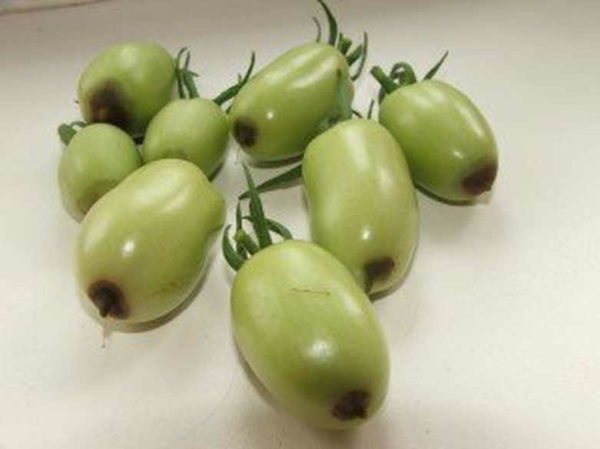
Top rot is a physiological disease of tomatoes that is not associated with pathogenic factors. It appears with improper care and affects tomatoes both outdoors and in the greenhouse. Peppers are more sensitive to the disease, and are affected first. If apical rot appears on them, then simultaneously with their treatment, preventive measures are taken on tomatoes.
What is this disease?
Top rot is a common disease affecting tomatoes that is not associated with a bacterial or fungal infection. It appears as a result of non-observance of the rules for caring for plants and a deterioration in the quality of nutrition of the root system.
The fruits are affected. Moreover, the decay process can begin simultaneously on tomatoes of varying degrees of maturity. Fruit spoilage starts from the top - the area farthest from the stem. Rot captures both ovaries, and green and red tomatoes.
The disease affects bushes growing both in an open area and in a greenhouse. But greenhouse vegetables get sick more often, which is associated with microclimatic conditions and the peculiarities of growing in an enclosed space.


The first signs of defeat
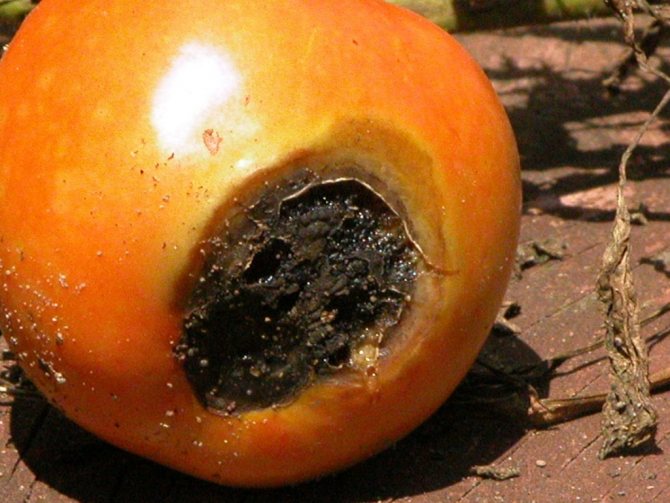
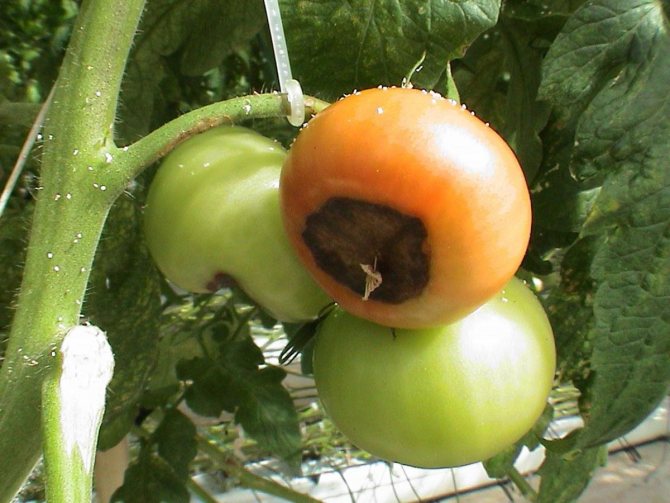
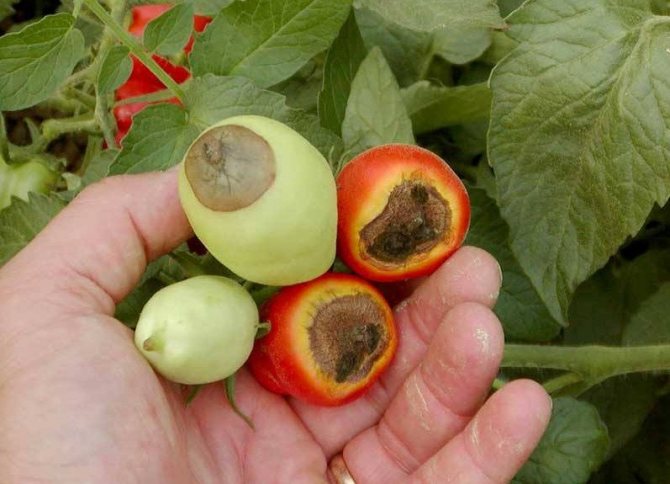
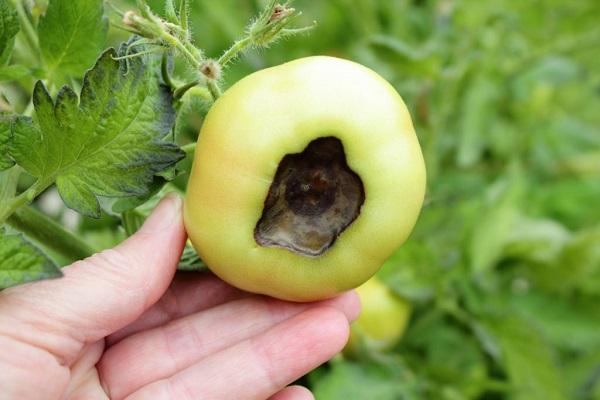
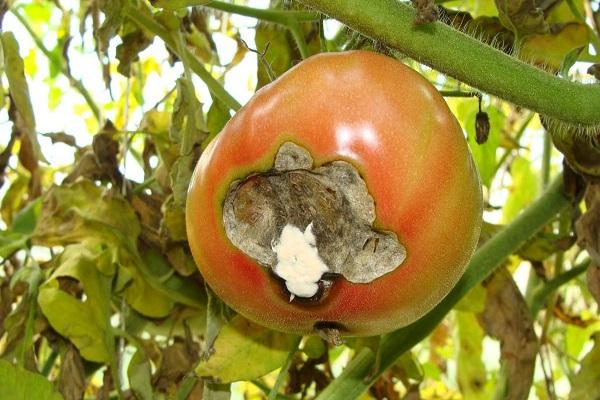
Top rot on round-fruited tomatoes most often begins to appear in the area of the flower scar, that is, in the place of the fruit that looks down when the tomato hangs. It is this place that is the top of the tomatoes, and not the place where the stalk is attached. Talking about the onset of tomato apical rot disease, gardeners mean the appearance of dark spreading spots on the tops of green fruits. They can cover up to half the top of the tomato.
Gradually, the top of the fruit is pulled inward, as it were. The shape of the tomato is changing. The apex becomes flattened. The necrotic spot grows and hardens. The tomato begins to blush prematurely, shrink, decrease in size. With increased air humidity, the affected areas begin to crack, bacteria and fungi colonize them.
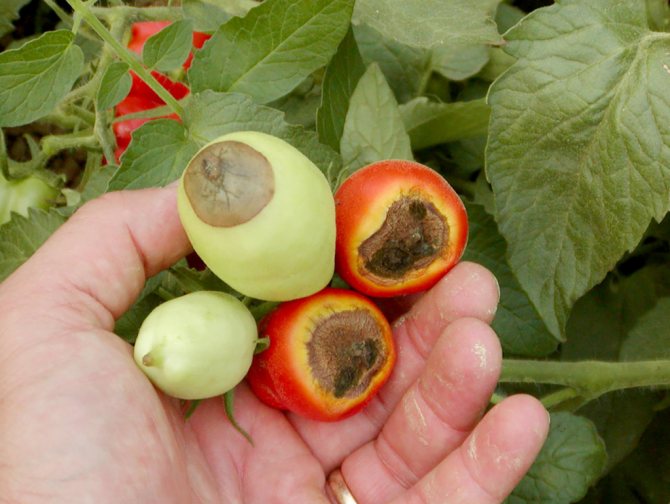
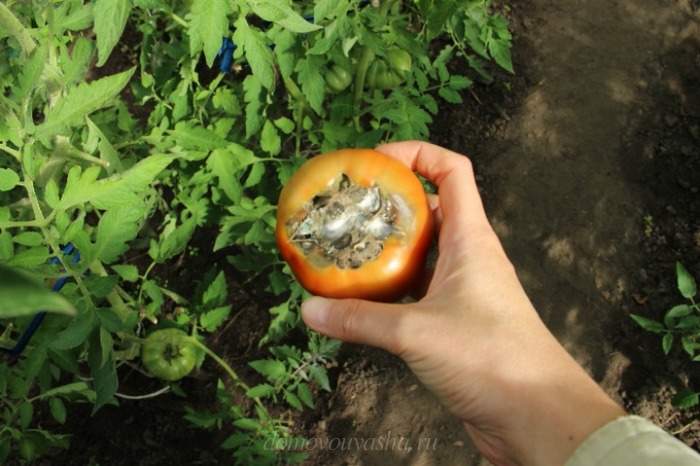
Tomatoes with elongated fruits get sick secretly. Top rot on them by external signs can be seen when they begin to blush ahead of time. Only after the diseased fruit is cut will the blackened dead pulp be found. Damage to the tops of all types of tomatoes can also occur if the already fully poured fruits ripen while lying on the ground. From contact with the soil and the bacteria in it with high humidity, weeping rotting spots appear on the tomatoes.


Reasons for the appearance
The most common factor in top rot is calcium deficiency in plants. This mineral element is essential for the formation of the tissues of the fruit pulp.
Once in a plant organism, it is included in the composition of salts, without which tissue necrosis begins in tomatoes, outwardly looking like rotting of the apex.
There are several reasons why calcium is not absorbed in sufficient quantities by the roots.
Moisture deficiency
When the soil is poorly moistened, the root system simply cannot absorb the mineral.
A similar situation is observed with waterlogged soil.When moisture stagnates in the soil, which is observed during overflow or occurrence of groundwater close to the surface, calcium is washed out. The roots cannot absorb a substance that simply does not exist.
Micronutrient imbalance
Top rot is inevitable if tomatoes are planted in the wrong area, where the soil is poor in calcium. Before transferring tomato seedlings to a permanent place, the soil must be saturated with minerals.


Excessive level of salts in the soil
It is useless to grow tomatoes in an area where the soil is salty or has high acidity. In such a land, there is always a calcium deficiency.
Reasons for the development of top rot on tomatoes
Lack of moisture and hot air lead to intensive evaporation of liquid from the leaves and trunk. If during this period the access of moisture through the root system is not provided, the plant begins to suck it out from the fruit. As a result, some of the fruit cells die off and the top rot of tomatoes develops, the treatment of which is much more difficult and labor-intensive than the prevention of infection.
Among other reasons for the development of tomato top rot are:
- Lack or excess of calcium;
- Excess nitrogen;
- High soil acidity.
Symptoms of tomato infestation
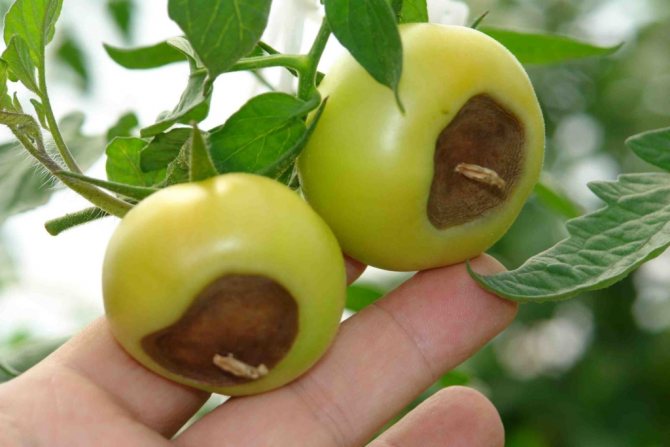
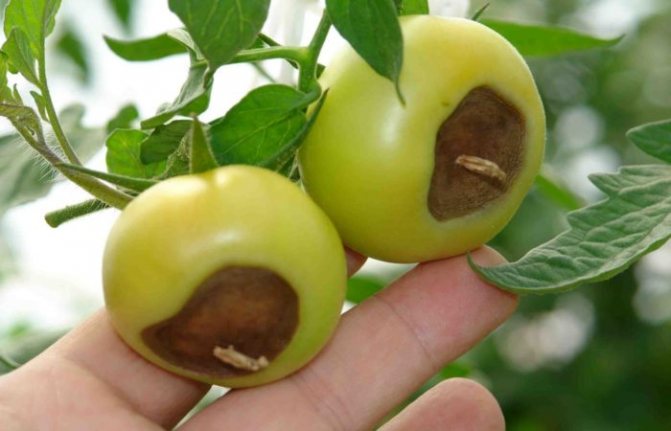
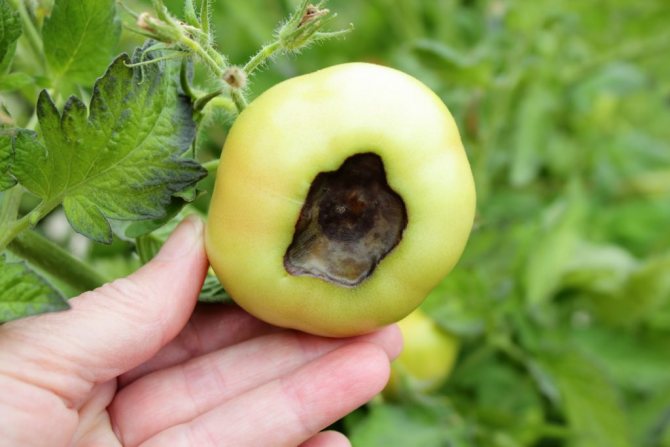
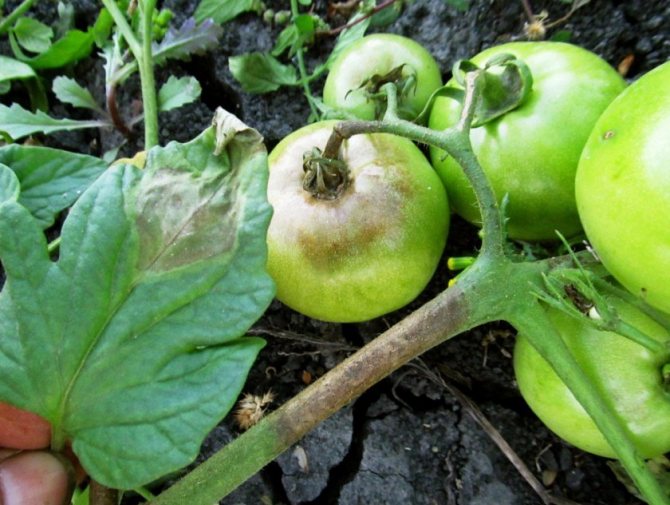
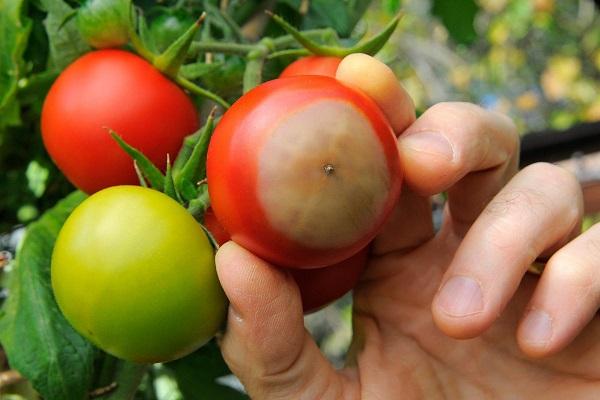
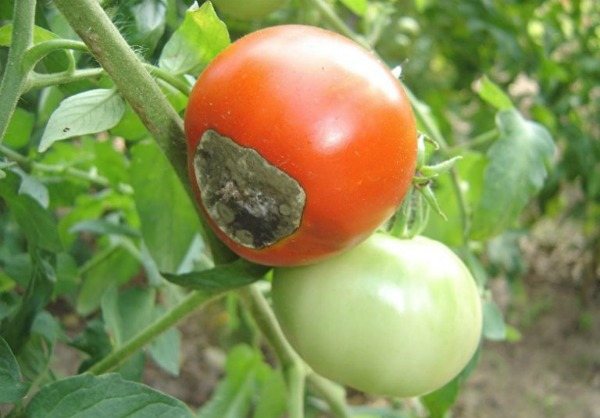
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance and spread of a soft brown spot on the top of the fruit. As it expands, the putrefactive formation darkens more and more, from yellowish brown to brownish brown. It also becomes softer, as if pressed into the pulp.
Sometimes the disease develops asymptomatically, the fetus rots inside. The pulp decomposes, but the peel remains intact, seemingly healthy. It is impossible to detect the disease before harvesting.
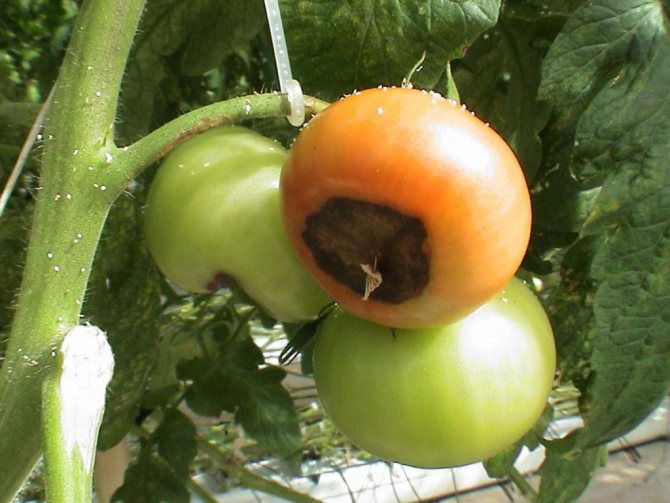
Fruits spoiled by apical rot turn red earlier than healthy ones. But usually the disease captures all the tomatoes on the bush at the same time.
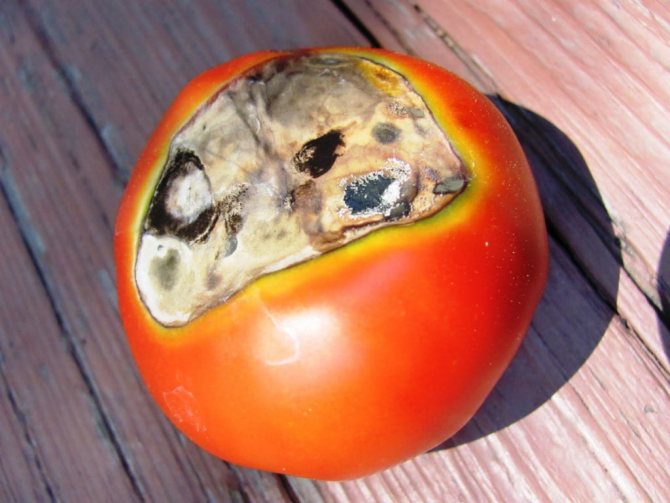
Top rot does not occur as a result of an infectious lesion, is not associated with the vital activity of harmful insects. However, the area of the fetus captured by necrosis often becomes a fertile place for the reproduction of pathogenic fungi.


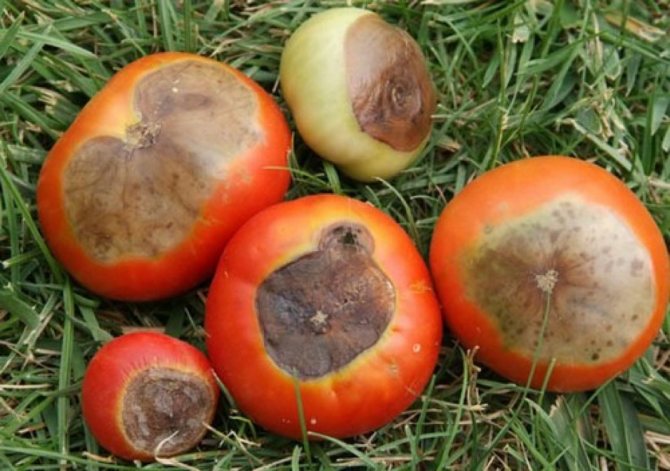
Symptoms of the disease and photos of affected fetuses
- The tomato looks a little flattened.
- Spots are visible on its skin: at first they are dark green, small, eventually darken and increase in size. In hot dry weather, the fruits are hard to the touch, but if the humidity is high, the spots soften, and the decay process begins earlier. Defeat has uneven boundaries.
- The surface of the spot wrinkles over time, the twig withers, the fruit turns red (and it does not increase in size) and falls off.
Apical rot primarily affects fruits growing on the lowest cluster.
Here you can see how the diseased tomato fruits look in the photo.
How to deal with an illness - the most effective remedies
Tomato treatment includes the use of calcium supplements, folk remedies, as well as copper sulfate and other fungicides to prevent fungal infection.
What methods to save the plants, the gardener chooses at his own discretion, taking into account the degree of neglect of the disease, the state of the bushes captured by rot.
Biofungicides
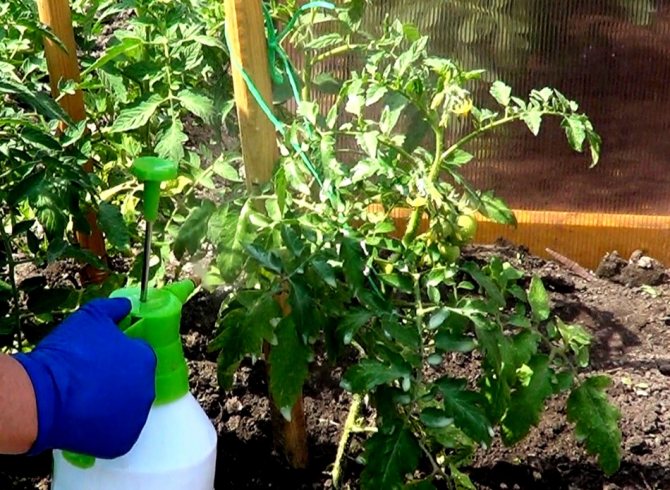
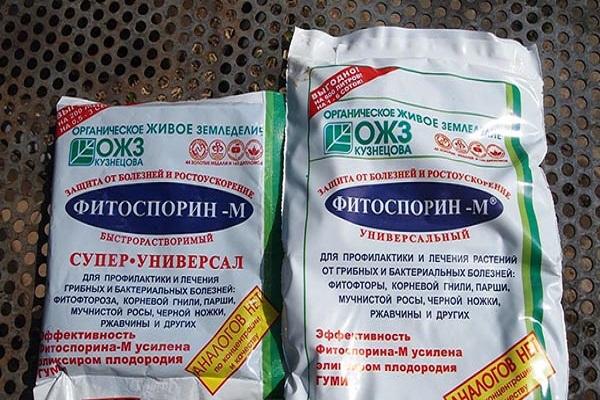
Since apical rot provokes the spread of fungal infection, one cannot do without the preventive and therapeutic use of fungicides. The biological product Fitosporin is used to process tomatoes.
In case of extensive fungal infection, spraying with copper-containing compounds is recommended. Bordeaux mortar can be used. They do it like this: take 100 g of copper sulfate in a 10-liter bucket, dissolve in 9 liters of water. Separately, make a solution of 100 g of quicklime and 1 liter of liquid. The compositions are connected.


Chemicals
To eliminate soil calcium deficiency, the following chemicals are used:
- Calcium chloride solution - 3 g of substance per 10-liter bucket of water.
- Fertivant preparation - 3 g per 1 liter of water. Or its analogues in action - Nutrivant, Brexil Ca, Gumfield.
- Limestone nitrate solution - 1 g per liter of water. It should be treated by spraying.
- A mixture of calcium nitrate and boric acid - 1 g of each substance per 1 liter of liquid.
- Any mineral fertilizer suitable for nightshade crops. Processing according to the instructions on the package.
Folk remedies for the treatment of apical rot
If the fruits are set, and you do not want to use chemistry, then the problem can be solved with the help of folk remedies. Of course, they will be effective only at the very beginning when the first signs of the disease appear.
- Ash decoction. Pour 300 g of sifted ash into 1 liter of oxen and simmer for 15 minutes. Then strain the solution and pour it into a bucket with 10 liters of water. Spray the tomato bushes with the resulting solution. Within 10-15 minutes, the plant will assimilate the necessary element.
- Eggshells and wood ash, it is good to add them to the hole when planting seedlings, as a source of potassium, phosphorus and calcium.
- Bordeaux liquid - it is good for treating plants with bacterial rot. How to use Bordeaux mixture correctly?
- Calcium chloride is a medicinal solution for intravenous administration that is sold in any pharmacy. The box contains 10 ampoules per ampoule of 5 or 10 ml of solution. For foliar feeding, 5 ml of calcium chloride are diluted in 5 ml of water, and an ampoule with 10 ml is diluted in 10 liters of water, respectively. The resulting solution is immediately sprayed with the plant. This method is easier and safer. Such treatments are carried out at least three with an interval of 10-14 days.


Terms and rules for processing tomato beds
Both chemicals and folk remedies are used immediately after the symptoms of apical rot are detected. The duration of treatment is determined by the degree of neglect of the disease. But with regular spraying, the condition of the affected tomatoes will return to normal in a short time.


In greenhouses and hotbeds
To effectively combat top rotting in closed beds, it is necessary to eliminate calcium deficiency in the soil, to normalize the growing conditions for tomatoes.
Care for both greenhouse tomatoes and those growing in an open area is almost the same. There are only minor nuances to cope with rot when growing in a greenhouse:
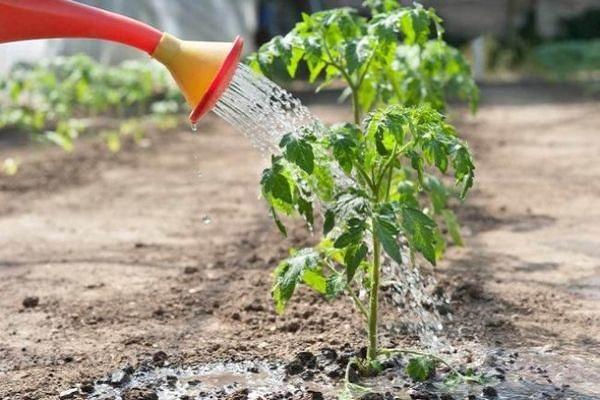
- Watering tomatoes should only be done manually. It is necessary to draw up a watering schedule. Moistened greenhouse soil must be loosened.
- It is necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse, let fresh dry air inside.
And in general, the fight against greenhouse vertex rot is carried out by the same means and methods as with the one that appears on tomatoes in the open field. Plants are treated with a solution of calcium chloride or limestone nitrate every 3 days. The frequency of treatment with fungicides and mineral fertilizers is indicated in the instructions on the package.
In the open field
If the disease has just begun to develop, the first symptoms have appeared, then the rot can be stopped by observing the watering rate in the dry summer months. For tomatoes, such moisture is optimal, in which the soil does not dry out deeper than 3 cm.
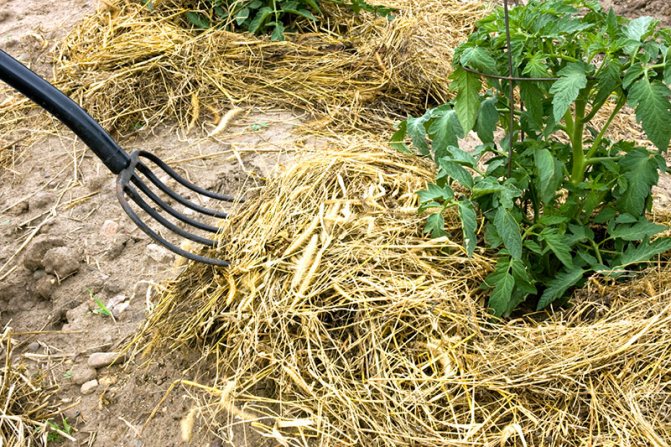
So that the soil moisture evaporates more slowly, the tomato beds are covered with mulch - sawdust, straw.
If the reason for the appearance of top rot is the drying out of the soil, then these measures are sufficient to normalize the state of the plants.


If the calcium deficiency in tomatoes is due to the disturbed mineral composition of the soil, then fertilizing will have to be used to combat fruit rotting. Moreover, it is necessary to act in two stages:
- Urgently eliminate the calcium deficiency by applying mineral fertilizers. This will save this year's harvest.
- In the fall, apply fertilizer for digging to prevent the appearance of top rot in the next growing season.
Why does this disease occur on tomatoes


Several factors lead to calcium deficiency, which the gardener is able to eliminate:
- lack of watering leads to slow transport of the element from the soil to the plant tissues;
- high acidity of the soil brings calcium to a state that does not allow the tomato to assimilate it;
- too cold water used for irrigation combined with hot weather;
- excess nitrogen in the soil;
- stressful situations (a sharp drop between day and night temperatures, uneven watering) provoke disruptions in the plant's intake of nutrients from the soil.
Mechanical damage to the tomato root system during unsuccessful hilling and weeding can indirectly lead to calcium starvation. Damaged roots absorb nutrients from the soil worse.
On a note. Cultivars that have very large fruits or are elongated in length are more susceptible to apical rot disease. The farther the tip of the fruit is from the stalk, the greater the likelihood of injury.
Greenhouse plants are more likely to suffer from top rot than open field tomatoes due to their high height and yield.
Is it okay to eat top rot tomatoes?
Fruits with a rotten top will have to be disposed of. It is absolutely impossible to eat them. A necrotic spot in a short time becomes a breeding ground for a fungal infection. And the pathogen, in turn, spreads rapidly through the pulp.
Having eaten a tomato affected by rot, a person is faced with a disorder of the digestive tract, intestinal dysbiosis.
But if you cure tomatoes, then the fruits that appeared after the disappearance of rot can be safely consumed.


Popular insecticides


How to get rid of top rot when most of the plants have been affected? Here, saltpeter, oak bark or calcium chloride will no longer help and specialized insecticides will be needed.
Metronidazole (available in 0.25 gram tablets)
For prophylaxis - 1 pc. into each of the holes before landing.
For watering - 5 pcs. for 10 liters of water.
For spraying - 20 pcs. for 10 liters of water.
Fitosporin
Available in powders or pastes.
For watering or spraying infected plants - 3 teaspoons of paste or 20 grams of powder per 10 liters of water.
IMPORTANT! Such procedures are best done either in the morning or in the evening.


Various growth stimulants, as well as compositions that help to increase the immunity of tomatoes (EPIN, MEGAFOL and others), help well.
Protection and prevention measures
To prevent top rot on tomatoes, you must:
- In the fall, dig up the soil in the area set aside for nightshade crops.
- Water the tomatoes correctly. Use lukewarm water that has settled. Do not overflow.
- Monitor the temperature and humidity in the greenhouse. Air it out.
- Fertilize tomatoes 2-3 times per season with fertilizers in accordance with the recommended dosages and schemes. Carefully use organic matter - manure and bird droppings, do not exceed the dose.
- Treat plants foliarly with calcium chloride or limestone nitrate. For preventive purposes, it is enough to feed once a week.
Preventive measures


In order to avoid the appearance of apical rot on the site, experts recommend not to forget about the following preventive measures:
- The plot on which tomatoes will be grown next season is subject to mandatory digging in autumn.
- Provide correct and timely watering to tomatoes. As soon as the fruits are formed, the bushes begin to water systematically, but in moderation.
- Maintain the optimal temperature and humidity in the greenhouse. Ventilate it if necessary.
- Be sure to feed your tomatoes properly.In no case do not arbitrarily increase the frequency of fertilizing and the concentration of fertilizers. Pay special attention to poultry droppings and manure.
- If the soil in the area is dense, heavy and prone to acidification, this should be corrected by liming. To do this, the soil on the site is dug up in the fall or spring, adding ground chalk, bone meal, dolomite flour or fluff into it. For 1 square meter of the site, take 1 kilogram of any of the additives.
- If the area is swampy, it must be well drained. Instead, you can make high beds, for this you should use light soil, into which a small amount of substances are poured, which contain lime.
How to protect tomatoes from late blight in a greenhouse
Top Rot Resistant Tomato Varieties
To fiddle with prevention less, it is advisable to choose tomato varieties that are not susceptible to apical decay. Rot most often attacks early maturing, hybrid and large-fruited nightshades. The most susceptible varieties include:
- Alabai;
- Openwork;
- Sprint Timer.
These tomatoes spend a lot of nutrients on the formation of fruits. Therefore, without careful care and application of mineral fertilizers, the bushes quickly fall ill.


Non-capricious tomatoes are least susceptible to top rot:
- Volgograd;
- Astrakhan;
- Bolshevik;
- Raisa;
- White filling;
- Benito;
- Pandarose.
The more unpretentious the variety, the less demanding it is on conditions and care, the lower the likelihood of rotting the fruit.
Resistant varieties
List of resistant varieties:


- Gourmet;
- Katya F1;
- Lyubasha F1;
- Explosion;
- Eupator F1;
- Successful;
- Yamal 200;
- Butuz;
- Chocolate;
- Budenovka;
- Far North;
- Chocolate cream;
- Lyrics F1.
There is no one hundred percent guarantee that these varieties will not get sick, but the likelihood of an ailment (compared to conventional varieties) is significantly reduced (since it has been noted that, first of all, rot affects large-fruited and early-maturing varieties).
Useful advice from gardeners
Experienced growers share tips to help you grow top rot free tomatoes:
- A couple of months before sowing, tomato seeds are soaked in a solution of potassium sulfate or manganese potassium (1%) or in succinic acid (17 mg per 1 liter of water). Immediately before sowing, the seed is immersed in any growth promoter.
- Before transferring tomato seedlings to a permanent place, the soil in the selected area is treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, heated to 50 °.
- If the greenhouse soil is dry, then a little turf is added to it.
A balanced mineral composition of the soil, moderate watering, proper feeding are factors, taking into account which you will never have to fight top rot. Careful plant care is the key to getting a rich harvest.
How to treat top rot with baking soda and ash on tomatoes
Experienced gardeners say that treating top rot with soda is unnatural. After all, the composition of soda ash (sodium carbonate, in another way anhydrous sodium carbonate) Na2CO3 will not add calcium either to the soil or to the plants. The formula for baking soda (sodium carbonic acid salt) NaHCO3 indicates that there is no calcium in this substance either. Mixing wood ash and baking soda will also not produce the expected results. Therefore, it is better to treat the top rot of tomatoes with an extract from wood ash without adding some kind of soda.
Why it happens and how to treat tomato apical rot
Other diseases of tomatoes
Tomatoes are susceptible not only to top rot, so it is worth paying attention to the main diseases that can make all the efforts of the gardener useless.
- Late blight. The disease is typical for tomatoes grown in the open field. It manifests itself in brown spots that initially appear on the back of the lower leaves. Subsequently, it spreads throughout the bush, affecting shoots and fruits.
- Cladosporium (brown spot). The disease affects the leaves and manifests itself in the form of small dark spots with a gray coating. Subsequently, the affected leaves dry out, and the bushes die.
- Mosaic. A viral disease that cannot be treated. It can be recognized by spots that have a light shade in the middle, and dark along the edge. Subsequently, the damaged leaves completely wrinkle and curl. Over time, the bushes also die.
It is possible to avoid the defeat of tomato bushes only if the basic rules of care and prevention are observed. Therefore, do not neglect useful recommendations, and then a generous harvest is guaranteed.
Top Rot Control Techniques
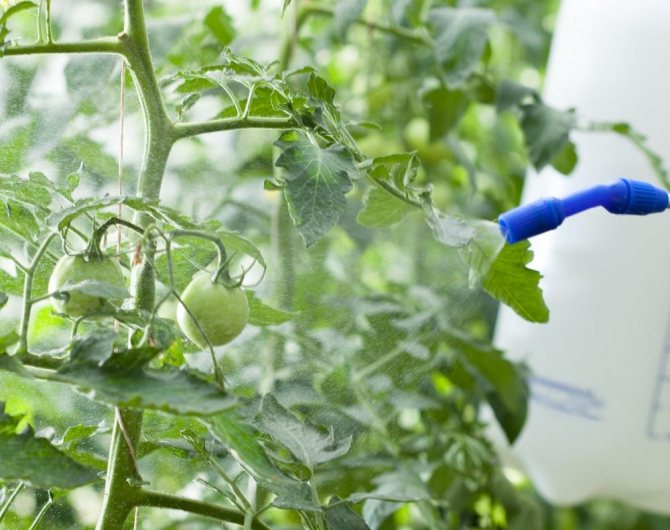


Processing tomatoes in the greenhouse
Measures to combat the pathology of tomatoes growing in the greenhouse include an integrated approach. This is the only way to overcome the disease and save future crops from a dangerous disease. This consists of a number of measures aimed at destroying fungi and factors that provoke tomato disease. In particular, the following applies:
- agrotechnical measures (establishment of a watering and loosening regime, pruning of damaged stems and fruits, ventilation);
- processing with special means;
- saturation of tomatoes with calcium fertilizers.
Normalizing the composition of the soil and saturating it with calcium is the only way out that will help cope with top rot. The purpose of all measures in the fight against top rot on tomatoes in a greenhouse is to remove damaged parts of the plant and saturate healthy shoots with a sufficient amount of nutrients.
Agrotechnical procedures
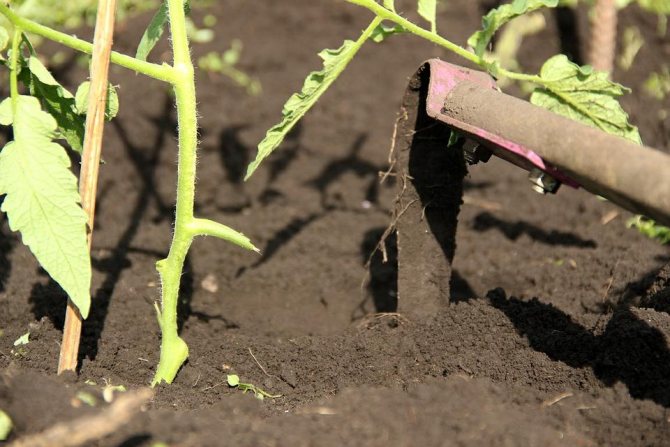


Loosening the soil
Having established the causes of the disease and starting to fight the disease, the first thing to do is to sanitize the greenhouse. This is a whole complex of measures that will help get rid of a fungal infection, which has probably already settled in damaged shoots, as well as get rid of infected plant parts. To normalize the situation in the greenhouse, you will need:
- regular loosening of the soil (the main thing is not to damage the root system);
- pruning disease-damaged shoots, fruits and burning them in neutral territory, away from cultivated plantings;
- the introduction of an irrigation regime (in order to establish the water-salt balance in the greenhouse, it will be necessary to water the plants so often that the soil does not have time to dry out by more than 2 - 3 cm);
- airing the greenhouse (in order to prevent and fight the disease in the greenhouse, they arrange night ventilation, leaving the doors open at night);
- fertilization (dressings with a high content of minerals are used, in particular, calcium nitrate and others).
Fertilizers with a high calcium content will help save tomatoes or only part of the crop, but will definitely help fight top rot. Experienced agronomists advise to carefully monitor the fertile soil layer in the greenhouse in order to avoid painstaking treatment of tomato diseases.
Processing with special means
Experienced gardeners advise using store products only for large lesions of tomatoes with apical rot. Balanced dressings with a high content of beneficial minerals help to enrich the fertile soil layer and provide the cultivated plant with sufficient calcium.
Most often used:


Brexil Sa (complex fertilizer, 15% consisting of calcium with the addition of boron in an amount of 0.5%, this substance helps to absorb calcium more reliably and faster, contributing to its rapid advancement, the substance consists of organic complexes that are harmless to tomatoes, processing is carried out every 10 - 15 days after abundant watering of plants in the greenhouse);
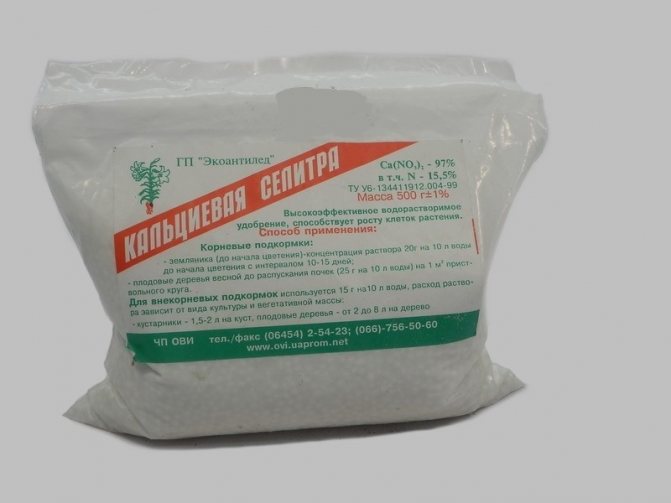


Calcium nitrate (also called "calcium nitrate", nitrogen nitrates help the rapid movement of calcium through the soil, and then in the plant, enriching and saturating it with important trace elements, 20 g of calcium nitrate and 10 g of boric acid are selected to dilute the desired composition, the substances are stirred in a 10-liter a bucket of clean water, processing is carried out on the leaves, about once every 14 days);


Calcifol 25 (25% calcium in an easily digestible form of oxide has a beneficial effect on tomatoes in the greenhouse, the fertilizer is free of nitrates and chlorides, which is safe for the cultivated plant and does not contribute to the growth of green mass, the leaves of the plant should be sprayed at intervals of 1 week).
Traditional methods
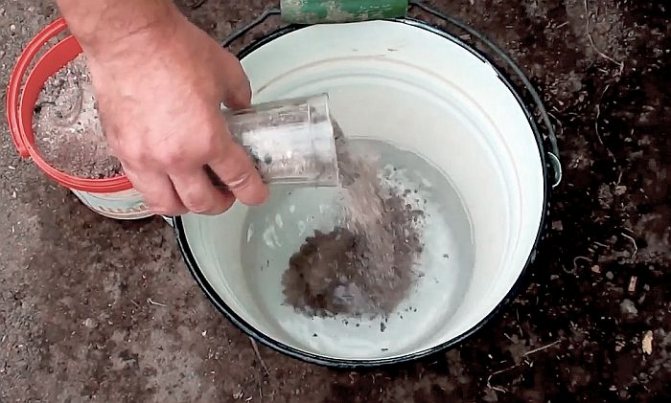


Preparation of a solution with ash
Measures to combat top rot include various folk methods that were used by our grandmothers. The most effective solution is wood ash. It's quite simple to prepare it:
You need to take 2 cups of sifted wood ash. It must necessarily be ash from burnt wood or dried plant residues.
- Raw materials are poured with a liter of boiling water and insisted for half an hour, until the boiling water cools down.
- Then the concentrated solution is mixed with irrigation water and a useful substance is added under each tomato bush in the amount of 1 liter per copy.
You can carry out foliar dressing with the same solution. To do this, add shavings of laundry soap to the mixture in an amount of about 50 g. Mix thoroughly and spray the tomato leaves in the greenhouse. Add soap shavings after diluting the concentrated solution in a bucket of water.
Preparations for the treatment of gray top rot of tomato: names, list, recipes for use


"Copper oxychloride" to protect tomatoes from gray top rot
Signs of top rot of plants (tomatoes and other nightshades) have not yet appeared, or you have collected and destroyed diseased fruits, it is advisable to spray healthy plants with universal means:
- "Brexil Sa" - powder containing calcium and boron. The solution is prepared from 10 g of powder per 10 liters of water.
- "Copper oxychloride (HOM)" - greenish powder. A solution is made from 40 g of powder and 10 L of water. They are treated with tomatoes 3-6 times per season.
- "Tomato rescuer" - ampoules with liquid. The remedy also helps against fungi. Once sprinkled with the drug, it acts for about 1 month, and then you need to spray again.
- Megafol - liquid in bottles from 25 ml to 25 l. A solution for tomatoes in open ground is made from 30-35 ml of liquid and 10 liters of water (weaker for a greenhouse).
- The following drugs are also used: "Nutrivant plus", "Fertivant", "Tekamin Max".
Top rot in tomatoes, how to save tomatoes?
Many gardeners are perplexed when the tops of the fruits begin to turn brown and rot on a carefully cultivated garden bed. Trying to find the best remedy for tomato top rot, you need to correctly understand the cause of an unpleasant disease, which is not always directly related to the effects of fungi or bacteria. Spraying plantings with fungicides against late blight, the owners often forget about other factors - overheating of the soil, lack of moisture, soil quality.
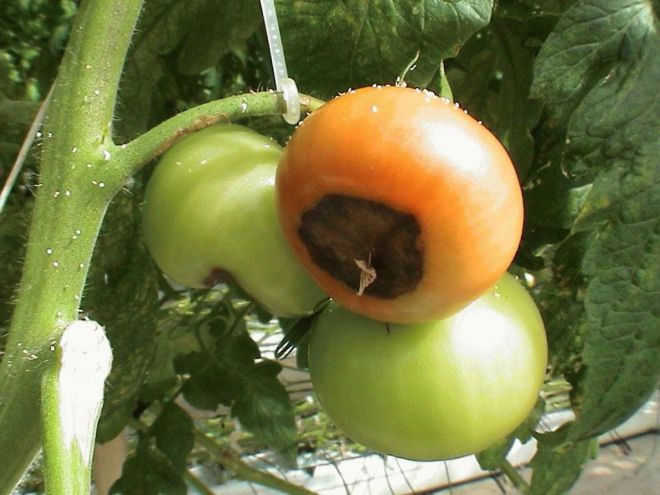


Signs of top rot on tomatoes
What is insidious about the disease of tomatoes, top rot - this attack affects the fruits on quite healthy-looking bushes that are entering fruiting. The plant with infected tomatoes does not die and continues to lay buds. Inexperienced gardeners often begin to spray the bushes with their usual means, trying to take control measures by analogy with treatment for fungal diseases, but signs of decay continue to appear on the new ovary. The disease looks like this:
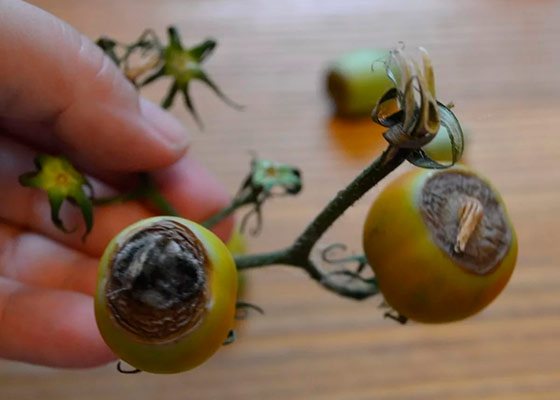
- Dark gray spots are localized on the top of the tomato.
- The spots are slightly flattened.
- The infected fruit ripens and stains earlier, its pulp is dry and firm in consistency.
- As it grows, the putrefactive specks darken.
- In advanced cases, necrosis covers up to a third of the volume of a ripe tomato.
- In unfavorable rainy seasons, if no control measures are taken against the disease, a secondary fungal infection affects the tomatoes. The gray-brown spot turns black, the apical part is covered with a fluffy bloom.
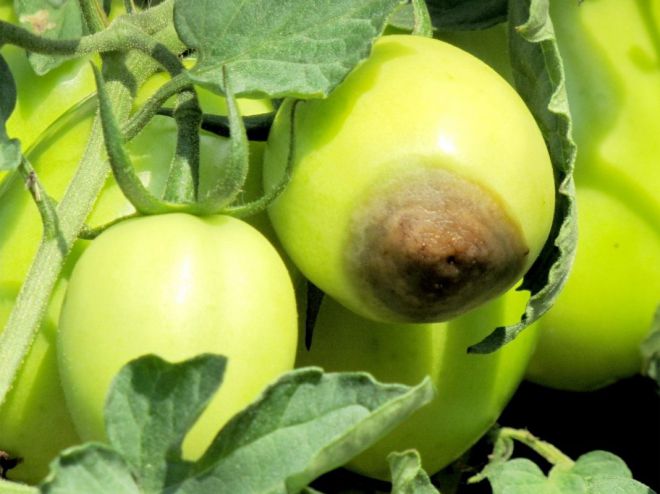


What causes top rot on tomatoes?
To find out how to defeat the top rot of tomatoes, choose the control measures quickly and correctly, you need to understand the reasons for its occurrence. Let's try to figure out how the process of defeating tomatoes occurs:
- The disease begins in hot weather in the absence of normal watering.
- The leaf plates begin to vigorously evaporate moisture.
- The roots do not have time to replenish the liquid deficit, which is why the plant begins to draw it out of ripening tomatoes.
- The strongest outflow of moisture occurs in the apical part, which begins to rot first.
In addition to poor watering, the problem is provoked by a lack of calcium, which is responsible for the normal development of cells. The conducting vessels through which it enters the plant tissues are the weakest in the apical part, therefore it suffers first. Elongated tomatoes rot more often in the absence of normalization and pinching. The availability of Ca reduces the surplus of its competitors - Na, Ma, and K - on saline soils. The next nuance that can aggravate the situation is the deficiency of boron and fluorine. Rot control measures should include measures to correct micronutrient imbalances.
The reasons for the appearance of top rot on tomatoes:
- Prolonged heat.
- Drying out of the soil.
- The calcium content in the soil is below normal.
- In the garden, the soil has a light and non-moisture-consuming structure.
- Increased acidity of the soil.
- Growing tomatoes on saline soils.
- Nitrogen fertilizing was applied in excess of the norm.