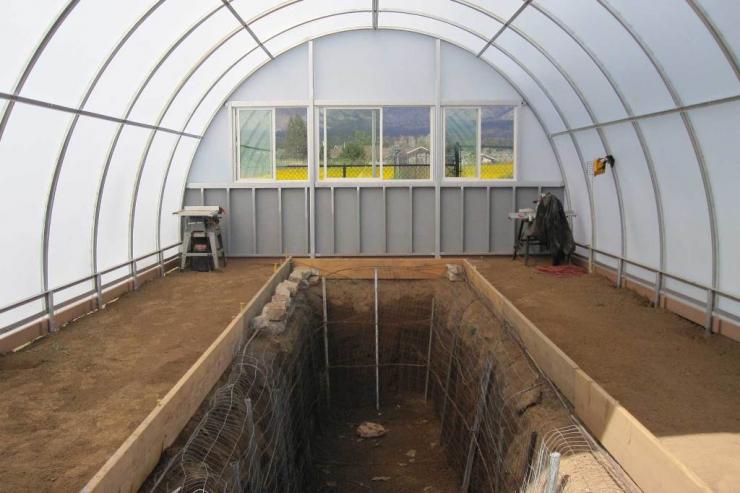
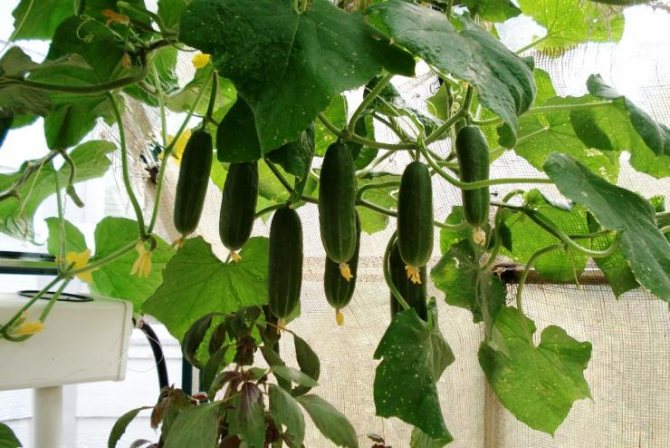
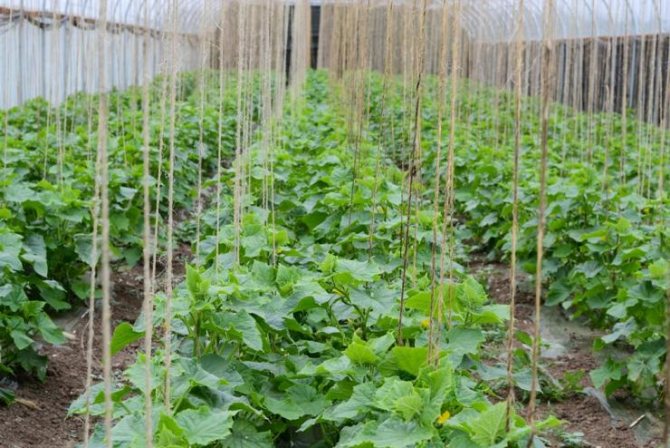
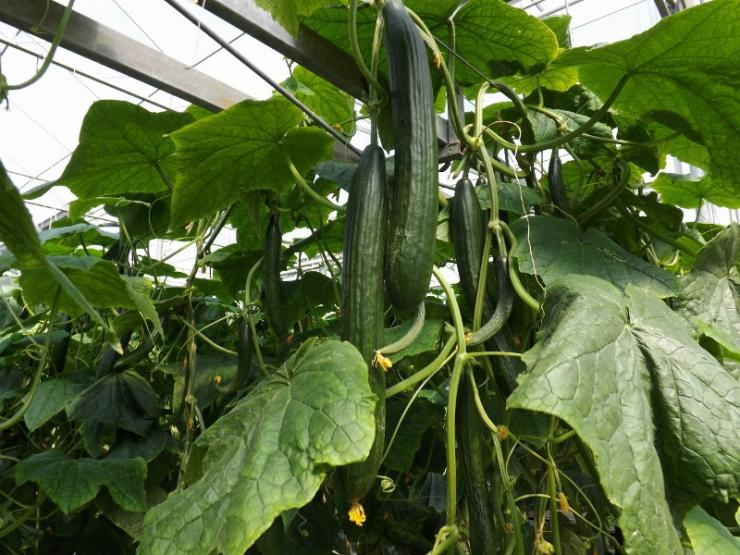
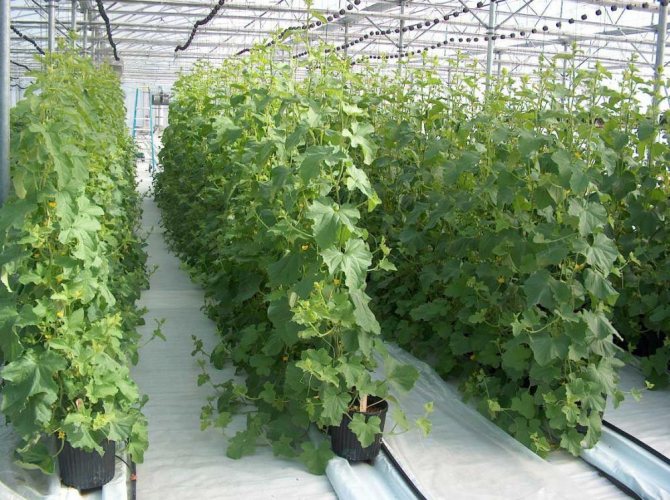
In the climatic conditions of the middle and northern regions of Russia in winter, cucumbers can only be grown in winter greenhouses. Modern greenhouses for the cultivation of vegetables in winter can be bought ready-made and installed at their summer cottage. They differ from other types of shelters by the ability to create the desired microclimate (heating, lighting, air humidity, soil). However, their price is quite high. Some artisan gardeners buy building materials and build greenhouses with their own hands. It is much cheaper, especially if the construction is small. A wooden greenhouse with a polycarbonate coating can last 12 or more years at no additional cost and delight home-made fresh vegetables all year round.
Preparing the greenhouse for winter ↑
Cucumbers are a delicate culture, they cannot stand temperature extremes, lack of lighting and are immediately exposed to soil and vegetative infection with fungal diseases.

Before planting cucumbers, the greenhouse must be disinfected.
To grow a decent harvest of cucumbers, it is necessary to carry out a number of preparatory work in a winter greenhouse:
- clean the greenhouse from debris, weeds and various auxiliary tools and equipment (boxes, boards, covering film, seedling cups, etc.),
- carry out disinfection, which will significantly reduce the possibility of infection of the culture in winter,
- check, repair and adjust heating, lighting and irrigation systems, prepare the soil.
Nuances of different regions
It is impossible to imagine the festive table of a Russian person without numerous cucumber-based dishes. Fresh, pickled, pickled vegetables are used. Therefore, it is not surprising that cucumber is one of the most grown crops throughout Russia, including the Krasnodar Territory. But most of the regions of Russia do not have a high yield of this crop, especially when grown in the open field. Only the Krasnodar Territory, due to climatic conditions, is the main producer of this crop.
Since Krasnodar is the southern region of Russia, there is enough sunlight there for the entire ripening cycle of cucumbers. The only problem is the lack of water, which a cucumber cannot do without. But the problem can be solved. The easiest way is to mulch the soil, which allows you to retain precious moisture.
If we talk about growing cucumbers in greenhouses, then the full provision of plants with light and heat equalizes all Russian regions. You can get excellent yields both in the Krasnodar Territory and in Siberia.
Work with soil ↑
Soil preparation must be completed in such a way as to sow at the end of September and get a crop harvest by the New Year. The next sowing can be done in the second half of January.
If the greenhouse is new, a mixture rich in organic matter is prepared, the soil is disinfected, fertilized and dug up to 25-30 cm.
Replacement and disinfection of soil ↑
If the greenhouse was used, then it is necessary to remove the top layer of soil and replace it with a new one (10-15 cm). The soil mixture can be made up of humus and forest and / or sod land (1: 1).In areas rich in peat bogs, high-moor peat is used as a base and garden soil that has not been treated with herbicides and other pesticides and humus is added, respectively 50:20:30 percent. The mixture is shoveled well and the ridges are filled.


It is advisable to replace the soil in the greenhouse.
The next stage of preparation is soil disinfection. The most acceptable way is to spill the substrate with a 5-7% solution of copper sulfate.
Application of fertilizers and EM preparations ↑
The matured soil is fertilized with mineral fertilizers: kemira, nitrophos or other complete complex fertilizer (40-50 g / sq. M). Dig up to 25-30 cm. The soil for sowing should have +18 .. + 20 ° С. Approximately 7-9 days before sowing seeds / planting cucumber seedlings, a solution of the biological product "Ecomik Urozhainy" or "Baikal EM-1" can be added to the soil at a concentration of 100 ml of the drug per 1.0 liter of water. Effective microorganisms of biological products will enrich the soil with beneficial microflora and destroy the negative. Seeds are sown in the prepared soil at the end of September, or seedlings are planted in the last decade of October.
Care features
In order for seedlings to grow quickly in a greenhouse, the following requirements must be met:
- Apply fertilizer once every 2 weeks.
- Maintain humidity 80-85%. For this, the heating pipes and the floor are watered.
IMPORTANT: You need to ventilate the greenhouse very carefully so that cold air does not get on the plants. Otherwise, the yield will be low.
- Before flowering, they are watered once every 2 weeks, then it costs more and more often. Leaves on cucumbers will signal the state of moisture in the soil. So, if they curl, dry, then you need to water more.
- The temperature should be from 25 degrees during the day to 15 at night.
- Intensive lighting is necessary. There should be a bright light bulb above the seedlings; as it grows, it should be raised higher.
If you follow all the conditions and requirements, you can get a rich harvest of cucumbers all year round.


Cucumber varieties for winter cultivation ↑
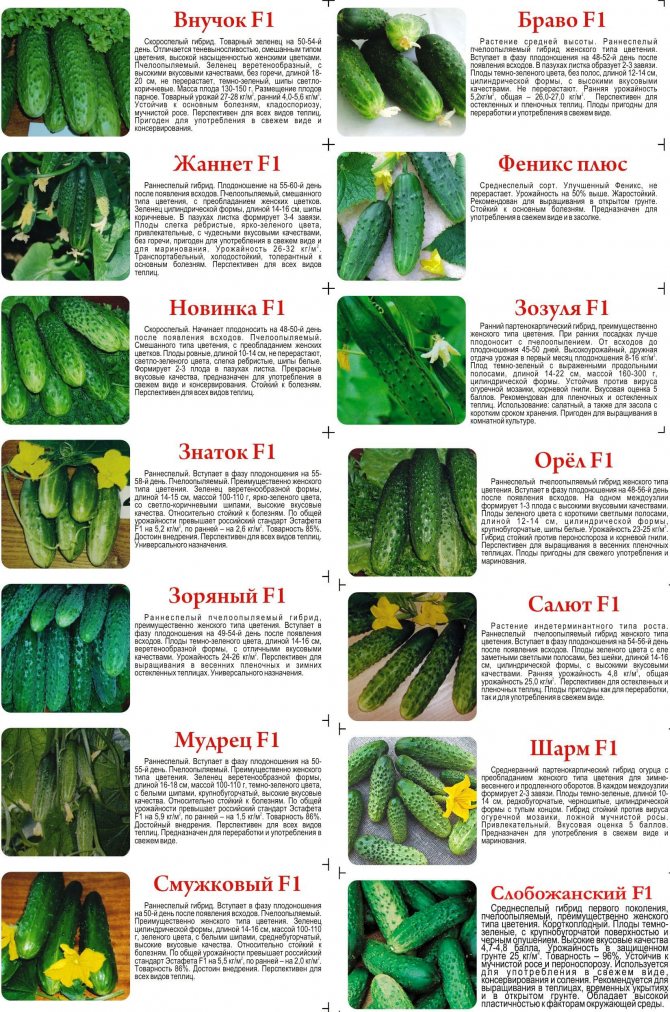
For greenhouse cultivation, it is better to use hybrids. They do not require pollinators and thrive in low light conditions. Such varieties and hybrids of modern selection include "Rossiyskiy", "Domashny", "Moscow Nights F-1", "Iva", "Ladoga F-1", "Marfinsky", "Rykovsky", "Relay", "Northern Lights F-1 "," Olympics F-1 "and others.


The choice of cucumber seeds for growing in winter must be approached carefully.
Seed preparation ↑
Go through the seeds, removing damaged and empty ones. Dip into salt water and separate all floating ones. Wash off salt under running water. Each owner selects a solution for disinfecting seeds independently. For disinfection, it is convenient to use a solution of boric acid or potassium permanganate. Disinfected seeds can be hardened for 5-7 days in the refrigerator, placed in wet gauze, which is periodically moistened, on the lower shelf, or simply dried at room temperature and used for sowing.
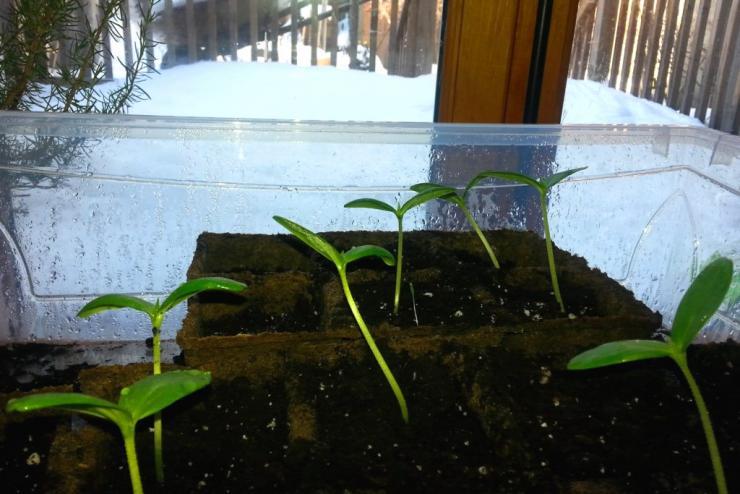
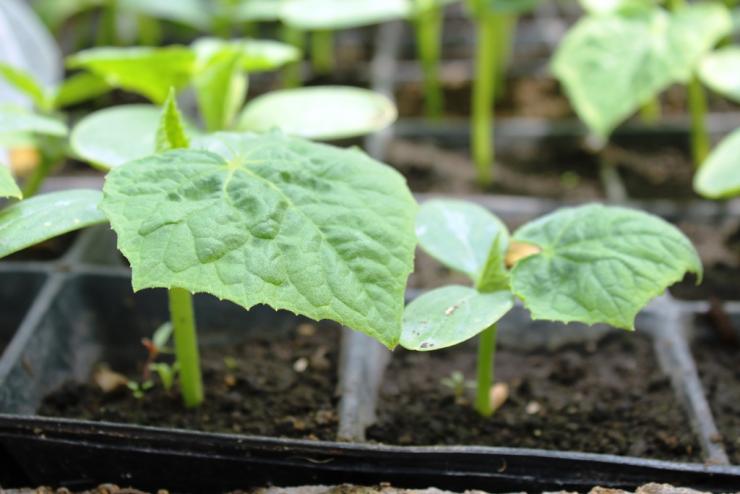
Growing seedlings ↑
The roots of cucumbers are painful to transfer. Therefore, the seeds are usually sown in peat pots or special tablets and the seedlings are already planted in the ground, without violating the integrity of the soil coma on the roots. If the seedlings are transferred from pots and other containers when planting permanently, then the root collar is left above the ground. This will reduce the possibility of plant rot infestation. Seedling care is normal. 25-30 day old plants with 3-4 leaves are planted in the ground.


In winter, it is imperative to supplement the seedlings of cucumbers.
Agrotechnics of cucumbers in a winter greenhouse ↑
Sowing by seeds and planting seedlings ↑
Density of sowing seeds / planting seedlings directly depends on the variety (hybrid) and averages 2-4 bushes per sq. m of area so that during the formation there is enough space for growth and optimal lighting.When planting in a row, a distance of 40-45 cm is left between the bushes. Immediately after planting, wire trellises are installed, to which twine or a special net is tied.
Temperature conditions ↑
During the entire period of cucumber development, the soil temperature is maintained at + 15-18 ° C. A decrease in temperature increases the infection of plant roots with fungal rot. Daytime air temperatures for optimal development are +23 .. + 25 ° С, night temperatures can drop to +18 .. + 20 ° С.
Watering and air humidity ↑
Cucumbers are moisture-loving crops, so they need regular and sufficient watering. Changes in the moisture state of the soil are unacceptable.
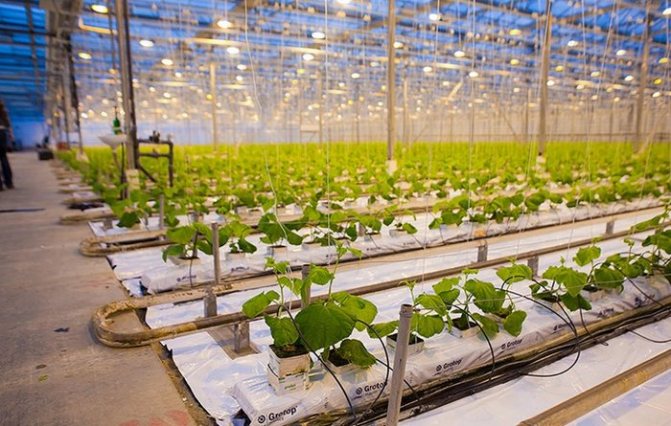


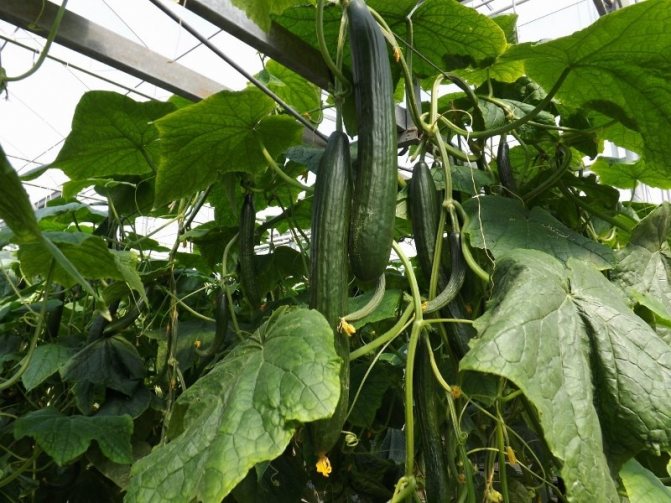
Cucumbers in an industrial greenhouse in winter
From the period of germination or planting of seedlings to flowering, watering is maintained moderate so that a large leaf surface does not form. Watering is carried out in 4-5 days. From the phase of mass flowering, the water rate is increased, watering is carried out 2-3 times a week. In the phase of active fruiting, the water rate is brought to 10 liters per sq. m area. It is watered with heated, settled water, at a temperature close to the temperature of the soil (+18 .. + 20 ° С). It is usually watered along the grooves of the rows so that the soil around the bush is dry. This significantly reduces rotting of the crop root system.
The wilting of leaves is a signal for increased aridity of the air. In this case, urgent watering by sprinkling or additional spraying of plants with a fine sprayer is necessary. If the roots of the plants are exposed from watering, it is necessary to huddle or add a sand-soil mixture. Watering is preferable in the morning and / or evening, so as not to burn the plants during the high solstice. At a greenhouse temperature of +25 ° C, draft-free ventilation is required.
Top dressing ↑
The first top dressing when sowing with seeds is carried out in the phase of three leaves with full fertilization. When disembarking - seedlings in 2-3-4 days. It is best to feed with fertilizer solutions (kemira, crystallon, urea, nitrophoska), the concentration of which does not exceed 1-1.5%.


Complex fertilizer for cucumbers
The second feeding in the phase of mass budding is carried out with nitrophosphate. The concentration of the nutrient solution is 5-10 g / 10 l of water.
The third feeding is performed at the beginning of fruiting. During this period, cucumbers need magnesium, potassium, phosphorus. The solution is prepared with the following composition: 1 glass of ash is infused for 2 days in 3-4 liters of warm water. Filtered. Potassium nitrate, water-soluble superphosphate are added in one teaspoon, the solution is brought to 10 liters and watered along the furrows. The same composition can be used for foliar feeding, just add trace elements to the solution. During the fruiting period, fertilizing is carried out with a gap of 10-12 days with a phosphorus-potassium composition or filtered ash infusion. You can use nitrophoska solution for feeding - 1.5 table. spoons in a bucket of water. Cucumbers respond well to feeding with special mixtures containing microelements - "Fertility", "Breadwinner" and others.


Cucumbers can be grown in winter
Hydroponics - an alternative to soil
Method 1 is more familiar to a wide range of gardeners. But in this case, this is not the best choice. If you paid attention, large agricultural holdings rarely use soil mixtures for growing vegetables. This is really a risk factor for greenhouse crops, since any soil contains spores of all possible fungal diseases, which develop instantly in greenhouse conditions of high humidity.
Hydroponics is causing massive denial among fans of “natural food”. Even all the methods of chemical analysis of vegetables grown by this method will not convince persistent “naturalists”.
Vitamin C in “underground” cucumbers grown in artificial lighting and hydroponics ... is several times higher than in ordinary, soil from the garden.Their sugar content is also higher than that of terrestrial ones ...
By the way, they grow faster. Most likely, this is due to the constancy of the ambient temperature and the absence of natural pests.
The simplest hydroponic system is easy to set up on your own. The roots of plants will “live” in containers filled with a fraction of gravel up to 30 mm in size from granite or quartz with a layer of 200-250 mm.
The solution is fed using a simple system of tubes by gravity from the tank, where the nutrient mixture is gradually added. The essential components of this solution are N, P, K, Ca and Mg (the ratio of the components varies somewhat with the age of the plant). In small doses, the composition also contains trace elements - Mn, B, Zn and Cu.