Fruits and berries »Grapes
0
832
Article rating
The etymological assignment of some crops to fruits, berries or vegetables does not always coincide with external characteristics. For example, for this reason, tomato and watermelon are classified as berries. You can determine whether a grape is a fruit or a berry by the type of plant growth and the type of Fruit

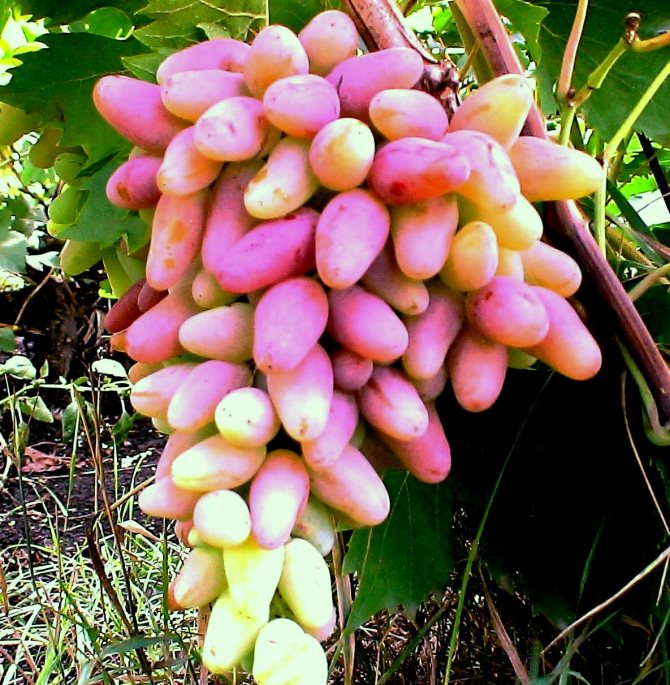
Etymological characteristics of grapes
Botanical description [edit | edit code]
The grape shoots are called vine
[3] .
The seed of the grape produces a small shoot in the first year after germination. From the buds in the axil of its leaves, elongated, well-developed shoots grow the next year, and then, next year, each bud of this shoot gives weaker shoots, which by autumn freeze to their lower bud, so that only one lower one remains from such an shoot. internode - a shortened shoot.
A single bud of a shortened shoot develops powerful elongated shoots in the next growing season, which, in turn, then bring shortened shoots. Elongated shoots bloom and bear fruit, but shortened ones do not. In culture, thanks to the short pruning of grapes, this alternation of shortened and elongated shoots is imperceptible, and the plant blooms and bears fruit every year.
Flowers are small, collected in inflorescences (complex brush or panicle). Depending on the presence of male and female parts in the flower and the degree of their development, the following types of flowers are distinguished: true female, male, bisexual, functionally male, functionally female. The last three types are the main ones in grapes. The bisexual flower is characteristic of the vast majority of cultivated varieties.
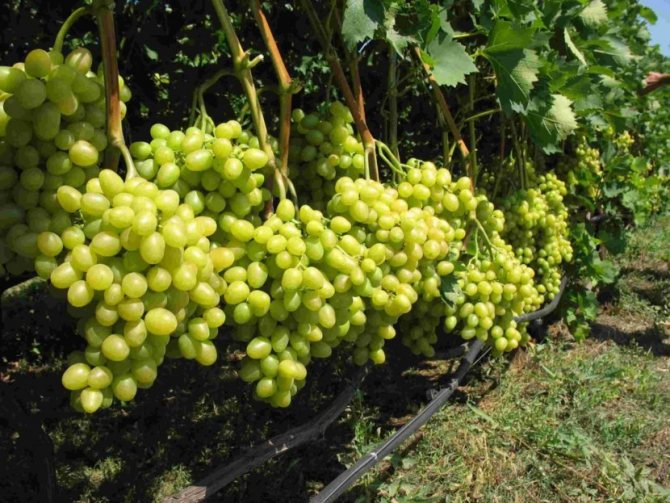
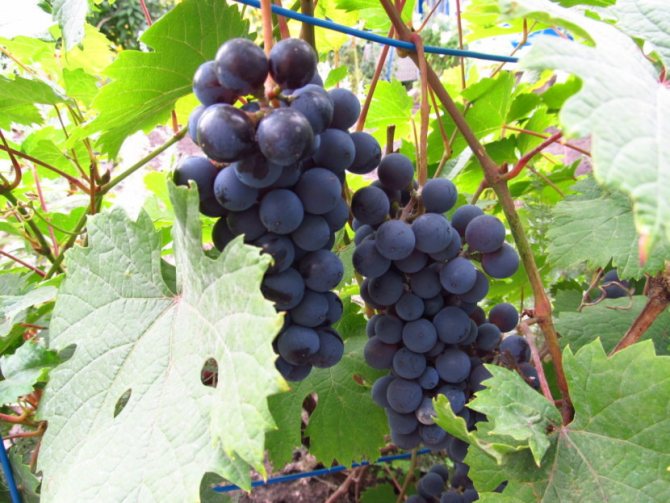
Grape fruits are spherical or ovoid berries, collected in more or less loose (rarely dense) bunches. The color of the berries varies greatly depending on the variety (yellow, greenish, dark blue, purple, black, etc.).
What is the growing season
Grapes in Altai for beginners
During the growing season of grapes, all parts of the plant develop actively:
- shoots;
- leaves;
- inflorescences;
- antennae.
It was at this time that the root system is actively functioning in the plant, the leaves breathe and accumulate organic matter. In addition, fruits are formed, grow and ripen.
In this period, there are six phases:
- The first is sap flow. During this period, the liquid actively moves along the vine, and drops of juice appear at the cut point. The liquid is called soda. Drops on the cuts - crying. This process takes place due to the activation of the cells of the grape root system. It absorbs water and substances useful for plant growth and moves them under pressure throughout the plant. The duration of the phase is from twelve to sixteen days.
- During the second phase, the plant begins to bud. The active development of shoots, leaves, inflorescences, antennae begins. Right now, the plant continues to actively develop and at the same time "feed" on minerals, water and starch accumulated in the roots. It begins to accumulate new reserves, produces substances that are necessary for life and development. During this period, you need to periodically loosen the ground to ensure the supply of oxygen to the roots of the plant.They also break off the lower shoots that formed under the vaccination site.
- The third phase of the plant is the period from the end of flowering and the moment the ovary appears on the bunch. Now the plant needs the largest amount of nutrients. The resulting ovary is already showing the grower for the next harvest.
- In the fourth phase, the fruit ripening process takes place. And the plant begins to gradually fade and stop the development of all its parts.
- In the fifth phase, the fruits become fully ripe and take on a natural color. The formation of buds is taking place, which will winter and develop already next year. In this phase of the growing season, the grapes are harvested. This process lasts for a month and a half.
- The sixth phase is the period of the plant falling asleep. After harvesting, the leaves of the grapes begin to change color, dry and crumble. The root system begins to actively accumulate starch. The same substance accumulates in other parts of the culture. Thanks to this process, the plant is resistant to frost. This phase lasts for a month and a half.
Botanical classification [edit | edit code]
The genus Vitis is represented by 78 species and is divided into two subgenus: Euvitis Planch and Muscadinia Planch. In subgenus Euvitis
includes 75 species, which, taking into account the areas of their origin and distribution, as well as the totality of botanical and morphological and anatomical signs and properties, are divided into 3 groups:
- European-Asian;
- North American;
- East Asian.
N.I. Vavilov identified the following main centers of origin of grapes and its introduction into culture:
- Central Asian, covering Northwestern India, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Western Tien Shan;
- Near East, covering inland Asia Minor, Transcaucasia, Iran and the mountainous part of Turkmenistan. In this region, grapes are represented by a huge variety of cultural and wild forms.
The European-Asian group includes one species: Vitis vinifera
L., which includes the subspecies Vitis vinifera subsp. sativa (cultivated grape), which gave a huge number of cultivars, and Vitis vinifera subsp. silvestris (Forest grape).
A.M. Negrul, taking into account the peculiarities of the morphological and biological characteristics of cultivated varieties, developed a classification of grape varieties of the species Vitis vinifera L., in which all cultivated varieties are divided into three ecological-geographical groups:
- eastern group Vitis vinifera convar. orientalis Negr.
- Western European group Vitis vinifera convar. occidentalis Negr.
- the Black Sea coast Vitis vinifera convar. pontica Negr.
The American group consists of 28 species. In viticulture, these vines are widely used as a rootstock. Among them, the most famous are Vitis rupestris, Vitis riparia and Vitis labrusca. The latter is the ancestor of most North American grape varieties with a characteristic strawberry aroma, which is called "isabel" or "fox" (cultivated since the middle of the 17th century).
The East Asian group includes 44 species, which are poorly studied to date. The most famous and widespread of them is the Amur grape ( Vitis amurensis
). In turn, the Amur grapes are divided into three ecotypes: the northern ecotype (grows at the latitude of Khabarovsk), the southern ecotype (grows at the latitude of Vladivostok) and the Chinese ecotype (common in the southern regions of China).
Almost every one of us in our life has tried such a fruit as grapes. But is it really a fruit, as some of us are used to thinking, since there are quite a few opinions confirming the fact that grapes are berries. This is due, perhaps, to the fact that there is a substitution of concepts: it is called a berry, but the raisins that are obtained from it are considered dried fruit. In order to more accurately determine what it really is, consider the history and features of terminology that will clarify this issue.
Why grapes have no fruit
If the grower does not receive grapes for several years, he has a question: "Why does not the grape bear fruit?"
In this case, there are several important reasons why fruits do not appear on the bush:
- The planting site was not chosen correctly, and the plant does not like it;
- A large amount of organic fertilizers has been applied to the soil, this reason can be established by fast-growing shoots and large leaves;
- The trimming was done incorrectly, that is, it is trimmed too short. For this reason, there is no room on the plant for the formation of fruits;
- The bushes are damaged by frost. They can damage uncovered grapes.
It should be noted that the plant simply could not be pollinated. Accordingly, the fruits will not appear. Diseases and pests cause a lot of harm.
The most dangerous diseases are:
- gray rot;
- mildew.
Among the pests, the most dangerous are:
- Snail;
- Ticks.
For this reason, berries may also be missing.
Important! Before you take any measures due to the non-yield of grapes, you should determine the reason why the plant does not bloom and does not form berries.
History of grapes
Grapes are considered to be one of the most ancient fruits. Its history begins even more than 60 million years ago, although the wild variety was widespread on the planet even before that. In those days, they began to grow it in rather large quantities, and archaeologists now and then find jugs, drawings and other utensils with its images.


Asia is considered the birthplace of this berry. In later times, grapes spread widely throughout Europe. Everyone knows the Roman and Greek feasts, where it was almost impossible to do without wine and grapes.
By frost resistance
This is a defining characteristic when choosing a variety for growing in a particular region.... Frost resistance - the ability to survive during short-term or winter frosts. The parameter depends on the conditions of ripening and the quality of hardening of the vines, so the indicators may vary in different years. The table shows the critical and absolute temperatures for varieties with different degrees of frost resistance:
- Highly resistant - up to -35оС;
- With increased resistance - up to -27оС;
- Medium resistant - up to -22оС;
- Weak-resistant - up to -17оС.
Most often, frost-resistant varieties are hybrids bred specifically for growing grapes in northern latitudes. They are unpretentious in care and disease resistance. Recommended not only for harvesting, but also for landscape design. Frost-resistant grape varieties:
- Amursky;
- December;
- Isabel;
- Riesling;
- Alpha.


These varieties were characterized by high yields and berries, quite suitable for fresh consumption.
Frost-tolerant varieties are most optimal for home growing for novice farmers. Usually they do not require shelter for the winter, and additional feeding.
Features of terminology
Returning to the main question, is it a fruit or a berry, it is imperative to pay attention to the terminology of both concepts. There are several points of view that help determine what grapes belong to.


Why is the fruit of the grape fruit
In our language, the words "fruit" and "fruit" can be equated and substituted for each other. In some cases, only one of them is used, for example, "fruit from the tree", since almost no one says "fruit from the tree".
“Fruit” is considered a more common and everyday word, while “fruit” refers to botanically correct and verified terms.
In the botanical dictionary there is such a definition of a fruit - a part of a plant that develops from a flower, with seeds inside. Very often, berries are also called fruits, as they are more common in everyday speech.


Why are the fruits of grapes berries
The Encyclopedic Dictionary says that a berry is a fruit with pulp, thin skin and seeds inside. By checking with Ozhegov's dictionary, you can also define a berry as a fruit growing on shrubs and shrubs, as well as herbaceous plants.
The botanical term "berry" refers to a fruit with many seeds, a juicy intercarp and an intracarp. At the same time, there is no such word as fruit in botanical terms - it is borrowed from the Polish language, simply means a juicy fruit and is used to name larger berries.
So grapes, according to these opinions, can be considered exactly a berry.


Formation of the first fruits
The first fruits of grapes after planting a seedling can be obtained in four years. Prior to this, the shrub is actively developing, the formation of the crown occurs. Thanks to pruning, the plant begins to grow stronger and gain strength. Throughout this period, it is necessary to carefully look after the plant, do weeding, loosening and timely watering.


Formation of the first fruits
If you take proper care of the plant, then it can bear fruit earlier. This can happen in the third year of active plant growth. Grapes can discard inflorescences already in the first year of planting, but in order for the fruits to be full during this period, it is best to remove all the flowers and wait until next year.
A little more terminology: are grapes a tree or a shrub?
Although many people will confidently say that the plant is a bush, and the name "grape bush" has already taken hold among the people, it is still not a shrub, and not even quite a tree. The grape is a liana, or rather a woody liana under the Latin name Vitis.
This perennial ligneous vine reaches 20-25 meters in height and clings to the support with antennae. Liana belongs to heat-loving plants, and therefore grows in hot countries.
But today there are also such types of lianas that are less demanding on weather conditions and can be grown in temperate climates.


Gardeners reviews
I have an EXTREME vineyard this season. I water the bushes with imported water. I watered only twice, I try to grow early grapes without watering. While it blooms without top dressing, I observe inflorescences on new varieties planted last year (Velika, Tason, Transfiguration). Baikonur, Julian, Ayuta, Finger Manicure, Zarya Nesvetaya, Black Cherry - according to the results of flowering, the largest inflorescences in Early Pink and Arcadia (in comparison with Transfiguration, Libya, Descendant of Rizamata, Julian) grow in the same trench, the age is the same ( the strength of growth is very different). These early maturing species have never failed.
Peter
End of July, city of Kamyshin. I have on the way to the Memory of the Teacher (more precisely, half of the harvest has already been eaten), in 5 days there will be Super Extra and Libya at the same time - the exuberant flowering promises a good harvest, Delight is already with good nutmeg, and the Transfiguration is colored and it will hang for another week and will be ready. Even Arcadia has already softened completely and with decent sugar, I think she is 10-12 days old before ripening.
Evgeny Polyanin
Most of the early maturing varieties deserve the universal love and respect of experienced winegrowers for their early maturity and resistance to fungal diseases of the vine. Having a couple of ultra-early varieties on the site, you can enjoy juicy, aromatic berries in the middle of summer. The abundance of very early varieties of grapes and the variety of quality characteristics open up tremendous opportunities for both experienced winegrowers and novice gardeners.
The benefits and uses of grapes
Berries have a fairly wide range of useful properties. Not only pulp is used, but also bones, which are widely used in cosmetology and skin treatment. It is also the main constituent of the wine industry. In addition, berries are often used for cooking or decorating dishes.
In cooking
Berries are often used to make juices and jams. Everyone is also familiar with raisins - dried berries of various varieties that are used in baking, making salads and other dishes.
Light snacks or desserts are also prepared with it, often added as a decoration to chilled desserts and jellies. Wine vinegar is also in demand, which is used by many chefs in various main dishes.


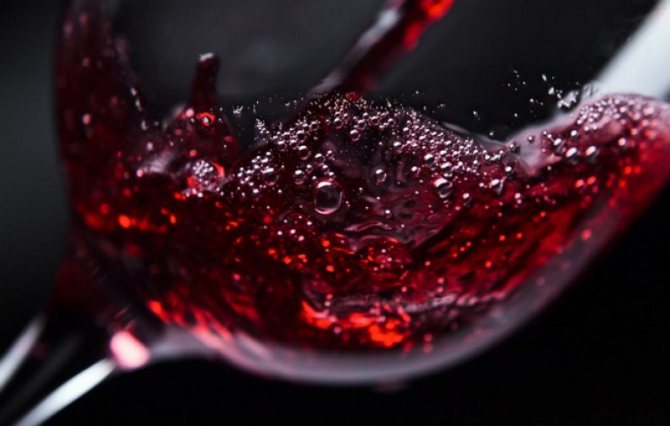
In winemaking
There is nothing to say here - it is grape berries that are the main component of winemaking. At the same time, there is no exact number of cultures that exist today - there are more than five thousand of them, however, not all of them are suitable for making wine.
For the production of the drink, about a hundred technical varieties are used, of which about a third are taken only for making red wine, and another third for white. Not only the quality of the drink depends on their choice, but also the taste, color, bouquet and aftertaste.
The most popular red grape varieties are Cabernet Sauvignon, Merlot, Sangiovese, Syrah, or Shiraz, and others. For white grape varieties are suitable: Chardonnay, Muscat, Riesling and others.


All varieties can also be divided into 4 categories:
- The wines that are used to make wine and liqueurs are characterized by their small size and small berries.
- Canteens are a large group that includes large varieties. Mostly used on their own.
- Drying rooms, from which raisins are prepared. They can be white or dark. The group is rather small.
- Versatile, which are used both for making drinks and for eating.
For the production of wine, mainly European varieties of such berries are used.
In medicine
The fruits contain quite a lot of useful substances, include fiber and vitamins of the P and B groups. Also, pectin and beta-carotene are included in the berries. Useful acids such as tartaric, succinic, citric and malic acids are also found here in large quantities.


There is also iodine, potassium, manganese, fluorine, iron and many other useful components.
Early grape varieties for regions with description and characteristics
Early grape varieties are subdivided into ultra-early, super-early and early. Grape forms are selected for the climate of the region and the qualitative composition of the soil on the site. The correct choice of the variety affects the survival rate on the site and the yield of the crop.
Varieties for growing in Ukraine
In Western Ukraine and in the eastern regions of the country, early and ultra-early grape varieties are grown not only in the open field, but also in greenhouses.... Whole hectares in the Kherson, Odessa, Nikolaev regions are occupied by greenhouse grape fields. Such agricultural technology allows you to get large, sweet grapes of the varieties Julian, Harold, Galahad, Delight, Alyoshenkin in the second decade of June.
Dark-fruited Lorano and Nesvetaya's Gift ripen after 90 days, the amazing Rhombic variety with finger-shaped fruits becomes sweet and tasty after 80–90 days from the beginning of the growing season.
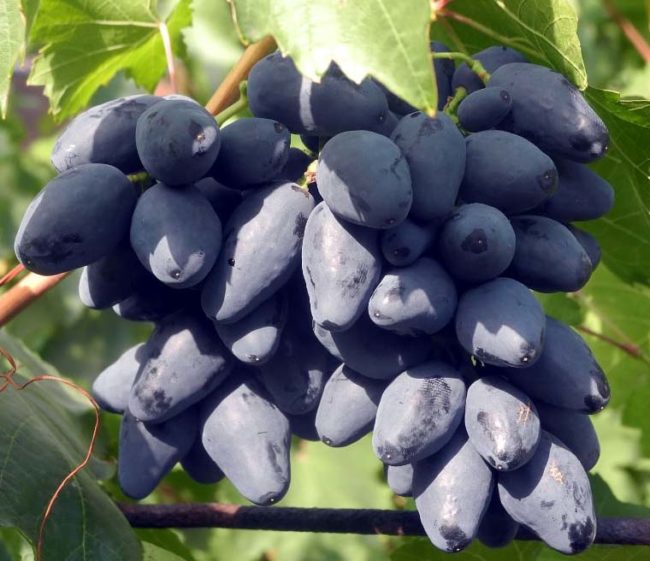


Ultra-early variety Rhombik, known in Ukraine
And also in Ukraine, an incredibly early harvest is obtained from the early ripening variety Catalonia, the first bunches of which ripen in 85 days. The berries are dark blue, juicy, with a cherry aroma and light astringency; with delicate skin; contain up to 24% sugars and 6 g / l acids. The maximum weight of bunches is 1200 g. The hybrid is resistant to gray rot, does not crumble and stays on the bushes for a long time at full ripeness.


Super early grape variety Catalonia
Growing ultra-early grapes in greenhouses requires forced additional pollination and timely organic and mineral fertilizing.
Video: overview of early grape varieties in Ukraine, end of July
Varieties for growing in Volgograd
Early ripening varieties and grapes with a late ripening period are grown on the Volgograd land in a sharply continental climate. The experience of gardeners shows that proper care, regular pruning and rationing of bushes, feeding and treatment from mildew and powdery mildew are a guarantee of stable and decent yields in the vineyard.
Libya and Kishmish 342, Julian and Vega are grown here; Super extra, Arcadia, Tason - vigorous varieties with a vegetation period of up to 110 days, and a weak Superearly Red Muscat, have long taken possession of the vineyards of Volgograd residents. Very often on the plots of winegrowers there is an early Volgograd with dark blue berries and elongated bunches (period 110–120 days).
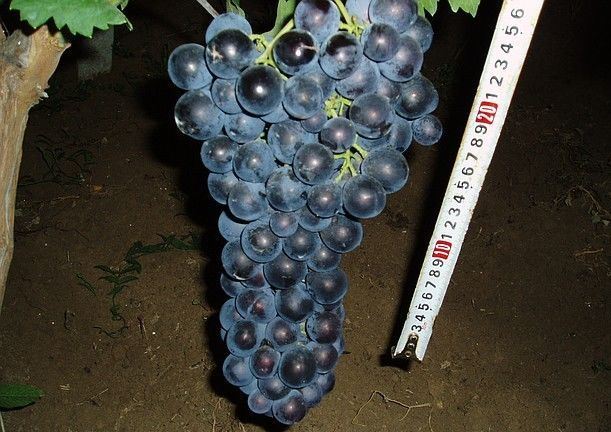


Early ripe variety Volgogradsky early
Video: early ripe grapes in the Volgograd region
Varieties for growing in the Rostov region
In the climatic conditions of the Rostov region, most of the ultra-early table and technical grape varieties fully ripen. The most famous grape hybrids:
- Julian;
- Delight;
- Libya;
- Laura;
- Galahad;
- Codryanka;
- Arcadia.
In the Rostov region, wine viticulture and the cultivation of dessert and wine varieties of seedlings are developed. Despite the fact that the region is located in the northern zone of industrial agriculture, not only domestic varieties have spread here, but also grape forms bred in the USA - Pink Seedlis, Ainset Seedlis. The vine requires shelter in the winter and preventive treatments against powdery mildew and fungal diseases of grapes.
The most famous zoned early ripening varieties: Delight, Pearl Sabo, Zorevoy. A covering universal variety Druzhba is grown with white-yellow moderately sweet fruits with fruity notes. The growing season is 110–120 days.
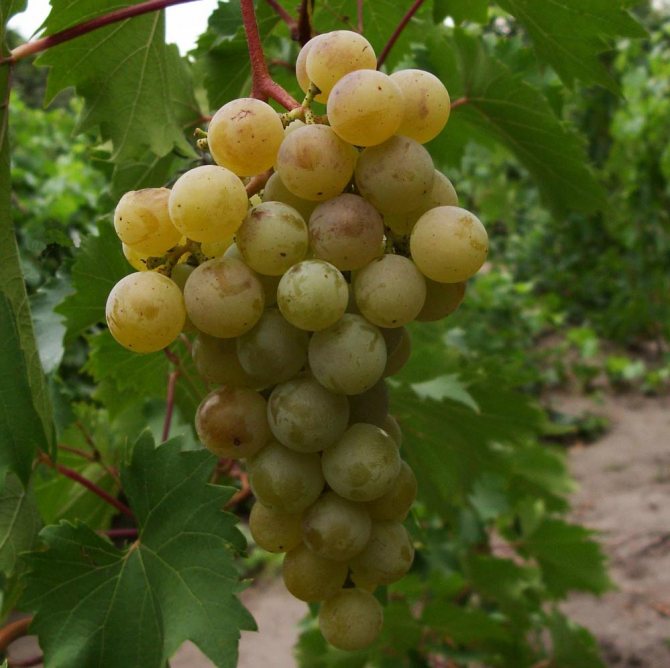


Early universal variety Druzhba
Varieties for cultivation in Belarus
On the Belarusian land, they often cultivate early and ultra-early forms of grapes in order to get the maximum yield from each vine in a temperate continental climate with the impact of Atlantic cyclones. Gardeners are trying to choose the most frost-resistant varieties that are practically not exposed to powdery mildew.
Popular varieties are Aleshenkin, Minsk pink, white-fruited with pink Tukai, Transfiguration, Julian. In the Vitib region, the ultra-early Riddle of Sharov of Altai selection with round purple berries was very fond of. The variety tolerates frosts down to -30 ºС and does not require shelter for the winter.
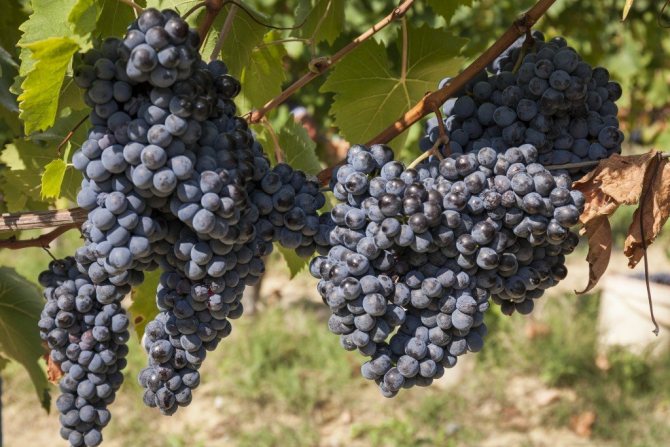


A hybrid of Siberian selection Sharov's Riddle has long taken root on the Belarusian land
Rusbol and Tason are prized for their large bunch and sweet fruits. These varieties ripen in Belarus at the end of July and require shelter in winter. Ultra-early Super Extra and Arcadia allow you to get up to 8-12 kg per bush, if planted on well-heated, fertile soils. Large brushes and sweet berries are obtained with timely normalization of the shoots and a moderate load on the bush.
Varieties for growing in Siberia
In Siberia, a decent harvest is harvested from zoned varieties of early ripening. For the northern regions, ultra-early varieties of grape forms are most relevant, which in 95-110 days manage to grow the vine, give a strong ovary and gain juiciness and sweetness. It is important that the varieties are adapted to the harsh Siberian climate and firmly endure return spring frosts, the influence of northern winds and early autumn colds.
Here they grow an early-ripening variety of Siberian selection Tukai with soft green, sweet fruits ripening in early August, a white-bellied Muscat Rusoven and a dark blue frost-resistant variety Muromets. Popular here are Kodryanka, Hercules and Bashkir early, Russian early and "local" varieties of the Riddle of Sharova. In Siberia, all grapevine varieties require abundant moisture recharge in the fall and a reliable shelter for the winter.
Video: early grape varieties for cultivation in Siberia
Homemade grape seed oil recipe
The seeds of fully ripe berries must be washed with water, dried in an oven at a temperature of 40–45 degrees, chopped in a meat grinder or in a coffee grinder, fill a half-liter jar with them, compacting the crushed mass, and pour refined sunflower oil. As it is absorbed, the oil should be added to cover the raw material by 0.5–1 cm.
Then the composition should be tightly closed with a lid and kept in the refrigerator for 7 days, stirring from time to time. After insisting, you need to squeeze the bones through two layers of gauze and again leave in a closed jar for 2-3 days. Carefully, trying not to shake up the greenish oil collected at the top is poured into a bottle.
To obtain a more concentrated grape oil, the resulting oil is poured into a freshly crushed mass of seeds and the whole procedure is repeated.
Features of growing vines
The plant matures normally in a warm climatic zone. In colder areas, the inflorescences will bloom and bear fruit later, planting in greenhouses is required. In order not to look for a pollinator, it is preferable to take the bisexual form.
Reproduction is carried out by cuttings, grafts or layering from an old bush. The culture is not demanding for watering. An adult bush is watered with warm water several times a season, a young seedling every week. To exclude diseases, they are sprayed with fungicides and insecticides. For proper growth, the vine is fixed on a support. In the fall, after the fall of leaves, a formative pruning of the bush is carried out and covered for the winter.
Thus, grapes are a special culture, not like fruits and vegetables. It is characterized by special growing conditions and rules of care, which must be strictly observed in order to get a rich harvest in a season.
Characteristics of dessert types
Each person has his own taste preferences. Some will like the sugary taste, others prefer the kishmish seedless types. But for viticulture lovers, other factors are important:
- Taste qualities of berries;
- Decorativeness of bunches;
- Good survival rate in a specific climatic region.
There are simply a great many dessert varieties in the world. Within the framework of the article, we will consider only some of the plant representatives.
"Arcadia"
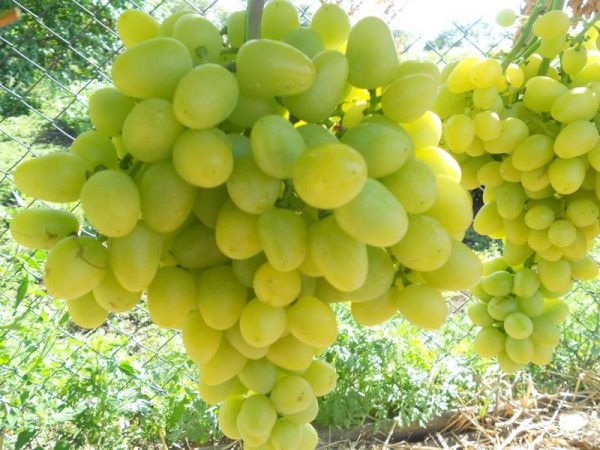


Arcadia grapes
This vigorous type of grape belongs to the early maturing varieties. Two varieties were used for breeding: "Cardinal" and "Moldova". The variety was developed in Ukraine.
The bunches are very large, sometimes they can weigh up to 2 kg, but the vine does not suffer from overload. They give good indicators even in the Far East.
The berries are mostly transparent green or yellowish in color. The pulp is quite juicy with a slight nutmeg flavor, practically pitted (2-3 pcs.). The ripening period is from 105 to 114 days.
Every year, the vine needs to be treated twice for powdery mildew diseases. Pruning is done deep, literally for 8-12 eyes.
Prices for seedlings of Arcadia
saplings grapes Arcadia
"Laura"
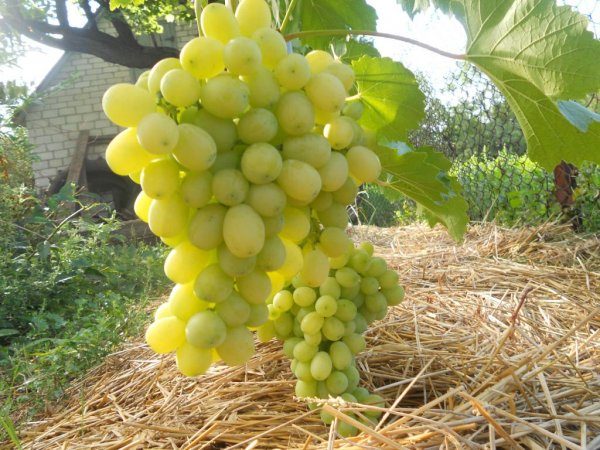


Laura grape
More than 2 decades ago, this hybrid type of grape was bred. Berries-ovals have a pointed shape at the bottom. They are distinguished by a light milky color. The peel is firm, the pulp is moderately sweet with a nutmeg flavor. The ripening period of berries is 110-115 days.
One bunch of the strain often reaches a weight of 800-900g. The plant is actively developing if the vine was shaped like a fan. After planting, the fruits appear already in the 4th year. Circumcision is recommended for up to 8-10 kidneys. The variety is popularly appreciated for its excellent adaptation to the terrain and its tolerance to severe frosts.
"White Kishmish"


White kishmish
The most favorite children's delicacy is “White Kishmish”. He is a representative of seedless varieties. Its round berries are fragrant and juicy. So they shine in a transparent emerald tone, and when the brushes are overripe, they shimmer with blush.
The bunch is long and loose. Relatively heavy hands reach a weight of 500-1200g. The berries are distinguished by their balanced taste and moderate sugar content. They lend themselves well to drying or freezing. Full ripening occurs after 140 days and lasts up to 160 days. Medium pruning.
Where and how it grows
- The grape shrub grows actively in the subtropical and temperate regions, and is also widely cultivated in many countries of all continents. Widely distributed in the countries of the Middle East, Western Asia, Bulgaria, Greece, USA, South Africa, Australia, China and Chile.
- On the territory of the former USSR, forest grapes are most often found in Moldova, Crimea and the Carpathians, as well as in the Caucasus, the eastern coast of the Black Sea and in the southwest of Turkmenistan.
- In horticulture or viticulture, grapes are usually grown on a trellis, a trellis structure that supports the plant.
- Grape clusters bloom from May to June, and bear fruit between August and September, some varieties in October.
Disembarkation start
To plant grapes, it is recommended to season them. Quenching is carried out as follows:


To begin with, the vine is taken out for ten days in fresh air, gradually increasing the hardening time, from five minutes to thirty. For the last three days, leave it there constantly, but do not forget to check the weather forecast.


Reproduction
Cutting method
Cuttings with 2-3 eyes are harvested in the fall from ripe vines. The diameter should be like a pencil. Make a bottom cut at an angle of 45º, stepping back 4 cm from the kidney. After cutting, the cuttings should not be kept in the sun. The optimum air temperature is 0-5ºC.
Fragment of grapes
The cuttings should be dipped for 7 minutes in a solution of ferrous sulfate (1%), dried, wrapped in paper, put in a plastic bag and placed in a storage location, for example, next to potatoes. Grape shanks should be obtained in early March. Brown bark, absence of spots and mold, peephole and cut of the cutting are green. It is necessary to soak suitable cuttings in a pale solution of potassium permanganate. Then put them in a jar with water and a drop of honey 5-6 cm and put a plastic bag on the shanks. The cuttings should be saturated with water, and then a cut should be made under the lower knot.
On a note. Pour the mixture (sand + humus + peat in equal proportions) into plastic glasses, make 5 cm depressions, pour some sand on the bottom and insert the handle. Fill the voids with sand. For a whole month, you need to heat the cuttings on a common pan so that the temperature below is about 25ºC. Water the dry soil periodically with water, loosen it, cut off excess shoots and inflorescences. In early May, the shanks need to be hardened on the balcony or terrace. After that, they are ready to plant.
Layers
This breeding method is used in spring and autumn. In the ground, you need to make a groove 50 cm deep. Pour black soil with humus into it, lay down an annual vine and cover it with soil. The top with 3 leaves and a growing point should remain on the surface. Pour 3 buckets of water over the vine. In spring and summer, the soil should always be slightly moistened, then young shoots will appear, each of which will have its own root system.
Diseases
Grapes can be susceptible to two types of diseases - infectious and non-infectious. And although bushes affected by a non-communicable disease are not infectious to their neighbors, they become very weak, with reduced yields.
Experienced gardeners distinguish grape diseases by the appearance of plants. Describing them will help you to determine the condition of the bushes and heal them.
- grape anthracnose is immediately visible on the leaves, they are covered with brown spots, turning into ulcers;
- powdery mildew (false) appears on the leaves, which are replete with round spots, as if sprinkled with white dust, it also affects shoots, inflorescences and fruits;
- oidium is very similar to the previous disease, only it manifests itself even more strongly: at first the plant is simply strewn with whitish spots, and then the affected parts begin to die off;
- rot (gray and white) affects the stems and berries, which are covered with brown-purple spots and soon dry out.


To combat these infections, there are now many remedies suitable for different types of diseases. Among them are copper or iron vitriol, Bordeaux mixture, Antrakol, Ridomir and others.
A well-groomed vineyard will delight its owner for many years with both the abundance of the harvest and the appearance. The most important thing is to make every effort and knowledge to ensure that the plant grows healthy, strong and resistant to climatic fluctuations.
As you can see, the hassle of growing grapes is enough. But even beginners, observing all the rules of care, will be able to grow it and enjoy the fruits of their labor.
Beneficial features
Grapes have a huge amount of useful elements. Moreover, they are contained both in the pulp and in the bones. The latter have found good application in the cosmetic field. Besides, grapes - the basis of winemaking... Berries are also used in various dishes and as a decoration for them.
It is noteworthy that not only the pulp and seeds have healing properties, but also the leaves and wood. In folk medicine, there is such a direction as ampelotherapy, which specializes in the treatment of chronic diseases with the help of grapes.
Grape seed oil
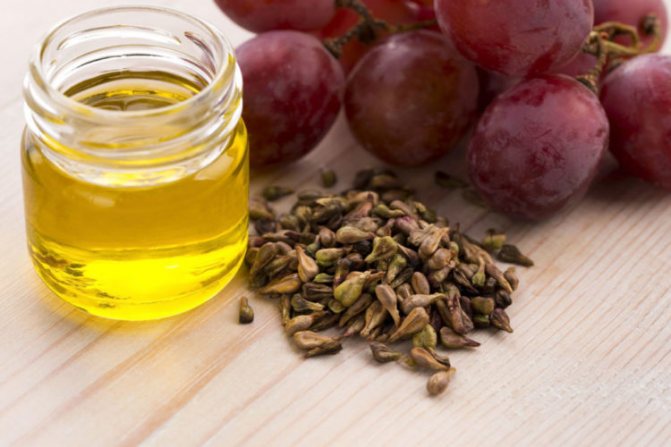


Grape seeds are endowed with many properties that have a beneficial effect in the treatment of many diseases. But biologically active substances are preserved only in the oil obtained by the cold pressing method. It contains bioflavonoids that resemble female hormones (estrogens) in structure, a large amount of vitamin E, vitamin C, as well as zinc, copper, selenium have been identified. Grape oil is considered to be the most powerful natural antioxidant that increases the elasticity of blood vessels.
The oil helps to reduce blood cholesterol levels, is useful as a prophylactic agent in the initial stage of hypertension. Daily consumption of a teaspoon of grape oil significantly reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis and arthritis. It is also recommended to take the oil to enhance immunity, protect against infectious diseases. Grape seed oil supplies the body with polyunsaturated fatty acids, tannins, enzymes, chlorophyll, potassium, sodium, and iron.
Healing oil prevents strokes, heart attacks, thrombosis, rosacea. The use of grape seed oil in combination with therapy for varicose veins and hemorrhoids provides a quick recovery. Such an excellent remedy has regenerating properties to maintain skin elasticity, and is suitable for the treatment of acne, acne, abrasions, cuts and burns.
Indications for taking grape seed oil are problems associated with disruption of the digestive system, hepatitis, diseases of the biliary tract. Cooking grape seed oil at home is based on the mutual penetration and substitution of oils, in physics this process is called diffusion.
Planting grapes in central Russia
When properly planted in a good location, grapes can grow and bear fruit for many decades without reducing yields.
Selection and preparation of a plot for a vineyard
Ideal vineyard plots in central Russia:
- well-lit and sun-warmed slopes of the southern, southeastern and southwestern directions;
- protected from cold northerly winds by building walls, capital fences or dense forest belts;
- fertile, deeply cultivated sandy loam or light loamy soils, easily permeable to water and air.


Grapes thrive on warm and light southern slopes
Strongly unsuitable for the vineyard:
- northern slopes;
- areas shaded by buildings or large trees;
- peatlands with close groundwater;
- damp lowlands with heavy clay soil, where water stagnates in spring.
The optimum acidity of the soil should be in the range of 6.5–7.2 for traditional European grape varieties, or 5.5–7.0 for complex hybrids of the Labruskov and Amur groups. It is necessary to analyze the soil no later than a year before planting the vineyard, in order, if necessary, to reduce the acidity by adding lime or dolomite flour. Lime materials are evenly scattered over the site before deep digging and embedded in the ground. It is impossible to bring them directly into the pits during planting, this can burn the roots of the seedlings.
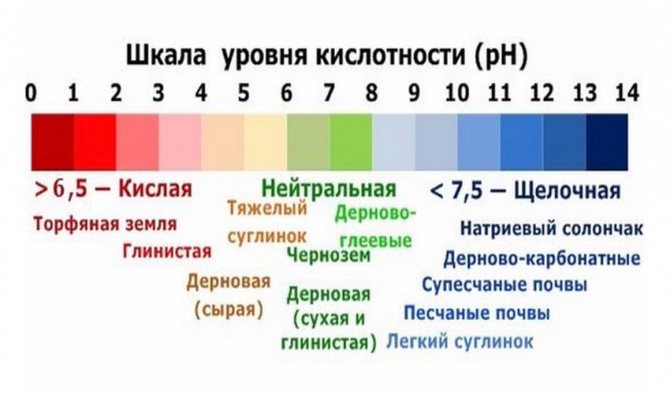

Optimum soil acidity for grapes from 5.5 to 7.2
Arrangement of trellises and arbors
For their normal growth and fruiting, grapes need reliable support, the frame of which is made of durable metal pipes or wooden beams impregnated with an antiseptic. Winter-hardy non-sheltering varieties can be grown on arbors of any height and configuration. Various supports attached to the south side of the house are well suited for grapes.
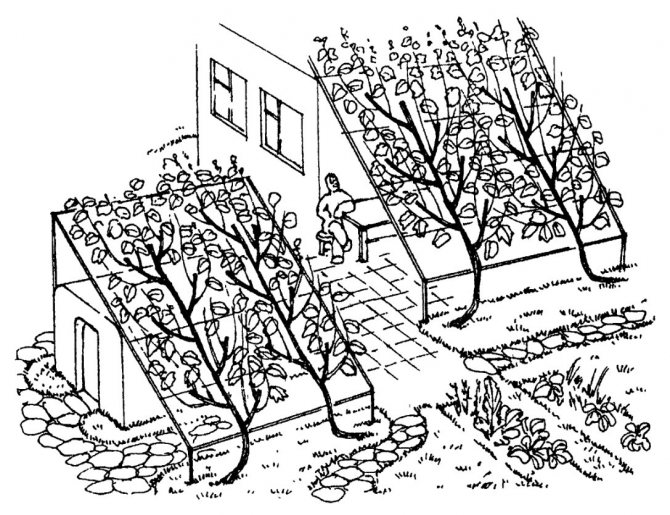

Supports for grapes can be conveniently attached to the southern walls of buildings
For covering grapes, it is not advisable to arrange supports higher than two - two and a half meters. When planning the entire structure, there should be sufficient space for the autumn laying of the vines on the ground.
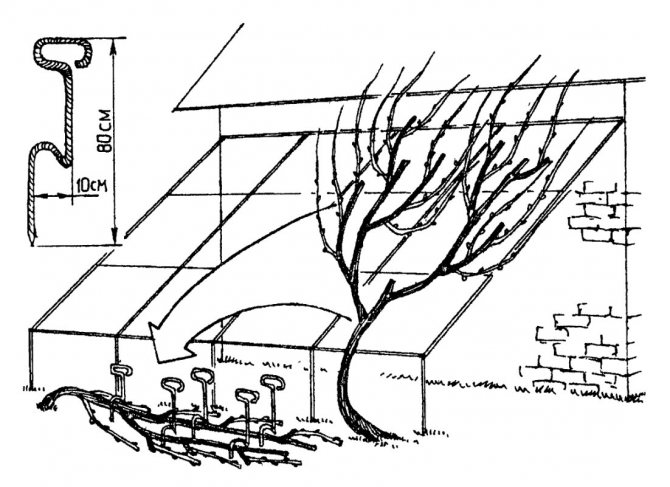

Covering grapes for the winter are removed from the supports and laid on the ground
The simplest support for grapes is a trellis of several pillars with a wire stretched between them. The distance between adjacent pillars is about two meters, they are dug into the ground for at least half a meter, and for reliability it is better to concrete. On long trellises, the extreme pillars must be reinforced in one of the following ways:
- from the outside of the trellis, small anchor posts are dug into the ground under a slope outward, the extreme posts are tied to them with a tightly stretched thick wire;
- the extreme pillars on the inner side of the trellis are firmly supported by inclined additional pillars-stops, the lower ends of which are dug into the ground.
The distance between adjacent trellises should be about two meters. They are placed in the north-south direction so that the grape bushes are better and more evenly illuminated by the sun throughout the day.
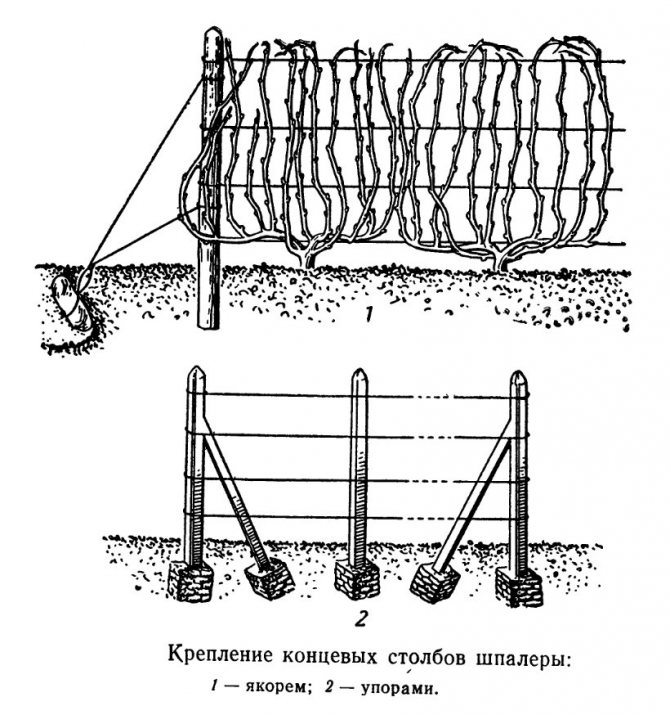

The extreme pillars of the grape trellis should be carefully strengthened.
The wire on the trellis is pulled in three or four parallel rows with a distance between them from thirty to fifty centimeters. If the grapes are covering, instead of the traditional wire, you can pull on a strong synthetic rope that can withstand one or even several seasons.
For long-term supports, especially for uncovered grapes, all wooden parts must be impregnated against decay, and the iron parts must have a protective coating against rust.
Selection and planting of seedlings
In central Russia, it is best to plant grapes in spring, from late April to late May. With a later planting, he runs the risk of not having time to root well over the summer. Seedlings should be purchased only in specialized nurseries in your region.
In no case should you plant seedlings of dubious origin brought from the south: firstly, they have insufficient winter hardiness, and secondly, with southern seedlings, you can bring into the garden the most dangerous quarantine pest - phylloxera, which is not yet in central Russia. Any seedlings from an unnamed roadside bazaar are a potential source of danger.
Before buying, check that the seedling is alive, not dried out or rotted. Seedlings with an open root system can only be taken before bud break. Container seedlings can also be with blossoming leaves, in this case, after planting, they need light protection from bright sunlight and possible return frosts.
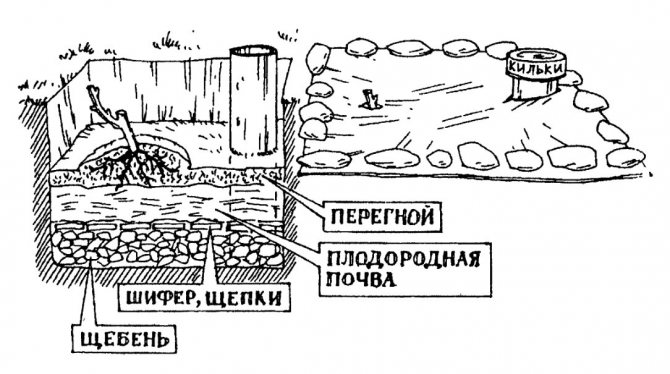

For planting grapes, deep holes are dug with a drainage layer at the bottom.
- Pits for grapes are needed large, 60–70 centimeters deep and 80–100 centimeters in diameter. It is better to dig them in the fall. The distance between adjacent pits should be at least a meter; to save energy, you can dig holes in two to three meters and plant two seedlings in each from opposite sides of the pit.
- At the bottom of the pit, a drainage layer of broken brick, crushed stone, fragments of slate and other similar materials must be placed. Drainage is especially necessary on loams and clays, where water stagnation is possible.
- On the side of the pit opposite from the future planting site of the seedling, it is advisable to place a piece of asbestos-cement pipe in such a way that its lower end rests against the drainage layer, and the upper one slightly rises above the soil level around the pit. From above, this piece of pipe must be closed with a lid from a tin can or a cut plastic bottle to avoid the entry of various debris. This system will allow in the future to properly water the grapes, supplying water to a sufficient depth directly to the roots. The irrigation pipe must not be placed very close to the seedling: in winter, the roots may freeze. The optimum distance from the seedling to the pipe is about 70 centimeters.
- A layer of fertile soil mixed with humus and fertilizers should be poured over the drainage. The approximate rate of fertilizers per pit: 1-2 buckets of decomposed humus or compost, 200-300 grams of superphosphate, 50-100 grams of potassium salt. Nitrogen fertilizers, lime and fresh manure should not be applied during planting.
- In the process of planting, a small mound of prepared fertile soil is poured into the pit, on which it is necessary to lay the seedling with an inclination in the direction where the vines will be laid when sheltering for the winter. Non-covering varieties can be planted vertically.
- The roots of the seedling must be evenly spread to the sides and covered with a layer of earth. With proper planting, the bottom of the seedling (heel) should be at a depth of about half a meter from the soil surface.
- If the buds of the seedling have not yet woken up, you can immediately completely cover it with earth so that one bud remains above the surface. If a seedling with blossoming leaves, it is planted at first shallow, and then, as the shoots grow, the earth is gradually added. For the first summer, all the land taken out during the digging should return back to the pit.
- The planted seedling must be carefully watered with two buckets of water from a watering can with a spray, so that the soil evenly settles and compresses.
- After planting, you can cover the pit with the seedling with a piece of film or agrofibre, pressing the edges of the covering material with stones to the ground. Such a shelter is especially important for early planting of seedlings with already blossoming leaves.
Caution
You should not use grapes and grape juice when:
- diarrhea
- diabetes
- edema
- hypertension
- chronic pharyngitis
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
- if you are overweight or obese
- oncological diseases of the stomach
Also, grapes and its juice should not be consumed at the final stage of pregnancy, as this negatively affects the functioning of the mammary glands.
Nutritional value and chemical composition
Grapes contain sugar, mainly in the form of glucose. One kilogram of grape fruits, regardless of the variety, contains on average 300 grams or more of sugar.


Among other things, berries also contain:
- tartaric, malic acid - from 0.5 to 1.4%;
- other organic acids - 0.3-0.5%;
- minerals - mainly iron, phosphorus, calcium;
- protein substances - 0.15-0.9%;
- pectins - 0.3-1%;
as well as such vitamins:
- carotene (A);
- thiamine, aneurin (B1);
- riboflavin (B2);
- ascorbic acid (C);
- pyridoxine (B6);
- niacin (PP);
- vitamin R.
Grape juice contains:
- a large amount of fructose and glucose, which are easily absorbed by the body;
- potassium cation;
- organic acids;
- trace elements.
Grapes of any variety are quite high-calorie foods: 100 grams - 70-150 calories.
With the help of bunches
The appearance of a bunch is of several types:
- branched;
- cylindrical;
- bladed;
- conical.
When determining the variety, attention is paid to the density of the grapes. The bunch is loose, dense, very loose and of medium density. It should be noted that the size of the bunch also depends on external factors, for example, climate and fertilization. But the size of the fruit, in any case, should not be radically different in size.


Tips for growing grapes
Every novice winegrower can grow grapes with a little effort and some knowledge. A favorite business can be both useful and profitable, but with the right approach to business. Let's take a look at some tips for growing grapes.
- Before planting, you should decide on the choice of a variety. Understand the difference between dessert and technical look. Wine products are usually made from the first category, and dessert varieties are for home use, or you can have a good income from the sale.
- An important factor is the place of planting and the quality of the soil cover. This is the basis for the future harvest. The place should be sunny, but without open drafts and winds. It is best to plant grape cuttings from the south side near the building.


It is necessary to choose the right place for planting grapes
- Eliminate the accumulation of moisture, rainwater. Cuttings should be planted early in the fall so that they take root, and cover for the winter, protecting them from freezing.
- Grape varieties should be selected with different ripening times. Then, from the middle of summer, bunches of grapes can flaunt on your table until late autumn.
- Do not forget to water the vine, loosen it, and apply sufficient mineral fertilizers.
- To carry out timely processing of cuttings and adult vines with special preparations from diseases and insect pests.


Substances required for feeding grapes
You can read more about how to care for grapes in our article.
Important! Today in European countries in medicine there is such a concept as "grape treatment". According to some doctors, one course of ampelotherapy is equivalent to a course with mineral waters.
Mineral fertilizer prices
mineral fertilizers
Disembarkation of shanks in the garden
You can plant seedlings sprouted at home on a permanent place in May. It will be better if, before disembarking, you harden the shanks for 5 days, exposing them to the street. After planting the cuttings, the soil must be watered regularly so that it remains constantly moistened. The grapes reproduce very well by cuttings.
If you follow these guidelines, you can grow strong and healthy seedlings at home, ready to be transferred into the soil. By autumn, vines with a strong root system will grow from the cuttings planted in the garden.
Extract from grape seeds
Grape seed extract is used to treat venous diseases. This is a powerful antioxidant agent that strengthens capillaries, is effective in thrombosis, helps well with varicose veins, trophic ulcers, increases hemoglobin, normalizes blood count, prevents platelet adhesion, has a wide spectrum of bactericidal and antiviral effects.
It has been proven that with pathologies of the retina and optic nerve, grape seed extract improves visual functions and eye hemodynamics. The tonic properties of the healing agent improve sleep, relieve psycho-emotional arousal. There is a decrease in chronic fatigue syndrome. In case of mental and physical overload and stress, the useful substances of the extract replenish the body with an energy charge.
Grape seed extract


Grape seed extract contains glycosides, fructose, flobafen, enin. In large quantities, this product contains malic, phosphoric, silicic, salicylic, citric, succinic, oxalic acids. Due to the presence in the extract of salts of potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, vitamins B1, B2, A, C, tannins, flobafen and lecithin, cell renewal occurs. The value of the remedy is powerful antioxidants that neutralize enzymes that destroy the structure of connective tissues.
As a result of their action, the walls of blood vessels are strengthened and the level of collagen of the skin, tendons, and cartilage is normalized. The extract is able to restore the function of the retina, is taken as a prophylactic agent that prevents myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis. Smoking, drug side effects and poor environmental conditions affect human health; grape seed extract will help remove toxins, reduce the negative effects of harmful substances on the body.
Harm and contraindications
With frequent use of grapes, as well as viticulture products, it should be borne in mind that grapes are not recommended to be eaten when:
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- peptic ulcer (especially during an exacerbation);
- chronic suppurative processes in the lungs;
- heart failure, accompanied by severe hypertension and edema;
- intensification of fermentation processes in the intestines and colitis, accompanied by diarrhea.
It is quite common to experience severe stomach upset if you combine grapes with:
- fresh or pickled cucumbers;
- milk;
- melon;
- any fatty food;
- fish;
- mineral waters;
- beer.
It is worth remembering that when grapes get on carious teeth, it only intensifies their destruction. To save teeth from damage, experts recommend that after each intake of grapes, including raisins, thoroughly rinse the mouth with a large amount of a solution of water and baking soda.































