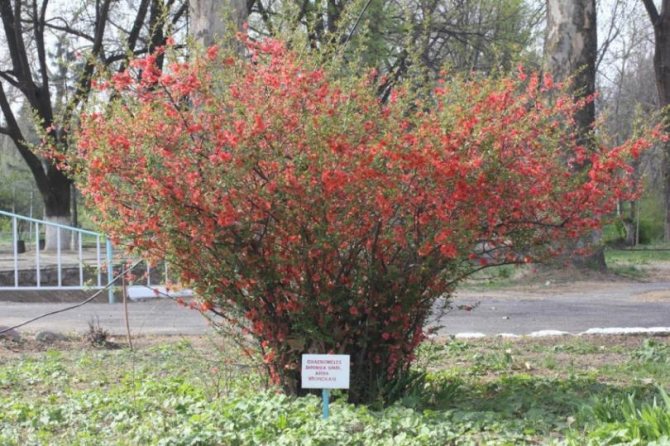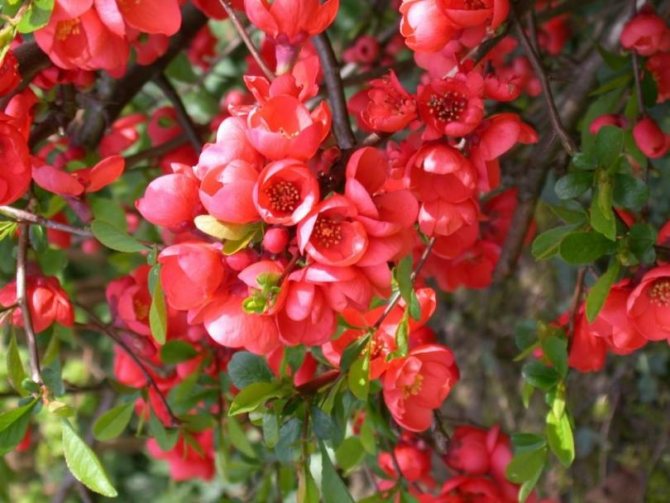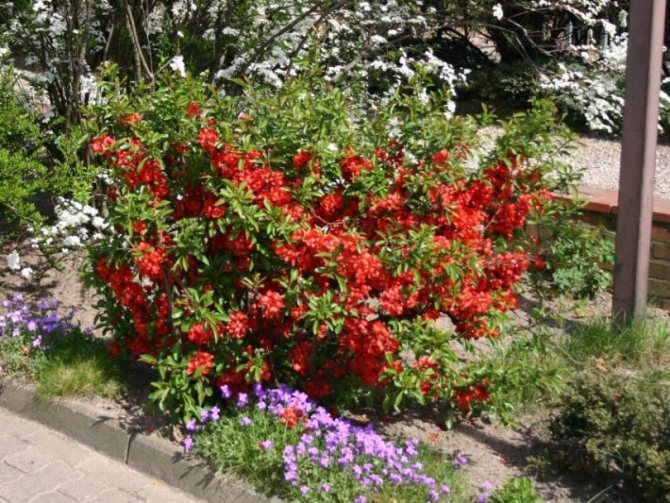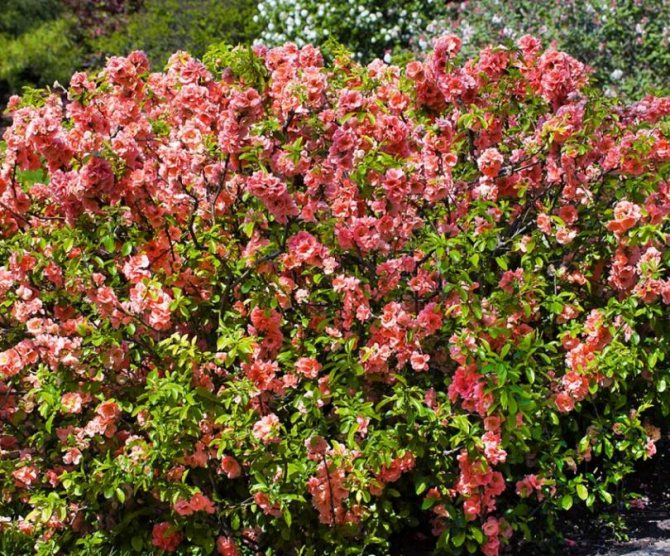
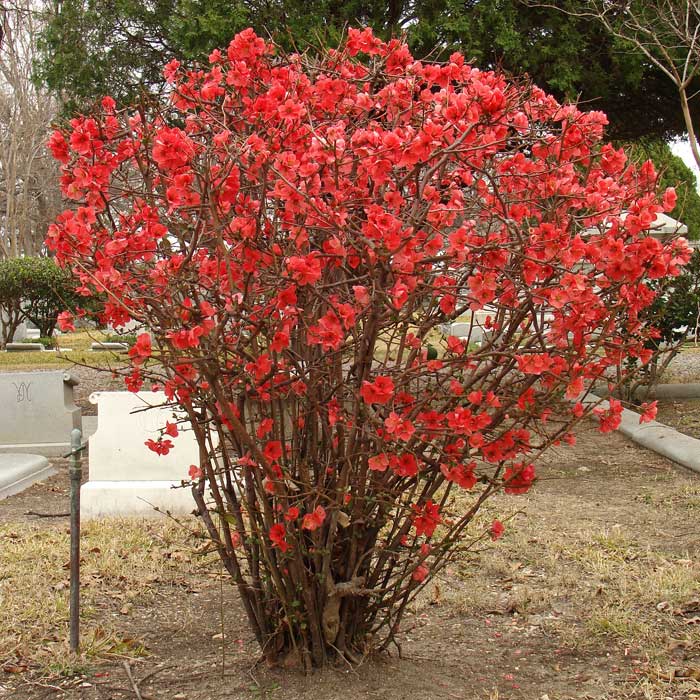
At home, the height of the Japanese quince reaches three meters, in the Moscow region, the shrub often grows by 1–2.5 m. Distributed from East Asia, the shrub is prized not only as an exotic fruit plant, but also for its wonderful decorative qualities. The culture blooms beautifully, is unpretentious to care, easily adapts and grows in a difficult climate. It is easy to plant and with minimal maintenance you can expect excellent results.
Characteristics of Japanese quince
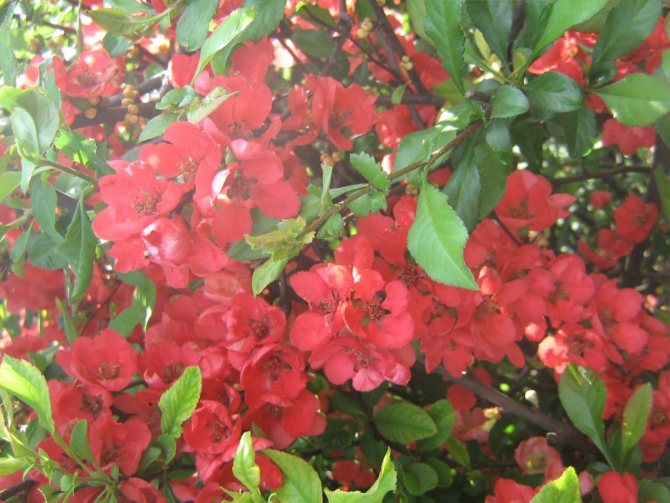
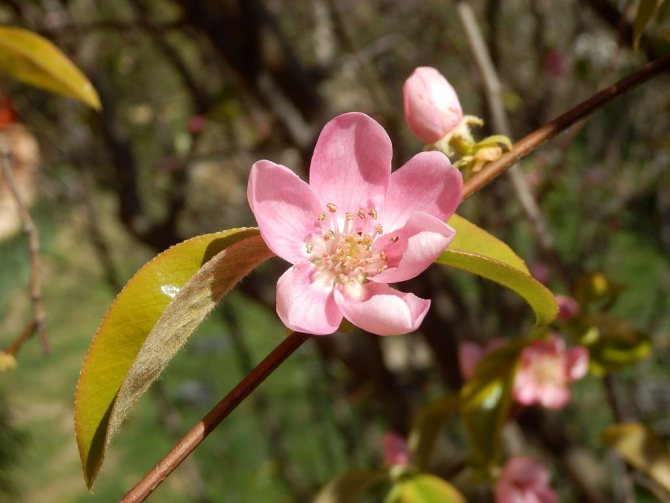
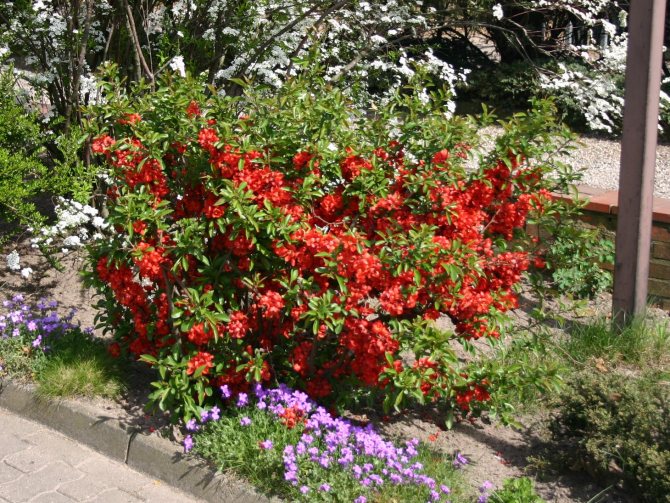
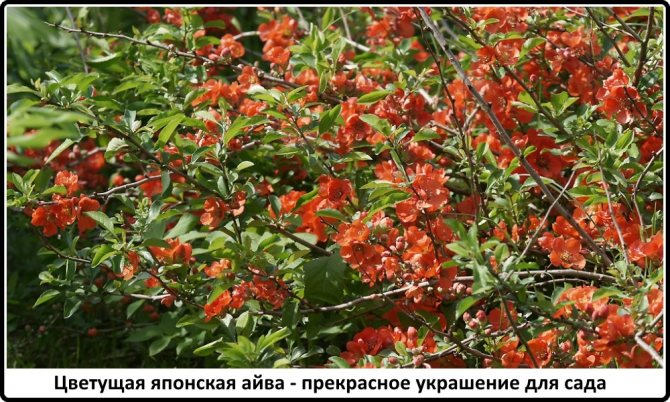
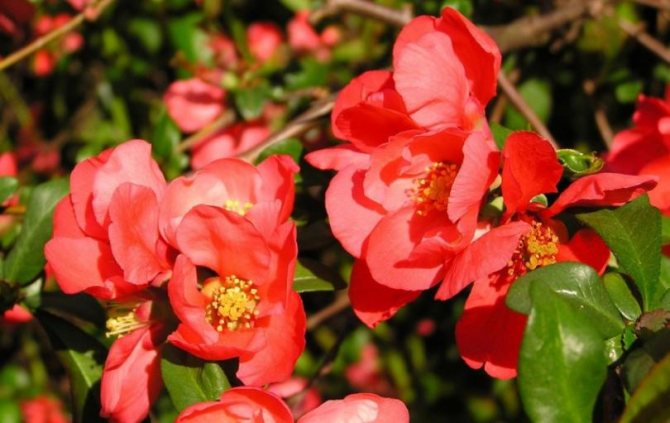
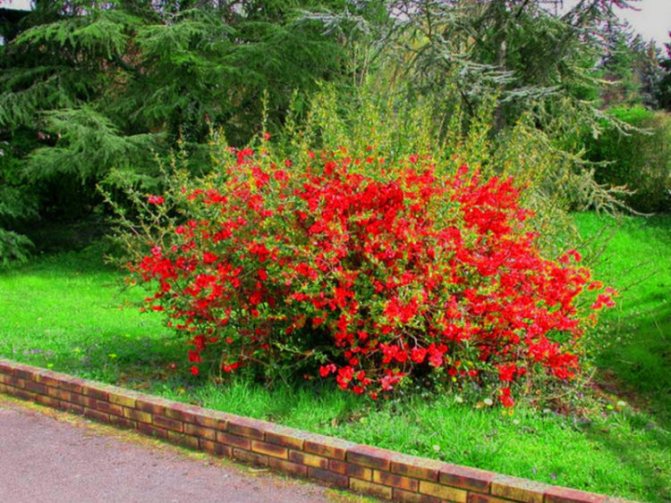
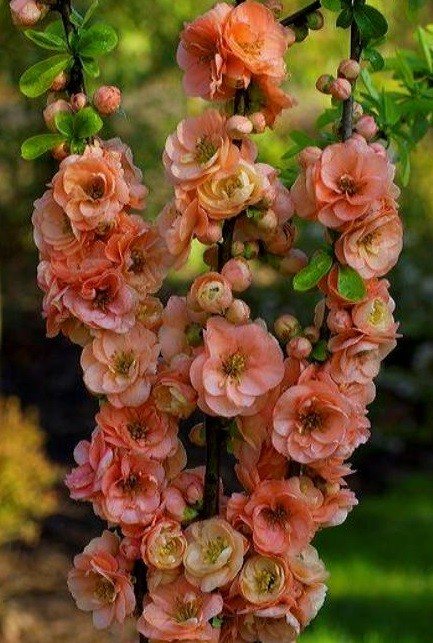
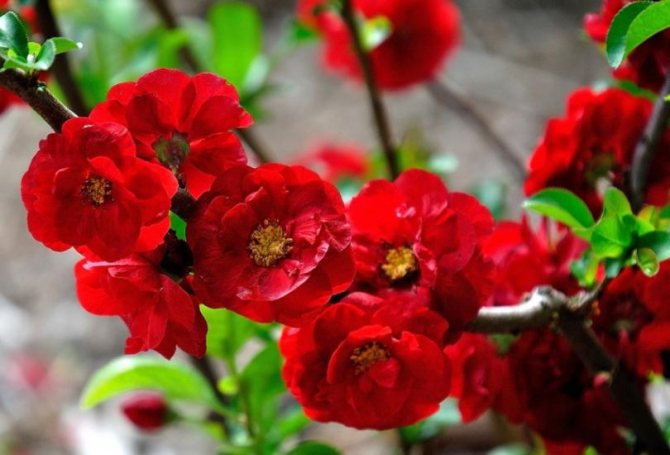
Among other plantings, chaenomeles bushes stand out due to their bright colors. They simultaneously serve as a decoration of the garden, blooming up to 3-4 cm in diameter with flowers, very often of original colors, with double petals. The shade, like the shape, mainly depends on the variety, therefore, when choosing plantings in order to make it dominant on the site, this factor must be taken into account.
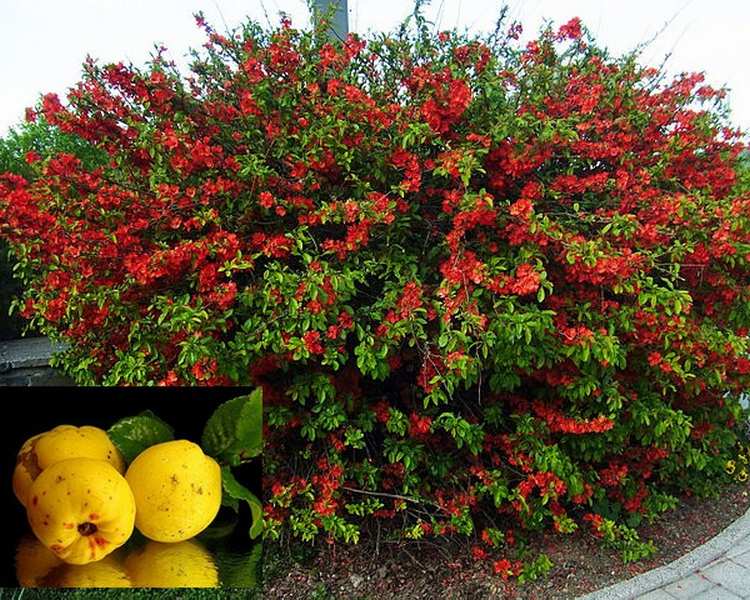


Japanese quince inflorescence petals can be:
- pear-shaped;
- ovoid;
- convex;
- elongated.
Often there are varieties with jagged petals at the edges, which, given the size and color of the inflorescences, looks original. The branches of the plant can have thorn-like processes, scaly, adult shoots, as they grow, acquire a dark, black-brown color. Possessing good immunity and resistance to most diseases typical for the culture, the plantation has been growing and developing for several decades.
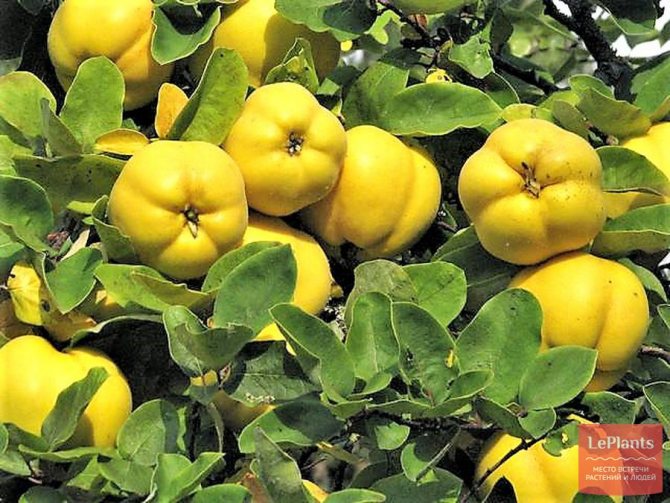
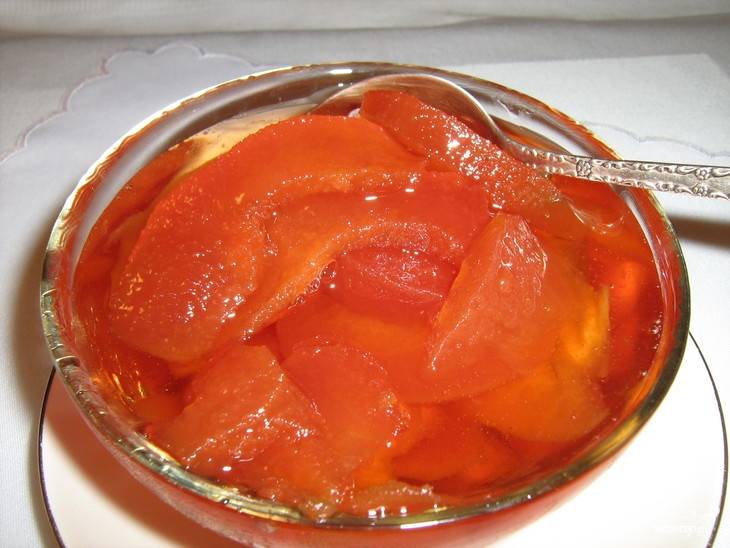
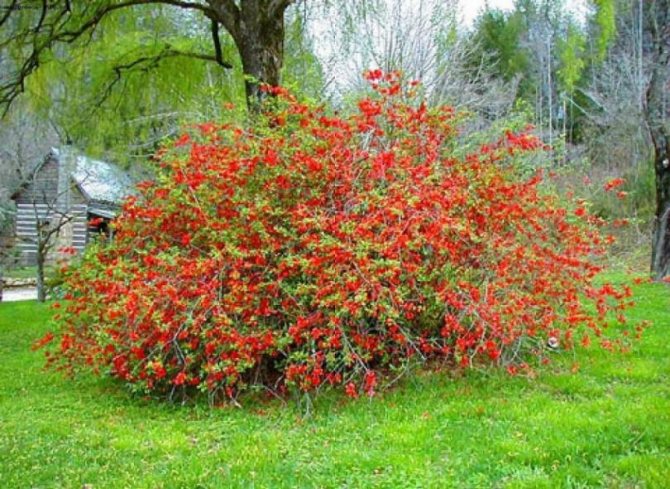
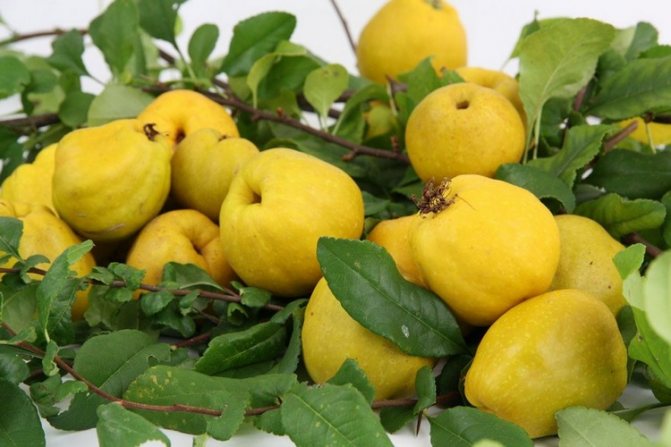
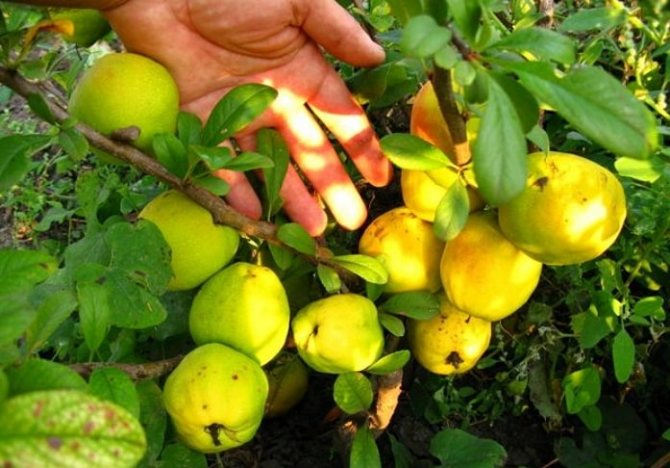
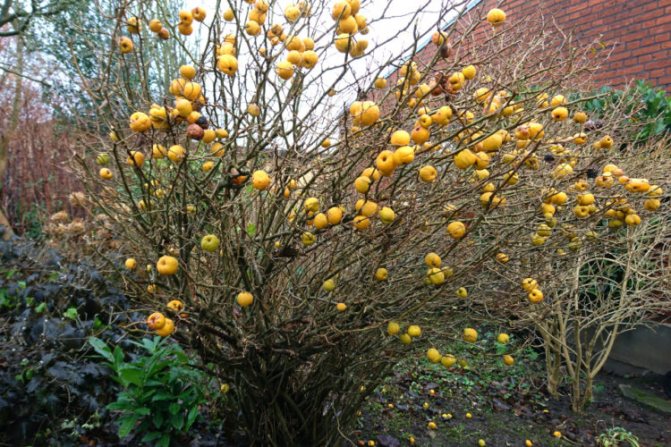
After planting in a permanent place, the first fruits ripen for 3-4 years. Fruiting of the bush is uniform, on average, with good care, it is possible to collect about 3–3.5 kg annually. Ripening of the harvest occurs in the autumn months, outwardly the quince resembles the size of the usual apple in size, differing from it in its bumpy skin, bright yellow color. The pulp of the fruit is tart with a sour taste, therefore, in most cases, the harvest of chaenomeles is used to create jams, candied fruits, marshmallows, and jams.
Characteristic features of culture
Japanese quince is a relative of all familiar apple and pear trees. In gardens, it is used as an ornamental crop. Distinctive features of the plant:
- there are tree-like (up to 3 m) and bush (up to 0.6 m) forms;
- shoots are flexible, have thorns up to 2 cm long;
- the branches are densely leafy, the color of the leaves is emerald green;
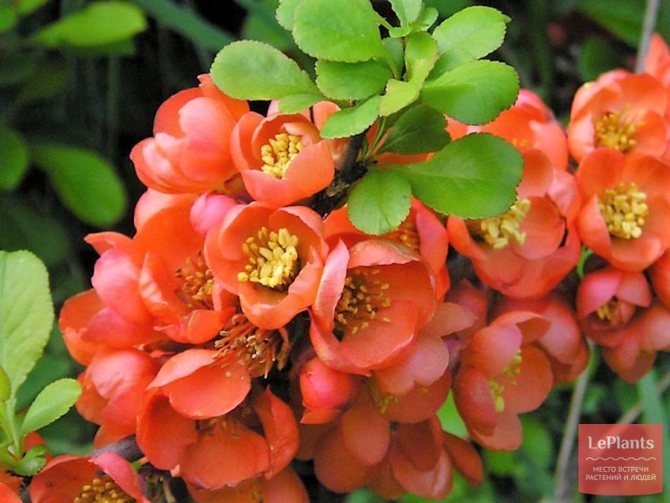
- the plant blooms with pink-red, orange-red, white flowers;
- fruits with a diameter of 3-5 cm;
- fruit color is yellow-green or orange;
- the skin is dense, covered with a characteristic waxy bloom;
- 1/2 of the fruit is occupied by the seed chamber.
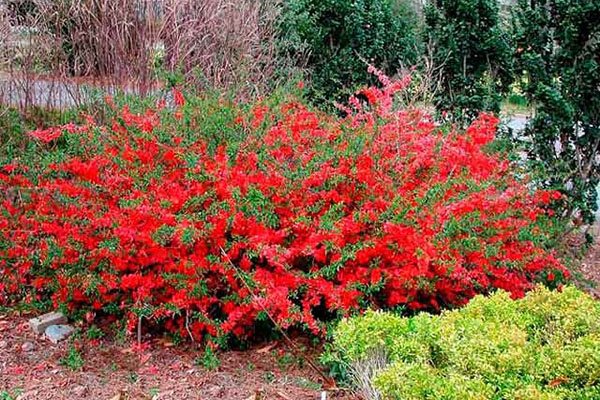
The taste of the fruit is bittersweet, the pulp is dense, aromatic. Due to its rapid growth and decorativeness, low shrub quince is used in summer cottages to create hedges.
Japanese quince: varieties for the Moscow region


The shape of the shrubs is spreading, the branches grow luxuriantly, like arches. Japanese quince and its varieties for the Moscow region:
- Vitamin - a compact structure, yellow fruits, resistant to frost, prolonged cold weather.
- Fragrant - the weight of the fruit can exceed 50 g, cold-resistant, the height reaches 1.5 m.
- Nutmeg quince - large fruits up to 200 g, self-pollinated, winter-hardy.
- Teplovskaya - ripens late, the fruits are well stored, the plant is unpretentious.
- Nikitskaya - bushes grow moderately, early ripening, long-term storage of fruits.
Also, bred interspecific hybrids of Japanese quince, which are especially winter-hardy, will be a good choice. They are guaranteed to take root and bear fruit in the Moscow region:
- Simonias are expressive flowers, slightly muted red, fruits of a delicate greenish hue, spreading shrub.
- Nivalis is a sturdy shrub with dense foliage, the height of which reaches about 1.5 m, the flowers are white.
- Geisha Girl is a tall, pompous plant, peach-colored inflorescences, a light cream shade is also possible.
- Pink Lady - grows quickly, compact shape, inflorescences are crimson or pale pink, tolerates pruning well, keeps a given shape, can grow in a shaded place.
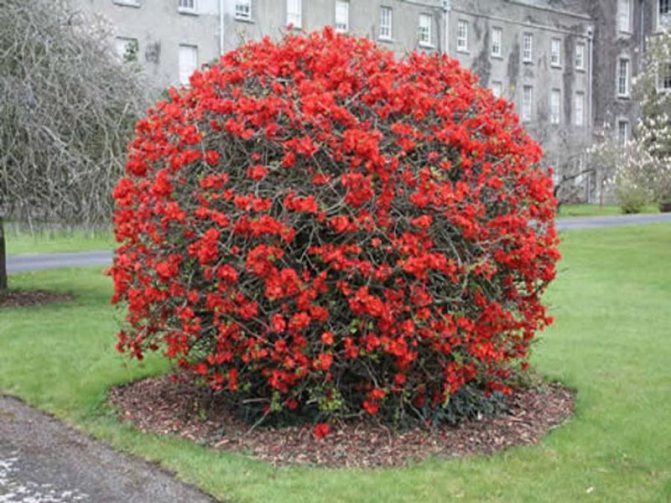
Charm with flowers sprouting in a group is a good choice. Quince inflorescences of dark purple color, due to their extraordinary beauty, are often used to create flower arrangements.
Specificity of the genomeles family
Henomeles is originally from East Asia, that is, Japan and China. That is why one of the chaenomeles varieties received the right to be called Japanese quince. In total, there are four pure varieties of this culture, plus several hybrid ones with flowers of different colors and different ripening periods. Shrubs can be deciduous or semi-evergreen. Hybrids are more decorative, however, unlike their progenitors, they tolerate winter worse.
Photo gallery of chaenomeles varieties


Henomeles Maulea


Quince fine grade "Nivalis"


Henomeles katayansky


Japanese Henomeles (Japanese quince)


Quince magnificent grade "Nikolin"


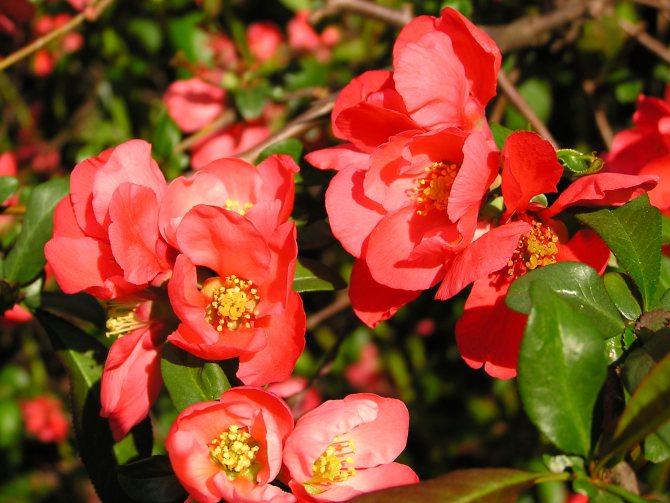
Quince is a beautiful variety "Geisha Gel"


Quince medium grade "Cameo"
The heroine of our story, the Japanese quince belongs to deciduous varieties and can grow in the best conditions up to three meters in height. In the northern regions, its height is, of course, less. Chaenomeles pleases with its fruits for a long time - as much as 70 years. And at the same time it is resistant to disease and is not attacked by pests.
In cities, chaenomeles decorates flower beds and parks as part of the landscaping program, but gardeners also successfully grow it on their plots.
When and how to plant Japanese quince in the Moscow region
Choosing the right place is the main point that needs to be paid special attention. Chaenomeles prefers to grow in an area that meets the following requirements:
- lack of drafts, strong wind;
- loose light soil;
- low humidity;
- acidity not higher than 6.5 pH.
In a sunny, protected area, the shrub grows beautifully, its flowers will be especially bright, and the hearths are much more fragrant and sweeter.
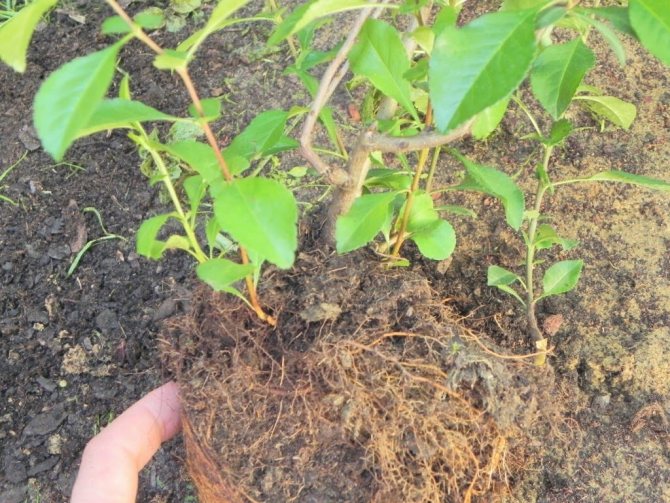
Japanese quince has strong roots that penetrate deep into the ground. Therefore, for planting or transfer to a new place, seedlings no older than 1.5-2 years are used. It is desirable that the root system is closed or the young plant is in a pot. Such conditions guarantee ease of planting and provide the bush with the opportunity to more easily transfer the procedure due to the presence of a "native" substrate on the roots.
Advantages and disadvantages of the plant
The main advantage of the plant is its incomparable appearance during flowering. Also, the undoubted advantages include:
- fragrant and healthy fruits;
- the possibility of a wide and varied use of the plant in landscape design;
- exceptional unpretentiousness of culture;
- high resistance to diseases and rare attacks from pests.
The disadvantages can rather be called the features of the plant:
- frequent sharp thorns on the shoots;
- tendency to quickly thicken;
- insufficient winter hardiness.
However, thorniness turns into dignity when using quince in a hedge, thickening is easy to avoid by regularly taking time to prune the plant, and frozen bushes, like the Phoenix bird, are revived again.
Recommendations for planting Japanese quince in the Moscow region
Planting seedlings requires compliance with certain conditions, without which the bush may die:
- Standard pit sizes are about 45-50 cm deep and 35-40 cm in diameter.
- Planting can be carried out after the soil has completely warmed up, somewhere in the 2-3 months of spring.
- If chaenomeles is used to create an original hedge, the distance between the shoots is 0.7–0.8 m, for garden decoration and fruiting - 1–1.5 m.
- The planting pit must be filled with a mixture of ash (500 g), humus (1 bucket) and superphosphate (300 g).
To prevent nutrients from burning the delicate roots, a thin layer of crushed soil is poured over it, with which it will be possible to prevent direct contact.
Then the plant is set vertically with the root collar parallel to the soil, the roots are straightened and sprinkled. Finally, the earth layer is lightly compacted. It remains only to carefully pour 10-13 liters of water under the root, you can mulch the trunk circle.
Planting Procedure and Necessary Preparations
Chinese quince can be planted in spring and autumn. In the first case - immediately after the snow melts and the threat of frost is minimized, in the second - at least 30–45 days before the first frost. The tree prefers fertile soil with good aeration (sandy loam, loam) and acidity in the range of 5.5–7.5. The place is chosen open, well-lit and warmed by the sun.


Chinese quince is quite difficult to find on sale, so in order to avoid deception, purchase seedlings only from trustworthy suppliers.
The depth and width of the planting pit is 65–70 cm, the interval between them when planting two or more seedlings is 2–2.5 m. For spring planting, it is dug last fall, for autumn planting - a couple of weeks before the procedure. Drainage is poured onto the bottom with a layer of 5–8 cm. The top 15 cm of the most fertile land is poured back, mixed with 10 liters of humus, a half-liter can of wood ash, 200 g of superphosphate and 120 g of potassium sulfate. From this soil, you need to form a mound and cover the hole before planting so that it does not wash out.
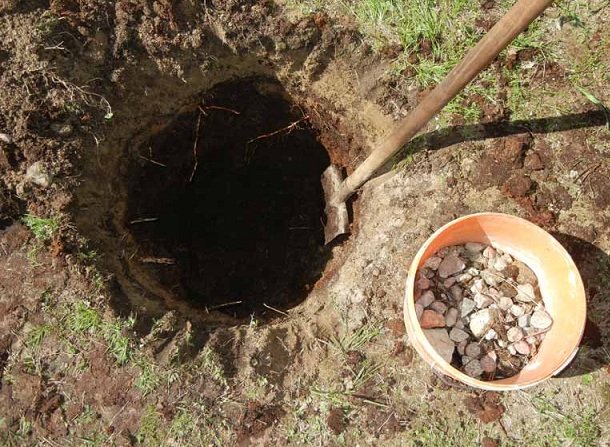


Drainage at the bottom of the planting pit will prevent moisture from stagnating at the roots, provoking their rotting
The procedure itself is standard, as for most fruit trees:
- After stepping back from the top of the mound at the bottom of the pit, stick in a peg for support. Its height is 10-15 cm more than the seedling, taking into account the depth of the pit.
- A day before planting, soak the roots of the tree in water with the addition of any biostimulant.
- Place the seedling on the top of the hill, straighten the roots along its "slopes" so that they do not stick up.
- Gradually cover the hole with earth, compacting it from time to time and shaking the tree so that no air pockets remain. The root collar should be at ground level.
- Water the plant (15–20 L). When the water is absorbed, mulch the soil.
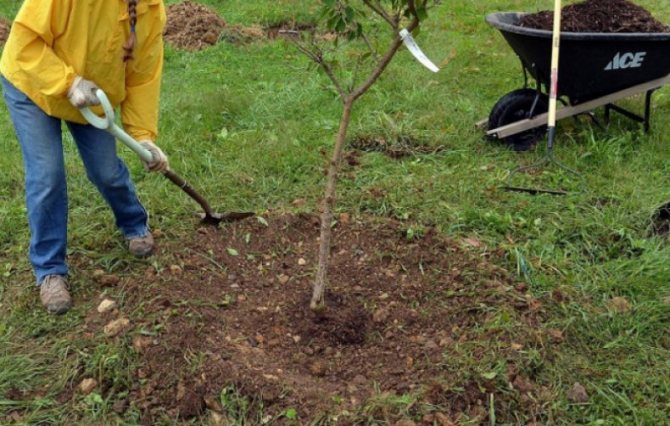


Planting Chinese quince is no different from a similar procedure for other fruit trees
Video: how to plant quince correctly
Chaenomeles care
Although the origin of the Japanese quince can be called exotic, caring for it is quite simple. You just need to try to carry out in a timely manner:
- top dressing - enough after planting in the second year;
- watering - abundant in the summer heat;
- pruning - remove dead branches, form a shrub;
- protective measures are the creation of shelters from spruce branches on the near-trunk circle in especially harsh winters, simple cold will not cause harm.
It should be noted that the Japanese quince variety for the Moscow region, which takes root well, does not react well to fertilizers diluted in water. It is recommended to use dry and granular mixtures of potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen as a recharge. An excellent reaction is guaranteed by the use of wood ash and leaf humus. As mulch - organic materials such as sawdust, peat.
Nuances of planting culture
In order for the plant to please with decorativeness and give a good harvest, it must be properly planted.
In the open field
Chaenomeles requires certain conditions for successful fruiting:
- The soil can be any (sandy, loamy, clayey, sod-podzolic), but with a lot of humus. The exception is alkaline soils: on them, the plant becomes ill with chlorosis.
- The place should be sunny and warm. Ridges near the southern walls of garden buildings are perfect.
- In the garden, you should choose a place with deep groundwater: the roots of chaenomeles easily rot.


Planted in the right place, Japanese quince grows well, bears fruit successfully, is not damaged by pests and does not get sick.
In a greenhouse or greenhouse
Gardeners in regions with cold winters are interested in: how to plant chaenomeles so that it grows and bears fruit? To prevent freezing, it is recommended to place the quince in a greenhouse or greenhouse. At the dacha, a heated greenhouse is arranged, in which the temperature is maintained in winter from -5 to +5 degrees. Additional shelter is provided in an unheated greenhouse. This double protection helps prevent freezing in winter.
See also
Planting and caring for actinidia (kiwi) in a greenhouse, open field and at home, growing rulesRead
Different types of pruning Japanese quince
Sharp thorns of Japanese quince sometimes injure hands during pruning, therefore, to make the work less painful, you need to purchase protective gloves. Shrub pruning begins in the spring and is classified as sanitary pruning. The gardener is required to remove dried and broken branches that have not survived the winter.
After the quince reaches 8 years of age, it's time to do anti-aging pruning. The slow growth of the bush will help to visually determine the need for the procedure, during the year it no longer stretches up so actively, the branches grow from strength by 10-11 cm. During rejuvenation, thin, weak and too long shoots are removed. During thinning, only 3-4 year old matured branches are left, the older and younger material is cut off.
Formative pruning, on which the aesthetic appearance of the plant depends, also requires considerable attention. It can be carried out only after 4 years, when the bush begins to actively branch out. Root shoots are cut out, making the bush more slender, not allowing it to develop in breadth, as well as internal sterile shoots. It is advisable that all sections are still fresh, in order to exclude the possibility of infection, they can be treated with special means with a garden pitch.
Plant crown formation
Pruning for adult chaenomeles ages 4–5 and older is an annual procedure, as thin shoots break easily and become tangled. It is carried out in the spring, before the start of sap flow, but always at above-zero temperatures. The plant tolerates the procedure very well. Autumn pruning often provokes the complete freezing of the Japanese quince.


The chaenomeles bush, pruned annually, looks very neat and bears fruit more abundantly
Pruning begins with the removal of all dried, frozen and broken branches under the weight of snow to the point of growth. They also do the same with those that lie on the ground, and with those located vertically. Be sure to leave horizontal or close branches at a height of 25-50 cm from the soil surface.
On an adult plant, 15–20 fruiting shoots are left at the age of one to five years. The number of “uneven” branches should be approximately the same. Three-year branches are the most productive in chaenomeles. All shoots over five years old are removed by anti-aging pruning. They won't harvest anymore. Once every 8–10 years, the bush is cut off radically, leaving 10–12 healthy and strong shoots no older than three years. This will help prolong his productive life.


A properly formed chaenomeles bush consists of a maximum of 20 shoots
If the chaenomeles is formed in the form of a standard tree, all small branches below the grafting site are additionally removed. Also, the plant in large quantities gives root shoots. For reproduction, you can leave no more than 3-4 layers, the rest are dug out, carefully chopping up the roots with a shovel.
Pruning is carried out only with a sharply sharpened and disinfected knife or pruner. If the branches reach a thickness of 5–7 mm or more, the "wounds" are disinfected with a 2% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish or covered with oil paint in several layers.


The instrument used to trim the chaenomeles must be sharpened and sterile.
Breeding methods for quince bushes
There are several breeding options for Japanese quince. Knowing about them, every gardener can choose the most suitable method for him.
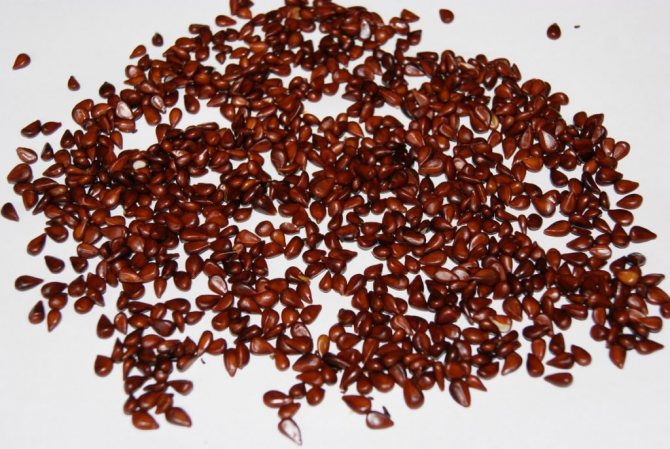
Seeds
The use of seeds in this case is considered quite impractical, since the daughter plant, especially if it is a hybrid, loses most of its characteristics. The method is effective, but it is used mainly for growing rootstocks, which are re-grafted a little later.
Planting material can simply be buried in a suitable protected dry area, covered with fallen leaves and plastic. The place is marked with a flag or pegs and shoots are expected to appear. Seeds can also be sown in small boxes in early February, growing like seedlings, remembering to stratify before this if spring material is used.
In less than 1.5–1.7 months, the material is planted in cups, then, with the June warming, the plantings can be transferred to the site. This is followed by a series of care procedures: watering, fertilizing, winter foliage insulation. Since good germination is typical for chaenomeles, seedling thinning is inevitable.
Cuttings
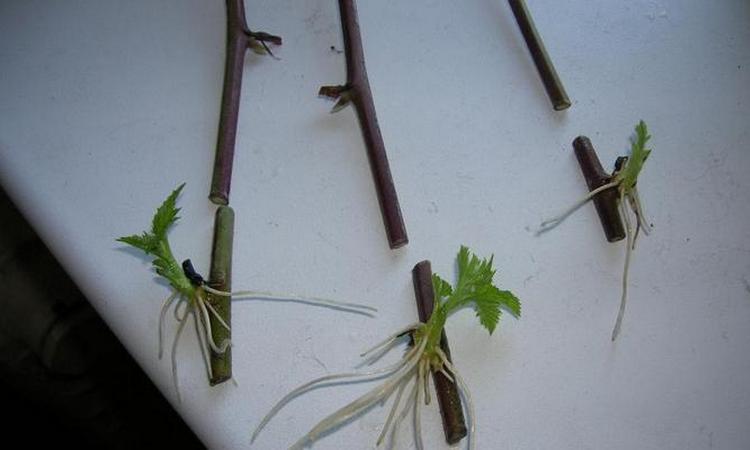


They are engaged in cuttings in June and early July, performing the following operations:
- Cuttings are cut with a piece of old wood, the so-called "heel".
- All sections are soaked with a stimulating drug "Kornevin" with the presence of acid, due to which accelerated engraftment occurs.
- A mini-bed of a school is created, where the resulting cuttings are carefully planted. Growing time depends on the growth rate of the plantings.
- It is necessary to create high humidity, a film coating helps to achieve this effect.
In autumn, but best of all in spring, the sprouts can be replanted. A simplified version of cuttings is cutting the planting material in the fall with planting them under the native bush. The place is indicated, in the spring, with good survival rate, the plants can be planted permanently.
By dividing
A very simple and affordable method to avoid risks and ensure that Japanese quince (varieties for the Moscow region) fully inherit the characteristics of the mother bush. It is enough to take the root shoots of an adult plant and transplant it into the ground. In fact, these are ready-made young bushes, requiring at the initial stage only standard care, which consists in feeding, mulching and watering.
Layers
Shoots spreading along the surface of the soil do not always have to be cut off. Such shoots are used to propagate the bush by burying them. After a while, seedlings with an independent root system appear from the material, which are transplanted. In the same way, to obtain layering, do with the lower horizontally growing shoots.
Features of growing and care
Caring for Chinese quince is easy. It is limited to maintaining cleanliness in the trunk circle, periodically loosening the soil, watering, fertilizing and pruning.
In the first season after planting, the tree is watered every 10-15 days (depending on the weather), the norm is about 15 liters. Fruiting Chinese quince does not need such frequent watering - it suffices five times per season, but the rate increases to 30–35 liters (the last time is 50–60 liters):
- when the leaves are blooming;
- during the formation of buds;
- two weeks after the end of flowering;
- at the time of the formation of ovaries;
- about two weeks after harvest.
Of course, watering intervals are adjusted based on how often it rains and how hot it is outside.
Fertilizers
There is no need to fertilize the tree in the first year after planting. Further, before the first fruiting, they are limited to the introduction in the middle of spring and at the end of October of humus (5–7 l) and mineral fertilizers - respectively nitrogen (15–20 g) and phosphorus, potassium (20–25 g). Fruiting Chinese quince is fed three more times, at about the same time as watered. Any fertilizer for fruit trees is suitable.
Pruning
Chinese quince bears fruit on the shoots of the last season, therefore, shortening pruning is not practiced for them. In the spring, they are limited only to sanitary pruning, removing broken, frozen, dried shoots. To increase the size of the fruit, experienced gardeners recommend leaving no more than 10 fruiting branches, cutting off the others to the point of growth.
Pruning takes place according to the following rules:
- With the onset of spring, damaged, broken, dry branches are removed.
- In order for the tree to have a beautiful shape and decorative appearance, shaping pruning is carried out. In addition to aesthetic goals, she also has the task of increasing the size and quality of the fruit.
- Since the shrub should not have more than 10 fruiting branches, the remaining branches, one year old, are removed.
- Do not leave side shoots of the current year.
- The ring cut removes all thickening crown and shoots.
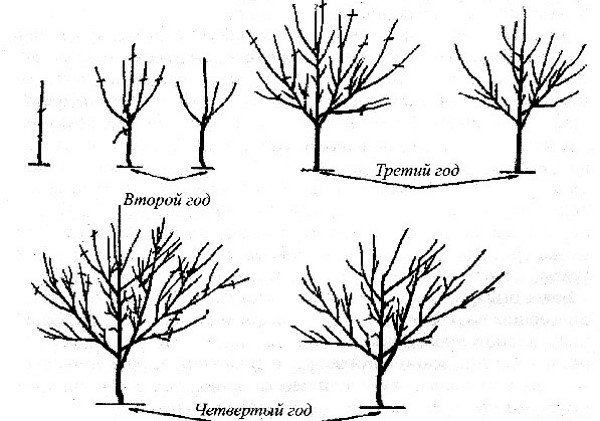

It takes 4 years to form the crown of a Chinese quince, by this time the tree, as a rule, begins to bear fruit.
Harvest at a temperature of 0-2 ° C is stored for up to six months. If there are few fruits, each is wrapped in foil or soft paper. A large crop is stored in boxes, sprinkled with sand or sawdust.
Preparation for winter includes cleaning the tree trunk circle from plant debris, mulching it (a layer about 10 cm thick and up to 20 cm thick at the trunk) with peat or humus, fallen leaves, spruce branches. The base of the trunk is wrapped in several layers of burlap or covering material that allows air to pass through. When enough snow falls, it is scooped up to the tree, creating a snowdrift.
Typical diseases and pests of quince
Chaenomeles has an excellent immune system and can withstand most pests and diseases. But since the Japanese quince is adjacent to other plantations, a combination of negative circumstances can affect. Rainy weather is especially dangerous, high humidity provokes the development of the following fungal diseases:
- ramulariasis - the formation of brown spots on the leaves is characteristic;
- cercosporium - dark brown unsightly spots appear, which gradually brighten;
- necrosis - drying of leaves due to the appearance of a gray coating at the edges.
The neighborhood with fruit trees threatens to become infected with an apple shield, fragrant buds attract a leafworm or weevil. Invasions of mites, moths, and other most common and tenacious pests are possible.
How to choose a variety for different regions of Russia
Chaenomeles is a warm and light-loving culture. The part that is located above the snow cover freezes. In order to choose a suitable variety, the frost resistance of the species must be taken into account. In the Moscow region, chaenomeles winters without shelter. But at temperatures below -25 degrees, annual shoots and fruit buds freeze. They showed themselves well: Garnet bracelet, Falconet, Scarlett, Cameo.
It is impossible to grow Japanese quince in Siberia without shelter. The shrub freezes out. But some gardeners cultivate the plant in heated greenhouses. There, the chaenomeles is created conditions close to the climate of his homeland.The Urals have hot but short summers, and winters are long and harsh. The air humidity is different from the required one. But some varieties with increased frost resistance can be tried to grow with shelter for the winter. In Siberia and the Urals, it is possible to grow (with the right shelter) the Zubutlinskaya variety.


Preventive maintenance
The protection of the plant from such a misfortune can first of all be ensured by preventive work in the spring and before wintering, during which Japanese quince is sprayed with special solutions. Against bacteria and at the same time diseases provoked by a fungus, treatment with copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid helps. You can also use fungicides specially formulated for plants (Fundazol). Saving flowers from decay will be provided by the preparations Horus and Kemifos.
If the Japanese quince is planted exclusively for decorating or dividing the site into zones, and its fruits are not consumed, the shrubs are sprayed repeatedly, if necessary, several times throughout the season. After ripening from a diseased plant, fruits are harvested and pruned, removing diseased and too damaged branches completely. It is also preferable to thoroughly cleanse the ground to burn the fallen leaves in order to prevent the larvae of pests and disease-causing spores from attacking the chaenomeles again from spring.
Where is used
The beneficial properties of fruits have ensured their use in various fields.
In medicine
Doctors prescribe chaenomeles as the main or complementary medicine for:
- flu and colds to strengthen the immune system;
- coughing to increase expectoration;
- asthma to prevent attacks;
- anemia and blood loss to restore blood;
- liver disease to restore damaged cells;
- poisoning as an astringent;
- kidney disease as a diuretic;
- liver diseases as a choleretic agent.


But it is not recommended to prescribe treatment with chaenomeles on your own: it is important to undergo an examination and find out compatibility with the medications taken.
In gardening
Gardeners use the plant to create hedges. The thorny plant forms impenetrable thorny thickets. Chaenomeles is decorative, therefore it is used for landscaping the site.
See also
How to properly propagate pomegranate cuttings at homeRead
In cooking
The unusual taste of the fruits ensured their use in cooking. Chaenomeles produces:
- jam;
- candied fruit;
- compotes;
- jam;
- wine;
- liqueur.


The fruits can be eaten fresh or brewed with tea, like lemon.
How to ensure the safety of Japanese quince fruits
Japanese quince fruits are valuable for their high content of vitamin C, because of this they are sour, but have an excellent aroma, firm. In early October, when the crop ripens, it is important to ensure its safety, especially since the bushes bear fruit every year without any changes in quantity.
In general, quince is placed in boxes, trying to avoid blows, not to damage the skin. The temperature in the room or basement where they will be located should be kept within 1-3 ° C. After 3–3.5 months of such a regime, the owners will be in for a surprise, the fruits will become sweet, soft and even more fragrant. Now they can be safely consumed, used for compotes, creating delicious preserves.
For those who prefer the sour taste of fruits and do not want to wait for their transformation, we can recommend the following storage method:
- Clean and wash the resulting crop.
- Cut and core.
- Grind or grate until smooth.
- Mix with sugar in a 1/1 ratio.
The resulting mass is packaged in containers and stored in a freezer or refrigerator. It is used for baking, cooking jams, compote, as a tasty addition to tea. Darkening of the pieces immediately during processing is not a sign of poor condition of the workpiece.This is a normal process and occurs due to the high iron content of fruits.
Vaccination procedure
Chaenomeles can be used both as a scion and as a stock. In the first case, you can form an unusual flowering tree, at the same time grafting 4-5 cuttings of Japanese quince on the trunk of mountain ash, pear, apple, irgi (a plant grafted with cuttings of different varieties looks very impressive). In the second - to propagate a rare and valuable hybrid, because seed germination does not guarantee the preservation of varietal characteristics. There is no time limit for the procedure. Most often it is carried out from late spring to mid-summer. Do everything you need to do as quickly as possible. Due to the high concentration of tannins, the cuts are oxidized almost instantly.


The standard trees obtained by simultaneous grafting of chaenomeles cuttings of different varieties look very unusual
The easiest way is cleft vaccination. The stem of the rootstock plant is cut horizontally at a height of 40–50 cm, leaving a "stump", a graft-graft (it must have at least three growth buds) - so that a V-shaped wedge is formed. It needs to be soaked for 2-3 hours in a solution of any biostimulant. Then a perpendicular incision 4–5 cm deep is made on the stock cut - the so-called splitting. A stalk is inserted into it.
The entire structure is fixed by wrapping it with several layers of electrical tape or plastic wrap. There is also a special grafting tape. It does not stick to the trunk, but it fits very tightly. Under the influence of sunlight, the material from which it is made slowly "evaporates".
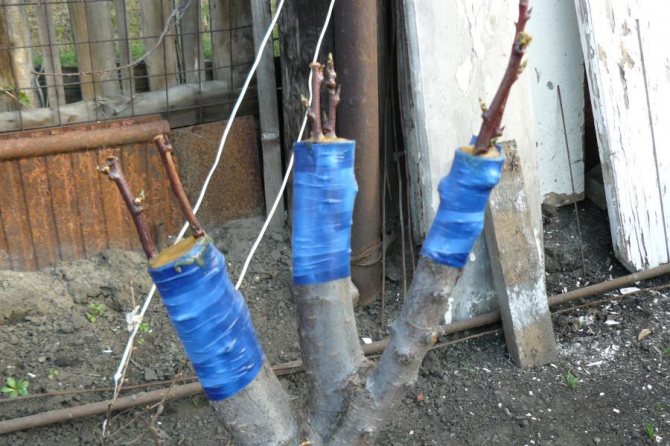


The tape fixing the vaccination site must not be removed until it is not clear exactly how the operation ended.
The result will have to wait 3-4 weeks. If new leaves began to form on the cuttings, this means that the operation was successful. Another indicator is the formation of an "influx" at the site of vaccination. The presence of callus means that the plants have formed a common conducting system.
Budding requires a certain amount of experience from the gardener. This is essentially the same vaccine. But not a whole stalk is used for this, but one single growth bud. It is cut off with a scalpel or razor blade along with a "shield" from the surrounding tissue. In the process, you need to try to touch her as little as possible.


The growth kidney is cut off, if possible without touching it
On the bark of the rootstock plant, using the same tool, make an incision in the shape of the letter T or X with a depth of 2-3 mm. Its edges are carefully folded back, a "shield" with a kidney is inserted there. Then the bark is returned to its place, the joints are covered with garden pitch. Next spring, a new shoot should begin to form at this place. If this happens, the rootstock is cut by 4–5 cm of the grafting site so that all the plant's strength goes to its development.
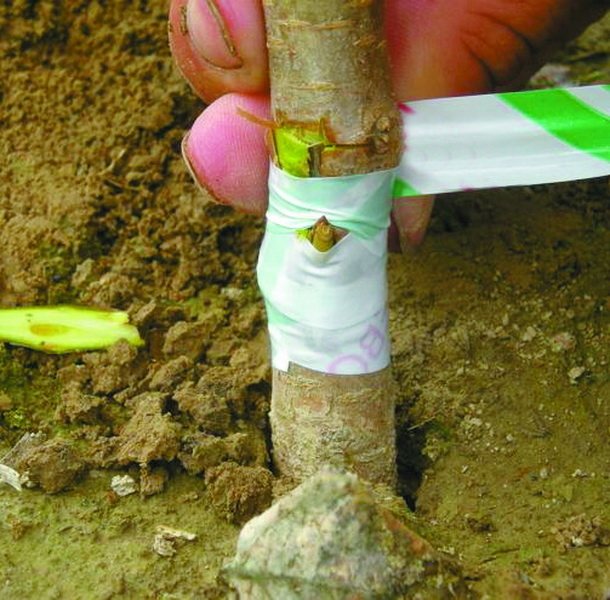


Some experience is required to properly carry out the budding procedure.
The benefits of Japanese quince
The high content of vitamin C, PP, A, E, group B and many others in fruits, as well as pectin, carotene, fiber, essential oils, tartronic acid, iron, magnesium, allows, with systematic use:
- stabilize the intestines;
- strengthen blood vessels, especially capillaries;
- cleanse the body of heavy metals and other harmful substances;
- strengthen bones, improve the condition of teeth and gums.
The inclusion in the diet of processed or raw fruits of Japanese quince normalizes cholesterol levels, strengthens the immune system, guaranteeing resistance to inflammation and colds.
Digested in compote or jam, fresh fruits normalize stool, serve as a natural diuretic. The broth is indicated for patients with gastrointestinal problems, relieves anemia, is used to remove phlegm, treat pustules, and as a lotion for tired eyes.
However, in some cases, eating fruit is discouraged. They are included in the diet of children only from 3 years old because of the danger of causing an allergic reaction.The rich content of chaenomeles requires careful handling, it should not be consumed very much, especially not fully ripe specimens. Although the help of quince for strengthening immunity, fighting tracheitis, colds and infectious diseases is invaluable, it is advisable not to use it for people involved in singing, declaring, whose work requires a lot of stress on the vocal cords.
It is also worth exercising caution if you have a tendency to constipation in order to further aggravate the situation. From the frequent use of quince, the blood thickens, which threatens significant harm with a tendency to thrombosis. Fruit-based home cosmetics also require careful handling. Before applying a cream or mask, be sure to test for the possibility of an allergic reaction.
Using chaenomelis
Japanese quince in landscape design is most often used to create decorative flowering borders and low hedges. Blooming quince is stunningly beautiful in the design of an alpine slide or a Japanese garden. Ornamental quince is also very effective in single plantings, in the company of perennial flowers or in a group of shrubs along with golden currants, barberry, weigela, forsythia, hawthorn and others.


Quince is a plant valued not only for its beauty, its small cute fruits are very fragrant, tasty, and healthy. They are harvested in the fall, as they ripen, before the onset of cold weather, in dry, sunny weather. Frost can spoil their taste.
There are many different vitamins (especially C) in the fruits of quince, there are tannins. They help fight colds, raise immunity. Pectins are also present, which lower cholesterol levels, remove salts of heavy metals and some other toxic substances from the body.
Marmalades, jams, jam are prepared from quince fruits. Used to add to semi-acidic fruit preparations.
Quince has not only beneficial properties, but also contraindications. So, due to the presence of tannins, it cannot be used by people suffering from constipation. Fresh fruit pulp can irritate the walls of the stomach, therefore it is contraindicated in gastric diseases. The bones can cause poisoning, they cannot be eaten.
So we got acquainted with an amazingly beautiful and useful plant. Growing Japanese quince will not cause much trouble. Observing simple rules, you will provide a chic decoration of the site for many years and pamper yourself with healthy fragrant fruits. See how wonderful the Japanese quince is in the photo. Are you still in doubt?


Contraindications
In addition to useful properties, this plant has some contraindications. This product is a strong allergen and should therefore not be consumed:
- people prone to allergic manifestations of food;
- during pregnancy and lactation;
- children under 6 years of age.
With extreme caution, the Chinese fruit should be consumed by patients with gastric ulcer and intestinal ulcers. Also, you can not eat it in large doses for gastritis, increased gastric acidity and pancreatitis.


The use of the fruits of Chinese quince should be limited with gastritis
Autumn care, shelter
Preparation for the onset of cold weather is carried out at the end of October-November, taking into account the period of the onset of frost. It is imperative to mulch the area around the shrub, approximately 1 m in diameter. Use a thick layer of fallen leaves and spruce branches.
It is useful to wrap the shortened twigs with a special agromaterial - spunbond to protect them from frost. If the florist grows a stunted species on the site or the seedlings did not have time to grow, then you can create a shelter from a wooden box or cardboard box.
Wintering
"Northern Lemon" can withstand moderate frosts well, but it is useful to mulch the soil to avoid problems with the root system. Some chaenomeles species tolerate temperatures as low as -20 degrees.
Breeders have bred many frost-resistant varieties for the Central strip and more northern regions. How to grow quince in the suburbs? Does chaenomeles tolerate temperate and harsher climates? Experienced gardeners argue that, subject to the rules, problems rarely arise, the shrub blooms profusely and bears fruit, and actively grows in breadth.
Brief description of popular varieties
There are so many types and varieties of Japanese quince that it's time to write an encyclopedia. Therefore, we will focus on several of the most interesting varieties and briefly describe them.
Geisha Girl
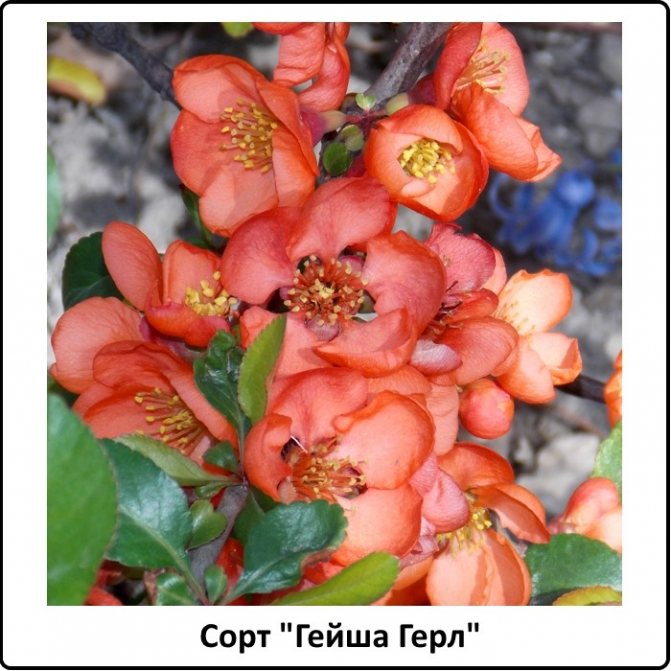


Refers to the type "beautiful quince". Shrub 1-1.5 meters high, twigs are densely covered with dark green foliage. Against this background, creamy pink inflorescences that appear on the plant from the first week of May stand out favorably.
The plant is thermophilic, prefers sunny areas. You can use Geisha Girl both in group and in single plantings, the bush looks equally beautiful with different options for landscaping the site.
Yukigoten
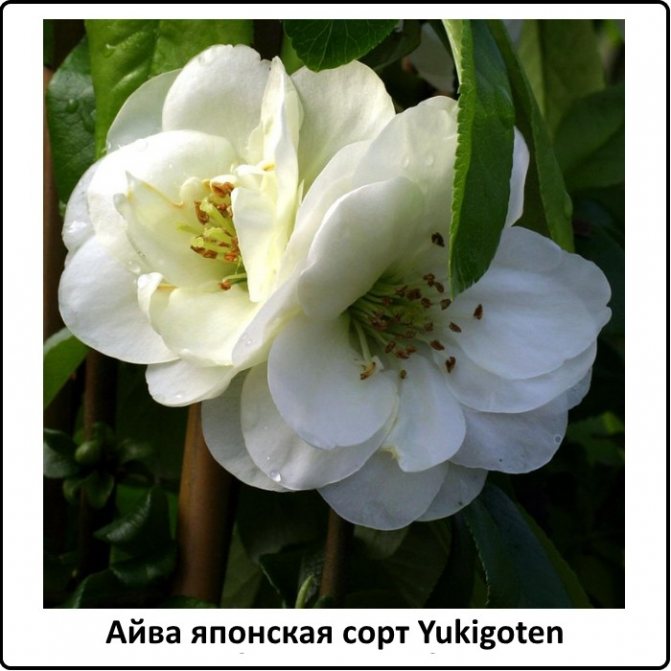


A significant drawback of the variety is its extremely slow growth. For 5 years of life, chaenomeles reaches a height of only 30 cm. For 10 years - about a meter. But, if you are patient, Yukigoten will delight you with white flowers, with a slight green tint.
The bush is literally covered with them and, in combination with emerald green foliage, has a noble appearance.
Elly mossel


This short bush (from 0.4 to 0.6 meters) will decorate your site with its bright green foliage. The fiery red flowers have a yellow center. The variety looks bright, it can be used to focus attention on a certain area of your summer cottage.
A wonderful solution would be the use of Elly Mossel in flower arrangements on the alpine slides.
Nicoline
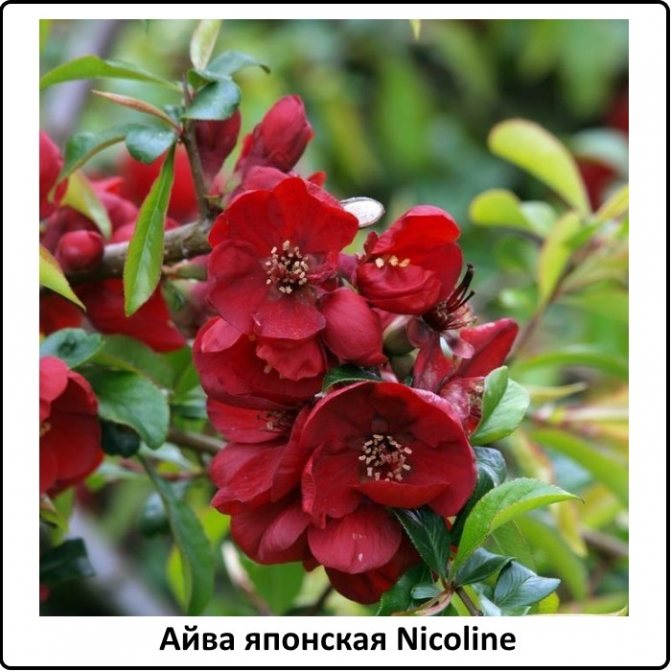


A variety of the Maulei species, suitable for growing in Siberia, Moscow and the Moscow region. This is a low shrub with a spreading crown: at a height of no more than 1.2 m, the diameter of the crown is 1.5 meters. Flowering occurs in late May, the inflorescences are bright red, large.
A good solution would be to use the Nicoline variety for the formation of hedges.
Pink lady
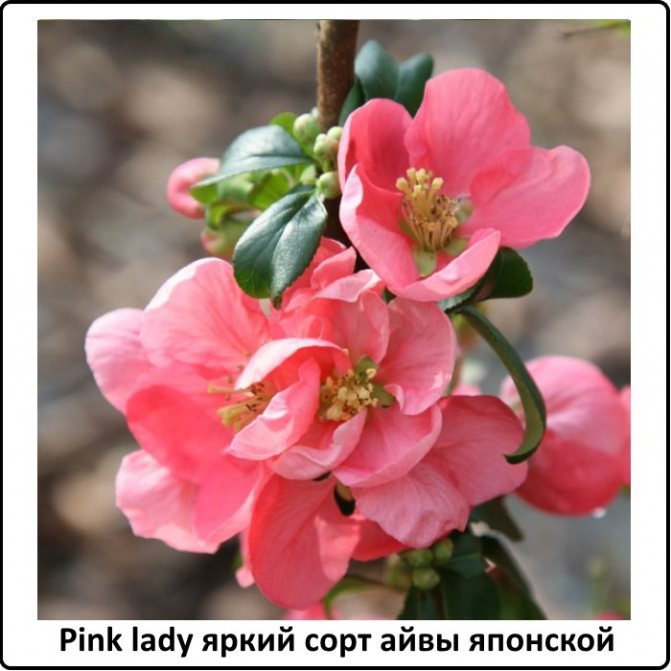


The variety attracts with its growth rate: in just 2 years it reaches the maximum possible height of 1.2 meters. The crown is oval, lush, densely covered with dark green foliage. Pinklady inflorescences are pink, tender, the middle is yellow. This Japanese quince is frost-resistant; in severe frosts, only young shoots are slightly affected.
Use Pinklady when setting up alpine slides and rose gardens.
Sargentii
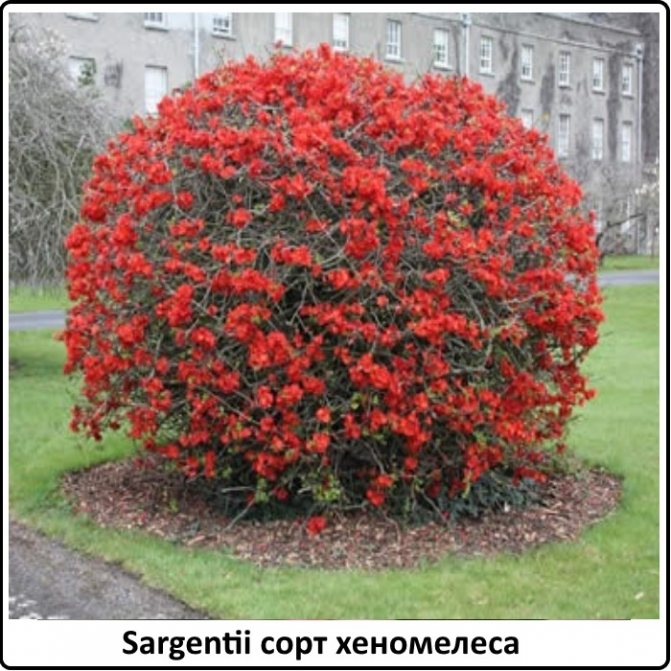


A bright and attractive shrub that can be easily rounded. Blooms for 3 weeks. Flowers are orange in color, of different shades: from dark to bright. Suitable for growing on all soils, except for highly alkaline soils.
Sargentii can be used both in single planting and in group compositions.
You can familiarize yourself with other varieties while reading the article in the photographs.


Quince variety Cameo
Reproduction by root suckers
The Japanese quince tends to produce numerous root suckers. Due to them, the bush gradually spreads in all directions. At the age of 20, it covers an area of up to 2 m2. Due to the overgrown offspring, the root system of the Japanese quince is able to firmly hold the soil on the slope. It is so branched and resilient that if there is a desire to completely get rid of an adult bush, it will not be so easy to do it.
When digging up root shoots, shoots 10-15 cm long and 0.5 cm thick with a well-developed root system are selected. From one bush, you can get no more than 5-6 root suckers. They are planted vertically, watered regularly, maintaining sufficient soil moisture, then mulched around the bush with humus, wood chips or shavings. However, the disadvantage of this method of reproduction is that some offspring growing from the taproot have a poorly developed root system, and the resulting seedlings have to be grown.It is noticed that at first such seedlings have even smaller fruits than usual.
Collection and storage of fruits
With proper care, by the end of September - beginning of October, the Japanese quince bush produces up to 3 kg of fruit. If the summer turned out to be cool, damp, even with anxious care, the harvest may not ripen.
But the harvest of quince is certainly harvested before frost, otherwise it will end up on the ground. Frozen fruits will become soft, watery.
They cannot be saved or recycled. Japanese quince ripens at room temperature and humidity. It may wrinkle, but does not rot, while maintaining taste. For storage until spring, you need a temperature a couple of degrees above zero and high air humidity. The crop is laid out in one layer in a box or box with air ventilation.
What problems do gardeners face
Often gardeners are interested in: why does the Japanese quince not bloom? The reasons:
- lack of sunlight;
- excess alkali in the soil;
- lack of nitrogen fertilizers;
- an abundance of creeping shoots;
- illiterate formative pruning;
- freezing of fruit twigs in winter.
The lack of flowers in a plant may be the result of excessive soil moisture.


Nutritional value and chemical composition


The fruit has a high nutritional value. 100 g of fruit pulp contains approximately 48 kcal. Also, 100 g of quince contains:
- proteins - 0.4 g;
- fats - 0.1 g;
- carbohydrates - 15.3 g;
- water - 83.8 g;
- ash - 0.4 g.
The composition of quince includes vitamins of groups A, B, C, E, PP. It also contains useful trace elements: calcium, zinc, iron, copper, sodium, potassium, selenium, phosphorus.
Famous and cultivated varieties of Chaenomeles
Blooming profusely from May to June, ornamental quince is distinguished by smooth leaves and small thorns on the branches, fruiting is carried out by the formation of round or oval medium-sized fruits.


The varietal variety makes it possible to choose exactly the kind that will become a magnificent and original decoration of the local area of a summer cottage or garden, most often gardeners prefer such varieties as Crimson and Simony, Jet Trail and Pink Lady.


Features of agricultural technology
Growing chaenomeles is a simple undertaking. But you need to follow the advice of agronomists.


Spring care
After the snow melts, the main spring activity is pruning. After removing the winter shelter, it is required to cut out frozen and dry shoots. Then you should add mature compost or humus.
Summer treatments
In summer, it is recommended to apply phosphorus-potassium fertilizer after flowering. After the formation of ovaries, the formation of the crown should be carried out. This activity involves the removal of shoots creeping on the ground, cutting out weak branches. On a tree or shrub, it is required to leave up to 20 fruiting branches.


Autumn care
In the fall, mineral fertilizers are required: top dressing for the successful wintering of a tree.
Chaenomeles is also transplanted in the fall. At this time, chaenomeles takes root better.
Pruning is also done in the fall. How to prune a plant during this period:
- creeping shoots are removed;
- not ripe are shortened;
- the top is cut off for shelter for the winter;
- thinning pruning is carried out.


Autumn activities are necessary for the successful wintering of the plant.
Preparation for wintering
Preparation for wintering includes autumn activities and plant shelter. The shrubs are covered with cardboard boxes, the trees are wrapped in white lutrasil. The trunks of plants are tied with twigs to prevent gnawing. It is recommended to keep the plants covered with snow as high as possible.
Disease and pest control
Healthy chaenomeles rarely gets sick and is damaged by pests. But with excessive watering, its roots rot. With an excess of nitrogen in the soil, aphids appear on the leaves, chlorosis develops on calcareous soils.


To prevent trouble, you should follow the rules of care.When attacked by pests, it is recommended to spray the plantings with insecticides.
Watering while growing
Quince is responsive to watering. In dry weather, water often. The first watering is carried out at the very beginning of flowering. This will improve the fruit set.
The second time is watered in June, this protects the fruits from shedding. Until the end of fruiting, it is watered 2-3 more times.
Watering is stopped in September so that the number of shoots does not increase and their frost resistance does not decrease.
Use water that has settled and warmed up well. Cold water can reduce the number of ovaries and cause fruit shedding.
Fruit processing
From the fragrant fruits of the Japanese quince, you can cook jelly, marshmallow, jam, syrup, liqueur. The aromatic taste of the fruit improves the quality of jam and compote made from apples, chokeberry (Michurin's chokeberry), apricots and peaches. Dried fruit slices can be used in dried fruit compotes. We offer recipes for some processed products: Tea with Japanese quince, Jam from Japanese quince with apples, Marmalade from Japanese quince, Fruit compote with Japanese quince, Quince liqueur.
Photo by the author
Cooking applications
The fruits of this tree are widely used in culinary recipes. Fragrant jams, preserves, juices, compotes, jellies and candied fruits are prepared from them.
Quince juice is very useful for the body, which is made from fresh pulp, then diluted with boiled water and a little honey is added. This healing drink helps to strengthen the immune system against many diseases.
The fruits of the Chinese quince are added to baked goods, sauces to meat. Quince slices keep well in the freezer. Many people harvest it in this way for the winter.






































