Organic and inorganic substances containing nitrogen are nitrogen fertilizers. They are added to the soil to increase yields. Nitrogen is very useful for plants, it is the main element of their life. This substance saturates plants with nutritious and useful components, affects the metabolism and growth of crops. Nitrogen fertilizers are able to stabilize the phytosanitary state of the soil. But misuse, overuse, can backfire.

Why do plants need nitrogen?


Nitrogen is one of the macronutrients, the importance of which for plant development is fundamental.
Any nitrogen-containing fertilizer meets the needs of the plant during the period of crop growth. Thanks to him:
- chlorophyll is formed - a protein involved in photosynthesis;
- there is a proper compaction of the root system;
- greens have a healthy glossy appearance;
- branched system and healthy ovary;
- plant growth accelerates;
- the quantitative and qualitative growth of the yield increases.
Natural resources alone are not enough to obtain a good harvest. Every gardener dreams of home-grown vegetables and fruits to grow quickly, be beautiful and healthy.
What is nitrogen
Nitrogen is an element of the periodic table with the designation (N) at number 7. It is a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas, belongs to the four most important elements (the other three are oxygen, carbon and hydrogen), without which the existence of micro and macroorganisms is impossible.
Protein compounds, which make up the basis of all living things, contain nitrogen. It is present in the nucleic acid, which is the basis of any cell. Nucleic acid is involved in protein synthesis and DNA formation.
The bulk in a free state is in the air (78.09%), in the soil nitrogen is present in the form of compounds (the total content is 0.01%). The saturation of the soil varies depending on the soil and climatic zones. Chernozems are provided with them to the maximum, the minimum amount is present in sandy soils.


A large part of nitrogen (up to 5%) is contained in humus, which feeds plants with all the necessary substances for their normal growth. Considering that the decomposition of nitrogen-containing compounds is very slow in it, plants can receive only up to 1% nitrogen from the soil.
Main sources of nitrogenin the soil:
- organic - nitrate compounds in the soil, dead organic residues, waste of living organisms in the form of manure. Available only after mineralization with microorganisms;
- atmospheric - enters the soil with precipitation in insignificant quantities. It can be used only after many years of accumulation in the soil (in virgin or non-arable lands).
Nitrogen is a part of chlorophyll, with the help of which solar energy is absorbed, which is necessary for plant growth.
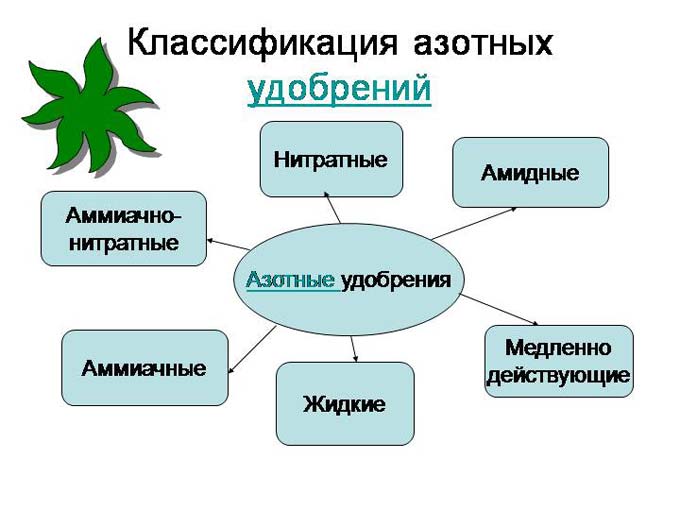
Varieties of fertilizers containing nitrogen


Fertilizers are called nitrogen fertilizers if they contain nitrogen as the main component.
Fertilizers are classified according to two main characteristics.
By state of aggregation:
- solid - in the form of granules, used, as a rule, in the spring-summer period due to rapid leaching from the soil;
- liquid - in the form of solutions, easily absorbed by plants and evenly distributed in the soil.
Ammonia and ammonia-nitrate substances
This group includes the following subspecies:
- ammonium sulfate;
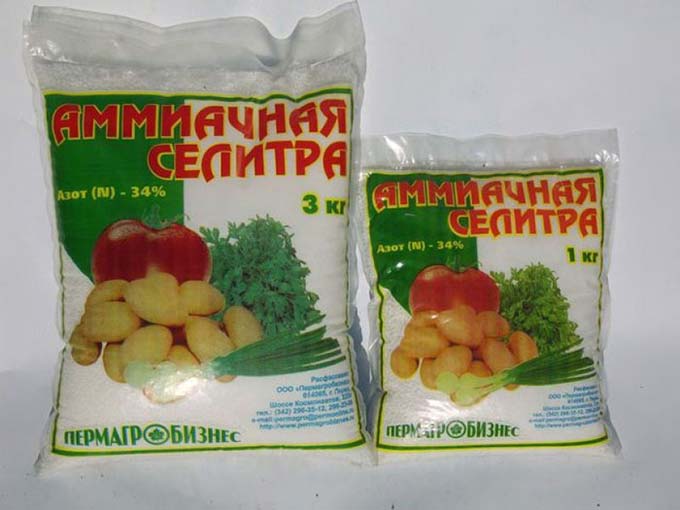
- ammonium nitrate;
- ammonium sulfonitrate;
- ammonium with added chlorine.
All of these substances have a different percentage of nitrogen, and in addition, they also contain other trace elements, so before feeding, you need to make sure that this is the best option for the plant.
Separately, it should be said about ammonium chloride - along with nitrogen, chlorine also enters the soil, which has a very negative effect on the development of plants. Therefore, this kind of substance can be used only in late autumn - harmful components will go deeper into the soil, and there will be no harm to plants.


With the introduction of nitrogen fertilizers, the yield of almost all crops increases
The amount of nitrogen in various types of fertilizers
Mineral
Industrial nitrogen fertilizers are conventionally divided into simple and complex.
The former contains one basic chemical element and several others in small quantities. As part of complex up to 3 basic elements and several additional in small quantities.
Each type of nitrogen-containing fertilizer differs in the proportion of nitrogen contained in the total mass.
Simple mineral fertilizers:
Ammonia:
- liquid ammonia - 82.3%;
- aqueous ammonia - 17-21%;
- ammonium sulfate - 20.5%;
- ammonium chloride - 24-25%;
Nitrate:
- sodium nitrate - 16.4%;
- calcium nitrate - 13.5-15.5%;


Complex:
Ammonia-nitrate:
- ammonium nitrate - 34-35%;
- lime-ammonium nitrate - 20.5%;
- ammoniaates based on ammonium nitrate - 34.4 -41%;
- ammonia based on calcium nitrate - 30.5-31.6%;
- ammonium sulfonitrate - 25.5-26.5%.
The rate of absorption of fertilizers by the soil does not depend on the concentration of nitrogen.
Phosphoric


Phosphorus fertilizers containing nitrogen are called nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizers. These are complex two- or three-component fertilizers based on nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium.
Application
Now you have figured out which fertilizers are nitrogen fertilizers, and we can talk a little more about how to use them in your summer cottage. Do not forget that the time and amount of complementary foods directly depends on the type of soil and the lack of nitrogen in it. It should be borne in mind that when using a large amount of nitrogen-containing fertilizer, flowering occurs much later, and fruiting may not occur at all. What plants need to be fed with nitrogen? Absolutely everything except alfalfa and clover. However, each crop has its own requirements for feeding, and this must be taken into account.
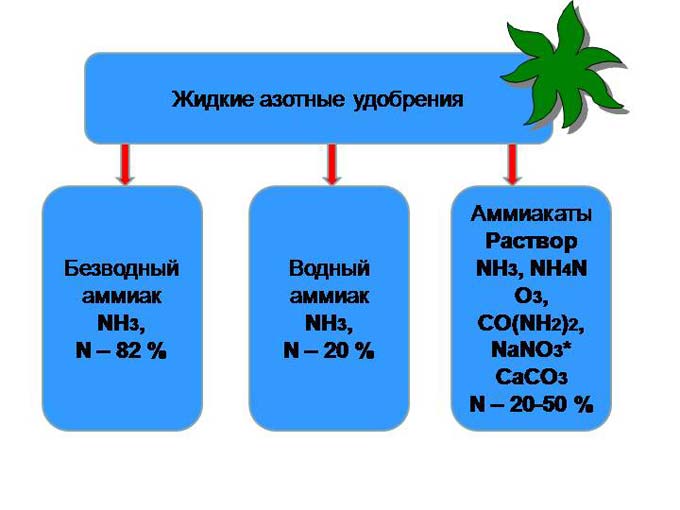
Liquid types of nitrogenous fertilizers
There are currently three main types of nitrogen fertilizers in use:
- Liquid ammonia - refers to anhydrous compounds (NH₃), the maximum nitrogen content (82.3%). It is produced in the form of gas under a pressure of 18-20 atm, stored and transported in tanks with a capacity of up to 50 m³. It is applied by special machines in autumn and spring. A prerequisite is moistened soil, application depth - 12-15 cm, consumption - 0.6 - 1 centner per 1 hectare of land.
- Ammonia water - aqueous ammonia, the most budgetary of the three types. It is obtained by dissolving coke-chemical or synthetic ammonia in water. May contain 21% nitrogen (1st grade) or 17% (2nd grade). It has a pungent odor, the fertilization process requires compliance with safety precautions (the presence of a special suit, rubber gloves, a gas mask, and goggles). It is applied in spring and autumn, and is not inferior in efficiency to dry species. Stored and transported in sealed tanks up to 50 m³. Consumption - 2-3 centners per 1 hectare. Safer to use than anhydrous ammonia, but loses out in lower nitrogen content.
- Urea-ammonium nitrate is a liquid solution of urea and ammonium nitrate. Nitrogen content - 28-32%, can be used as the main fertilizer and foliar feeding. Stored in pressurized hermetically sealed tanks.
Dissolution of ammonia occurs much faster in moist soil, as a result, much lower evaporation of nitrogen and its loss.
Features of the introduction of liquid dressings into the soil


Liquid nitrogen fertilizers have pros and cons.
Benefits:
- low cost, do not require costs for granulation and evaporation;
- the minimum period of assimilation by plant crops;
- uniformity of distribution over the volume of the soil;
- the process of transportation and application to the soil is fully mechanized;
- long period of maintenance in the soil.
Chemical Precautions
Working with fertilizers of any class can turn into a tragedy not only for plants, but also for the gardener. Therefore, it is worth listening to the advice of chemists.
Safety is observed from the moment of purchase. Namely, carefully inspect the fertilizer bag / package to see any tears or other damage to the container.
The means always indicate the degree of danger during transportation, use. But it is better to take care of yourself and engage in the cultivation of chemicals in special clothing, rubber gloves, and a respirator.
Most nitrogen fertilizers / fertilizers are granular, but this does not mean that they are not capable of dry spraying.


After dilution and other procedures with a chemical, they must take a shower with laundry soap. Work clothes and utensils are stored in a separate place, they are not used to dilute other substances without preliminary treatment.
Effects of nitrogen deficiency on plants
In addition to the visually visible consequences of nitrogen deficiency, unseen changes occur in the soil.
Most often this can be observed in early spring, when the earth has not yet had time to warm up. The low temperature impedes the mineralization process, due to which the resulting nitrogen deficiency occurs at an early stage of plant development.


This leads to improper plant growth. Each species can have its own special changes:
- in apple trees, the number of fruit ovaries is noticeably reduced, the leaves become smaller, not reaching the desired size;
- strawberries do not give normal shoots, the leaves turn yellow ahead of time;
- the lower leaves of potatoes and tomatoes turn yellow and fall off, not having time to grow;
- unripe tomato fruits fall off even with a slight wind;
- in pome plants, the leaves are noticeably narrowed;
- the growth of new shoots of roses slows down;
- in fruits, the content of chlorophyll decreases, which leads to a change in the color of the leaves, small fruits have a bright color and easily crumble;
- cabbage may experience chlorosis, which is accompanied by yellow leaves around the veins;
- beet leaves turn yellow, become lethargic and fall off.
How to determine if a plant needs feeding?
Lack of nitrogen easy to identify even visually at home. The main symptoms are:
- foliage color loses its green saturation;
- leaves turn yellow and fall off;
- plant growth slows down;
- the size of the leaves becomes smaller;
- the growth of shoots and branches of trees stops;
- ovary or unripe fruits fall off;
- in stone fruit cultures, reddening of the bark may be observed.
but excess nitrogen also unsafe for plants:
- there is an unnatural increase in leaves;
- greens take on a rich dark green hue;
- flowering, ovary and ripening are significantly late in time.
Especially the consequences of nitrogen deficiency are manifested on soils with high acidity and a large amount of weeds, which take away deficient nitrogen from crops.
Plants need nitrogen throughout the entire period of development. A correctly selected and calculated amount of nitrogen fertilizer will not only accelerate growth, but by enriching it with protein, will increase the yield and quality of plant crops.
Terms of use
Nitrogen is an element that plants need at all stages of development. But most of all it will be needed during intensive growth: from seed to seedling / sapling.
The result of using nitrogen-containing dressings is an increase in yield. But the percentage increase is provided by the correct use of fertilizers.
How to calculate norms for different types of soil
The selected drug is applied according to a specific scheme. The recommended doses and method of administration are clearly stated on the package. The dosage and application rate for all crops is different.