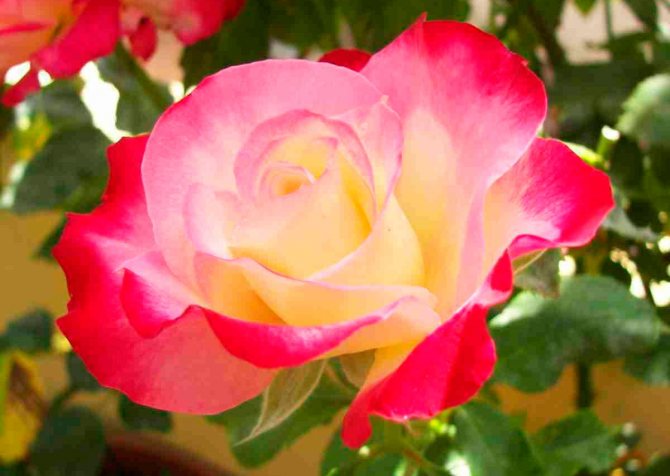
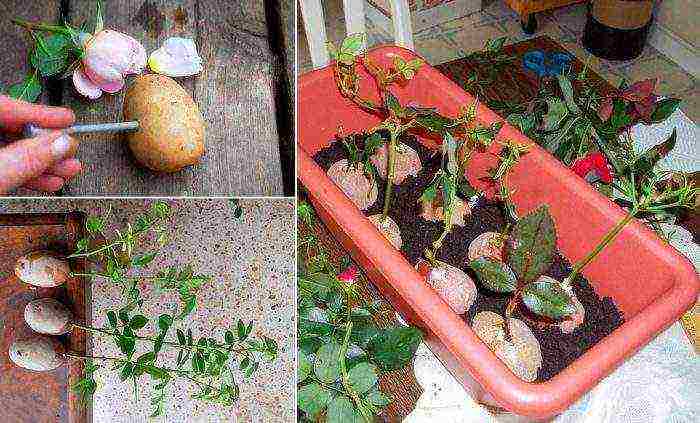Planting roses on a personal plot is the dream of, if not all, then very many gardeners. But seed material is usually expensive, and there is no guarantee that a rose of the same variety will grow from a nondescript seedling, the name of which flaunts on the label. Breeding roses with cuttings in potatoes makes it possible to grow a bush even from a presented bouquet.
In a store or on the market, grafted plants are sold, it also happens that the miracle of selection does not live up to expectations, the graft does not take root. And instead of a purebred beauty, an ordinary rosehip grows, on which the vaccine was made.
If reproduction is carried out in a vegetative way, then there will be no surprises, an exact copy of the plant that served as a "donor" of the planting material will grow from the cuttings. Such bushes are called own-rooted.
For the cultivation of roses by cuttings, it is advisable to choose domestic zoned varieties. Material from roses with white and greenish flowers is not suitable for vegetative propagation. The percentage of rooted cuttings from bushes with orange and yellow flowers is also low. Roses of red and pink varieties take root very well.
Climbing and semi-climbing, dwarf, polyanthus and bush roses are excellent for cultivation by cuttings, this is due to their genetic proximity to their ancestor - wild rose hips, which has excellent survival rate.
Imported roses are unfortunately not the best option. Before sending flowers on the road, growers treat the plants with chemicals and preservatives. Of the total number of planted stems, only 10-15% take root. But it makes sense to at least try! Procurement of planting material
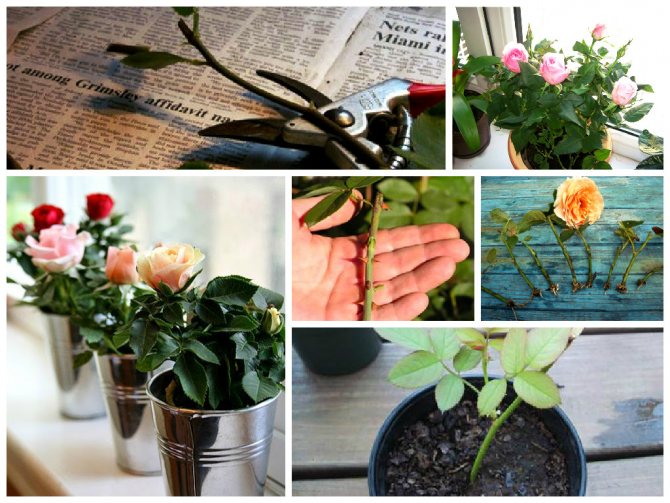
Cuttings are taken both from a bush and from cut flowers from a bouquet. You were presented with luxurious roses as a gift, just the same you have always dreamed of planting in your country house? This is a good opportunity to give flowers a second life.
If it is decided to grow a bush from a cutting, it is better to take fresh flowers for this: after a long standing in a vase, the stems are depleted, the likelihood of rooting and survival decreases. Before putting the bouquet in water, the stems of roses are cut obliquely with a sharp knife under running water so that air does not get into the cut, and a biostimulator (a drop of honey) is added to the water. The water is changed daily and the cut is updated. Before grafting, the bud must be cut off.
The best time for harvesting cuttings from a bush: June - July, before flowering or immediately after it. Much depends on local weather conditions. Dense stems of green color or with a brown tint (a sign of the beginning of lignification) are chosen, without any defects, with a diameter of about 1 cm.If the shoot is ripe for grafting, the thorns from it should easily break off.
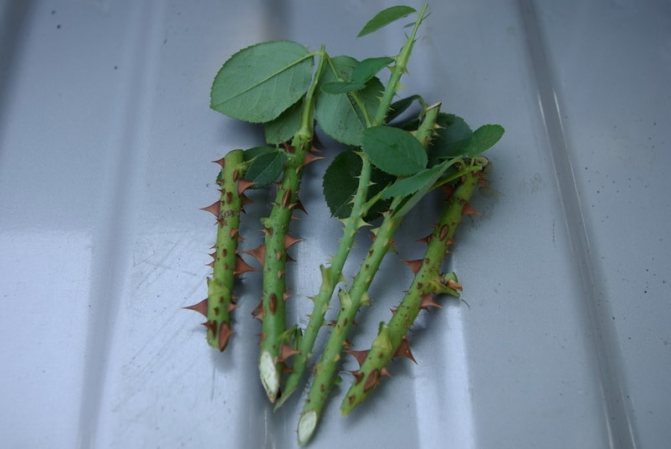
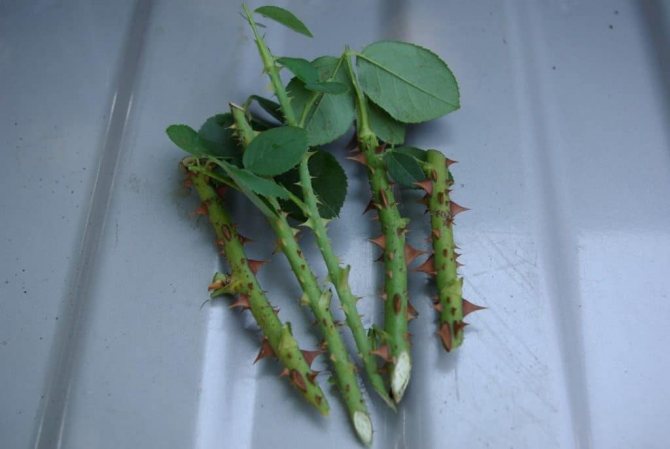
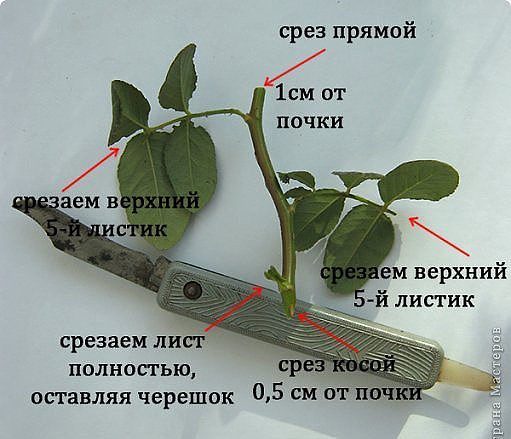
Several cuttings 15-20 cm long can be cut from one shoot so that each of them has three active buds. Experienced gardeners recommend making the lower cut immediately under the bud, about 2 mm lower, beveled at 45 degrees, and the upper cut at a right angle, 1-2 cm higher than the first bud.

Before kilchevaniye (preparation for rooting and activation of growth) you need:
- remove thorns;
- cut off all leaves, except for the top two, which should be shortened by 1/3;
- cover the upper cut with either paraffin or garden varnish so that there is no excess moisture evaporation.
- These manipulations are carried out so that the cuttings do not rot when they get into a humid environment.
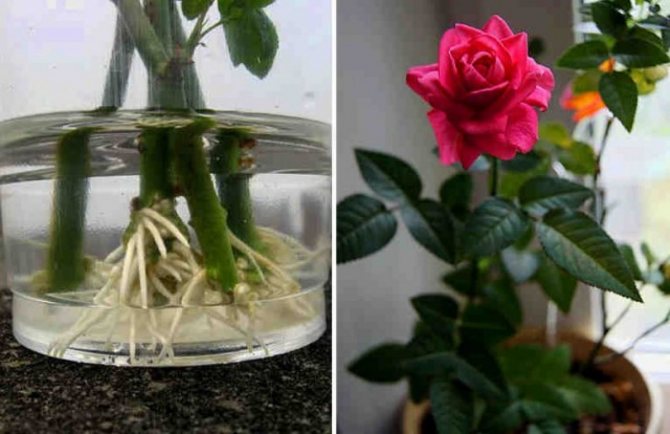
There are several ways in which they cause the growth and development of the root system in rose cuttings before planting in a permanent place, they are placed:
- in a container with water;
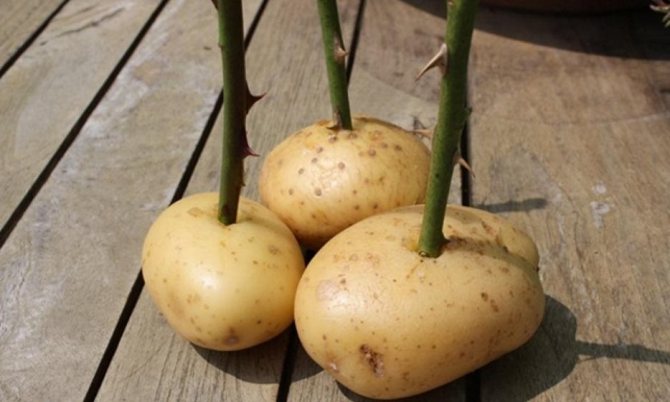
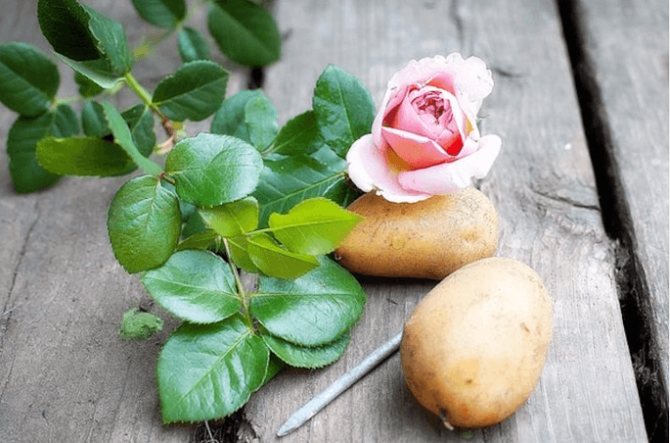
- in a potato tuber;
- into a wet cloth;
- in several layers of the newspaper (burrito method);
- into the ground, instilled with an inclination of 45 degrees (Tranois method).
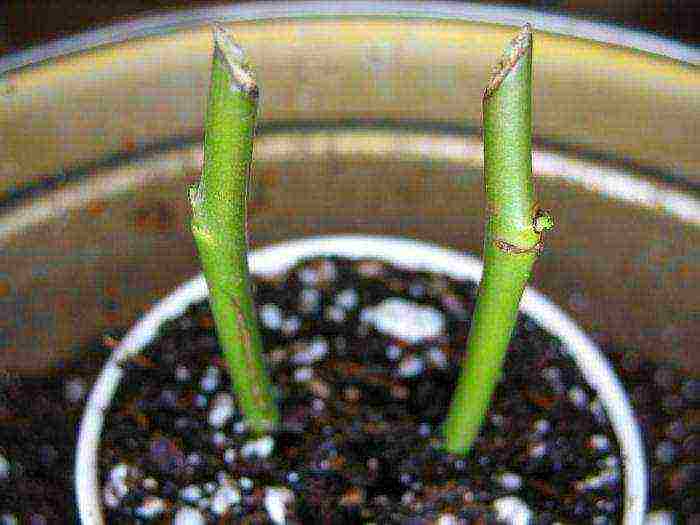
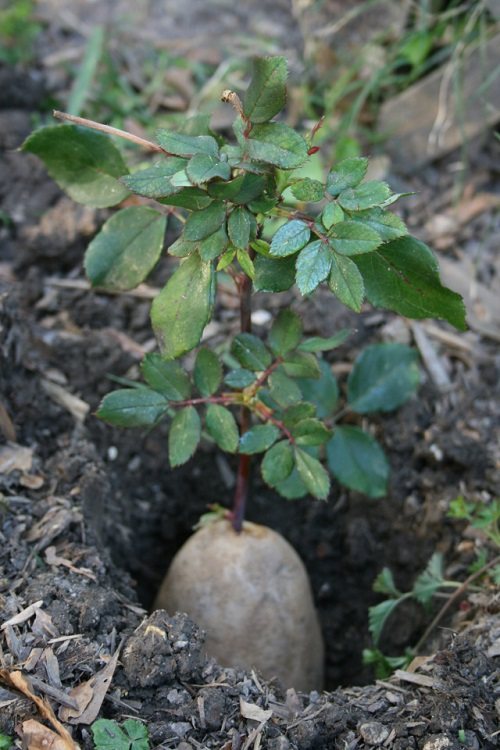
Roses in potatoes
This method is the easiest for those who have just started planting roses. The essence of the method of reproduction of roses in potatoes is that the cuttings are not planted directly into the ground, but are first placed in the tuber, which supplies the stem with nutrients: starch, vitamins, phytohormones, moisture. Also, the potato serves as protection from hypothermia, drying out, from various pests and pathogens living in the ground.
The disadvantage of the method (however, like any of the above) can be considered the fact that about 15% of seedlings do not take root when transplanted to a permanent place of growth, despite the fact that they have a well-developed root system. Sometimes it is possible to save a part by transplanting it to another place.
Rooting roses in potatoes requires:
- several cuttings prepared in advance;
- the same number of potatoes without signs of disease, medium or large;
- root system growth stimulator (Kornevin, Epin, Heteroauxin, 20 drops of aloe juice diluted in a glass of water, or honey at the rate of 1 teaspoon per glass of water).
Cutting care
Planting roses in potatoes has its advantages over the classic method of propagation - germination in water or soil. Juicy roots contain moisture and can supply the cuttings with nutrients for a long time, the most valuable of which are starch and mineral salts. Tubers protect the planting material from hypothermia, rot, pathogenic microorganisms and viral infections that often harm roses at the initial stage of rooting.


It is important to remove all the eyes from the tubers, otherwise the potatoes will sprout and may "strangle" the flower.
During the germination period, care for the cuttings should be as follows:
- seedlings must be regularly moistened;
- make sure that the soil does not dry out;
- periodically spray the plants with warm water;
- ventilate daily - remove transparent caps for 15-20 minutes.
It is recommended to increase the duration of the seedlings' stay outside the mini-greenhouse every day, so that by the time the roots appear, the roses adapt and transfer the transplant into open ground more easily.
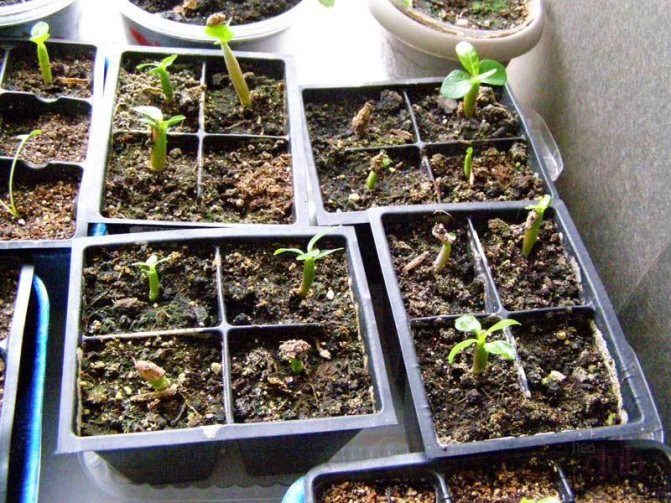
Later, young leaves should appear on the roses - one of the signs of successful rooting. In 14-21 days after the appearance of the first leaves, the seedlings can be fully opened. Some varieties of roses during rooting can manage to form a full-fledged bud, which will take away the strength of the seedling and weaken it. To prevent the plants from dying after transplanting to a flower bed, the buds that appear must be removed.
Step-by-step method of planting roses in potatoes
1.Working with soil. First you need to prepare a place for planting rose cuttings in potatoes. To do this, choose a site on the site, protected from the wind, with good lighting. There they dig a groove 25-30 cm wide, about 20 cm deep, and pour a layer of river sand at least 5 cm thick (for drainage), after which the hole is covered with fertile soil mixed with peat.
2. Preparation of cuttings. Before planting in tubers, the cuttings are soaked for a day in a solution of a root formation stimulator (you can choose one of the above).And immediately before sticking it into the potato, the obliquely cut end of the cutting is dipped into a bag of powder or dipped in a solution with a rooting agent.
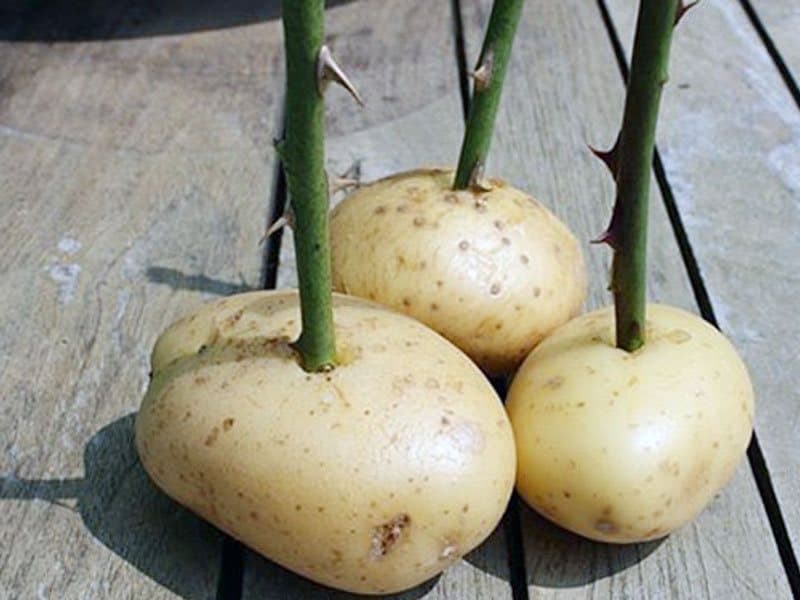
3. Preparation of potatoes. Be sure to cut out all the "eyes" (to prevent germination) and make a hole in the tuber 2.5-3 cm deep, depending on the size of the potato, using a screwdriver or some other sharp object.
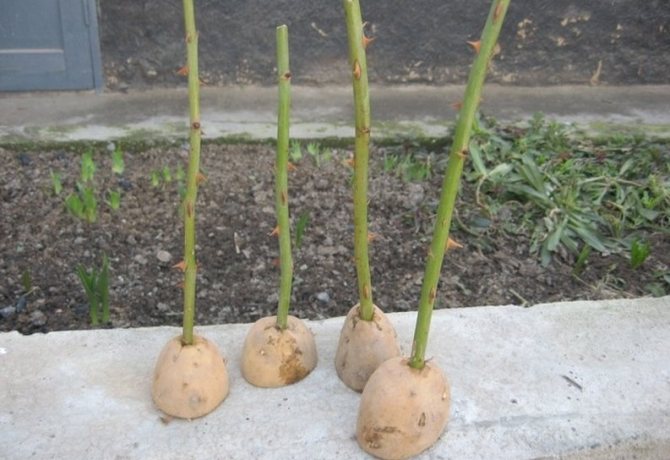
Stick the bottom end of the rose stalk into the hole in the potato so that the bottom bud is all inside. Then lower the shoot together with the tuber into the hole and cover with earth 2/3 of the length, there should be a distance of 15 cm between them.
Planting a rooted cuttings in a flower bed


Roses grown in potatoes, in comparison with ordinary seedlings, have a slightly reduced immunity. Therefore, it is recommended to transplant them into open ground in the spring, so that the bush has time to get stronger before the onset of frost.
For the winter, a young rose should be covered. To do this, you can take coniferous branches or sprinkle the bush with fallen leaves from fruit trees and shrubs, and put earth on top so that the leaves are not blown away by the wind. It is necessary to insulate the rose only after a persistent cold snap (5 degrees of frost), if it is done too early, it will begin to germinate.
www.glav-
Growing a flower in a potato in a pot at home
When propagating by cuttings, the following problem arises: cuttings of roses are very whimsical and often dry up when grown in soil, and when grown in water, they rot from lack of oxygen. So how do you provide both oxygen and constant humidity at the same time? It turns out that this dilemma can be solved with the help of ordinary potatoes.
Rooting rose cuttings using potatoes is a very common method among the people. and the most efficient. You will not regret using potatoes to plant a rose cut. He will feed the cutting and protect the flower from disease.
Growing roses according to the Trannois method
The Trannois technique will help improve the way a rose is grown in a potato tuber. Start rooting roses between May and June. To do this, cut off the top of the stem, about 20 cm long, on which the buds have just faded. The lower buds during this period will just begin to swell to give life to new shoots and leaves. Remove all leaves on the stem except for the top pair.
After that, insert the formed stem into the potato tuber to a depth of 1-1.5 cm and lay it in the ground. Then cover the stem with a half-cut plastic bottle with a screwed-on top and shade slightly from the sun.
Moisten the soil around the container every 7-10 days
On the first days of spring, air should be provided to the flower - this is easiest to do if you unscrew the lid. In cloudy weather, remove the shelter so that more light gets on the rose.
By the beginning of July, you can remove the shelter, and the rose will begin to bloom. The first buds are usually cut off to allow the plant to form a good root system and not waste energy on flowering. By autumn, the first shoots will appear, and under cover the rose will stand until next spring.
Choosing young potatoes as a container for planting a cuttings of a rose, you will not go wrong. Basically, you will have a long-term source of moisture, starch, and carbohydrates. It will "work" better than any vitamin supplement, besides, it will protect the flower from many diseases typical for young plants.
Pros and cons of this rooting method


Cutting potatoes not only create a moist environment, but also provide the nutrients necessary for growth. After all, it contains starch, proteins and mineral salts, which are so necessary for the shoot for growth and root formation. Without a root system, the stalk is not able to take these substances by itself, and the potato supplies it with everything it needs.
Also potato serves as protection against hypothermia, drying out, from various pests and pathogens... This is the undoubted advantage of this method. And the only drawback is that, despite the developed root structure, according to statistics, approximately 15% of seedlings do not take root when transplanted to a permanent place of growth (however, the same thing happens with other methods).
Step by step instructions: how to plant and root a flower in a potato?
To grow a rose in a potato, you should strictly adhere to the following algorithm for planting and rooting cuttings:
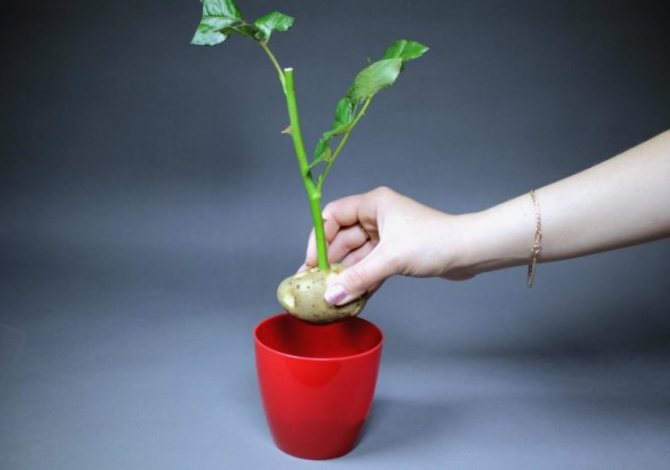
- Prepare your inventory. You can take medium-sized pots (at least 20 centimeters high) or even use plastic bottles. Divide the bottle into two parts: the handle can be placed in the lower half, and the upper half can be covered. We get a small greenhouse.
- Prepare a rose. When preparing the cutting, consider the following: the lower cut should be done 2 centimeters below the kidney at an angle of 45 degrees, and the upper one - 1 centimeter above the kidney at a right angle (90 degrees). The length of the cutting is 20-25 cm. It is better to cut the shoot under running water so that air does not get into the cut, with a pruner or a sharp knife.
All thorns and leaves should be removed from the cutting, as moisture is lost through the leaves. To make the cuttings germinate faster, you can put them in a biostimulant solution for a day: root, epin, heteroauxin. If for some reason there is no biostimulant, put the cuttings in a weak manganese solution for 30 minutes.
- Prepare the potatoes. Large or medium sized tubers are suitable, without damage or signs of disease. If the potatoes have eyes, remove them to avoid sprouting.
- Plant potatoes with cuttings. Burn the cuttings with a solution of potassium permanganate and stick the cuttings into the potato, up to about the middle. Lay drainage at the bottom of the pot (you can take small pebbles), and sand on top - 3-5 centimeters thick. Put a potato with a shank there, cover it with humus or soil mixture on top, any store-bought flower mixture will do.
- Create a greenhouse effect. To maintain warmth and humidity, a greenhouse effect should be created: if the cutting is planted in a pot, it should be covered with a jar, if in plastic, then with the top of a plastic bottle. Place the pot with the plant in a place where there is a lot of light, but there is no direct sunlight.
- Waiting for the result. Now it remains to look forward to the result. How do you know if the cuttings have roots? After about 10-15 days, you need to carefully pull out the plant, if it came out easily, then it has not yet taken root. It should be reinstalled in place, and the check should be repeated after a week.
Humus should be disinfected in advance with 2-3 frosts in the freezer for 2-3 days. From time to time, microflora reducing agents should be added to the soil - Fitosporin or Baikal M-1.
Care features
After the planting procedure, it is necessary to create a greenhouse effect for the seedlings for faster and more effective engraftment by covering them with plastic bottles and glass jars. At first, it is necessary to make regular almost daily watering of the planted tubers with future roses, since the soil must be sufficiently moist.
After 5 days, rose seedlings should be watered with a sugar solution (2 tablespoons of sugar per 1 glass of water). Such replenishment contributes to a more productive formation of the root system. The presence of sunlight at the root of the seedlings helps to quickly grow a full-fledged rose bush.
After the appearance of the first sprouts, it is necessary to begin to remove the protective cover made of plastic, glass or cellophane from the seedlings, gradually making them longer in the open space. So the seedlings will quickly and without problems go through the process of adaptation to environmental conditions.
Did you know? Natural rose oil is the most expensive in the world and more valuable than precious metals.
Further care


A prerequisite for rooting cuttings is to maintain constant soil moisture. Watering should be done regularly, but not very intensively. Besides watering, the cutting should be constantly sprayed with water at home temperature.To give the plant additional feeding, once a week you can water it with a sugar solution: for 0.5 liters of water - half a glass of sugar.
Difficulties and ways to solve them
Successful cuttings of roses do not require large material costs, but certain theoretical knowledge is needed. To avoid difficulties and get excellent results, novice rose growers can use the following tips:
Well, we got acquainted with all the nuances of growing a rose from a cutting at home. To increase the likelihood of removing a rose, it is better to root several cuttings at the same time.
If you didn't succeed right away, do not despair, keep experimenting, everything will certainly work out. But we will delight the beautiful flower obtained as a result of your labors for years with its divine appearance and incomparable aroma. In addition, it will become a reliable amulet for your family nest, take away all the negative energy and give you good luck in all your endeavors.
Roses from cuttings of a bouquet


Rooting cuttings of roses from a bouquet is also very popular. But it is worth considering that for this it is necessary to use not imported, but domestic flowers. And all because imported flowers, before going to Russia, are treated with special chemicals that have a preservative effect, and therefore the cuttings are not capable of forming a root system. A few tips:
- For rooting, cuttings are used only from a fresh bouquet.
- The shoot must be a little lignified.
- The stalk should be of medium thickness and the buds are located at the very top and bottom (the stalk is cut in the same way as described above).
Rooting roses from a bouquet should be as soon as possible. This means that if you were presented with a bouquet, then they should be donated immediately. To do this, you need to cut off all available flowers and buds. The length of the cuttings can vary from 15 to 30 centimeters. From below, all sheet plates must be cut off, and those that are on top should be shortened by 2/3 of their length. The prepared cuttings are placed in a vase filled with distilled water. Next, you need to systematically replace the water until the first roots appear. After that, the cuttings should be planted in a pot in the cold season, and in the open ground in the warm season. Cover them with a glass jar.
Useful video
Watch a video on how to grow a rose from cuttings in potatoes:
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
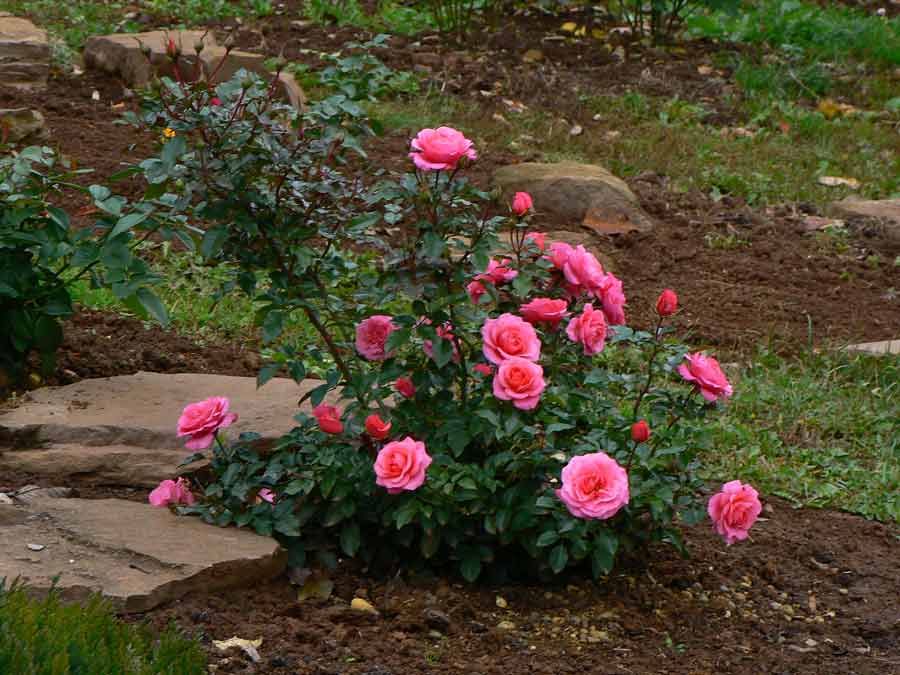
Beautiful roses grown from a donated bouquet on their own are the dream of any florist.There comes a time when lovers of the "queen of flowers" think about how to germinate it correctly and what method to use to achieve the result. Sometimes such an event seems simply impossible. Experts assure that the way to root a rose in potatoes at home is simple, and even a beginner can do it.
Having received a fragrant bouquet of red, yellow, white or pink roses, you can not only enjoy its appearance and aroma for several days, but also grow it in your own garden or on a windowsill in the future. Roses from the bouquet are suitable for propagation and creation of independent full-fledged small copies of the mother plant.
It is not difficult to sprout a queen of flowers, the main thing is to follow all the recommendations of experts. The bushes of blooming beauties are obtained from rooted cuttings that have taken root in:
- several layers of non-glossy newspaper;
- a glass of water;
- wet cloth;
- soil;
- potatoes.
If, when using the first three methods, the percentage of the appearance of roots and shoots is from 10 to 20%, then by growing cuttings of a rose in a potato, the grower will receive a 95-99% result. The success of the plan depends on the type of flower and the country of origin.
Flowers obtained by cuttings are called "own-rooted".


Scientists have found that not all roses are suitable for potted germination. Recognized as well rooted:
- climbing;
- semi-pebble;
- dwarf;
- polyanty;
- bush.
The phenomenon is explained by the fact that these varieties are closest to their progenitor - the dog rose. The ancestor of domestic roses is known to have a high survival rate and grow in the most unexpected places.
The method of growing a plant in a potato went to modern summer residents from their ancestors. Before a young healthy rose bush blooms in the garden, the cutting of the plant needs to be prepared for rooting and planting. Selected specimens from a withered bouquet are separated from the rest of the flowers. Material is rejected with:
- dry bearing stem;
- drying out at the base of the "body" leaves.
The main stem of the flower queen is divided into several cuttings. The length of each of them should be 15-20 cm. 2-3 green sticks are obtained from a standard bouquet rose. The thickness of the stem should be equal to the diameter of a pencil. The top of the cutting is cut at right angles. Bottom - under the sharp, it is desirable that the cut was made at 45 degrees. Experts recommend pruning under cold running water.
Make sure that 2-3 living buds remain on the planting material. The upper cut is made at a distance of 1 cm from the first bud. The last bud should be at the same distance from the end of the stick. Pruning is done with a sharp pruner or knife to cut off unnecessary parts in one go. If there are leaves and thorns on the stem, they are cut off. It is allowed to leave only the top greens, and then its length is shortened by half. Live shoots on the cuttings are an additional expenditure of the seedling's strength, which is useless when rooting.
Before placing the stick in a potato, it is treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and placed in a nutrient mixture for root growth. The top of the cutting is smeared with paraffin, natural beeswax or garden varnish. This will save you from unnecessary moisture consumption.
To stimulate active root development, planting material is placed for 5 or 10 hours in growth stimulants, purchased in the store or made by yourself. Of the proven specialized tools suitable for such purposes:
If there is no desire to saturate the seedling with artificial preparations, it is worth preparing a root stimulator with your own hands. To do this, the lower part of the cutting is coated with honey and placed in the juice of aloe frozen in the refrigerator. It is recommended to maintain a fleshy leaf of a green desert eukaryote for 24 hours at a temperature from 0 to +2. When germinating, you can do without freezing the aloe, but just drip 20 drops of a freshly cut plant into a glass of water.
How to propagate at home, step by step
Preparing inventory
To grow a rose from potatoes, you do not need any additional equipment. An ordinary pruner, a knife and a small spatula are enough.
Selection of material for propagation


The choice should be taken seriously so as not to waste your time and work. You cannot cut off an unripe bud. It can be easily distinguished from a ripe bud - it is more difficult to tear off thorns from an unripe bud. It is difficult to grow a rose from cuttings with immature buds, they often do not take root.
When rooting a purchased cut rose, you should make sure that the flower was grown in Russia, since foreign suppliers often process the cut with a special solution for longer storage, which makes cultivation difficult or impossible.
The potatoes should be young, preferably recently dug (such potatoes contain the maximum amount of useful and nutritious substances), medium in size, without any signs of rotting or disease.
Flower and potato preparation
This is the most important step in growing a healthy rose. In order for everything to go well, you need to adhere to the rules:
- The cuttings must be cut with a sharp pruner, leaving the top cut straight and the bottom cut at a 45-degree angle to make it easier to stick into the potato. Experienced gardeners are advised to leave a couple of upper leaves on the stem and remove all the lower ones.
- Then the cuttings must be treated with potassium permanganate and left for 12 hours in aloe juice (honey can be added) to stimulate growth. It is allowed to use purchased biostimulants - Kornevin or Giley. After that, the cuttings of the rose must be kept in a heteroauxin solution for a day.
- Next is the turn of preparing the selected potatoes. To do this, it is enough to cut out all the eyes to prevent germination.
Important! At least three buds should remain on the handle. It is recommended to cut a cut below the kidney by 2 cm. The upper cut is at a distance of 1 cm above the kidney.
Care and greenhouse effect
- When everything is ready, stick each stalk into a separate potato with the lower, sharp end about halfway up and plant shallowly in pots, placing a drain on the bottom of the pot and mixing the soil with sand. The first watering must be carried out with an unsaturated solution of potassium permanganate.
- Grown roses require constant watering, and it is also advisable to saturate the tubers with a sugar solution once a week (1 tablespoon per mug of water). Spray the plant regularly as it is best to root it in a humid environment.
- The shank should be kept under the jar and provided with good lighting. The stem leaves should not come into contact with the glass of the jar.


The first shoots can be expected in a month, and sometimes even earlier.
Two weeks after planting, you need to briefly remove the jartaming the plant to the environment. First, the jar is slightly raised and fixed. In this position, the flower begins its acquaintance with the open air. Every day you need to increase the time to familiarize the rose with the space, and after a week the jar can be removed altogether. It can be removed immediately, but after half a month, put back on time.
We offer for viewing a video lesson on the topic of rooting a rose in a potato:
Transplanting outdoors in autumn or spring
Now, when the stalk does not need the protection of the jar, it is ready for transplanting into open ground. If a bud is found on a premature stem, it must be removed. Half a month before transplanting, it is advisable to start hardening the plant, for this it is enough to take it outside for a couple of hours.
Attention! You can plant it either in the spring, in order to get an adult bush by the fall, or in the fall, so that the plant has time to get stronger and take root. The place is preferably open, well protected from the wind.
- For planting, a pit about 20-30 cm deep is needed. It is very important to fill the bottom of the pit with sand so that the potatoes do not come into contact with the ground, this will help prevent rotting of the tuber and, accordingly, the stems. Then we stick the cuttings into the hole. If you plant roses nearby, then for further growth the distance between them should be at least 15 cm.
- We fill the hole with earth, leaving the root collar a couple of centimeters from the surface, and tamp it a little. It is very important to maintain soil moisture, to make regular but moderate watering so that rotting does not begin.
- For a while, it is recommended to keep the plant, which is planted in potatoes, under a container with a hole (an ordinary plastic bottle with an unscrewed lid will do) so that the plant gets used to it, but does not deprive it of oxygen. In sunny weather, direct rays should be avoided by shading the plant. On cloudy days, the jar should be removed.
When the plant gets stronger (this can take about a month), it will no longer need shelter. - In winter, the planted rose is sheltered from the cold, when the night temperature drops to 5 degrees below zero. The roots should be hidden under organic mulch (dry hay, leaves, grass, straw, bark, sawdust), and the stalk itself should be covered with some kind of dense material (polyethylene, oilcloth).
- The first year the seedlings are not pruned.
ABOUT
Result
The first flowering will begin in six months. Watch the plant and, having gained strength, it will delight with its luxurious flowers.