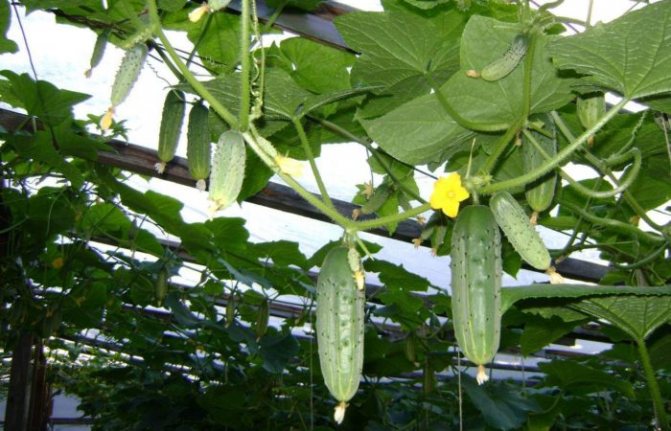
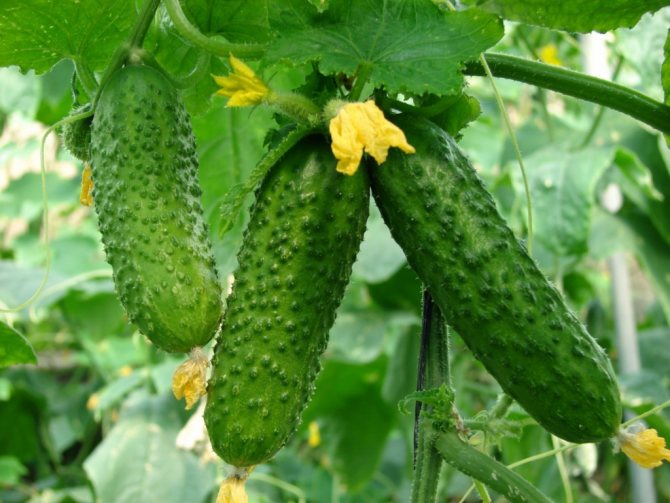
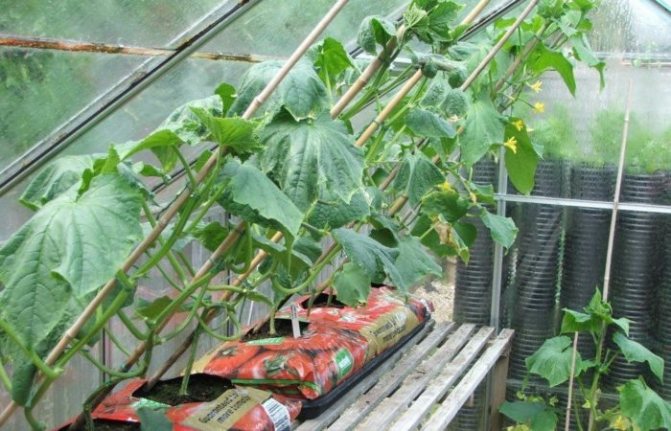
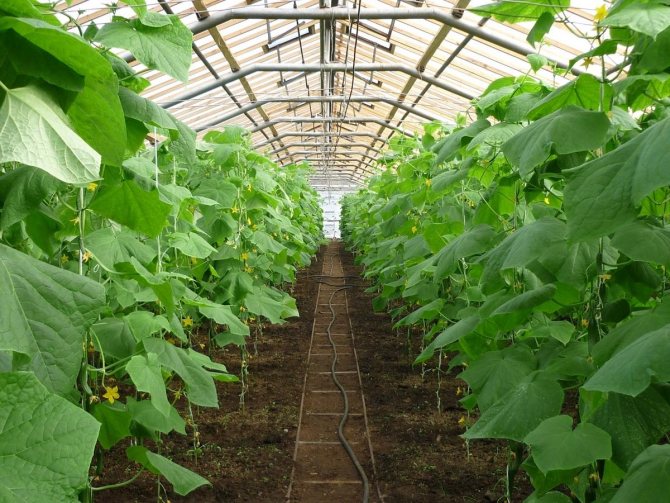
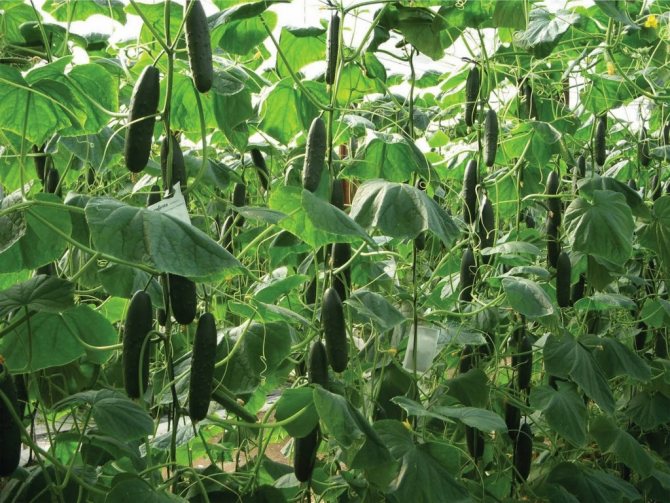
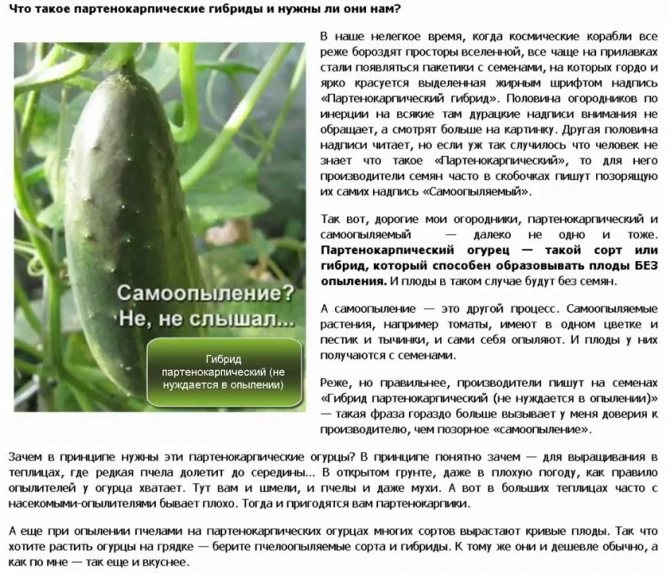
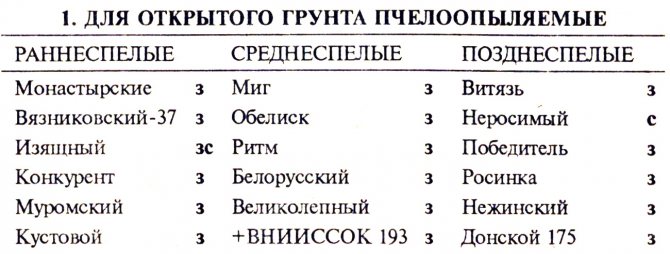
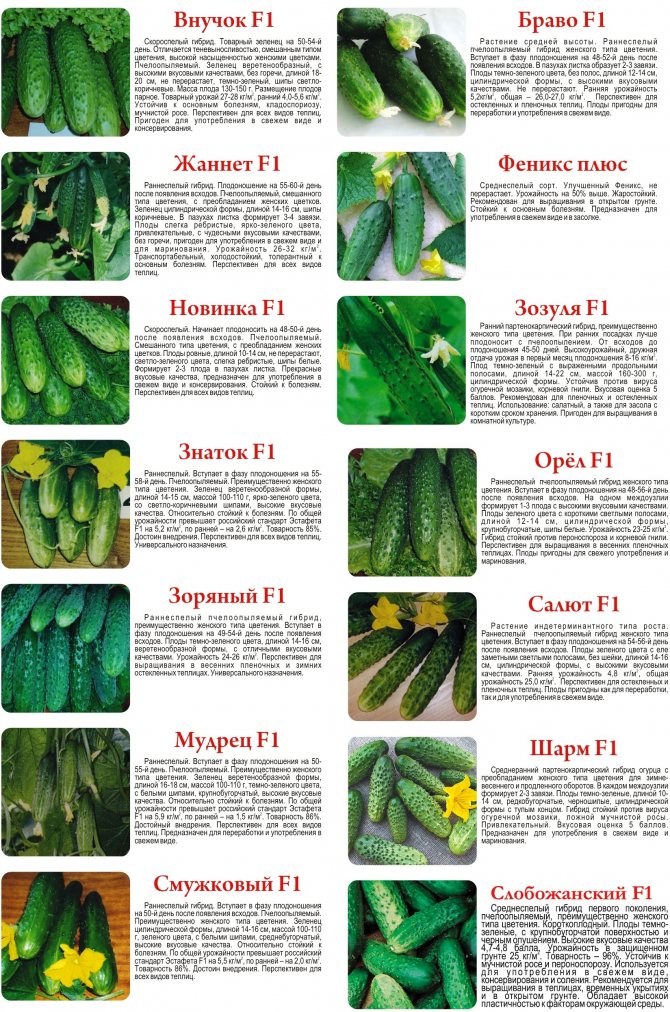
Types of greenhouses for cucumbers
Those who decide to set up a greenhouse on their site have two options - to assemble it with their own hands, or to purchase a ready-made one. And in fact, and in another case, there are a number of features. Read what greenhouses and greenhouses for cucumbers exist here.

The initial investment is reduced to the purchase of materials for the construction of a greenhouse
If the greenhouse is purchased, there is no need to think about the choice of material and design. Such a greenhouse will be delivered and installed by specialists. The disadvantage of such a greenhouse is its high cost and standard parameters, which may not be suitable for a specific site. The self-assembled structure is modeled for the required dimensions and is easier to disassemble. However, you need to spend your time and effort in collecting it.
- Film greenhouse, usually assembles on its own. Such a greenhouse is assembled from arcs, which are covered with a film. Polyethylene is pressed to the ground with stones or boards. Caring for such a greenhouse is simple. You just need to lift the film and you can water and ventilate.
- Greenhouse butterfly - a convenient design that helps to maximize the profitable distribution of space on the site. It is a box that looks like a small house with a semicircular roof. Both sides of the greenhouse open and provide access to the inside. There are both ready-made greenhouses, sold in stores, and self-assembled.
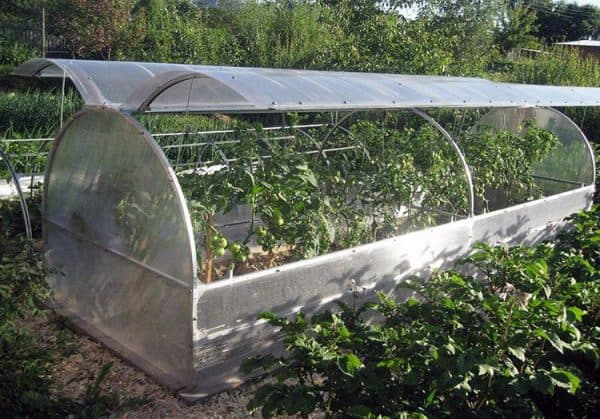


Butterfly greenhouse takes up little space, which is its advantage
- Polycarbonate greenhouses have a transparency of about 80%, are not subject to deformation during hail or snow, and also slowly give off heat.
- Winter greenhouse - the most laborious in construction. However, only it allows you to get a harvest of cucumbers during the winter cold. Such a structure must be completely sealed, there must be light and warmth. These greenhouses are either shelving (cucumbers are planted on shelves) and non-shelving (planted in the soil). Previously, such greenhouses were almost all glass. Most of them are now constructed from polycarbonate.
Diseases and treatment
There are several of the most common diseases that the cucumber crop is exposed to:
- powdery mildew. The main causes of this disease are a large amount of nitrogen in the soil and an incorrect temperature regime. They are treated by spraying with a solution of mullein, sour milk or soda;
- cladosporiosis. Brown spots cover the plant and fruits in just a week. The main cause of a fungal disease is a sharp change in temperature, for example, watering with ice water. For treatment, stop watering, increase the temperature in the greenhouse and spray the bushes with solutions containing copper;
- gray rot. Brown spots on leaves turn into mold at high humidity. The disease appears at low temperatures and high humidity. For treatment, the greenhouse is ventilated and watering stops, the affected leaves are removed, the plant is sprayed with copper-chalk powder, and ash is applied.
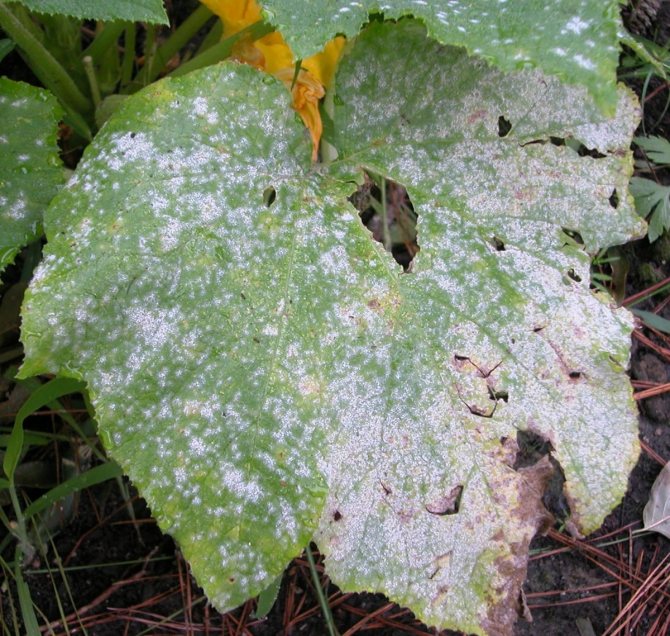


Powdery mildew
Greenhouse processing
The first step is to properly position the greenhouse. It is necessary that it is not blown by the north and north-east winds. If there are wooden elements near the greenhouse, they must be disinfected with copper sulfate before use. If there are metal parts, it is better to paint.
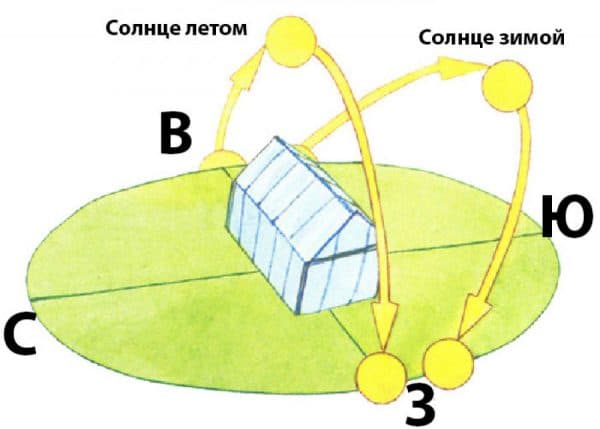

Correct placement of the greenhouse
The soil
Before planting cucumber seedlings, you need to prepare the soil. Cucumber seedlings develop well on loose soils equipped with organic matter. Fertilize the soil before use. This can be done with non-rotten manure at the rate of 22 kg per 1 sq. M. land, lime 220 g, potash and phosphorus fertilizers about 55 g. Then loosen the earth. What fertilizers and fertilizing are used for grapes is described here.


It is best to plant cucumbers on loose soils.
Humidity
Each vegetable crop requires a certain percentage of moisture. Cucumbers require high humidity. The best option on sunny days is 85% -95%, on cloudy days - 70% -80%. To increase humidity in hot weather, avoid drafts and watering the paths between the rows. It is necessary to lower the humidity in rainy weather by heating and ventilating the room.
It is necessary to ventilate at a time when there is no wind, opening air access only in one direction.
For a film structure, more frequent airing is needed than for a glass one, since overheating occurs faster under the film. It is necessary to ventilate very carefully, since cucumber seedlings are susceptible to changes in humidity, drafts and sudden changes in temperature.
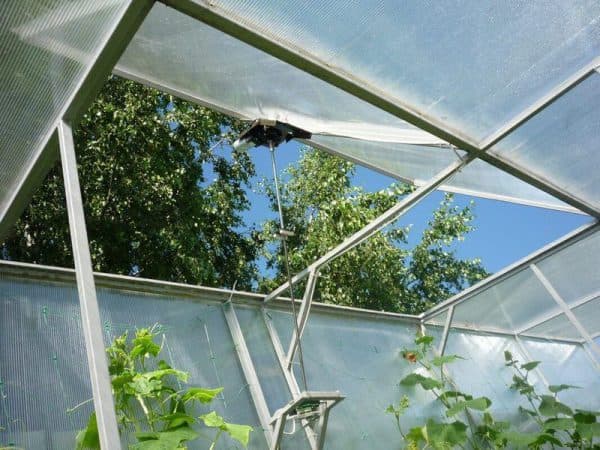


Greenhouse ventilation is the simplest prevention of most fungal diseases.
Watering
The soil in a cucumber greenhouse must be moist, not too much. A deficiency and excess of water are harmful to cucumbers. If there is a lot of moisture, the leaves fall off, the fruits are deformed.
A very high temperature leads to stretching and weakening of the seedlings. However, a slightly lower temperature regime has almost no effect on the development of a cucumber, it can simply slow down its growth a little. The temperature in the greenhouse is regulated by ventilation. It can be increased or decreased over time.
During planting, cucumbers are watered with exceptionally warm water. In cold weather, you need to water in the morning, when there is sun. In the warm season, it is better to water 2 times a day. If you water it once, then you need to do it in the evening and in large quantities, since cucumbers grow most at night. Loosen the soil periodically so that the roots have access to oxygen, and they do not rot. A spray bottle is placed on the tip of the watering can. The rules for watering cucumbers are described here.


Depending on the variety, cucumbers are watered from 2 times a day to 4 times a week.
This is done so that during watering the soil does not erode at the roots of the plant, and the roots are not exposed.
Pests and the fight against them
The warm environment and constant humidity required by the cucumber is a beneficial environment for diseases and pests.
The prevention of this will be the mandatory ventilation of the greenhouse, washing the greenhouse with non-aggressive chemicals, such as laundry soap. A sulfur checker successfully fights against mold and fungi.
Important! Before planting, the soil is pre-spilled with a solution of copper sulfate.
The land for the cucumber should be 4 years old, not planted with pumpkin crops.
Suitable varieties
In a greenhouse microclimate, it is better to plant hybrid varieties with shortened lashes on the side, which do not need shaping (do not pinch). The most optimal greenhouse varieties of cucumbers, which yield a harvest literally in 30 days from the moment the first fruits appear, are the “Bouquet” and “Temp” hybrids.
- Suomi F1 - resistant to cold and ailments, very early variety, the fruit does not outgrow.
- Valaam hybrid also very early and weather resistant. The fruit grows up to 5 cm in the form of a cylinder. There are not many tubercles. Long fruiting.


- Sarovskiy F1 - also early maturing. In this variety, several pieces of the crop come out of one axil of the leaf.
- Long fruiting times are characterized by such varieties as Uglich, Okhotny Ryad, By the Pike's Command, Shik and Zadavaka.
In a greenhouse, it is inconvenient to breed varieties of cucumbers pollinated by bees, so it is better to plant self-pollinating varieties, or fruiting ones and those that do not need pollination at all. These include: Orpheus F1, Cheetah F1, Emerald F1, Glafira F1, Mazay F1, Blik F1, and others.
There are varieties of small gherkins. These varieties can also be grown in greenhouses. These are Alex, Alekseich, a friendly family, a Merry company, Konrad, Pyzhik, Charodey, Shchedrik.


How to properly grow cucumbers in a greenhouse
Varieties
In greenhouses, various varieties are grown in terms of maturation, frost resistance, and pollination methods. It all depends on the technological capabilities of the protective structure and product requirements. In winter heated greenhouses, in the presence of pollinating insects, bee-pollinated varieties give the best result, otherwise self-pollinated varieties are planted.
From the point of view of product sales, short-fruited cucumbers are in the best demand, but in spring greenhouses, early-ripening, long-fruited varieties give a higher return in a short time.
Conditions for landing
Cucumber reacts negatively to low temperature and its sudden changes. Temperatures below + 13 ° C are unacceptable for him, there is a risk of developing diseases, and during the fruiting period, fruits are not tied. The soil should be moist, but not waterlogged, daylight hours should be long.
After what crops is it better to plant
It is more difficult to alternate crops in a greenhouse than in an open field, since thermophilic tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers are often grown in greenhouses. In periods free from their cultivation, it is necessary to maximize the use of green manures: grain, oilseeds.
Landing dates
Planting dates depend on the type of protective structure, the possibility of heating, the region, the weather conditions of the current year. In winter heated greenhouses, sowing for seedlings in the presence of additional lighting begins in November, and planted in a permanent place from the end of January. In spring greenhouses without heating, seedlings are planted not earlier than April - May, as soon as a suitable temperature level is established.
Lighting and temperature for growing
The cucumber grows well in lighted greenhouses, does not tolerate constant shading, but in hot, very sunny weather without shading, it can get burns.
Optimum temperature before fruiting:
- at night - not lower than + 17 ° С;
- during the day - not lower than + 20 ° С;
during fruiting:
- at night - + 20 ° С;
- during the day - from + 23 ° to 28 ° С.
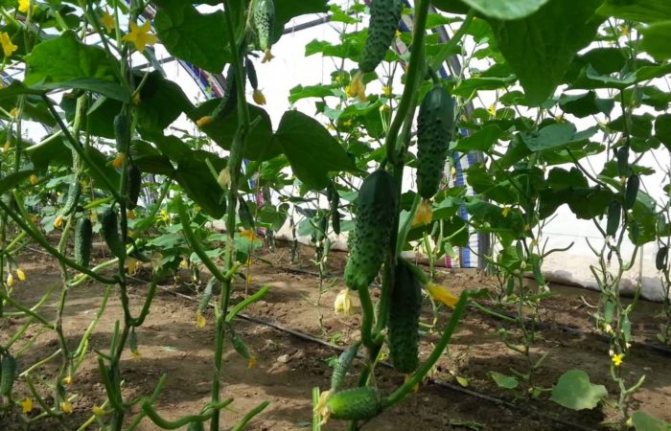


Watering features
Watering a cucumber is carried out using a watering can, a hose or a specially arranged sprinkler or drip irrigation. It should be carried out in such a way as not to wet the plants, erode the root system, and ensure uniformity.
Watering is carried out during the day, in clear weather, with the vents closed, with warm water. The first watering after planting seedlings is carried out a few days later, when the plants are acclimatized.
Planting methods
There are several ways to plant cucumbers in the greenhouse.
In a barrel
It is necessary to prepare containers for planting in advance. Place dry twigs or small stones on the bottom of the barrel to create drainage. In order to fill the barrel, you can use garden waste, paper. Next is the soil. You can use your own primer or buy. You can add manure to it as fertilizer. Next, you can build a frame so that the cucumbers can curl over it. You can make it from any available material. You need to plant no more than 6-7 cucumbers in one barrel. However, it is better for a barrel with a volume of 200 liters - 4 bushes. Read more about growing cucumbers in a barrel at this link.
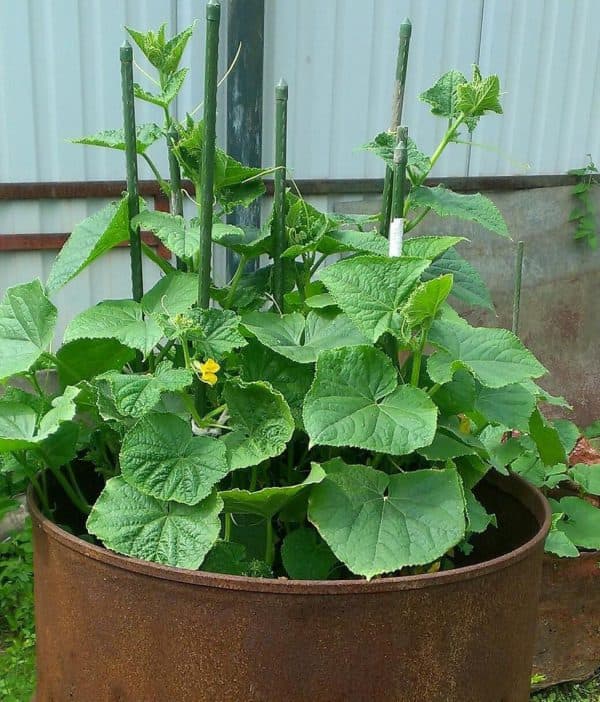


Growing a cucumber in a barrel
As the cucumbers grow, you only need to add earth to the barrel as it will settle.
In bags
The method of growing bagged cucumbers has a number of advantages. Plants will not be destroyed by the bear, there will be no rot in the ground if the plants are properly looked after. Saving space and early maturation of the plant is also an advantage of this method. Moreover, such a crop is easy to harvest, it remains clean. To install them, you need to take a tight plastic bag or bag of sugar and fill it with soil with manure. Place a two-meter stick in the middle of the bag. At the end of the stick, hammer in a nail and tie the seedlings onto it. Three tubes with holes are installed in each bag to water the cucumbers. In hot summer, it is necessary to water seedlings in tubes daily.
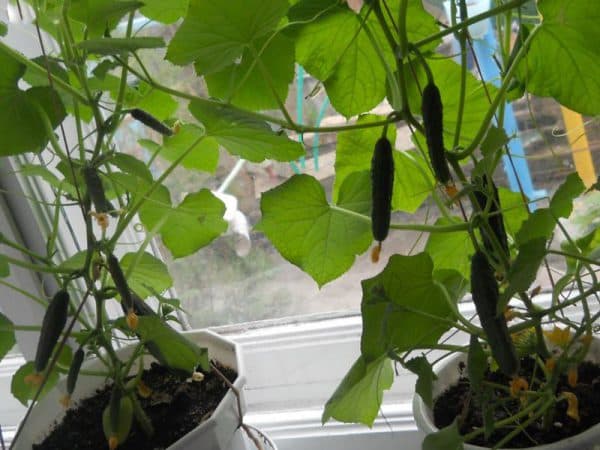


You can even grow cucumbers in bags in an apartment.
After 6 leaves appear, you can tie the stem to a stick with threads.
Garden beds
Seedlings are planted in the beds. There are several options here as well. Seeds are best planted in the following two ways. You can create a manure bed. To do this, it is necessary to prepare fresh manure in the spring and place it in a high, long bed in a greenhouse. The width of such a bed is 1 m, the length is optional. Sprinkle soil on top of the bed with a layer thickness of at least 20 cm. Water abundantly. Then you can plant seeds - 4 pieces per 1 sq. M. Next, you need to make an additional greenhouse by covering the seeds with a film or special material.
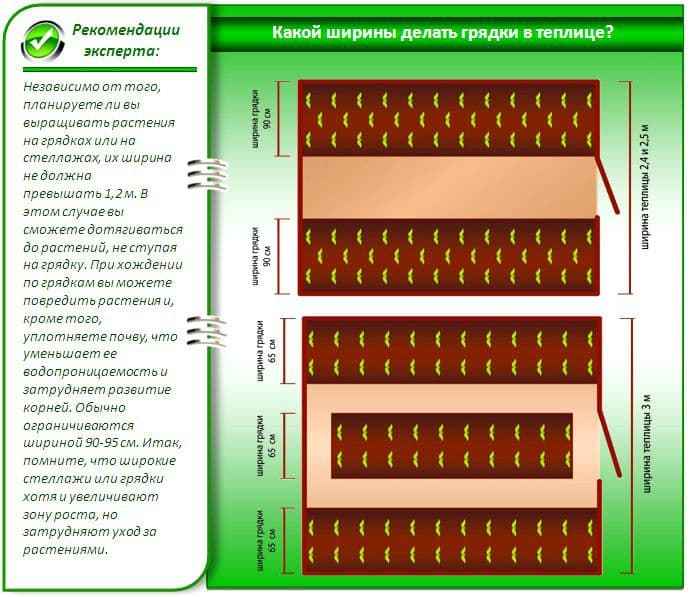

You can also equip a compost bed. You need to collect last year's leaves, tops, vegetable waste, sawdust and more. The principle of creating a bed is like compost. The more greenery, the warmer the bed. Also cover 20 cm of soil and plant, preferably germinated seeds. The principle of care is the same as for a manure bed.
One of the modern methods is hydroponic growing of cucumbers. Suitable for both greenhouses and open ground.
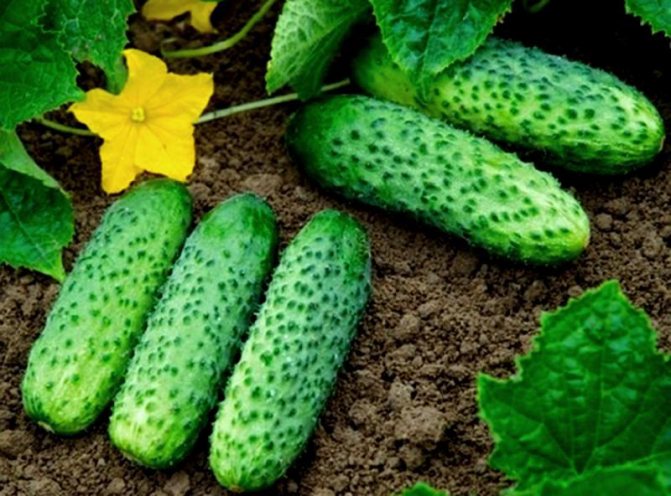
Collection and storage of the harvest of cucumbers
The opinions of gardeners about the harvest of cucumbers are very different. Someone thinks August is the best time. For the rest, the size of the fruit and the degree of its maturity are important.
In most cases, cucumbers are harvested immature. It all depends on the purpose of using the crop. For preservation, a size of up to 10 cm is needed, for salting - up to 20 cm.
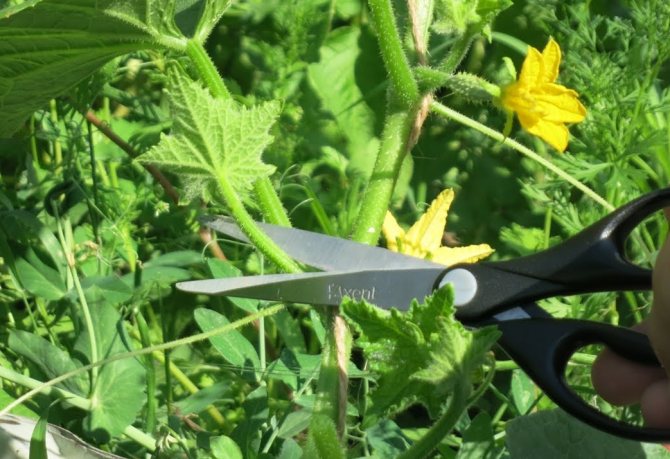
Important! The fruits from the bush should be harvested regularly. The more nutrients enter the unharvested fruit, the less the plant will give new ovaries.


Storing cucumbers
Fresh cucumbers are not stored. Varieties with thick skin are more likely to lie in the refrigerator for a couple of days longer than their thin-skinned counterparts, so the culture is preserved and salted immediately.
For your information! For storage for up to several days, cucumbers can be placed in a container with water, stalks down.
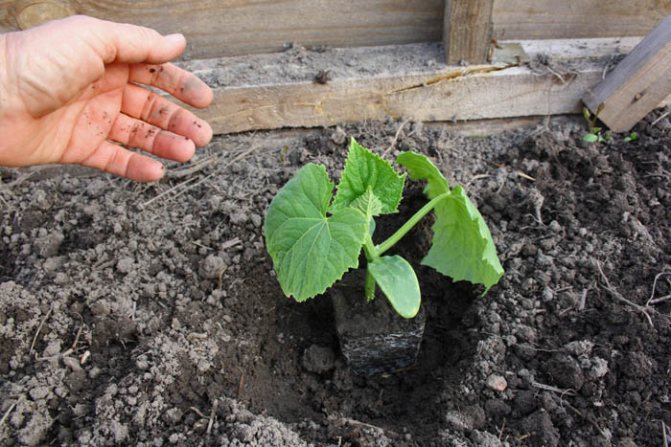
Landing
Seeds or seedlings
For the greenhouse, both methods are chosen. If the seedling method of planting cucumbers is chosen, then it is necessary that the earth in the prepared soil warms up to at least 15 ° C. The wells are pre-disinfected and watered. The same is done with the seed method, but in this case the harvest is obtained much later.


Seedlings of cucumbers should be stored under a film until the first leaves sprout.
Basic requirements for arranging a greenhouse
The size of the greenhouse is chosen relative to the suburban area. If the area allows, and you want to harvest as much as possible, then the greenhouse will be as spacious as possible.
The optimal height of the greenhouse should be 2 m. It makes no sense to do higher, since the air will warm up unevenly. It is also not desirable to make a greenhouse below this level. Cucumbers by the end of the season grow up to 3.5 m. If the height of the room is lower, the loops of the plant will be too twisted, which will interfere with the formation of fruits, obtaining a sufficient amount of light.
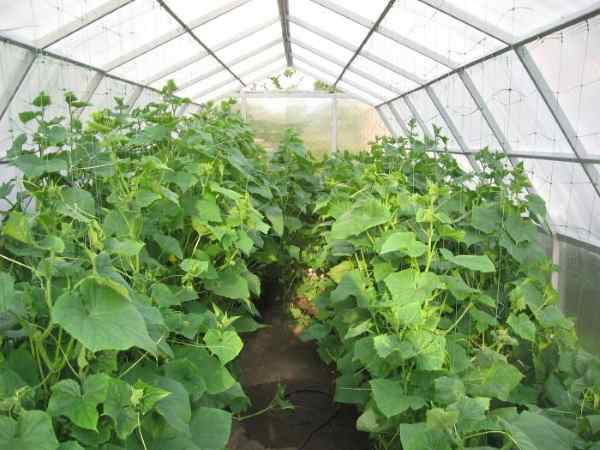


Greenhouse frame
Ideally, the greenhouse frame should be positioned with a ridge. The middle is higher - up to 2.5 m, the edges below - up to 2 m.
Everyone chooses the covering material independently based on their capabilities.An important nuance is only the presence of vents for airing the room.
For your information! For better lighting, it is advisable to locate the greenhouse from north to south or with a slope to the south.
Arrangement of beds
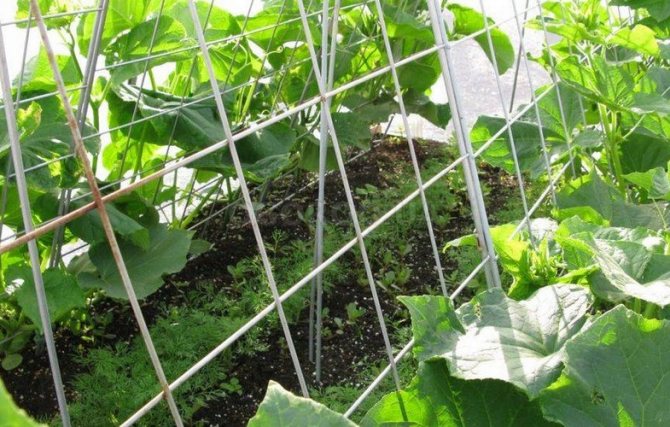
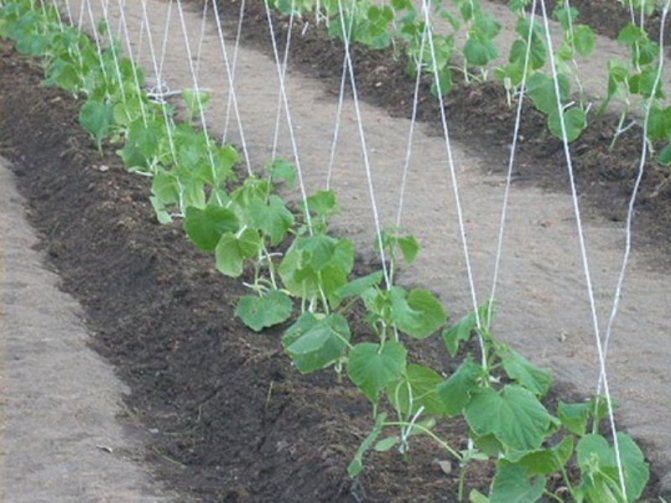
For seedlings, prepare the soil with fertilizer. Then, along each of the ridges, at a height of 1.5-2 m, a wire is pulled in two rows. The distance between them is 20-30 cm. Before placing the soil pot with seedlings in the ground, recesses are made in the beds, watered and organic fertilizers are added if desired. Seedlings are planted standing, you only need to fill in a pot of soil. Cucumbers are planted at a distance of 50-60 cm from each other.
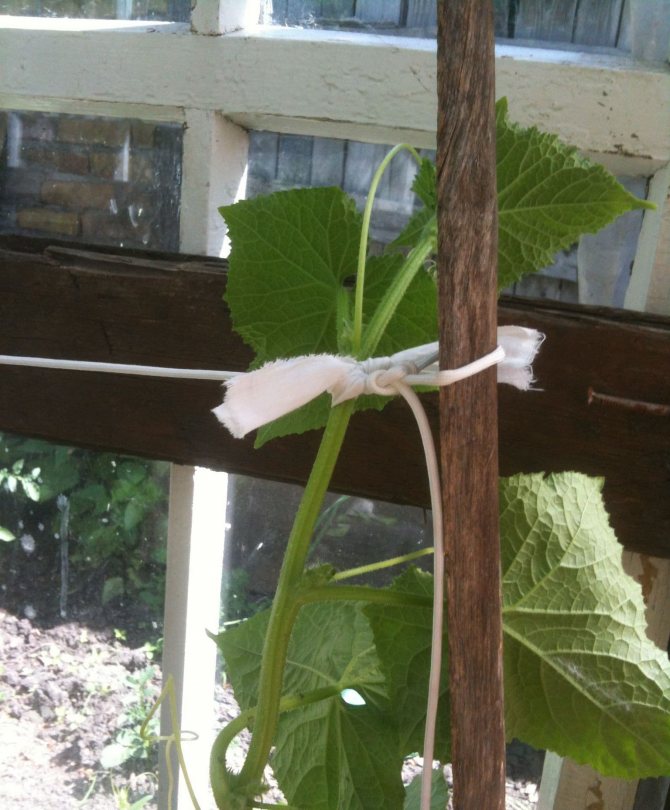


You can even tie up cucumber seedlings
It is advisable to do this in a checkerboard pattern. This way, the light gets better on each seedling.
Pros and cons of growing cucumbers in a polycarbonate greenhouse
Growing cucumbers in a greenhouse allows you to:
- significantly expand the growing season and yield of the crop;
- create optimal conditions for the growth and development of plants and ensure that the maximum return per unit of area is obtained;
- use the structural elements of the greenhouse to improve working conditions for plant care and harvesting.
With all the positive aspects, it should be taken into account that:
- the production of cucumber in a greenhouse requires rather high costs for materials, depending on the type of greenhouse, which increases the cost of production;
- requires constant disinfection of structures and soil, soil replacement, due to the accumulation of pathogens in an enclosed space;
- when planting pollinated varieties, it is necessary to ensure the presence of pollinating insects.
Care
Watering modes
The amount of water used for irrigation depends on the stage of seedling growth and weather conditions. Before flowering, 5-6 liters are watered, during the flowering period - 8-10 liters, during the ripening of the crop - 12-18 liters per 1 sq. M. At the same time, the temperature regime in the greenhouse should fluctuate between 23-27 ° C during the day and 17-19 ° C at night. The gap in day and night temperatures is no more than 5-8 ° C.
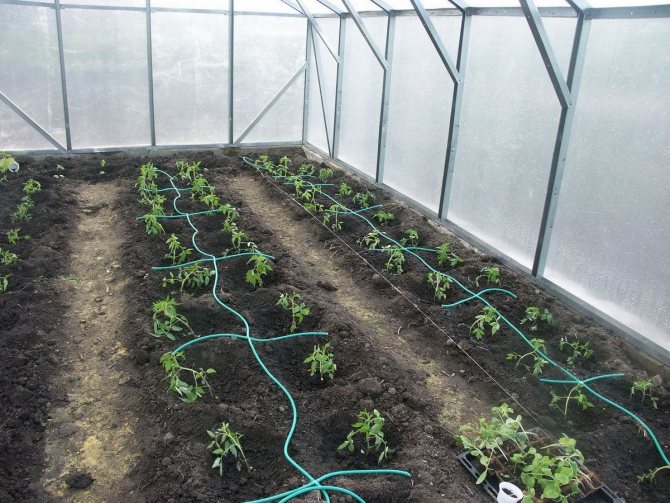


Drip irrigation is very helpful in maintaining humidity in the greenhouse.
Feeding cucumbers
During the growth of cucumbers, about 4 dressings are carried out. This is done with mineral and organic fertilizers. Before flowering - liquid "Agricola" (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). You can also prepare the solution yourself. It includes 20 g of double superphosphate, 15 g of potassium sulfate, 10 g of ammonium nitrate and 10 liters of water.
Further, all top dressing is carried out during the appearance of fruits. In 10 liters of water dissolve 2 tablespoons of "Efekton-O" and 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska. Consumption - 5 liters per 1 sq.m. land.
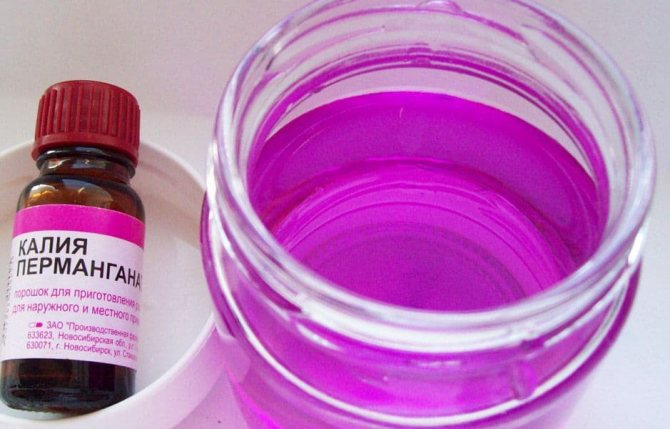


Also, for the good development of seedlings, foliar feeding is carried out. For 10 liters of water, 2 g of copper sulfate, boric acid and potassium permanganate. Spray on the underside of the leaves early in the morning or in the evening.
Disease prevention
Most often, greenhouse plants are affected by fungi, bacteria and viruses. They usually appear due to non-observance of the temperature regime, crop rotation and improper methods of caring for cucumbers. The correct prevention of the variety is:
- buying good seeds, treating them before sowing;
- soil treatment is important;
- feeding seedlings;
- treatment with agents that increase the immunity of the plant;
- cucumbers planted on time in a permanent place;
- the desired quality of soil in the greenhouse;
- pretreatment of supporting structures and basic materials with disinfectants, if these are not used for the first time.
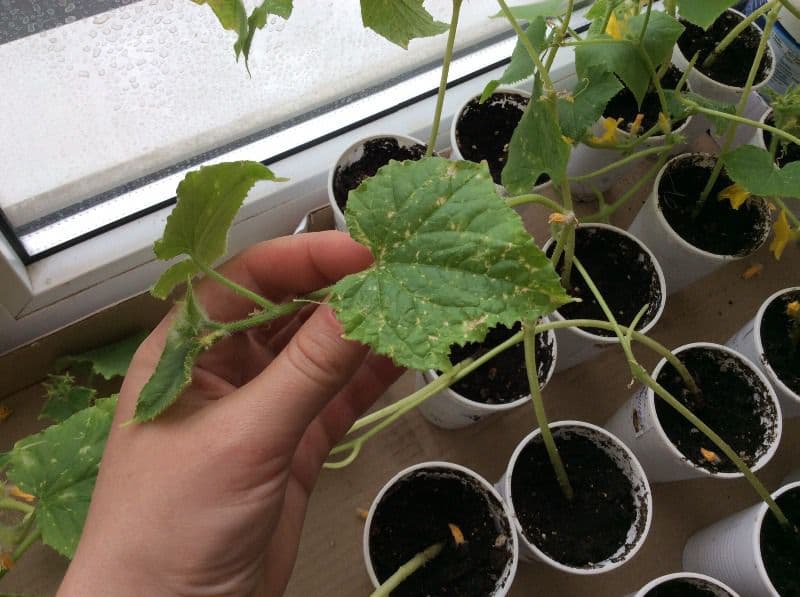


Double-check each plant before purchasing cucumber seedlings
These are all important points in the strong chain of cucumber disease prevention during cultivation.
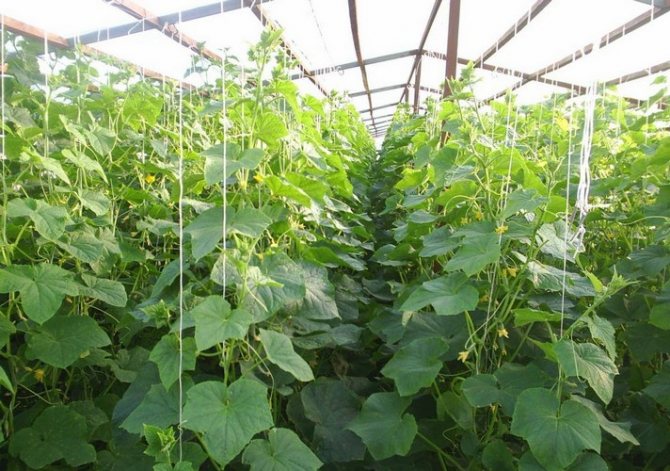
Garter
In order to get a high-quality harvest, it is necessary to provide light access to each leaf of the plant. This can be done by tying cucumber stalks. Plants can be tied up in three ways: vertically, horizontally and with a mixed method. Vertically - the rope is pulled at the top. With the help of a rope or twine, each unit of seedlings is tied to it from the bottom up. Horizontally - place two two-meter supports at different ends of the cucumber row. Several ropes are tied horizontally to them. The disadvantage of this method is that the cucumber, having reached the first rope, winds along it, not trying to grow up. You can read more about how to tie cucumbers in a greenhouse here.
Growing seedlings
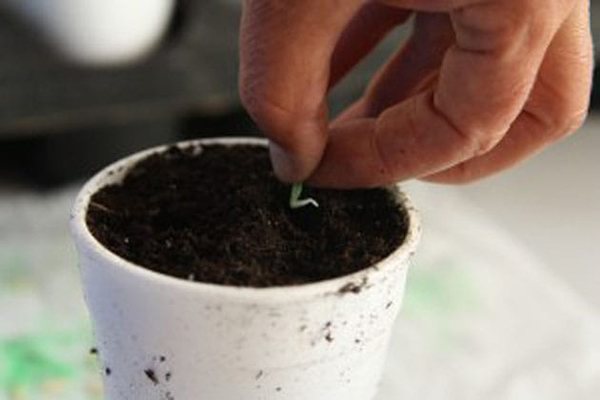


Growing seedlings for the greenhouse and for the soil is almost the same, the difference in activities begins later. Gardeners need to properly process the container and soil substrate, harden and disinfect the seed material, and take care of the sprouts properly.
Preparation of soil and containers
For planting seeds for seedlings, two types of soil are used:
- shop;
- cooked by yourself.
There is less hassle with a one-stop shop product used for all vegetables, but a DIY substrate takes into account all the subtleties of growing cucumbers.
The land from the garden is categorically unsuitable for seedlings: it contains too many impurities and harmful microorganisms, as well as eggs of insect pests. Also, the already used land is not suitable, then it will need to be brought to the desired state. Most often, the secondary soil is disinfected by steaming in the oven at 80 ° C. It is impossible to raise the temperature higher, then useful organic matter will burn out in the soil.


Cucumbers need light soil, so turf, river sand and peat are taken for it. The components must be pre-crushed and sieved. Pathogenic flora and pests are destroyed with a hot solution of potassium permanganate or such a proven folk remedy as saturated garlic infusion.
To prepare it, you need to thoroughly chop the garlic (you can not peel it) and fill it with cold water at the rate of 300 g of garlic per liter of liquid. Insist 12 hours.
The containers must be treated with potassium permanganate before loading the substrate.
If the seeds will be dipped in ready-made peat pots, soil treatment is not necessary. There is another time-tested container for seedlings. This is an eggshell (from under raw eggs). In order to process such a "container", it is enough to quickly rinse the shell with boiling water.
Experienced gardeners recommend using eggs as containers: the grown seedlings are immersed in the beds along with the shell, which is then successfully pierced by the plant roots, and the shell itself is an excellent organic fertilizer.
Preparation of planting material


Purchased seeds are used. Although such bagged material can give annoying failures when growing, homemade seeds increase the risk of such troubles. For greater confidence, the seeds are sorted out, rejecting small and too light ones, with visible damage, discoloration, etc.
Further preparation goes through three stages:
- disinfection;
- soak;
- hardening.
Disinfect the seed with a pink solution of potassium permanganate, half an hour is enough, after which you need to rinse the seeds with warm water. Such processing is also useful in that empty seeds are immediately discarded, they will float.
Seed material is laid out on cotton wool, gauze or other soft natural light fabric and watered (water should be at room temperature, settled - and even better to melt snow from an environmentally friendly area). The seeds should not be immersed in water, but lie on a damp cloth so they can breathe.
The room should be warm, at least 23-25 ° C. If the temperature is higher, the seeds will hatch much earlier, you just need to monitor the moisture. But if the temperature is cool (below 16 ° C), the seed will rot and die.
When a sprout is shown from a seed, the sprouted seeds must be placed in the refrigerator in the section where the temperature will not be lower than -2 ° C, or taken to an unheated room, if there is a guarantee of temperature control. Hardening lasts 2 days, after which the sprouts are immediately planted in a container with soil.
Sowing


It is best to sow cucumber seeds for the greenhouse in such a container so that later you do not have to remove the plant from the soil. Peat cups (pots) or eggshells are ideal.But for this they also use small plastic packaging for food products, and egg containers, and other products.
An important point! It can only be food grade plastic or other non-oxidizing materials - cellulose, glass, ceramics, cardboard tetrapacks, packaging with a layer of food foil inside, and more.
In each container with pre-moistened soil, two seeds should be placed in a small depression, sprinkling with a layer of 3 mm. After that, the dishes with future seedlings are moistened with water at room temperature from a spray bottle.
Seedling care
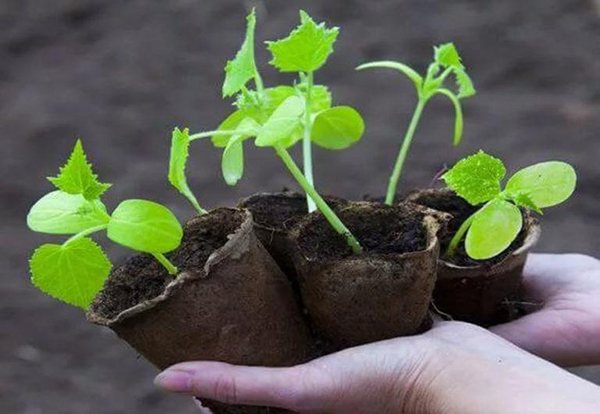


In the ground, the seeds will feel comfortable if the temperature is 25-27 ° C, but when sprouts appear, the temperature regime must be changed so that the temperature fluctuates between 18-20 ° C.
Watering should be moderate: cucumbers do not like waterlogging or overfeeding. But usually ready-made substrates already contain everything necessary for the growth of seedlings, and a small amount of top dressing is added to the substrate prepared with your own hands immediately during preparation.
To prevent the seedlings from growing too much, it is necessary to provide it with sufficient lighting. But in any case, as it grows, it is necessary to fill up the soil substrate. Experts do not recommend diving seedlings in dishes, since young sprouts are unjustifiably injured during such a procedure.
Overexposure of seedlings in pots leads to subsequent adaptation problems after transplanting into a greenhouse, therefore 2-3 weeks is the maturity period for a cucumber sprout. The finished sprout does not exceed 30 cm in length of the central conductor, it has good roots and short internodes, and the presence of 3-4 leaves of a bright dark green color is mandatory.
Seeds and rules for their selection
When choosing a variety of cucumbers, you should give preference to self-pollinating (parthenocarpic) with early ripening. These can be the following varieties:
- Barcelona;
- Cartoon;
- Courage;
- The matrix;
- Bobrik;
- Hercules;
- Shchedrik.
These are all those varieties that are able to pollinate independently, and Shchedryk gives the largest yield. The prefix "F1" may be present on seed packs. This suggests that there are hybrid varieties in the pack. They are slightly more expensive, but more resistant to various diseases and have high yields.
10-12 days before planting, the soil can be fertilized with urea. This will help neutralize possible pests in the ground.
To ensure a continuous greenhouse harvest, it is advisable to plant seedlings several times with a two-week break. This secret rule will help ensure a simply huge harvest throughout the year. Directly before planting, the preparation Bioclad can be added to the prepared wells.
When the first three full-fledged leaves appear, you can design supports in order to form bushes later. Don't forget about lighting. Make sure that the daylight hours in the greenhouse lasts at least twelve hours, and the temperature does not drop below 18 degrees. Regular watering and loosening of the soil are also important.
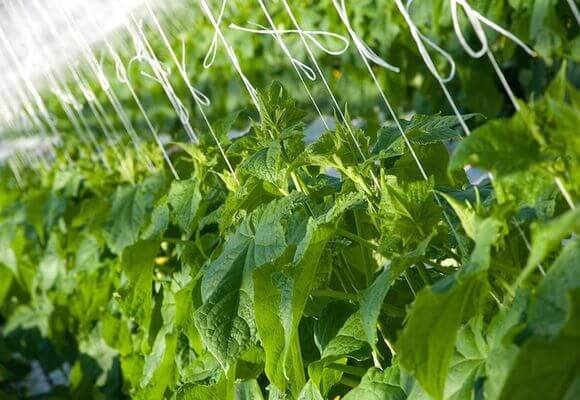


Constant temperature, optimal lighting, watering, top dressing will lead to the fact that in forty-five days the first and already bountiful harvest will appear. If everything was done correctly, then from each bush it will be possible to collect at least twenty kilograms.
Preparing seeds for sowing
More recently, gardeners, before sprouting cucumber seeds, warmed them up. The seeds were laid out next to the heating devices for a long time. This procedure increased the formation of female flowers. The seeds of self-pollinated varieties do not need to be warmed up, they do not form barren flowers.
Now on sale there are seeds treated with thiram, a fungicide that protects against a complex of diseases. The poisonous green color of the seeds indicates their toxicity. Such seed material does not need to be soaked and germinated before planting.
Ordinary seeds, on the contrary, are recommended to be pre-treated with a fungicide or held for 15 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
After processing, they need to be washed and put on germination, which does not affect the amount of the crop, but only allows you to exclude the planting of empty seeds.
The advantages of the seedling method include:
- the result of germination and development of cucumbers occurs faster than when planting seeds directly into the greenhouse;
- plants grow in comfortable conditions (no temperature changes are observed);
- not all seeds develop equally well: some do not germinate at all or freeze in growth. They can be sorted.
To get an early harvest of cucumbers, you need to follow simple rules when growing.
- Seeds must first germinate - the sprouts should not be large so as not to break them when planting.
- It is better to plant each seed in a separate glass, then the root system will form correctly. If we plant seeds in containers, then the distance between them should be at least 5 cm.
- Before planting, pour the hole with a hot solution of potassium permanganate of low concentration. Put a cucumber seed in the hole, sprinkle it with loose soil, layer thickness 2 cm.
- Cover the container with seeds with a transparent bag until shoots appear (1-3 days).
Soil preparation
The first step in planting cucumbers is soil preparation. Vegetable crops love soft, loose soil, which also needs to be fertile.
When growing cucumber seedlings, you can purchase a ready-made substrate in the store. The soil should not only be loose and fertile, but also retain moisture, as cucumbers love to "drink".
There should be a minimum of peat, since the land with its high content dries very quickly in greenhouse conditions.
The optimal composition of the soil substrate for cucumber seedlings is as follows:
- 3 parts of sod land;
- 2 parts of humus;
- 1 part sand.
This mixture must be free of lumps. Before planting, it is recommended to bake it in the oven for 10-20 minutes or freeze it (prepare it in the fall and take it to the balcony for the winter). Such procedures help to destroy disease-causing microbes. Before sowing seeds, it is recommended to add 1 liter of vermiculite (for loosening), a glass of ash, two tablespoons of superphosphate to 10 liters of the mixture.