Category: Organic Fertilizers Read: 11 min Views: 66
Manure is a quality tool for restoring soil fertility and improving its mechanical properties. Inorganic fertilizers nourish the soil with the necessary microelements, but do not improve its mechanical characteristics. Manure, which is pre-processed, successfully copes with this. Consider all methods of processing and disposal of animal and poultry manure.
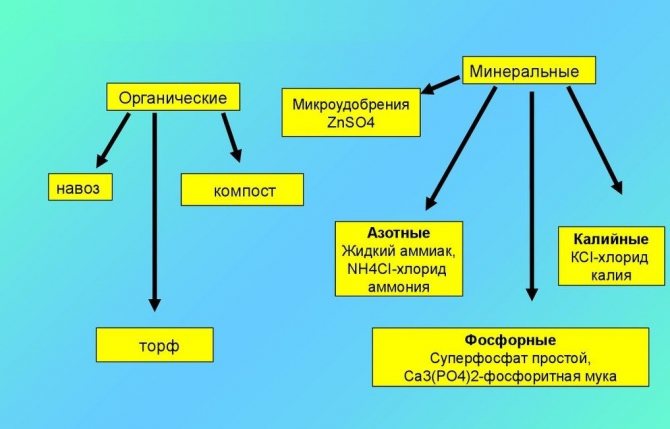
What is the difference between organic fertilizers and mineral fertilizers?
Mineral fertilizers are produced at chemical plants and, when applied to the soil, are a foreign substance for plants that must be converted into an accessible form of use.
- To become available to plants, the nutrient elements must be chelated.
- Mineral fertilizers contain only a narrow list of chemical elements necessary for plants.
- Tucs are introduced into the soil, taking into account its parameters and the needs of plants.
- Mineral fertilizers do not contribute to the formation of humus, thereby reducing the natural soil fertility.
The nutrients of organic fertilizers are more available to plants, as they are a product of the vital activity of animals, and in the ecosystem it is its natural element. The only limitation in agriculture: with improper agricultural technology, nitrites accumulate in fruits and vegetables. During processing, organic waste forms humus, which determines the level of soil fertility.
Freshness
The processes occurring in fresh manure change its characteristics and chemical composition, which is why its effect on plants and soil changes.

Therefore, conditionally manure can be
divided by the degree of freshness into:
- fresh;
- stale;
- badly stale;
- partially rotted;
- humus.
Fresh only that material is considered, from the moment of the release of which by animals no more than a week has passed, because during this period the processes occurring in it do not have time to change the properties of the material.
Stale consider the material, the shelf life of which does not exceed two months, during which it manages to lose some amount of nitrogen and moisture, and bacteria process part of the organic matter into intermediate substances that are not yet humus.
Badly stale manure can be considered, the shelf life of which does not exceed 6–8 months, because it has already lost almost all the properties inherent in fresh excrement, but still retains a little toxicity and contains almost no humic acids.
Partially rotted consider the manure that has lain for about a year, during which time it completely loses its toxicity, and the bacteria have time to process part of the organic matter into humic acids. Humus is considered to be material that has lain for 2 or more years.
Types of manure and its features
The following types of manure are obtained from animals:
- cow (mullein);
- horse;
- pork;
- bird (chicken);
- rabbit;
- sheep, etc.
Each type of manure has its own characteristics and composition, differs in the duration of the impact on the soil.
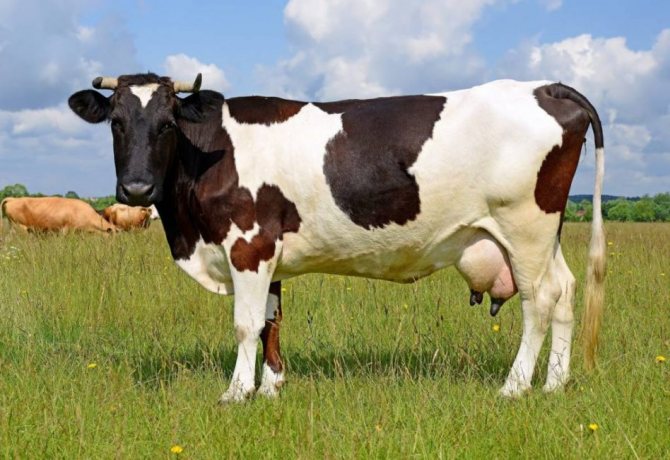
Efficiency cow dung: it shows its greatest efficiency within 2 - 3 years on light sandy and sandy loamy soils and 4-6 years - on heavy clay soils.
Bird droppings decomposes within a year. It is the fastest-acting organic fertilizer.It is convenient to use it in top dressing. However, the concentration of poultry droppings is so high that its use in the form of top dressing is possible only when diluted 10-12 times.
Horse dung - one of the best. Porous structure and rich chemical composition, high decomposition temperature, it is most effective when used outdoors and greenhouses. In connection with the mechanization of agriculture, the amount of horse manure on farms has decreased significantly. It has become less available than the mullein.
Pig manure used by gardeners to a lesser extent. It contains an increased nitrogen content (pungent ammonia odor), a large number of helminths. You cannot use it fresh. Usually mixed with horse, dolomite flour is added, composted for a year for natural disinfection (from helminths) and only then is it introduced into the soil. Pig manure is good because it has a high decomposition temperature. In combination with horse for a year of fermentation, high-quality compost is obtained.
If necessary, use the manure of other animals and birds to improve soil characteristics and increase soil fertility.


Chicken droppings.


Horse manure.


Cow dung.
Features of humus as fertilizer
Humus is animal waste, decomposed for a long time to the state of black earth, mixed with litter, the remains of feed, hay, and other biological substances.
Analyzing what to use: humus or manure as fertilizer, one can come to the conclusion that it has no drawbacks, it is considered homogeneous in composition, does not have a characteristic manure smell, but smells like earth, is an ideal fertilizer for all crops.
Types of humus in demand in agriculture:


from cattle;- horse;
- sheet;
- compost.
There are other, not so often used types of organic fertilizers: rotted sawdust from deciduous trees, pome or rice husks; recently, the use of green manure as an alternative to manure has attracted interest. Alternatively, it is also possible to use a coconut substrate.
Useful properties of manure
The basis of manure is the excrement of various animals mixed with bedding (straw, grass, sawdust and other plant residues). According to the degree of decay, manure can be divided into 3 categories:
- fresh litter and litterless manure;
- slurry;
- semi-rotten manure;
- rotted manure, or humus.
Fresh manure without bedding, not diluted with water - a thick, non-flowing form, the consistency of homemade sour cream (you can cut it with a knife like butter).
Fresh litter manure easily holds its shape, mixed with straw or other materials (sawdust, small shavings).
Slurry is less concentrated than fresh manure. Basically, this is a nitrogen-potassium liquid fertilizer, which is used for feeding all garden and berry and vegetable crops. In order not to burn the plants, the slurry is diluted in a ratio of 1: 5-6. Apply after watering. Used for moisturizing when laying compost.
Semi-rotted - this is lying in the open air for some time (3-6 months), partially dried out and decomposed. The litter is rotten, it crumbles easily in the hands. It is used as the main fertilizer for digging, especially on humus-depleted soils.
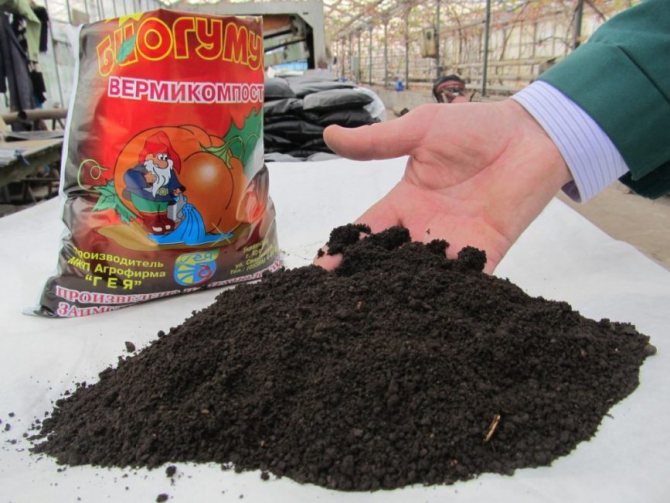
Humus is a completely rotted bulk mass, in which individual components of litter and other inclusions are not visible. The most common natural fertilizer used by summer residents.
In humus, the content of nutrients and nitrogen, in comparison with fresh manure, is 2-3 times less, which makes it possible to use it directly during the growing season of plants for feeding.
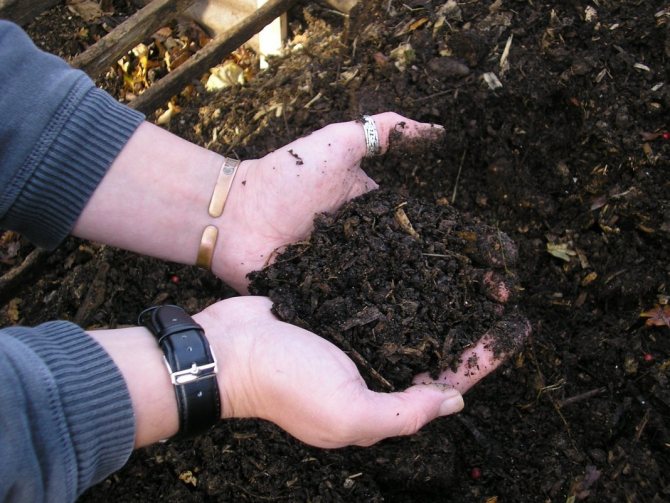


Manure-based humus. <>
Buy or do?
Most modern summer residents decide this issue in favor of independent production of fertilizers from manure. After all, it is known that buying humus is more expensive than using one prepared with your own hands.
But there are situations when there is no fertilizer of its own, but organic matter is needed (for example, in winter to feed greenhouse crops). Here, the purchase of fertilizer is advisable, but you should definitely make sure of the quality of the composition.
The activity of humus as a fertilizer is much lower than that of slurry, fresh or rotted manure.
The content of the main nutrients in manure
The composition of manure includes components that provide nutrition to plants, improve the physicochemical properties of the soil, its structure. Being a source of organic matter, during fermentation, manure forms humic compounds that increase the natural fertility of the soil.
Manure in any state (fresh, semi-rotten, humus) is a source of macro- and microelements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, silicon, sulfur, chlorine, magnesium, boron, manganese, cobalt, copper, zinc, molybdenum. Active microorganisms of manure are the main source of energy for soil microflora.
All types of manure are distinguished by alkaline properties, the alkalinity index reaches pH = 8-9 units. For cow manure it is 8.1, for horse manure - 7.8, for pig - 7.9 units. Naturally, their introduction alkalizes the soil, reducing acidity. The content of the main nutrients is presented in the averaged values of Table 1.
Table 1. Chemical composition of the main types of manure and dung
| Manure, droppings | Content, g / kg mass of manure | |||
| nitrogen | phosphorus | potassium | calcium | |
| Cow (mullein) | 3,5 | 3,0 | 1,4 | 2,9 |
| Horse | 4,7 | 3,8 | 2,0 | 3,5 |
| Pork | 8,1 | 7,9 | 4,5 | 7,7 |
| Avian (chicken) | 16,0 | 13,0 | 8,0 | 24,0 |
Why is humus not compost?
Many amateur farmers do not understand the difference between these organic fertilizers. What is compost and why can't it be considered humus?
Experts note that the difference between fertilizers is in the number of structural components. Compost contains more of the original components. The chemical composition of this combined top dressing assumes a triple predominance of carbon components (contained in straw, foliage, paper, acorns) over nitrogen ones obtained from cut grass, plant residues, and manure.
The formation of humus implies the complete decomposition of the original elements. This is necessary to exclude the presence of harmful bacteria in the composition.
When choosing which type of fertilizer is best suited for a particular site, experienced farmers examine it with their hands. The compost composition does not release water when squeezed. A quality fertilizer looks like black soil. It is moist but not liquid. Good compost smells like forest soil and is almost black in color.
Correctly aged humus (from 2 years old) does not have a nitrogen smell, its appearance resembles a dark earth. Once in the soil, it becomes food for microorganisms that produce humus, which increases soil fertility. This is the main function of such feeding. Fertilizer includes 3 initial components: manure, plant litter and soil.
Overdried humus crumbles in the hands. This indicates improper storage. A dehydrated formulation is less effective because it contains fewer beneficial bacteria.
Manure use.
Unlike mineral fats, the content of nutrients in organic fertilizers is much lower, but organic matter improves the physicochemical properties of the soil, loosens, increases the absorption capacity, enriches it with useful microflora, and provides plants with the necessary nutrients in an accessible, easily assimilated form.
Table 2. The rate of application of manure
| Manure, droppings | Introduced into the soil, kg / sq. m area |
| Cow (mullein) | 7-10 kg / m² |
| Horse | 3-5 kg / m² |
| Pork | 4-6 kg / m² Some gardeners recommend up to 10-15 kg / m² for autumn digging |
| Avian (chicken) | 1-3 kg / m² for autumn digging. In top dressing, a solution of 1: 10-12 liters of water. |
What processes are taking place in it?
In fresh excrement, many processes occur simultaneously, but for gardeners or gardeners the most important are the following:
- decay;
- loss of moisture;
- loss of nitrogen.
Decay


Rotting is a natural mechanism of the cycle of substances in nature, due to which any organic matter returns to the beginning of the cycle and becomes plant food.
Active participants in decay are:
- many types of bacteria;
- various mushrooms;
- worms.
Each of the participants in this process has its own metabolism, due to which it uses various chains of transformations of some substances into others, which provides different properties of humus, which is a waste of their life. Therefore, the more species of living beings are involved in the decay process, the more balanced the resulting humus will be.
The prerequisites for the activity of these living creatures are a sufficient level of humidity and a temperature within the range of 10-40 degrees Celsius.
Some types of bacteria remain active even at a temperature of 65 degrees, however, for most participants in the process, heating above 40 degrees leads to death or a sharp decrease in activity. Therefore, thermal drying and granulation of fresh manure suppress the activities of all participants in the decay process and keep all organic matter intact.
In addition, some types of b
The bacteria participating in the decomposition process raise the temperature of the substrate to values that are comfortable for them. This effect is often used to warm the soil or accelerate decay.
Loss of moisture
There are 2 main reasons for moisture loss:
- absorption into the soil;
- evaporation.


From the manure lying on the ground part of the water goes into the soil, taking with it some of the enzymes and various compounds that have the same toxicity as excrement.
Therefore, pus, that is, areas of fields intended for rotting or storing manure, are used for growing plants only after 5–7 years, when the toxic substances that have gone along with the water completely rot.
Water molecules do not have a rigid bond with each other, so the kinetic energy of their movement and collision pushes individual molecules out of the total mass, which is why they leave in the form of vapor into the atmosphere. Together with water molecules, manure loses molecules of ammonia and other nitrogen-containing substances, however, at a lower rate, therefore, the greatest losses of these substances occur during long-term storage of manure.
Loss of nitrogen
Fresh manure contains nitrogen in the form of various compounds, some of which are volatile, so they gradually evaporate into the atmosphere.
During drying of any kind of excrement, ammonia and skatole are lost, substances with a very strong odor and high toxicity, therefore, the material that has been lying for several months emits a very weak odor, and dry completely free from unpleasant odor.
Another part of nitrogen goes into the soil along with the seeping liquid, but the greatest losses of this material are due to the activity of humus-forming bacteria, which feed on compounds of this element.
Rules for the use of fresh manure
Since fresh manure is the most concentrated fertilizer, it is applied to the soil in autumn and winter in a field free from fruit and vegetable plants. Close up to a depth of 25-30, less often - up to 40 cm.
Spring application is provided for medium and late crops only. For early crops, manure is introduced only for autumn digging (Table 3).
Table 3. Frequency and rate of application of fresh cow manure
| Culture | Application rate, kg / m2 area | Frequency of application |
| Onions, cabbage, garlic | 4-6 kg / m² | From autumn or spring for digging |
| Cucumbers, zucchini, squash, pumpkins, melons | 6-8 kg / m² | From autumn or spring for digging |
| Tomatoes late, medium and late varieties of white cabbage | 4-5 kg / m², for cabbage up to 6 kg / m² | From autumn or spring for digging |
| Dill, celery | 5-6 kg / m² | From autumn or spring for digging |
| Carrots, potatoes, beets | 4 kg / m² | From autumn or spring for digging |
| Berry (currant, raspberry, gooseberry) | Layer up to 5 cm | Annually only in autumn |
| Pome and stone fruit crops | Up to 3 kg for each tree | Autumn with an interval of 2-3 years |
| Strawberry wild-strawberry | 10 kg / m² in row spacing | In autumn, once every 3 years |
| Grapes | Solution: 1 part mullein to 20 parts water | In autumn, once every 2-4 years |
In winter, fresh manure is spread over the snow. After the snow melts, it falls on the soil and is dug up in the spring. The planting depth is the same as in autumn.
The application rate on snow is 1.5 times higher. This is due to the fact that during the winter, part of the nutrients is lost (nitrogen). Usually, manure is left in a pile for 2-3 months before application. During this period from the high temperature of "burning manure" part of the weed seeds die. If the manure from the barn immediately fell on the field, then it is better to leave it fallow, destroying the weeds in the summer.
Remember that any crops, especially vegetables, overfed with organic matter, sharply reduce keeping quality. Vegetable and especially root crops are more often affected by root rot, the incidence of late blight and powdery mildew increases. In order not to overfeed the plants, use the data in Table 3.
Table 3. The volume of the mass of manure, kg / 10 l bucket
| Fresh manure | 10 l bucket |
| Cow without bedding | 9 Kg |
| Cow bedding | 5 Kg |
| Horse | 8 Kg |
| Slurry | 12kg |
| Humus | 7 kg |
What humus consists of. 1 Technology of preparation and storage rules for perennial fertilizers
At home, the production of humus fertilizer depends on the material you choose. If we are talking about rotted manure, then the substrates of animals are placed in a box or bag, often dug out. Each layer is overlaid with peat or straw in order to preserve the maximum amount of nitrogen and other minerals. In winter, a pile of manure is covered with soil, under which the process of overheating takes place until the spring period.


The combined cooking method is the most optimal. "Svezhak" is laid out in a box or other container in layers, at first it was loose. Within 5 days, the temperature in the stacks will rise to 60 degrees. Only after that do the layers begin to be compacted. This is how they do it with each new portion of animal excrement. The layer is brought up to 1.5 m, covered with peat (layer - 30 cm), mown grass. It is recommended to let the mass brew and brew for 5-6 months.
The storage of humus is carried out in two ways: cold and hot. Hot provides for a loose content of humus heap. In this case, the decomposition of manure is faster and more vigorous, but a lot of nitrogen is volatilized. For a cold one, a site of compacted soil is needed. Animal excrement is placed on it, covered with earth and dry leaves (30 cm) Covered will prevent the risk of freezing and getting wet from the rain. As with compost, it is stacked and transferred in layers equal to the layers of manure.
The resulting mass is brought under the trees mainly in the autumn. requires 15 kg of fertilizer. Top dressing is repeated after 2-3 years. Vegetable crops need 5-8 kg. Dates of fattening - spring-autumn. Those who are interested in whether it is possible to add a decomposition product under the currant will receive a positive answer. Gooseberries, currants and mulch should be done in the autumn, moreover, annually.
Leaf humus is most often used to fertilize crops.But you can make this nutritious fertilizer not only from leaves. It is also important to store it properly so that it does not lose nutrients.
Humus - what is it? Inexperienced summer residents often ask such questions. Fertilizer of organic origin is called humus. With its help, you can saturate the poor soil with all trace elements necessary for the growth and development of plants. Humus is easy to do with your own hands. All the ingredients necessary for this can be found in any subsidiary farm.
Using fresh mullein for top dressing
Mullein can be used to feed vegetable and horticultural crops during the summer season. Low-concentrated water fermented solutions are used for feeding.
Preparation of the solution: any container (more conveniently a galvanized barrel) is 1/3 filled with manure, filled with water to the top, and closed. Stir once a day. Fermentation lasts 1-2 weeks. This is a stock solution.
To feed berries and fruit trees, a working solution is prepared: 1 bucket of mother liquor from a container is diluted with water 3-4 times. Top dressing is carried out in the phase of young leaves. The working solution is applied after watering under the root at the rate of 10 liters of working solution per 1 m². Be sure to mulch.
For vegetable crops, the working solution is prepared at the rate of 8-10 liters of water per 1 liter of mother liquor. Top dressing is carried out during watering or after watering for mulching, 1-2 times during the growing season, alternating with mineral fertilizers (if necessary).
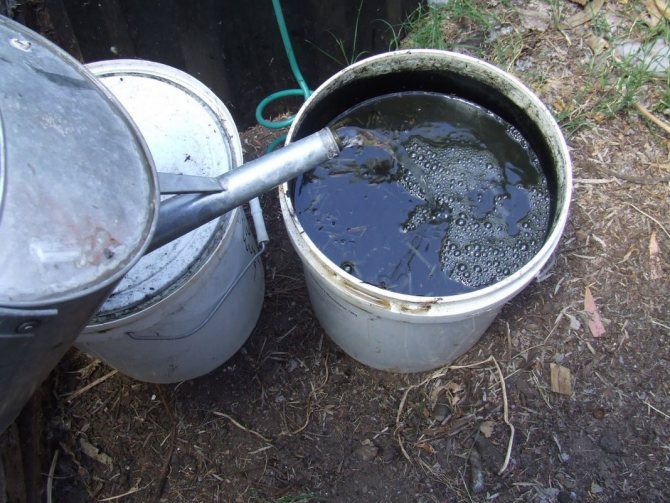


Preparation of liquid fertilizing from manure.
Humus and feeding
Even the most humus-rich soil, for example. steppe chernozem, in agriculture it needs to replenish humus reserves. Under natural conditions, its natural inflow is provided by winter-spring decay of dead plant residues and waste of wild animals. This is not the case in the cultivated area, and the humus horizon is continuously thinned out by commercial crops during the growing season, leaching under the influence of precipitation and simply irrigation water. Operational fertilizing with mineral fertilizers allows you to take good harvests on lean land, but replenishing the natural loss of humus will significantly reduce the cost of them, as well as eliminate the risk of overfeeding the plants or a sharp drop in yield in unfavorable years.
Application of semi-rotted manure
Semi-rotten manure is less concentrated and can be used directly in top dressing or as mulch.
For dressing, a solution is prepared in a concentration: one part of the fertilizer to 10 parts of water. Stir and bring under garden and berry crops.
Trees are watered along the outer diameter of the crown on loosened soil or in furrows cut in 1-2 rows around the crown.
Under the bushes, top dressing is applied, departing 15-20 cm from the bushes.
Under vegetable crops in the furrows of the row spacings (if they are wide) or in the furrows cut along the bed.
It is impossible to pour a solution of a semi-rotten mullein under the root of plants.
Top dressing is covered with soil, if necessary, watered and mulched.
The semi-overripe mass is a good fertilizer for cabbage, pumpkin seeds, and spinach. With such fertilization, these crops will be excellent predecessors for root crops, sweet peppers, tomatoes, eggplants.
Effects of manure on crops
But here, too, you need to be careful. Manure is not suitable for all vegetables as a fertilizer. Cucumbers love this kind of feeding. And for beets, potatoes, cabbage, carrots and other vegetables in this type, manure is unacceptable. It is more optimal to scatter it by the fall. Having mixed with plant residues, part of it will decompose until spring. If the soil is loosened with a garden pitchfork, the manure will remain on the surface of the soil and continue to decompose, bringing the maximum benefit to the plants.
Manure has another great quality: it decomposes very slowly.And this is good, because as they release useful substances, plants absorb them almost completely, and only a small part of useful substances can be washed out or evaporated from the soil.
Application of rotted manure
Formation of humus
Rotted manure, or humus, is the main source of humus entering the soil. Humus is a homogeneous, loose substance of dark brown color, with a spring smell of a healthy soil substrate. Formed by fermentation of manure under the influence of microorganisms. As a result, humus, humic acids and simpler mineral compounds are formed. The composition of humus is light. 1 m³ contains 700-800 kg of humus. In a standard 10 liter bucket, its amount is 6-7 kg. Healthy matured humus is odorless.
The higher the humus content in the soil, the more fertile the substrate is considered. So, in chernozems, the humus content is 80-90%, and in soddy-podzolic soils, its amount decreases to 60-70%.


Putting manure into compost for roasting
Humus properties
Humus has the following agronomic properties:
- improves soil porosity;
- increases the ability to retain moisture;
- enhances photosynthesis, thereby increasing the productivity of agricultural crops;
- activates the growth and development of plants;
- increases resistance to diseases and pests;
- populates the soil substrate with useful microflora;
- reduces the accumulation of heavy metals in products;
- improves the decorativeness of flower crops, etc.
How to prepare quality humus?
- provide a shaded area for storing components;
- Fencing with improvised material so that the front wall is open;
- the components are stacked in layers, 10-15 cm; components - straw, straw cutting, leaves, fresh, semi-rotten manure;
- each layer is spilled with water or diluted slurry, mullein solution;
- cover on top with a film or other material that does not allow water to pass through (from rain);
- air access through the vents with a film shelter is required;
- periodically shovel and watered with water in dry weather; humidity during fermentation within 50-60%, temperature under + 25 ... + 30 * С;
- to accelerate fermentation, it is recommended to spill layers of components with preparations (Baikal EM-1, Ekomik yielding, Shining-3 and others).
If all requirements are met, mature humus can be obtained within 1-2 months.
In addition to the proposed one, there are other methods of rapid processing of manure into humus or compost, which is also used for fertilizing and feeding garden crops. For example, vermicomposting with California worms, aerobic and anaerobic composting.
Processing methods
The waste product of livestock and poultry is a large amount of dung and manure. This fact can be a good source of income if properly managed. Incorrectly stored and disposed waste becomes a source of groundwater pollution and infection, therefore, it poses a certain danger to the environment. For manure to be beneficial, it must be properly processed.
Fresh manure is not used to fertilize seedlings, since it heats up very much during decomposition and burns the root system.
Manure processing methods:
- composting;
- vermicomposting;
- granulation;
- fermentation with bacteria;
- infusion.


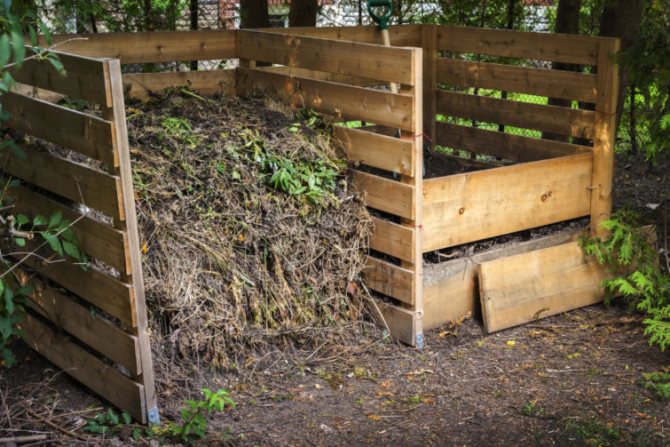
Composting
This method is widespread among gardeners, it is also used on livestock farms. Wastes of all types of agricultural animals and birds are composted. During composting, a high temperature rises, with the help of which the manure is converted into a valuable agricultural product - compost.
The advantages of the method:
- The high temperature destroys pathogens (disinfects).
- As a result of processing, high-quality humus is obtained for soil fertilization.
To improve the properties of the final product (humus), plant components are added to the compost heap - straw, hay, weeds without seeds, peat, fallen leaves, sawdust.
At the first stage of composting, fermentation of feces occurs with the formation of an elevated temperature. After the mass has been repaired, sawdust, peat or straw can be added. This is necessary to conserve valuable nitrogen.
Peat or sawdust compact the mass and block the free access of oxygen, which ensures the preservation of nitrogen. After a couple of months, high-quality humus is formed from the compost heap. Sometimes it takes three months to transform, depending on weather and other conditions.
Processing is carried out by special bacteria that naturally form in the compost heap.
Vermicompost
This method involves the use of special worms that recycle the compost heap. In the first case, the processing is carried out by microorganisms, and in the second (vermicomposting) - by earthworms. Worms have a double benefit: they process manure and loosen the soil after fertilization.
The vermifarm is a common occurrence in modern horticulture. These compact structures can even be stored in an apartment: the vermi farm consists of boxes with a worm. Worms eat any food waste and plant organics, converting them into vermicompost.


You can buy a vermicomposter or make yourself from plastic boxes. The number of crates depends on the amount of food waste in your household. Small holes are made on the bottom and side panels of the boxes using an awl, and then inserted into one another. Since worms prefer to dwell in the dark, opaque boxes are best.
Even ordinary earthworms are suitable for vermicompost. They can be dug up in the forest or in the park.
In the lower drawer, the bottom is not pierced, since moisture will collect in it. The topmost drawer is covered with a lid. The openings in the drawers are necessary for ventilation, but they should not be large. If you make large holes, flies will fly in.
Dry foliage, sawdust or cardboard egg trays are placed on the bottom of the boxes: they will retain moisture and provide air ventilation. Fill a third of the container with filler and moisten well with a spray bottle. Put the sweet ingredients (fruit peelings) on top and place the worms. After about a couple of days, food waste can be added to the containers.
Experienced gardeners advise against overloading containers with food for worms. Until they have processed 2/3 of the waste, do not add a new batch.
The vermicomposter can be located in any place convenient for you, in the summer it is taken out to the balcony. However, if the containers for vermicompost are made of transparent plastic, it is not recommended to take them out onto the balcony (or open space). put these containers in a closet or closet: worms love the dark.
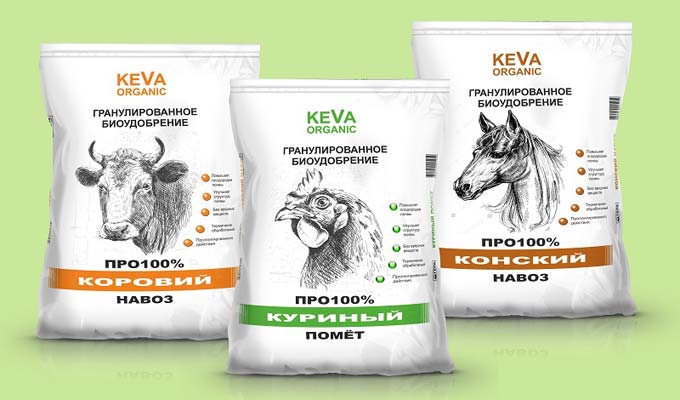


Granulation
Granulation is the drying of a product at high temperatures, depriving it of moisture. Granular manure has an unlimited shelf life. This fertilizer never goes bad.
Characteristics of granular fertilizer:
- Universal food for garden plants;
- dissolves quickly in liquid;
- is in a form, convenient for plants, easily assimilated;
- nutrients are in organic form;
- it has a prolonged action: it gradually releases nutrients to the soil;
- nutrients are practically not washed out of the soil by precipitation;
- there are no helminth eggs, weed seeds and pathogenic microorganisms;
- perfectly retain their shape, do not cake and do not deteriorate;
- there is no unpleasant smell;
- non-toxic and safe for humans and animals.
The introduction of organic fertilization into the soil increases the yield by 25-30%. This is already a confirmed fact. The ripening time of the fruits is noticeably reduced, and the taste characteristics increase. A sufficient amount of vermicompost in the soil evens out its acid-base balance, which also has a positive effect on increasing productivity.
In granular manure, a large percentage of nitrogenous substances are retained, which volatilize during composting.
The granulated manure is pH neutral. Granules dissolve well in liquid. In the ground, the granules behave selectively: in the presence of moisture, they swell, in the absence, they give it to the soil. They structure the soil well, loosen it and make it crumbly. This is very important for heavy soils - loam, clayey rocks. Structuring the soil enriches it with oxygen and provides air exchange.


Method of using granules
In the spring, the soil is prepared for planting by mixing the fertile layer with the granules. 0.1 kg of granules is consumed per 1 m2 of plot. The fertile soil layer is enriched to a depth of 10 cm. After fertilization, the site is thoroughly irrigated with water. The next day, you can plant agricultural crops (vegetables).
You can also make an aqueous solution for irrigation under the root from the granules. To prepare a working solution, the granules are poured with water and left for two weeks. Then the solution is thoroughly mixed and used for irrigation of horticultural crops. Details of using granules for irrigation can be found in the instructions for the preparation. Also, the instructions indicate the features of watering various horticultural crops.
Fermentation
Compost can also be prepared by fermentation. This process involves the decomposition of biomass by microbes without oxygen. An example of fermentation is sauerkraut, yogurt.
To create conditions for fermentation, dig a hole 60-70 cm deep and fill it with plant components. Then the raw material is well moistened and crumpled to displace the air. After that, the raw materials are covered with a thick layer of earth so that it exerts pressure with its mass. After that, the soil is irrigated with a preparation with microbes diluted in water. Instead of a pit, raw materials can be placed in plastic containers of a suitable volume. After a couple of weeks, the compost is fully ripe, it is used as mulch or fertilizer for the soil.
Fermentation bed
Livestock and poultry produce huge amounts of droppings that require environmentally friendly disposal. Together with manure and urine, ammonia is released, the vapors of which negatively affect the well-being of the cattle.
To eliminate ammonia vapors, powerful ventilation is required, which leads to additional costs. Regular cleaning of the barn is also not profitable, as it requires additional investments. There is only one way out - the processing of waste with special bacteria in the barn itself. For this, a fermentation bed is produced.
Litter benefits:
- removes the smell of ammonia in the barn;
- reduces the cost of additional ventilation of the barn;
- cleaning of the litter is carried out once a month or once a quarter;
- used as fertilizer in the garden without additional preparation.
The bio-litter must be activated in the warm season, otherwise additional energy will be consumed for heating. Activation is carried out only in a layer of middle fraction sawdust, since this is a natural breeding ground for bacteria. First, sawdust is poured onto the floor in the barn, then bacteria are scattered on them - and the litter is mixed. It is necessary to strictly follow the instructions in order to properly activate the activity of bacteria.
Litter fermentation will start in 6-7 days. At subzero temperatures, bacteria die.


Advice
The mat should be placed on a clean floor and kept warm and dry. When sawdust and bacteria are spread on the floor, the mat should be well moistened with a watering can (shower).The water should not be tap water, as the chlorine will kill the beneficial bacteria immediately. It is better to take rainwater, or ordinary water is pre-defended. After thorough moistening, the litter is mixed with a shovel. Care must be taken to spread the bacteria evenly among the sawdust.
After a week, check the temperature of the litter. If it has increased, then the microorganisms have begun their work. Launch animals. In order for the bacteria in the litter to process the droppings well, it is necessary to observe the temperature regime in the barn and humidity. If there is too much or too little moisture, bacteria can die. With a lack of manure, they will start starving, with an excess of waste, they will poorly process raw materials. To ensure breathability, the bedding is periodically turned over.
Bacteria are very sensitive to various chemicals, so it is not recommended to process the bedding to kill rodents and parasites.
In order for the litter to work at full strength, it is necessary to periodically renew it - pour in powder with fresh bacteria. However, the rate of introduction of microorganisms to maintain the working condition of the litter is significantly reduced: by about two times.
The use of a fermentation bed solves the problem with the disposal of waste from livestock and poultry. The legislation prohibits storing untreated manure on the site, as well as disposing of it in an illegal way. Therefore, the purchase of litter frees you from problems with legislation and serves as an aid for fertilizing a garden plot, a greenhouse and a flower garden.


The use of humus in summer cottages
Humus is used for:
- improving soil fertility;
- fertilizing and feeding crops during the growing season;
- preparation of soil mixtures for growing seedlings;
- preparation of soil mixtures for indoor flower crops, etc.
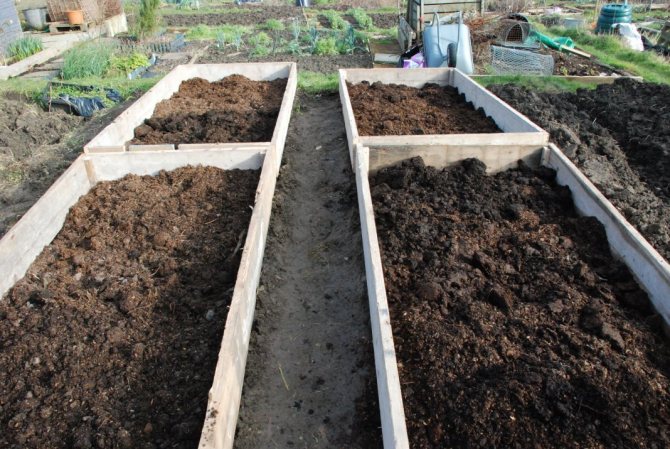


Adding manure to the beds. <>
How to apply it in the fall?


Method of applying manure in autumn depends on the subsequent use of the site - if it is left under steam, then it is enough to scatter the fertilizer over its surface and then dig it up, if in the spring it will be used for planting seeds or seedlings, then excrement must be prepared.
The fastest preparation methods are:
- hot composting with bacterial treatment;
- production of fertilizing concentrate.
For hot composting, manure and shredded garden vegetation are placed in layers in an insulated box or insulated pit. To grind it, you can use one of the devices that we talked about in this article.
The compost is then watered with water and bacterial preparations, and then covered with a tarpaulin to reduce heat loss and reduce air access. Every 2–3 days, the mixture is thoroughly agitated... After 2-3 weeks, such compost is ready, so it is scattered over the area by hand or using a manure spreader, then the area is plowed, watered and treated with bacterial preparations.
The concentrate is made in the same way as described above, in sunny weather it is kept for 7 days, in cloudy 10, then it is applied to the fields without diluting with water, and after a week the site is plowed or dug up.
Top dressing will be more effective if use shredded garden or garden vegetation together with excrement, the same weeds or grass cuttings. Top dressing with crushed vegetation not only saturates the soil with organic matter and attracts worms, but also has a beneficial effect on the structure of the soil, because even highly crushed plant residues perform the same function as sand, that is, increase the ability to pass water.
disadvantages
Natural fertilizer has practically no drawbacks. The only nuance that many farmers or gardeners may not like is the specific smell of droppings.For this reason, some people find it unpleasant to work with such a fertilizer.
But all the advantages of cow dung override those uncomfortable sensations that a person can get in the process of corresponding work.
There are also adherents of the use of mineral supplements. The use of organic feeding for such people is a relic of the past, outdated methods that have lost their relevance and effectiveness.
In fact, this opinion is erroneous. The manure contains a number of trace elements and substances useful for plants.
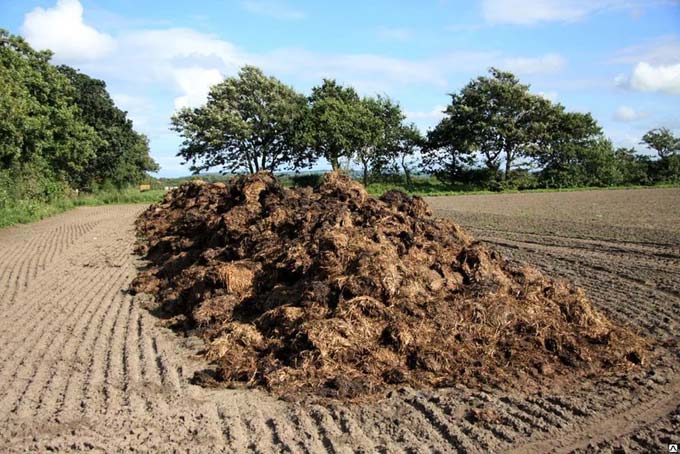


Steps to follow when laying compost
To create humus from plants you need:
- Knock down a wooden box, you can replace it with a regular pit.
- Plants are laid inside, which will be used for compost. Better to shift the pile in layers, alternately mixing soil, plants, manure, droppings or fertilizers with a high concentration of nitrogen. The land must be shifted, as it provides access from microorganisms, worms and insects. You can replace the land with manure or bird droppings. If possible, it is better to give preference to manure.
- From above, the pit should be covered with a film or roofing material. It should be in this state for 1 year.
- The compost should be moistened and stirred periodically.
If it is possible to add raw materials to the heap, the same sequence can be used. It is recommended to create a pile with up to 5 layers. The surface layer is 7 cm thick.
Worms and larvae


When a pile of manure or dung lies on fertile soil, various worms penetrate from it into the pile, which, like bacteria, feed on organic matter.
Having found worms in manure, as well as in almost ready-made humus, do not be afraid, on the contrary, such humus will be more balanced for plants than obtained without the participation of these organisms.
After all, earthworms (they are often called dung) are the same participants in the cycle of organic matter, like bacteria, but they recycle organics according to a different principle, resulting in vermicompostcontaining humates and effectively supplementing humus.
The situation is the same with various larvae, with the exception of bears, which pose a serious threat to vegetation.
The bear larvae look pretty
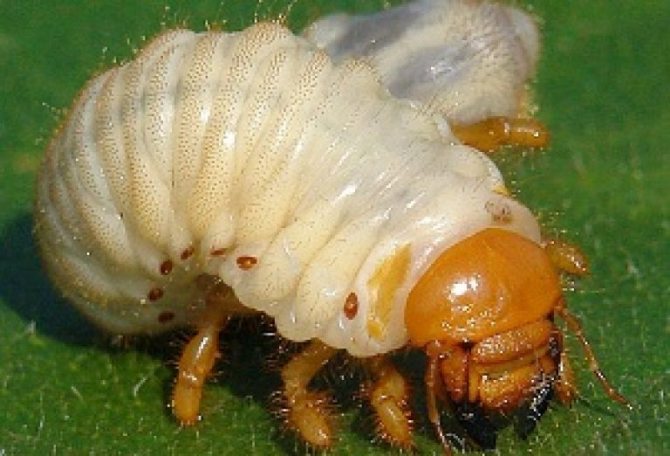


To avoid their appearance in the finished humus, it is necessary to carefully examine the substrate during each tedding and remove the detected pests from it. In addition, they do not survive hot processing of manure or dung.
Sapropel or lake (river) silt
Sapropel is the bottom sediments of relict lakes containing a large amount of minerals and organic matter. They have been forming over thousands of years. Silt is of less value, it is obtained from swamps, ponds and rivers. These materials were used as fertilizers in ancient Egypt. So, when the Nile flooded, river silt fell into the fields, turning the poor sandy soil into fertile.
In appearance, sapropel resembles a semi-liquid or granular black mass. Silt is lighter. In wetlands, the fertilizer contains a lot of peat, it has an acidic reaction.
Sapropel is formed by the decomposition of the remains of algae, plankton, crustaceans, fish and their excrement. As a result of the work of the anaerobic flora, organic matter is processed to humus. Sapropel contains many substances that stimulate the development of plants, vitamins, hormones, amino acids. With complete decomposition, trace elements are released - iron, magnesium, manganese, zinc, selenium, boron, molybdenum, bromine. They come in part from the bottom soil.
The composition of sludge and sapropel is always mixed, depending on the specific place of its production.
On average, the material contains:
- Organics - 40-79%
- Nitrogen - 2%
- Sodium - 0.6-3.4%
- Potassium - 2.7-33.5%
- Phosphorus - 0.14-0.5%
- Ash - 2-19%
According to the predominance of the main element, sapropels are conventionally divided into:
- Carbonate
- Silica
- Organic
- Glandular
Organic fertilizers are best suited for fertilization. Material is extracted in swampy areas from reservoirs with stagnant or running water, using excavators or dredgers. The equipment is produced both for large industrial developments and for small amateur ones. Summer residents living near lakes and ponds receive silt using ordinary garden tools (shovels, pitchforks, rakes).
After receiving the sapropel, it is dried so that the processes of decay or fermentation do not begin in the mass, and nitrogen does not evaporate. The dry material is sold as a powder, granule or tablet. At home, sludge can be spread out on a site near the shore or in a special pit. When the material dries, it is crushed and transported to the fields.
Silt deposits contain little phosphorus, so it is often added artificially. Mixtures of material with crushed serpentinite are widely used. Enrichment is also carried out with superphosphate, bone meal or ash. The proportions depend on the primary composition of the fertilizer.
Silt and sapropel are excellent fertilizers that replace manure. Even when it dries, nitrogen is not lost in it, since it is in a bound form. The material does not contain harmful microorganisms, helminths or weed seeds. Many substances have a bactericidal effect and can disinfect contaminated soil. Sapropel is often included in composts based on animal excrement. It makes fertilizer safe and accelerates decomposition processes.
After adding silt, the soil becomes loose, but at the same time it retains water better. Useful material for sandy and sandy soils. For clay and loam, it is recommended to mix it with straw, grass or bedding manure. The average pH of sapropel is 7, but there are varieties for acidic and alkaline soils.
The yield of agricultural crops after the application of such fertilizer increases almost 2 times, because it stimulates the growth of the green part, strengthens the root system. It can be applied to the soil at any time of the year, but it will be most beneficial for spring feeding. The positive effect on soil and plants lasts 8-12 years, which is 3-4 times longer than that of manure.
Comparison
Many gardeners consider poultry droppings to be the best humus. It ripens quickly and contains all the beneficial trace elements. However, it has its drawbacks: strong odor, concentrated organic matter. Humus must be applied with great care so as not to harm the root system of the seedlings.
Humus from cattle and horse manure does not emit any smell, but the maturation process takes several years. In this regard, bird humus is much more effective if it is necessary to urgently fill the soil with food.
Humus from the leaves of trees does not contain nutrients, however, it perfectly structures the soil and retains water at the roots of plants. Also, the leafy substrate attracts soil worms, which loosen the soil and promote air exchange.
It can be made quickly, without worrying about overdose and harm to seedlings. Making leaf fertilizer is not difficult, humus material can be found everywhere. Leaf humus is also brought in immature: it will come in the ground. To do this, after harvesting, foliage is distributed over the ground and dug deeply. Ripe foliage is brought into the ground in the spring.
Leaf fertilizer is used to shelter vegetable seedlings during dry weather. A layer of rotted leaves retains moisture and prevents it from quickly evaporating from the surface of the earth. The leaves are also used to protect flower bushes and vineyards during the winter season.


When not to use
You cannot use fresh mullein to fertilize plants. In the process of decomposition of feces, chemical reactions occur that negatively affect the roots of vegetation.
It is also not recommended to use fertilizers that have white blotches or plaque, indicating the presence of fungal spores. Do not rush to throw away moldy manure, as in the process of decomposition this problem will be eliminated, and as a result, you can get a high-quality fertilizer that is suitable for use.
Direct feeding of some plants with manure has a detrimental effect on the further growth process, therefore it is important to practice planting crops in soil that was fertilized with manure at least a year ago. Such plants include celery, parsley, carrots, beets and radishes.
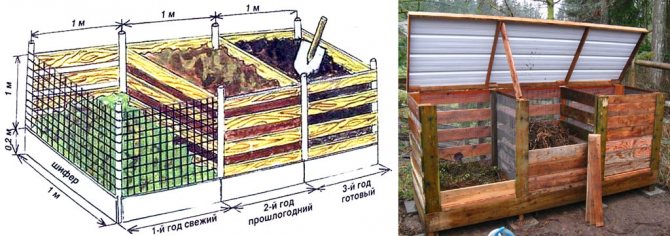
How to make a compost bin?
The easiest to use for this purpose matching wood-plywood box from any oversized equipment, in most cases such boxes are sheathed with thick plywood and have sufficient strength.
If there is no such container, then the box can be made from sawn boards 25 mm thick and plywood of a suitable thickness (for walls 5–7 mm, for floors and lids 10–15 mm). The outer body (frame) is assembled from the boards, which is then sheathed with plywood from the inside, butting it only on the boards.
If there is no plywood, then the box can be made from some boards, but in this case the outer body and bottom are made of ordinary boards, and the walls are sheathed with a board 15–20 mm thick.
Regardless of the cladding material the outer frame is reinforced with metal corners or tape so that the substrate does not squeeze the walls out. It is not necessary to put the planks close to each other, however, the distance between them should be 1–5 cm, the smaller it is, the easier it is to deal with the spillage of the substrate, and the more, the fewer boards will be required for its manufacture.


Boxes with a large gap between the sheathing boards must be lined with a mounting mesh, which is used when plastering surfaces with low adhesion to cement mortars.
The mesh is attached with a stapler or small nails. If the box is sheathed with plywood or boards laid close to each other, then ventilation holes with a diameter of 1–3 cm are drilled in the walls and bottom, located in increments of 20–40 cm.
In cold regions, as well as where it is impossible to insulate the box with dry grass from the inside, it is sheathed with polystyrene from the outside, sealing most of the cracks and leaving only small slots at the bottom and top for exhausting gases.
Description of natural fertilizer
One of the most common ways to improve the quality and nutritional value of the soil is to apply manure. Cow dung is very popular with gardeners. It is affordable and healthy for plants.
The mullein is suitable for almost all types of soil. Regular application of such top dressing contributes to the improvement of soil quality, active development of agricultural crops and obtaining a rich harvest.
On an agricultural scale, mullein is of great value. Thanks to him, crop yields increase, the immune system of plants is strengthened, which reduces the risk of developing serious pathological processes.
Cow manure is actively used in small summer cottages, as well as garden plantations. Many agricultural crops (with the exception of some plant species), as well as garden flowers, prefer to “feast on” manure. It is advisable to periodically introduce organic fertilizing into the soil of indoor plants, but many growers refuse this method due to the specific smell of the mullein.
Siderata
Siderata are annual plants that are planted as organic fertilizers. They quickly gain green mass. Within a few weeks after planting, they can be mowed or buried in the ground. The name comes from the Latin word "sidera" - "a star that receives strength from the sky."
There are about 400 types of green manure. They belong to different families, each with its own characteristics.
Most often, the following is used as a green fertilizer:
- Legumes (peas, vetch, lupine, alfalfa, clover) Bacteria collect near their roots that can accumulate nitrogen from the air. The content of the element in the soil increases by 40-60%. At the same time, it is in a bound form, does not volatilize and is completely available for plants.
- Cruciferous (mustard, oil radish) They are able to convert sparingly soluble phosphorus compounds into an accessible form, repel nematodes and other pests. In the process of decomposition, cruciferous plants replenish the soil with lipids, sulfur, potassium, lignin, and organic acids.
- Cereals (rye, oats, timothy, wheat) Cereals prevent the growth of weeds, have an antifungal effect (prevent root rot, powdery mildew). Detrimental to nematodes. They enrich the soil with potassium, phosphorus, nitrogen.
- Buckwheat Thanks to the developed root system, they loosen the earth, increase the amount of oxygen and water permeability in it. Since the rootlets are 100-150 cm long, buckwheat crops mobilize nutrients from deep soil layers. They reduce the acidity of the soil.
- Compositae, or aster (calendula, sunflower) These species provide a lot of green mass - the main source of nitrogen for the soil and the basis for the formation of humus. The roots penetrate to a depth of 1.5-2 m, loosen the soil.
- Hydrophils (phacelia) They have a developed root system, a large volume of stems and leaves. Attract melliferous insects. They are recommended to be planted near orchards, beds with zucchini, watermelons, pumpkin, tomatoes, cucumbers.
Siderata are sown at different times of the year. In the spring, they need to be dug into the ground no later than 3 weeks before the planting of the main crop. Many cereals and vetch are sown for the winter. By spring, they are already green and can serve as an excellent fertilizer. In the summer, between the beds, you can plant mustard, phacelia, which will scare off pests and attract honey plants.
After mowing, the green part of the plants can be left directly on the field, dripping. But a more efficient method of use is to add to the compost. The grass is mixed with low-lying peat, kitchen waste, dung or slurry. By the next season, they receive a complex fertilizer.
If you are interested in what can be used instead of manure, then green manure is an excellent solution. In terms of their characteristics, they even surpass animal waste.
Here are the benefits they bring to soil and crops:
- Enrich the soil with nutrients - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, sulfur
- They are a source of organic matter for the reproduction of useful microflora, increase the amount of humus
- Suppress the growth of weeds
- Prevents soil erosion and degradation, increases soil fertility
- Ward off insect pests, nematodes
- Prevents the growth of harmful fungi and pathogenic microbes
- Attract pollinating insects during flowering
- The roots of green manure plants push the soil, improve its aeration, and retain water
- Some species with a developed root system are able to move useful minerals from deep soil layers to the surface, making them more accessible to vegetables.
Composting organic
Enrichment of a mullein in a personal plot is possible with the help of composting. A compost bin with one or more sections is used. Drainage from small branches is laid at the bottom. In layers, organic waste is laid (mowed grass, tops, cleaning, etc.), manure and garden soil, it is possible to add peat. You can use special EM drugs to speed up the process. The total height of the shoulder should be between 1 and 1.5 meters. On average, composting takes about a year.
A popular trend in organic farming is vermicomposting. A method of processing organic substances using worms, invertebrates and microorganisms. This method allows you to get environmentally friendly, safe food for the site.
After processing the organic matter, the worms, along with the fertilizer, are applied to the beds, where they continue to process the soil.
Cow dung compost can be used for digging. The application rates are different for different crops. For cabbage and tomatoes, 100-200 g of compost per square meter is enough. meter of beds. To create a site for planting cucumbers requires the introduction of 300-500 g of compost.
How to apply in spring?


If the manure is not stale, but really fresh, then it can be applied in the spring only to the area left under fallow, after which it is necessary immediately plow it up and treat it with bacterial preparations.
If there are any necessary plants on the site, then fresh manure can be applied only after it has been converted into liquid top dressing or humus. If the "fresh" manure turned out to be very stale or almost rotted, then it can be laid out in a ring around mature strong plants, stepping back from them by 5-15 cm.
So it will not harm the trunk and fill the soil with microelements, and after rotting, which can be accelerated by treatment with bacterial preparations, heavily stale manure will restore the humic acids spent by the soil.
Most often this method is used for fertilizing trees and shrubs, because even if it soon rains, which will push the manure to the trunk, the bark will protect the wood, which cannot be said about annual plants.
Important information about cow dung
Fresh cow dung is a semi-liquid substance, which contains a significant amount of eggs of worms and pathogenic microflora. When working with liquid mullein, you need to be careful, use gauze bandages and rubber gloves.
The recommended way to get rid of harmful parasites is to compost or infuse cow dung.
As a biofuel, cow dung is not used by gardeners as often, as it creates a not very high temperature - only 24-45 degrees. A good result can be achieved if you make beds for cucumbers about 1 meter high.
Humus is used as top dressing and mulching, to which cabbage, salads, cucumbers and zucchini react well. It is useful in the fall to add rotted manure under the placement for next year of tomatoes, radishes, carrots, potatoes, beets and other root crops.
Structure
This type of fertilizer is rich in microelements that protect plants from many types of diseases, help to process nutrients, affect fertilization and fruit formation.
There are many useful chemical elements in cow dung:
- nitrogenwhich helps to accelerate plant growth. They are especially rich in litter manure, which contains rotten remains of straw and hay.
- phosphorus, which is needed by plants for the formation of fruit ovary
- potassium, which is needed by plants for the productive use of water, increasing the movement of juices in them, the development of a powerful root system. Potassium is especially necessary for tomatoes at the beginning of flower formation and fruit growth. That is why they are so responsive to feeding with liquid mullein during the growing season. Potassium makes plants more resistant to drought, frost, fungal diseases and pests
- calcium, which neutralizes organic acids, turning them into a form that does not harm plants
- magnesium, which is directly involved in the production of energy for the growth of the plant organism, its productivity and fruiting
Types of cow dung
It is classified according to its moisture content and the degree of its decomposition.
According to the moisture content, it is divided into 3 types:
- humidity up to 80% - solid consistency (litter of sawdust, straw, peat, leaves, etc.)
- humidity 80-90% - semi-liquid consistency
- humidity over 90% - liquid
The degree of decomposition is distinguished:
- fresh - straw of natural color, decomposition is weak. Fresh litter is of little value
- half-matured - straw of a dark color with a brown tint turns into a loose, easily torn mass. This species is the most valuable, since the loss of nutrients is only 20-30%. It turns out after 3-4 months of storage. It is it that is recommended for use in gardens and vegetable gardens.
- humus is a dark, loose, crumbly mass. All its trace elements are perfectly absorbed by plants. It turns out after 6-12 months of storage
Chemical composition
Manure is characterized by a rich chemical composition, due to which a positive effect is achieved from using the material as fertilizer.
| Component | The number of grams per 1 kg of manure |
| Nitrogen | 3,5 |
| Calcium | 2,9 |
| Phosphorus | 3 |
| Potassium | 1,4 |
| Magnesium | 1,1 |
| Sulfur | 0,9 |
Did you know? In India, manure is used to make tablets. It is the basis of the pill, in contrast to the chalk we are used to.
Agrovit Cor
Agrovit Kor is another fertilizer that can be used instead of manure. An innovative drug was created in the 80s of the last century. Its organic basis is chicken droppings, manure, peat, sawdust. Minerals are obtained from shale, waste heaps, ash, ore.
First, organics are processed at a high temperature. This is how all harmful impurities are destroyed. The resulting extract is mixed with minerals and special bioactive substances are added. They are microscopic supramolecular systems and are called Centers of Soil Formation (CPO).
Upon contact with the soil, CPOs promote the transition of minerals into a form accessible to plants. Microelements form conglomerates around the systems, organic substances, humic acids are attracted to them, microflora is activated. Thus, the formation of humus is accelerated (during the growing season its amount increases by 0.2-0.7%), the depletion of the fertile layer stops.
For one hundred square meters, you will need about 3-6 kg of fertilizer. It replaces 100-150 kg of conventional manure. You can make it in a year. The yield of plants increases by 50-70%, the ripening period is accelerated by 1-2 weeks. Earthworms actively begin to multiply in the ground, which improves its structure and increases the amount of useful organic matter.
Agrovit Kor is several times more effective than mineral fertilizers. Almost a hundred times - manure and other organic fertilizing. It is safe, does not contain harmful impurities and pathogenic microbes. The effect of the drug is fully supported by scientific research.
Cons and possible harm


When used correctly, this material will never harm the ground or plants, however misuse can cause serious damage soil and destroy the planting.
Indeed, many substances found in fresh excrement are not only incompatible with the metabolism of plants, but are also poison for them.
Therefore, an incorrect attempt to fertilize the garden with fresh or even partially rotted manure leads to sad consequences. However, this is characteristic of the excrement of any animals or birds, because they all contain substances that pose a threat to plants.
Organics by type
- Litter manure. It is a mixture of liquid and solid excretions and bedding material (hay, etc.). When used, straw contains a lot of potassium, phosphorus and magnesium. Peat-based litter contains ammonium nitrogen, which is easily assimilated by all types of plants; there are very few other useful substances. Used fresh and for processing.
- Litter-free manure. Consists of a mixture of liquid and solid excreta, parts of water and feed. Contains 50–70% nitrogenous compounds. Phosphorus is contained in large quantities, which makes it possible to use the fertilizer as a phosphorus fertilizer. Application rates are calculated using nitrogen.
- Slurry. Contains a large amount of potassium and nitrogen, very little phosphorus. Depending on the type of feed and storage conditions, the amount of nutrients varies.It is applied to the fields in spring or throughout the season; processing into compost or infusion is possible.
- Concentrated mullein. Factory made organic fertilizer in liquid form. It has a high concentration, before use it is diluted with water according to the instructions on the package. Can be used for horticultural crops, flower beds and potted flowers.
- Manure in granules. It is a dry manure obtained as a result of composting and subsequent drying to the state of granules. A complete organic fertilizer that does not lose its properties for three years. 1 kg of organics in granules is equivalent to 4 kg of fresh.
How does it look in finished form, and how to distinguish it from fresh or not completely rotted?
Finished fully rotted material looks like loose black soil black or dark brown.
To the touch, it is soft and crumbly, if you take it in your hand, then there will be no unpleasant sensations, as if you took just plowed or dug earth.
Ready humus emits a persistent earthy smell... Manure or droppings cannot be considered completely rotten if the outside or inside of the substrate contains:
- barely noticeable smell of manure or droppings;
- swamp smell;
- slime.
What plants love this fertilizer?
And later, during flowering, the formation of fruits - that's it. I fed ashes closer to summer.
Cucumbers love manure. Usually the beds are made high on manure with straw on top of the ground and plant cucumbers. This is a top dressing for cucumbers and the manure becomes warm for them. If you cover cucumbers, the manure gives off carbon dioxide, which contributes to crop yields. A pumpkin can be planted next to a dung heap, it also grows well. I put the rotted manure under all the plants. In general, it is better to apply manure in the fall under the trees and on the beds.
Safety regulations
When feeding even with organic compounds, you need to remember three main rules:
- do not feed a newly transplanted or weakened plant - for the latter there should be a weak concentration of fertilizer;
- to carefully study the needs of a particular variety - what it lacks and what effect the organic matter with which it is planned to fertilize will give;
- before fertilization, it is worth watering the flower well - if the concentration of organic matter is high, then the roots will be protected by water.