Cucumbers are one of the most popular crops to grow. In greenhouse conditions, they feel great. The fruiting period of cucumbers in greenhouse cultivation is two months longer than that of those growing in open ground.
And the very amount of fruits harvested is about 25% more. And, nevertheless, even in greenhouse conditions, growing cucumbers can present a number of unpleasant surprises. One of the main concerns for any gardener is the yellowing and further falling off of the cucumber ovaries in the greenhouse.
Description

Fig. 1 - Cucumber ovary
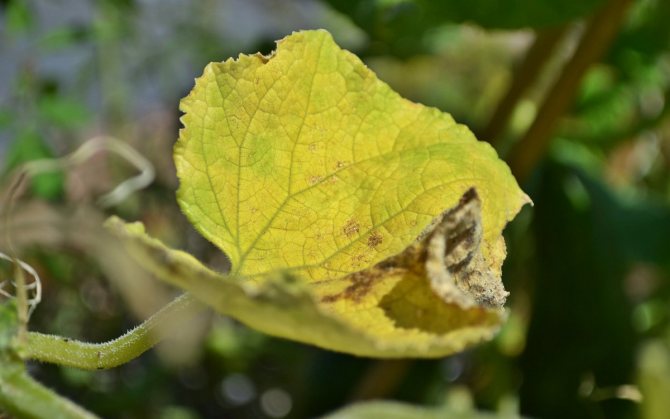
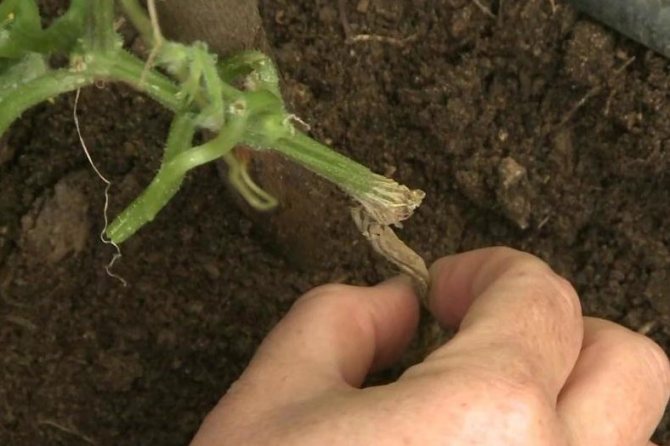
The withering away of the ovaries is actually a natural process. Moreover, each variety has a certain percentage of ovaries that can die. It can be from 5% in especially large varieties to 20% in bunch varieties.
However, if such a process becomes massive, or when yellowing and subsequent wilting occur in a large number of ovaries at the same time, this is a serious reason for the gardener to think about the reasons for this phenomenon. And not just think, but take adequate measures, since in some cases such symptoms can have serious consequences.
Fig. 2 - Withering cucumber ovary
Let us consider in more detail the main causes of yellowing of the ovaries and possible methods of dealing with this negative phenomenon.
Containment breach
Little light
The thermophilicity and photophilousness of cucumbers are well known. These plants react very negatively to lack of light. Therefore, if it is planned to grow cucumbers in a greenhouse, then even at the design and construction stages the greenhouse should be located in such a way that the required part of the time (at least 12 hours a day) the cucumbers are well lit.
In addition, often poor lighting is associated not only with the location of the greenhouses, but also with a large amount of greenery in the greenhouse itself. The reason for this can be either the crowded planting and the excessive growth rate of the vegetative parts of the plant, or simply the use of too spreading plant varieties.
Fig. 3 - Greenhouse with too much shading
That is why it is necessary to correctly select both the amount of planting material in the greenhouse and the issues of varietal and hybrid compatibility of theses or other varieties of cucumbers. For example, bee-pollinated hybrids traditionally have a small amount of foliage and can be planted at a density of up to 3 plants per square meter. m. Artificially pollinated or self-pollinated cucumbers can be planted at the rate of 2-3 plants per 1 sq. m. m.
But cucumbers, which do not need pollination at all (parthenocarpic), have the most branched vegetative system and the largest leaves and should be planted with a much lower frequency - from 1 to 1.2 sq. m.
Wrong temperature
Most plants feel comfortable in a certain temperature range. It is undesirable to go beyond its limits, since the conditions of its maintenance will not simply worsen in the plant, but irreversible processes may begin, leading to its death. But that's not all: plants have not only norms for the temperature range, but also maximum daily temperature fluctuations.
Cucumbers in this regard are no exception. They feel comfortable in the range from + 18 ° С to + 35 ° С. The temperature drop during the day should not exceed 6 ° C.
Violation of temperature conditions adversely affects the plants, which leads to the death of the ovaries. Correct maintenance of the temperature inside the greenhouse is a rather difficult task and requires from the gardener either constant temperature control or the use of any thermal control systems. Naturally, the use of temperature control systems in greenhouses is a task that seems to many to be either too expensive or does not make sense at all.
Fig. 4 - The temperature in the greenhouse when growing cucumbers should not exceed + 35 ° С
And, nevertheless, for the time of fruit setting, at least for a few days, the temperatures should be maintained within acceptable values and not allow large drops.
The implementation of these actions depends on each situation separately and only general recommendations can be given here. In extremely cold climates, you should use different heaters with temperature controllers or heat guns.
If the summer is too hot, it is necessary to regularly ventilate the greenhouse. In some cases, it is advisable to partially disassemble its structure. For example, remove the roof or one of the walls.
Incorrect humidity
The confined space of the greenhouse, as well as irregular ventilation can lead to a significant increase in air humidity. By itself, it does not pose a serious danger until condensation appears directly on the leaves, stems and fruits of cucumbers.
Water droplets that appear on certain parts of the plant can not only cause sunburn, but also provoke the appearance of various diseases in cucumbers, primarily fungal.
For the ovaries, this is doubly destructive: firstly, the flower itself or the ovary can be damaged, and, secondly, a disturbance in the health of the plant can lead to the complete death of already formed ovaries.
Fig. 5 - Condensation in the greenhouse at high humidity
Cucumbers require relatively high air humidity (above 75%)however, it is not worthwhile to exceed its value and bring the air to a very obvious condensation of water vapor.
Ventilate the greenhouse regularly and remove condensation on the ceiling and walls.
Poor pollination


Lashes may turn yellow without insect access
They try to plant self-pollinating varieties in greenhouses, but they also need pollination. Without this, there will be no bountiful harvest. It is necessary to find out if the ovary is not sufficiently pollinated, then from this it may turn yellow. This happens mainly without aerating the greenhouse, and when there is no access for insects to the greenhouse.
Spraying the bushes with a solution of boric acid or special preparations for the ovary will help to correct the situation.
To attract bees, plants are sprayed with sweet water (with sugar or honey) or boron - magnesium fertilizers, which increase the secretion of nectar on the flowers. Can be planted in a greenhouse borago and hyssop. Insects love these honey plants and make their way inside, pollinating the seedlings. Having picked a male flower, you can pollinate several female buds with it yourself.
Care problems
Irregular watering
The intensity of watering for cucumbers depends on the stage at which the plant is. During fruit setting or fruiting, watering should be increased. Lack, or vice versa, an excess of moisture, can disrupt the processes in the formation of fruits and lead to yellowing and dropping of the ovaries.
In order for the plant to feel normal, watering should be carried out regularly, with a frequency determined by the properties of the soil, temperature, degree of illumination of the greenhouse, and so on.... There is a very simple criterion for the need for watering - excessive dryness of the topsoil.
Fig. 6 - When the plant lacks moisture
After observing cucumber seedlings or adult plants for several days, it is easy to understand how to adjust the watering schedule. It is necessary to do this and continue to constantly monitor that the soil is constantly moistened.
Too intensive watering is also not worth it, since excess moisture leads to decay of the roots and an increase in air humidity in the greenhouse. All these factors together also lead to yellowing and shedding of the ovaries.
Problems with feeding
Yellowing of the ovaries is also possible due to a disturbance in the supply of the plant with the necessary fertilizers and trace elements. Such violations include both deficiencies in the "diet" of a plant of certain substances, and their incorrect ratio.
Fig. 7 - Foliar feeding of young cucumbers
So, for example, a lack of nitrogen leads to the fact that the plant loses its pigmentation, becomes first white and then yellow, leaves and fruits begin to curl. Excessive excess of nitrogen can generally lead to the absence of flowers, and to the appearance of ovaries. Parthenocarpic cucumber varieties have the greatest vulnerability to incorrectly selected dressings.
In order to avoid the death of ovaries from a lack of fertilizers, you should use the following feeding scheme:
- First feeding - is carried out when planting a plant in the ground. It uses urea at a concentration of 20 g per 10 liters of water. You can use mullein in a 1 to 20 ratio.
- Second feeding - produced 2 weeks after the first. The same urea is used in the same doses. Sometimes niroammofoska is added instead of it at a concentration of 15 g per 10 liters.
- Third feeding carried out during flowering. At this stage, the plant needs any potassium fertilizer. In this case, it is advisable to use foliar feeding, a solution of 5 g of potassium fertilizer in 2 liters of water.
- Fourth feeding is performed after the appearance of the fruit. It is also foliar for this 15 g of nitroammofoska is dissolved in 10 liters of water.
- Tried feeding produced one week after the fourth. It is done at the root and consists of potash fertilizers; 5 g of potassium in any form is dissolved in 10 liters of water.
Improper pollination
The plant should create conditions for pollination. Successful pollination is a guarantee of the health and safety of the ovaries. Depending on the type of pollinator and the method of pollination, appropriate action should be taken.
If the plant is pollinated by insects, the greenhouse should be kept open throughout daylight hours so that bees, wasps and other insects have unhindered access to the flowers of the plant. Sometimes, to lure pollinating insects, it is recommended to install a saucer of sugar syrup at the entrance to the greenhouse.
Fig. 8 - Artificial pollination of cucumbers
Its composition is as follows: sugar is mixed with water in a ratio of 1 to 2 and 1/20 of the yeast is added to the resulting syrup. Then the mixture is brought to a boil and cooled. Sometimes to give it a cucumber smell, male cucumber flowers are immersed in it.
It is necessary, even at the stage of planting, to make sure that there are plants in the greenhouse with both male and female flowers.
You can also pollinate the plants by hand. In this case, either a freshly plucked male flower or a brush is used, with the help of which pollen from male flowers is transferred to female ones.
For self-pollinated plants, you just need to regularly ventilate the greenhouse room.
Other violations of agricultural technology
No less widespread errors in the cultivation of cucumbers associated with incorrect soil cultivation, or with incorrect alternation of predecessor and follower plants.All of them lead to the fact that the plant nutrition will be insufficient. This will cause a lack of nutrients, which in turn will lead to the death of the ovaries.
It is necessary to understand that a greenhouse is the same vegetable garden, only protected from the weather. And all the rules applicable to the vegetable garden should be applied to the greenhouse as well. One of these rules is maintaining the correct crop rotation. One of the most common reasons for a plant to lose its ovaries is the cultivation of cucumbers in the same place for several years.
Fig. 9 - Too dry soil, partially crusty. Loosening is necessary
Detailed practice not only depletes the soil, but also leads to the accumulation of pathogens and pests, "specializing" exclusively in cucumbers. On the other hand, greenhouses are specially created to grow some of the same crops from year to year.
The way out of this situation can be the use of siderates. For example, plant some legumes or winter wheat after cucumbers.
Another frequent violation of the rules of agricultural technology is the use of deliberately poor soils, without any fertilizers whatsoever. Or, the use of exclusively mineral fertilizers to increase the fertility of a particular site.
You should not rely on mineral fertilizers alone. At least once a year (usually at the beginning of the season), fertilize the soil in the greenhouse with humus or compost. Mullein or chicken manure solutions can be used. As a last resort, use regular wood ash. Moreover, excellent results are obtained by a combination of this and the previous method: the use of organic fertilizers and green manure.
Another common cause of wilting and yellowing of the ovaries is overgrown fruits. You should not grow giant cucumbers in a greenhouse, more than the sizes indicated in the description of the variety. The grown fruits, when they are already fully formed, very much inhibit the growth and the appearance of new ovaries. Therefore, ripe fruits should be harvested as soon as they reach the required size.
Well do not forget about the elementary rules of plant care - the obligatory loosening of the soil after watering and weeding. After all, even in greenhouses unwanted guests can start.
What to do if cucumber ovaries turn yellow, dry up and fall off
Digging in
It is used if the plant is affected by rot. Since the roots are damaged, the ovaries of cucumbers turn yellow, wither, and then fall off. The lower part of the bushes should be lowered to the soil and sprinkled with earth. New roots will be formed on the stem, which will be able to fully nourish the plant.
Steying
If there are too many shoots on the plant, they should be removed. It is necessary to remove all the lower shoots up to 5 leaves. After that, the plant almost immediately throws out powerful lateral shoots, on which many female flowers are formed.
If the lashes quickly stretch upwards, they should be pinched (remove the tip of the shoot up to 10 cm in size).


Drying the soil
If the soil is excessively moist, the cucumbers will bloom, but the ovaries will not be able to form. To solve this problem, you should stop watering for a few days. After the leaves begin to wither, many female flowers form, and the barren flowers on the cucumbers will fall off on their own.
Pollination
The types of cucumbers can be divided according to the type of pollination:
- Pollinated by insects.
- Self-pollinated hybrid plants.
- Varieties that do not require pollination (parthenocarpic).
When grown in closed greenhouses or balconies of bee-pollinated varieties, the flowers will need to be processed manually. This can be done with a soft brush, with which you need to transfer pollen from male flowers to female ones.
To attract bees to the planting site, you can spray with a sugar solution or honey water.


Fertilizer
If the ovaries turn yellow and begin to dry, a lack of nutrition may be a possible cause. In this case, an urgent need to fertilize with complex fertilizers.
The following drugs are suitable:
- Diammofosk.
- Ammofoska.
- Potassium sulfate.
If the concentration of the solutions used is too high, plants can get severe chemical burns, so you must adhere to the dosages indicated in the instructions.
It is recommended to spray the plantings in the evening, after sunset. Otherwise, water droplets remaining on the leaves and stems can cause sunburn.


Excessive tightness
Many plants
One of the most unpleasant reasons, since it is not always obvious, and in addition, its elimination brings the owner many unpleasant moments. After all, not everyone wants to get rid of beautiful, self-grown, giant pets.
An overly dense planting of cucumbers, especially in several rows, is dangerous, first of all, by a violation of the lighting and airing regime. And this, like a chain reaction, leads to the following unpleasant consequences: poor nutrition, poor pollination and excessive waterlogging. This is followed by a weakening of immunity and an attack by a causative agent of the disease or some kind of bug.
Fig. 10 - Too close planting of cucumbers in the beds
Correct planting of plants even at the stage of planting them in a greenhouse will help to avoid this. Recommended areas have been listed earlier. Excess seedlings can be "held back" for some time, so that with the arrival of warmer weather, they can be planted in open ground. So that it does not grow very quickly, it is either placed in colder conditions, or watering is reduced to a minimum.
Naturally, when the awareness of too close planting comes at the stage of ovary formation, almost nothing can be done, except how to remove excess plants. And no matter how sorry it is, you have to sacrifice the less strong and tall to get a good harvest.
Many ovaries
Most of the modern varieties and hybrids of cucumbers were created for higher yields. Therefore, they all have one good, but at the same time a bad feature - ovaries are formed in almost all leaf axils.
The plant is forced to expend its energy to support all of them. Naturally, this situation does not suit the gardener, since the plant simply does not have enough strength to form so many fruits.
Fig. 11 - Excessive number of ovaries on the bush
The solution to the problem is quite trivial - all extra ovaries that have formed either in inconvenient places, or where they should not have been at all, should be removed... Usually, this is done before the formation of the ovaries themselves, at the time when the flowers appear.
How to prevent yellowing of ovaries
Cucumbers do not require special growing conditions, but before planting, the following recommendations should be observed, which will subsequently prevent yellowing and falling of the ovaries:
- The choice of the variety. Self-pollinating and parthenocarpic varieties are best suited for balconies or closed greenhouses. In the open field, you can plant cucumbers, which are pollinated by insects.
- Choosing a place. The area set aside for cucumbers should be well lit during the day and protected from drafts.
- Selection and preparation of seed. Warming up and hardening the seeds can promote the formation of more female flowers on the plant. Planting will be protected from diseases and pests by preliminary soaking of seeds in a solution of potassium permanganate.


Planting norms should be observed - excessive planting density will lead to the occurrence of fungal diseases.
Yellow ovaries in greenhouse cucumbers are a common problem that can be caused by various phenomena.In any case, all possible options must be taken into account, including non-compliance with the conditions for growing a crop.
Biological factor
Diseases
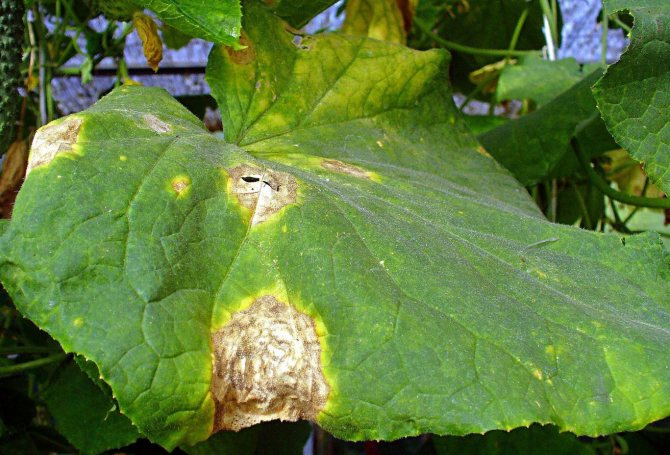
The ovaries can turn yellow and fall off if the plant is sick with some kind of disease. Usually, if not only the ovaries, but also the leaves turn yellow and fall off, the cause of this is bacteriosis.
Bacteriosis is one of the most common diseases in cucumbers, which significantly reduces the yield. The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- first, small specks or droplets of liquid appear on the leaves;
- over time, they turn black and dry, while the tissue around the lesion begins to dry out;
- after 2-3 days, the lesion spreads to the entire leaf, it turns yellow, shrivels and falls off.
Fig. 12 - Bacteriosis. The most common disease
The fight against bacteriosis consists of two stages: removal of damaged plant parts and preventive treatment of the remaining, unaffected parts. After removing the affected leaves, ovaries and flowers, the cut sites must be treated with a 0.2% solution of potassium permanganate.
The rest of the plant and its neighbors should be sprayed with a mixture of the following composition:
- Bordeaux mixture - 100 g;
- copper chloride oxide - 40 g.
- water - 10 liters.
Another, no less dangerous disease of cucumbers, leading to yellowing of the ovaries, is powdery mildew.... This fungal disease in all plants has the same symptomatology, which consists in the appearance of small "cobwebs" distributed over some part of the plant. Over time, the cobwebs turn black, and ulcers appear in their place.
Fig. 13 - Powdery mildew on cucumber leaves
Usually, when affected by powdery mildew, like any fungal disease, the plant stops flowering and fruiting. If the disease is in an early phase, or it cannot completely overcome the protective barriers of the plant, then the effect of the disease will be, although not so harmful, but still unpleasant. The fruits will become significantly smaller, they will become more faded and curled.
Powdery mildew control is carried out using almost any fungicide with the obligatory removal of the affected plant parts.
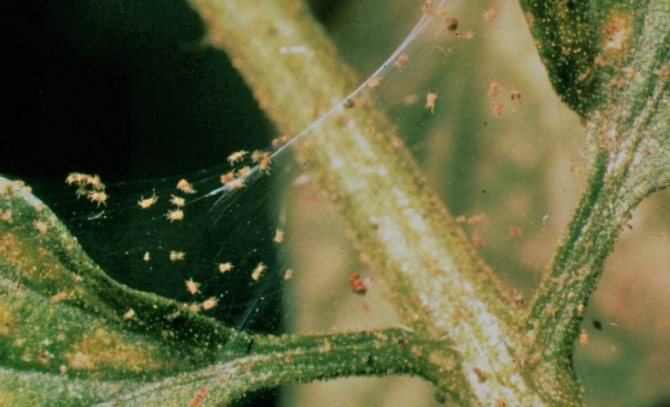
Pests
The pest can also affect the formation of ovaries. This is not surprising, because, feeding on plant juices, they disrupt his nutrition and natural metabolic processes. At the same time, as in the case of diseases, not only yellowing or wilting of the ovaries is possible, but also a complete cessation of fruiting.
Fig. 14 - Typical pests on seedlings - thrips or aphids
Most often cucumbers are attacked by aphids.... Usually, aphids appear on cucumbers at the end of June. These are small insects, up to 1.5 mm long, usually green or yellow. Usually, they appear together with ants, with which they live in symbiosis.
Despite its small size, due to its abundance, aphids are capable of destroying any plant in the shortest possible time. Therefore, you should not postpone the destruction of these pests on the back burner. The best means against aphids are acaricidal insecticides. As a folk remedy, you can use a solution of soap and copper sulfate in water (10-30 g of copper sulfate are dissolved in 1 liter of water and 20 g of liquid soap is added). This mixture is applied directly to areas of the plant affected by aphids.
Another common pest in cucumbers is the spider mite. Its activities also have a significant impact on fruiting. The mite is a small beetle about 1 mm in size, red or yellow.
Fig. 15 - Spider mite
Acaricides should also be used against this pest (for example, Mayt, Ortus and others).
Lack of light
Cucumbers are light-loving plants, so first of all, pay attention to the following factors:
- Obstacles in the path of sunlight due to the density of the planted plants. Thickening leads to a lack of lighting and nutritional deficiencies.
- Lack of stem formation. In a greenhouse, it is recommended to pinch all side shoots and form cucumbers into 1 stem. Plant the bushes at a distance of 1 m from each other. For open ground, the optimal distance is about 45 cm.