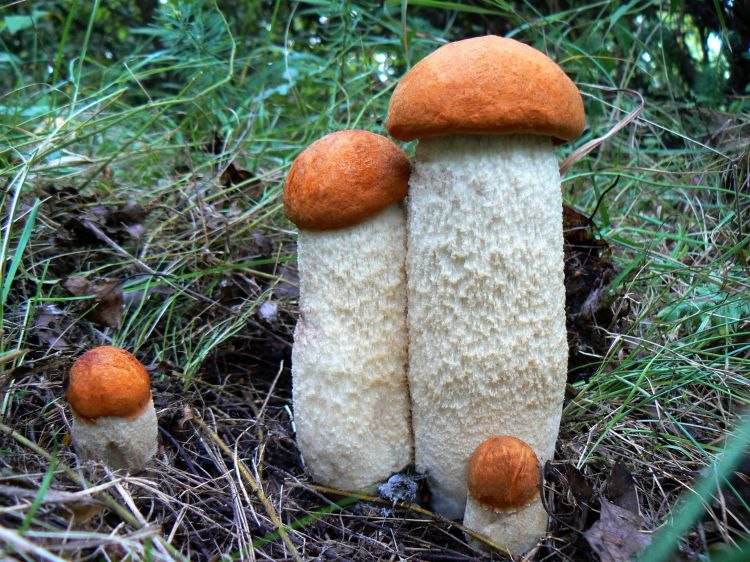


Names and descriptions of popular symbiont mushrooms
Usually referred to as a mixed type of food, which can receive organic matter, both from plant roots and humus.
- Boletus. Interacts with oaks, willows and poplars. The hemisphere-shaped brown hat has a reddish or orange tint.It is impossible to separate the skin layer without pulp. The height of the gray leg is up to 18 cm. The fruit body is fleshy and dense. Young individuals are elastic, and old ones become loose. At the break, the white pulp turns blue over time, and then turns black. Does not have a pronounced aroma.
- Boletus. Grows near birch roots. Over the course of life, the mushroom cap turns from a spherical shape into a flat, pillow-like shape. It becomes sticky to the touch with high humidity. The white pulp with a dense structure is oxidized at the cut point. In older individuals, it becomes watery and loose. Cylindrical stem covered with dark gray scales.
- and camelina. They settle under coniferous trees. Oil is characterized by a slimy skin, as if covered with oil. The hemisphere-shaped hats, reaching 16 cm in diameter, are colored in a range of colors from brown-chocolate to yellow-brown. As they grow older, the shape straightens, turning into a flat one. The stem color is usually lighter. The pulp is juicy. The saffron milk cap is characterized by a round cap with concentric circles and a depressed center. Orange pulp oxidizes on contact with air, acquiring a greenish tint.
If you destroy the host tree, then the mushrooms growing under them will disappear.


Forms of interaction of living beings
To understand who the saprophytes and parasites are, it should be recalled that any relationship between organisms can be described by the term symbiosis. There are several forms of such interaction:
- Obligate symbiosis - in natural habitat, species cannot exist separately. Example: symbiotic relationship between algae, yeast and chlamydomonas.
- Optional symbiosis. The phenomenon describes a mutually beneficial coexistence, however, each of the species can live alone (crab and anemones). There are two known examples of such symbiotic cooperation. It is a lichen formed by the union of fungus and algae, and mycorrhiza is the interaction of the root system of a deciduous tree and mycelium.
- Commensalism is also a form of interaction in which one of the symbionts has some benefit, while the other does not receive any visible benefit from the interaction.
- Parasitism as a phenomenon is also one of the variants of symbiotic relationships, in which one of their creatures uses the other to obtain food, habitat. The other participant in the relationship does not receive any benefits from the interaction.
On a note!
There is a category of obligate parasites, the metabolism of which is closely related to the host. They cannot synthesize products on their own. Optional species use the host only at certain stages of the life cycle.
Vital activity of parasites
Almost all the life of parasites takes place inside another organism, they not only live in it, but also feed on living cells. It can be a plant, an animal, a person - in other words, just the owner.
Anything can become a source of parasite infestation. Sometimes it is enough to eat an unwashed fruit or vegetable, as the eggs of the parasite will be inside the body. Often this also happens in contact with animals, because most of them are carriers of parasites.


The fact of infection is not only unpleasant, but can also be dangerous, because in the absence of treatment, very serious complications can appear, up to and including death.
Physiological processes of saprotroph bacteria
In the form of an effective medicine against parasites, doctors advise taking the drug "Gelminton". The composition of the product is based only on natural components of natural origin, they were grown in places with 100% clean ecology, and have a proven effect that allows you to quickly cope with any types of worms.
- anaerobes (Escherichia coli, it can live in an oxygen-containing environment, but all vital processes take place without the participation of oxygen);
- aerobes (putrefactive bacteria that use oxygen in their vital processes);
- spore-forming bacteria (genus Clostridia);
- non-spore-forming microorganisms (E. coli Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa).
Almost the entire variety of saprophytes, as a result of their vital activity, produces various cadaveric poisons, hydrogen sulfide, cyclic aromatic compounds (for example, indole). The most dangerous for humans are hydrogen sulfide, thiol and dimethyl sulfoxide, which can lead to severe poisoning and even death.
Saprotrophs take their part in the process of decay.
The main difference is Saprophytes versus Parasites
Saprophytes and parasites are two life forms that follow a heterotrophic diet. This means that saprophytes and parasites cannot produce their own food. The main difference between saprophytes and parasites is that saprophytes rely on dead and decaying organic matter for their nourishment, while parasites are completely dependent on another organism for their nourishment. Saprophytes are mainly fungi and bacteria. They play a key role in ecosystems, releasing nutrients from dead matter into the soil. The parasites can be unicellular or multicellular animals or plants. Protozoa, helminths and ectoparasites parasitize humans. Rafflesia and Cuscata are parasitic plants.
Key areas covered
1. What are saprophytes - definition, characteristics, role, examples 2. What are parasites - definition, characteristics, role, examples 3. What are the Similarities Between Saprophytes and Parasites - A Brief Description of the Common Features 4. What is the Difference Between Saprophytes and Parasites - Major Differences Comparison
Key words: bacteria, decomposers, ectoparasites, fungi, helminths, heterotrophs, parasitic plants, parasites, protozoa, saprophytes


Major differences
In summary, the main differences between these two broad groups of fungi and bacteria can be deduced:
- Parasitic organisms consume nutrients from living beings or plants in which organic reactions occur, and saprophytes are products of dead organic matter.
- When the host is healthy, saprophytes do not cause health problems, while parasites always have a negative effect.
Despite the potential danger, both types of microorganisms are successfully used in many areas and industries: medicine, agriculture, food industry, etc.
It is wrong to assume that any microorganisms that feed on organic food are parasitic. Parasites include those organisms that survive at the expense of others. They can settle both inside a body and outside.
Saprophytes feed only on the remains of plants or animals. These include soil and mold fungi, as well as mold bacteria. Thus, the main differences between saprophytes and parasites are several features:
- The method of existence and the nature of the feeding of organisms: parasitic individuals feed on the organic structures of the living host; saprophytes live on dead plant bodies.
- Unlike parasites, saprophytes usually do not harm the human body.
- The habitat for saprophytes can be both living and nonliving structures. Parasites live only in a living organism.
In some cases, fungi from parasites turn into saprophytes, which initially settle on living plants, and after their death continue to live, feeding on dead wood. Such mushrooms are called symbionts.
Separation of living beings by type of food
To ensure its existence, every living organism needs certain substances or energy from outside. The process of consuming these resources is called nutrition.
According to the method of nutrition, all living organisms are divided into two types:
- autotrophs;
- heterotrophs.
Autotrophs are organisms capable of independently producing the organic substances necessary for them from inorganic ones. These include most plants that feed themselves from carbon dioxide and water using the energy of the sun.


Heterotrophs are creatures that need ready-made organic substances. This is a huge group of living organisms, within which there are many more classifications. Heterotrophs are divided into biotrophs and saprotrophs. The former feed on living organisms: animals or plants. They also include parasites that have adapted to such a life when their host is both food and home for them.
Saprotrophs, on the other hand, extract food from dead creatures or their excrements (including excrement). This group includes bacteria, plants, fungi (saprophytes) and even animals (saprophages). They, in turn, are also divided into different subgroups: detritophages (feeding on detritus), necrophages (consuming animal corpses), coprophages (feeding on feces), and others.
Classification
The division into saprophytes and parasites arose according to the principle of feeding these microorganisms and fungi. This is precisely their main feature. Both groups belong to the broad biological concept of "heterotrophs", that is, such forms of existence of living things in which the body is not able to independently produce organic matter after the consumption and processing of inorganics (as plants are able to do). Instead, he consumes organic matter in a ready-made and available form for him.
Saprophytes
The overwhelming majority of bacteria studied by humans at the moment belong to this group. The second name for saprophytes is saprotrophs. It came from two Greek words: sapros - "rotten" and trophy - "food". This name, given several centuries ago, perfectly illustrates the principles of nutrient intake by these microorganisms.
For nutrition, they extract everything they need from those organic sources that are no longer living organisms. This can be excrement, food waste, rot, dead animals, etc. Before extracting everything necessary for food, most of the saprophytes secrete enzymes into the nutrient substrate that partially trigger chemical decomposition reactions, and only then, in a prepared form, they absorb such a “semi-finished product ”And recycle it.
In nature, saprophytes have spread very widely and populated various niches: they can be found in large quantities both in soil and in water. In addition, they are found on the surface of any organism - human or animal. Most often they are located in cavities, especially in those that communicate with the external space: the oral cavity, nose, vagina, rectum.
Doctors know that these bacteria and fungi behave in two ways in terms of human health, depending on the conditions. If they live in a healthy body with a normal level of immune mechanisms, then they behave like typical saprophytes. Such microbes do not have a pathogenic effect on the body, peacefully exist in it, and do not provoke any harmful effect.
One of the striking examples can be considered hay bacillus, which is always present in the gastrointestinal tract of people. Its presence has certain benefits, since this bacterium is involved in the digestion process, facilitating the breakdown of proteins and carbohydrates. With its help, the body limits the growth of pathogenic microflora of the intestines and skin, suppresses the growth of microbes in wounds, etc.
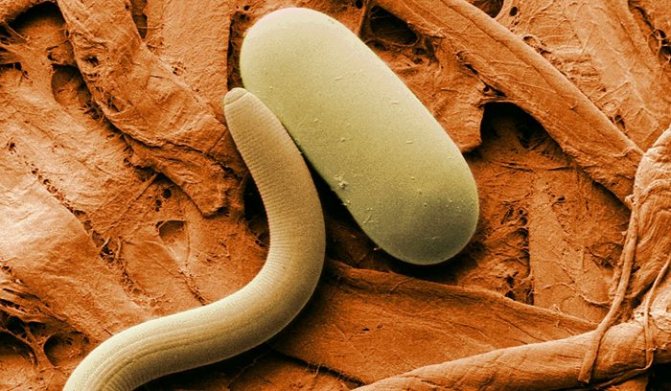

But in the event that a person is weakened by an illness or any other factors, the hay bacillus begins to behave aggressively: it provokes food poisoning, causes eye infections, activates allergic reactions on the skin, etc. Such dual behavior often raises the question: to the group of saprophytes or parasites to carry the hay stick? Knowing the main characteristics of saprotrophs, any specialist understands that she is a common saprophyte.
Focusing on the main beneficial properties of hay sticks, it is used in many medicines and food supplements. The role of the hay bacillus in the fight against diseases is indispensable, in which antibiotics play the main role in therapy, but for various reasons they cannot be prescribed to the patient.
Parasites
Parasites include those microorganisms that spend their entire life or a separate part of the life cycle inside the host, from whose living cells it extracts everything that it needs for development. Both an animal and a plant can act as a host. The parasite always causes a deterioration in the health of its host, but the differences in this negative impact can be huge: from minor diseases that do not prevent the affected plant or animal from living, to the death of the feeding organism.
To extract nutrients, parasites use juices, organic liquids, soft and hard tissues. Many species, as they multiply and increase in population, can invade various organ systems, quickly causing irreversible consequences.
There are forms with obligate parasitism. This means that they can live only inside their host, and if he dies, then the parasite dies with him. Such species are aimed at preserving the normal functioning of the host, therefore, they are rarely fatal.
Parasites, in turn, are divided into two categories:
- Microparasites. Their entire life cycle takes place within one host, and offspring most often live here.
- Macroparasites. They actively reproduce by spores and are transferred to new habitats, actively infecting new food sources.
Among the parasitic life forms there are many that cause diseases that are dangerous to humans, sometimes of an infectious nature.
In addition to the standard parasitism, there is an erroneous one. This pattern is quite rare, but it is often the source of fatal infections. This happens when the parasite enters the organism of a biological species that is not its typical host, but for some reason does not die, but begins to grow and develop.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: How to remove carpet fleas
All human parasites by type of habitat are divided into ectoparasites (living on the skin, hair or nails) and endoparasites (living in internal organs and structures). Most of them show high resistance and variability, so treatment can be continued for a long time and dangerously frequent relapses.
The value of mushrooms in nature
The nutrients decomposed by the mushrooms are further absorbed by other plants. Living creatures (animals and insects) feed on hat species. There are also such mushrooms that are specially grown artificially. These are champignons and oyster mushrooms. Moldy mushrooms (aspergillus, penicilli) are used to obtain antibiotics and even hard cheeses. Ergot (formed on cereals) is used to fight malignant tumors.
Many parasitic fungi harm living organisms and plants, causing disease. A lot of damage is done to wood. It is not recommended to use contaminated building material for wooden buildings.
Since the mushroom culture can cause fatal poisoning, experts advise that you be very careful when harvesting it.
What exactly does saprophyte bacteria feed on?
The bulk of naturally occurring microorganisms refers specifically to saprophytes. Like people, they have their own tastes and exactingness to the food they eat, that is, organic substances should contain more / less certain compounds that help them develop, lead an active life.
For example, some organisms of this class need to use the decaying bodies of animals or plants containing rotten compounds for full life, while others just need to penetrate into milk, as a result of which its fermentation is observed.
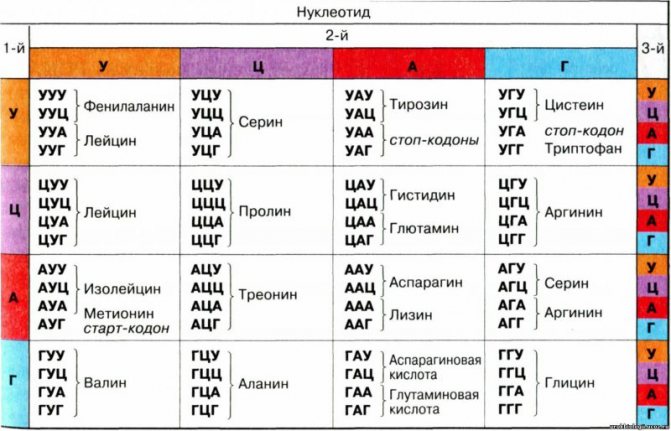

Therefore, for the life of saprophytes, the following may be required:
- Five-carbon nitrogenous bases or nucleotides.
- Amino acids.
- Nitrogen.
- Vitamin complexes.
- Carbohydrates.
- Peptides.
- Proteins.
Vital activity of parasites
Parasites spend almost their entire life inside another organism and feed on its living cells. A plant or animal inside which a bacterium lives and whose cells it feeds on is usually called a host. Parasitism is the relationship between one type of living organism (parasite) and another (host), during which the former lives and feeds at the expense of the latter.


Viruses
Viruses are parasites that do not show any signs of life, being outside the cell of a living organism. Due to the fact that the viruses themselves do not have a cellular structure, they also do not generate energy, do not feed, do not grow and are capable of metabolism. Being outside a living cell, viruses are similar to inanimate matter, however, there are two properties that distinguish them:
- The ability to reproduce, that is, to reproduce forms similar to oneself.
- Heredity and variability.
The life cycle of a virus consists of the following stages:
- Penetration into a living cell.
- Changes in metabolism within the cell, forcing the production of viral nucleic acids and proteins.
- Self-assembly of the virus inside the cell from the produced viral acids and proteins.
- From an overabundance of newly formed viruses, the cell dies
- Viruses leave the host cell.
Inhabiting human and animal cells, viruses provoke the development of many dangerous and sometimes fatal diseases.
The structure of microorganisms
- Features of the structure of bacteria
- Mushrooms in microbiology
- Pathogenic microorganisms
- Viruses as an object of microbiology
- Rickettsiae - primitive bacteria
Microorganisms (microbes) are single-celled organisms less than 0.1 mm in size that cannot be seen with the naked eye. These include bacteria, microalgae, some lower filamentous fungi, yeast, protozoa (Fig. 1). Microbiology is engaged in their study.
In fig. 2. you can see some representatives of unicellular protozoa. Sometimes the objects of this science include the most primitive organisms on Earth - viruses that do not have a cellular structure and are complexes of nucleic acids (genetic material) and protein. More often they are isolated into a completely separate area of research (Virology), since microbiology is more likely aimed at studying microscopic unicellular organisms.
Sciences such as algology and mycology, which study algae and fungi, respectively, are separate disciplines that overlap with microbiology in the study of microscopic living objects. Bacteriology is a true branch of microbiology. This science deals with the study of exclusively prokaryotic microorganisms (Fig. 3).
Unlike eukaryotes, which include all multicellular organisms, as well as protozoa, microscopic algae and fungi, prokaryotes lack a formalized nucleus containing genetic material and real organelles (permanent specialized cell structures).
Prokaryotes include true bacteria and archaea, which according to modern classification are designated as domains (super kingdoms) Archaea and Eubacteria (Fig. 4).
Features of the structure of bacteria
Bacteria are an important link in the cycle of substances in nature, they decompose plant and animal residues, cleanse reservoirs polluted with organic matter, and modify inorganic compounds. Without them, life on earth could not exist. These microorganisms are found everywhere, in soil, water, air, animal and plant organisms.
Bacteria differ in the following morphological features:
- Cell shape (round, rod-shaped, filamentous, convoluted, spiral-shaped, as well as various transitional variants and star-shaped configuration).
- The presence of devices for movement (immobile, flagellate, due to the secretion of mucus).
- Articulation of cells with each other (isolated, linked in the form of pairs, granules, branching forms).
Among the structures formed by rounded bacteria (cocci), cells are isolated that are in pairs after division and then disintegrate into single formations (micrococci) or remain together all the time (diplococci). A quadratic structure of four cells is formed by tetracocci, a chain - streptococci, a granule of 8-64 units - sarcins, clusters - staphylococci.
Rod-shaped bacteria are represented by a variety of forms due to the great variability of the length (0.1-15 microns) and thickness (0.1-2 microns) of the cell. The shape of the latter also depends on the ability of bacteria to form spores - structures with a thick shell that allows microorganisms to survive adverse conditions. Cells with this ability are called bacilli, and those that do not have such properties are simply rod-shaped bacteria.
Special modifications of rod-shaped bacteria are filamentous (elongated) forms, chains and branching structures. The latter is formed by actinomycetes at a certain stage of development. "Curved" rods are called coiled bacteria, among which vibrios are distinguished; spirillae with two bends (15-20 microns); spirochetes resembling wavy lines. Their cell lengths are 1-3, 15-20 and 20-30 microns, respectively. In fig. 5 and 6 show the main morphological forms of bacteria, as well as the types of spore location in the cell.
The main cellular structures of bacteria: a nucleoid (genetic material) intended for protein synthesis of the ribosome, the cytoplasmic membrane (part of the cell membrane), which in many representatives is additionally protected from above by a cell wall, a capsule and a mucous sheath (Fig. 7).
According to the classification of bacteria, more than 20 types are distinguished. For example, extremely thermophilic (lovers of high temperatures) Aquificae, anaerobic rod-shaped bacteria Bacteroidetes. However, the most dominant type, including diverse representatives, is Actinobacteria. It includes bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, actinomycetes. The uniqueness of the latter lies in the ability to form mycelium at a certain stage of development.
In the common people, this is called mycelium. Indeed, the cell branching of actinomycetes resembles fungal hyphae. Despite this feature, actinomycetes are classified as bacteria, since they are prokaryotes. Naturally, their cells are less similar in structure to fungi.
Actinomycetes (Fig. 

Some representatives concentrate in the zones of oil fields, and create a special bacterial filter that prevents the penetration of hydrocarbons into the atmosphere.Actinomycetes are active producers of practically valuable compounds: vitamins, fatty acids, antibiotics.
Mushrooms in microbiology
The object of microbiology is only the lower mold fungi (rhizopus, mucor, in particular). Like all mushrooms, they are not able to synthesize substances themselves and need a nutrient medium. The mycelium of the lower representatives of this kingdom is primitive, not divided by partitions. Yeast (Fig. 9), which lacks mycelium, occupies a special niche in microbiological research.
Currently, a lot of knowledge has been collected about their beneficial properties. However, yeast continues to be studied for its ability to synthesize practically valuable organic compounds and is actively used as model organisms in carrying out genetic experiments. Since ancient times, yeast has been used in fermentation processes. Metabolism is different for different representatives. Therefore, some yeast is more suitable for a particular process than others.
For example, Saccharomyces beticus, which are more resistant to high alcohol concentrations, are used to make strong wines (up to 24%). Whereas S. cerevisiae yeast is able to produce lower ethanol concentrations. According to the directions of their application, yeast is classified into fodder, baking, brewery, alcohol, wine.
Pathogenic microorganisms
Disease-causing or pathogenic microorganisms are found everywhere. Along with the well-known viruses: influenza, hepatitis, measles, HIV and other dangerous microorganisms are rickettsia, as well as strepto- and staphylococci, which cause blood poisoning. Among rod-shaped bacteria, there are many pathogens. For example, diphtheria, tuberculosis, typhoid fever, anthrax (Fig. 10). Many representatives of microorganisms dangerous to humans are found among the simplest, in particular, malaria plasmodium, toxoplasma, leishmania, lamblia, trichomonas, pathogenic amoeba.
Many actinomycetes are not harmful to humans and animals. However, many pathogenic representatives are found among the mycobacteria that cause tuberculosis, leprosy (leprosy). Some actinomycetes initiate a disease such as actinomycosis, accompanied by the formation of granulomas, sometimes an increase in body temperature. Certain types of mold fungi are capable of producing substances toxic to humans - mycotoxins. For example, some representatives of the genus Aspergillus, Fusarium. Pathogenic fungi cause a group of diseases called mycoses. So, candidiasis or, simply put, yeast-like fungi cause thrush (Fig. 11). They are always contained in the human body, but are activated only when the immune system is weakened.
Fungi can cause a variety of skin lesions, in particular all kinds of lichen, except for herpes zoster, which is caused by a virus. Malassezia yeast - permanent inhabitants of human skin with a decline in the activity of the immune system can cause seborrheic dermatitis. Do not immediately run to wash your hands. Yeast and opportunistic bacteria, in good health, perform an important function, prevent the development of pathogens.
Viruses as an object of microbiology
Viruses are the most primitive organisms on earth. In a free state, no metabolic processes take place in them. Only when they enter the host cell do viruses begin to multiply. In all living organisms, the carrier of genetic material is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Representatives with a genetic sequence such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) are found only among viruses.
Viruses are often not classified as truly living organisms.
In addition to parasites specializing in animals and humans, there are phytopathogenic representatives among them, that is, damaging only plant cells; bacteriophages - "eaters of bacteria". It is known that viruses are even capable of developing in dead cells, in which a relatively intact structure remains, and the genetic material has died. Previously, during epidemics, the bodies of the dead were burned, both for bacterial and viral diseases.
The morphology of viruses is very diverse (Fig. 12). Typically, their diametrical dimensions range from 20-300 nm.
Some representatives reach a length of 1-1.5 microns. The structure of the virus is surrounded by the genetic material with a special protein framework (capsid), which is distinguished by a variety of forms (spiral, icosahedral, spherical). Some viruses on top also have an envelope formed from the membrane of the host cell (supercapsid). For example, the human immunodeficiency virus (Fig. 13) is known as the causative agent of the disease, which is called (AIDS). It contains RNA as a genetic material, affects a certain type of cells of the immune system (helper T-lymphocytes).
The reproduction cycle of these parasites begins with the stage of attachment to the cell. The target contains special molecular ends (receptors) by which viruses recognize it. Further, the penetration into the genetic material of the parasite is carried out, often with some other components of its structure. Reproduction of the virus occurs due to duplication (replication) of genes and the subsequent formation of the desired proteins. After that, the copies of the viruses are released from the cell and again form their structure.
Rickettsiae - primitive bacteria
It might seem like there is a big chasm between viruses and bacteria. However, it turned out that there are transitional forms in nature, called rickettsia. According to the modern classification, these microorganisms belong to the type Proteobacteria (proteobacteria). Rickettsiae are comparable in size to large viruses and are intracellular parasites. Like viruses, rickettsiae can reproduce only in the host's cells. The cells of these bacteria are motionless. Rickettsiae, as a rule, are rod-shaped; cocci and filaments are also found.
Diseases that cause rickettsia in humans are often very difficult. Symptoms of fever, accompanied by damage to the central nervous and cardiovascular systems, appear. As a rule, rickettsiae are transmitted to humans by the bite of ticks, fleas, lice. In carrier cells, parasites are kept in a dormant (inactive) form and are activated only when they enter the host. Rickettsiae can also be transmitted through warm-blooded animals (rats, mice, dogs), which they do not bring any harm.
Comparison
If we compare these two microorganisms with each other, then initially it should be said that their daily routine is practically the same. In some cases, these microorganisms become very difficult to distinguish. The fact is that some parasites can behave in the same way as saprophytes. And saprophytes can use living organisms that have been greatly weakened due to the overtaken disease for living and further nutrition.
In order to understand how to distinguish between these microorganisms, some comparison should be made:
- Saprophytes, which have the ability to pass themselves off as parasites, develop without the help of another living organism. After a while, they become completely safe for the human body, but only if they are not affected by negative factors. This type is of great importance in the process of the circulation of substances.
- The conditional type of parasitic forms can live, just like an ordinary parasite, but at the same time feeding will occur as in saprophytes.But this happens before full maturation, and then the parasites take root in the tissues and already fully lead their parasitic lifestyle.
- Mandatory parasites. This type uses exclusively living cells for its nutrition, and after their death, the cells die along with these bacteria. Throughout the entire life cycle, bacteria lead an exclusively parasitic lifestyle.
Taking into account the information received, it can be noted that both presented forms of microorganisms can equally harm the little man. Only saprophytes are also of some benefit.
In any case, the detection of any of these types of organisms requires immediate treatment.
Tongue fungus treatment
- 1 Prevalence
- 2 Symptoms of the disease
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 Treatment of tongue fungus 4.1 Folk methods
- 5.1 Drug therapy 5.1.1 Local treatment
The fungus can affect the mucous membranes of various organs, including the mouth and tongue. Fungus on the tongue is a manifestation of the same disease as thrush (damage to the mucous membrane of the internal genital organs with Candida fungi), which many women are familiar with firsthand. With timely and competent treatment, you can get rid of unpleasant symptoms quickly enough.


Prevalence
Candida fungi are present in the organisms of most people on the planet, but for the time being they do not manifest themselves. When a person's protective functions of the body decrease, the fungus begins to multiply intensively and affects the oral cavity. Especially often it appears in newborn babies, in the event that the child acquired the parasite from the mother during childbirth.
At risk are the elderly, smokers, people who have inflammatory processes in the teeth. When treating oncological diseases, taking hormonal agents, the fungus also often "wakes up". Fungus of the tongue is a concomitant disease in tuberculosis, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus. Such a disease is transmitted easily, it is enough to touch the mucous membranes or even just use one towel with a carrier of the pathogen.
Back to the table of contents
Symptoms of the disease
Sour breath signals a disease in the mouth.
The fungus in the oral cavity is different from other strains in the family. He is not able to create a mycelium, therefore it is fixed in individual cells of the mucous membrane of the tongue, thereby destroying it. From here there is a feeling of discomfort, itching and burning, a characteristic cheesy white bloom. The main symptom is considered to be fermented milk smell from the mouth.
The consequences of an advanced form of candidiasis are even more dangerous. The disease quickly becomes chronic, and each subsequent relapse is more difficult to treat. From the oral cavity, the disease can spread to the digestive organs, and there it is already more difficult to influence the plaque directly and localize the foci. The damaged mucous membrane cannot qualitatively absorb nutrients, which causes the whole body to suffer.
If you do not take timely measures and do not start treatment of the disease, then it will not be limited to one raid. Deeper damage to the mucous membrane occurs:
- ulcers and microscopic wounds;
- cracks in the corners of the mouth;
- inflammation and enlargement of the papillae in the tongue;
- fever, especially in children of the first year of life.
Back to the table of contents
Diagnostics
At the first examination of the patient, the doctor quickly diagnoses the tongue fungus.
It is difficult to confuse this disease with others, since the external manifestations are quite specific. White plaque, which cannot be removed, consists of grains, which is why the doctor quickly diagnoses tongue fungus. The pathogen affects the tongue already as a complication, since the focus of the oral cavity is usually located in the throat.For more effective treatment, the doctor may prescribe a scraping to determine the resistance of the parasite to different types of antibiotics.
Back to the table of contents
Tongue fungus treatment
Folk ways
In the initial stages of the disease in young children, in order to overcome the fungus, it may be enough to use a soda solution. A teaspoon of baking soda must be diluted in a glass of boiled water and the affected areas in the mouth and tongue should be treated. The spread of the fungus in the environment created by the soda solution is difficult, therefore, the disease will recede.
Carrot juice is an effective remedy against pathologies of the oral cavity.
For adults, medicinal herbal teas, which also heal lesions, can be effective first aid. Yoghurts are able to restore the beneficial microflora and thereby squeeze the fungus from the tongue. Such universal medicinal components as lemon, honey, garlic, onions will help in this case, if you add everything together in boiled water. Carrot juice is rich in many essential oils and is known as an established folk remedy for fighting fungus. Folk remedies are also tincture of calendula, freshly squeezed onion juice, and a decoction of St. John's wort.
Taking local and general medications without the knowledge of the doctor is prohibited, especially when treating children.
Back to the table of contents
Treatment of severe forms
Drug therapy
If the disease has gone far, then antibiotics are used. The type of antibiotic that will be most effective in each case is determined by a bacterial culture of the fungus. Significant relief usually occurs within a week. For the fastest possible result, the doctor may suggest using a candidiasis vaccine. Such a drug promotes the production of antibodies and white blood cells, which quickly destroy the source of the fungus. Antimicrobial agents may be prescribed. Since the fungus of the tongue manifests itself in an organism with a weakened immune system, vitamins and agents are shown that restore a healthy microflora.
Back to the table of contents
Parasites, viruses, bacteria and humans
Viruses, parasites, bacteria - all these microorganisms had a direct impact on human evolution. Yet Microorganisms benefit humans despite the harm they cause.
Helping microorganisms to humans
Ten facts about the help of parasites, viruses and bacteria to humans:
- ... Thanks to modern science and genetics, it is now reliably known who infected our ancestors, which, as a result, turned out to be an evolutionary impetus.
- The use of larvae and leeches. For many years, European leeches have been used in medicine. But in connection with the evolution of the microbial theory, their use has ceased in many countries. But later, beauticians and surgeons returned to them. Leeches relieve swollen face, black eyes, help with reattachment of body parts (ears, skin, and so on). In addition to leeches, their larvae are also effective, therefore, thanks to them, a separate industry has appeared - biotherapy.
- Parasites and the immune system. Parasitic therapy is parasitic, since negative outcomes so far prevail over positive ones. However, one cannot ignore the successful consequences. Intentional infestation with parasites can cure neurological, allergy, and other diseases. And this has been proven through the experience of a large number of scientists.
- Virotherapy. This therapy consists of introducing a reprogrammed virus into a person. So, some viruses have been transformed to treat cancer, measles, and tumors.
- Viruses for the treatment of bacterial infections. Bacteriophages are viruses that hunt bacteria. Bacteriophages change the metabolism of bacteria and in this way destroy it. With the help of phages, at the present time, certain diseases are also treated in humans.
- Vaccines are the same virus of the disease, but weakened, which is introduced so that the immune system has an idea in advance how to compete with the disease.
- Recycling. Bacteria living in the surrounding world and feeding on dead plant and animal cells benefit nature by clearing the land of waste.
- ... Without bacteria that naturally reside in the gastrointestinal tract, a person might even die, as they help to digest food and work in tandem with the immune system to protect life.
- Skin bacteria. Thanks to evolution, we are not born dead. And that's why - after leaving the mother's womb, the child is attacked by bacteria, and, more specifically, the skin. Bacteria have been living on the skin since the very appearance in this world, and this is completely normal, because they in a certain way protect it from other harmful microorganisms.
- Cyanobacteria or algae are one of the oldest microorganisms living on Earth. Thanks to algae, we and other living organisms appeared on our planet, since cyanobacteria are the first photosynthesizers. It was they who produced oxygen, which is vital for all life on our planet.
Many of the species of bacteria, viruses and parasites have their place in the living environment and have a unique purpose.
Symptoms of parasites in the pancreas
Very often, experts diagnose diseases provoked by various parasites. Many pathogenic microorganisms have settled in the organs of the digestive system.
The most favorite places are the small and large parts of the intestine, the liver, but they can also parasitize in the area of the pancreas. Therefore, it is very important to know how parasites manifest themselves in this organ. Symptoms and treatment of the invasion will help to pinpoint the location of the parasites and provide effective therapy.
Types of helminths
Worms that have penetrated the gland pose a serious danger to the entire body. They are able to block the lumen of the organ of exocrine and endocrine secretion, disrupting its functions, and provoke the development of pancreatitis.
There are several types of virulent parasitic individuals that infect the pancreas. For the most part, these are various groups of helminths. These include:
- Ascaris - roundworms, which are the causative agents of ascariasis. They parasitize in the small intestine, attaching to the mucous membrane. Migrating, helminths are able to get into the producer of pancreatin, which can lead to the formation of a plug from the helminths in the duct of the gland. As a result, there is a violation of the movement of pancreatic juice.
- Feline flukes belonging to the class of flatworms. They are very small in size. They provoke a parasitic disease opisthorchiasis. They are located in the gallbladder and its ducts, liver and pancreas. When the pancreas is infected, pancreatitis develops, which is characterized by girdle pain in the hypochondria, dyspeptic disorders, and impaired excretory function of the gland.
- Echinococcosis, causative agents of severe long-term pathology - echinococcosis. The main symptom, which is considered the appearance of echinococcal cysts in the places of localization of parasites. Parasitizing in the pancreatic region, they cause complex organ disorders.
- Chains of different types, which belong to the group of flatworms. Their habitat, as a rule, is the gastrointestinal tract. Being in the ducts of the gland, helminths cause significant harm to the body, causing disruption of the functioning of the organ, the occurrence of an inflammatory process.
- Strongyloids, very small nematodes that provoke strongyloidiasis. This nematodosis is characterized by a variety of organ pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system. This type of helminths, being in the body for a long time, may not manifest itself in any way and, migrating through it, it can be localized in any organ.
These are some of the most common and well-known helminths to be aware of.
Their pathogens can be various kinds of harmful organisms that manifest their vital activity in the organs of the digestive system:
- Giardia is a protozoan that parasitizes in the small intestine, liver, pancreas. They inhibit the work of organs, contribute to the allergization of the human body.
- Microsporidia are intracellular parasites that cannot exist outside the host. Their development occurs in conditions of a weakened general and local immunity.
- Dysentery amoeba is a parasitic protozoan microorganism that provokes a severe amoebiasis disease. Affects the large intestine, causing inflammation and ulcers. They can be transferred by blood to other organs, primarily to the liver, where additional foci are formed.
- Toxoplasma is a unicellular parasite whose sexual reproduction occurs only in the cells lining the intestines of cats. It is the cause of toxoplasmosis. It affects many organs: skeletal muscles, heart muscles, and others.
The symptomatology of diseases caused by parasitic microbes is identical, and therefore the determination of the pathogen is possible only after a thorough hardware examination and laboratory tests. After a comprehensive examination, the specialist will prescribe adequate treatment.


Symptoms
Helminthic invasion of the pancreas is manifested by a large number of characteristic signs. The most common symptoms include:
- Pain in the abdominal cavity, sometimes sharp and intense.
- Feeling of nausea, sharp vomiting, after which there is no relief.
- High temperature reaching a maximum value of 39.7 degrees.
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Frequent bowel movements up to 15 times per knock.
- Difficult defecation.
- Discomfort in the abdominal region.
- The skin is yellowish.
- Pain in the abdomen when performing the slightest physical activity.
- Manifestation of allergies.
- Ruby drops appear on the skin of the chest and abdomen.
Also, with lesions of the pancreas by helminths, pain in the right hypochondrium can often appear. On visual examination and palpation of the abdominal cavity, the doctor may notice an increase in internal organs.
In medical practice, the chronic form of parasite infection is the most dangerous, since the manifestation of symptoms is practically not noticeable. But, at the same time, they continue to have a negative effect on the body. Therefore, experts recommend not to wait for a vivid manifestation of symptoms, but for the purpose of prevention, periodically conduct a laboratory examination of feces.

Treatment
With helminthic invasion, treatment should be comprehensive, containing not only antiparasitic medications, but also traditional medicine. The duration of the course directly depends on the degree of development of pathology and general condition. On average, a therapeutic course can last from several weeks to several months.
Also, in combination with treatment by a parasitologist, special dietary food is prescribed. At the same time, the intake of carbohydrate-containing products is completely excluded. This is due to the fact that these food products create a favorable environment for the reproduction of helminths. It is recommended to fill the diet with fermented milk products and foods containing dietary fiber.
In order to restore the protective functions of the body and normalize health, it is recommended to use alternative medicine. Phyto decoctions help to strengthen the body and tone it up. They also contribute to the gentle disposal of helminths and prevent the development of a relapse of helminthic invasion.


Folk remedies
Blueberries. The berries and foliage of the plant are used in most cases in the treatment of the eyes. An infusion of blueberry leaves is used.Throughout the day, you should drink 0.5 liters of the product.
Method of preparation: 15 grams of dry blueberry leaves, pour 0.25 ml of boiling water and leave until the product cools completely.
It is taken in small portions throughout the day. The duration of the course is 14 days. After a week break, repeated treatment with this remedy is carried out. In the first days of admission, the general condition may worsen, but you should not give up the drug. An alternative effect has an infusion of wild strawberry or lingonberry foliage. An infusion of the three indicated herbs is also allowed.
Buckwheat flour with kefir. Strict adherence to therapeutic nutrition during therapy is quite often one of the main methods of treatment. In this case, parasitologists recommend drinking antiparasitic yogurt every morning, which quickly and effectively restores the functional activity of the pancreas.
Method of preparation: 25 grams of buckwheat flour must be poured over 0.25 ml of classic natural yogurt and left to infuse overnight. It is taken once before meals.
Kissel from oats. Treatment with folk remedies, and in particular with oat jelly, will help you quickly and gently get rid of uninvited guests. It is one of the most laborious, but at the same time effective methods of treating parasites.
Method of preparation: Rinse a gram of unpeeled oats thoroughly, mix with 1.5 liters of water and boil over low heat for an hour. After 40 minutes, the grains should be overheated and in this state, continue to cook them for another 20 minutes. After removing the broth from the heat, it must be passed through cheesecloth. Take the resulting white thick mixture 0.1 kg before each meal. Store for no more than two days in the refrigerator.
Phytoseeds. They are a universal tonic, which is used to maintain the health of the organ. The formulation of such funds is quite diverse, but their effectiveness directly depends on the correctly selected herbs.
The most effective recipes include:
- Mix the inflorescences of wormwood, chamomile and immortelle in equal amounts. 3 tbsp. l of herbal collection is poured into 1.5 liters of boiling water and infused for three hours. After the infusion is filtered and taken every two hours, 150 ml.
- 2 tbsp. l of chicory pour a glass of boiling water and boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Having removed the broth from the heat, it is immediately filtered and cooled to room temperature. The finished product should be taken in full within 24 hours.
- Mix iris and wormwood inflorescences in equal amounts. Brew 25 grams of the collection in 0.25 liters of boiling water for 15 minutes. It is taken 50 ml three times at knocks before the main meals.
In the treatment of helminth invasion, traditional medicine will help not only expel parasites from the body, but also restore the protective functions of the body and the functional activity of the digestive tract. In acute forms of pathology, they are used exclusively in combination with methods of conservative therapy.
In order to more quickly restore the body after undergoing treatment, it is recommended to use the following means:
Rosehip decoction. 50 grams of dried rose hips pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and boil for 15 minutes over low heat. Permeates 0.25 liters daily.
Pumpkin seeds. The use of such a product in its raw form contributes to the rapid natural excretion of worms from the body. Take 25 grams of peeled seeds on an empty stomach every morning 30 minutes before the main meal.


Medicines
Medical treatment of helminthic invasion is based on the intake of anthelmintic pharmacological agents. Most often, in their practice, parasitologists use the following drugs:
- Piperazine.
- Pirantel.
- Nourished.
- Decaris.
Their scheme of admission is prescribed by a doctor and can consist of either one admission or a short course. Treatment with medications is carried out with the parallel administration of antibiotics belonging to the group of ornidazole and albendazole.
In order to restore the normal absorption process in the intestinal region, enterosorbents are prescribed. If allergic reactions occur, antihistamines may be used. Taking hepatoprotectors helps to restore the functional activity of the liver.
In medical practice, cases of damage to the gland by large individuals of parasites have also been observed. With such a pathology, treatment is carried out by performing an operation, followed by antimicrobial therapy.
Systematic examination and timely referral to a specialist when the slightest signs of this pathology are detected will allow timely and high-quality cure of this ailment. Since the treatment of advanced forms of helminthiasis is quite complex and lengthy. In addition, there is a high likelihood of developing serious side effects for the general condition.
With a competent combination of methods of conservative and alternative medicine, the effectiveness of the treatment of parasites increases significantly. Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, strict adherence to cleanliness in the house and systematic prevention will minimize the likelihood of a recurrence of the invasion.
Throughout life, the pancreas is constantly exposed to negative factors. This organ takes an active part in the processes of digestion, the production of hormones, is responsible for the production of pancreatic juice and stimulation of metabolism in the body. That is why timely and effective treatment of this organ is very important, since the state of health of the whole organism as a whole depends on its full functionality.
Video
Saprotroph fungi and parasites
Considering the representatives of this kingdom, a person who is far from the natural sciences will not always be able to say what exactly is the difference between different species.


Saprotroph fungi and parasites
The main difference between saprotroph fungi and parasites is what substrate they use as a food source. This trait determines the size of their bodies, their habitat, the number and way of distribution of spores.
Saprophytes
These creatures get their energy from dead organic produce. Saprophytes free the environment from the remains of plants and animals, decomposing them with the formation of simple inorganic compounds. They return mineral salts to the soil, which will later be useful to plants.
The group of higher saprophytes includes such well-known representatives of the kingdom as:
- boletus;
- Champignon;
- morels and lines;
- fly agarics;
- dung beetles.
Among the known lower genera are yeast, penicillus. They have found their application in medicine, food industry.
Saprophytes can be harmful. So mushrooms of the Mukor genus, which are formed on stale bread, are dangerous to humans and animals. When ingested, they cause mucoromycosis.
Parasites
Unlike saprophytic fungi, parasites take nutrients from the host and can lead to its death. They settle:
- on plants;
- on animals;
- on a person;
- on other mushrooms.


Parasitic fungi
According to the degree of development, size, they are divided into 2 categories:
- Microparasites. Inferior fungi that multiply directly in the body, host cells. These include: slug, candida.
- Macroparasites. They are spread by spores from one host to another. Among the typical representatives are enemies of agricultural plants: scab, late blight, cabbage olpidia, ergot, smut.
Among the macroparasites of animals and plants, fungi of the genera Trichophyton, Epidermofiton, Microsporia are known. They cause contagious diseases.
Also among the fungi there are such species that manifest themselves as saprophytes and parasites. They use an atypical substrate for themselves when living conditions change.
Saprophytes can feed on the host. So autumn or winter mushrooms settle on dead wood residues (stumps). But when the mycelium spreads, they grow on damaged spruces, aspen birches. In this case, the fungi begin to parasitize and worsen the condition of the living host.
Polypores are initially parasites. They grow on tree trunks. But after the death of the owner, these mushrooms continue to live on them as saprophytes.
According to the type of nutrition, all organisms are divided into those who independently produce organic products from mineral products, and those who are deprived of this ability. Representatives of the second group belong to saprophytes or parasites. One of them uses dead organic matter as a food source, others settle on living organisms. In nature, mushrooms are found with various types of nutrition. Their mutually beneficial cohabitation with representatives of other kingdoms is also possible.
Edible and inedible species
Among the whole variety of saprotrophs, there are lamellar, marsupial and tubular species, which belong to the highest, and imperfect mold fungi and yeasts.
Some marsupials, lamellar and tubular saprotrophs are edible. So, edibles include:
- Champignon;
- morels;
- honey mushrooms;
- raincoats;
- dung beetles;
- umbrellas, etc.
Not suitable for consumption and are poisonous:
- pigs;
- toadstools;
- Helwell, etc.
Almost all types of yeast are used in the food industry and winemaking, and a representative of mold, penicillus, is a source of raw materials for the production of antibiotics.
Saprophytes in nature
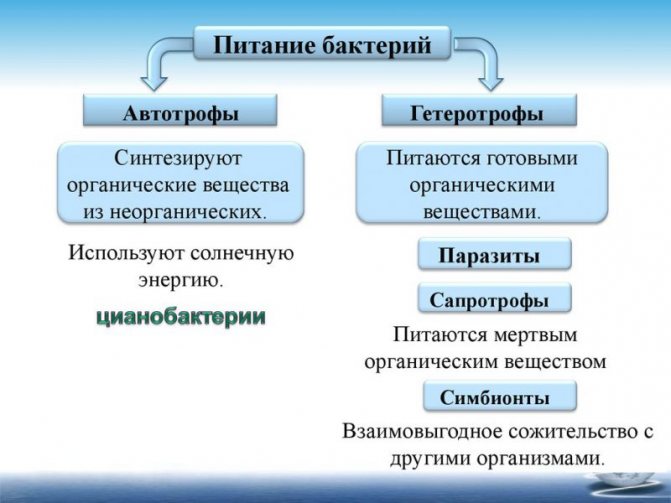

In nature, saprophytes are very important, because thanks to their participation, the processing of environments of organic origin occurs, because any living organism (including plants) dies over time. For the same reason, saprophytes always have an object to feed. In addition, due to the processing of organic waste, through their decomposition, new components arise that are subsequently used by other organisms, which provokes a kind of circulation of substances in nature.
Saprophytes mean a lot in nature, because their task is to transform chemicals and mineralize them, from where fermentation, phosphorus, carbon, nitrogen and other useful processes, substances and minerals arise. Without these organisms, other, more developed creatures could not exist on the planet.
The concepts of bacteria and saprophytes are inseparable. The fact is that all living organisms in nature are divided into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Autotrophs can provide themselves with food on their own. Heterotrophs, on the other hand, need ready-made nutrients. Heterotrophs are subdivided into saprophytes, symbionts, and parasites. This division of organisms allows for a more detailed study of the living world. Each of these types of representatives of the bacterial world has its own meaning.
Features of saprophytes
Most of the representatives of the kingdom of bacteria are saprophytic. They are, to varying degrees, demanding on organic compounds, which are of great importance in the processes of their development and life. There are bacteria in nature that can normally exist only in complex sources (substrates), as an example, it can be putrefactive decaying remains of plants and animals, milk, etc. Thus, for the vital activity of bacteria, some essential nutritional components are required. These substances are:
- nitrogen (or a set of amino acids),
- carbohydrates,
- proteins,
- peptides,
- vitamins,
- nucleotides (possibly components suitable for their synthesis, such as nitrogenous bases, five-carbon sugars).
To meet the needs of saprophytes in laboratory conditions, cultivation is carried out in media that contain plant extracts, serum, yeast autolysates, hydrolyzed meat products.
Similarity of saprophytes and parasites and their differences
Saprophytes in nature lead a lifestyle similar to parasites. Moreover, sometimes it is problematic to clearly separate heterotrophic organisms into these two species, since some parasitic organisms in the process of their vital activity have such behavior that is more reminiscent of semi-saprophytic.
Based on this, it became necessary to isolate facultative parasites and saprophytes.
Facultative saprophytes (they are also called semi-parasites or conditional saprophytes) are bacteria that develop in the absence of a living host organism. At some stages of their own development, they behave like saprophytes, while other situations are characterized by a predominantly parasitic existence. They have a limited range of potential owners. Such microorganisms do not germinate well on nutrient media. However, they play an important role in the circulation of substances.
Facultative parasites (they are also called conditional parasites or semi-saprophytes) are bacteria that live according to the saprophytic type of nutrition. But under certain conditions or after reaching certain stages of development, they settle on the living tissues of weakened plants and lead a parasitic lifestyle.
The place of saprophytes in nature
The role of saprophytic organisms in the living world is of paramount importance. Most of them are needed in nature for the purpose of processing organic waste. Since the life path of any living organism ends in death, there is always food for saprophytes. Thus, they play the role of environmental orderlies. Also, these bacteria are an important link in the cycle of organic matter, as they decompose dead tissue into components that are then used by other organisms.
The environmental value of these bacteria is not limited to organic processing. They are active participants in the processes of mineralization and transformation of chemicals. As an example of the participation of saprophytic bacteria in the circulation of substances, the following processes can be considered: the transformation of phosphorus, sulfur, nitrogen, carbon, fermentation processes.
Thus, the importance of saprophytic bacteria in the environment is quite high.
Effective remedies for toenail fungus
According to the results of recent studies, it was revealed that every third inhabitant of the earth becomes infected with nail fungus in one form or another. At the same time, even half a century ago, fungal infections were not so widespread. This is explained primarily by the high population density, because the pathogen gets on its feet in swimming pools, locker rooms and other public places.
Have you been trying to get rid of PARASITES for many years?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed how easy it is to get rid of parasites by taking every day ...
Read more "
Due to the widespread occurrence of the disease, a large number of medicines for it have long been invented. The drugs are classified into three main groups. Folk recipes also stand out. Let's consider the various options in more detail and try to find out if there is a better remedy for toenail fungus.
Effective pharmacy products
Therapy against toenail fungus can be carried out both with the help of sprays and smearing with a paste, and by ingestion of antimycotic tablets with capsules. Modern pharmacology offers a wide variety of substances of both groups. In terms of their effectiveness, they differ in their effect on the pathogen. Some will have a better effect on yeast, while others will deal better with mold.There are also universal effective remedies for toenail fungus, however, high-quality treatment is impossible without understanding a clear diagnosis.


Azole group
Therapeutic complexes of this group have a double effect on parasitic organisms:
- They interfere with the reproductive activity of microorganisms by destroying their spores.
- These antifungal drugs for nails affect the cellular structure of parasites, dissolve the cell membrane, which leads to their death.
A similar medicine against the fungus can be produced in any form: tableted, capsule, in the form of suspensions, ointments and gels. An azole remedy is best for treating infections against yeast and molds.
As an example of remedies for nail fungus, you can take:
- Miconazole. Cheap but effective;
- Ketoconazole;
- Clotrimazole. Widespread complex;
- Fluconazole. It is included in any rating of drugs for onychomycosis;
- Nizoral. One of the most famous drugs.
Each of these drugs has its own analogues. In general, the substances of this group are quite widespread, and it is not difficult to buy them in a pharmacy.
Morpholine group
A common characteristic feature of such formulations is the presence of amorolfine, as the main active ingredient. Its effect leads to disruption of intracellular processes in fungal spores, therefore, parasitic forms stop reproducing, and ultimately die off.


The most effective remedy for this group of nail fungus is Lotseril. The disadvantages of the drug are its high price, about 2,000 rubles, and the course of treatment reaches from 9 months to one year.
Allylamine group
A feature of the drugs in this group is the rapid removal of irritating symptoms of the nail fungus: itching, burning and peeling of the skin. They are used only when a fungal infection has affected only part of the plate, without affecting the internal tissues. Most of these drugs are topical substances, so they are most often prescribed in the initial stages, at which you can do without a course of treatment with pills.
The best effect of allylamine preparations is achieved against candida, dermatophytes and mold. Gels and tablets from foot fungus and nail tissue destroy the cellular structure of these parasites the fastest.
Well-known drugs in this group include:
- Lamisil;
- Terbinafine;
- Butenafine;
- Naftifine;
- Exoderil.
Such complexes are also well advertised and can be easily purchased at any pharmacy store. The powerful remedy for nail fungus Lamisil is the most famous of these.
How to choose the best remedy
All of the above drugs for the fungus can be purchased without a doctor's prescription, but this should not be done. The fact is that it is possible to effectively cure a fungus only by knowing the specific type of pathogen, and the patient cannot determine it on his own. Therefore, the best choice would be to seek medical help in a timely manner and undergo diagnostics.


The negative consequences of incorrect diagnosis and violations during treatment can be expressed in the following:
- Usually, with onychomycosis, the course of treatment takes from one to several months. In severe forms, it can take years to get rid of the fungus. Treatment throughout this period with the wrong drugs will not bring a positive result, it will take a lot of time and money.
- If, in the process of self-medication, even effective pills for nail fungus and medicinal ointments are constantly changed, then instead of a positive effect, the parasite, on the contrary, will acquire immunity to substances, and will only intensify.
- After an interrupted course of therapy, symptoms of infection usually recur and the disease progresses even more severely, although recently it may seem that the drug is helping.
These main factors determine the need to contact a dermatologist or mycologist in order for the doctor to prescribe an effective treatment for onychomycosis. However, it also happens that the doctor prescribes several drugs to choose from. Therefore, knowledge of the most common of them can be useful to anyone who is faced with a problem with the health of the nail plates on the feet:
- Mycosan. The serum is applied to the surface of the affected nail. As a good basic effective remedy, it can be used in the initial period of infection. In the later stages, Mycosan is prescribed in combination with tablets and other ointments. The plus is the absence of an unpleasant odor. One package, which costs 500-600 rubles, is enough for a course of treatment (one and a half or two months). An inexpensive drug can also be used as an ointment for foot fungus.
- Lamisil fungus cream is also widespread. It is best to use an effective ointment for toenail fungus in the early stages of the disease, then you do not need to drink a course of tablets. The duration of treatment is about a month, and such an antifungal agent costs about 2,000 rubles. The main advantage is the quick relief of inflammation, irritation, itching and other unpleasant symptoms.
- Healing varnish Batrafen is perhaps the best in its category of varnishes. In a few weeks of use, they can completely cure the initial stage of toenail fungus. This result is achieved using the active ingredient ciclopirox. One tube of the substance for toenails will take 1.5 thousand rubles.


Effective folk remedies
In addition to medicines, it is possible to treat toenail fungus with folk remedies. However, it is still preferable to trust specialists, since:
- the concentration of the active substance in medicines is always higher than in home methods;
- pharmacological preparations for the treatment of infections are specially adapted to maximize the effect on the pathogenic organism;
- treatment of nail fungus with vinegar, iodine, tar and other substances can cause skin irritation and other related complications.
In general, traditional medicine recipes are best used as an additional treatment for an infection on the toenail. Which one is better depends on the pathogen, but several of the most common can be distinguished, the action of which is quite effective.
A common method is kombucha treatment. It is an effective remedy against nail fungus. At the same time, several recipes are popular:
- You can take a two-month tincture of the tea organism and boil it. Then the liquid is brought to room temperature. Before going to bed, cotton wool soaked in this tincture is applied to the infected nail. The bandage is removed in the morning. The softened area of the nail is shortened with scissors and sanded with a file. Then the procedure is repeated again.
- There is another way of using the mushroom itself. A small amount of it is ground into a puree and spread on the infected nail. The procedure is repeated 2-3 approaches daily. This method tops the rating of methods for using kombucha.


Other popular folk remedies are based on vinegar. You can do baths with this substance, and soar your feet. But before the procedure, you should definitely prepare the nail:
- it needs to be sanded with a file;
- cut off the edge destroyed by the fungus;
- soften in hot water.
When using this method, it is important to ensure that the concentration of vinegar in the bath is not high. Otherwise, skin irritation may result. The leg may even be scalded.
And before going to bed, be sure to wash your feet, put on socks soaked in vinegar. In an acidic environment, the spores of microorganisms will die, which will significantly slow down the spread of the disease.
There are also a number of recipes for traditional medicine based on natural birch tar:
- You can smear the affected nail plate with tar soap.
- Another option involves the application of a liquid substance.
- Still grated soap is applied at night, making a bandage or gluing the nail with a plaster. After a few months, this will allow you to forget about the fungus.
The methods of alternative treatment of pathologies on the nails are universal. But nevertheless, in order to improve the results of therapy, it is better to negotiate their use with the attending physician. Only a specialist can tell you the best way to treat nail fungus.
There are many medications available to treat toenail fungus. They differ in the form of release, type of active ingredient, cost and duration of therapy. The best cure for toenail fungus is extremely difficult to find, because each of these types is to varying degrees effective against certain pathogens of fungal infection. Therefore, it is best to entrust the choice of treatment to specialists.
Mukor
This representative belongs to the generic branch of the lower molds of the zygomycete class. In total, the class includes 60 different types of mushrooms. They can be found in the upper layer of the earth, they can develop on food and organic parts. A certain amount of mucor can cause disease not only in animals, but also in humans.
But there are a number of mushrooms that are intended to be used in the production of antibiotics or as a fermenting agent. In production, only those mucor mushrooms are used that have high enzymatic activity.
Reproduction of mucor mushrooms is asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, the shell of a mature fungus quickly and simply dissolves from moisture, while several thousand spores come out. In the sexual form of reproduction, two branches take part: homothallic and heterothallic. They connect to each other in a zygote, after which a hypha with an embryonic sporangium begins to germinate. As a leaven, people use Chinese mucor and snail mucor. Many people call these mushrooms Chinese yeast.


Mukor can cause disease in humans and animals
Living organisms related to saprophytes
Saprophytes are bacteria and microorganisms that feed on the remains of animals and plants. As inferior creatures, almost all microorganisms are safe for humans. But there are some that can be harmful, such as a dust mite. This inhabitant lives on any surfaces, feeds on dust. Another example of harmful bacteria is Escherichia coli, which causes severe pathologies when ingested into a living organism. Causing an infectious disease, the bacillus can provoke pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis - diseases with a high risk of death.
Important! The habitat of the species of protozoa is the dead carcasses of cattle and other animals. Despite the fact that organisms do not feed on living tissues, food must still be organic in nature. Microorganisms never settle in chemicals and other substances - this environment is destructive for them. That is why preventive measures against ticks, E. coli include hand treatment and wet cleaning using soap solutions.
The life cycle of organisms is not complex. In the process of symbiosis, a viable individual is formed, capable of further reproduction by spores.
Differences between saprophytes and parasites

The difference between saprophytes and parasites is more obvious when considering the nature of existence and nutrition. So, fungi, microbes, parasites and saprophytes, characteristic differences:
| Parasites | Saprophytes |
| exist only at the expense of the carrier | do not feed on living organics |
| affect the host's body in a negative way, causing infections, toxic poisoning | microorganisms and bacteria that rarely have a harmful effect on humans |
| a living carrier is necessary for existence: a fish, a person, an animal | enough non-living biological structures |
Regardless of the nature, bacteria, microorganisms, fungi, parasites and saprophytes can be harmful, so prevention, personal hygiene, caution in eating raw food and other precautions will come in handy
Why mushrooms are dangerous for humans (video)
Parasites are lower class creatures of plant or animal origin. The concept itself is translated as "freeloader", which fully reflects the essence of parasitic organisms. Examples of parasites for humans:
- worms (helminths);
- simple / complex viruses;
- fungi (candida).
Organisms can survive only at the expense of the host, feeding on the tissues of a living creature or plant. The habitat is chosen inside or outside the carrier: foliage, fruits, dermis, internal organs, mucous membrane. Almost all types of microorganisms are dangerous to humans. Viruses threaten life, helminths poison the body with toxic secretions, the fungus destroys the microflora, causes necrosis. In some cases, the lack of medical care is fatal.
The life cycle of any species is almost always multi-stage, this is the difference between saprophytes and parasites. The latter have many intermediate stages of reformation. For example, for helminths, an initial developmental environment (water) is required, then an intermediate carrier, and only then the final host, in whose body the full maturity of the worm is achieved.
Fact! When infected with "freeloaders", therapeutic treatment is always required. It can be a folk technique or medical, surgical intervention.
This type of bacteria plays a very significant role in the cycle of nature. At the same time, things that are more or less important for a person serve as the subject for their nutrition.
Saprotrophs play a very important role in the processing of organic residues. Since any organism dies at the end of its life path, the nutrient medium for these microorganisms will exist continuously. Saprophytes produce in the form of products of their vital activity many constituent substances necessary for the nutrition of other organisms (fermentation processes, transformation of sulfur, nitrogen, phosphorus compounds in nature, etc.).
Saprophytic mushrooms
Mushrooms are the oldest inhabitants of the Earth, their history goes back at least one billion years. They are so unusual that for a long time biologists could not decide on their classification and did not know to which kingdom they belong. Indeed, fungi have characteristics that are characteristic of both animals and plants. As a result, they were separated into a separate kingdom.


Fungi are single or multicellular living organisms, heterotrophs, whose cells have a nucleus (eukaryotes). All mushrooms feed by absorbing ready-made organic substances from the environment, preliminarily releasing special dissolving enzymes, that is, digestion occurs outside the body.
By the way of feeding, mushrooms are divided into three broad groups: parasites, saprophytes and symbionts. This division is inherent in other kingdoms as well. Parasites have become accustomed to life on other living organisms (or even inside), feeding entirely on them. Among the edible mushrooms, the parasite is the mushroom known to all of us.
Mushrooms-symbionts, although they live off other organisms, at the same time benefit them by releasing the necessary minerals and recycling waste. Among them are porcini mushroom, boletus, butter dish, camelina, boletus, flywheel and many others.
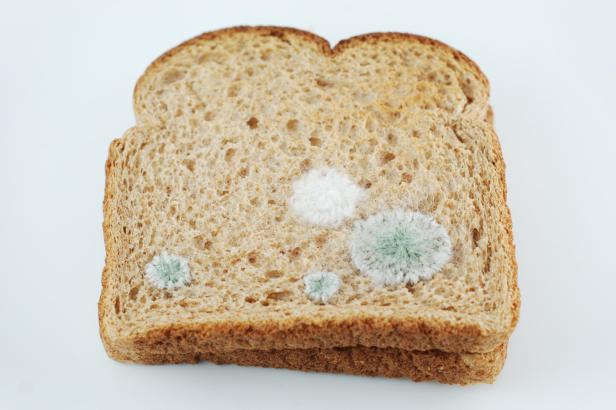


Fungi that feed on organic matter left over from dead animals and plants or their secretions are called saprophytes. Examples of such mushrooms that are familiar to us: morels, lines, champignons, raincoats. Also, this category includes a huge number of molds that infect food.
In order to provide themselves with the necessary nutrition as much as possible, all these mushrooms have an appropriate structure - long and powerful myceliums, completely immersed in an edible substrate for them.
What benefits does
When the symbiosis is not parasitic in nature, its role in the plant and animal world has a positive side and is important for the coexistence of participants in the biocenosis.
So, symbiont fungi form mycorrhiza with the roots of higher plants (fungal root). This association of fungal mycelium and root system brings about a mutually beneficial cohabitation:
- penetrating into the root system of plants, fungi receive nutrients (organic) substances necessary to maintain their own vital activity, which they are not able to synthesize themselves;
- thanks to the overgrown mycelium of the symbiont, plants quickly and better extract the water and mineral nutrients they need for life from the soil layers.
Symbiotic fungi have gained wide practical importance for the agricultural industry, playing a significant role in the growth of many plant crops:
- the absorbing surface of the root system of plants expands due to mycorrhiza up to a thousand times;
- mycorrhizal fungi significantly improve the qualitative structure of the soil, increase its porosity and fertility, thereby having a beneficial effect on the productivity of cultivated plants;
- due to symbiosis, plant cultures better resist pathogenic pathogens, because mycorrhizal fungi stimulate their protective properties;
- under the influence of secreted hormones, the fragile roots of young plants begin to actively develop and thicken, as a result of which friendly and strong shoots appear, the adaptation period is shortened and the survival rate of crops increases, a beneficial effect on the growth of green mass is exerted;
- in the autumn, they take away excess moisture from the plants, which can lead to freezing in winter.
Definition
The word itself is borrowed from another language, more precisely, it is combined from two Greek words: sapros - "rotten" and phyton - "plant". In biology, saprophytes are fungi, plants and bacteria that consume dead tissues of animals and plants as food, as well as products released by those in the process of life. They are distributed everywhere - in water, earth, air, as well as in the organisms of living beings.
Most often, saprophytes are individuals that do not harm their host. A person does not even know how many different microorganisms are constantly on his skin and inside the body, while not causing any disease. However, under the influence of negative factors (decreased immunity, an excessive increase in the number of microbes), everything can change, and saprophytes can cause an infectious disease.
Specificity of nutrition of saprotroph bacteria
Nutrition is the process of storing energy and nutrients. Bacteria require a number of nutrients to thrive, such as:
- nitrogen (as amino acids);
- proteins;
- carbohydrates;
- vitamins;
- nucleotides;
- peptides.
In laboratory conditions, for the reproduction of saprophytes, autolysate from yeast, whey from milk, meat hydrolysates, and some plant extracts are used as nutrient media.
An indicative process of the presence of saprophytes in products is the formation of rot. The waste products of these microorganisms are dangerous, as they are quite toxic. Saprophytes are kind of orderlies in the environment.
The main representatives of saprophytes:
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pseudomonas);
- Escherichia coli (Proteus, Escherichia);
- Morganella;
- Klebsiella;
- Bacillus;
- Clostridium (Clostridium);
- some types of mushrooms (Pénicilum, etc.)
Features of saprophytes
Most of the representatives of the kingdom of bacteria are saprophytic.They are, to varying degrees, demanding on organic compounds, which are of great importance in the processes of their development and life. There are bacteria in nature that can normally exist only in complex sources (substrates), as an example, it can be putrefactive decaying remains of plants and animals, milk, and so on. Thus, for the vital activity of bacteria, some essential nutritional components are required. These substances are:
- nitrogen (or a set of amino acids),
- carbohydrates,
- proteins,
- peptides,
- vitamins,
- nucleotides (possibly components suitable for their synthesis, such as nitrogenous bases, five-carbon sugars).
To meet the needs of saprophytes in laboratory conditions, cultivation is carried out in media that contain plant extracts, serum, yeast autolysates, hydrolyzed meat products.
conclusions
Saprophytic mushrooms are of great importance in nature. Their main role is the processing of dead residues of plant and animal origin. They are widespread everywhere, feed on dead material, depending on the choice of the nutrient medium.
They are similar in structure to simple multicellular or unicellular fungi. There are species that have wide practical application in human life, for example, yeast and penicilli.
Some of these mushrooms are eaten, but some saprophytes are poisonous.
Pros and cons of the Trichomonas reference study
Sowing for Trichomonas is the standard for diagnosing Trichomonas infection. This is a very sensitive study. It is used to confirm the diagnosis or when the microscopic results do not reveal the pathogen, but the patient has clinical symptoms of trichomoniasis.
The analysis allows you to detect Trichomonas vaginalis in people with asymptomatic form of trichomoniasis. The method is included in the list of mandatory examinations of patients who have consulted a venereologist, as well as their sexual partners.


- Trichomoniasis and its causative agent
- Infection symptoms
- Diagnosis of the disease
- Types of analyzes
- Microscopy
- Immunological tests
- Polymerase chain reaction
- What is bacseeding?
- Research Objectives
- In what cases is an analysis assigned?
- General information on treating an infection
Trichomoniasis and its causative agent
Trichomoniasis is the most common sexually transmitted disease. The causative agent of the infection is Trichomonas vaginalis.
Trichomonas is a single-celled protozoan, therefore antibiotics do not act on it. The parasite belongs to the class of flagellates, has cords and a membrane that allow it to move along the surface of the mucous membrane.
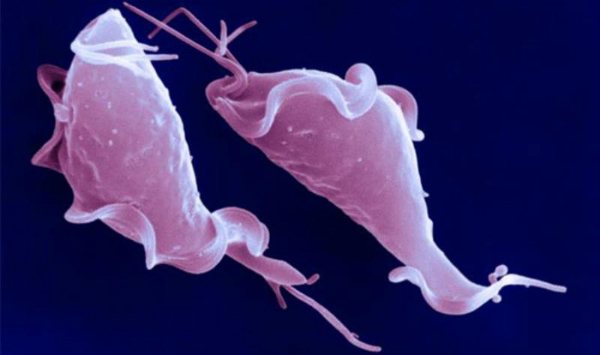

Trichomonas is a typical human parasite. In men, it lives in the urethra, in women - in the vagina and urethra. Under certain circumstances, the protozoan can penetrate into the upper parts of the genitourinary system up to the kidneys.
Trichomonas are not able to live outside the human body, instantly dying upon drying, therefore trichomoniasis is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. It is very difficult to get trichomoniasis in the household. For this you need to use a shared towel or hygiene items.
Infection symptoms
The World Health Organization identifies the following types of trichomoniasis by assigning the ICD 10 code to infections:
- urogenital;
- vaginal;
- Trichomonas prostatitis;
- other localizations;
- unspecified.
The international list does not reflect the variety of options for infection, therefore, practicing doctors use a different classification, dividing the disease into three forms according to the severity of the inflammatory process:
- explicit;
- sluggish;
- hidden.
The acute form of trichomoniasis is best diagnosed, as it proceeds with well-pronounced clinical symptoms: itching in the genitals, dysuria, urinary disorder, discharge from the urethra and vagina.
In about half of cases, trichomoniasis is secretive, without clinical signs. In this case, the patient is a source of infection for his sexual partners. Asymptomatic trichomoniasis is more common in men.


If trichomoniasis is not treated, it becomes chronic, after which it can persist in the body for years. Chronic trichomoniasis is almost asymptomatic.
The disease is difficult to identify, while a person is a source of infection for healthy people. The patient develops a number of serious complications: infertility, prostate tumors (in men), ovarian cysts (in women).
Diagnosis of the disease
The detection of protozoa in the patient's biomaterial is a necessary stage in the diagnosis of urogenital trichomoniasis.
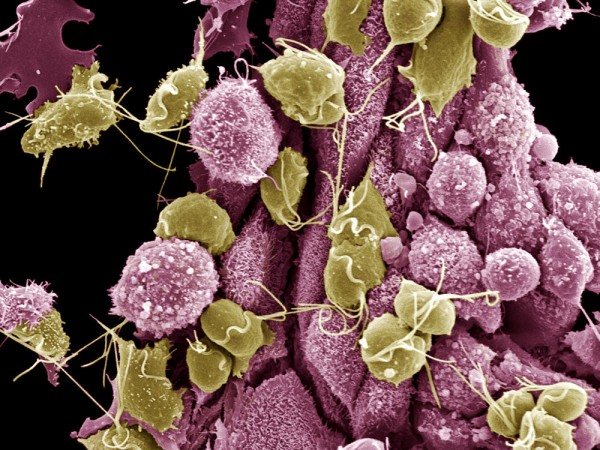

Since the clinical signs of Trichomonas infection may be mild or absent altogether, laboratory diagnostic methods are used to reflect the real picture of the disease.
Types of analyzes
Currently, four laboratory methods are used to detect trichomoniasis:
- study of biomaterial directly;
- pure culture;
- study of the immune response;
- gene.
Microscopy
The microscopic method consists in examining the smear under magnification. Trichomonas can be found in native and stained smears.

Native smears are examined immediately after the selection of the biomaterial - after leaving the human body, Trichomonas, after a few minutes, lose their ability to move and become unobtrusive in the eyepiece of the microscope.
When staining the drug with methylene blue or Gram, Trichomonas die. In such preparations, protozoa are found not by their characteristic movements, but by their shape and structure. Trichomonas have a correctly delineated asymmetric nucleus, colored in the preparation more brightly than the cytoplasm.
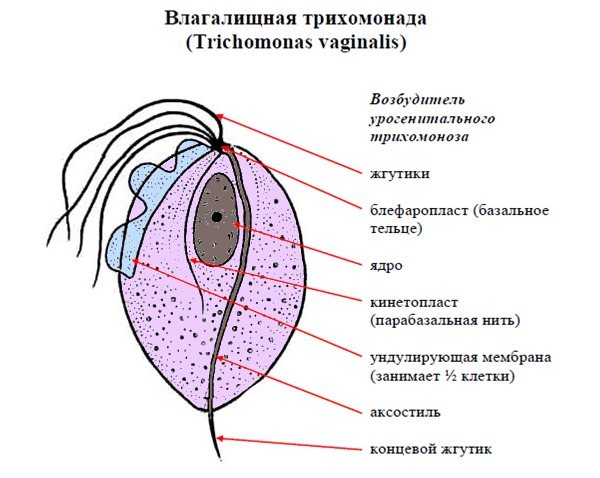

To make the flagella and membrane visible, the preparation is stained according to Romanovsky-Giemsa or Leishman. The sensitivity of microscopy reaches 82%.
You will be surprised how many parasites will come out if you drink a glass of ordinary in the morning ...
The parasites will leave the body in 3 days! You just need to drink on an empty stomach ...
Immunological tests
Immunological methods - direct enzyme immunoassay / immunofluorescence analysis of vaginal scraping - a highly accurate diagnostic method. Its advantage is speed - the diagnosis can be made within one hour.
Direct elisa is possible as a result of advances in cellular technology and other high-tech disciplines. Now ready-made kits for enzyme-linked immunosorbent diagnostics are being produced, which are supplied to laboratories and treatment-and-prophylactic institutions. They improve diagnostic accuracy.


In direct enzyme immunoassay, antibodies to a detectable antigen are used. The biological material to be examined for the presence of Trichomonas is placed in special wells for 15-30 minutes. Then, industrially produced antibodies are added to the biomaterial.
The mixture is kept for 15 hours. During this time, antibodies find their antigens. If there are no antigens in the sample, the antibodies will remain free.
At the second stage, an enzymatic reaction is carried out. Enzymes are added to the wells and wait 30-60 minutes. The enzyme stains the antibody-antigen complexes, after which the concentration of the colored substance in the unstained one is found by calorimetry.
Thus, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay answers the question of what is the concentration of trichomonas vaginalis in a milliliter of biomaterial.
Polymerase chain reaction
Genodiagnostic technologies were widely introduced into laboratory practice in the nineties of the last century. The polymerase chain reaction allows you to find the causative agent of infection in any biomaterial: blood, urine, scrapings, saliva. To detect trichomoniasis, mucous membranes are examined.

PCR is called a smear for latent infections.Diagnostics gives a very accurate result, allows you to identify the genus and type of microorganism. In this way, the treatment can be as effective as possible. The method detects microorganisms, even if there are few of them. Thanks to him, trichomoniasis can be diagnosed at the initial stage of development and quickly cured.
Principle of PCR research:
- a piece of DNA is replicated in the laboratory;
- when the molecule grows to the desired size, it is determined which type of microorganism the laboratory assistant is dealing with.
What is bacterial culture?
The latest diagnostic methods (ELISA, PCR, etc.) make it possible to identify the pathogen, but do not solve the problem of selecting a targeted drug. The cultivation of a pure culture makes it possible to detect protozoa in the human body and study the effect of various drugs on them.

Sowing is the introduction of biological materials onto a nutrient medium for the cultivation of microorganisms contained in a smear. After holding for several days in a thermostat, the formed colonies are microscoped.
Its disadvantages are the high cost of analysis and the duration of the study. How many days is the bacterial sowing done? The diagnosis will take 5 to 7 days.
Trichomoniasis is highly contagious, so a person whose diagnosis is still being confirmed may infect several sexual partners by the day the bacterial culture results are ready.
In this regard, the method of growing Trichomonas in culture has not received widespread use as a direct diagnostic method, but is used as an auxiliary method when the infection does not lend itself to other diagnostic methods.
Advantages of the method:
- false positive result is impossible;
- very high specificity and sensitivity to the pathogen.
Disadvantages of the study:
- duration;
- high requirements for the qualifications of personnel;
- strict rules for the collection and processing of biological material;
- impossibility of automation.
Research Objectives
The purpose of seeding is to obtain a large number of microbes of the same species. In most cases, trichomoniasis occurs in conjunction with other infections of the urinary tract, in particular, with chlamydia. The culture method allows you to detect trichomoniasis and concomitant infections: streptococci, staphylococci, including aureus.
The reliability of the cultural diagnosis of trichomoniasis directly depends on the quality of the culture medium. Abroad, for the cultivation of Trichomonas, the СPLM medium is used.
In the eighties of the last century, Russian scientists developed an improved СPLM environment, which included:
- casein hydrolyzate;
- hydrolysin;
- aminopeptide;
- pharmaceutical waste;
- enzymes of biomass of microorganisms;
- feed yeast.
Modern domestic culture media consist of:
- protein powder;
- potassium salt;
- calcium salt;
- sodium bicarbonate;
- ascorbic and citric acids;
- orotic acid;
- lactate;
- maltose.
The mixture is sterilized, cooled, horse serum and antibiotics are added. Horse plasma is especially important for the reproduction of protozoa. It has everything necessary for the life of Trichomonas: lipids, fatty acids, amino acids, traces of metals.
Currently, ready-made culture media for commercial purposes are produced, which are supplied to domestic laboratories:
- substrate for the detection of vaginal Trichomonas (Omsk);
- the basis of the nutrient substrate (NPO Microgen, Makhachkala);
- SBT for visual diagnosis of Trichomonas vaginalis (St. Petersburg).
In what cases is an analysis assigned?
Growing crops is a reliable but expensive and inconvenient way. Meanwhile, it is widely used. The overwhelming majority of patients with trichomoniasis - up to 73% among patients of both sexes - are identified using the culture method.


How to get tested for trichomoniasis? There is a standard algorithm for examining a patient with suspected trichomoniasis:
- Bacterial culture is prescribed after physical examination of the patient and examination of his native smear.
- If the smear is negative, a rapid antigen test is performed to obtain a result within a few hours.
- If in this case the result is negative, cultivation is used.
About the diagnosis of trichomoniasis in the video:
Thus, cultivation is preceded by a series of faster, but sufficiently informative tests, which make it possible to detect trichomoniasis faster than multi-day cultivation of colonies in an incubator.
General information on treating an infection
The drug of choice for the treatment of trichomoniasis is Metronidazole. The substance is included in group 5 of nitroimidazole, has antibacterial and antiprotozoal activity.
The gynecologist educates about the analyzes in gynecology:
Metronidazole is active against trichomonas vaginalis, amoebas and a number of other pathogenic microorganisms, which makes it possible to use it in combination with antibiotics for the treatment of mixed urinary infections. The drug is incompatible with alcohol.
Metronidazole analogs: Tinidazole, Secnidazole, Ternidazole and other drugs from the 5-nitroimidazole group.
For the treatment of trichomoniasis with Metronidazole, the following regimens are used:
- 250 g in the morning and in the evening for 10 days;
- 400 mg 2 p. 5-8 days per day.
Women are prescribed Metronidazole additionally in the form of vaginal suppositories or tablets.