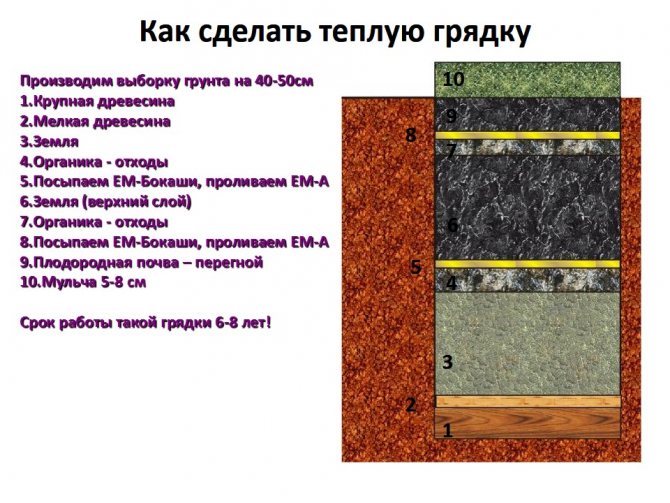
Types and varieties of peanuts for planting in the garden
A representative of legumes, peanuts are 70 plant species. Most of them are grown in their homeland - in South America. Outside its borders, only two species are known - cultural and Pinto.
All cultivars of a cultivated variety can be divided into 4 broad categories:
- Virginia. Selected peanuts, which are fried immediately in the shell.
- Runner. It is believed that peanuts in this category are the most delicious.
- Spanish (Spanish). Differs in a high concentration of peanut butter.
- Valencia. A group of tall (up to 1.2 m) plants.
I like to try different varieties, with a preference for large and high yielding varieties. I am definitely studying whether the plant will be able to develop in Russian conditions.
The benefits of peanuts
Many beneficial properties of peanuts have been known for a long time. Scientific studies that have revealed the chemical composition of peanuts have confirmed the effectiveness of its use in organizing proper human nutrition. Use as a prophylactic, supportive agent in the treatment of many diseases. Vegetable fats, proteins, well absorbed by the body, vitamins, minerals are collected in it in a harmonious complex. It improves memory, hearing, sleep, attention. To help with exhaustion, overexcitation of the nervous system. Prevent the appearance of some forms of cancer. The high caloric value of peanuts does not lead to weight gain due to the lack of cholesterol. Of course, you need to stick to the reasonable amounts recommended by your doctors. A high protein content may well reduce the amount of meat consumed. For small snacks, you can eat a peanut butter sandwich, a few delicious nuts. The use of peanuts for the prevention of atherosclerosis, heart disease increases with heat treatment. Healing substances are found throughout the plant. Shells, stems, nuts serve not only as food products, but are used in pharmacology, cosmetology, and solving agricultural problems. It will seem even more useful if you learn how to grow peanuts at home, do it yourself, see all the stages of its development. Some care tips can be found below.

When to plant peanuts in the garden
The culture is actively developing only at temperatures above 20 C. Even a decrease in the thermometer by a couple of marks becomes the reason for the inhibition of development. Consider this when choosing the optimal planting time.
By region
The southern regions of Russia are more suitable for growing peanuts by seeds. The right moment for sowing the nut coincides with the flowering time of the acacia. In cooler Russian regions, it is recommended to breed peanuts using the seedling method.
Nutlet, seedlings are planted only in warm soil - the temperature of the upper layers of the substrate should be at least 12-14 C. Such conditions do not occur until mid-May. Before planting, be sure to make sure that there is no threat of frost, harmful to the southern culture. I will tell you in detail about the conditions for its cultivation in the Russian regions.
Middle lane
Prepare the bed - remove weeds, add phosphate-potassium compounds, dig up. Keep nuts in a damp cloth just before planting. Another option is to pre-grow the seedlings at home or in a greenhouse.
After transplanting, the plants need timely watering, careful loosening. When the temperature drops below 18 C and the heat is more than 28 C, peanuts may stop growing. Development will continue after the temperature becomes normal for the culture.
Ural
In the Northern Urals, getting tasty nuts in open ridges will not work - only in greenhouse conditions. A little secret: compact peanuts can be easily planted in the aisles of a tomato bed.
In the Middle Urals, culture develops well only in warm ridges. Ridges-trenches are dug, and compost and plant residues are laid in their depressions. Complete the "slide" with a layer of garden soil. When decomposed, the contents will give off heat, warming the plants. Peanuts are planted with seedlings - they are planted in the spring, the first weeks in the open field are kept under a film.
In the South Urals, a ridge for peanuts is prepared in the fall - they add top dressing, dig up. In April, it is covered with an opaque film - for better heating of the soil. The seeds are sown in May - they are also protected with "non-woven".
Only when the weather is stable, the film is removed. With the first flowers, the hilling of the shoots bending down to the ground begins. The plant needs it until mid-August.
Siberia
In Siberian conditions, a good harvest of peanuts can be dug out by first arranging warm beds. For the region, I advise you to choose a bush variety of peanuts - after flowering, the plant forms ovaries, which will sink to the substrate for underground ripening of fruits. Pay attention to ultra-early varieties that ripen in 3 months. Other varieties simply won't have time to harvest in harsh climates.
Lunar calendar
For gardeners and gardeners following the lunar calendar, I will present favorable dates for sowing peanuts in 2020:
- April: 8-13, 15-19.
- May: 7-11, 13-17.
- June: 5-9, 11-15.
If it is not possible to carry out planting work on these days, then transfer them to another date. The main thing is that this is not an unfavorable date:
- April: 5-7, 14, 20-22, 28.
- May: 4-6, 12, 18-20, 26.
- June: 2-4, 10, 16-18, 25.
The sowing date for soaking is the day the seeds are placed in a humid environment.
Features of planting and growing crops
When growing a peanut on a site in the Moscow region, it is necessary to take into account the special conditions of agricultural cultivation:
- lack of shading of the site;
- compliance with the temperature regime;
- fresh air access;
- low soil salinity;
- sufficient moisture level, no flooding;
- high nutrient content;
- neutral soil acidity.
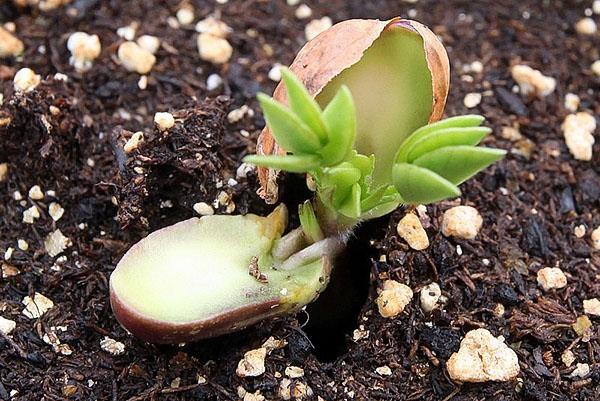


Seed preparation
For seeds, use raw peanuts that have not dried out and still retain the integrity of the red skin. There should be no mold, rot or damage on the surface of the nuts. Preparatory work is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Soak the nuts for 5 hours in warm water with the addition of potassium permanganate or a growth stimulant.
- Transfer the peanuts to a damp natural cloth and cover with the second edge.
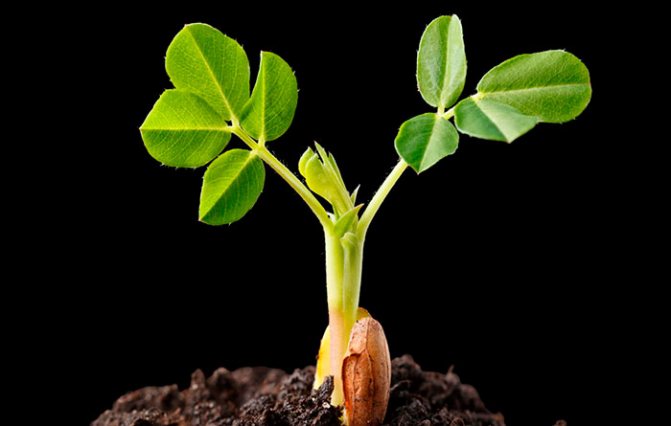
- After 1-3 days, the nuts should open and sprout.
Selecting a site for planting
A site suitable for growing peanuts is selected based on the following requirements:
- Peanuts require a lot of sunlight, so areas with partial or complete shade should be avoided.
- Waterlogging and stagnant moisture negatively affect the growing season of peanuts. The landing site should not be in the lowlands, and the groundwater should not rise close to the surface.
- Air access is necessary for normal crop growth, but plantings must be protected from blowing winds and drafts.
See also
Description of the main pests and diseases of cedar, the best control measures
To read


Optimal soil composition
Peanuts are suitable for growing even on poor soils, enriching the soil with nitrogen compounds during the growing season.Planting peanuts is recommended in areas rich in humus and minerals such as calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. In terms of morphological composition, sandy loam and light loam are best suited. Clay soils need to be loosened, mixed with sand and top dressing, while sandstones are mixed with clay and compost.
The soil, sour and salty in composition, is not suitable for peanuts; such areas must be limed.
Recommended predecessors
For the cultivation of peanuts, it is best to use the plots on which they were previously located:
- cabbage;
- onion;
- cucumbers;
- beet;
- tomatoes;
- corn;
- potatoes.
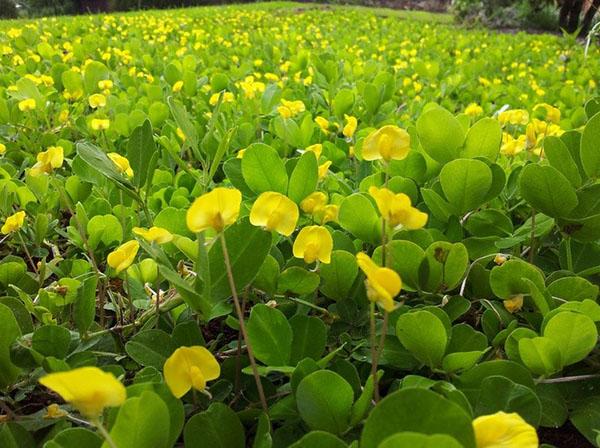


In order to avoid the appearance of rot on the roots, it is not recommended to plant a peanut after crops of the legume family.
Sowing technology
The peanut sowing scheme involves the preparation of trenches 10 cm deep, which are located no closer than 40 cm from each other. The second option for planting peanuts is possible in squares with a side of 60 cm.It is recommended to plant seeds as follows:
- Water the soil in places of sowing with warm water.
- Place the nuts at a distance of 30 cm along the entire length of the trenches or in the corners of the squares.
- Cover the seed with soil to a height of about 8 cm.
- Protect nuts from birds with a special net.


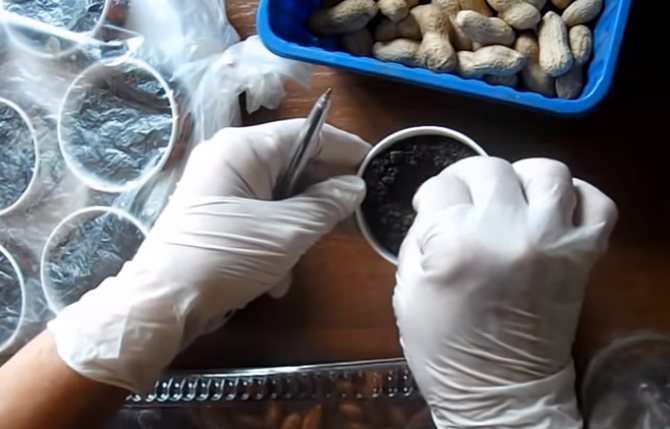
Selection and preparation of seeds
The seeds of my first, experimental peanut, I bought in the vegetable market - I bought ordinary raw nuts from the seller. You can follow my example - as long as the seed is not fried, salted or candied. Another option is to buy in a garden center, order a certain type of culture on the Internet.
Peanut seeds do not require any preparation - they have excellent germination capacity. But I still soak before sowing - I put it in a damp cloth envelope. Then - in a tight plastic bag, which I tie tightly. After a day, the nuts are ready for sowing.
Peanuts: useful properties and contraindications
The benefits of peanuts have been proven for a long time. But since it is considered one of the strongest allergens, it can only be consumed in moderation. The beneficial properties of the product include (Figure 1):
- Antioxidants that are part of the composition serve as a reliable means of preventing cancer;
- Improves the digestion process and the outflow of bile;
- Normalizes the work of the cardiovascular system, as it contains substances that can expand blood vessels and improve blood circulation;
- Effectively relieves the feeling of fatigue, stress and insomnia, as well as increases memory and attentiveness, therefore it is recommended to use it for people engaged in mental work;
- The substances contained in the nut slow down the aging process of the body, since they accelerate the regeneration of cells;
- This nut is good for men as it increases potency. The only condition is that you need to eat it regularly, but in small portions.
A useful product is also peanut butter, which is used in folk medicine to heal wounds and eliminate abscesses.


Figure 1. Features of the nut and its beneficial properties
Despite the benefits of the product, it also has some contraindications. First of all, it is not recommended for people with serious liver dysfunctions. A large amount of proteins and fats carry an additional burden on this organ and can worsen a person's condition. In addition, it is contraindicated in people with increased blood clotting. The product thickens the blood, which can lead to blood clots.
Fresh nuts can also cause digestive upset, which is why it is recommended to pre-fry them. It is also important to remember that the use of the product in large quantities can provoke the formation of excess weight, and if mold appears on the fruits, they should not be eaten, as this can cause severe poisoning.
Site selection and soil preparation
This light and heat-loving plant prefers areas that are open to the sun throughout the day. Shading from higher buildings, neighbors negatively affects the development of peanuts.
Do not forget to follow the rules of crop rotation. Peanuts feel great in the place of their predecessors:
- Cabbage.
- Potatoes.
- Tomatoes.
- Cucumbers.
Do not plant a nut after legumes:
- Peas.
- Beans.
- Lentils.
- Beans.
Peanuts can inherit rot from these plants.
The culture feels great on a site that has been fertilized with organic fertilizers for many years. The most suitable substrate for peanuts:
- Lightweight, "airy".
- Moderately hydrated.
- Fertile, with a high humus content.
- Rich in calcium, magnesium.
- Sandy loam or black soil.
Peanuts will not thrive on salty, acidic soil. Therefore, before planting the culture, in the fall (if necessary) carry out liming.
Also in the fall I am preparing a bed for peanuts:
- I bring in 1-3 kg of humus per 1 m2.
- I dig a bed deeply (by 25-30 cm).
In the spring, for every 1 m2 of land I bring in 50 g of nitrophoska. I'm digging again, but not too deep.
For growing in Russia
But the love of exoticism among farmers in temperate countries pushed breeders to develop varieties adapted for cultivation in central Russia.
These varieties include:
- Adyg,
- Accordion,
- Stepnyak,
- Klinsky.
If the selected varieties show good results on the site, then your own seeds will be suitable for further cultivation, which by the third generation will fully adapt to the conditions of your region and district.
How to plant peanuts in the garden
I will tell you about two methods of growing peanuts - seeds and seedlings. Let me remind you once again that they are chosen depending on the climatic characteristics of their region.
In open ground
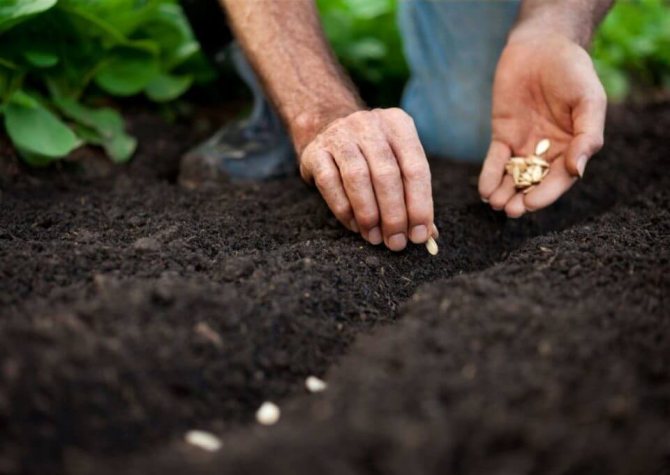
I plant nuts according to a simple scheme:
- I make holes 5 cm deep.
- I place the grooves in a checkerboard pattern, maintaining a distance of 50 cm between them.I leave a gap of 25-30 cm between the individual rows.
- I put 3 large nuts in each hole.
- I fall asleep with soil, compact it a little.
- I water the garden abundantly from a watering can, a hose under a slight pressure, through a fine nozzle.
Here are the popular schemes for planting peanuts in the garden:
- Square-nested. The holes are made according to the scheme 60x60 cm or 70x70 cm.
- Wide-row. Between plants in one line - 15-20 cm, between separate rows - 60-70 cm.
The choice of the scheme depends on the size of the plot, which are ready to be allocated for peanuts.
Growing seedlings
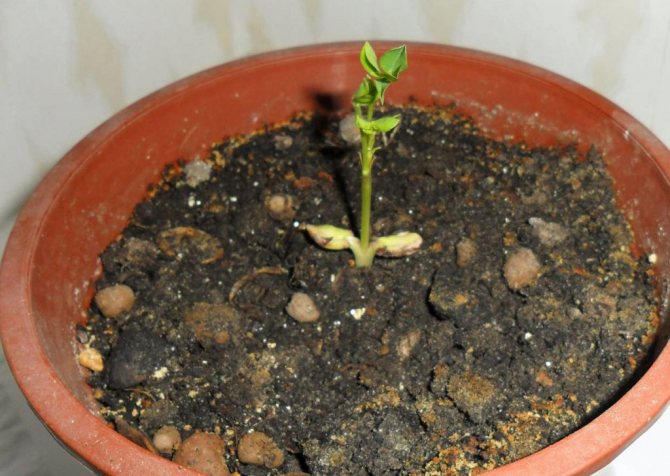
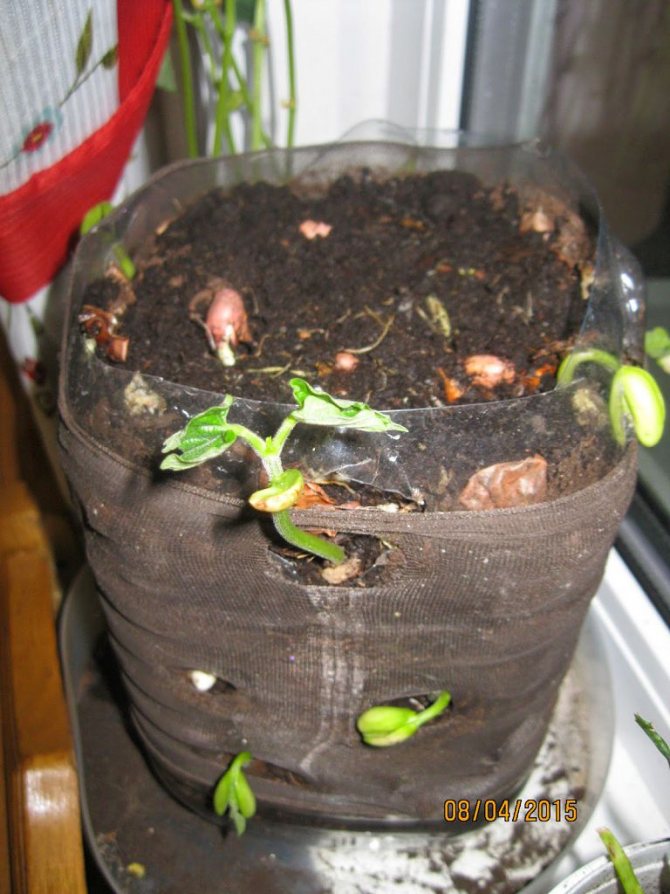
As an experiment, I bred peanuts and seedlings. This approach allows you to harvest a rich harvest in cool climates. My simple instruction:
- Buy seeds or raw nuts around April.
- Fill pots, cups with any loose, fertile substrate.
- Plant 1-3 seeds in each container (if in doubt about germination). Deepen the nut by about 3 cm.
- Transfer to a warm, sunny location.
- Water the seedlings as they dry, and after water procedures, gently loosen them.
In June, the peanut seedlings are ready to be transplanted to a permanent location.
In central Russia
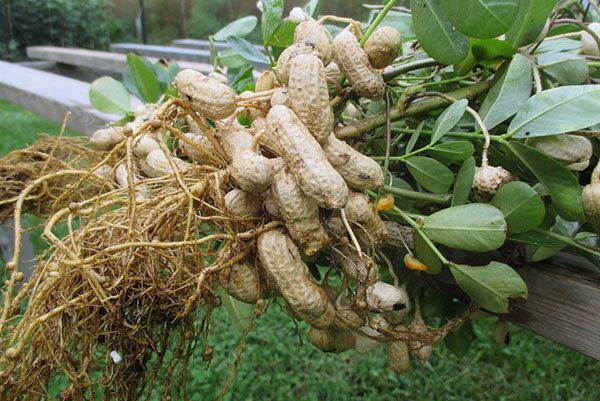


Growing peanuts
Under industrial conditions, peanuts have long been grown in central Russia. Therefore, it is quite possible to harvest at your own dacha. For this you need:
♦ Properly prepare the site - the soil is loosened thoroughly, weed rhizomes are removed and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied. Since peanuts are legumes, they cannot tolerate organic fertilizers (bird droppings, mullein, or dung).
♦ Planting: before adding seeds and beans to the soil, they are wrapped in a damp cloth for a day. You need to plant only in warm ground. seedlings can be grown at home on a windowsill or in a greenhouse
♦ Maintenance: After planting, the soil is regularly loosened and watered to promote the formation of nuts underground.
As the fruit ripens, the tops begin to dry. This is an absolutely normal process. However, severe temperature fluctuations can slow down or stop the development of fruits. If the indicators fall below 18 or rise above 28 degrees, the nuts stop growing until the temperature returns to normal. Watering should also be done in moderation. Excessive moisture can cause fungal diseases, and lack of water provokes the death of bushes.
Before harvesting, watering is stopped so that the soil dries up a little and it is easier to remove the bushes from the ground. On average, up to 50 pods are formed on one bush. They are taken out and dried in a dry, shaded room.
Caring for peanuts in the garden
The thermophilic nut is not the most capricious plant in the garden. Caring for him converges to simple, traditional procedures. If you remember to properly care for the plant, each bush will give you 30-40 beans. Each of them contains 1-7 nuts.
Watering
Peanuts are a lover of moderately moist, but not waterlogged soils. I turn to watering only when the upper layer of the substrate dries up. Guided by a simple instruction:
- When flowering - the most abundant watering. It is best to schedule water treatments in the morning. 1-2 waterings per week.
- At the end of flowering, the plant no longer needs watering, but spraying. The procedure is carried out in the evening in 1-2 days.
Prolonged rains are not the best conditions for ripening peanuts. To prevent the nut from rotting, protect the garden bed with a piece of dense polyethylene. In conditions of prolonged drought, sprinkling is shown to the plant. If you cannot resort to such a procedure, limit yourself to watering the row spacings. In total, peanuts require at least 4-5 water procedures per season.
Loosening
Peanuts are a lover of light and soft soils. Therefore, do not forget to loosen it after weeding, watering, heavy rain. Be careful not to damage the roots that ground the stems.
Top dressing
Peanuts are a plant that is not demanding on systematic fertilization. I carry out two simple dressings per season:
- As soon as the seedlings reach 10 centimeters in height.
- By the beginning of fruiting.
In both cases, I carry out complex fertilization. For 10 liters of water:
- superphosphate - 70 g;
- ammonium nitrate - 20 g;
- potassium salt - 45 g.
The second feeding is not necessary - I turn to her if the plant is developing slowly.
Weeding
Peanut shoots are not high - weeds can easily "strangle" them. Therefore, do not forget to weed the beds. Proceed carefully so as not to pull the cultivated plant out of the ground together with the weeds. I usually combine weeding with loosening - it is easier to pick up the roots of the weeds with a hoe.
Hilling
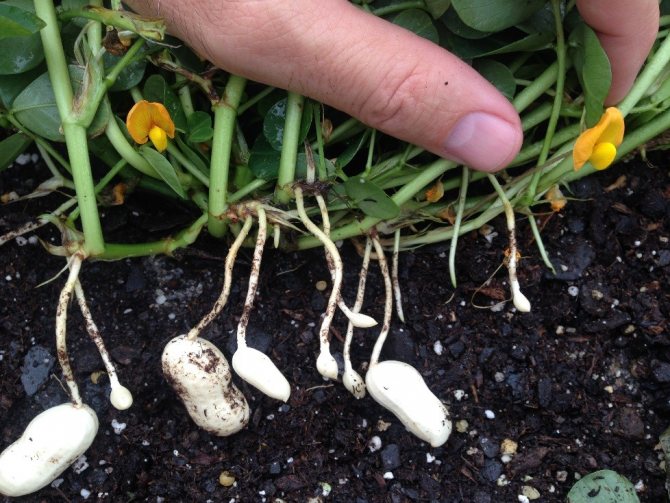
1.5-2 months after sowing (with the end of flowering), the growing peanut shoots begin to gradually descend and germinate into the soil. It is in the ground that our harvest will ripen.
As soon as the stalks begin to bend, I do not forget to huddle them up, following the example of potatoes. Gently sprinkle the "landed" shoots with loosened moist earth. So the receptacle quickly reaches the desired nutrient medium.
An alternative to hilling is to sprinkle the stems with a layer (5 cm) of mulch. In this role, use peat, last year's humus, sawdust, coarse sand.
Care
In a normal summer for the middle lane, peanuts require watering no more than 2 times a month, and in drought and during flowering after 7 days.
Caution!
Excess water is detrimental to the nut, especially at the time when the fruits begin to ripen.
After each watering, it is necessary to loosen the soil and get rid of weeds.
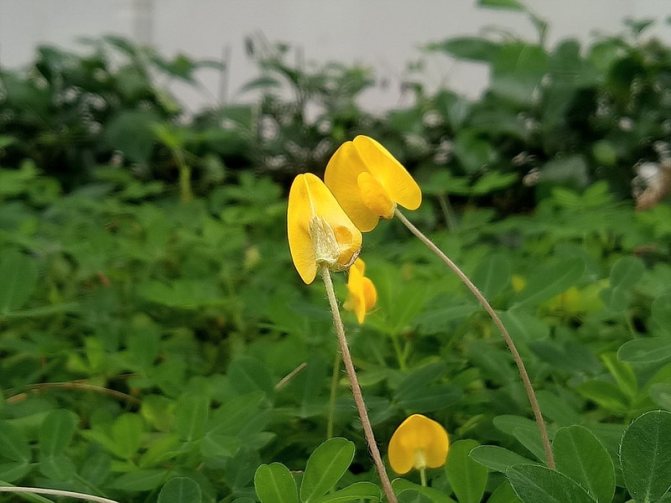
Around the second half of summer, the bushes begin to gain an intense yellow color. The flowering phase lasts 15 - 20 days, and after a month, the plant reaches a height of slightly less than half a meter. The next step is to huddle the bush, just like hilling potatoes.


Peanuts are unique in that, for the formation of fruits, it throws out arrows that grow into the soil, and future nuts are already tied there.The ovary grows rather slowly, and here it is important that, due to an excess of moisture, they do not start to rot.
What difficulties can arise when growing peanuts
Little difficulty in growing peanuts - the crop is prone to infection with common infections. Also, the plant is not averse to eating well-known pests.
Pest control
The following intruders harassed my peanuts:
- Aphids, thrips, caterpillars. I fight such pests by dusting the plantings with ash and tobacco. If this method is powerless, I turn to insecticides.
- Wireworms. Larvae of click beetles are most dangerous for peanuts. They easily gnaw the shells of the fruit and feast on nuts. A safe and effective way to deal with wireworms is with traps. I dig small holes along the perimeter of the peanut bed, where I lay out the delicacy - pieces of potatoes, beets, carrots. I cover the recess with glass, metal, slate. From time to time I open traps to catch feeding pests.
I try to prevent the spread of pests, weed the beds in time, follow the rules of agricultural technology.


aphids in the garden
Disease prevention
I will present the common diseases of peanuts:
- Powdery mildew. Separate whitish specks appear on both sides of the leaf plate. Over time, they grow, disperse throughout the leaf, which turns yellow, dries out. Then the lesion moves to the stems, inflorescences. In case of large-scale infestation, the plant can be helped by treatment with fungicides. I use Bravo, Topaz, Skor, Quadris, Horus, Switch, Ridomil.
- Gray rot. The disease affects peanut crops towards the end of flowering. The foliage is covered with brownish spots, which then move to the petioles - the latter wither and die. Fruiting stops on the plant. The formed nuts are deformed and become unfit for human consumption. Favorable conditions for the development of rot are a humid, warm environment. You can prevent the problem by planting peanuts on a hill, observing the irrigation schedule.
- Alternaria. The disease gives rise to planting in both warm and humid conditions. I define it by the black spots that grow and merge. The affected foliage dies off, and the spot becomes covered with a dense fungal bloom. In order to prevent alternaria, I do not forget to follow the rules of agricultural technology - I follow the crop rotation, disinfect the soil and seeds before planting.
- Spotting. I recognize the beginning of the lesion by small brown blotches, which grow into specks up to 6 mm in diameter. The middle of such a spot fades, becomes covered with dead tissue, surrounded by a dark purple border. The disease affects peanuts in conditions of high humidity. It can be resisted by using systemic fungicides.
- Fusarium wilting. This is root rot, which initiates the inhibition of the growth, development of the plant, and its quick death. The disease is dangerous because for a certain period it can develop secretly, and towards flowering, fruit formation, it shows itself in full force. This leads to the death of the plantings before picking the nuts. In order to prevent a dangerous disease, I try not to forget to follow agrotechnical rules, to collect nuts on time.
Now you know that growing peanuts in your own garden is real. Culture does not require scrupulous care, but it is necessary to observe important conditions for its development. Do not forget to follow the irrigation schedule, prevent freezing, properly prepare the bed, and spud on time.
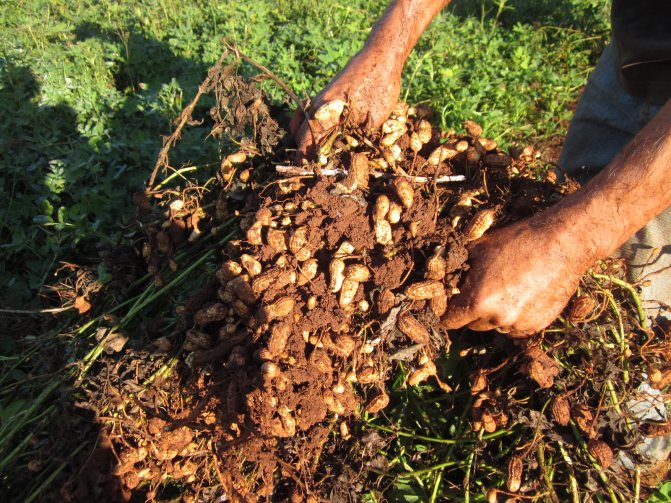
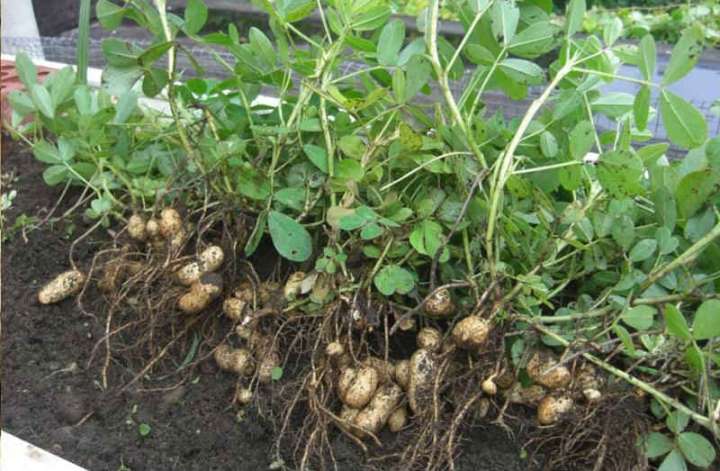
Harvesting
The peanuts are harvested before the onset of cold weather. When the nuts are frozen, they lose their taste and become unusable. When the leaves of the plant begin to turn yellow, dig out several fruits. If the seeds are easy to clean, then they start harvesting.
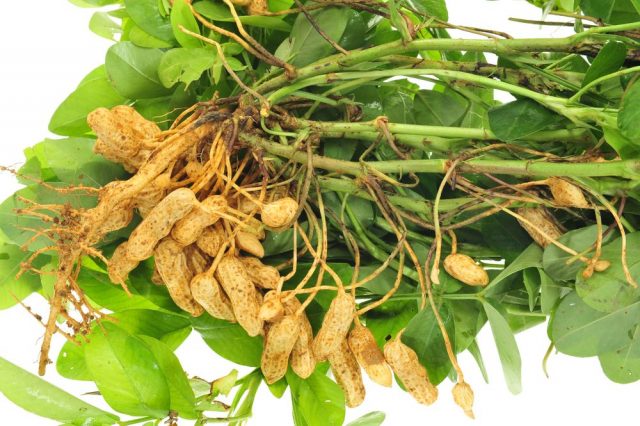


Usually, the crop is harvested when the temperature settles at +10 ° C. A dry day is chosen for work. The plants are dug up with a pitchfork or other garden tool.
The beans are collected in bunches and hung with the roots down. The peanuts are kept in a dry, ventilated area. These nuts ripen well and contain a maximum of nutrients.
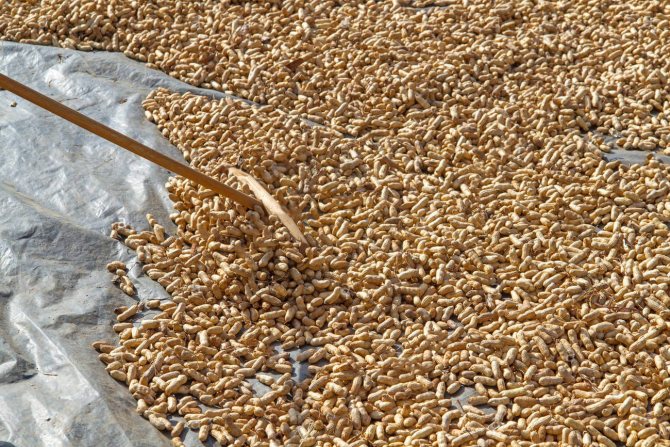
After 2 weeks, the fruits are cut off and washed with running water. Then the peanuts are dried in the heat. As a result, the shell becomes brittle and the nuts acquire a flavor. The harvested crop is kept in a dry and warm room. The beans are protected from direct sunlight and high humidity.
Pests and diseases
Peanuts can get both infectious and non-infectious diseases, signaling this by their appearance:
- Iron deficiency immediately affects the yellowing of the leaves, the manifestation of necrosis spots, gradually occupying the entire leaf area. This leads to plant death. Iron deficiency is formed as a result of blocking the absorption of iron by carbonates contained in the soil. This causes metabolic disturbances.
A lack of substance is observed in compacted soil, sudden temperature changes, waterlogging, and when the soil is oversaturated with nitrates or phosphorus. To avoid such a phenomenon, varieties should be selected that are suitable for the conditions of the area and for the soil (Orpheus, Rositsa). If the process is in progress, the drug Kugoplex is introduced into the ground according to the instructions. - Powdery mildew. Spots with a mealy bloom appear on both sides of the leaf, gradually increasing. The foliage turns yellow and falls off. The disease spreads to the stems, from which the plant dies. The pathogen (mycelium) of the disease remains on the weeds, it is not afraid of even winter frost.
Optimal conditions for the development of powdery mildew are high humidity at any temperature, plant weakness caused by various negative factors. To combat, use means of complex action. - Phylostictosis caused by the fungus Phyllosticta arachidis M. Ghochr. At first, small, then reaching 5-6 mm in diameter, brown spots all over the leaf cause it to die and fall off. The time of manifestation is the end of the growing season. The fungus is transferred from the remains of infected plants. The pathogen is released at high humidity.
Note! To prevent the disease, you should not leave infected stems in the soil, sow in one place for more than three years. When the disease occurs, a fungicide is used. - Alternaria (black spot). On old leaves, black spots appear, 10-15 mm in diameter, in the shape of a circle. At high humidity, fungus plaque (Alternaria (Fr.) Keissl.) Also affects the fruit. It appears from plant debris preserved in the soil.
Subject to agrotechnical standards and timely cleaning, the disease will not occur. - Gray rot. From flowering to harvesting, there is a danger of infection. The pathogen fungus Scklerotiniaarachidis Hanzawa penetrates through wounds and appears as brown spots on leaves, stems, fruits. The bush does not bear fruit or its beans are of poor quality.
Since there is always a threat of infection, it is necessary to change the sowing site after 2-3 years, do not overmoisten, and harvest on time. - Aphids, caterpillars are removed with wood ash and tobacco dust, sprinkled on the garden bed. Thrips are destroyed by insecticides. The worst pests for peanuts - wireworms (click beetle larvae), which eat beans, get rid of by digging holes in different places. They put pieces of vegetables in them and cover them loosely with boards or slate. When enough larvae crawl into the traps, they are destroyed.