Horseradish is an amazingly tenacious perennial plant, which many gardeners consider almost a weed. However, horseradish turns into a weed only with improper care.
Even a beginner can cope with planting this culture on his site. It is for novice gardeners that we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the features of planting horseradish in the fall, the planting scheme and detailed instructions.
The article will tell you how and when to plant, how to properly care for the plant after planting.
How to plant horseradish in the fall - seed and cuttings propagation technology, cultivation and care
In relation to horseradish, gardeners are divided into several camps. Some repeatedly plant it on the site, but fail to grow it, others try to get rid of it, as if it were a malicious weed. The root crop is moisture-loving, unpretentious with proper care, frost-hardy, and therefore it takes root well even with autumn planting. The density, elasticity and taste of the rhizome are determined by the conditions of maintenance and the period of harvest. Knowing these subtleties, experienced vegetable growers successfully grow a complex culture, preventing the plant from turning into an invader of new territories.
Horseradish is picky about the soil. He prefers sunlit fertile loamy soil of average composition and moisture. The rhizome grown on light soil acquires a woody structure, on heavy soil it branches. To correct the situation, sand and humus are added to the landing site with too dense soil, clay and black soil are poured into the poor sandy soil, in each case with the obligatory subsequent digging.
Crop problems arise in acidic soil. If you first reduce its acidity with slaked lime, chalk, dolomite flour or wood ash, the plant will take root and delight you with the harvest. Excessive soil moisture leads to root rot. You can reduce the likelihood of this by planting horseradish on prepared bulk ridges.
Every autumn, superphosphate and potassium chloride are introduced for digging. The use of peat, manure and humus, which helps to build up the root system, is encouraged. The difficulty lies in the fact that with long growth, the roots run wild and grow uncontrollably.
In order to avoid clogging the soil in the garden, it is customary to dig horseradish in the first or second year after planting, in order to subsequently propagate it by cuttings. Otherwise, the old rhizome acquires a large number of branches.
Perennial blooms in the second year. The collected seeds are sown before winter with a distance between them of 7-10 cm and a width between rows of 90 cm, seeding to a depth of three centimeters. Germination of seedlings in spring begins already at five degrees, they are not afraid of frosts.
If it is impossible to sow in autumn, seed material for stratification is pre-mixed in a bowl with moistened sand in a ratio of 1: 3, placed in a basement or refrigerator for three months, mixed regularly and sprayed if necessary.
Then the container is rearranged to a warm place. The ideal temperature for germination is 21 degrees. Sometimes the buds are already pecked in the refrigerator. When two true leaves appear, the sprouts dive into pots or boxes. After a month and a half, the bushes can be transplanted to a new place. By this time they have grown 4–5 leaves.
Planting horseradish is recommended with a row spacing of 40 cm and a row spacing of at least 60 cm. In the first season, the bush develops slowly, forming only a leaf rosette. In the early spring of next year, greenery grows, and the plant develops rapidly. At the end of the third season, the rhizome is ready for digging.
Horseradish seeds do not ripen well, their germination is low, cultivation is long and laborious, so this method is rarely practiced.
The vegetative method of reproduction is mainly used - by parts of the roots of the mother plant. The division is made as follows:
- Cuttings are harvested in the fall during harvest, removing lateral branches from the rhizome. Their length is 20-30 cm, thickness is about one centimeter.
- The top is cut off at a right angle, the bottom is obliquely, this will help to distinguish them when planting.
- If there is not enough material, pieces of rhizome 5–6 cm long with an apical bud are used. To prevent them from branching, thin lateral roots are cut off.
- It is necessary to plant no later than the beginning of October at an inclination of 45 degrees with an oblique cut down to a depth of 10 cm, leaving 3-5 cm of soil above the upper buds.
Four to six cuttings are enough for one square meter. The distance between the plants is 30 cm, between the rows - 70 cm. The soil is slightly compacted so that the roots are in close contact with it for better survival.
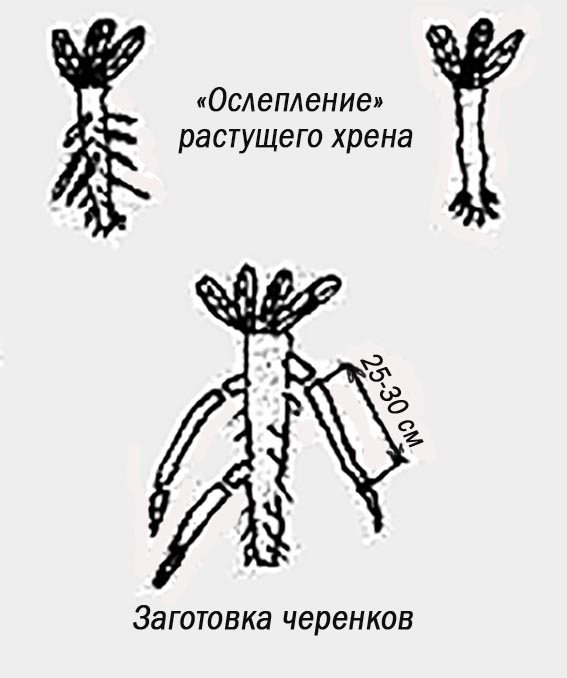
Care consists of weeding, loosening row spacings and watering during dry times. To make the central root thick and even, the buds in its upper part are blinded with a leaf height of no more than 20 cm.To do this, they rake the earth around the plant and scrape the rhizome up to 25 cm long with the back of the knife blade, cover it with soil, compact and water it abundantly so that around the bush did not remain empty. Numerous leaf rosettes are removed, leaving no more than two.
The plant is harvested in late autumn. Having dug up the rhizome, they pull out all its parts, without shaking off or cleaning in the garden, so as not to clog the ground. If necessary, dug out at any time of spring or summer. If you cut the leaves several times per season, the yield will be lower than usual.
The particles torn off during the sampling of the roots, germinating, can strongly clog the garden. Digging does not give the desired result, and in the case of cultivating with a cultivator, small trimmings of the roots turn the site into a horseradish plantation. The problem is solved by the use of potassium salt or ammonium nitrate, which are applied to the growth points.
Or, having made a depression in the root collar, moisten it with water, cover it with a large amount of salt and cover it with a plastic bottle. Another option is to inject Roundup solution into the stem. A more environmentally friendly and time-consuming way is to shade the plantings or pluck all the leaves, depriving them of the opportunity to feed the roots and depleting the plant.
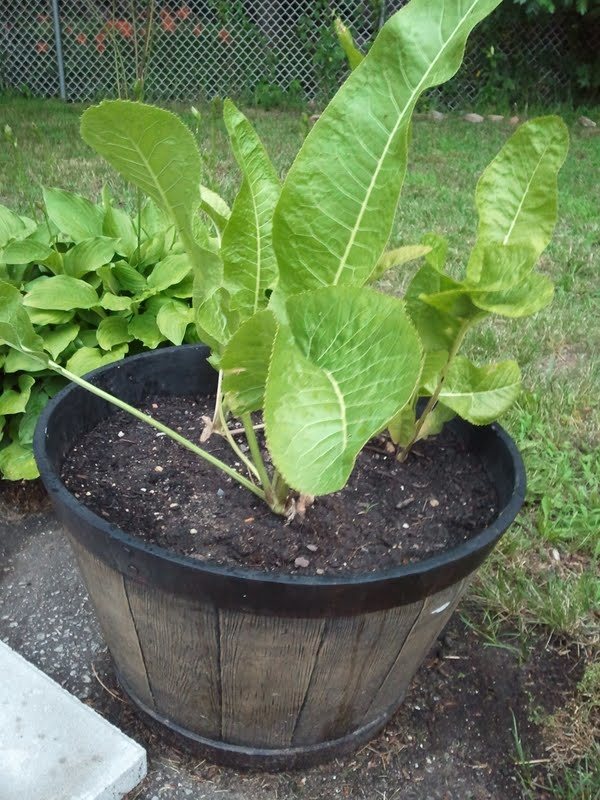


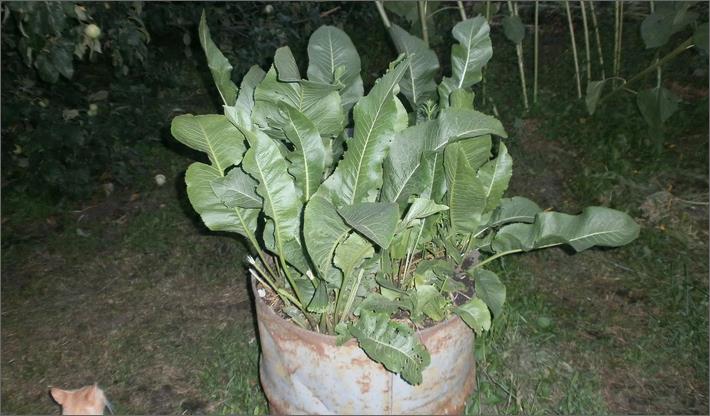
In order to not give the horseradish a chance to turn into a weed in the country, they immediately restrict its freedom by planting it in a metal barrel or a bucket dug into the ground. The edges of the container must rise above the surface. When harvesting, you can lift the barrel and lay it on one side to get the whole rhizome. If you grow a perennial in a bucket set on the ground, it is easy to turn it over and shake out the contents. After sampling marketable roots, the rest should be planted in the same container.
With this method of cultivation, you will have to carefully monitor the soil moisture in the container.
Anyone who tames horseradish and provides proper care in the open field, he will reward with a bountiful harvest of succulent roots containing many useful substances.
Care and harvesting
In the process of horseradish growth, it is necessary to carry out several weeding and hoeing. In addition, it is desirable to provide the plant with fertilizing with the help of mineral fertilizers. In mid-July, it is recommended to open the roots and remove the side branches, which are large in size.True, after such a procedure, it will no longer be possible to obtain planting material. Harvesting is carried out in autumn. Horseradish is dug out of the ground, the rhizomes are cut from the leaves and sorted. There are various videos on the Internet on how to properly care for horseradish.
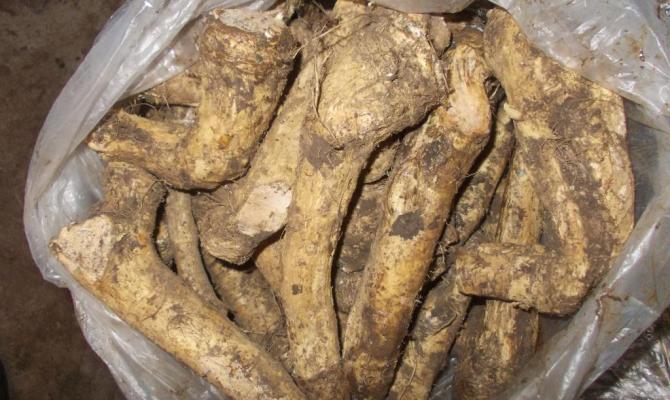


Harvest
In addition, it should be remembered that the plant is capable of growing rapidly. Therefore, it is not recommended to leave trimmed roots in the ground. In order to prevent excessive growth of horseradish, after harvesting, the land plot is carefully dug up.
When to plant horseradish before winter and why: a word to experienced gardeners
Not all summer residents are aware of the possibility of winter planting. Meanwhile, horseradish has long been planted in Russia before winter - at the end of September and in October. And today, experienced gardeners practice planting before winter. There are several reasons for this.
- In regions with late spring, planting before winter will give an early harvest: horseradish is ready for harvesting not at the end of autumn, but just in time for the canning season - without it, you cannot pickle the right cucumbers, or tomatoes, or adjika.
- This is hardening: the plant is cold-resistant, but germinating buds do not welcome return frosts. Winter crops are not afraid of spring frost.
- The optimum temperature is up to + 20 ... + 25 ° C: at high temperatures, growth is inhibited. When planting in autumn, part of the growing season takes place at temperatures comfortable for the culture.
- In the spring, there is a lot of work in the garden and in the country: one joy - at least horseradish has been planted in the fall.
Video
Horseradish is a spicy vegetable used in cooking and traditional medicine. The agrotechnology of its cultivation is simple, it is important not to let the plant "run wild", horseradish is able to fill the entire plot, oppresses many garden crops, and is unpretentious to soil and illumination. For planting crops, they choose remote empty corners of the garden.
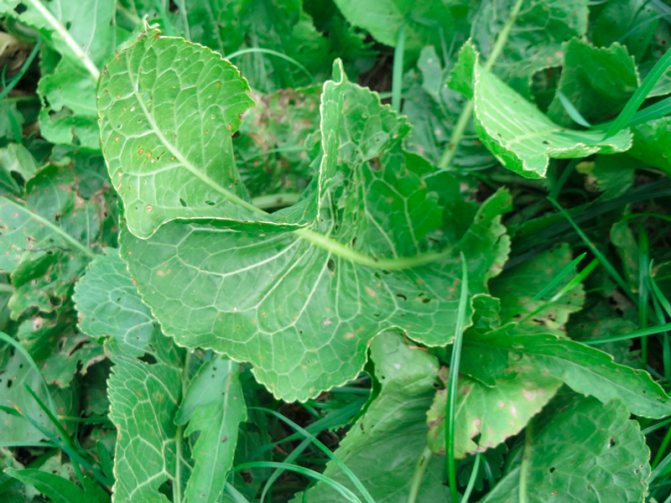


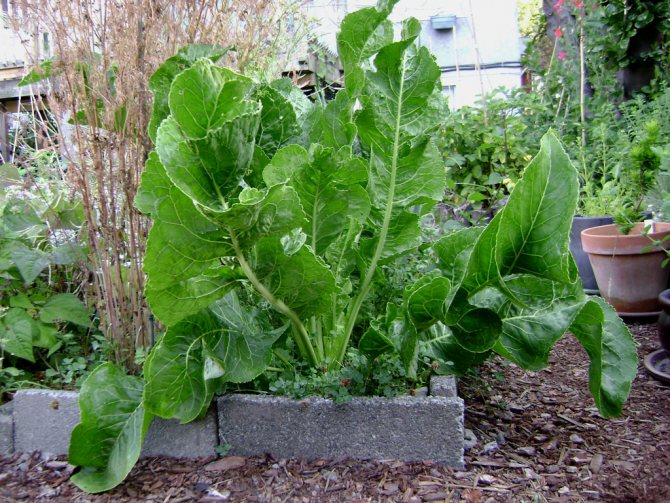
The leaves and roots of a spicy plant are harvested, in order to get a good harvest with a high content of nutrients, it is necessary to adhere to several rules for growing a crop. At the dacha, the bush looks very decorative: dense dark greenery, wavy erect wide leaves will perfectly disguise an unsightly fence, a compost heap.
Planting horseradish before winter: theory
Horseradish culture is frost-resistant: rhizomes withstand t -45 ° C, and young leaves are not afraid of return frost. It is known as an unpretentious culture, a kind of aggressor on the site, but it makes high demands on growing conditions.
Did you know that horseradish is not a root vegetable? It is a cruciferous plant.
- Loves fertile soil. On sandy, heavy and poor loam, it does not gain size, the required amount of essential oils that determine the pungent taste. The best soil is black soil, sandy loam, light and humus-rich loam.
- Dislikes alkaline soils, prefers acidic, moist, but not too moist.
- Demanding to the mechanical composition of the soil: on dense, damp it grows tough, rough.
- Photophilous, but it takes root better in partial shade: the shadow, as well as strongly illuminated areas, does not like.
- Moisture-loving, but poorly tolerates waterlogged soil.
- Horseradish does not require fruit replacement - it grows in one place for up to 10 years. The best predecessors are legumes, grains.
Growing features
Several bushes are able to exist on the site by themselves, without the attention of the gardener. However, if the purpose of planting horseradish is to obtain tasty juicy rhizomes, it must be cultivated as a garden plant, planting rhizomes every year and harvesting the finished crop. The agrotechnology of growing crops is not difficult, everyone can master it.
Soil preparation
Horseradish will grow on any piece of land. But he prefers fertile, cultivated soils, well filled with nutrients. Sandy loams and loams, with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction, are best suited for it. Beds are set aside for planting in partial shade or in the sun, in full shade the plants develop poorly.
Good predecessors of horseradish are cucumbers, tomatoes, early potatoes, beets per bunch. You can also plant it after representatives of the legume family. A bad choice for placing plants will be the beds on which cabbage, rutabagas, mustard, radish, radish, turnip grew before.
The most important thing: how to prepare planting material
The root crop is propagated by dividing the root - by the vegetative method, by root cuttings: the rhizome is capable of producing at least 4-5 cuttings.
Horseradish propagates well and root scraps of 8-10 cm, which are placed horizontally when planting, without removing the buds.
Horseradish is planted at an angle of 30-45 °.
- The bush is dug in, thin root cuttings are separated from the rhizome - they are best suited for planting.
- Lateral roots are separated up to 20-30 cm long and about 1 cm in diameter.
- The lower cut is made at an angle - oblique, the upper - horizontal, to mark the top and base of the cutting, so as not to plant horseradish upside down.
- From the top edge, according to experienced gardeners, they retreat up to 2 cm, from the bottom - up to 3 cm.
- The buds located on the middle part of the cutting are wiped with a coarse glove, burlap, leaving a few on the upper and lower cut, where leaves and roots will form.
- If storage is necessary, the cuttings are sprinkled with sand so that the slices do not rot.
If horseradish planting is carried out for large, even rhizomes, the middle part of the cutting is cleaned of buds, which will give a lot of small roots. If the purpose of planting is the reproduction of the horseradish population, all the buds are left.
How to grow horseradish in the country: features of planting and care
Horseradish is a well-known garden plant that can be seen on any garden plot. It is not capricious and tenacious, and its agricultural technology is simple, therefore the cultivation of this vegetable does not cause problems for vegetable growers. But, all the same, horseradish cultivation must take place according to certain rules so that the gardener can get a sufficient harvest of roots and leaves, but the plant does not turn into an occupier of the garden, which it can become with improper agricultural technology.
General information about the plant
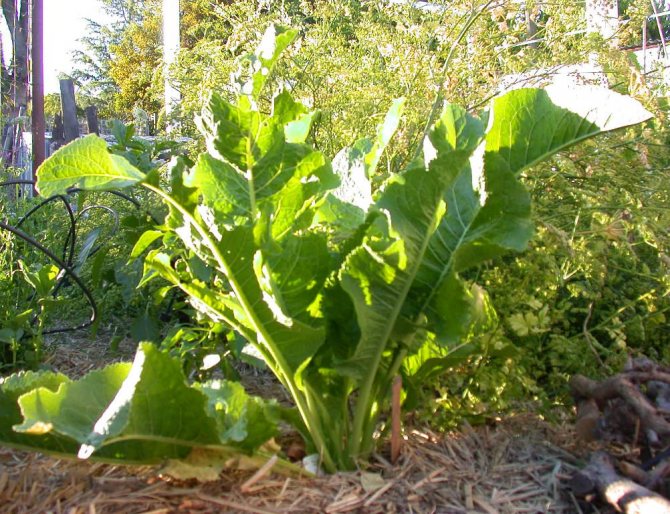
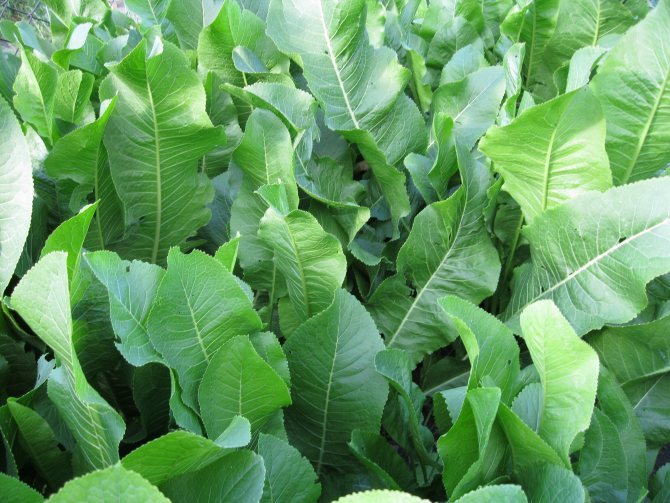
Horseradish is a plant of the Cruciferous family, a relative of cabbage, radish and radish, turnip, rutabaga, mustard. His homeland is unknown, but presumably it is Eastern Europe. It is a perennial plant with a long thick rhizome and a lush rosette of leaves. It consists of large oblong-oval basal, oblong-lanceolate middle and smaller upper linear leaves.
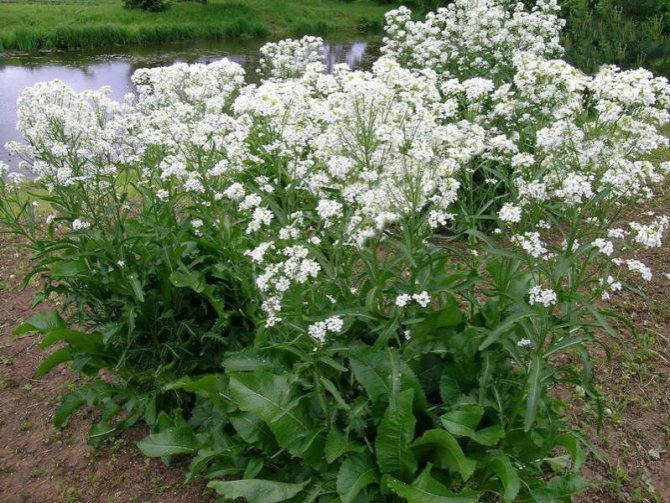
The length of the horseradish stalk can reach 0.5-1.5 m. The plant blooms in the second year in May or June, throwing out a peduncle with white small flowers characteristic of all cruciferous forms. Horseradish fruits are pods 0.5 cm long, they contain 4 seeds. Seeds are similar in shape and color to cabbage seeds, but are rarely formed due to infrequent flowering.
The plant's rhizome is powerful, the length of horseradish roots can reach 1.5-2 m. A strong specific aroma and burning taste are given to them by an essential oil, a component of which is allyl isothiocyanate. It is formed as a result of hydrolysis of the sulfur-containing substance sinigrin, which is included in the chemical composition of the plant. Fresh roots contain the enzyme lysozyme - a substance with an antibacterial effect, vitamins C, PP and group B, carotene, starch, resinous substances and alkaloids. They contain many mineral salts of elements important for the body: P, Ca, K, Fe, Cu, Mg, S.
The value of horseradish for the gardener lies in its roots and leaves. They are used in cooking and traditional medicine. The most widespread use is found fresh roots, which are used in grated and chopped form:
- as a spicy flavoring for jellied meat, boiled cold, fried and smoked meat, sausage and fish;
- for the preparation of hot sauce (horseradish), alcoholic tincture (horseradish);
- as an ingredient for sauces with red beets, sour cream or apples, homemade mayonnaise, kvass.
Pieces of roots and fresh leaves are used for pickling and pickling tomatoes, cucumbers, mushrooms, pickling cabbage. Once in the stomach, horseradish stimulates the secretion of juice and digestion, increases appetite.
An aqueous solution from the juice of fresh roots is used for colds and flu, for sanitizing the mouth and throat for bacterial diseases, relieving inflammation in the ears, tincture - to reduce toothache. Horseradish is also useful in diseases of the organs of the excretory system, vitamin C deficiency, physical and mental stress, a tendency to bleeding. Gruel from fresh roots is used as a local remedy for the treatment of sciatica, rheumatism, arthritis, gout, and fungal skin lesions. The plant is also used for cosmetic purposes: freckles, age spots and sunburn are removed.
Growing features
Horseradish is a cold-resistant plant, unpretentious to growing conditions. It can grow and develop on any type of soil, easily tolerates winters, does not require mandatory maintenance. Growing horseradish in the country is possible in a perennial and annual culture.
Several bushes are able to exist on the site by themselves, without the attention of the gardener. However, if the purpose of planting horseradish is to obtain tasty juicy rhizomes, it must be cultivated as a garden plant, planting rhizomes every year and harvesting the finished crop. The agrotechnology of growing crops is not difficult, everyone can master it.
Soil preparation
Horseradish will grow on any piece of land. But he prefers fertile, cultivated soils, well filled with nutrients. Sandy loams and loams, with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction, are best suited for it. Beds are set aside for planting in partial shade or in the sun, in full shade the plants develop poorly.
Good predecessors of horseradish are cucumbers, tomatoes, early potatoes, beets per bunch. You can also plant it after representatives of the legume family. A bad choice for placing plants will be the beds on which cabbage, rutabaga, mustard, radish, radish, turnip grew before.
Areas intended for growing horseradish are dug deeply. Previously, for each 1 m2 of area, up to 10 kg of organic matter, humus or compost and mineral fertilizers are applied. Complex compounds are used, for example, nitrophoska, or nitrate, superphosphate and potassium sulfate are mixed. Fertilizer consumption rates depend on the condition and type of soil. Heavy clay and light sandy soils are also structured with sand, sawdust, peat, turf soil. Acidic soils are lime in advance.
Horseradish is grown both on ordinary beds and on the ridges. The latter option is practiced in regions with excessive moisture or with a close occurrence of groundwater at the site. Planting in ridges is also advisable in the case when the soil on the site is not fertile enough and contains little humus.
When to plant
Horseradish on personal plots is propagated mainly by rhizomes. Planting of planting material is possible from early spring to late autumn. To obtain a harvest in the year of planting, beds with horseradish are laid in the spring, from March to April, as soon as the soil thaws. At any time, the tops of plants are rooted, which also take root well, but give marketable rhizomes only in the next season. Podzimny planting horseradish is performed in October-November, while digging it out in the fall of next year.
Preparation of planting material
Cultural propagation of horseradish requires preliminary preparation of rhizomes. Cuttings for planting are harvested in autumn or early spring. If storage is necessary, the shoots of the roots are saved in the cellar or buried in the garden. The best planting material is considered to be a one-year growth with a diameter of 0.5 to 1.5 cm and a length of 20-30 cm. Such cuttings are separated from the older maternal root.Its upper part is cut evenly, and the lower part is cut with a slope. This allows you to subsequently correctly determine the future top and root of the plant.
Before planting horseradish cuttings on the garden bed, in their middle part, remove all the buds and small roots using a coarse cloth. Only the top and bottom of the planting material are not treated to a height of 1-1.5 cm. At this point, the roots and leaves of horseradish will then grow. Preparation is carried out in the same way both when planting in spring and autumn.
Some gardeners use this method as well. First, the rhizomes are removed from the cellar, kept in wet sawdust or peat for up to 3 weeks at a temperature of 18 ° C. Then the sprouted buds are removed in the middle of the cuttings. Subsequently, smooth, thick, even rhizomes grow from them. For podzimney planting, germination is not used. Short - up to 10 cm, and thick - more than 2 cm rhizomes are not cleaned.
Landing
Horseradish is planted in the beds in an inclined position. When planting, the cuttings are buried in the ground at an angle of 30-45˚; a peg is used for marking. A rhizome is placed in the resulting depression, so that the top is 2-5 cm underground. After that, the soil around the cutting is compacted.
For planting horseradish, the following scheme is used: 60-70 cm are left between the rows in the garden, in a row the plants are placed 30-40 cm apart. Further, the beds are abundantly watered and mulched with improvised materials.
When rooting the tops, small pieces of rhizomes 1-2 cm long are used. They are planted in grooves up to 7 cm deep, 10-15 cm are left between the plants. Irrigation and mulching are also carried out. The grown rhizomes are then used as planting material. Short cuttings are planted vertically without stripping.
Planting horseradish before winter: practice
Without lengthy prefaces: planting horseradish for the winter, step by step instructions.
Horseradish planting scheme: before winter and not only.
- For digging, humus, a nitrogen-mineral complex - potassium nitrate, superphosphate, potassium salt are introduced.
- Planting holes are prepared with a depth exceeding the height of the cuttings by 5-7 cm - it is convenient to do this with a wooden peg.
- It is correct to plant horseradish at an inclination of 30-45 °: the upper part of the cutting as a result deepens by 4-5 cm, the lower, with an oblique cut - by 10-15 cm.
- When planting a large number of root crops, they are planted in rows according to the scheme 30 × 70 with a distance of 70 cm between rows and 30 cm in a row between plants, or 60 × 40. Thus, the planting density is about 4-6 plants per m2.
- Landings are sprinkled with a layer of soil not higher than 4 cm, moderate watering is carried out. No watering is required for late planting in damp soil.
Before planting for the winter, it is better to store the harvested roots in a cool place. Before spring - in a warm, humid - for this it is wrapped in a damp cloth for rapid bud germination. For winter planting, germination is not required and the best storage method is cool and sandy.
Harvesting and storage


Horseradish leaves begin to be harvested in August - they are used as a spice for pickling cucumbers, tomatoes and other vegetables. Try not to cut off all the leaves from one plant, as their absence will prevent the root from growing further. Leaves are cut at a height of about 10-15 cm from the ground level on the site so as not to damage the young leaves and the upper bud.
Mass harvesting of fruits begins in the third decade of October or early November, before the onset of frost, when the horseradish leaves have already turned yellow and began to dry out. If you planted large cuttings, then the horseradish harvest falls on the year of planting, if the cuttings were small, then good root crops will sprout only the next year. Before harvesting, the leaves of horseradish are cut off, the root is digged in with a shovel and removed. Try not to leave even the smallest roots in the soil, because by next year there will not be a place free of horseradish on the site.
How to grow horseradish from seeds: sow before winter
Propagated by horseradish and seeds. It is better not to try to prepare your own seeds: the perennial blooms in the second year, but most often the seeds do not ripen, and are not suitable for planting. As a way out - buy ready-made seeds.
And the plant also knows how to bloom beautifully: no wonder the cruciferous family.
When planting horseradish in autumn, the seeds are buried in prepared furrows at a distance of 7-10 cm with a row spacing of 60-70 cm. Seed consumption is 7-10 pcs. per m2. Seeds are planted to a depth of 2.5-3 cm, depending on the texture of the soil.
The seed propagation method is not often used: seed germination is not high at any planting time - in autumn, spring, and this event is laborious and time-consuming: a full-fledged root is formed in the second year.
Often, instead of horseradish, it is planted with its "substitute" Katran Tatar horseradish, a perennial herb with a powerful rhizome. According to connoisseurs of spicy seasoning, this is a completely different culture and a different taste.
Spring care is a separate story. The plantings are loosened, watered, fertilized, side roots are removed in order to exclude spreading over the site and form one powerful, non-branching root. This is an informative and interesting story, but springtime. In the meantime, let the autumn planting horseradish grow tart, sharp and evil: good harvest!
Popular horseradish varieties
Despite the fact that in Russia there are several excellent varieties of horseradish, semi-wild or wild horseradish grows in almost every first vegetable garden. Some grow horseradish of Polish selection, but many consider it not vigorous enough.
Polish horseradish - it's bad, too sweet.
A FORUMHOUSE member has compiled a list of varieties that are grown by true lovers of this crop.
Suzdal - this variety of Vladimir selection has only good reviews. Valkovsky - late-ripening variety, dug out 200 days after planting, with a one-year cultivation, the rhizome reaches 3 cm in diameter. Resistant to flea beetles. Tatar - this variety is grown in the southern regions. Tolpukhovsky - common in Central Russia. This is a late-ripening variety, the rhizome is large, weighing up to 250 grams. Atlant - mid-season variety, can be dug out on 85-120 days of average size. Alpo - a variety of Polish selection, medium-sized rhizome with bright white pulp. Malinsky - a variety of Czech selection.
How to plant horseradish
Horseradish is an essential spice in Russian cuisine. It is called "mid-stripe ginseng". It is believed that it contains more vitamin C than lemons and black currants.
Old people treated all colds with horseradish. And with rheumatism, and now they are successfully fighting with its help.
Legs get very tired when working in the garden. And, here, if you put a sheet of horseradish in your shoes, you will forget about fatigue. And the heels will be soft without cracking.
Horseradish in the front garden of the yard
Look today - wherever you will not see horseradish leaves: in the front gardens, and in the flower beds, and, most often, behind the fences in the garden. Recently I saw him growing freely in the cemetery.
But, after all, it is not easy to overcome horseradish that has grown without leaving. It will take years. Remember the humoresque of Mikhail Evdokimov - how he rolled horseradish into the asphalt, and he sprouted.
Nevertheless, the agrotechnology of horseradish growing is not complicated.
How to grow horseradish in the garden
To start off by memorizing one main rule:
Horseradish must be grown in an annual culture.
Only in this case will it grow juicy, the most useful. And without pretending to be a malicious weed. So, first, don't let the horseradish grow for years without a transplant.
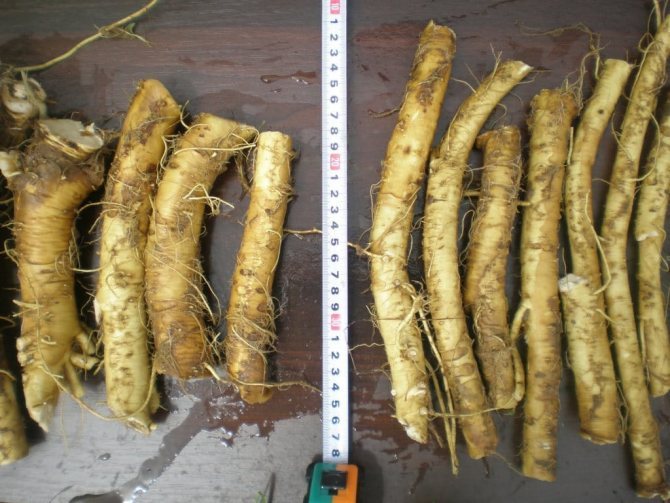
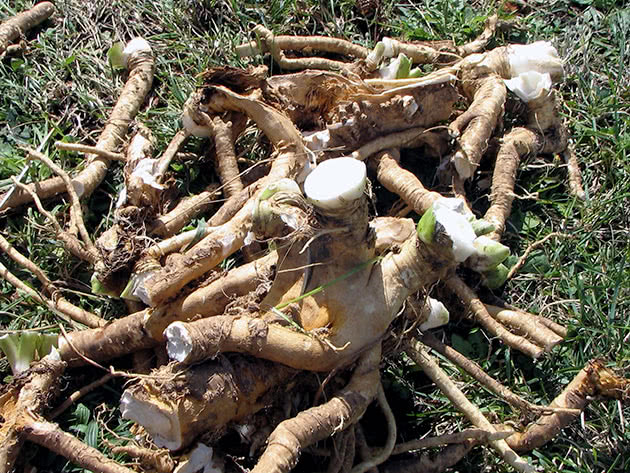
Planting material - lateral roots of the main root. When digging horseradish, try to get as many roots out of the ground as possible. Separate the lateral shoots from the large tree root. Ideally they are 15-20 cm long and approx. 1 cm. Can be thinner.
How to multiply horseradish in the garden quickly and correctly


Horseradish is a spice widely used in Russian cuisine.It not only gives a variety of dishes and homemade products an original taste and piquant pungency, but also benefits health as a valuable source of vitamins and minerals. Therefore, the plant can be found in the vast majority of household plots. As a rule, gardeners do not have problems with horseradish reproduction, but there are some important nuances here.
How can you multiply horseradish in the garden
It is recommended to grow horseradish in the same place for no more than 10 years, so sooner or later the problem of its reproduction arises in front of all gardeners. For this, both generative (seeds) and vegetative (parts of the plant) methods are suitable. Even inexperienced gardeners will not have problems - the culture is very hardy and unpretentious, quickly and without problems takes root in a new place.
Growing horseradish does not require practically any effort from the gardener, even beginners can cope with its reproduction
The most suitable times for horseradish breeding are spring (from late March to late April) and autumn (from mid September to late October). Specific dates are selected taking into account the characteristics of the local climate. But in principle, if you have chosen a vegetative method, no one forbids doing this throughout the summer.
The simplest option, practically guaranteeing success, even if you just bury small pieces of rhizomes in the ground in the chosen place. But it is better to follow the simple landing rules.
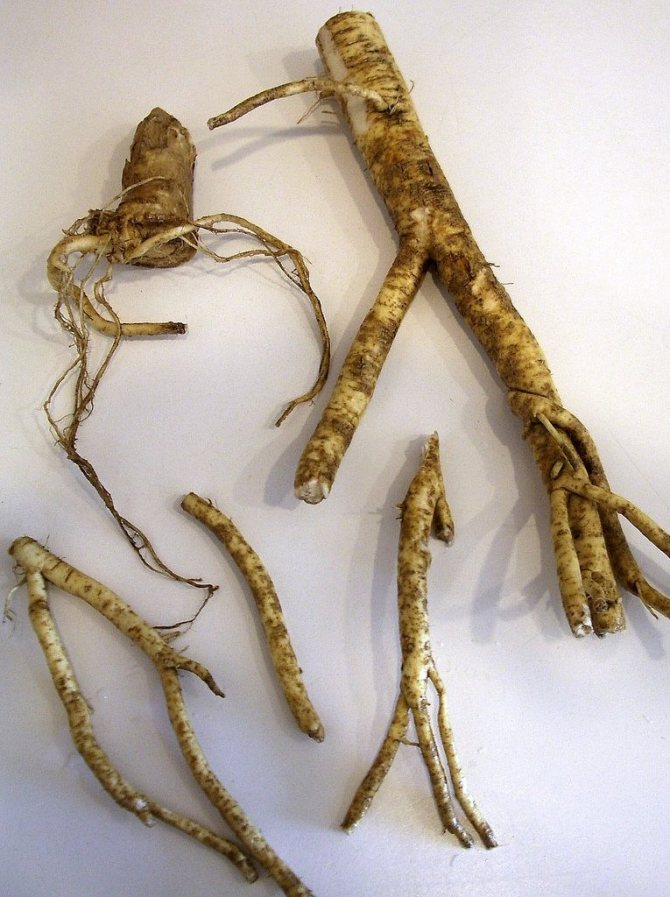
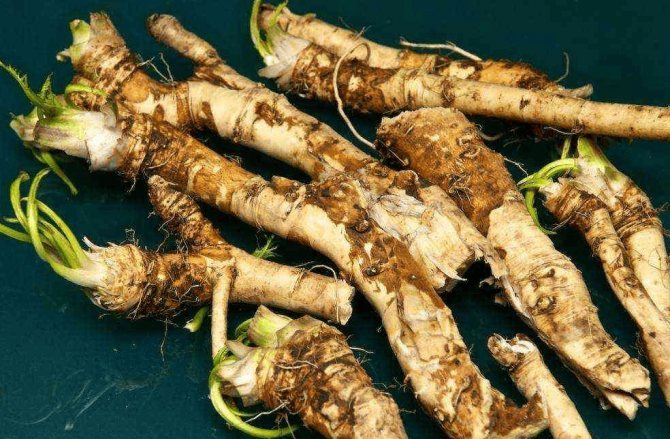
Lateral branches from the main rhizome of the most powerful, healthy-looking plants 1–1.5 cm thick are used as planting material. The higher they are located on this root, the more active development will be. They are dug up in the fall, cut into cuttings up to 20-30 cm long (at least 8-10 cm). The upper cut is made even, the lower cut oblique so as not to be confused when disembarking.
The preparation of planting material can be combined with digging up horseradish roots; minimum cutting length - 8-10 cm, thickness -1 cm
If the procedure is planned for the fall, you need to proceed as follows:
- Do not touch the upper and lower 5 cm of the cutting, rub the rest of the root in the middle with a coarse cloth (for example, burlap) to remove the existing growth buds and small roots. This will prevent the root from over-branching and thinning.
- On a pre-dug bed, mark furrows about 10 cm deep with a row spacing of about 70 cm.
- Plant the cuttings at intervals of 25-30 cm, placing them horizontally at an angle of about 45 °. The bottom of the root should be about 10 cm deep, the top 5 cm below the ground.
- Cover the cuttings with soil, water abundantly (up to 10 l / m²). When the water is absorbed, compact the soil, mulch the surface of the beds with peat chips, humus, cut grass (layer up to 5 cm).
- Planting care during the summer is standard. They need regular watering, loosening the soil, weeding and, if possible, fertilizing.
The main feature of preparing horseradish rhizomes for planting is the removal of growth buds and small roots on most of the cutting, so that more powerful roots form from the rest
Those who are going to plant horseradish in the spring need to keep the cuttings during the winter. To do this, they are placed in a container with sand, sawdust, wood chips, peat chips. Its walls must be breathable (wood, cardboard). The planting material is kept in any cool, dry place with good ventilation, for example, in a cellar.
About a month before planting in the garden, the cuttings are transferred to a bright, warm (23–25 ° C) room. The middle part is covered with any opaque material, leaving 5 cm open at each end. Twice a week, the planting material is sprayed with heated water. Growth buds begin to swell in about 15-18 days.
Horseradish is planted in a permanent place in the same way as in the autumn planting. Leaves from new plants can be obtained at the end of the next season, marketable rhizomes - in another year.
Seedlings after planting cuttings appear quickly and amicably, but do not expect the rapid development of the aerial part - first, horseradish bushes must grow roots
Where and when is it better to plant horseradish
Planting horseradish in the fall should take place on fertile soil, then the plant will grow really tart and tasty. For this, chernozems, dry peat bogs are suitable. The culture does not grow well on clay, stony soils. The roots of the plant will be weak, and the taste will be expressionless. More often, experienced gardeners grow horseradish on sandy loam, loamy soils.
Horseradish propagation in the fall occurs vegetatively. An adult plant is dug in with a pitchfork and 2-3 thin root cuttings are selected for planting. The length of each spine should be 15-30 cm.


Horseradish roots before planting
Prepared cuttings need to be cut at the bottom at an angle. So during planting it will be possible to distinguish the upper part from the lower one. Until planting, the roots are recommended to be stored in the basement, in boxes with dry sand. Root vegetables need to be rubbed with coarse burlap to separate the lateral buds. The rhizomes will grow evenly, without branches.
For Russia, the optimal planting time is considered to be from the first half of September to mid-October. Although the plant is hardy, planting horseradish before winter is not the best solution.
Optimal timing
The optimal timing for planting horseradish in central Russia is from the second half of September until mid-October. The plant is winter-hardy and almost always takes root well and tolerates the subsequent winter without problems.
Some summer residents regularly plant horseradish on the site, others consider it a weed and pull it out with them. This plant loves moisture, is unpretentious in care, tolerates frost and takes root well when planted in autumn. Knowing the intricacies of the content, you can plant horseradish in the fall without harm to neighboring plants (for example, potatoes).
Preparation of soil and planting material
The roots should be planted in well-loosened soil. Pre-make narrow holes for planting using wooden pegs. Make sure that the depth of the hole is 5-6 cm longer than the petiole. The plant has the ability to capture the nearest space, so slate is dug in along the perimeter of the site. It will restrict root overgrowth.
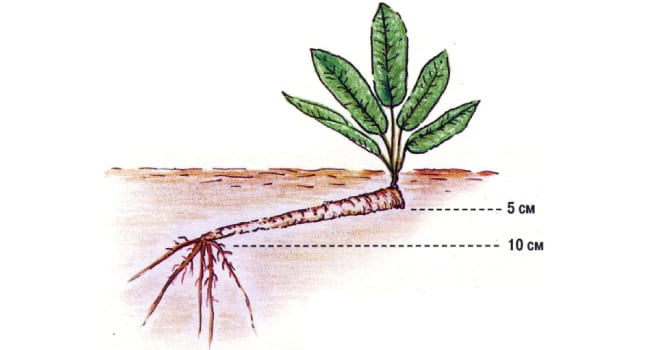

Correct horseradish planting
When planting, the root is placed in the hole with an oblique cut down. Then the pits are covered with soil and lightly watered. For 1 square meter, you need to prepare 3-5 holes for the roots.
Horseradish: three ways of planting
The soil for planting horseradish is prepared as follows: they dig up the soil to a depth of about 40 cm, into which fertilizers have already been applied for the autumn digging.
For 1 square meter - 5-9 kilograms of compost or rotted manure, 25 grams of urea, 50 grams of superphosphate and 35 grams of potassium chloride. If necessary, horseradish is grown on bulk beds.
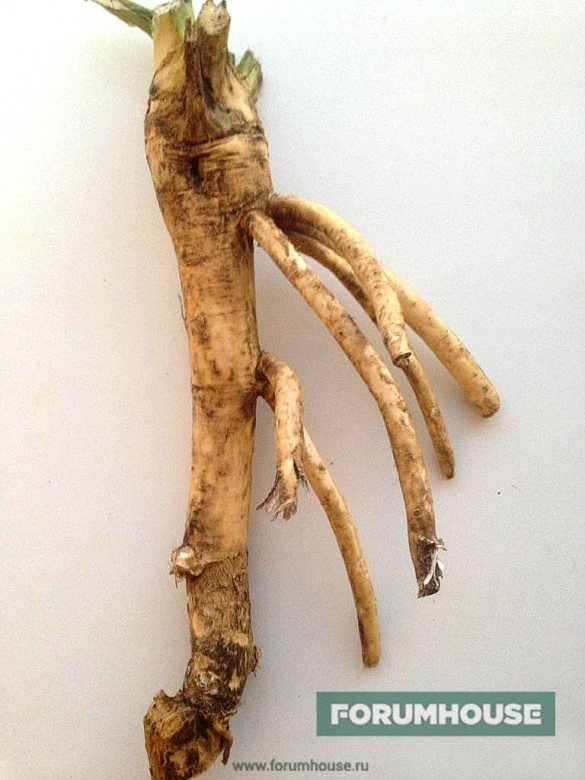


Horseradish is propagated only by cuttings. Cuttings for planting material are prepared in the fall, when the horseradish crop is dug up. All small branches, which are cut off from the rhizome, go to the cuttings. Requirements for cuttings:
- For the southern regions - the length is about 25 cm, the thickness is at least 0.5 cm.
- For the Central, Northwestern regions and Siberia - about 25 cm long, at least 1 cm thick.
Since the planting material will have to be stored until spring, the lower part of the cutting is marked so as not to confuse it with the upper one later. The easiest way to mark is by making an oblique cut. Cuttings are stored in a cellar or basement, covered with any available material or digging into a box with earth. About a month before planting, the cuttings are brought into a bright room. To awaken the dormant buds, the middle of the roots is covered with burlap, and the top and bottom are left open.When the cuttings germinate, they are "blinded" just before planting in a prepared place.
The "blinding" procedure consists in removing all the buds from the middle of the cutting, which was under the burlap - both dormant and growing. "Blinding" is done with a hand, wearing a mitten, or a piece of burlap. The buds that have begun to grow in the lower and upper parts of the cutting are not removed.
Blinding helps prevent the lateral branching of the rhizome, so that in the fall we get cylindrical, even roots.
Now you can start planting cuttings, which is carried out using planting pegs. A peg is stuck into the prepared loose soil, which is about 5 cm longer than the cutting, and the cutting is planted into the hole that remains after the peg is removed. Here we need an oblique cut made in the fall - it should be at the bottom. The cuttings are sprinkled with earth, the layer thickness is 3-5 cm, depending on the composition of the soil, the lighter it is, the thinner the layer should be. Distance between cuttings 30 cm, between rows -70 cm.
We told you about vertical planting of horseradish; there are two more planting methods: horizontal and inclined.
For biennial cuttings, the maximum yield is for inclined cuttings. For annuals (planted in spring - harvested in autumn), the maximum yield is from horizontally planted ones.
But horizontal planting has a big drawback - a lot of extra buds awaken, the root will turn out to be branched, sloppy and inconvenient for storage.
Immediately after planting, you can "postpone the tambourine" until autumn - horseradish will not require any more dances from us, you will only need to weed it a couple of times a season and water it several times.
All the intricacies of growing horseradish
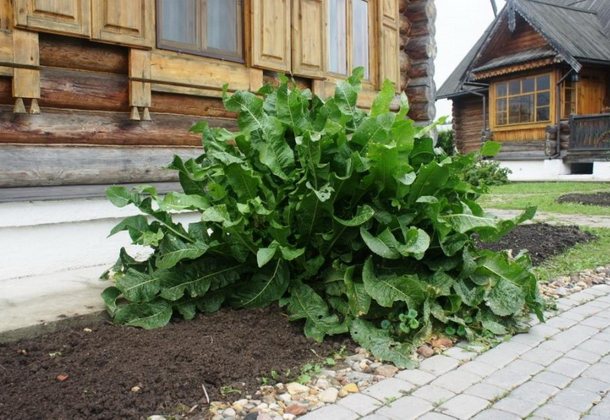


Horseradish - a well-known plant that can be found in many summer cottages. Horseradish comes from South-Eastern Europe. Even the ancient Slavs used it as a food and medicinal plant. The specific sharp taste and smell of horseradish is due to the content of mustard oil.
Growing horseradish and caring for it does not require special skills. However, many gardeners treat horseradish with prejudice, since it has only one drawback - it heavily clogs the soil. But this problem has a simple solution - so that the plant does not creep to the sides, it is necessary to dig in a fence around the perimeter of horseradish plantings, for example, a strip of old tin or slate. The main thing is that the obstacle goes to a depth of at least 50 cm, since the horseradish root penetrates very deeply into the soil.
Read about the rest of the intricacies of growing this medicinal plant further in the presented material.
Reviews of gardeners about planting horseradish
It is advisable to plant horseradish generally separately from all plants or in the corner of the garden and always make sure that it does not sprout to the sides. You can plant it in an iron pot so that it doesn't grow all over the garden. It's easy to dilute, but how to get rid of it later? My neighbor in general, behind the fence under a birch tree, determined a place for him. So I'm using it. As the people say: if a mother-in-law has annoyed her son-in-law, then he threatens to plant horseradish on her grave!
TatyanaE
I would generally not recommend planting horseradish in the garden or in the garden. It is best to plant it somewhere behind a fence. Horseradish is an unpretentious plant, does not require any special care or frequent watering. But it takes such roots and grows so that later it cannot be uprooted without a tractor.
Tata all red
Planting horseradish is not difficult. You just need to choose the right place so that the plant not only develops well itself, but also does not oppress other inhabitants of the garden. With the right care, you can get a bountiful harvest of this healthy, spicy vegetable every year.
What a horseradish plant looks like: photo and description
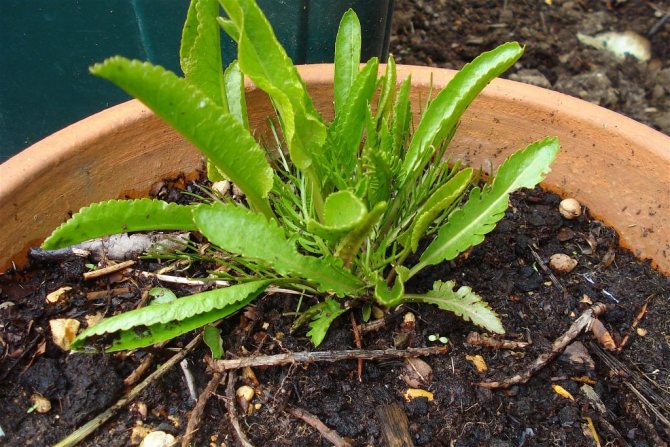
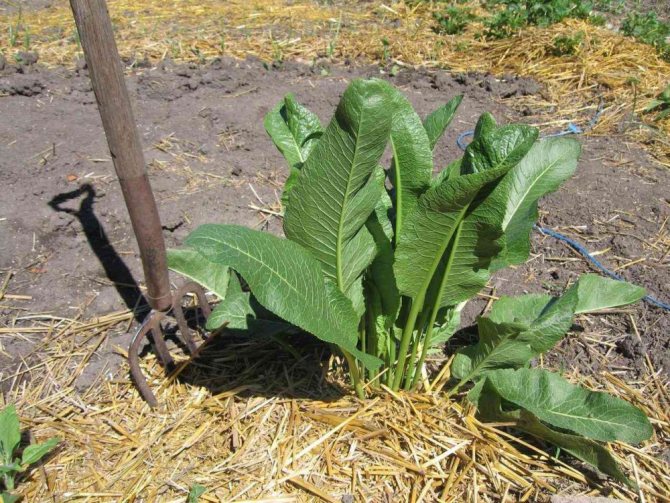
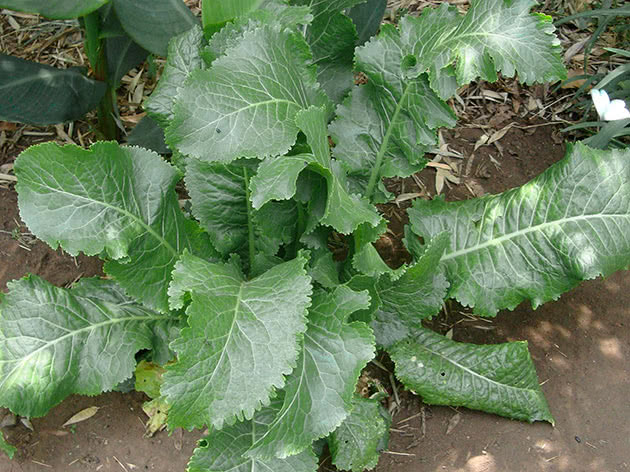
A description of what a horseradish plant looks like should start with the fact that it is a perennial rhizome plant that forms a tap, thick and fleshy root with a large number of dormant buds along its entire length. The root penetrates into the soil to a depth of 2.5-5 m, reaches a diameter of 8-10 cm. In the first year, horseradish forms a basal rosette of 6-11 large oblong leaves. The leaves are dark green, whole, with a crenate edge.


In the second year, the plant throws out an erect, branched flowering stem 50-150 cm high and more.The flowers are small, white, clustered in a racemose inflorescence with a pleasant aroma. The fruit is an oblong or spherical pod. In cultivated forms, seeds are not set, the plant reproduces mainly vegetatively.
See what the horseradish plant looks like in the photo, the description of which is given above:


Horseradish culture is frost-resistant and moisture-loving, adult plants can withstand temperatures down to -25 ° C, young leaves in spring to -8 ° C. It can grow on any soil, but it gives high yields on loose, fertile soils, responds well to the introduction of organic and mineral fertilizers. It can grow in one place for more than five years, but the old central roots of a perennial plant produce products of poor quality, coarse consistency and bitter taste. The roots of plants of the first - second year of development are harvested.
General information about horseradish
Horseradish belongs to the type of perennial grasses, it is a cruciferous plant with a long dense, long, up to 2 m long rhizome, a lush deciduous rosette. Leaves grow up to 0.7 meters in height, peduncles - up to 1.5 meters. Blooms in the second year of life in May – June, forms pods up to 5 mm long with 3-4 small round seeds.
The plant propagates:
- by the seed method;
- apical kidneys;
- using cuttings.
The roots contain the bitter allyl isothiocyanate, which has antiseptic properties. The plant is prized for its high content:
- vitamins C, PP and group B, carotene;
- microelements P, Ca, K, Fe, Cu, Mg, S;
- organic resins;
- essential oils;
- alkaloids.
The culture winters well in temperate latitudes, normally adapts in hot climates, and is drought-resistant. Traditional early selection varieties:
- Suzdal, late ripening, is distinguished by its sharpness, pungency;
- Valkovsky early maturing, forms a thick root, up to 3 cm in diameter per season;
- Latvian or common, late ripening, blooms in mid or late June, common in western and central Russia;
- Rostov mid-season, recognizable by wide leaves with a high content of essential oils;
- Atlant of medium ripening, with dryish pulp of cream-colored rhizomes, characterized by slight spreading during growth, good keeping quality;
- Tolpukhovsky, the seed ripens in 200-250 days, it is recommended for mechanical cultivation, the root system is compact, the flesh of the rhizomes is white, medium-sharp.
Horseradish can remain in one place for many years, but as a garden crop it is recommended to dig it out annually or 2 years after planting, until the rhizomes have gone deeply. Fighting horseradish like a weed is very difficult.
Preparing the soil before planting
Under planting horseradish root - Allocate a site with a deep arable layer, loamy or sandy loam soil with low-standing groundwater. Lands from old garbage dumps are suitable. Place it along the fence or in the corners of the garden plot.


Soil preparation is carried out in the fall. After early crops, the soil is preliminarily loosened, provoking the germination of weeds. After crops with late harvesting periods, the soil is dug immediately to a depth of at least 30 cm, while the rhizomes of perennial weeds are removed. In autumn, 8-10 kg of organic fertilizers, 30-40 g of superphosphate, 25-30 g, potassium salt per 1 m2 are introduced for digging. During pre-sowing soil cultivation in the spring, add 20-30 g of nitrogen fertilizers per 1 m2. Strongly acidic soils are limed at the rate of 2-8 g per 1 m2.
Planting horseradish and caring for it is much easier to carry out than to clear the area of it later. To clean the area where horseradish used to grow, a fence is dug in around the perimeter, in the fall they dig up the soil as carefully as possible and manually select the smallest remnants of the roots. In early spring, as soon as the young leaves begin to grow from the stumps of roots, the fenced area is tightly covered with roofing material, blocking the access of light to the plants.The coating is not removed for two years.
Useful properties of horseradish
Horseradish has long been grown in the gardens in Russia. This herbaceous plant of the cabbage family is distinguished by very large leaves with a straight stem and a thick root with a pronounced taste, which is traditionally used for food. The homeland of this plant is the countries of the Mediterranean coast. In Siberia, as well as in the Caucasus, horseradish grows in the wild. Currently, in nature, it can be found mainly in places with high humidity (on the banks of water bodies), in addition, horseradish is successfully grown in many garden plots.
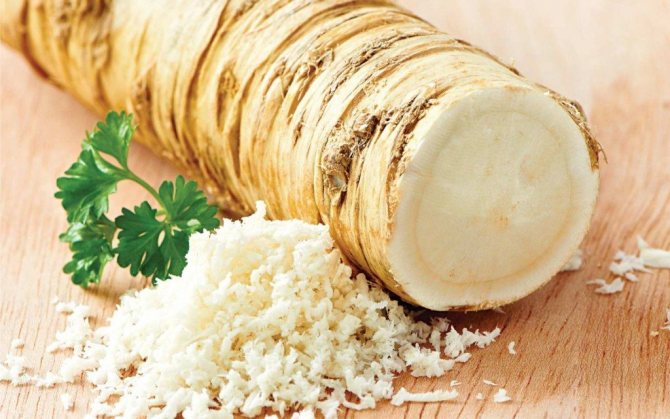


The pungent spicy taste of the root of this plant will come in handy for preparing sauces, savory snacks and seasonings for a variety of meat and fish dishes. Its roots and young leaves are indispensable for preparing various types of vitamin preparations for the winter. Horseradish root juice contains significant amounts of B vitamins, ascorbic and niacin, phytoncides, carotene, mineral salts and organic compounds, as well as lysozyme, which has antimicrobial activity. For a long time, horseradish root is considered one of the most valuable antiscorbutic agents, in addition, it is known for its antitumor activity, as well as for its properties of a natural antibiotic. In the cold season and during the spread of infections, it is very useful to eat a small amount of horseradish daily to prevent flu and colds.
The characteristic smell and specific burning taste of horseradish is due to the content of allyl mustard oil in all parts of the plant. Horseradish root has the ability to stimulate appetite and stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, improves digestion and normalizes metabolism. In addition, the numerous healing properties of this plant (choleretic, light diuretic, anti-inflammatory and expectorant) are successfully used in folk medicine for external or internal use. Horseradish will help eliminate a hangover, it will be useful in the treatment of colds, gastritis with low acidity, migraines, diabetes mellitus, mild hypertension, joint aches and sciatica, skin diseases and many other ailments.
Preparing the soil for horseradish
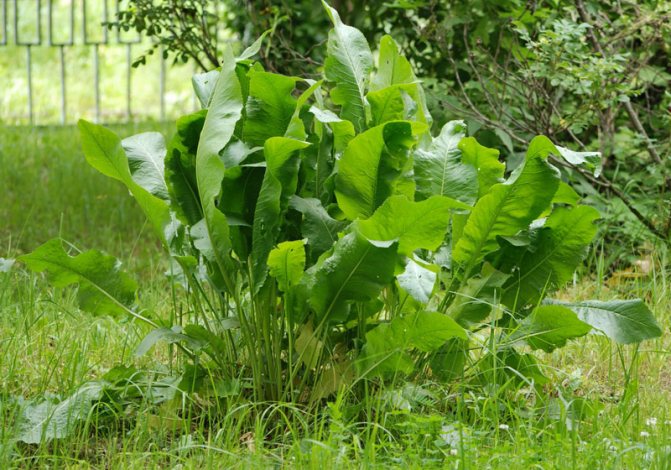


Growing horseradish in the country is possible on almost any type of soil, but you still need to know what kind of soil table horseradish likes. He prefers light soils with a sufficient content of vermicompost (for example, black earth or loam). Clay soils are too dense and heavy. In them, the root develops poorly and begins to branch strongly, forming adventitious roots. But at the same time, on too light sandy and sandy loam soils, the horseradish root quickly becomes woody and does not acquire a pronounced pungent taste. On heavy and wet soils, it is necessary to loosen and structure the soil with sand; you can also equip a fill bed.
As for the illumination, the more sun, the better the plant grows and acquires a sharp taste. Horseradish does not like shaded areas, there is never too much sun for him. It is better to plant horseradish in open areas that are in the sun all day.
Horseradish is planted mainly in spring or autumn before winter. Since this is a cold-resistant plant, it overwinters well, and in early spring, as soon as the ground thaws, it will give young shoots. Many gardeners prefer spring planting, after the ground on the site thaws and warms up. In the middle lane, it is about mid-April.
Planting horseradish
Planting material is prepared from cuttings at the age of one year. It is necessary to prepare strong healthy rhizomes with a length of 20 to 30 cm, the thickness of which should not be thinner than 1 cm. All shoots, buds and lateral branches must be removed. The long root can be cut into several pieces. Cuttings prepared in this way are stored until spring in a cool, dry place.
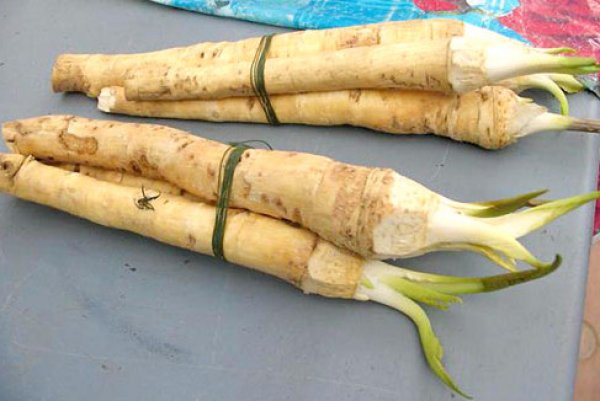


When going to plant horseradish, we clean the root cuttings from small processes, without affecting the areas above and below the root, where roots and leaves are then formed. It is better to bury it obliquely, the distance between the roots is from 30 cm, sprinkle with earth on top by about 4-5 cm.
Horseradish care
Horseradish is not picky about growing conditions, so you won't need much labor and time to care for it. It is only necessary to weed the weeds in time, and also periodically loosen the soil. You should also not allow it to dry out; during the dry period, you will need to water the plants.
About a week after planting horseradish cuttings, it is necessary to loosen the soil with a hoe a few centimeters deep, after the sprouts appear, the depth of loosening must be increased to 7-8 cm.When young horseradish plants reach a height of 20-25 cm, it is necessary to carefully loosen the soil 10 cm deep. Such loosening, as well as hilling, should be done several times during the horseradish growing season. In addition, it is useful, once a month, to feed it with a nutrient solution at the rate of 40-50 g of mineral fertilizers per 10 liters of water. Horseradish should be watered in dry weather, consuming 3-4 liters of water per 1 m2 of beds.


Sometimes this plant is affected by pests in the form of powdery mildew or cruciferous fleas - to combat them, you can prepare a spray solution (for 10 liters of water, 100 g of ground red pepper and 200 g of dry mustard powder are required). In biennial plants and in older ones, it will be necessary to break out the peduncles in the future.
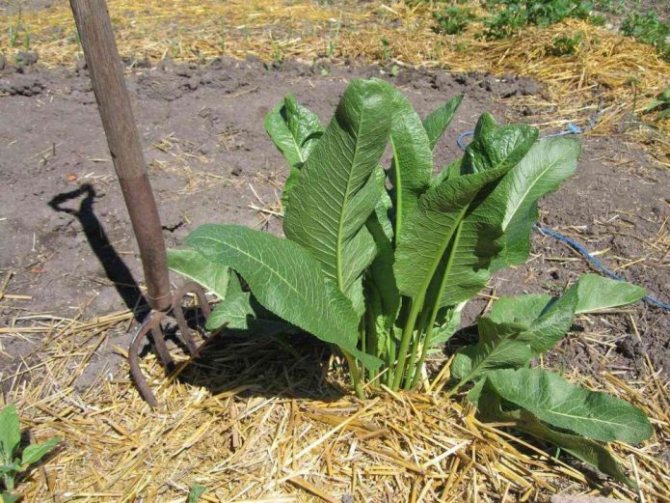
It is believed that after the lower leaves of the plant turn yellow, you can start harvesting. It is most convenient to get them out of the soil with a garden pitchfork. After removing it from the ground, it will be necessary to cut off the horseradish leaves and clear the roots from the side branches for harvesting planting material for the next year. The harvested horseradish roots must be stored in a box and covered with sand, and stored in a cool place (cellar or basement) at a temperature of about 2-3 ° C.
How to prevent horseradish overgrowth
When harvesting, it is necessary to take into account that the roots of this plant left in the ground for the next year can grow significantly, making it difficult for the subsequent crop rotation. Since horseradish has a branched root system and multiplies vegetatively, developing without proper care, after a few years it pretty much runs wild, turning from a horticultural crop into a weed. In this case, horseradish is able to manifest itself as a kind of pest, largely spreading in the beds and drowning out other crops.


To prevent this from happening, you will need to thin out the horseradish roots in a timely manner. It is most convenient to do this with a pitchfork, since they will not cut the rhizomes (it should be borne in mind that small cut roots can grow to a large extent). You can remove the spread excess horseradish from the garden by covering the area with overgrown plants with an opaque material like roofing material from the beginning of spring - in this case, after a while they die from a lack of light.
To avoid excessive root growth, before planting horseradish, some gardeners specially prepare a hole with closed impermeable walls (for example, from plywood), and then fill it with soil with the addition of fertilizing. In addition, in order to limit the rhizomes of horseradish in territorial distribution, you can use a long wooden box dug into the ground, without a bottom, filled with earth.
How to plant horseradish in the fall: video instruction
Amateur vegetable growers grow mainly local horseradish varieties in their gardens, although selective varieties have also been bred.


Horseradish propagation is mainly carried out by dividing rhizomes. Cuttings are cut from the lower parts of the rhizome, since they form fewer flowering shoots and give the best quality marketable products.Cuttings are harvested in late autumn or early spring, pencil-thick, 15-20 cm long.
When planting thicker cuttings, production is obtained in the fall of the same year, and from thinner and shorter cuttings, you have to wait only for the next year.
When horseradish breeds in the fall - the upper end of the cutting is cut straight, the lower end is made oblique, cutting at an angle of 45 ° for orientation when planting. Finished cuttings are stored in winter at a temperature of about 0 ° C, sprinkled with wet sand, earth, peat or in plastic bags, as well as in trenches covered with earth. 2-3 weeks before planting, cuttings are germinated in wet sawdust or sand at a temperature of 10-17 ° C.


Before planting horseradish in the fall by the root - the cuttings are rubbed with a coarse mitt, removing all germinated buds, except for the apical and at the base of the cuttings. At the top of the cutting on a strip 1-1.5 cm wide, buds are left, from which leaves will develop, at the base of the cutting - a strip 2-3 cm wide, where roots are formed. This technique contributes to obtaining even two-year marketable roots.
Horseradish cuttings are planted in rows in furrows at an angle of 15 ° with row spacing of 70 cm and a distance between plants in a row of 25-30 cm, or with ribbons according to the scheme, 50 × 70 cm.Above the upper end of the cutting, a soil layer of 1-3 cm is left.On the ridges cuttings are arranged in a three-line way with a distance between rows of 30-35 cm, between plants 25-30 cm. After planting, the site is rolled, slightly compacting the soil.
Watch the video on how to plant horseradish in the fall, where this process is demonstrated step by step:
Watering and fertilizing
Although horseradish belongs to drought-resistant crops, in dry years the taste of the roots deteriorates: the pungency and piquancy decrease. In a period of severe drought, the plant is moistened so that the central part of the rhizome grows. With insufficient watering, the yield will be less, many lateral thin roots are formed, coarse fibers grow. An excess of water leads to decay of the center of the rhizome, it acquires an unpleasant aftertaste of rotten hay.
It is not necessary to water the horseradish regularly, it is enough to shed the bush once a week. The roots will absorb moisture from a great depth. They use the osmosis method: the soil is covered with a film, then moisture from the lower layers of the soil rises up. The method is effective when the groundwater is close to the ground.


Top dressing improves the chemical composition of horseradish. Complex mixtures are annually embedded in the soil in the spring in the amount of ½ indicated on the package. During the rains, after the morning dew, they gradually dissolve. If desired, you can water the plant with fertilizers prepared for vegetables in open or closed ground.
Plant care
Planting horseradish and caring for it in the open field consists in the timely loosening of the row spacing 3-4 times during the growing season and systematic weeding in the rows. Watering is provided during dry periods. They destroy pests (cruciferous fleas; cabbage whitefly caterpillars, cabbage, horseradish leaf beetle, horseradish flea). Measures are taken to protect against diseases (white rust, black rot, leaf spot), deterrents are used - a mixture of tobacco dust with lime at the rate of 30-40 g / m2.


Horseradish "training" can be carried out on personal plots: in the middle of summer, the soil is removed from the rhizomes, the upper, lateral shoots of the central rhizome are removed with a knife by about 2/3, then the plant is spud. This technique allows you to increase the marketable yield and improve its quality. Rhizomes are smooth, with minimal branching. At the beginning of summer, use a sharp knife to remove excess rosettes of leaves, leaving no more than two on one plant. Otherwise, multi-headed rhizomes grow.
Horseradish is harvested in late autumn or next spring, depending on the quality of the planted cuttings.
Horseradish vegetable - description
The horseradish root crop is thick and fleshy, the stem is straight, but branched, reaching a height of 50 to 150 cm.Leaves are basal, very large, oblong-oval, crenate, cordate at the base. The lower leaves are pinnately separate, and the upper ones are linear, entire. The flowers of the plant are white, with petals up to 6 mm long. The fruits are swollen, oblong-oval pods 5-6 mm long with a mesh-veined pattern on the valves. Inside the pods are nests with four seeds.
Horseradish is a surprisingly unpretentious plant, and if you once plant it on your site, then it will be forever - this perennial winter-hardy culture behaves aggressively, like a real weed.
All parts of the plant contain an essential oil with a pungent taste and aroma. Horseradish root juice contains ascorbic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, carotene, starch, carbohydrates, fatty oil, resinous substances and lysozyme protein, which has antimicrobial action. Horseradish root contains mineral salts of calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur, phosphorus, copper and iron. The healing properties of horseradish have long been known to medicine: it improves bowel function, has antiscorbutic, choleretic and expectorant properties, heals colds, liver, gastrointestinal and bladder diseases, rheumatism and gout.
- Luffa at home: care and photos


In this article, we will tell you how horseradish growing outdoors is carried out:
- when and how to plant horseradish;
- how to water horseradish;
- how to fertilize horseradish;
- what horseradish is sick with;
- how to treat horseradish from diseases and pests;
- when to dig the horseradish;
- how winter horseradish is planted;
- how to store horseradish until the next harvest.
A little about the plant and its use
In Russia, horseradish garden has been known since time immemorial and is one of the national spices, although its homeland is considered to be the southeast of Europe - the southern Mediterranean. It is also mentioned in recipes for dishes and snacks since the times of Ancient Egypt, Greece and the Roman Empire, and then, by the 9th century AD, it appeared in Russia. At present, it is widespread everywhere, up to the regions of the Far North and the Caucasus.
Modern science classifies this culture as a cruciferous family. It is a perennial herb, sometimes reaching a height of 1.5 m, usually looking like a bush. The length of the root can reach 50-70 cm. The shoots are erect, the stems are hollow, with grooves. The leaf plate is large, has a bright green color. Horseradish blooms with pretty white flowers, collected in inflorescences, usually from May to June. By autumn, pod-shaped fruits are formed containing horseradish seeds. Blooming horseradish in the photo below.


Of particular value is the rhizome, which is loved for its pungency and healing properties. It contains the following substances:
B vitamins;
vitamin C (ascorbic acid);
antimicrobial substances (phytoncides, lysozyme, etc.);
Thanks to such components, it has long been considered a natural antibacterial agent that can cope with many microbes, as well as malignant formations in the body. During periods of off-season exacerbations of ARVI, doctors advise to eat a little horseradish root along with garlic.
Many summer residents breed horseradish in their backyards and use all parts of the plant in cooking - both leaves and roots. Growing horseradish in the garden is not difficult.
Planting horseradish in open ground
When to plant horseradish in open ground
Horseradish can be planted in April and even at the end of warm March - this winter-hardy plant is not afraid of either cold snaps or frosts. Set aside a small sunny area for horseradish near the fence.
Horseradish propagates vegetatively - by cuttings, that is, by parts of a root crop. You can, of course, try the generative method of reproduction, since horseradish seeds are not in short supply, but growing horseradish from seeds has not gained popularity among amateur gardeners due to the laboriousness of the process.
Horseradish soil
The soil for horseradish needs fertile.The culture grows best in loam, black soil and in sandy loam soil, but if you adjust clay soils in accordance with the tastes of the plant, you can also grow a decent harvest on them. To do this, in the fall, manure (10-12 kg per m²), peat and sand are introduced into the clay for digging, and in the spring - mineral fertilizers at the rate of 30 g of potassium salt, superphosphate and ammonium nitrate per 1 m². If you are going to grow horseradish on his favorite soils, then organic fertilizers need to be applied under the previous crop - cereals or legumes.
How to plant horseradish in open ground
Horseradish cuttings are harvested in the fall during harvesting and stored in a basement or cellar in dry sand or sawdust. You can prepare cuttings in the spring, but you need to have time to do this before the leaves appear.
One and a half to two weeks before planting, the roots are removed from the cellar and kept in a warm place, covered with a damp cloth, waiting for the buds to sprout. Before planting, lateral processes up to 25 cm long and up to 12 mm in diameter are chopped off from the main root, long cuttings are cut into pieces, making the upper cut horizontal and the lower one oblique, after which they are planted on a garden bed, placing 4-6 cuttings on one square meter at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other with a row spacing of 65-70 cm.
- Luffa at home: care and photos


If you need a good harvest of even root crops, peel the middle part of the cutting with a coarse cloth from the buds before planting, keeping them only at the top for the formation of leaves and at the bottom for regrowth of the roots. If you are planting horseradish in order to get planting material, then do not remove the germinated buds - the root crop will grow branched and give many cuttings.
Planting horseradish in open ground is carried out at an angle: the upper part should be deepened only by 5 cm, and the lower - by 10. Small pieces of roots can be used for growing horseradish - about 8 in length and not more than 2.5 cm thick, but they are located horizontally in the ground, keeping all the buds.
Ways to multiply horseradish
To prevent the soil from clogging up with many horseradish root branches, the plant should be dug up annually, and then propagated in one of the known ways.
These include:
- seed method;
- reproduction by tops;
- cuttings.


So that the overgrown horseradish does not greatly clog the soil, it should be dug out annually
Horseradish reproduces especially well in open areas where there is a lot of sun.
Seed method
Horseradish will bloom and give seeds if it is not dug up for 2 or 3 years, the leaves are not plucked from it.
When planting seeds in autumn, they are sealed to a depth of about 3 cm at a distance of 10 cm between them.In order for the plant to develop normally, 70 to 90 cm are left between the rows.When the seeds collected in autumn are sown in the spring, they are mixed with wet sand in ratio 1: 3 and placed for 3 months in a cool place (refrigerator, basement).
Periodically, the mixture is stirred and sprayed with water if the seeds dry out in the sand. Then the container is placed in heat. The ideal temperature for germinating seeds is 21 ° C. In the 2-leaf phase, the shoots dive into boxes or pots.
When the seedlings have 4-5 leaves, they are planted in a permanent place (after a month and a half). With this method of reproduction, the rapid development of the bush will begin only after a year, and it will be possible to dig up the root at the end of the third season after planting.... Since this method is quite time consuming, horseradish is rarely propagated by seeds.




























