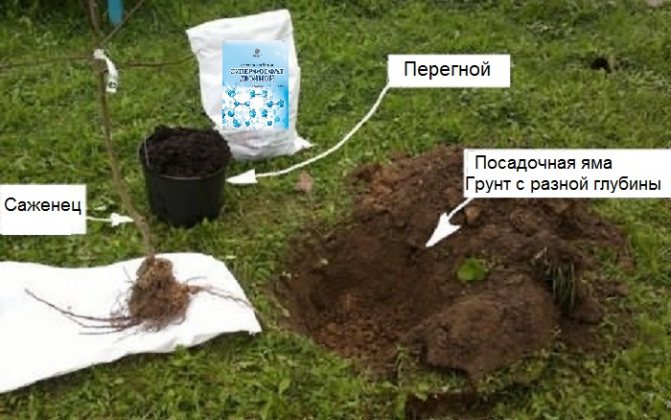
Superphosphate is a mineral fertilizer based on phosphorus. From 20 to 50% of the filling of the mixture falls on this component. Usually in the composition of fertilizers, granules are present both in the form of free phosphoric acid and in the form of monocalcium phosphate. The main advantage of top dressing is the oxide-containing composition, which, as you know, is a water-soluble element. Read on to learn more about what the double superphosphate formula looks like and what features this fertilizer has.

How best to fertilize plants
According to experts, nutrients are supplied to the root system faster if the treatment is carried out by irrigation with an aqueous solution. Superphosphate consists of:
- nitrogen;
- sulfur;
- calcium sulfate (in the form of gypsum);
- boron;
- molybdenum.
The formula is modified depending on the species.
For the production of fertilizers, raw materials of natural origin are taken, which are formed during the natural mineralization of the bone material of deceased animal organisms. Less commonly, they resort to using a secondary product obtained during steel smelting - tomoslag.
Phosphorus is an element that is rarely found in nature, but is indispensable for the normal development and fruiting of plants. Therefore, none of the farms can do without the use of such a type of fertilizer as superphosphate.
Testimonials
“Today I tried to make a superphosphate extract myself. It seems like it happened. But I cannot judge for myself on the first day. I can say one thing, this is the most detailed description that I have seen on the Internet. Of course, it may seem to someone in great detail, but this is how you can understand a completely specific question. "
“So the potato superphosphate solution is working. I am a research assistant and part-time gardener. I decided to test superphosphate for the sides of potatoes and at the same time measure the level of natural substances in the soil. Strange as it may seem, but it works! It would seem a simple recipe, but effective! I recommend to everyone!"
Growing plants for our own needs, we deprive the earth of necessary microelements, since nature provides for a cycle: the elements removed from the soil return to the ground again after the death of the plant. Removing dead tops in the fall in order to protect the garden from pests and diseases, we deprive the soil of the elements it needs. Double superphosphate is one of the means for restoring soil fertility.
“Natural” organic fertilizers alone are not enough to get a good harvest. "Clean" manure is useless without a sufficient amount of urine containing nitrogen. But the manure must be "sustained" for at least a year in order for it to peel. And do not forget to correctly arrange the collar. In the process of overheating, the urine in the pile decomposes, "producing" ammonia containing nitrogen. Ammonia evaporates, and humus loses nitrogen. Nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizing makes it possible to compensate for the nitrogen deficiency in humus. Therefore, top dressing is mixed with manure during spring work and the mixture is already introduced into the soil.
The value of a chemical element for representatives of flora
The existence of any living plant is threatened without the presence of phosphorus.This element provides energy exchange at the cellular level, as a result of which the transition from phase to phase occurs several times faster. This means that the crop grows faster and immediately begins to bear fruit.
Receiving phosphorus in sufficient volumes, the root system more actively assimilates a number of other macro- and microelements, which it cannot do without.
Did you know that this element contributes to the balancing of nitrogen, which leads to a significant decrease in the content of nitrates in the manufactured products, and therefore, to obtain quality food for humans and animals?
Where is applied
The fertilizer has no dangerous contraindications and is allowed for use both in small gardens and in fields where cereals are grown industrially.
A separate topic is compatibility with different types of soils. For chernozems, a moderate dosage is recommended for infrequent treatments. Weaker alkaline soils are more willing to take an extra dose of this "medicine".
But in the case of acidic soils, you will have to take less, because phosphorus in combination with calcium strongly oxidizes the fertile layer.
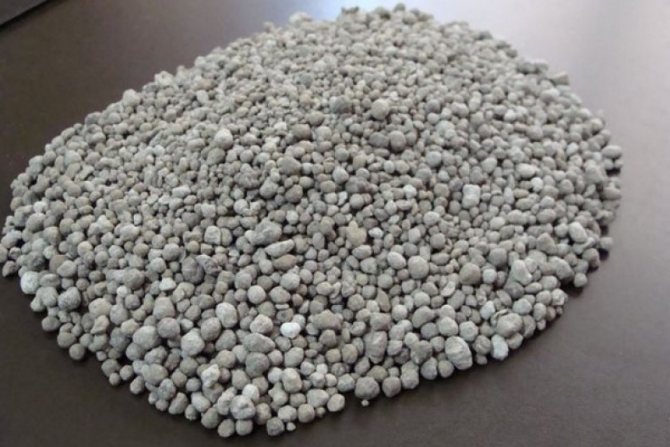


On overly saline areas, "double" is not used - the phosphate may simply not dissolve. The concentrate can be used several times per season.
The main application is made in April or September. In this case, the agent is placed shallowly, at the level of the seeds. When applied superficially, digging is required (otherwise phosphorus will be unevenly absorbed in the area).
In May, when sowing and planting, a basic top dressing is done - the granules in the required amount are placed directly into the hole, at the same depth as the seedlings.
Current treatment is carried out as necessary if the ovaries are weakened or the leaves have acquired an unhealthy purple hue. This is where nitrogen comes into play, which has a beneficial effect on the vegetative system.


How to identify a lack of phosphorus in plants
With a lack of minerals, the characteristic color of the leaves changes to an atypical, special bluish color, sometimes with a purple, yellowish, green tint. Leaf discoloration most often occurs in young seedlings and seedlings, which is associated with early planting in open ground or with the hardening of young shoots.
Low temperatures have a negative effect on the assimilation of the element, therefore, a change in the color of the leaves in plants is observed. As soon as the temperature rises, the blue from the leaves disappears. Although some owners, for the purpose of safety net, carry out additional feeding of flowers with double superphosphate.


It is advisable to pay attention to the fact that young seedlings dived in winter also suffer from a lack of phosphorus. In this case, it is recommended to ration the application of fertilizers for the next ten days after transplanting each sprout into peat cups.
Phosphorus
The raw material for this element is phosphorites, which are sedimentary rocks. Phosphorus is essential for plants. They signal that it is lacking by changing the color of their foliage from green to bronze, purple, violet. Phosphorus and its compounds help plants become more frost-hardy, tolerate drought more easily, and accumulate starch, fats and sugars.
The introduction of superphosphate promotes earlier ripening of fruits precisely due to the phosphorus it contains. This element is a constituent of complex proteins that are involved in cell division. As a result, fertilization with superphosphate promotes the formation of new branches, buds, ovaries, leaves. Plants that receive such top dressing grow stronger, have a lush crown (trees), and produce more fruits.
You are wrong if you think that plaster is used only in medicine for limb fractures. This element in its raw form is a very valuable fertilizer, as it is a rich source of calcium and sulfur.Its formula is CaSO4.
Plants need calcium to increase yields, regulate nitrogen consumption, and most importantly, to increase immunity to various diseases.
If there is not enough of this element in the soil, small fruits are tied. Even before harvesting (being green), they crack. In flowers, with a lack of calcium, the buds die off and fall off. In fruit crops, the apical buds of the shoots dry out.


Fertilization with superphosphate, which contains gypsum, helps to avoid all these phenomena, to increase productivity, to make flowering of ornamental crops more lush, and to increase the shelf life of harvested fruits.
Species variety of superphosphate class fertilizers
Both professionals and amateurs of agriculture can purchase one of the types of fertilizers available on the market. Mixtures differ depending on the method of obtaining this or that composition, technological features of production, indications for use. Most often, gardeners and farmers use the following types of fertilizers:
- monophosphate (simple superphosphate);
- granulated;
- double;
- amonized.


When superphosphate can harm
Superphosphate dust irritates the respiratory tract and causes watery eyes. It is necessary to pour the granules in personal protective equipment: a respirator and glasses.
The product is slowly absorbed by plants, so there are never symptoms of phosphorus overdose. If there is a lot of it in the soil, the plants speak about it with the following symptoms:


- interveinal chlorosis;
- thin leaves;
- the tips of the leaves turn brown;
- internodes become short;
- yield falls;
- at the bottom, the leaves become spotty and curl.
Fertilizer does not burn or explode, is not poisonous. It is recommended to store it in a closed room where there is no access to pets.
Superphosphate has a long duration, does not wash out from the soil, and promotes plant growth and development. It is the most popular plant fertilizer on the market.
Watch the video! Extract from simple superphosphate. Superphosphate solution
Monophosphate
Outwardly, it looks like a gray powder. In the composition - up to 20% of the main substance, 8% of nitrogen, no more than 10% of sulfur and calcium sulfate in a large volume, contained in the form of gypsum.
The substrate practically does not cake if stored in a room with moderate humidity - no more than 50%.
The product is characterized by a pronounced acidic odor.
This type of fertilizer shows less efficiency compared to double and granular superphosphate. However, due to the low cost, the demand for the powder for use in large farms and farms, industrial agriculture is growing rapidly.
Monophosphate is used to enrich compost, plant dressings, since the powder dissolves easily and quickly in water, which cannot be said about double or granular fertilization.
Compatibility
A simple variety of complementary foods can be used in mixes, enriching complementary foods with potassium chloride, potassium salt, potassium sulfate, ammonium sulfate. It is forbidden to use it together with agents, in the list of which you can see carbamide, lime, dolomite flour, chalk, ammonium, sodium and calcium nitrate.


Granular agent (single and double) is not combined with lime, dolomite. It combines well with agents like ammonium, sodium and calcium nitrate, potassium chloride, potassium salt, ammonium sulfate.
Granular superphosphate
It is made on the basis of monophosphate, amenable to moistening, pressing, rolling in industrial production conditions. This fertilizer contains up to 50% phosphorus and 30% calcium sulfate and is more concentrated.
Granular dressings are easier to use and have a long shelf life.They are distinguished by a prolonged action, since they dissolve more slowly in water and soil, which contributes to the extension of the effect from feeding to several months.
Most often, this type of fertilizer is used to grow the following crops:
- legumes;
- cruciferous;
- bulbous;
- cereals.
Double superphosphate
Do you know how superphosphate differs from double superphosphate? The advantage of the latter is the minimum number of impurities in the composition, which makes the use of fertilizers more profitable in economic terms. Especially when it comes to hectares of plantings or entire plantations.
A distinctive feature is the content of easily assimilable phosphorus and calcium in a water-soluble form. See the table below for what the double superphosphate formula looks like.
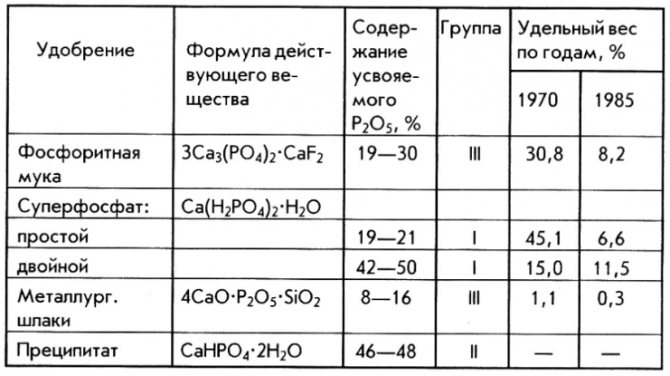

What it is?
Double superphosphate (SF) - mineral phosphoric fertilizer, obtained by the action of concentrated phosphoric acid. Unlike simple superphosphate, the amount pure phosphorus it is much higher - about 26%, and practically no impurities.
Chemical formula: Ca (H2PO4) 2.
Simple superphosphate obtained with sulfuric acid. Its formula is: Ca (H2PO4) 2 * H2O + 2CaSO4.
The content of pure phosphorus in it is about 12%. Since the fertilizer is obtained from natural minerals, it contains small amounts of sulfur, magnesium, calcium and other trace elements.
By appearance both fertilizers are similar: light gray granules, slightly darker in simple SF. You can also find double SF in the form of a light gray powder.
Ammonized superphosphate
It is used for the cultivation of cruciferous and oilseeds that require a high sulfur content. In the composition of top dressing, the content of this component reaches 12%, and calcium sulfate - up to 55%.
A number of other varieties of superphosphate are also distinguished, containing boron, magnesia, molybdenum and used in the cultivation of individual crops in order to feed them with additional microelements.
Now you know what types of fertilizers are emitted and what is better to use in order to get an effective effect.
What is superphosphate and what is its role in plant development
You should first find out what superphosphate is. Superphosphate is a fertilizer with a high concentration of phosphorus, it also contains a number of other useful substances. There are various types of drugs, depending on their types, the composition may contain: calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur ... Chemical formula: (CaH2PO4) 2 x H2O + 2CaSO4 x 2H2O.


Fertilizer Superphosphate 1 kg
The action of superphosphate in the garden is characterized by a wide spectrum of action:
- the composition of the substances stimulates the earliest hatching of seedlings;
- enhances the development of rhizomes, from the action of phosphates, the root becomes powerful and strong;
- acts as a stimulant for flowering;
- reduces the intensity of aging processes;
- stimulates the best quality of white cabbage heads. The heads of cabbage become firm, firm and healthy;
- enriches the taste of various root crops, berries and trees. When used in relation to berry bushes and fruit trees, an increase in the sugar content of the fruits is noted. For seeds, the amount of oil increases. When used as a fertilizer for tuberous crops, it increases the starch content in them;
- reduces the amount of nitrate compounds in fruits;
- by combining nitrogen and phosphorus, improved absorption and processing of magnesium is provided;
- stimulates natural immunity against diseases and viruses.
In plants, the amount of phosphorus is 0.2% of the total mass, excluding water. The largest amount of phosphorus is contained in the organs of the reproductive system and new shoots of the plant, which have intensive growth.
The highest consumption of phosphorus compounds occurs during flowering and ripening of fruits.With a deficiency of a trace element, a low number of fruit ovaries is formed even with a sufficient level of pollination, and immature fruits tend to crumble.


Superphosphate enhances rhizome development
What soil is superphosphate suitable for
The fertilizer is suitable for neutral-alkaline soil. In acidic soil, phosphorus oxide reacts to form iron and aluminum phosphates. They are practically not absorbed by plants, therefore, before applying superphosphate, the earth is deacidified. For this, wood ash or slaked lime is used.
The process takes about 30 days, so it is worth taking care of early deoxidation and only after that apply top dressing. It is worth noting that the quality of the supplements is not the least important, and for the purposes described above, it is worth using only formulations from trusted manufacturers. It will cost more, but this is the case when saving is not worth it.
It is common among some manufacturers to reduce the cost of fertilizers and stimulate sales growth by changing the double superphosphate formula and adding various impurities to the formulations. In acidic soil conditions, they contribute to the formation of phosphates, indigestible by plants.


Basic facts for understanding the mechanisms of action of superphosphate
Superphosphate is a phosphate fertilizer.
The role of phosphorus in wildlife
Phosphorus is a vital part of any organism:
- into molecules of heredity - DNA, in which the genetic code of the organism is encrypted;
- into the RNA transport system, which delivers nutrients and organizes protein synthesis;
- into ATP, which is a universal fuel for the cells of all living organisms, providing them with energy for functioning.
Plants need phosphorus for growth, the use of sugar and starch, photosynthesis, nucleus formation, and cell division. Phosphorus compounds are involved in the transfer and storage of energy within plants. Energy from photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism is stored in phosphate compounds for later use in growth and reproduction.
Phosphorus moves easily within plants, transitioning from older to younger tissues as the plant forms cells and develops roots, stems, and leaves.


Adequate phosphorus levels lead to rapid growth and early maturity of the plant, which is important in areas where early frost is possible.
How to determine the lack of phosphorus
The plant lacks phosphorus if the following symptoms are observed:
- weak, undeveloped roots, unable to keep the plant in the ground;
- low plant growth in contrast to the standard;
- delayed flowering;
- small flowers and fruits;
- folded edges of leaves;
- non-standard color of leaves and (or) fruits for the variety.


Phosphorus starvation is especially pronounced in early seedlings and plants planted in the ground at low air temperatures.
With a decrease in temperature, the transport arteries of the plant narrow, and if a lack of phosphorus is added to this, then protein synthesis stops almost completely, the plant sharply slows down growth and may die.
Note! The plant's response to phosphorus deficiency begins with old leaves located close to the ground. Their downside becomes purple. Sometimes the lower part of the stem, cuttings, and leaf axils acquire a red-purple hue.
Signs of phosphorus starvation in the most common crops:
- cherry, plum, blackthorn berries are small, abnormally green-violet, sometimes with a bright "barrel";
- corn has lower leaves with lateral purple stripes, crooked rows of grains on the cob, the top dries up;
- the cabbage has purple veins at the bottom of the leaf. Heads of cabbage are small. Seedlings have lower leaves of a purple hue;
- brown spots appear in the potato tuber, which become hard after heat treatment;
- in legumes, delayed flowering and fruiting, stems are red-brown;
- cucumbers have weak flowering, thin and weak shoots, leaf axils are red-violet, lower leaves with blue-green spots;
- tomatoes have small, slow-growing fruits, leaves with a reddish-purple tint on the reverse side, the stem is curved, with purple spots in the lower part.
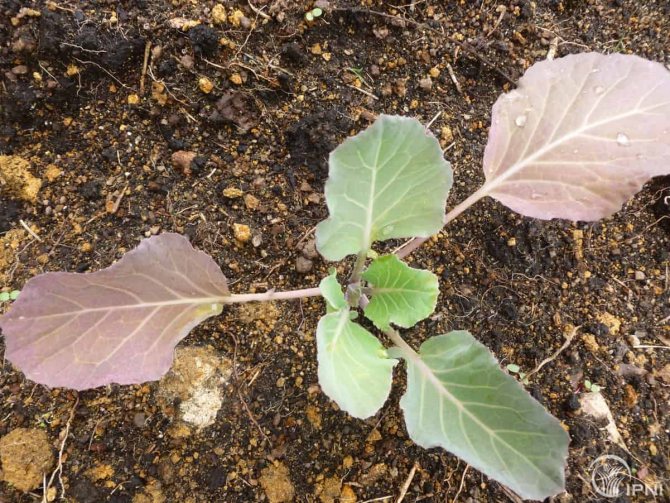


Features of the use of fertilizers on soils
Superphosphate is introduced in several ways:
- By adding to the compost.
- Introducing into holes or rows during planting.
- Including during autumn or spring digging.
- Scattering over the surface of the site.
- Preparing the solution for watering.
For the introduction of additives with a prolonged period of action, farmers recommend the autumn season. It is ideal for neutral and alkaline soils. To enrich acidic soil, superphosphate is used only when liming is excluded. The acidic salts of the substance react with lime when applied simultaneously, which leads to the mutual neutralization of the components and the enrichment of the soil with salts that are unnecessary for plants. In this case, when planning autumn liming, fertilization of the soil with top dressing - double superphosphate - is better to transfer to next spring.
The use of superphosphate with ammonium nitrate and urea - substrates belonging to acids is not recommended. After all, this leads to soil acidification.
Potash fertilizers will prove to be the best option to combine with superphosphate. Potassium is a trace element that allows plants to more actively assimilate phosphorus, which, in turn, has a positive effect on the gradual absorption of potassium by the root system.
Don't be afraid to overdo it with mineral fertilizers. Each living plant takes as many vitamins as is necessary for its healthy life. Moreover, this element does not affect the set of green mass, like nitrogen, therefore it is calmly used both in autumn and winter.


Safety precautions during application
When using superphosphate, precautions are required. Chemical fertilizer compositions can have a negative effect on the human body, adversely affect well-being and health.
Working with phosphorus-containing complementary foods requires the use of personal protective equipment such as waterproof gloves, cotton gauze bandages, or a respirator. It is also desirable to cover the head.
They are engaged in the manufacture of hydrate on the street; in the room, in the absence of a working hood with superphosphate, it is strictly forbidden to work. Its fumes are harmful to humans and pets.
It is forbidden to make fire and smoke near the fertilizer. Do not eat or drink in the immediate vicinity of the substance. After working in the garden using superphosphate, it is imperative to wash each open area of the skin with soapy water.
If the substance gets into the eyes or on the skin, rinse the affected area with plenty of water.
Superphosphate application rates
Double superphosphate is a fertilizer for use in the garden, so use the following proportions:
- Spring / autumn - 50 g / m2.
- Depleted and poor soil - 100 g / m2.
- When adding to compost, stick to 100 grams of monophosphate for every 100 kg of organic matter.
Before planting tubers or seedlings, a little less than half a teaspoon of fertilizer is laid in each hole, which is equivalent to 3 grams of top dressing. When planting in rows, no more than 20 g / m2 is added, and for ornamental, berry and horticultural crops, this dose increases to 50 g / m2. Now read the instructions for using double superphosphate in solution.
Instructions for use
When using a simple form of the substance, the application can be carried out equally - both in the fall and in the spring. Consumption is approximately the same for the seasons. When cultivating well-groomed lands, 40-50 g / m2 are used.For plots that are involved in crop rotation, the dosage is slightly increased to 55–70 g / m2. The listed doses are used to completely cover the earth.
Do you use folk signs in gardening?
For protected ground, 75–90 g / m2 should be used. It is better to apply in parallel with other mineral fertilizers before digging.
Fruit trees
When feeding fruit-type trees, it is worth adding powder of about 0.5 kg per 1 seedling. This will be enough for a relatively long period, the plant will independently absorb a suitable amount of the product. When using this technique, you can not add phosphorus for the next 3 years.
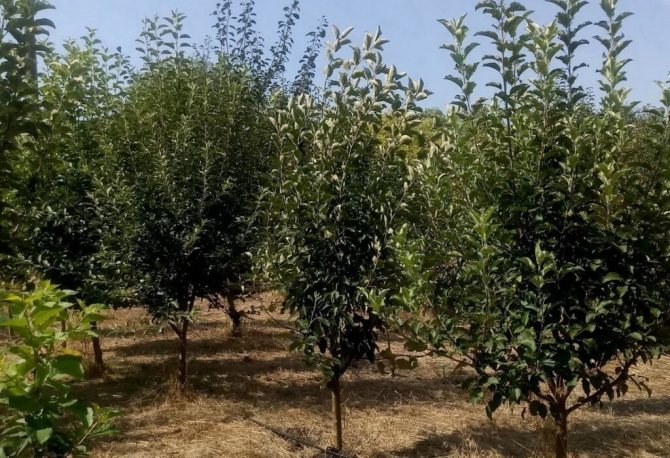


Fertilizing fruit trees with superphosphate
When applied under a planted tree, you can simply use it as a top dressing based on the calculation of 70–90 g per 1 circle of the near-stem type. Best results are obtained when used during color burst. For laying, surface coating and further loosening are used.
Seedling
Lack of phosphorus compounds in young animals is a frequent occurrence characteristic of many plants. The greatest deficit occurs during the first hardening or early planting in the garden. The reason is poor absorption of phosphorus at low temperatures. To compensate for the condition, superphosphate dressings are used.
When used in greenhouses, monophosphate is often used in a proportion of 100 g / m2. After surface treatment, loosening and digging are carried out. For seedlings, a standard solution is used - 20 g per 3-liter can of water. After receiving the concentrate, dilute it in a bucket of water. One plant requires about 40 ± 10 g of composition.
Vegetables and fruits
Superphosphates can be applied to almost all crops, including vegetables and fruits. When using a double form, you need to add the agent to the hole with a root crop at a ratio of 3-4 g per plant. For the cultivation of solanaceous, leguminous, cruciferous and other crops, 10–20 g of the substance are applied under the bush. It is preferable to use a granular form. When applied to fertilize the entire area, it is recommended to carry out a surface treatment of 20 g / m2 - the dose is optimal for most crops.


Superphosphates can be applied to almost all crops, including vegetables and fruits
For strawberries, it is worth using phosphorus during transplanting or planting. To improve the properties of the fertilizer, it is better to add organic impurities. Before the spring or autumn digging, a continuous coating composition can be used from the ratio of 5 kg of manure or compost to 60 g of the preparation and 15 g of calcium salt per 1 m2. To improve the next year's harvest, it is worth applying fertilizer in the fall. For this purpose, 10 liters of water is added with 1 kg of organic matter, 40 g of superphosphate compounds and ¼ kg of wood ash.
It is recommended to feed raspberries in autumn or late summer. For high-quality fertilization, 60 g of superphosphate and 40 g of potassium salt are used. The application is carried out in 20 cm depressions. There should be a distance of 30 cm between the bushes and the place where the mixture is applied. When planting, you can use 8 kg of organic matter, 200 g of the preparation and 80 g of potassium with sulfur.
Houseplants
The use of superphosphate fertilizers for indoor crops can be performed year-round. Especially often, fertilizing is added at the flowering stage and after its completion. During the entire spring-summer period, it is recommended to treat with ammonium nitrate (12 g), potassium salt (3 g) and superphosphate (5 g). The listed ingredients are diluted in 1 bucket of water. For 1 liter of earth, you will need up to 100 ml of the prepared solution.
Depending on the growth rate, the number of fertilization procedures changes:
- for fast-growing varieties, it is performed 2 times a month;
- for plants with slow growth - once every 30 days.
Before flowering, a solution is prepared based on the proportion: saltpeter (7 g), potassium (12 g), preparation (12 g) per 10 liters of water.
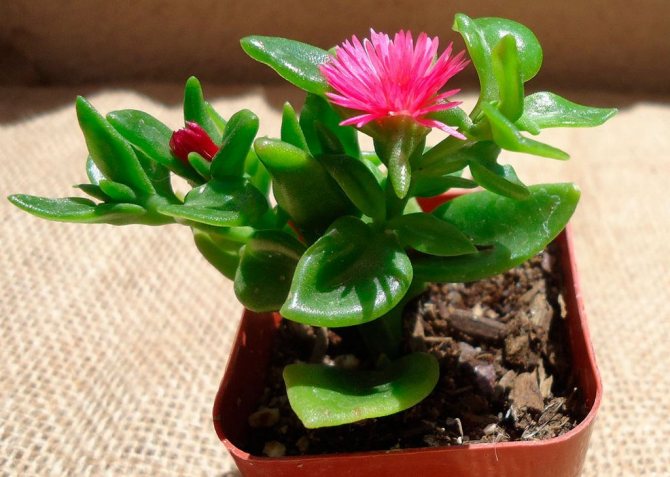


Using superphosphate fertilizers for indoor plants
How and where is superphosphate solution used
A common option for fertilizing among gardeners in a diluted form is through irrigation. Thus, nutrients are more likely to dissolve and enter the soil, which contributes to the accelerated absorption of trace elements by plants.
Note that phosphate fertilizers are practically insoluble, so to achieve the desired effect and turn the superphosphate into a liquid state, the water should be heated. They do this in two ways: pouring boiling water over the granules or placing them in a warm place (for example, in the sun in the summer). Please note that high temperatures do not have a negative effect on fertilization, that is, superphosphate does not lose its beneficial properties, and plant care through watering is particularly convenient.
To prepare a concentrated solution, you will need 300 grams of superphosphate (about 20 tablespoons) and 3 liters of water. The double superphosphate composition will have to be stirred periodically until the granules take a crushed form. Stir or shake the solution again before watering. Dilute the concentrate with 100 ml / 10 L of water. Up to 20 milligrams of fertilizers containing nitrogen and 500 milligrams of wood ash are added to the liquid in the spring.


Description
This mineral fertilizer affects all plants in several ways. The first link is an improvement in metabolism, as a result of which the yield level will increase. The second link is to improve the quality of the entire crop, due to the effect on the root system, as well as due to the improvement of the development and flowering process. In addition to all of the above, this product will help get rid of your plants from many different diseases and slow down the aging of plants. This product is used in agriculture as fertilizer for almost all crops on all types of soils.
Double superphosphate is a highly concentrated water-soluble phosphorus fertilizer. It contains about 42-46% phosphorus, which is located in a form that is easily absorbed by all plants. In addition to the above, the composition also contains calcium sulfate, monomagnesium phosphate, aluminum phosphate, iron phosphate. Compared to other species, there is a difference exclusively in the increased content of phosphorus, which is easily absorbed. This fertilizer is used for all types and types of plants and soils. The composition of this mineral fertilizer contains a small amount of ballast substances, which in turn helps to use it with economic benefits. This type of fertilizer is introduced in early spring before planting crops.


Superphosphate contains a large number of components. The most important component is phosphorus. It accounts for approximately 20-50% of the total composition. This element is often in the form of free phosphoric acid or in the form of monocalcium phosphate. The calcium salts of phosphoric acid are mixed with gypsum. Plus, salt of molybdenum, potassium permanganate, boron, and other microelements is added to all this. In addition to those mentioned above, other trace elements can also be found in the composition, such as magnesium, potassium, calcium, sulfur. Depending on the type of fertilizer, it will contain a different amount of chemical trace elements. The original mineral is created during the natural processes of mineralization of the bone composition of dead animals.
The double superphosphate contains the same phosphorus-containing elements, but in different proportions.Outwardly, it is no different from simple superphosphate, but in this type of fertilizer there is a double amount of phosphorus, here it is 45-55%. Another difference is that it does not have gypsum in its content. The nitrogen content fluctuates approximately in the range of 14-18%. There is also about 6% sulfur. Has good friability, low hygroscopicity.


All gardeners or agricultural workers are very fond of feeding agricultural plants with watering. But fertilizers containing phosphorus are poorly soluble in water, or rather practically insoluble. To change the state of aggregation of the fertilizer, it is necessary to increase the temperature of the water with which we directly dissolve the product. There are two main ways known - this is filling the granules or powder with boiling water, or the location of the vessel with the solution in a warm place, in summer, for example, you can put it in the sun. High temperatures are not able to reduce the beneficial properties of the product. To create a highly concentrated solution, you need to take 300 grams of fertilizer (this is about 30 tablespoons) and pour 3 liters of water. To grind and dissolve granules or powder, you need to stir the solution periodically. Just before watering, you will need to shake or stir the solution. In the spring, you can add about 20 mg of nitrogenous fertilizer or about 500 mg of wood ash to it.
Both professionals and amateurs of agriculture can purchase a variety of agrochemicals today. In connection with the expansion of the fields of use of soil fertilizers, several types of superphosphates have been developed, which are indicated below:
- Simple or monophosphate is a slightly concentrated water-soluble fertilizer that can be produced both in the form of powders and in the form of gray granules. The humidity in the place of its storage should not exceed 50%. Use and apply it to any kind of soil. Improves the growth of crops that require high sulfur consumption. Compared to new types of fertilizers, it has a reduced efficiency, but still has found great popularity among people, since it is the cheapest. In industrial agriculture, it is used to fertilize potatoes, legumes, beets, carrots, cereals, and so on. And also found its application for the enrichment of compost pits or plant dressings. Has the best water solubility compared to the following species.


- Granular superphosphate. This type is obtained using the process of humidification, pressing of fractions and rolling into granules by industrial methods. This method exists for ease of use and storage. Has a longer lasting effect compared to other species. It has low hygroscopicity, non-caking, explosive and non-flammable. It contains about 50% phosphorus, and about 30% calcium sulfate. It is used mainly for pre-sowing soil fertilization and as the main top dressing.
- Double superphosphate. It contains the same phosphorus-containing components, but in a different proportion. There is almost three times more phosphorus here. Poorly turns into a liquid state of aggregation. It has one major advantage over other species. It consists in the fact that this type of fertilizer contains a small amount of ballast, which allows to reduce consumer costs for transportation, storage and packaging. It is used for the application of various types of crops and various soils.
- Ammonized superphosphate. This species has up to 55% potassium sulfate and about 12% sulfur. It is very water soluble and easy to use. It is used mainly for feeding cruciferous and oilseed crops, which have a great need for sulfur.
Superphosphate for seedlings
Double superphosphate (GOST 16306-80) is used to compensate for the lack of phosphorus in young plants, which turns out to be quite common. Seedlings and young seedlings that have undergone a hardening procedure and planted too early in an open area of soil often suffer from such a problem.
In greenhouse conditions, monophosphate is used at the rate of 100 grams per 1 m2, applying fertilizer when loosening or digging the soil. When growing seedlings at home, they resort to using a base solution - 20 grams of superphosphate is diluted in 3 liters of water, and the resulting concentrate is diluted with 10 liters of water. To fertilize one young plant, approximately 30-50 grams of the composition will be required.


Benefits over others
This fertilizer is attractive because:
- does not contain "bonding" ballast;
- stimulates growth better;
- thanks to nitrogen, the number of ovaries on plants increases, and this is already the prospect of a larger harvest;
- sulfur "tones" the seedlings, increasing their vitality. When used for cereals, cereals accumulate protein more actively (and in oily species, the seeds become fatter);
- is not a highly toxic compound;
- granules do not cake, which is convenient for long-term storage.
The list is impressive, and the arguments are quite weighty. But any fertilizer, including double superphosphate, will be useful only if all the requirements are met, which the instructions for use remind of.
Fertilizing fruit trees
According to the instructions, the double superphosphate formula is also suitable for fertilizing the wells before planting at a dose of 500-600 grams per seedling. Using the first top dressing when planting, be prepared that the second will not have to be applied soon - after three years.
Superphosphate, intended for fertilizing trees, is laid by loosening or in the trunk circle when digging at the rate of 100 grams per tree at the end of the flowering period. This will help the plants develop in a balanced manner and store enough vitamins to feed during the dormant period that comes with the winter cold.
Now you know what the chemical formula of superphosphate is and what fertilizer granules look like. Now it will be easier to recognize this type of fertilizer, and caring for plants will turn into an easy and enjoyable activity that does not constitute much difficulty.
Superphosphate application for private plants
Potatoes
This fertilizer is quite versatile, but the greatest effect from its use should be expected in the garden. It can be applied to almost all crops, but potatoes will be especially grateful for the phosphorus feeding.
Superphosphate can be applied for spring application to each well, about 3-4 g. A granular chemical will be very handy for this type of application. It allows you to more accurately dose the rate for each bush.
Since the most valuable part of potatoes is tubers, it is necessary to strengthen the root system of the plant to increase productivity. Phosphorus is the main nutrient responsible for its high-quality development and regeneration.
If the whole area is fertilized, then about 20 g of superphosphate is taken per square meter. This dosage is applicable to most vegetable crops.
Tomatoes
Phosphorites are applied during planting nightshades, about 20 g per plant. It is not necessary to deeply deepen the fertilizer; proper nutrition for the tomato will be provided if the fertilizing is evenly placed under a loose layer of earth at the level of the plant roots. Tomato uses more than 95% of phosphorus for fruit formation. Therefore, the use of superphosphate is not limited to spring feeding. It must also be applied during the flowering period of tomatoes.
If the fertilizer contains a lot of potassium superphosphate, then it is great for tomatoes that "love" this chemical element and respond to its use with sweeter fruits.
Adult plants with a well-developed root system absorb nutrients much better. Young people, on the contrary, consume little phosphorus. Therefore, in order to save money, when planting seedlings in the ground, they are fed with granular superphosphate, which is better absorbed, and when feeding adult plants, you can use a simple form of this fat.






























