Among the splendor of life created by nature, a special place is occupied by cap mushrooms, which form a kind of kingdom of living organisms.
Several years ago, the study of mushrooms took place within the framework of the biology subject - in botany. However, later the opinion was established that mushrooms are neither plants nor animals.

So what is it? These are some living organisms in nature, which occupy an intermediate position between flora and fauna.
Unlike plants, they do not have chlorophyll, they cannot feed through photosynthesis, organic matter is obtained directly from the soil through the absorption of water together with inorganic substances or through penetration into the roots of trees.
What mushrooms are called cap mushrooms?
The concept refers to the fruiting body, which has the shape of a "stem with a cap".
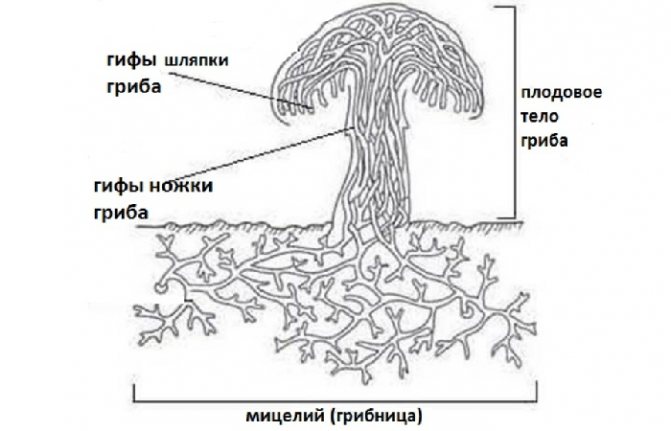

Themselves representatives of this kingdom of living nature are a plexus of thin plexuses of long branching filaments, called hyphae. You can consider them by slightly tearing the topsoil, litter, or moss.
The collection of hyphae is called mycelium or mycelium.
Filaments consist of one row of long, elongated cells with one or more nuclei.
Most often, white hyphae are found, but they can be bluish, reddish, yellowish, sometimes olive-brown or other shades.
In places where fruiting bodies appear, dense glomeruli-plexus of hyphae appear, capable of withstanding a weight many times greater than a single thread.
Mushroom brown cap yellow bottom turns blue. White mushroom turns blue on cut


Experienced mushroom pickers know how to distinguish edible specimens from poisonous counterparts by several external signs. Beginners who are just beginning to learn "quiet hunting" should be more careful not to accidentally put a poisonous mushroom in their basket that can cause severe poisoning.
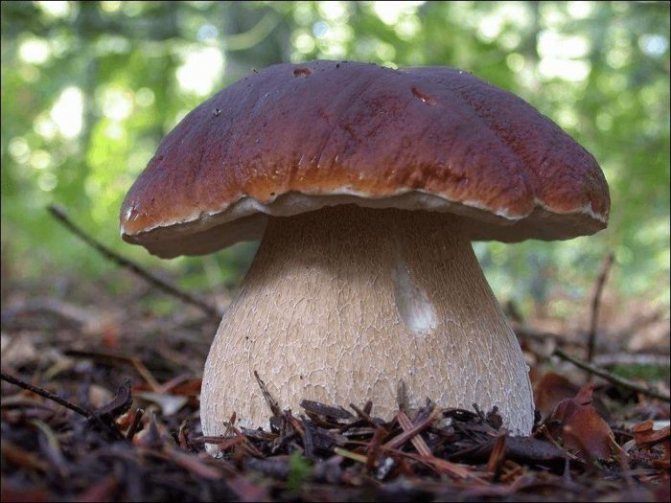
One of the signs that a specimen is poisonous is a change in the color of the pulp. As a rule, it starts to turn blue at the cut. However, this process does not always indicate that it is poisonous. Today we will consider the main nuances in which the porcini mushroom turns blue on the cut and provide information about edible and poisonous species, the pulp of which can darken if broken or mechanical damage.
White mushroom turns blue on cut
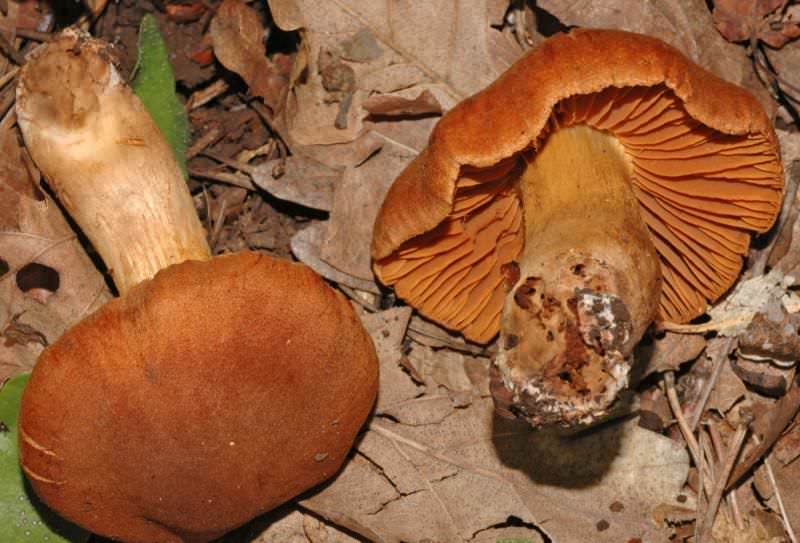
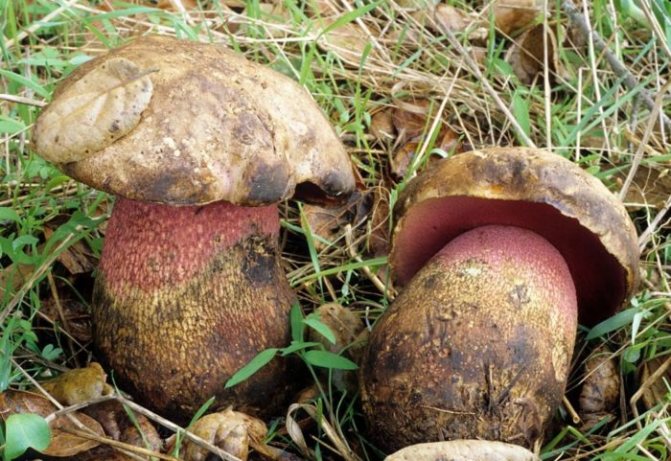
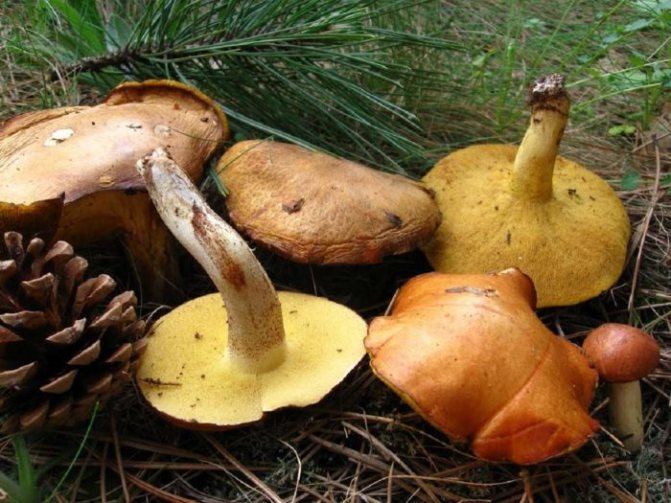
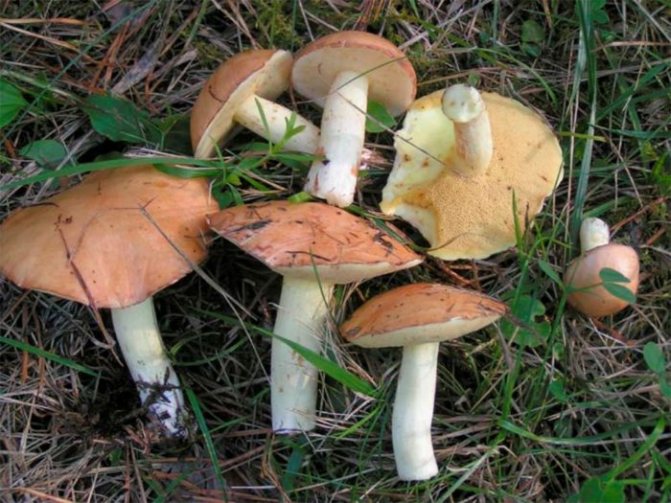
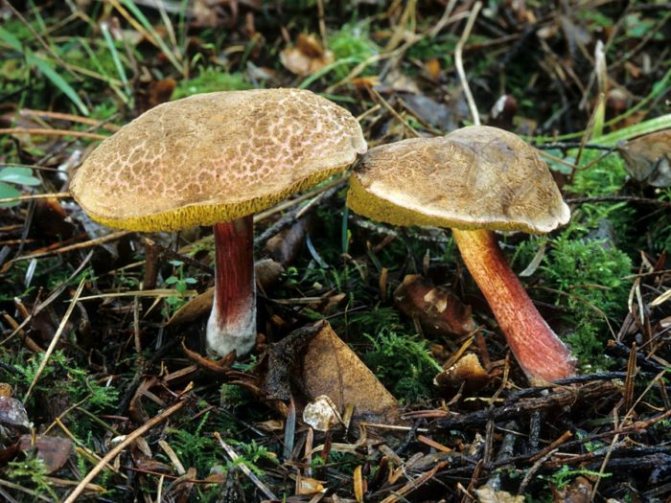
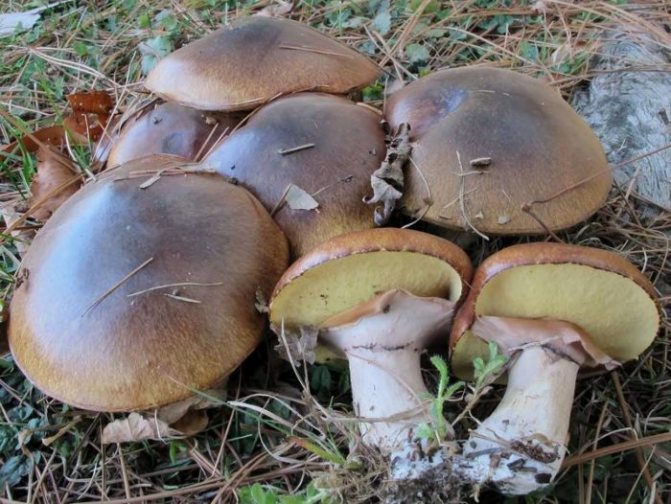
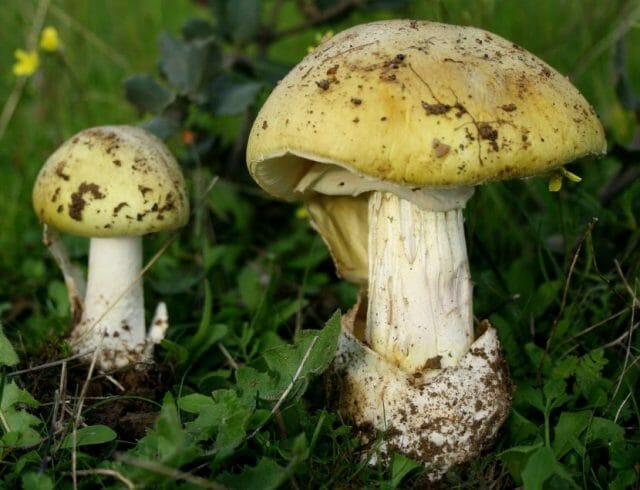
There are many subspecies of porcini mushroom, the flesh of which can turn blue when cut. As a rule, this process indicates that you have found a polish, or chestnut, which can indeed greatly change the color of the pulp when broken and raise doubts about the edibility of novice mushroom pickers (Figure 1).
Note: Outwardly, Polish is very similar to regular white, but upon close examination, certain differences between these species are still present.
In fact, it is considered quite valuable, despite the fact that in terms of external characteristics it is slightly inferior to white. It is usually found in coniferous forests where there are many mature pines, but sometimes it can also be found in deciduous forests.


Figure 1. Blue flesh of a Polish mushroom
Fruiting begins in August and lasts until September. It tastes like white and is great for eating fried, boiled, dried and pickled.The outer part of the cap is brown or chestnut brown. On the inside there are tubes of yellow-green color, which turn blue when pressed. At the same time, the pulp has a pleasant mushroom smell. It is noteworthy that the Polish mushroom is not capable of accumulating carcinogens, radionuclides and heavy metals, so even adult specimens can be safely collected.
Poisonous doubles of porcini mushroom
Despite the fact that the porcini mushroom is considered quite common, and it is difficult to confuse it with a toadstool, it has several inedible counterparts. They are extremely rarely fatal, but can still cause symptoms of severe food poisoning.
The danger of false whites is that they grow in the same area as the edible specimens, and sometimes in close proximity to them. In order not to accidentally put such a specimen in a basket, you should know the distinctive external signs of poisonous twins.
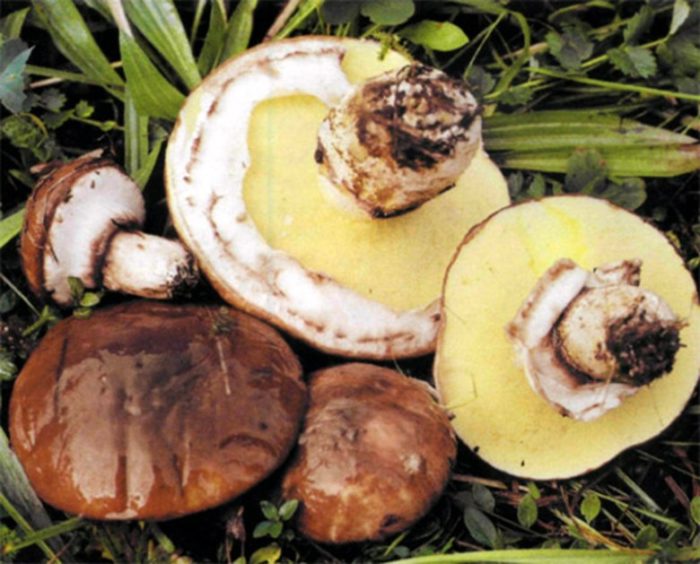
- Gall mushroom (gorchak)
Outwardly, it is very similar to white, but prefers to grow on well-heated clay and sandy soils. Most often it can be found on the edges and clearings of coniferous forests. Based on the place of growth, it should look like a white pine, although in fact, in terms of external characteristics, it looks more like an oak tree (Figure 2).
From the external characteristics of bitterness should be highlighted:
- The hat is convex, brown or brown.
- The stem is thick, cylindrical, covered with a characteristic mesh pattern, which is absent in true whites.
- The pulp is not of a pleasant creamy or white shade, but slightly pinkish or off-white. The flesh of the gallbladder also acquires pink color when cut or broken.
But the main characteristic feature of this poisonous twin is that it has a pronounced bitter taste, from which the mushroom got its name. This taste not only does not disappear, but also intensifies during heat treatment, so you cannot accidentally eat it. It is the bitterness that is the reason why forest animals and insects do not eat it.


The structure of cap mushrooms
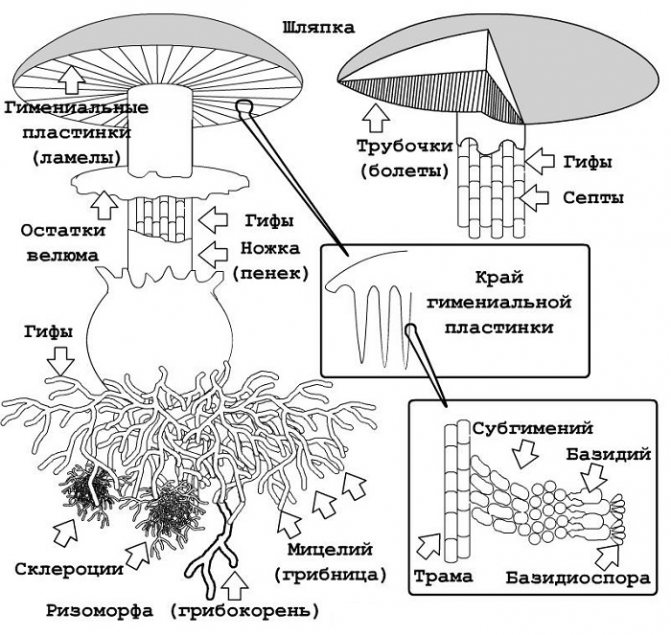

Fruiting bodies consist of a large number of threads, tightly adjacent to one another, intertwining with each other.
The cap contains two layers-layers, the upper of which is covered with a skin, and the lower part is a set of thin small tubes or plates.
The types of the lower layer determined the names of the subgroups: tubular or lamellar.
The diagrammatic diagram shows the difference:
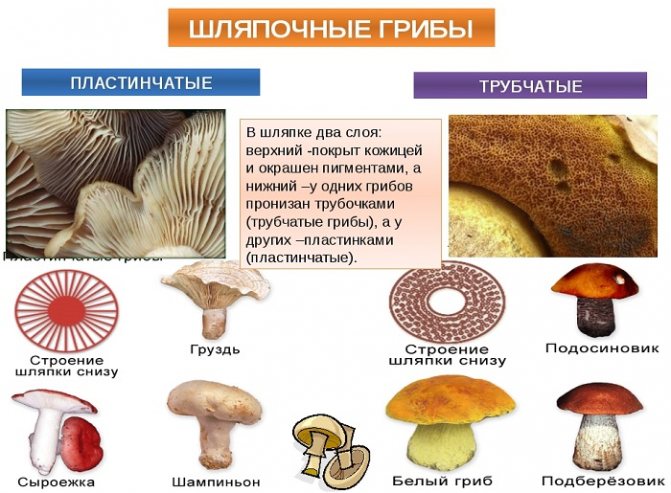

The captions show not only a schematic view of the bottom, but also some of the representatives defining the corresponding class.
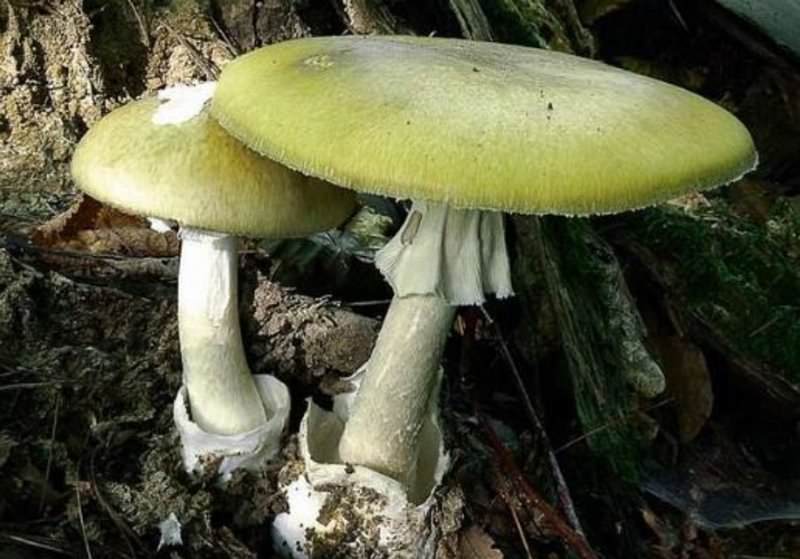
Amanita phalloides
It belongs to the group of deadly mushrooms. Occurs in summer and autumn in forests in the south of the country. It is large in size, the diameter of the cap is 10-15 cm. The color is pale green with an olive tint. The edges of the caps of toadstools have edges bent downwards, like in champignons. In the future, it is leveled.


Death cap
The leg is white, can reach a length of 12-15 cm. Below the cap there is a ring that resembles a skirt with frills, in the lower part of the leg there is a noticeable thickening.
Pale toadstool is odorless and tasteless. This dangerous mushroom can be confused with russula and champignons. Even if consumed in small amounts, fatal poisoning can occur. Its danger also lies in the fact that the symptoms of intoxication can manifest themselves after 6 hours from the moment of use. In medical practice, cases have also been recorded when they manifested themselves after 48 hours.
Lamellar mushrooms
Russula, wolves, milk mushrooms, mushrooms, champignons
have caps that look like a small accordion of thin plates from below. These are lamellar mushrooms.
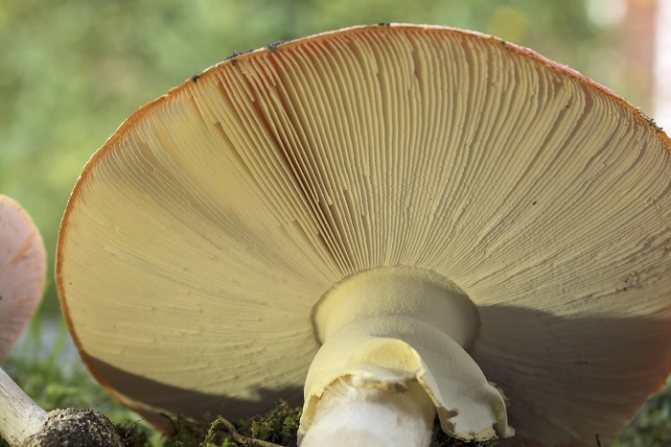


In determining them, an important role is played by the frequency of the location of the plates per square centimeter, width, thickness and color.
No less important are the methods and forms of attachment to the leg (in the center, side, edge).
Fly agaric or gray (Amanita pantherina)
This mushroom can be found in the forest in mid-summer and autumn. The diameter of the cap is 12 cm. The young mushroom has the shape of a bell, over time it becomes flatter. The color can be light brown or olive; a huge number of white spots can be seen over the entire surface. The pulp is white, has a fetid odor.
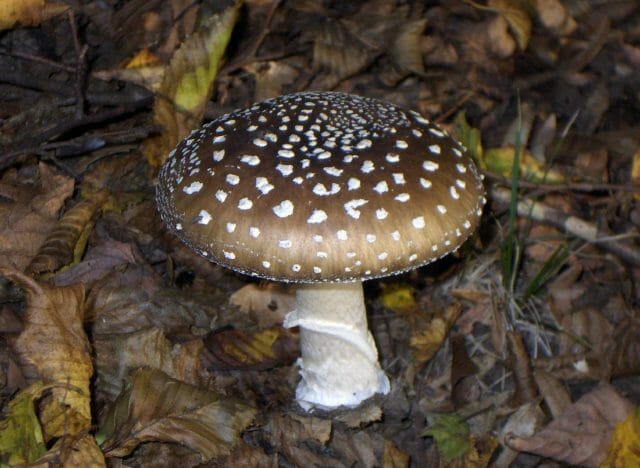


Amanita muscaria
The leg can reach a length of 13 cm. In the lower part it expands, in the upper part it narrows. Externally, the panther fly agaric is similar to the non-poisonous gray-pink fly agaric. Signs of intoxication after eating this poisonous mushroom appear in the shortest possible time (from 20 minutes to several hours).
Varieties of hats and legs
The external structure of the legs and caps can be different. In general, these parts of the fungus are soft fleshy, rotting after maturation.


Hats can be:
ovoid, hemispherical, convex, concave, flat.
Their edges are also diverse:
wavy, even, dissected, bent, raised, lowered.
The legs are also not alike. They are found with and without a tapered appendage, oblique-like, tuberous, cylindrical, narrowed.
Fly agaric white or spring (Amanita verna)
Occurs in forests from June to August. It has a white cap up to 10 cm in diameter. The pulp of this mushroom has a repulsive odor. The color of the leg is also white, the length is 7-12 cm. A coating in the form of flaky scales is observed on it.
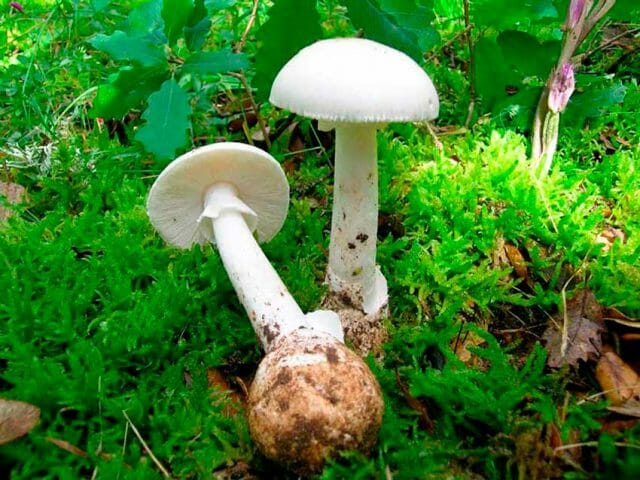


Amanita white
There is a slight swelling at the bottom of the leg. It is surrounded by a wide ring with stripes. Amanita muscaria is ranked among the group of deadly poisonous mushrooms. Its external features are similar to a white float, but the latter is devoid of ring and smell.
Food
Since fungi, unlike plants, do not have chloroplasts and other plastids, they cannot receive nutrition through photosynthesis.
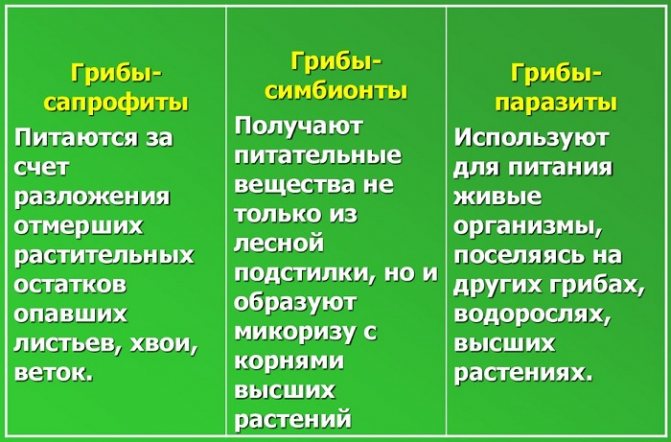

They acquire organic and inorganic substances useful for growth and development by absorbing water from the soil by the mycelium.
Often, hyphae penetrate the roots of trees, receiving organic elements from plants, giving back water and minerals taken from the soil. This union of fungi and plants is called mycorrhiza.
Poisonous row (Tricholoma pardinum)
Can be found in deciduous forest in late summer and early autumn. Can grow in pine forest. The color of the cap is off-white or off-gray. Its diameter can be 4-12 cm. Soon it takes on a flat shape, the edges curl inward.
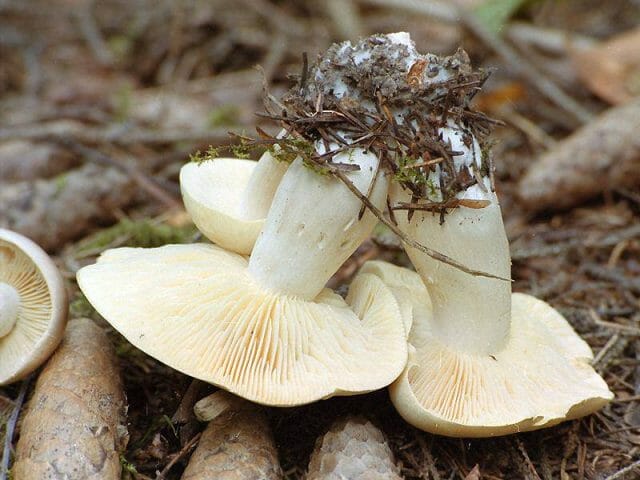


Row poisonous
The leg reaches up to 8 cm in length. The mushroom has a pleasant aroma and taste. Refers to deadly poisonous. Signs of intoxication make themselves felt in 1.5-4 hours from the moment of eating it. Poisonous ryadovka is not always possible to distinguish from earthy-gray ryadovka.
Reproduction
The functions of cap mushrooms are reduced to the reproduction of myceliums.
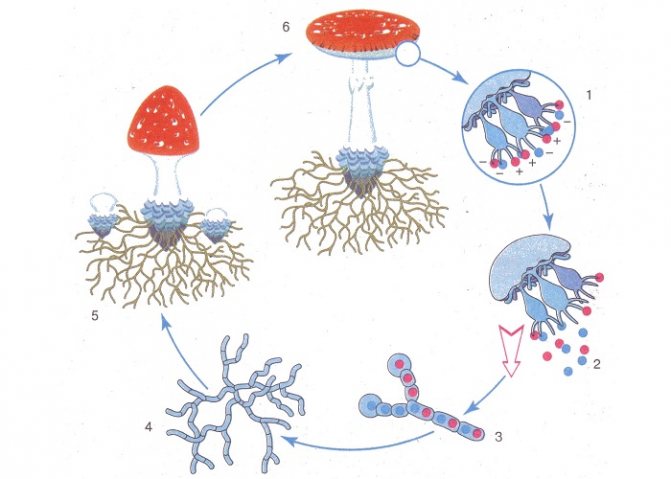

Small and light spores are formed in the tubes and plates of the lower layer of the cap. Each of them has a mushroom cell.
They crumble to the ground, are carried by the winds, enter the stomach of animals, without being digested, go out together with the droppings. Thanks to this method of distribution, many fungi arise at large distances from the fruit bodies.
In favorable conditions, spores germinate, gradually forming a mycelium.
After a while, new fruiting bodies begin to appear.
Many millions of spores can be formed by one cap fungus.
Amanita muscaria (Amanita muscaria)
Found in many regions of Russia. It grows mainly in forests, especially birch forests. This mushroom is immodest in size and looks pretty pretty. Its red cap with a lot of white spots is supported by a high thick stem with a ring.In a red fly agaric, the cap can also be orange. Mushrooms that have just grown have a round cap. With age, it becomes flat-convex.
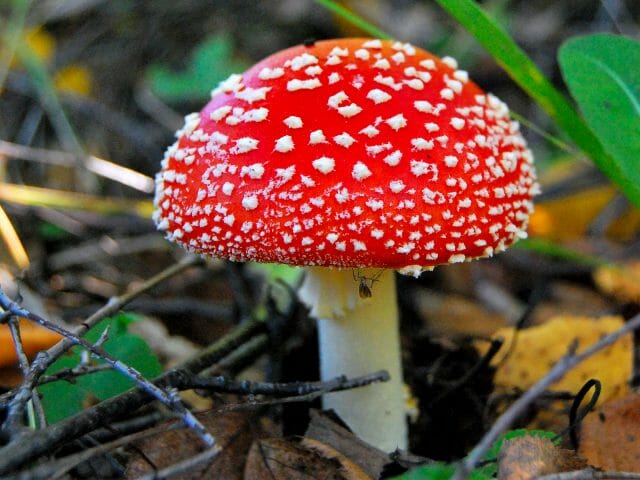


Amanita muscaria
Amanita muscaria is not one of the deadly poisonous mushrooms. After its use, a person has hallucinations, an intoxicating effect is observed. This phenomenon makes itself felt after 20 minutes -2 hours from the moment of eating. Outwardly, the red fly agaric is similar to the golden-red russula. Used in traditional medicine (in moderate doses).
Features of life
New myceliums appear in places with a large layer of humus, as well as next to the corresponding trees.


Different types of mushrooms "are friends" with certain types of trees
near which they are grouped.
The appearance of fruiting bodies in different species does not occur simultaneously. Dry weather is not favorable.
The most conducive to the emergence of fruiting bodies is a uniform change of heat with coolness, bringing light rain. An early cold snap also stops growth.
Galerina marginata
They grow in modest groups on rotten tree trunks. They can be found in forests throughout the summer season. The size of the cap is 1-4 cm. The color is dirty yellow. Over time, its bell-shaped shape transforms into a convex-flat one. The length of the leg is 2-5 cm. A thickening is observed in its lower part. It is surrounded by a yellow ring. Belongs to the class of dangerous mushrooms. Sometimes it is not easy to distinguish it from summer honey.
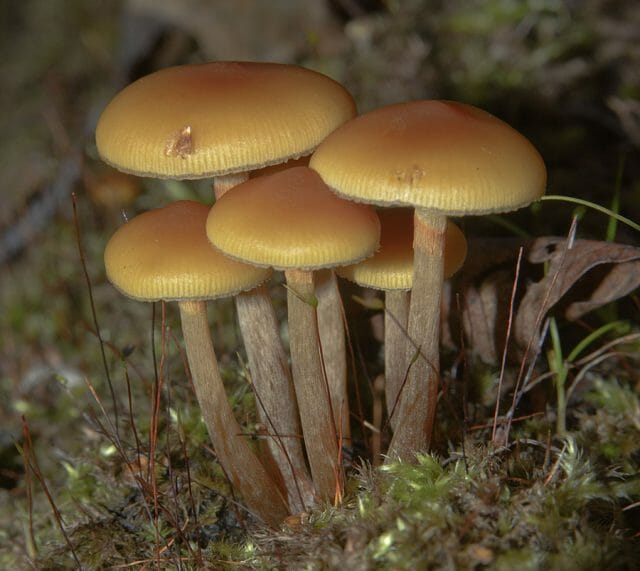


Galerina bordered
Edible cap mushrooms
There is a table showing which mushrooms can be eaten.


Examples of edible mushrooms:
- boletus;
- mushrooms;
- birch trees;
- russula;
- white;
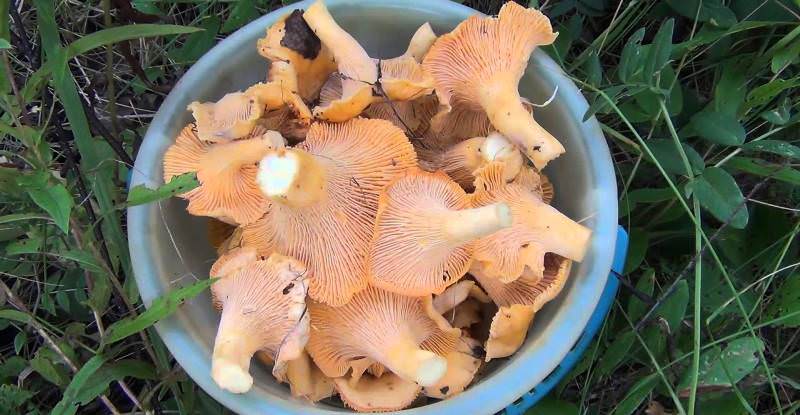
- chanterelles;
- milk mushrooms;
- moss and many others.
Among them there are mushrooms of various types and structures.
The mushroom is white on a thick stalk. Family Ramariyeva - Ramariaceae
Ramaria yellow (yellow horned, lemon yellow coral, sulfur yellow coral, deer mushroom)
Ramaria flava (Fr.) Quel.
Soil saprophyte
The fruit body is up to 20 cm in diameter, 10-15 cm high. Sometimes it reaches an impressive weight (1.5-2 kg). The mushroom has all shades of yellow: cream, apricot yellow, later ocher or almost orange. When pressed, the color of the fruiting body changes to wine-brown. The pulp is moist, the smell is herbal. The leg is thick, dissected into branching outgoing processes. Horned beetle can be found in damp-shady places of deciduous, coniferous and mixed forests, especially in lichen pine forests, among the cover of green mosses in August-September. It settles in large groups, forming rows or arcs. It grows directly on the ground or on rotten wood. The mushroom bears a very close resemblance to the golden ramaria.
Cooking. Suitable for food at a young age, later its pulp becomes coarse. Used fried and boiled.


Ramaria golden (golden horn)
Ramaria aurea (Schaeff .: Fr.) Quel.
Soil saprotroph
The fruit body is massive, 15-20 cm in diameter, 8-10 cm high, bushy, abundantly branching, ocher-yellow, golden-yellow or golden-ocher with a lighter base, fades when dry. "Twigs" are thick, densely spaced, their ends are blunt, 2-3 times incised. The leg is short, whitish at the base. Many branched horns radiate from one common root. Grows on soil in coniferous, rarely deciduous forests, often among mosses. Fruiting from July to October. The close relative of golden ramaria is yellow ramaria (Ramaria flava). The two are difficult to distinguish without laboratory analysis. Their nutritional value is the same.
Cooking. Edible mushroom. It is eaten fresh. These mushroom noodles can be boiled and added to the mushroom roast for a flavorful bouquet.


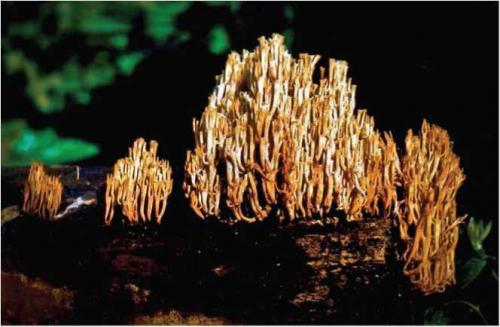
Ramaria Invala (Inval's slingshot)
Ra maria eumorpha (Karst.) Corner (Syn. Ra maria invalii (Cott. Et Wakef.) Donk.)
Litter saprotroph, xylotroph
The fruit body is bushy with branched ends, 2-8 cm high, yellow-brownish or ocher-brown, slightly bitter taste, with a sour odor. It grows on a litter or in whole curtains, forming whole rows, arcs or witch's circles on valezha in coniferous and deciduous forests. Occurs quite often, annually in July-September. After boiling, the mushroom is quite edible, but it is rarely harvested.

Views
There are a hundred thousand species of mushrooms in the world. These are not only those that we collect and see in the forest. Both mold and baker's yeast belong to the kingdom of fungi. A special, unique organism is lichens, which are a beneficial coexistence of algae and fungus. «>
Among those that a person collects in the forest, there are three groups: lamellar, marsupial and tubular mushrooms.
Lamellar - the most numerous species, they are called so due to the structure of the cap. Below it there are peculiar plates, diverging from the attachment of the cap and the legs of the mushroom. Among these organisms, there are both edible and very poisonous. The first include mushrooms, chanterelles, volnushki, honey mushrooms or russula. The lamellar pale toadstool is very poisonous; you should also not collect all types of fly agarics.
The group of marsupial mushrooms is not so numerous. These include stitching, morels and truffles. Spores in these mushrooms are formed in special sacs, for which the species got its name.
Sulfur-yellow false foam (Hypholoma fasciculare)
It prefers to settle in large groups on decaying trunks of coniferous trees, on stumps, near them. Grows in the forest during the summer-autumn season. The diameter of the cap is 2-7 cm. In young mushrooms, it has a bell-shaped shape, over time it straightens out. The color is yellowish or brownish yellow, darker in the middle. Leg length about 10 cm, thin, light yellow in color. The mushroom has a light flesh with a bitter taste and a repulsive odor.
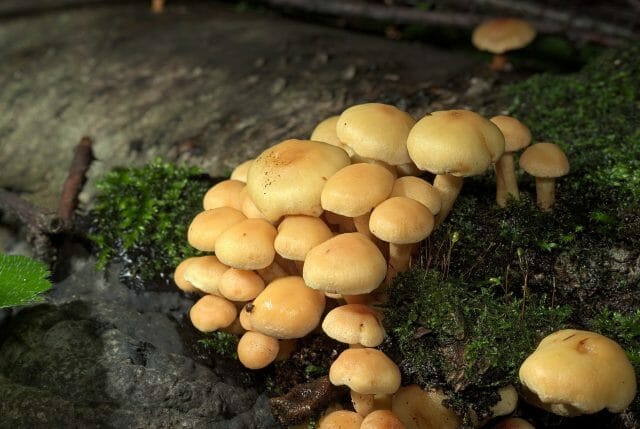


Sulfur-yellow false foam
The sulfur-yellow false froth differs from the rest of the mushrooms in the greenish color of the plates under the cap. Symptoms of intoxication make themselves felt in 1-6 hours from the moment of consumption.
Inedible tubular
There are many among the tubular mushrooms and those that outwardly are the very charm, but are absolutely unsuitable for food because of the bitter pulp. Some of them are easy to recognize by their unpleasant aroma, however, not everyone has it.
The most famous inedible tubular mushrooms include:
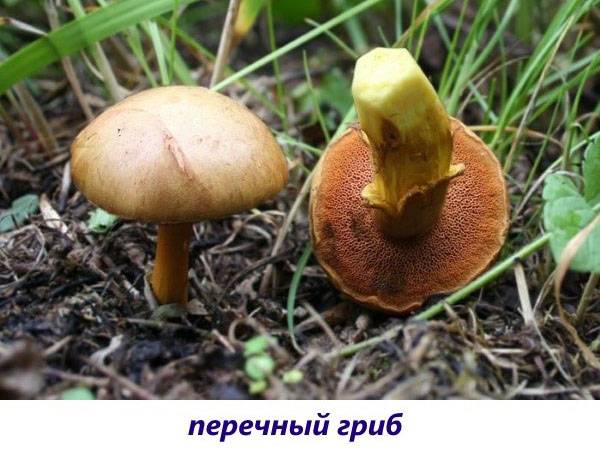
- Pepper mushroom (aka pepper oil can or pepper flywheel). Most often it forms mycosis with deciduous species (birches). Outwardly, it looks like a regular oiler, but the spongy layer is painted in brighter colors (reddish). Rusty convex cap, covered with a slightly velvety dry skin. The leg is of the same color, but lighter, yellowish near the ground. The pepper mushroom got its name for the peculiar pungent taste of the pulp. Because of this, it is considered inedible. However, some gourmets manage to use it as a condiment (instead of pepper).


- Gall mushroom (aka bitter mushroom). It has a thick, fleshy cap of a golden-red color with a matte dry skin, a spongy layer is white, in older specimens it acquires a pink tint. The yellow leg is decorated with a brown mesh pattern, and turns pink on the cut, which distinguishes the bitter from the porcini mushroom, to which it looks so much.


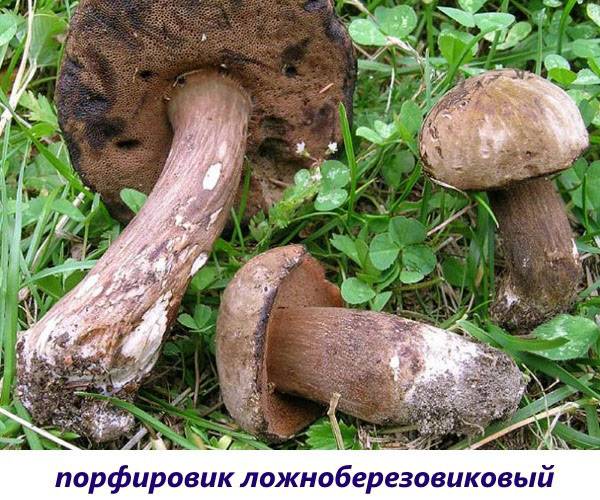
- Pseudo-birch porphyry. The thick cap is semicircular at first, then straightens, olive-brown, covered with a velvety skin. The dense leg is painted in the same color, in the central part it is thicker. The sponge in young fungi is light gray, turns brown with age. When broken, the white pulp turns red, is bitter and smells bad. However, some mushroom pickers assure that mushrooms can be eaten after a long heat treatment.


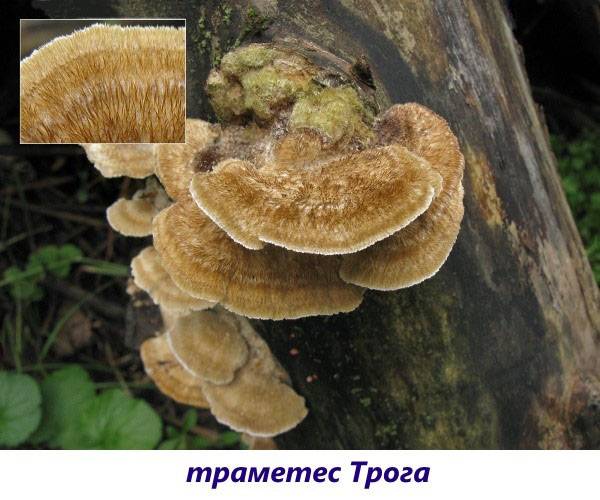
- Trametes Trog.One of the species of tinder fungus, grows on dry deciduous trees in the form of a multi-tiered outgrowth. A spongy thick layer in the form of large pores turns into a cork layer. The edges of the cap are thinner, and the surface is covered with a hard skin in the form of bristles, painted in a gray-yellow color. The pulp is light and very tough, without taste, therefore it is not eaten.


The importance of tubular mushrooms should not be underestimated. Despite some species that do not differ in taste, among the spongy mushrooms with fleshy pulp and thick hats are some of the most delicious and healthy gifts of the forest. Going for delicacies for a festive dinner, look carefully under the trees and be sure to put a couple of boletus or butter mushrooms in your basket.
www.glav-
Attention, danger - poisonous tubular mushroom false boletus
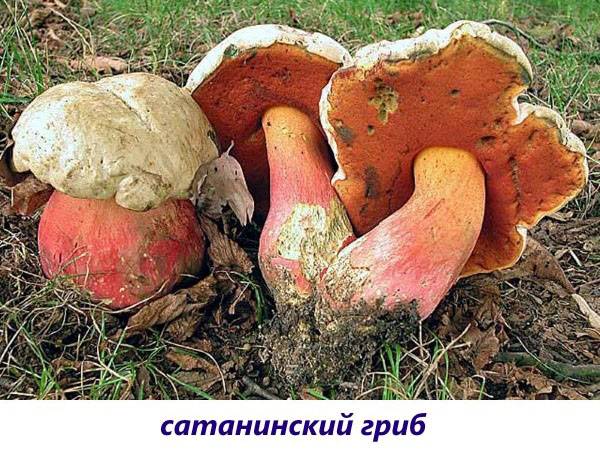


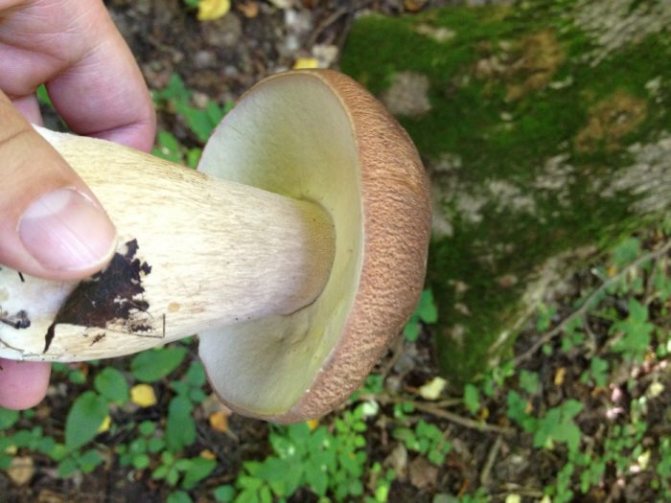
The only representative of the tubular that can harm a person is the satanic mushroom. He got into trust in them not by chance, because outwardly it has the maximum resemblance to a real boletus, as a result of which mushroom pickers call him so: "false boletus".
His hat is in the shape of a hemisphere, with a smooth grayish skin, slightly velvety. The dense leg resembles a keg, orange at the top and slightly tapering. The center of the leg of the poisonous tubular mushroom is decorated with a red mesh, which turns into a yellow-brown color near the ground.
You can distinguish a false boletus from a real one by the blue pulp after an incision, which first turns red. In addition, the middle part of the stem has a brightly colored red mesh.
Popular edible tubular
Edible tubular mushrooms with excellent taste characteristics are among the most favorite mushroom pickers:
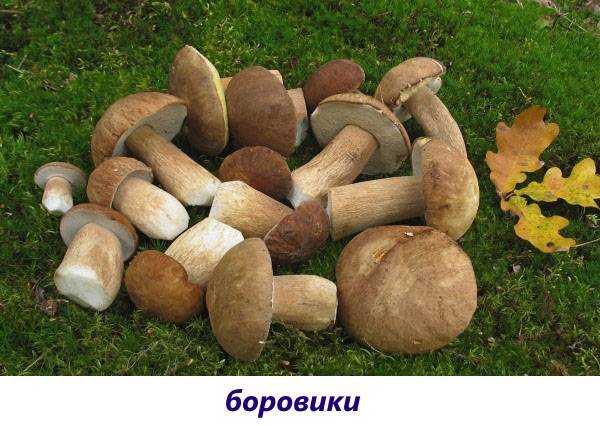
- Boletus (porcini mushrooms). They grow in small families, mainly under conifers or birches, depending on this, the color of the cap changes from dirty gray to dark brown. The sponge itself under the hat is also different, in some species it is white, in others it has a yellow-green color. The leg is in the form of a barrel, thick, fleshy. The pulp is light, emits a characteristic odor.


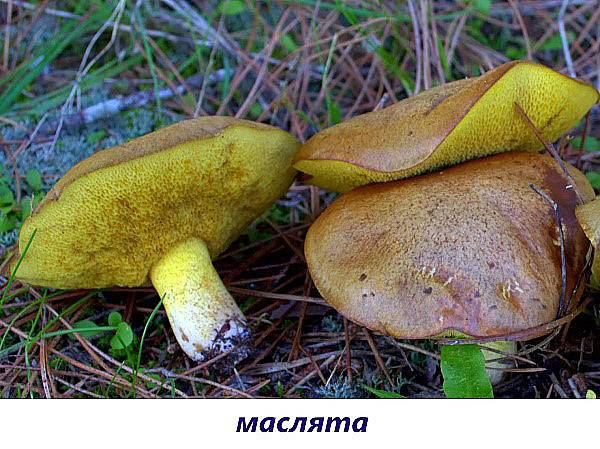
- Butterlets. Inhabitants of pine forests love to grow in families. The fleshy brown caps are covered with a very slimy skin. The leg can be lighter or darker, also of a dense structure. The sponge is most often yellow.


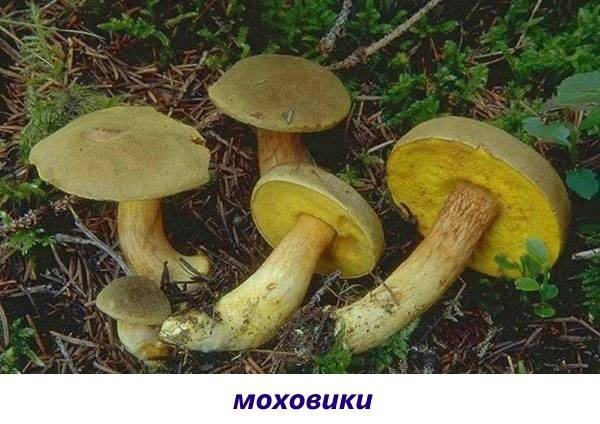
- Flywheels. Small mushrooms grow on sandy soils. The hats can be dirty yellow or pale green, the yellow flesh turns blue when broken. The leg is thick.


- Boletus boletus. They grow between the roots of birch families. Hemispheric hats are light at first, but then turn brown. The leg is off-white, covered with frequent gray scales. The pulp is light, but darkens after drying.


- Aspen mushrooms. Fleshy mushrooms grow, respectively, under the aspen trees. The convex cap resembles the color of autumn foliage, orange-brown. The leg is high, thickens in the lower part, covered with black scales. The sponge is yellow-gray, the pulp, when broken, becomes first blue, and then almost black.


- Polish mushroom. It grows among fallen pine trees on damp soils. The hat is dark brown, with a white-yellow sponge under the bottom. The leg is rather high, thick, light brown with a barely visible pattern. When cut, the light pulp turns blue, and then becomes brown, which distinguishes the Polish mushroom from the white one.


- Duboviks. They grow in oak and linden forests. Large caps up to 20 cm in diameter have different shades of brown, the skin is velvety at first, acquires a glossy shine with age. The spongy layer is yellow in young fungi, orange in adults. The yellowish leg is quite high, up to 12 cm, thick, covered with a reddish mesh. On contact with air, the yellow flesh quickly turns blue.


Some scientists classify oak trees as conditionally edible species, and the use of their raw pulp generally causes symptoms of poisoning.However, properly cooked oak woods are no less tasty than boletus mushrooms, and very edible.



























