Honeysuckle is a shrub that starts growing earlier than others. Its delicious and juicy berries contain a huge amount of vitamin C, rutin, B vitamins.
The first 5-7 years bush spends the main strength on growth, so care for honeysuckle should be aimed at maximizing growth.
It is believed that honeysuckle entered the full fruiting phase if 1 kg of berries were collected from one bush. Usually this is 5-8 year of life... The largest yields are from 8 to 15 years.
Seedlings begin to bear fruit in 3-4 years.
Rooted honeysuckle shoots can please harvest next year... From 20-25 years of age, it needs rejuvenation of skeletal branches.


Number of ovary directly depends on the weather. In hot dry weather, the pistils dry out quickly and the flowers fall off prematurely. And in the rain and wind, bees and wasps, which are natural pollinators, do not fly.
Leaves fall early - in mid-September. The dormant period begins in November.
Need to plant honeysuckle two different varieties nearby. The distance between the bushes should be at least one meter.


How to care for honeysuckle
The spring period is a very important stage in the life of any plant, since it is at this time that the beginning of vegetative processes occurs, a set of green mass, the formation of fruit buds, preparation for flowering and laying fruits.
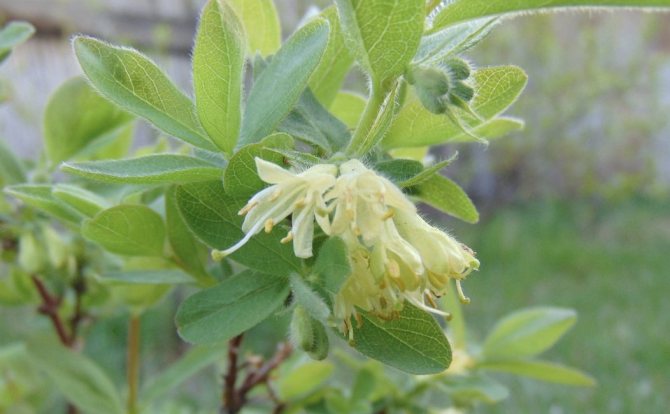


With regard to honeysuckle, this is all the more relevant because the fruiting period of this berry bush is very early: some varieties ripen at the very beginning of summer, even before the first strawberries or strawberries appear on the garden bed.
Thus, it is in the spring that the owner of the garden plot is required to carry out the main set of works that will allow the honeysuckle to actively grow and bear fruit successfully.
Did you know? Not all types of honeysuckle have an edible fruit. Moreover, the famous "wolfberry", which can cause severe poisoning, is the popular name for several types of shrubs, including Lonicera xylosteum, that is, real honeysuckle, or forest honeysuckle.
In particular, at the initial stage of the growing season it is necessary:
- carry out sanitary and rejuvenating pruning of the bush, removing all diseased, frozen and interfering shoots, as well as shortening the main skeletal branches;
- water the plant to stimulate the formation of young shoots. At the later stages of the growing season, honeysuckle will no longer need to regularly moisten the soil, moreover, a tasty and healthy harvest cannot be obtained if the berry bush is often and abundantly watered during the period of fruit formation, but in the first months of spring, watering the culture is simply necessary;
- loosen the soil for a longer retention of moisture in it and remove weeds, which are a place of accumulation of pathogenic microflora and compete with the fruit crop for the feeding area. It is possible to solve the problem of loosening and weeding once for the whole season with the help of mulching - now this method of soil care is gaining more and more popularity;
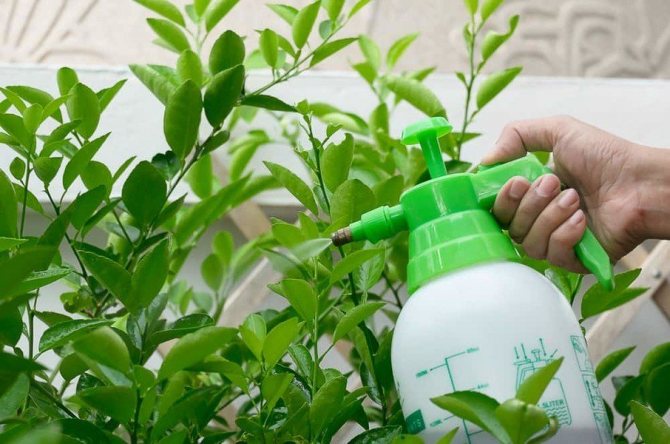
- process the bush from diseases and pests, most of which are activated with the arrival of spring;
- introduce various types of organic and mineral fertilizing into the soil.


It is worth dwelling in more detail on how to properly fertilize the edible species of honeysuckle.
Planting and care rules, breeding methods
A well-lit place is suitable for berry bushes. In extreme cases, partial shade. If you plant a bush in the shade, there will be no bountiful harvest, and the taste of the berries will change. In order for the plant to take root well, one-year-old or two-year-old seedlings are chosen. But it is cheaper and easier to propagate honeysuckle by cuttings or cuttings obtained from your own bush.
The shrub is transplanted in spring or autumn. No special care measures are required, except for watering. The plant tolerates frost well, therefore it is grown even on the shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, where frosts often drop to -50 degrees.
To propagate the bush, the lower branches are pressed against the soil, fixed with brackets and covered with a layer of soil. During the rooting period, only moisture is monitored. After rooting, the cutting is separated from the main bush. Honeysuckle does not need to be covered for the winter due to its winter hardiness.
When the shrub is formed, it must be pruned so that the branches do not thicken. Although the plant is not prone to disease and has a strong natural immunity, without pruning, the berries in the middle of the bush will ripen worse and have a sour taste due to lack of sunlight.
Important! To get a harvest, you need to plant 3 to 4 bushes of berries at once, so that cross-pollination occurs. Preferably, different varieties (edible, of course). Then multiply them to make a plantation of 6 - 8 bushes. In this case, you can count on a good yield.


Seasonal features of feeding bushes, how to feed
Every experienced gardener understands well that the fertilization scheme for any cultivated plant involves not only strict adherence to the dosage of one or another agent, but also the need to adhere to calendar dates when using a certain type of fertilizer - the plant's need for a particular nutrient can change dramatically during the growing season ...
Video: feeding honeysuckle during berry ripening
Before, during and after flowering
For clarity, standard recommendations for spring feeding of honeysuckle can be presented in the form of a table:
| Vegetation period (application time) | What to feed |
| Dissolving buds, budding | Fertilizers containing nitrogen and phosphorus |
| Flowering period | Organic matter: compost, mullein, or humus |
| After flowering | Organic matter: vermicompost, green dressing - green manure, etc. |
As a general rule, it is better not to carry out active feeding directly during flowering and fruiting. An exception may be mildly acting humates, which improve soil fertility, but do not cause additional stress or chemical burns to the plant.
Important! Honeysuckle assimilates fertilizers best within two weeks prior to the onset of active flowering. If you do not miss this moment, the harvest will be plentiful and tasty.
For rooting young seedlings after planting
Young honeysuckle bushes cannot be fed in the first months after planting, as this can cause burns to the fragile root system. Therefore, all nutrients necessary for the plant should be applied to the soil directly during the preparation of the planting pit.
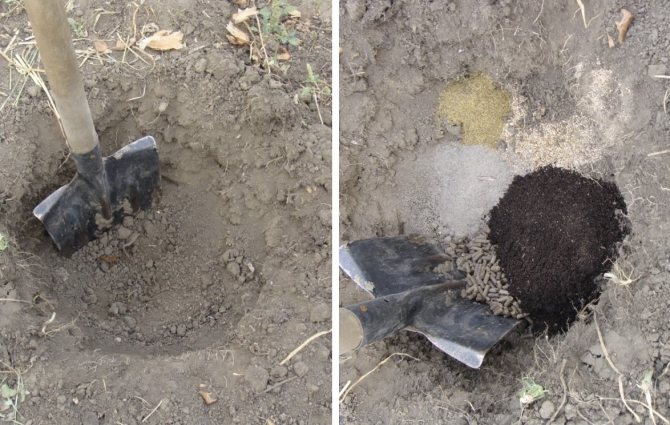


If this condition is met, you can forget about fertilizing for the next 2-3 years.
If the original composition of the soil in terms of acidity and texture is suitable for growing a particular horticultural crop, the top fertile soil layer extracted from the pit, on the advice of experienced gardeners, you need to mix with:
- 20 liters of organic matter (compost or rotted manure);
- 50 g superphosphate;
- 700 g of wood ash.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the composition of the soil when planting is preferable for honeysuckle.
For good growth and branching
The element responsible for the active recruitment of green mass by the plant is nitrogen. That is why it is very important to apply preparations containing it in the spring and it is strictly forbidden to use it in the fall: young leaves and shoots that appear on the bush at the end of the growing season do not have time to fully form before the onset of cold weather and still freeze in winter.


At the same time, honeysuckle spends a large amount of vitality on their growth, which, on the contrary, it is advisable to protect the plant before the onset of frost.
However, it would be wrong to think that nitrogen is the only condition for the active growth of garden shrubs. No less important for the formation of the aboveground part is also a powerful root system, and its strengthening and development, in turn, requires such an element as phosphorus.
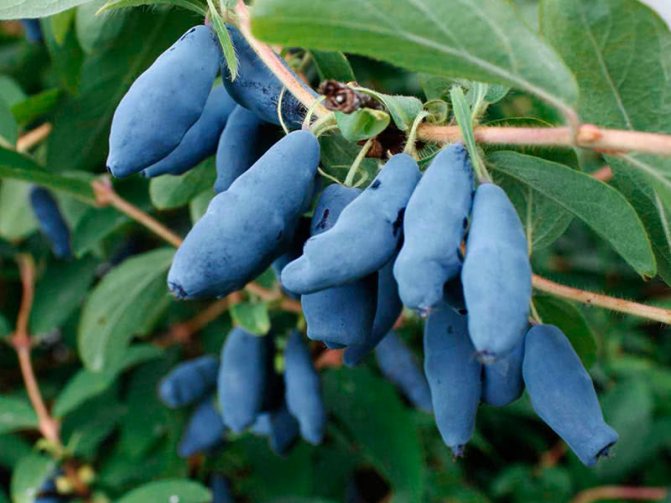
Did you know? In order to distinguish an edible variety of honeysuckle from a poisonous one, our ancestors used a simple, but completely reliable method - they looked at the color of a ripe fruit. Blue or black berries can be eaten safely, but red and orange berries contain glycosides and other toxic compounds that are hazardous to health.
To increase the yield
The third, in addition to phosphorus and nitrogen, an important mineral, without which the normal development of any plant is impossible, is potassium. However, if nitrogen provides intensive vegetation specifically for new leaves and shoots, then potassium and phosphorus in the complex stimulate the formation of other parts - the root system, buds, flowers and ovaries.


For these reasons, it is potash and phosphorus fertilizers that are used individually or in the form of complex preparations, such as, for example, Agrofoska (unlike Nitrofoska and Nitroammofoska, this agent does not contain nitrogen in its composition) that allow you to direct all the vitality of honeysuckle is not for the formation of a huge lush bush, but for accelerated budding, massive flowering and the laying of a large number of fruits.
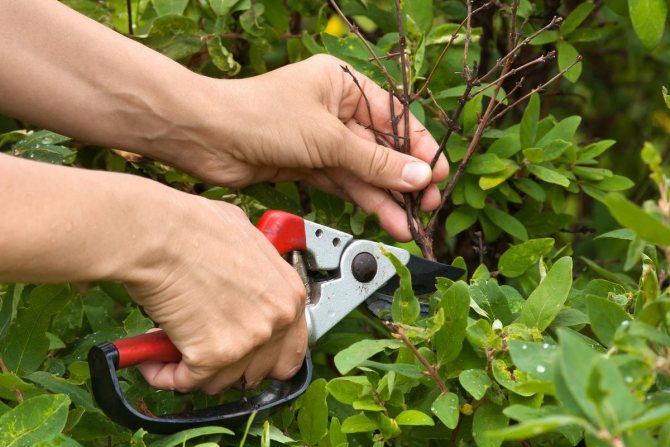
Stage 1. Carry out pruning of bushes
- Sanitary trimming
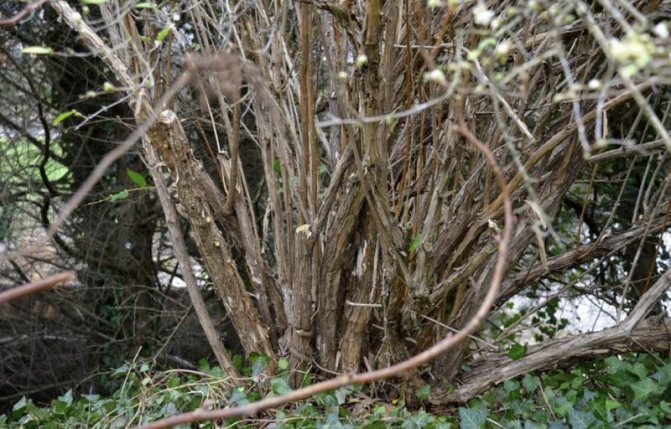
Honeysuckle is an early berry, it begins to ripen at the very beginning of June. During this period, carefully inspect the bushes for the appearance of dried twisted leaves, withered twigs, darkened areas of the bark. These may be signs of illness. Such "unconditioned" must be immediately removed and burned. It is precisely to burn, and not throw into a compost pit, where pathogens will begin to multiply.


If the bush is very ill, you need to cut off the diseased branches at the root. It is not necessary to completely cut out the bush - try to leave at least 4-5 more or less healthy trunks, and apply garden varnish to the sections of the cut - this is disinfection
- Preventive pruning
Honeysuckle branches are usually not too thick. They are flexible, and with intensive growth, they gradually begin to intertwine with each other. Over time, the bush can take on the appearance of a neglected plant. To prevent this from happening, prune branches from time to time.


Young bushes that are not yet five years old do not need to be cut. Let them gain strength, thin young twigs will be filled with juice
Bushes 7-8 years old can already be thinned out. It is better to do this in autumn, in October-November, or in early spring. I prefer the first option, when the crop has long been harvested, and the foliage does not hide old non-bearing branches that are no longer needed by the bush. Without regret, I cut them to the very root about once every 3-4 years.
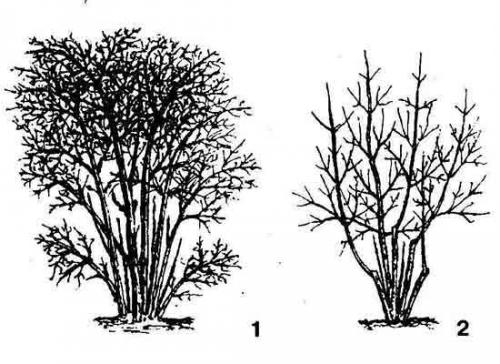

Rejuvenating pruning will provide the plant with better access to light for the next year and the growth of young branches. The photo shows what a honeysuckle bush looks like before pruning (1) and after (2)
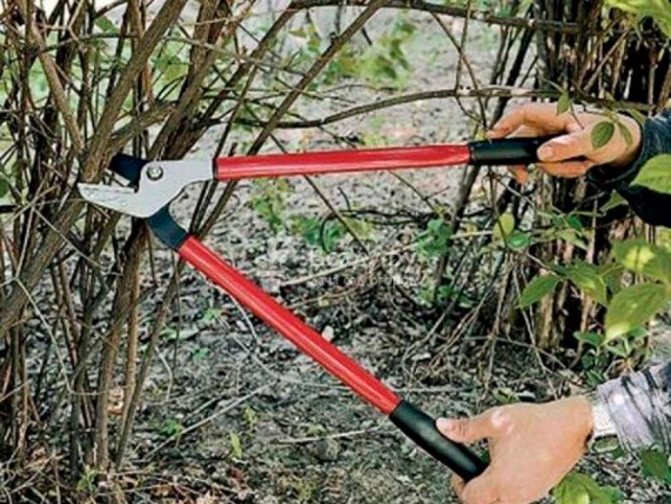


Do not uproot a bush that is too old - it can be reanimated by completely cutting off the crown in the fall at a height of about 35-40 cm above ground level
Fertilizers
Fertilizers are usually classified according to several criteria, but the most common is the division by origin, which can be organic or mineral.
Mineral
Mineral fertilizers are inorganic compounds in the form of salts of certain chemical elements that are necessary for the normal development of plants. Unlike organics, such means allow you to act on the culture in a more targeted manner, getting exactly the result that the gardener needs.
Important! Mineral fertilizers act on the plant faster than organic fertilizers, and have, in comparison with organic matter, a wider spectrum of action.
Modern agriculture cannot be imagined without this kind of intensification and a scientific approach, while the usual enrichment of the soil with organic matter increases its fertility in general, but does not allow normalizing the yield of a particular agricultural crop.


In addition, the stocks of organic fertilizers are depleted, while the chemical industry can produce mineral additives in any quantities.
Mineral fertilizers, in turn, are simple and complex: the former contain only one element important for the plant (potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen, etc.), others are a kind of mineral cocktail. For example, the above-mentioned "Nitrofoska" is a mixture in which three components are presented at once, namely, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
Organic
Until the chemical industry was developed, people used various organic matter to increase the yield of their crops - plant residues, animal waste, sewage sludge and other similar means.
Check out
Why does edible honeysuckle not bear fruit: the reasons for the low yield As it turned out later, all these organic substances in the process of decomposition release exactly those minerals that are necessary for the development of plants - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur, etc.
In addition, biological processes associated with the decomposition of organic matter are also accompanied by the formation of carbon dioxide, which stimulates the processes of photosynthesis in plants.
Finally, additional organic matter promotes the more active development of soil bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on it, which have a beneficial effect on the root system and help it better absorb minerals from the soil.


For these reasons, no matter how convenient and cheap modern mineral preparations are, one cannot count on a good harvest without the additional use of organic fertilizers.
The main types of organic matter used in the scheme for feeding garden plants are:
- manure (cow, horse, pork, rabbit, nutria);
- bird droppings (most often chicken and pigeon, less often - goose and duck);
- feces (contents of cesspools);
- peat (riding, lowland and transitional);
- silt (organic residues accumulating at the bottom of reservoirs);
- compost (rotted plant residues);
- siderates (stems of some annual and perennial herbaceous plants, mainly legumes);
- chopped bark and sawdust.
A separate group of fertilizers, which is not considered organic, although it has a biological origin, should include humus (soil-forming substances) and bacterial preparations (soil microorganisms that stimulate the development of the root system).
You may be interested in information about why young honeysuckle does not take root well and does not bear fruit.
Folk recipes
In addition to classic organic and mineral fertilizers, unconventional means are sometimes used as a top dressing for honeysuckle, which are a kind of product of collective folk experience.
The most common product in this category is regular bread yeast. However, it should be noted that the use of yeast as a fertilizer for the garden has both supporters and opponents.


Yeast does not contain any nutrients for the plant - it only accelerates the decomposition of organic matter. At the same time, since this process with the participation of yeast occurs in an unnatural way, the abnormally quickly enriched soil becomes impoverished with lightning speed.
Many gardeners in the spring sprinkle potato peelings or last year's tops under the honeysuckle bushes. Our ancestors also noticed that starch, especially in combination with ash, stimulates both the powerful growth of young branches and the formation of larger and sweeter berries in plants such as honeysuckle, currants and gooseberries.
To extract the maximum amount of starch from the peel, you can also prepare an infusion.
See also
Top dressing of currants in spring with potato peelings
To do this, cleaning is tightly placed in any container, poured with boiling water so that the water rises by about 1/3 of the volume above the potatoes, and left for 2-3 days.
Then the liquid is decanted and used to water the bush. In the same way, you can use the water in which the potatoes were boiled.
Among other unusual ways of fertilizing honeysuckle, passed by the people from generation to generation, it is worth mentioning the use for these purposes:
- water after washing the aquarium;
- coffee grounds;
- sleeping tea.
First summer berry
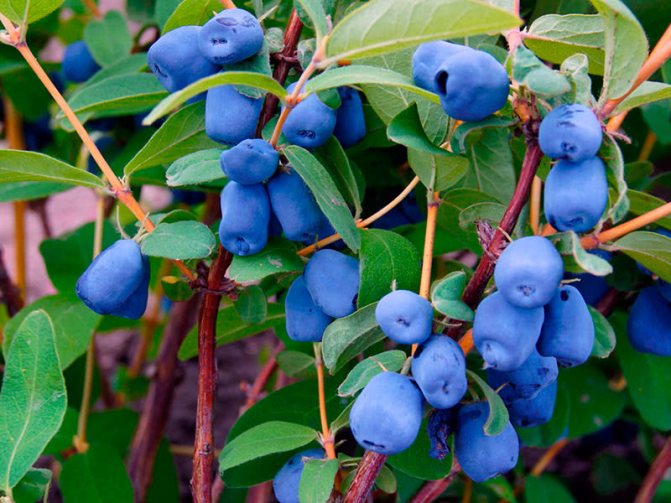
Edible honeysuckle is a vigorous (up to 2.5 m), durable, dense bush with a lot of stem growth. It blooms very early, usually in early May, with beautiful yellow or yellow-green flowers. After 42–45 days, the berries ripen - blue-violet, with a waxy coating, fusiform, cylindrical or pear-shaped. For old varieties, fruits with a slight bitterness are characteristic, new hybrids have a pleasant sweet-sour and sweet taste.
Gardeners are attracted by early fruiting, tasty and healthy berries, easy care for honeysuckle. The shrub is really very hardy, not demanding on the soil. It does not need to be covered for the winter, since the plant can withstand temperatures of minus 50⁰C without any problems, and open flowers retain the ability to set fruit after 8-degree frost.
Note! If we try to give the first strawberries to children and grandchildren, then honeysuckle is a high-vitamin berry, extremely useful for older people. It contains a large amount of P-active substances that have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system, cleanse capillaries, and increase their elasticity.
Types of nitrogen fertilizers and application rates
Mineral fertilizers containing nitrogen in their composition are divided into four main groups, each of which, in turn, is represented by several preparations.


So, the varieties of nitrogen fertilizers can be presented in the form of a table:
| Fertilizer type | Examples of drugs |
| Ammonia | Ammonium sulphate and sulphide, ammonium carbonate, ammonium chloride, ammophos, diammophos |
| Nitrate | Sodium, potassium, calcium nitrate |
| Ammonium nitrate | Ammonium nitrate, lime-ammonium |
| Amide | Urea, calcium cyanamide |
The consumption rate of nitrogen fertilizer when feeding honeysuckle can be seriously adjusted depending on which particular drug is used by the gardener. Accordingly, it is always very important to carefully read the manufacturer's instructions and strictly follow them.

There is another way, but it is suitable only for those who are well versed in chemistry and are able to calculate the amount of pure nitrogen in a particular fertilizer.
In this case, one can proceed from the requirements of honeysuckle in nitrogen, which are determined according to the following standards:
| Method of application | The amount of nitrogen per 10 l of water, g | Consumption rate of working solution, m2 |
| Root dressing | 10–15 | 10 |
| Foliar dressing | 2,0–2,5 | 10–15 |
Potassium
- Potassium performs a number of important functions in the life of a plant, in particular:
- stabilizes the water balance, increases the endurance of the crop in relation to the lack of moisture in the soil and air;
- improves metabolic processes in plant cells, including nitrogen and carbon (overfeeding with nitrogen with a lack of calcium leads to the accumulation of ammonia in stems and leaves, as well as nitrates in fruits);
- improves the taste of fruits (violation of carbon metabolism is the first reason for the weak accumulation of sugar in the berry), and also enhances their aroma;
- increases the winter hardiness of perennial crops (thanks to the same sugar);
- stimulates the processes of photosynthesis;
- activates fermentation mechanisms;
- increases the plant's immunity to certain fungal diseases, in particular, rust, powdery mildew, rot;
- prevents premature ripening of fruits - as a result, their chemical composition becomes more balanced (accelerated fruit formation suggests an excess of harmful phosphoric acid in the pulp).


The most common potash fertilizers are potassium chloride, potassium salt, potassium nitrate, potassium sulfate, potassium magnesium sulfate (potassium magnesium), and potassium carbonate.
At the same time, preparations containing chlorine that is unsafe for the human body should be used in the fall - they are not used for spring and summer treatment. The standard requirement of honeysuckle in potassium is 15 g of pure substance per 1 m², the frequency of application is 1 time in 2 years.
Phosphorus in spring for flowering
Phosphorus is just as important for honeysuckle as nitrogen and potassium. This element stimulates more active flowering, helps to strengthen the root system, and also regulates the respiration of the plant. Phosphorus is a source of fast energy, with a lack of which the shrub lags behind in development, loses its foliage, and delays the formation of the crop.


The most readily available phosphate fertilizer is superphosphate (regular or double). During the flowering period, it is enough to feed the honeysuckle once with a working solution of this drug at a concentration of 1 tsp. 10 liters of water. An alternative option is ammophos (nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer), applied to the soil in early spring at a concentration of 10 g per bush.
Seasonal Honeysuckle Care
Growing honeysuckle - a schedule of seasonal crop care works with a listing and detailed description of all the necessary elements:
| Month | Types of work and frequency | Method | Base substance (dosage / prescription / instruction) |
| March, before the kidneys open | Thinning carried over from autumn (see the corresponding season) 1 time in 2-3 years (see the autumn season) | ||
| April, before the start of sap flow (the length of the young growth is at least 20 cm) | Sanitary pruning (first 4-6 years annually) | Crown formation | |
| Fertilization with substances containing nitrogen | Scattering | Ammonium nitrate (once a year) 10-15 g / 1 sq. M. | |
| Urea (once a year) 8-10 mg / 1 sq. M. | |||
| March, snowmelt | Introduction of mineral solutions | Infusion with melt water, watering, sprinkling, | |
| April, before flowering (due to the fragility of the roots, they deepen by a maximum of 20 cm) | Slurry Annually 1:10 (ratio to water) | ||
| Chicken droppings Annually 1:20 (ratio to water) | |||
| Weeding, loosening, mulching | |||
| April-May, period of flowering and fruit setting | Abundant watering, sprinkling | Water (only in dry springs) - 30-50 l / 1 sq. M. | |
| May | Top dressing | Scattering | Humus 1 time in 2-3 g. 10 l (bucket) |
| Phosphate-potassium fertilizer 1 time in 2-3 g. 100-120 g | |||
| Wood ash 1 time in 2-3 g 0.5-1 l | |||
| June July August | Watering, sprinkling, treatment with insecticides, acaricides | Water Annually As required | |
| June | Fertilization with mineral solutions | Watering | Phosphorus Annually See the composition, dosage and recipe on the packaging of the ready-made mixture |
| Potassium Annually See the composition, dosage and recipe on the package of the ready-made mixture | |||
| Loosening, abundant watering of near-trunk circles - annually | |||
| September (The length of the young growth is at least 20 cm) | Sanitary pruning (First 4-6 years annually) | Crown formation, removal of branches growing inside the bush | |
| November, at the end of the leaf fall | Thinning | Pruning a third of the skeletal branches. Shorten another 1/3 for a strong lateral shoot. Complete pruning of old branches. If the shrub has borne fruit for 4 years in a row or more, the procedure is carried out 1 time in 2-3 g. Branches over 8 years old should be cut at the base, leaving stumps 7-8 cm high. | |
| Anti-aging pruning | The lower part of the honeysuckle bush is bare, the crown has risen higher along the trunk, the berries appear only on the periphery. If the shrub has borne fruit for 4 years in a row or more, the procedure is carried out 1 time in 2-3 g. Hemp should be left 40-50 cm high | ||
| September October | Top dressing | Embedding fertilizers in the root zone of the soil at a depth of 10 cm | Organic mixtures: rotted manure, compost 1 time in 2 g. 10 kg for each bush |
| Superphosphate Annually 100 g / 1 sq. M. | |||
| Potash salt Annually 30–40 g / 1 sq. M. | |||
| November, two weeks before the start of frost | Introduction of water charging irrigation | Water Every year 6–8 liters for each bush | |


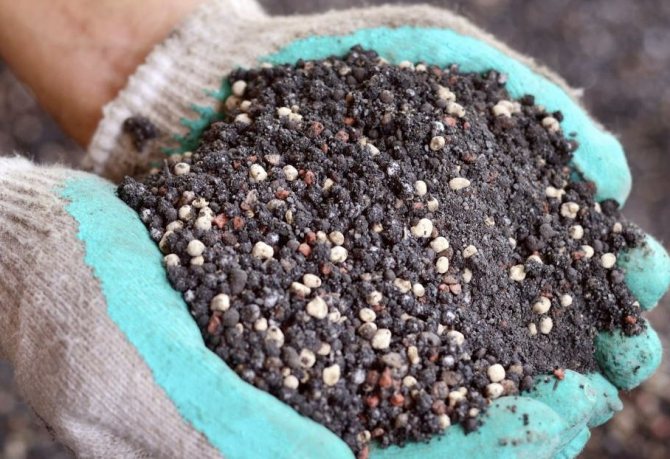
Ash - fertilizer for honeysuckle
Watering
The culture loves abundant watering and does not tolerate overdrying of the soil. During flowering and berry setting, honeysuckle needs a lot of moisture. Its lack can lead to dropping of the ovaries. From the beginning of May to the end of June, four to six abundant irrigations should be carried out: 40-50 liters of water for each plant bush.
Top dressing
The yield and growth of honeysuckle depend on seasonal feeding. Soil fertilization calendar:
| Season | Month | Top dressing | Application rates of the substance or mixture | Method (method) of feeding |
| Spring | March | Urea | 8-10 mg / 1 sq. M. | Root spreading with a depth of 20-30 cm in the soil |
| Ammonium nitrate | 10-15 g / 1 sq. M. | |||
| Nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus salts - amide, ammonia, nitrate | 15 g / 1 sq. | |||
| 10% aqueous solution | Watering, sprinkling, pouring along with melt water | |||
| April | Slurry | |||
| Chicken droppings | 5% aqueous solution | |||
| Phosphate Flour, Phosphate, Superphosphate, Double Superphosphate | 40-60 g / 1 sq. M. | Introduction into the hole by the root method | ||
| 10% aqueous solution | ||||
| May | Humus | 10 l (bucket) | ||
| Phosphate-potassium fertilizers | 100-120 g | Spreading under each bush with a depth of 20-30 cm into the soil | ||
| Summer | June | Urea | 20 g | |
| 20 g / 10 l for 1 bush | Watering | |||
| Phosphorus | Introduced as part of ready-made mixtures | See on packaging | ||
| Potassium | ||||
| July, after harvest | Slurry | 10 l (bucket) | Watering | |
| Nitrofoska (with water) | 20 g / 10 l | |||
| Fall | September October | Potash fertilizers - kainit, sylvinite | 40-60 g / 1 sq. M. | Introduction into the hole by the root method |
| Peat | 10 kg for each bush | Mulching, embedding in the soil by the root method to a depth of no more than 10 cm | ||
| Manure | ||||
| Humus, vermicompost |


Top dressing of honeysuckle
Pollination and cross-pollination
Honeysuckle is cross-pollinated. A single bush will not yield berries. Proper care of honeysuckle involves creating conditions for pollination and cross-pollination:
- At least a dozen different varieties of crops are planted using the alternation method.
- To attract bumblebees and bees at the beginning of flowering, the plant should be sprayed with a sweet solution of honey or sugar: two tbsp. l. 10 liters of water.
- Honeysuckle should be planted in curtains, not in rows. Bees and bumblebees prefer to visit groups of plant bushes.
Seasonal pruning
There are four main varieties of seasonal honeysuckle pruning that are helpful:
- Rejuvenating pruning is carried out in order to strengthen and prolong the life of the shrub. The procedure ensures normal growth of the shoots and improves the general condition of the crop. Old, dry branches are removed.
- Sanitary pruning is the removal of broken, deformed, shriveled, unhealthy shoots that affect the overall health of the crop.
- Formative pruning is carried out in the early stages of culture development.The seedlings are given the necessary habit - a standard spherical shape. In the central part of the bush, thick shoots are cut to the point of lateral growth. Branches growing inward and spreading along the ground are removed. Weakened shoots with low growth are cut off. Decoration is an optional feature of formative clipping.
- Detailed pruning is cleaning the bush from non-viable, spoiled shoots. The procedure is carried out once every 3-4 years to increase fertility.
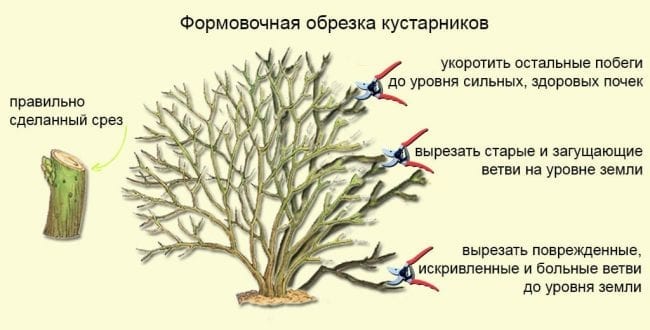

Honeysuckle pruning scheme
Loosening and mulching
Honeysuckle habitat is undergrowth with loose and damp litter. The roots of the culture are located close to the soil surface. Digging can harm them, so the trunk circle is only loosened 20 cm in depth. After completing the procedure, the soil under the bush is mulched. Types of mulching materials:
| Mulch types | Materials (edit) | Layer height (cm) |
| Organic | Wood chips | 3–4 |
| Fallen leaves | 40 | |
| Chopped hay | 5 | |
| Needles - spruce branches or needles | 3 or more | |
| Sawdust | 5 | |
| Peat | 10–15 | |
| Straw | 5–10 | |
| Tree bark | 3 or more | |
| Mowed and chopped weeds: clover, mustard, chamomile | 5–7 | |
| Cake | ||
| Paper, cardboard |
| |
| Inorganic | Tol | Up to 3 (1-2 layers) |
| Roofing material | ||
| Non-woven materials | ||
| Film | Up to 1.5 (1 layer) | |
| Pebbles | Up to 5 | |
| Crushed stone |
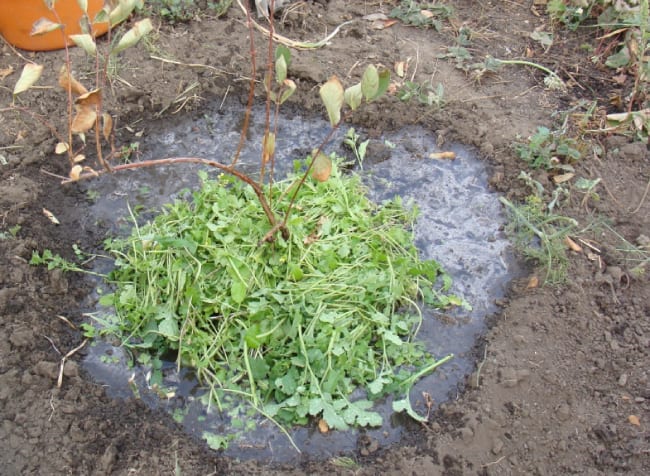


Honeysuckle mulching
Fight disease
To achieve fruiting, honeysuckle must be protected from diseases and pests. Infections and fungus enter the area with soil and planting material, and viruses are carried by nematodes. List of common diseases and agronomic measures to combat them:
| Disease | External manifestations | Control methods |
| Powdery mildew | Milky white bloom forms on the foliage of young shoots | Pruning affected branches, treatment with one of the drugs:
|
Spots caused by a fungus:
| Brown, red, red, olive, white, black roundish spots. The leaf at the site of injury is withered, thinned and dry. | Collection and removal of vegetation residues, preventive spraying of foliage after flowering with one of the preparations:
|
| Mosaic rash virus | Spots of green and white flowers on foliage and fruits of different sizes and shapes. The disease causes damage to the leaves, changes in their contour. | Timely removal and burning of affected shoots |

Terms of processing honeysuckle from pests
Elimination of pests
Description of pests and control measures: treatment methods, preventive procedures, insecticides:
| Insect name | External manifestations | Method of struggle | Funds |
| Spider mite | Causes drying and leaf fall.On the reverse side, a cobweb is visible in which the insect lays eggs. | Insecticide treatment | Fitoverm - 1 ml per 1 liter of water. The shrub is sprayed twice a season. Fufanon - 1 ml of emulsion per 1 liter of water. One seasonal treatment is required at the rate of 200-400 liters of solution per 1 hectare of area. Kemifos - 10 ml of the drug per 10 liters of water. Spraying is carried out 2-3 times a season in dry calm weather until 10 am or in the evening from 18:00 to 22:00. Aktelik - 2 ml of pesticide per 0.7 l of water. Watering at the rate of two liters of working fluid per 10 square meters. area. The maximum number of procedures is two with a ten-day break. Lightning - 2 ml of the emulsion is diluted in 10 liters of water. Two sprays per season. |
| Honeysuckle aphid | The leaves curl up and resemble corrugation. | ||
| Pruning and burning part of the shoot affected by the insect colony | Kinmix - 50 g of chemical per 10 liters of water. A maximum of two treatments per season are allowed. Spark - 1 tablet per 10 liters of water. Watering - a bucket for two hundred parts. Inta-Vir - 1 tablet per 5 liters of water. They are sprayed a maximum of three times per season in cloudy but dry weather. | ||
| Shielder | Bark damage. Strong, repulsive odor. | Annual preventive spraying, insecticide treatment | |
| Fufanon, Kemifos, Actellic | |||
| Zlatka | Turns the sheet into a sieve. The damaged areas take on a dark shade. | Fufanon | |
| Honeysuckle barbel | Gradual drying of damaged shoots. | ||
| Pruning and burning drying branches with larvae | |||
| Injection with an insecticide solution into the holes of lignified shoots | |||
| Collection and destruction of single beetles | |||
| Sawfly | The leaves are roughly bitten, the pest leaves only thick veins and a petiole. | ||
| Annual preventive spraying, insecticide treatment | Kemifos, Kinmiks, Actellik, Spark, Inta-Vir, Fufanon | ||
| Gallica | Galls are left on the wood - growths with eggs. The larvae disrupt the metabolism of the plant: leaves fall, damaged shoots can completely dry out. | ||
| Leaf roll | Dark rot at the sites of infection. | ||
| Honeysuckle moth | Damages the inner side of the sheet, which becomes transparent. | ||
| Autumn moth | Buds and flowers are nibbled. The pest hides between the leaves, holding them together with cobwebs. | ||
| Cabbage scoop | General wilting of the plant. Lead shade on the inside of the leaves. | ||
| Timely removal of cruciferous weeds | |||
| Collection and destruction of single tracks | |||
| Bumblebee honeysuckle hawk moth | Dried buds. | ||
| Annual preventive spraying, insecticide treatment |
How to choose fertilizers for different varieties
The rules for feeding honeysuckle are the same for all varieties of this plant - with the proviso that we are talking about a fruit, not an ornamental shrub, that is, the ultimate goal is to obtain a large harvest of large, sweet and, if possible, dormant fruits, and not just decorate the garden plot ...
Some adjustments to the fertilization scheme may occur depending on such factors:
- the initial composition and state (fertility) of the soil;
- the climatic conditions in which the shrub is grown;
- plant age, etc.
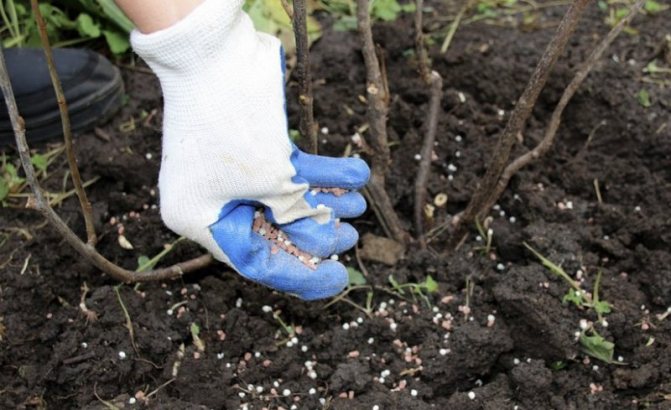


The peculiarities of the honeysuckle variety can only slightly affect the composition and dosage of the feeding. For example, the higher the initial yield indicators, the more intensive the feeding should be; for varieties prone to shedding fruits, you can slightly increase the dose of nitrogen fertilizers, etc.
Interesting facts about honeysuckle
- Vegetation begins at an average daily temperature of +3 degrees Celsius.
- Blooms at an average daily temperature of +9 degrees.
- The ovary almost never falls off before ripening, which makes it easier to care for the honeysuckle.
- Gives growth only in early spring.
- Fruiting annually on the shoots of the last year, so the care of honeysuckle is aimed at lengthening the growth.Young branches form shoots from 15 to 30 cm, on which in the spring there will be 18-50 fruits. And old ones - up to 5 cm and 2-4 berries.
- The flowers of the future harvest begin to form at the end of May.
- Honeysuckle is a long-lived bush. Under favorable conditions and good care, it can bear fruit from 20 to 130 years in one place. Therefore, choose your landing site carefully.


Application methods
Most often, the feeding of honeysuckle is carried out at the root, by watering with a working solution in which this or that fertilizer is preliminarily diluted, or by the dry method - by sprinkling the drug under a bush (urea, ash, etc.), mulching (peat) or embedding in the soil simultaneously with digging (compost, green manure, manure).
In addition, foliar dressing is also used - spraying the working solution on the sheet.
We recommend that you find out how to choose the best place for planting honeysuckle, taking into account the composition of the soil, humidity and lighting.
For this purpose, you can use standard mineral fertilizers (nitrogen, potash, phosphorus), for example, per 10 liters of water:
- urea - 1 tbsp. l .;
- superphosphate - 1 tbsp. l .;
- potassium sulfate - ½ tbsp. l.
But, as a rule, so-called microfertilizers are used for foliar dressing, the purpose of which is to saturate the aerial part of the plant with other chemical elements, in addition to the three main ones.


These drugs include:
| Type of microfertilizers | Examples of drugs |
| Borne | Boric acid |
| Copper | Copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture |
| Zinc | Zinc sulfate |
| Manganese | Manganese sulfate |
| Cobalt | Sulphate, chloride, cobalt nitrate |
| Molybdenum | Ammonium molybdate |
Urgent work calendar
In addition to feeding and pruning, honeysuckle requires such elements of care as loosening and mulching the soil in spring, watering in summer, and advice on pest control will be useful.
Spring. Before bud break
They start thinning the bushes if these works are not completed in the fall.
As soon as the soil thaws, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to the root zone so that they disperse and are absorbed into the soil along with the melt water.
If there is a threat of damage to the shrub by aphids, ticks and other pests, it is recommended to carry out early spring treatment with insecticides. This is done when the average daily temperature is within 5⁰ of heat, and the kidneys are swollen.
The period of flowering and growth of the ovary
In addition to these activities, caring for honeysuckle in the spring includes weeding, loosening, mulching the soil. The latter is especially important in areas with dry summers. A layer of mulch will keep the root system from drying out.
It is advisable to apply top dressing during this period in liquid form, combining with watering.
If the spring is dry, the berry must be watered during flowering and fruit setting. The approximate irrigation rate is 30-50 liters per 1 m² of area. If this is not done, the berries will be small, less juicy, and the harvest will decrease not only this year, but also next year.
Summer period
Caring for honeysuckle after harvest consists of regular watering, if necessary, pest control. From the scale insects, leaf-gnawing insects, immediately after harvesting the berries, plants are sprayed with insecticides, and acaricides are used to combat the honeysuckle mite.
In the summer period, the shrubs are given a phosphorus-potassium supplement.
Advice! Mid-June is the optimal breeding season for honeysuckle with green cuttings. Until autumn, the young seedling will form a viable root system and prepare for winter. The plant grown from the cuttings blooms for 2-3 years.
Subtleties of spring feeding with urea
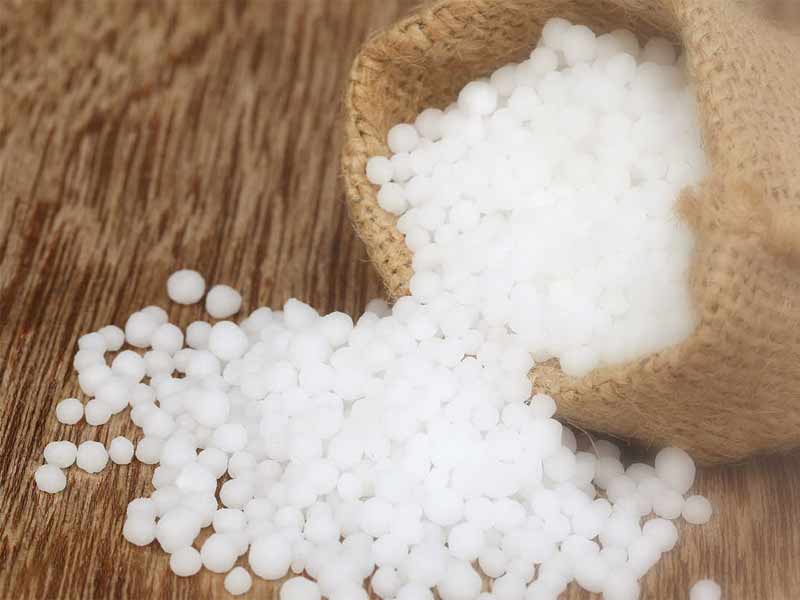
Urea, or carbamide, is the most common nitrogen fertilizer used in small household plots. As we already know, it must be introduced exclusively in the spring, but this can be done in two different ways - in a dry form, simply by sprinkling white granules similar to polystyrene over the feeding area of the bush (inside the trunk circle) or by preparing a working solution and then watering the plant with it ...


The first method provides a more prolonged action of the drug and, of course, is very convenient.The difficulty is that it can be applied only in the very early spring, ideally even before the snow melts, so that then the melt water will gradually carry the slowly dissolving carbamide into the soil.
If there is no snow under the bushes, but the ground is frozen enough, such an effect after warming will also be provided. Choosing the second method, you need to dissolve urea in water yourself. The standard concentration for honeysuckle is 20 g per 10 liters of water.
Did you know? Urea has a pronounced antifungal, bactericidal and antiseptic effect, due to which this drug is widely used in dentistry and some other branches of medicine.
If the urea content in the working solution is increased by about 30 times (500–700 g of the drug per 10 l of water), such a drug will turn from nitrogen fertilizer into a very effective insectofungicide - a drug against fungal diseases and harmful insects. In this case, it should be used not for watering, but for prophylactic or therapeutic spraying of the aboveground part of the bush.
Features of culture
To understand how to properly care for honeysuckle, consider the biological and physiological characteristics of this plant.
- Honeysuckle is a self-fertile, cross-pollinated crop. If the pistil of a flower gets pollen from its own plant, it does not set a fruit and does not give seeds. In one garden, at least 3-5 different varieties of shrubs should grow, otherwise there will be no berries.
- The plant starts slowly. And although the first berries give already 2-3 years after planting, a good harvest occurs only from 6-7 years, and the peak of fruiting falls on 15-25 years of life.
- The yield is growing on non-lignified shoots of the current year. This should be taken into account when caring for honeysuckle and do not cut the tops of the branches in the spring.
- The plant prefers moisture-absorbing fertile loam with good aeration and neutral acidity (pH 7.5–8), loves feeding with wood ash, which slightly alkalizes the soil.
- The root system of honeysuckle is superficial, it is easy to damage it when digging, loosening, in a dry period it requires irrigation. Like raspberries, an optional but desirable element of agricultural technology is the mulching of the trunk circle.
Note! Another feature of honeysuckle is peeling (flaking) of the bark - the older the branch, the stronger. This is not a disease, so you should not be afraid of it.
Is it possible to fertilize with manure
Manure is one of the most common organic fertilizers, the benefits of which are determined by a number of factors.
- In particular, manure:
- contains a large amount of potassium and phosphorus, and these elements are presented in a form that is most convenient for assimilation by the root system;
- rich in nitrogen, which penetrates into the soil slowly and remains in it for a long time;
- is a source of magnesium, zinc, iron, calcium, copper and other trace elements necessary for fruit bushes;
- lowers the acidity of the soil (thanks to calcium and magnesium);
- attracts earthworms, promotes the formation of humus and the development of beneficial microflora in the soil;
- in the process of decomposition, it releases carbon dioxide, which is necessary to improve the water and air permeability of the soil, stimulating the processes of photosynthesis and warming the plant in the cold season.
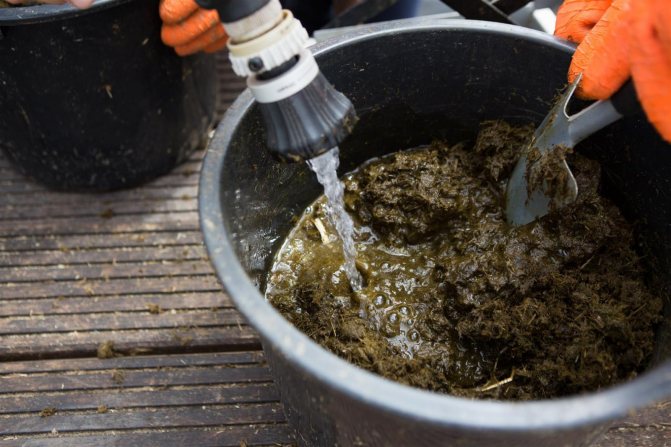


Taking into account all these circumstances, manure is an excellent top dressing for honeysuckle, and the best time to use it is late autumn, when, simultaneously with digging under a bush, you can lay 10-15 kg of rotted organic matter.
Pruning honeysuckle in the fall
If at first the shrub grows relatively slowly, then after 4-6 years, rapid growth begins, and without regular pruning, the shrub simply overgrows and begins to shade itself. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out lightening or thinning pruning honeysuckle, cutting out old and young shoots growing inside the bush
and shading the rest.
Naturally, you should never forget about sanitary pruning, which is necessary in general for all shrubs and trees.
Sanitary cropping includes complete removal of weak, as well as pruning dry and broken off shoots to healthy tissue.


Concerning timing of pruning honeysuckle, then it can be trimmed like autumn (preferable), and in early spring (during this period it is especially convenient to do sanitary pruning, because poorly overwintered shoots are visible, although they are usually few). Moreover, in both cases, it is advisable to cut in a leafless state, however, in spring, the shrub wakes up very early, so you may simply not be in time and damage the swollen buds.
Video: autumn pruning of honeysuckle - preparing for the new season
Features of pruning curly honeysuckle honeysuckle
Curly honeysuckle is most often called honeysuckle. This is a decorative climbing shrub, which is often used by landscape designers for landscaping various low objects - fences, gazebos, arches, gates.
Does honeysuckle love ash
Ash is a natural potash fertilizer, much loved by gardeners for its accessibility and safety for shrubs and other plants. In addition to potassium, wood ash also contains other elements useful for fruit crops, in particular, calcium, iron, magnesium.
Ash also has a pronounced antiseptic effect, it is able to scare away harmful insects and protect the plant from fungal infections. Due to the natural origin of the feeding, it is easily absorbed and rarely causes side effects even in case of an overdose.


You can fertilize honeysuckle with ash using the dry method, sprinkling powdered coal under the bushes in an amount of about 500 ml per plant, but you can also use top dressing in an aqueous solution with the same dosage: the required volume of ash is simply poured into 3-5 liters of water and the resulting a chatterbox around the perimeter of the trunk circle.
How to prune honeysuckle
The first 3-5 years, the bush is not pruned. Then only branches thickening the crown and dried tops are removed. The most effective way to prune honeysuckle in the fall is this pattern.
From the age of 15, the oldest skeletal branches are cut out to a strong young growth at the base of the bush.
Gradual renewal twigs helps to maintain stable yields for many years. Honeysuckle can be propagated by seeds.
Also, with proper care, you can easily grow a large harvest of tall blueberries.
Top dressing of honeysuckle after harvesting with folk remedies
Siderata are often used as a folk remedy. They successfully replace organic matter. After decomposition, the topsoil is enriched with humus. Peas, mustard, clover and other similar crops are sown as siderates.


Siderata are mowed and buried under bushes, where they decompose.
Sowing is carried out immediately after harvesting. The grown green manure is mowed, buried in the ground to a shallow depth, so as not to damage the roots. However, the best option is not to bury, but to cover the spread tops with soil on the trunk circle.


Potato peels are rich in nutrients
From folk remedies, they also use a decoction based on potato peelings. Ash is added to it, insisted for about 2 days. The finished solution is poured into a hole dug around the base of the bush.
Features of preparation for winter


Fall pruning as part of winter preparation should be done right on time. If the shoots are cut before frost, in warm weather, buds will begin to develop, which will subsequently freeze out in winter.
It is imperative to provide for the likelihood of damage to the shrub by rodents and birds. We advise you to focus on forecasts of weather forecasters: the more snow there is, the more difficult it will be to find food for these representatives of the fauna.By covering the honeysuckle with a net or a synthetic bag, we keep both the bark and the kidneys intact. And for birds in very cold and snowy winters, you can put separately, away from honeysuckle, feeders with appropriate bird food.
How to choose an autumn feeding for honeysuckle for the winter
To feed the berry, experienced gardeners make up their own fertilizer recipes. They observe the condition of the plant, take into account the varietal peculiarity, know the composition of the soil where the honeysuckle grows. It is easier for beginners to feed the culture with ready-made complexes offered by retail outlets.
From mineral complexes for honeysuckle, you can purchase phosphorus-potassium fertilizer
When choosing top dressing, first of all, bets are made on organic matter. It is enough just to scatter it under the mulch bushes. The best is humus obtained from horse manure. But not every gardener has access to it. Organics can be purchased at the store. For example, bone meal is a fluoride fertilizer. Wood ash is used to replenish calcium. It is easy to get it yourself by lighting a bonfire from cut branches of trees.
To feed the honeysuckle in the summer, choosing the period immediately after the release of the berries or in the spring with the onset of awakening, you can use mineral complexes. They are better absorbed during the growing season. Preferred potassium monophosphate, Diammofoske or other complex fertilizer. It contains phosphorus and potassium of the required proportion.
Attention! In order not to be mistaken with the choice of the complex, the packaging should be marked "Autumn"
It is better to dissolve any mineral complex with water and water the honeysuckle with a ready-made liquid. You can feed the berry with dry granules. They are brought into the ground. With each watering, the dry granules gradually dissolve, providing the berry with useful substances for a long time.
Time and method of autumn vaccination
In the fall, honeysuckle vaccinations are carried out after the fall of the leaves, so that the scion has time to take root, but does not grow and does not give new buds. This procedure is carried out according to simple instructions:
- Cut off the scion and rootstock using a sharp tool. The cut should be done obliquely.
- Tightly connect the scion and rootstock, securing the junction with tape.
- Cover the top with foil and a sheet of paper.
- Wrap the last layer with twine.
Vaccinations can be checked after 3 weeks.
When is the best time to fertilize
Honeysuckle begins to grow in early spring: buds open, buds bloom. And with the appearance of the first green leaves, it is necessary to feed with nitrogen-containing preparations.
After flowering, honeysuckle is watered with vermicompost infusion, after picking berries it is fed with ash. The last time fertilization is applied is in late autumn.


Use dry or liquid biohumus
The difference between dressings for decorative and fruit species
Ornamental shrubs do not need an annual phosphorus supplement. Mineral nutrients are introduced into the soil in the following order:
- end of March - root potato broth 1 time (optional);
- mid-April - nitrogenous solutions are applied once every 2 weeks for a month for better flowering;
- end of June - phosphorus granules 1 time (optional);
- end of August - potash mixtures 1 time.
Fruit crops need phosphorus, as it is involved in the growth and ripening of fruits. Mineral nutrients are added according to the above technology with the following amendments:
- end of June and beginning of July - phosphorus supplements 1 time in 2 weeks for 1 month.
Organic fertilizers are not mixed with mineral fertilizers. Transfer from one substance to another is carried out with the onset of a new vegetative season.
How to feed honeysuckle for a good harvest: timing of fertilization
Plants are fed according to their individual needs. The schedule is rigidly tied to the vegetative processes occurring in the bush during the season:
- The beginning of April and the middle of May are the phase of active growth of green mass, the laying of flower buds. During this period, the perennial needs mineral nitrogen fertilizers.
- June is a period of active flowering, the formation of berry ovaries. The beginning of summer is the time for phosphate fertilization. Ornamental shrub owners can skip this phase.
- Mid-August and early September - rooting of the bush. At the end of August, most honeysuckle varieties come out of the fruiting stage and prepare for wintering. During this period, potash fertilizing is necessary.
Honeysuckle is a thrifty crop and does not require a lot of nutrients. She needs 4 baits per season, 2 of which are nitrogen ones from April to the end of June.
Video with tips for resuscitating a plant in spring.
Do I need to feed honeysuckle
Like many berry bushes, honeysuckle is quite unpretentious. For good fruiting, she needs light and proximity to honeysuckle bushes of other varieties. In hot areas, additional watering will also be useful.
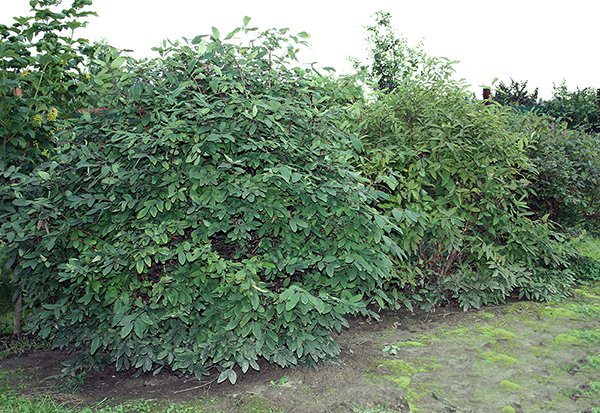


Do not forget to plant several honeysuckle bushes nearby - without cross-pollination, the berries will not be able to set.
Many gardeners, after planting berry bushes, leave them alone for several years, believing that the bush will find its own food. From such care, especially in arid regions, almost all plants are only fighting for survival, and not working for the harvest.
Since the root system of honeysuckle is superficial and shallow, it must be fertilized regularly for good growth and fruiting. Therefore, gardeners who want to get up to 6 kg of useful berries from a bush should make it a rule to feed the plants at least three times during the growing season.
Pruning
The pruning process is a significant period in the process of growing a shrub, which has its own characteristic features. The cut for honeysuckle is made according to - everyone in connection with the species. Bushes that are destined for the fencing site, in particular, have a need for rejuvenation. Pruning gives beautifying species an exquisite exterior type, can help a tense increase in greenish people, heals and provides power. In this case, it should be carried out any season. During the year, cut only the protruding branches, which destroy the outer type. The first time the bleed is carried out up to the required volume, then according to the lifting edge in order to strengthen the figure. In addition, it can help the bushes to bloom most vigorously. For edible species, a bleed is necessary for the best fruiting.
Better not to prune edible honeysuckle in any way for 5-7 years. After all, this segment must be treated very carefully, since the bush grows for a very long time.
Autumn rejuvenation of honeysuckle. After 8 years of existence, it should be rejuvenated through the season, paving the presence of this active removal. In order to rejuvenate edible honeysuckle, it is necessary to prune the upper old part of the structural branches, in addition to remove the dried branches. The cutting should be carried out only in the autumn time and after that, as well as the bush has thrown off all the leaves without exception. In order to navigate this issue not to make mistakes, it is more correct to watch the video material according to the segment of honeysuckle in the autumn.
When to prepare honeysuckle for winter by region


The preparation of honeysuckle for winter may differ from region to region, and the difference may also depend on the type of shrub. It is best to prune shrubs when the night temperature drops to 0 ° C and below, and honeysuckle is losing leaves. This usually occurs in November.
For each plant variety and each regional climate, select the thickness of the mulch cover.The northern regions should take into account that no less cold (and often more) the plant can be harmed by rodents and birds, which, due to a meager winter diet, gnaw the bark and peck the buds of the bush.
In outskirts of Moscow


The middle strip is not so severe in winter as to cover all honeysuckle varieties without exception. It is recommended to cover the curly variety of shrubs and non-frost-resistant ornamental varieties with mulch.
In the Urals
In the Urals, before winter, honeysuckle with low frost resistance is covered according to the usual scheme, and the winter care itself consists in adding snow if its natural layer can decrease.
In Siberia
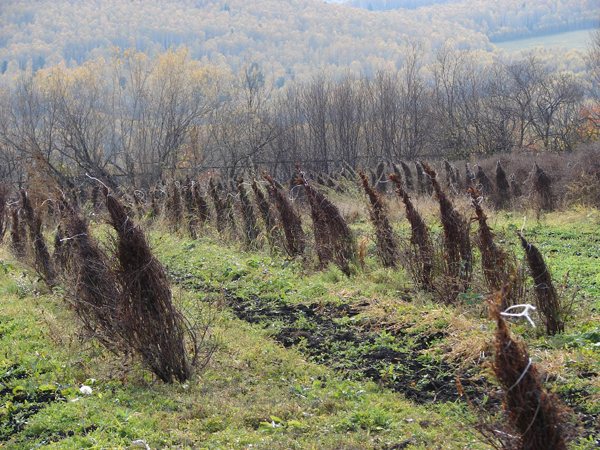


In Siberia, there is no shortage of snow, and this requires a garter of honeysuckle bushes in one bunch. This will prevent the branches from breaking off under the weight of the snow cover. Winter birds will not be able to peck buds from branches if a net is thrown over a connected shrub from above. You need to protect yourself from rodents with the help of special poisonous baits - they are laid out around the honeysuckle.
In the Leningrad region
The wet autumn of the Leningrad Region reduces the watering requirements; otherwise, only varieties that are not resistant to frost are covered with traditional mulch.
Folk remedies as top dressing after winter and another flowering
If there are no suitable drugs at hand, you can resort to proven folk remedies. These include:
- Sleeping coffee grounds as fertilizer are a rich source of nitrogen. Before feeding the honeysuckle, the soil is loosened and irrigated with water. Only natural ground coffee is suitable as a top dressing. The chilled drink is poured into the well in the calculation (100 ml per 1 bush) at intervals of 2-3 days for 2 weeks. The dry mixture is added dropwise next to the roots or poured around the tillering node.
- Boiled potato water contains the starch needed to feed the honeysuckle. Shrubs and seedlings are often fertilized with them after winter, when the plant needs additional energy to activate vegetative processes. For this, the cooled broth is poured under the root once a week for a month.
- Aquarium water has a neutral pH and has a beneficial effect on the general condition of the shrub. Due to its high concentration of nutrients, it is able to support a weakened plant in summer. It is recommended to fertilize honeysuckle with aquarium water after flowering 1-2 times.


Thick ready to use
In addition to the listed funds, gardeners use yeast, tea leaves, banana peels.
Cherry care in autumn, including processing and feeding trees
When the leaves fall off the cherry, they carry out sanitary pruning of branches, removing diseased and damaged branches, covering the cut site with garden pitch;
Preparing cherry tree trunks for winter
To get water directly to the roots of the cherry, dig shallow trenches around the perimeter of the crown, or stick pipes into the soil.
Autumn cherry care includes:
Cut off branches that have stopped growing to transfer to strong branches or tops located closer to the base of the bush.
- The best time for pruning honeysuckle is autumn, when the foliage has fallen, and the structure of the bush is well traced. The movement of juices in honeysuckle begins very early, if you do not have time to remove excess or old branches in March, you will have to wait until October. But dry shoots can be removed at any time. Honeysuckle in the first two or three years of life does not need much pruning. The development of shoots at this time is due to the upper buds, and the bush increases the green mass. Then the elongation of the branches gradually stops, and they begin to overgrow with lateral branches.
- The planting site is thoroughly watered.
- Saplings with a root system protected by a clod of earth and a container can be planted in the garden from April to October, without fear that the plant will be difficult to acclimatize and get sick.
- This year some creepy aphid covered the honeysuckle, they didn't even eat blackbirds)
- Tatiana Shcherbakova:
- And how do you protect honeysuckle berries from birds that pick every single berry in one sitting?
• Buy bushes that are 2 or 3 years old. In this case, after a couple of years, honeysuckle will give the first good harvest. • Branches should be flexible and dry, with no visible signs of damage. Be sure to inspect each bush carefully (both shoots and roots). • Do not be embarrassed by the appearance of seedlings if you see that their bark is peeling. This is a cultural feature. For which, by the way, people called honeysuckle "shameless". • Pay attention to the development of the root system (the denser and more massive the roots - the better) and the presence of buds on the branches. Discard stunted bushes without buds immediately. • Buy seedlings of different varieties (at least three). Subsequently, you can propagate the honeysuckle yourself, by dividing an already fruiting bush, by layering or green cuttings. By the way, honeysuckle also propagates by seeds, but I do not recommend using this method. It is quite lengthy and time consuming.
Clean up and cover up cracks and wounds in the tree, from which gum flows;
After digging the trunk circle, you can start feeding the cherries with fertilizers, and the introduction of nutrients can be carried out at the same time as watering. According to horticultural experts, feeding cherries in the fall is extremely important for their proper growth and development, and also contributes to obtaining a wonderful harvest.
Processing of near-trunk circles under trees;
Pruning dry branches to live, undamaged tissue.
It is generally accepted that from the age of 3, a properly formed young bush practically does not need any intervention in its growth.
How to feed cherries in autumn?
The soil under the planted bush is mulched to prevent rapid evaporation of moisture.
The seedling, carefully transferred to the planting hole, is quickly accepted and does not require, except for feeding and watering, any special care measures. If honeysuckle with an open root system is to be planted, then the most favorable time for this is the period from the second half of August to October. This is due to:
PLEASE SAY: HOW MUCH TIME IS NEEDED, APPROXIMATELY, FOR HONESTONE BEGINNING TO GIVE FRUITS STARTING FROM BREEDING AGE WHICH SELL? and what natural fertilizers does she like (for example, currants like potato peels) and honeysuckle?)))) Depends on the variety. I have Rebekah (Poland) - two years later there were berries. It grows on bellies)) Honeysuckle loves loose moist soil with peat. In nature it grows in floodplains, receives a lot of substances when rivers overflow. Loves fishmeal, just bury it from cats. Put rotten when planting. Select large-fruited varieties. Please answer my question: Is it necessary to form honeysuckle? Rosaland is certainly needed. Tell me what kind of bone the honeysuckle has and if we sell 2 varieties, this is enough for a good harvest or you need more different varieties
Edible berries contain selenium, the element of youth, iron. Lower blood pressure.
- Old tulle, tulle and tulle again, throw on the bush and tie at the bottom. Otherwise, starlings (smart birds) will creep up below and feast on. The gauze is heavy.
- Planting honeysuckle
- All plant residues, including fallen leaves, cut branches and diseased fruits, are removed from the trunk circle and destroyed;
- It is advisable to have time to make the last fertilizing of the cherry for the season at the beginning of autumn - feeding the tree later, you thereby increase the period of its sap flow, and as a result, the cherry can poorly endure the winter.
Autumn processing of cherries against pests and diseases
Water charging irrigation;
Places of cuts of large branches must be treated with garden varnish.If the bush is running, and thinning is not possible, it is worth removing the entire crown above 50 cm from the root collar in order to start the formation of honeysuckle again from the next season.
But if initially the plant had more than five zero-level shoots extending from the root, you will have to cut out the extra branches earlier. If this is not done, the shoots will begin to weaken and dry out on their own from the lack of light. Removal and pruning on honeysuckle in the fall are subject to:
- Spring planting of honeysuckle is possible only if the plant enters the growing season late. Most often these are decorative species, for example, alpine honeysuckle or small-leaved honeysuckle. It is better not to disturb fruiting varieties in spring. Caring for honeysuckle, planting fell on the time of revival of the kidneys and the beginning of growth, it threatens with serious complications.
- The end of the growing season;
- To wake up the buds, now it is better to introduce nitrogen fertilization, as mentioned above (urea, saltpeter) and then phosphorus and potassium for fruiting ..
- Gulya Pimanova:
Thanks for the article! She grew up in the North, ate honeysuckle wild, large, sweet! I planted it on my site (Chernozemye), a shallow, bitter sea, but greenery !!! I will look for adapted varieties.
Prepare your tree for winter
Although honeysuckle is a very unpretentious plant, it still requires attention. She loves well-warmed, fertile soil and does not like the wind very much; loves moisture, requires a lot of sun, but the lower branches should be in the shade (so, in general, it turns out, with a slightly thickened planting). When looking for a place for seedlings in your garden, consider these factors. You need to plant it in late May - early June, and if you want to plant it "in winter", then plant it no earlier than mid-September.After the first frosts, the cherry bush and its near-stem circle should be sprayed with a 5% urea solution - this is a high nitrogen fertilizer concentration destroys a large number of pests, fungal and infectious pathogens and prevents their reproduction.
Photo of cherry wood processing
Fertilization;
Phosphate-potassium fertilizing in autumn
Autumn fertilizers can be applied starting in September. The most common of these are superphosphate and potassium sulfate. Consumption rates per square meter are indicated on the packages. So, superphosphate will need 30 g per 1 m², and potassium salt - 20 g.
The rates are indicated for the entire season. Reduce them if phosphorus and potassium were included in the spring feed.
You can replace these chemicals with wood ash in the same doses as in the spring. In addition, there are ready-made complex mixtures for the fall. Such fertilizers are also produced under the already familiar Fertik brand. They are dominated by potassium and phosphorus.


Fertik's fertilizer composition for autumn: a large proportion of phosphorus (P) and potassium (K)
Fertika is not the only brand of ready-made complex mixtures; in stores you can see equally well-known ones: Agricola, Clean Sheet, Fasco, etc.




















