Why are grapes transplanted
Grapes are transplanted in cases where, for example, a redevelopment of the site has occurred, or the bush has grown too large and began to lay claim to new territories. Another reason for moving the crop to a new place may be poor growth of the shrub (perhaps it lacks light and heat, or the composition of the soil is not suitable).
Experts recommend replanting only young grapes that are no more than five years old. Bushes of one year take root most quickly on a new permanent residence. It is undesirable to touch older plants. There is a great risk that the roots will be damaged during digging and the plant will die.
Works prior to grape transplanting
If the owner wants to transplant the grapes to another place in the spring, he must take care of preparing the pit in the fall. It is recommended to dig a hole so deep that a bush can easily fit in it. Having dug a hole of a suitable size, the growers fertilize the soil with humus, minerals and ash. Already in the spring, in the area of the depression, a new hole is being dug, but of a smaller size. The rhizome of the plant should enter into it.
When transplanting several bushes of grapes, holes are dug with an indent of 2 - 2.5 m from each other.
Before transplanting the grapes to a new site, the prepared soil is heated by sprinkling with hot water with potassium permanganate. The substance is poured into a liquid until the color changes to a dark red hue.
Seat selection

The plot for the vineyard is prepared for the season ahead. A well-lit, windless place is chosen for culture. It is preferable to be on the southwest side. Although many argue that grapes are not picky about the composition of the soil, they still grow better on light loam and black soil, they do not like clay soils and salt marshes. The culture also feels uncomfortable on sandstones. It is also important that the groundwater flows at least two meters from the surface of the earth.
When planning your garden, you must take into account that the grapes need a lot of free space. It should not be placed next to other tall crops, otherwise there will be competition for nutrients.
Katavlak
To move bushes from ten years old (but not older than 20), it is better to apply layering with a whole bush - katavlak.
To do this, in early spring, they dig a ditch near the bush and free the root stem from the ground to the heel roots. Then, in the right direction, they dig a trench 60 cm deep to the planting pit in a new place. The bush, along with the root stem, is dumped into a trench and pressed to the bottom. Choose the best sleeve, leaving 1-2 developed shoots on it, on which all eyes, except 3-4 upper ones, are pinched off. Vine sleeves are laid in a trench, bringing out the upper part of young shoots in a new place above the surface. The planting hole and the trench are covered with earth with humus in a 2: 1 ratio. The sleeve is tied to a support, covered, and in the first year it bears fruit.
There are ways of katavlaka with different laying of bushes and vines. They are mainly used in vineyards that are rooted, to move the bushes in the transition from haphazard plantings to ordinary or to reorient the rows. Almost any mis-planted vineyard can be streamlined and repaired in this way.
Popular:
- When and what cover grapes for the winter. Shelter options.
- When is the best time to plant grapes, in spring or autumn. The subtleties of agricultural technology
- How to plant grapes correctly. Site selection, preparation of seats.
- Diseases and pests of grapes, description, photos, control measures, prevention
- How to make supports for grapes correctly? Materials and device.
The following:
- What kind of maintenance work for grapes to carry out before and after flowering.
- How to form a vine correctly
- Phyloxera is a very dangerous pest of grapes. How to fight
- What types of fertilizers to use for better fruiting grapes
- When is the best time to plant grapes, in spring or autumn. Subtleties of agricultural technology
Transplant timing
Many gardeners ask themselves: when is the best time to replant grapes? The answer to this question lies in the biological characteristics of the culture. The fact is that the root system of a plant is never dormant. Even in winter, when the aboveground part is "sleeping", the roots continue the growth process. But only on condition that it is warm and humid in the depths of the soil. This condition can be both spring and autumn. It turns out that grapes can be transplanted when the soil warms up above 8 degrees Celsius and in autumn, when the stems enter the dormant stage and the plant begins to spend all its strength on increased root growth.
However, one more factor should be taken into account - the climatic features of the region. If this is the north of the country, where winters are frosty and long, then the ground there quickly freezes over, which prevents the roots from developing. This means that if you transplant a bush in autumn, then it will not have time to take root before the onset of frost, since the roots will stop growing and the plant will no longer receive nutrition. It turns out that for the northern regions, as well as the central part of Russia, it is preferable to replant grapes in the spring. There is an opinion that this should be done as early as possible, almost in the month of March. But it is not so.
Remember, even if it becomes warm, this does not mean that the soil has warmed up thoroughly. The transplant is carried out only when the soil temperature is at least 10 degrees Celsius. For the Urals, this is mid-May - early June, for the Moscow region and the middle zone - mid-April.
In the southern regions, it is preferable to transplant grapes to another place in the fall. This is due to the fact that when transplanting at other times (for example, in spring or summer), due to extreme heat and lack of water, the bush may not take root. The optimal time for the procedure is mid-October.
Note!
Try to replant adult grapes in the fall.
The specifics of the autumn transplant


Transplanting grapes to a new place in the fall should be carried out only after all the leaves have fallen off. It is this time that will be marked by the onset of a dormant phase, the growing season ends. But this only applies to the upper part of the plant, while the roots continue to develop. If the autumn is warm (or the vineyard grows in the southern part of the country), then the transplant can be arranged until the beginning of November. But you cannot hesitate too: the grapes must be transplanted at least two weeks before the onset of stable cold weather. If you plant it later, then, most likely, the plant will die.
Attention!
Seedlings transplanted to a new place in the fall certainly require shelter for the winter, regardless of the region in which they grow.
Spring transplant: basic rules
In the spring, all procedures with plants begin to be carried out before sap flow begins and the buds wake up. But you also need to take into account the readiness of the soil to "work". It is not worth starting a transplant too early - in cold soil, the roots will not have time to wake up and begin to feed the ground organs of the plant, from which it can die. In most cases, the conditions for the survival of seedlings have to be created on their own: before planting, the soil is spilled with hot water to warm it up. And after planting, the stems are covered with cold soil so that the sun's heat does not awaken the buds ahead of time.
For the spring planting of grape bushes, planting pits are prepared in the fall. An 80-centimeter hole is dug under each seedling and filled with organic fertilizer (humus, compost). Then they are half covered with fertile soil. In the spring, when planting, a layer of soil mixture consisting of leafy earth, peat and mineral fertilizers is poured onto the bottom of the pit. In the spring, the seedlings take root quickly and by the summer they are overgrown with the first side shoots and lush bright green leaves.
Summer transfer


For the summer procedure, planting pits are prepared in the same way as in the fall. They are dug up a month before planting. A fertile mixture is also prepared, with which the seedlings will be backfilled. Since there is a lack of moisture in the summer, the soil is watered abundantly before planting. Immediately after planting the plants in a new place, the site is covered with compost or straw so that the roots do not feel thirsty during the survival period. After transplanting, the seedlings must be shaded from excessive UV exposure to the plants. Do not plant grapes close to tall fruit trees and bushes.
Preparatory work
We recommend reading our other articles
- How to feed cucumbers?
- Apple variety Idared
- Zucchini Cavili F1 - variety description, cultivation and care
- Omshanik for bees
Before replanting grapes, it is worth carrying out preparatory work. The place for planting grapes is always chosen sunny, so that the light falls on the bush and warms it up well. At the same time, the place must be protected from wind and drafts from at least one side. If there are other shrubs, trees on the site, they should be 2-4 meters away from the grapes.
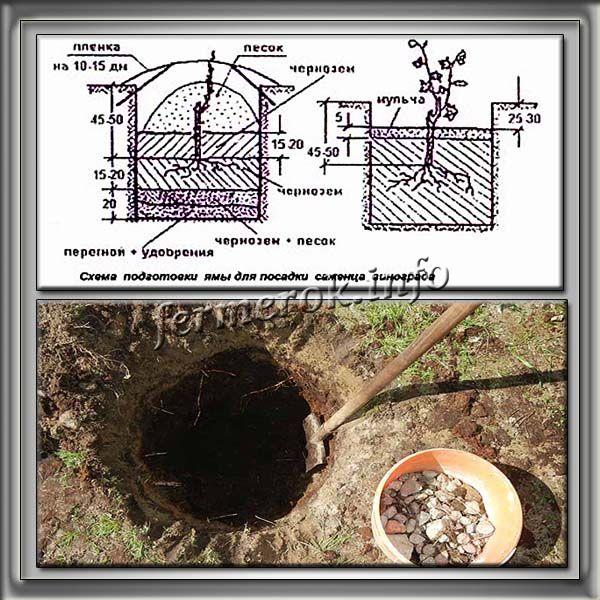

The planting hole is made at least 1 month before planting the bush.
Important!
The grape has a developed root system. The plot for it is chosen with a low level of groundwater (at least 2 meters), otherwise the root of an adult bush may begin to rot.
The planting hole is made at least 1 month before planting the bush. It is dug a meter deep and 60-80 cm wide, depending on the size of the seedling. Drainage is placed at the bottom if the ground is dense, heavy and poorly permeable to water. Broken brick, expanded clay or pebbles can be taken as drainage. The planting soil is interfered with from the soil obtained by digging a hole, humus, wood ash, superphosphate and potassium sulfate. The components are mixed and left for a month.
A seedling should be purchased in a specialized store or grown independently from a cuttings. A young bush should have a developed root system, an increase of 35 cm. Before planting, pagons are cut by 1-2 buds at the bush. Slices are smeared with garden varnish so that the bush does not start to hurt. Bare roots are shortened to 30 cm, diseased and damaged ones are simply cut off. You can soak the root system in a growth stimulator for 12-24 hours, then it will quickly take root in a new place.
Transplanting grapes of different ages
Grapes of different ages have their own biological characteristics that must be taken into account when transplanting. Rules for moving grapes depending on age:
- Annual grapes. For propagation of grapes, cuttings are used - small branches that are planted in a school for rooting. By the end of the season, the cuttings are overgrown with a weak root system and 2-4 green shoots. Rooted cuttings are transplanted permanently in spring or autumn. Their survival rate is very high.
- Biennial grapes. The plant is a fairly seedling with a well-developed root system and stems. Grape seedlings are transplanted to a new place in most cases without problems. The main thing is to trim the shoots, leaving one or two eyes on the stems. Of these, shoots will subsequently appear, which in the future will make up the main arms of the bush.
- Three year old grapes.This is already a fairly mature plant with lignified long sleeves and strong developed roots that go deep underground. Carry out a transplant of fruiting grapes in the fall. Shoots must be cut to four eyes, since the roots cannot immediately feed a highly overgrown plant.
- Four to five year old grapes. A mature plant that is very difficult to dig up, since the roots can go up to 100 centimeters underground. Dig the bush carefully, removing the entire root system with an earthen clod from the ground. Shoots are shortened to 4-6 eyes.
- The grapes are over five years old. This is an old plant that is difficult to tolerate various manipulations. Therefore, before replanting it, you should think about whether it is worth touching it at all. First, it is almost impossible to dig up the root system without damaging it. Secondly, the ground part has already grown too large and will have to be completely removed. It is better to propagate such grapes using cuttings or cuttings.
Transplant tips
Transplanting grapes to a new place in spring usually takes place without serious complications due to its excellent survival characteristics. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors that can negatively affect the survival rate or even lead to the drying out of the vine:
- You can not transplant a damaged bush.
- If there are many old vines and roots left, the plant may not take root.
- Early fruiting can negatively affect survival.
- Failure to comply with temporary regulations for transferring grapes to a new location.
How to transplant an apple tree in spring to another place
Pests are no less dangerous for a grape bush in a new place. It can be affected by phylloxera or black cancer. Also, a weakened plant is practically defenseless against diseases. This is what stops many growers from transplanting. They are trying to find alternatives. But about them a little later.
Important! The optimal time when you can replant grapes to another place is late autumn or early spring.
Rules for transplanting young grapes
Before moving the vine to a new location, you need to carefully select this location. It should be borne in mind that the bush will grow here for many years, take into account all the accompanying factors. Otherwise, a situation is possible when the procedure will have to be performed again, which is very undesirable. A large sunny area, well protected from wind and drafts, is best suited for these purposes.
It is important to prepare the necessary tools and additional fertilizers. For the procedure of transferring a grape bush from inventory, you will need: a shovel to dig it up, and a pruner to cut off all that is superfluous. The transplanted grapes are fertilized with manganese solution and cow dung.
Additional Information! The currant bushes and fruit trees planted along the edges will help protect the area on which the vine garden is located from draft and wind.
Step-by-step instructions for transplanting
To avoid unforeseen complications associated with violation of the rules for carrying out work, you need to adhere to the following tips:
- The transplant should begin with the preparation of the pit. Its depth and size depends entirely on the size of the root system and the earthy coma, which was preserved when the plant was dug up from the old place. At the bottom you need to pour mineral fertilizers and humus (from 6 to 8 kilograms). If the soil to which the young plant is transferred is rich in nutrients, the amount of humus and mineral additives can be reduced.
- When digging up the plant in a circle, you need to be very careful not to damage the root system of neighboring bushes (if any).The radius of the earthen coma left should be at least 50 centimeters. It is not necessary to dig up the entire root as it can be quite large. The main thing is to preserve the strong young parts of the root. Excess soil from the rhizome is shaken off very carefully to avoid damage to the plant.
- After removing from the ground, the root system must be immersed in a clay solution with the addition of manganese. This step will prevent not only drying out, but also rotting.
- Any excess from the vine must be removed with a pruner. It is recommended to keep the two main sleeves. After the preparatory stage, you should place the bush in the hole and spread the root.
- Further, the pit is filled up, and the bush is watered abundantly with warm water.
Attention! Young grapes less than three years old should be transplanted to a new site directly with an earthen clod, which will make it easier to settle down in a new place. To perform this procedure, the grapes are not watered for several days before digging.
It should be noted that, unlike young bushes, which bear fruit in the first year after transplanting without harm to growth, absolutely all ovaries must be removed on the old ones in the first season, and no more than a third should be left in the second. This procedure allows you to increase fruiting in the future.
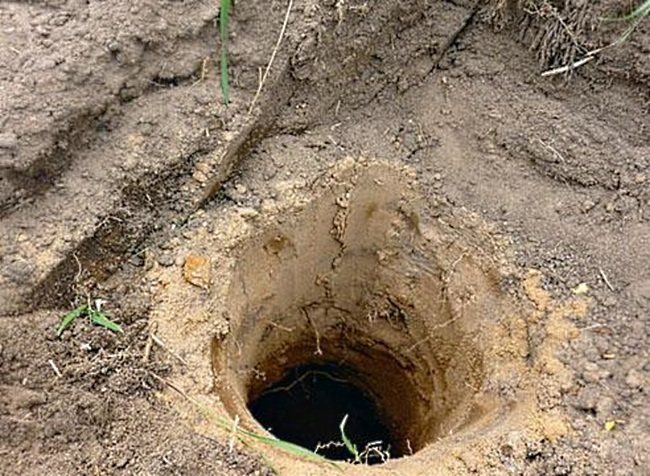


Vineyard planting hole
How to transplant grapes
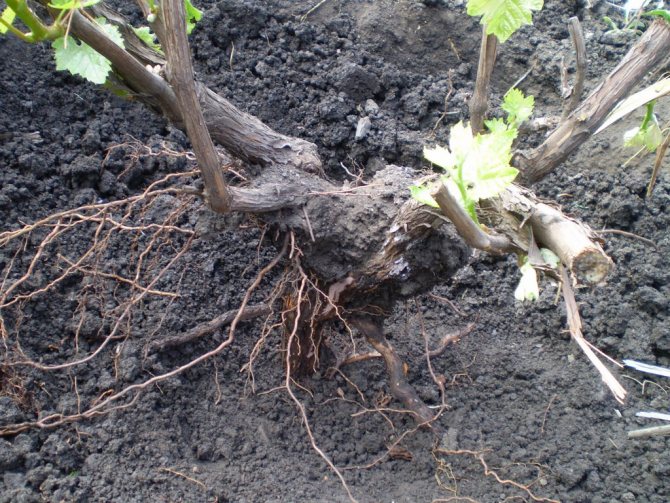


This crop can be moved to a new place of growth without losing varietal traits. For this, different parts of the plant are used.
Transplant by layering
Old grapes can be used to produce new fruit-bearing bushes. It is believed that this breeding method is the most accessible and effective.
The technique of propagation of grapes by layering:
- A long two-year developed lash with kidneys is selected as a "raw material".
- The shoot is laid in a shallow narrow groove, sprinkled on top with a layer of earth.
- The planting is watered abundantly with water.
- Over the summer, the buds located on the vine will sprout. The shoot will acquire its own root system.
You can transplant grapes to a new place in the fall. To do this, the layers are separated from the parent plant and planted as a separate plant.
Note!
The advantage of this method is that the cuttings are fed from the mother plant, so there is no need to worry that it does not receive enough nutrients.
As layering, you can use not only the whole vine, but also short green shoots. The essence of the method is to bend the ends of such shoots to the ground and dig them in, fastening the branches securely so that they do not crawl out of the ground. In the fall, the ends will be overgrown with roots, and then the branches can be cut off from the mother bush. Transplanting rooted cuttings can be done in the fall.
Planting cuttings
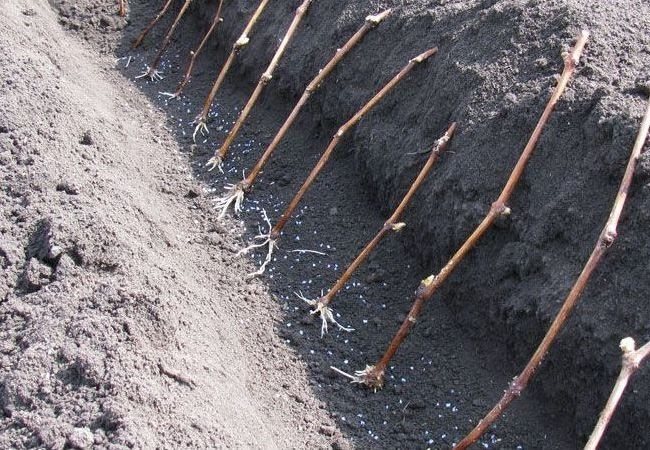


The shanks are cut from one long young (annual) vine. It is important that there are 2-3 eyes on each handle. Cuttings with one end are inserted into a moist loose substrate for rooting.
After a few weeks, the first leaves appear from the eyes. This means that the root system has already formed. Then the shanks are transplanted into a school (a separate bed). There they will grow until next season. They can grow in greenhouse conditions or at home. At the age of one year, the seedlings are moved to a permanent place of residence. Immediately after transplanting, they are protected from sunlight. When planted in spring, by autumn they will already root well and will give the first harvest the next year.
Katavlak
A kind of rooting by layering. This method is used to rejuvenate old grapes or to thicken the vineyard. For this, the lignified vines of the old grape bush are laid completely in the ground. Roots will grow from the sleeping buds of the sleeves in a few years.
Katavlak can be done in several ways. Vines can be laid in one line, on top of each other or in different directions.In any case, the procedure includes fertilization with humus and mineral compounds. The vines are laid in deep grooves on a fertile, well-fertilized soil layer. In certain places, the ends of young vines are brought to the surface - they will be the main component of the renewed bush. From the buds that remain above the surface of the earth in subsequent years, powerful fruitful shoots will grow. They will bring a new crop in the second year of planting.
Note!
Katavlak is made only on own-rooted grape bushes.
Additional transfer information
How to transplant jasmine to another place
One of the most painless options for replanting old bushes is not digging out, but using cuttings. Such a step will allow not only to rejuvenate the vine, but also guarantees the painlessness of the procedure and 100% survival rate.
To lay down one of the vines, separate and dig in. After a while, it will give its own roots. Thus, she receives useful substances not only from the mother bush, but also thanks to her own roots.
After two years, the rooted cut is completely ready for planting on a new site. This method is good both for transplanting, and for replacing a dried plant or grafting another variety.


Removing grapes allows you to quickly get new bushes
In order to transplant a very old bush that is more than 10 years old, but less than 20 years old, you need to use the katavlak method. It is similar to what is described above, but consists in the layering of the entire bush, which is planned to be transferred to a new location.
This method of vegetative propagation is possible in early spring (in areas with prolonged winters, you should wait for the frost to recede). It consists in carrying out the following steps:
- A hole should be dug in the immediate vicinity of the bush. Free the root system from the ground, including the heel roots.
- The bush is placed in a ditch, the most powerful arm is selected from the entire root system, the vine remains in the trench, and the shoots are brought out. Thus, the vine takes root in both the new and the old place. Fruiting begins in the first year after transplantation.
- This method allows you to systematize the growth of a grape bush and make some adjustments in its planting. Give the vine more light, which means higher yields.
All of the above recommendations and planting methods will avoid problems when transferring a plant to a new site. At the end of the article, there are a few more recommendations from experienced gardeners.
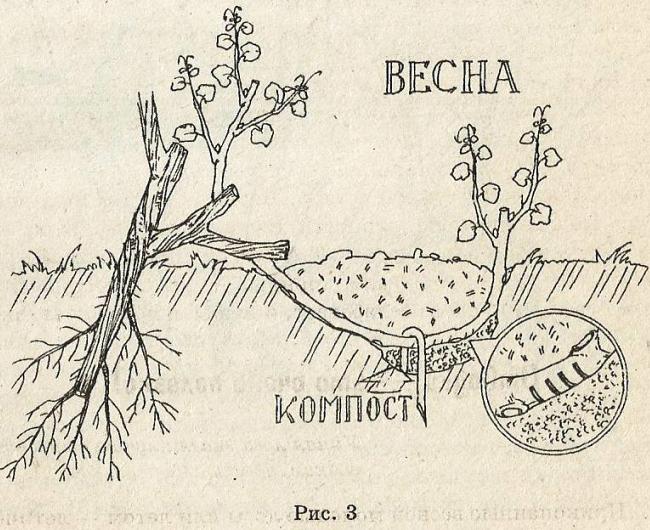

Underground grape layering scheme
How to transplant grapes in the fall
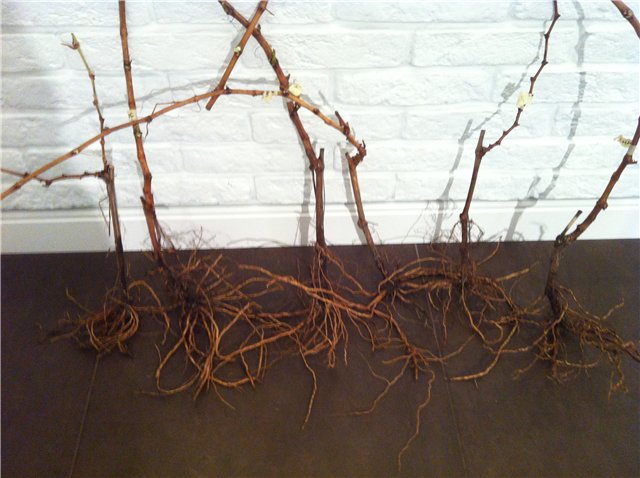


The transplant procedure requires lengthy preparatory measures. Planting holes are prepared in advance, preparatory procedures for the plant itself are carried out.
Grape preparation
Before starting to dig up the plants, their ground part is shortened. Long shoots (vines) are completely cut off. Prepared bushes have two short young arms, each of which has 2-3 buds. At the shoots themselves, the apical part is also shortened, and the places of the cuts are treated with garden pitch or crushed coal.
3-4 days before digging, the soil is watered abundantly, so that, firstly, it is easier to pull out the bush without damaging the roots, and secondly, so that the wet earthen lump will reliably adhere to the roots. In young bushes, the diameter of the coma is about 30 centimeters, in old ones - 45-50 centimeters. It is at this distance from the base of the stem that you need to start digging in the bushes. They dig in the plants from different sides, so that later they can pick up the root with bayonets and pull it to the surface without damage.If the transplant is carried out with a lump of earth, then the roots that stick out outside of it are pruned, and the plant is placed on a flat surface (plywood, shovel). So that the lump does not collapse, it is carefully wrapped in some kind of material.
Preparation of planting holes
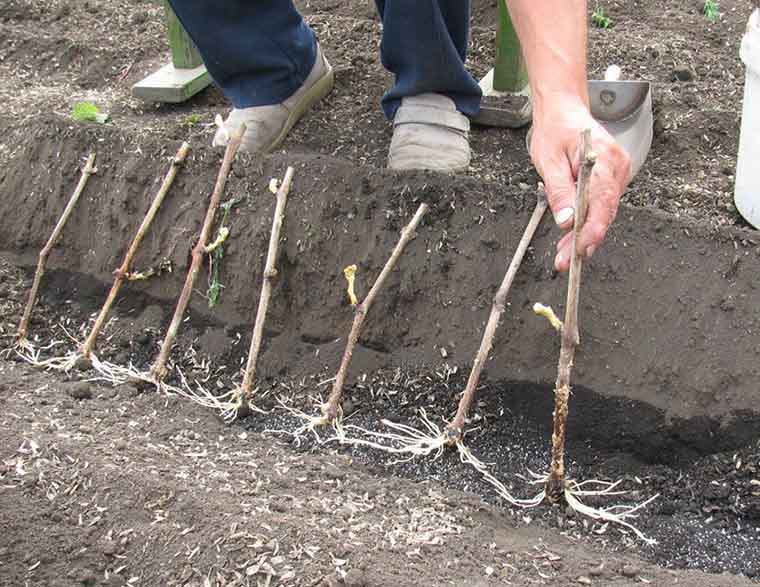


The size of the pit depends on the maturity of the grape bush. If he is young enough, and the roots have not grown too much, then the depth of the pit can be 50-60 centimeters. An adult bush is planted in a hole 100 centimeters deep. The depth of the holes also depends on the composition of the soil. If it is loose, fertile, then the roots in such soil will grow rapidly vertically. It is more difficult for them to develop in dense soil, and therefore it is better to dig a bigger hole so that they have room to grow. In addition, on clay soils, it is imperative to arrange a drainage layer.
The distance between the bushes should be at least two meters. For backfilling the bushes, a soil mixture is prepared, consisting of turf, peat, ash and phosphorus fertilizers. River sand is added to the clay soil.
How to dig up bushes correctly
Grapes are transplanted in three ways:
- with a clod of earth;
- with partially bare roots;
- with an open root system.
Transplant with a clod of earth
Planting by the transshipment method is preferable, since with this method the root system remains intact. In addition, the roots quickly take root in a new place, even without any additional procedures.
Transplant technology:
- The pit is half covered with earth.
- The plant is not watered a couple of days before digging so that the lump does not fall apart.
- An earthen lump along with the roots is inserted into the hole.
- The roots are watered with a root formation stimulant (Kornevin, Heteroauxin).
- All voids around the coma are covered with fertile soil, tamping each layer.
- Having completely covered the roots, they form a near-trunk circle.
- The plot is watered abundantly so that the poured earth grasps with a lump.
Transplanting grapes with semi-bare roots or completely open root system


It happens that during the digging of a bush, the lump partially or completely collapsed. This happens if the soil was too dry or the root system grew too much in different directions and the earth could not "envelop" it. If there are large pieces of dry earth left on some of the roots, then it is better to remove them by gently tapping on them with a stick so that they collapse.
Transplant technology:
- For an open root system, the depth of the pit should not be too deep.
- The roots are soaked in a growth promoter before planting. They are disinfected in a manganese solution. They are dipped in a clay-dung mash so that they are wet at the moment of adhesion to the ground.
- If the roots have time to dry out, they are shortened a little.
- A small mound is poured at the bottom of the pit, on which a bush is placed. The roots are straightened along the slopes of the mound so that their ends only look down.
- The pits are covered with soil mixture, slightly shaking the plant so that the voids are clogged with earth.
- Falling asleep, the bush is watered. If the planting is spring, then the trunk circle is mulched.
Timing
When to transplant grapes so that they quickly adapt to new conditions and do not experience stress? Let's figure it out.
Spring
Buds begin to bloom, sap flow is activated, the plant slowly emerges from hibernation, the soil warmed up to +8 ° С? Under such conditions, you can safely transplant adult grapes to a new place. Landing time depends on the characteristics of the region and weather conditions: in the south, the ideal period is March, in the middle lane - the end of April.
You can transplant grapes in the summer, but in this case, the bush is under great stress. Transplanting together with a clod of earth will help to minimize it and accelerate the survival rate in a new place, guaranteeing minimal damage to the root system. July is the hottest period, so it is better to postpone planting work for at least a month.
Fall
The most suitable time for transplanting grapes in the southern regions is late autumn. During this period, the foliage is shed, the plant slowly goes into a state of dormancy and will direct all its forces to rooting. In colder regions, a transplant is planned for early autumn, so that the plant has time to take root before the arrival of real frosts.
Caring for grapes after transplanting
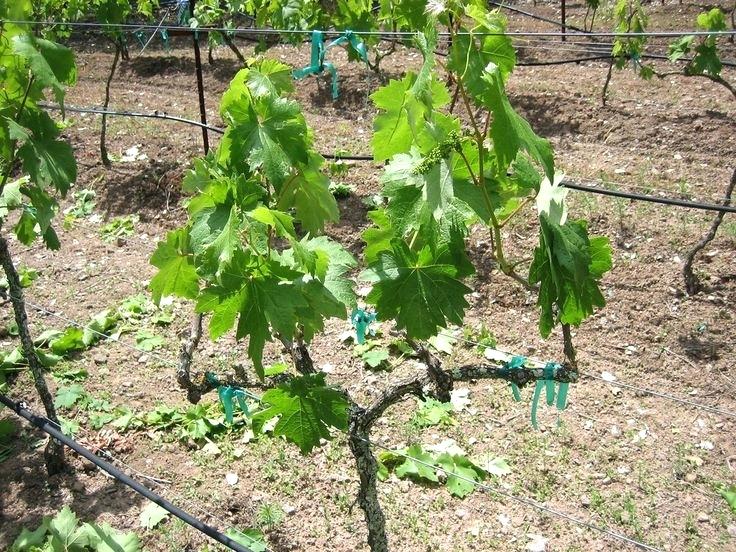


Care measures for transplanted grapes depend on the time of transplantation. Autumn plantings must be covered for the winter. A weakened plant requires reliable frost protection. The shelter involves backfilling the bases of bushes and near-trunk circles with earth or straw (sawdust, peat). The apical part is covered with ultrasil. To prevent fragile seedlings from breaking under the weight of non-woven material, a frame is installed above them, which is wrapped with agrofiber. You can put grass or hay on top.
In the spring, the shelter is removed, but they do it gradually. First, the base of the bush is exposed, and only then, after a few days, the stems. Bushes protect from aggressive sunlight for a couple of weeks, which, coupled with frost, can cause burns on plants. It is preferable to stretch a protective awning over the bushes. With the arrival of heat, the plants will "wake up", sap flow will begin, and the buds will swell. The fact that the grape bushes have taken root will be prompted by the appearance of the first leaves. During this period, it is important to feed with nitrogen fertilizers, which will stimulate the seedlings to build up green mass. Further, vineyard care consists of traditional agrotechnical measures related to watering, pruning, and pest control.
When planting grapes in summer, the plants are immediately mulched to protect the soil from excessive moisture evaporation. If the grapes are transplanted in the spring, then the soil contains sufficient moisture for the normal development of plants. Therefore, it will not be necessary to water the vineyard too often. It is optimal to "water" the plants every 10 days. When planting in summer, the seedlings should be watered more often, every 6-7 days. Rooted bushes are rarely watered, but abundantly, spilling directly into the base of the bush. It is best to arrange a drip irrigation system or small grooves around the bushes, through which moisture will flow directly to the roots. Water consumption per plant is about 20 liters. During flowering and ripening of the fruits, watering is stopped to avoid cracking the year. The last watering is carried out in August. If there is little precipitation in the fall, then in October, water-charging irrigation is carried out.
Advice!
Combine watering with soluble fertilizers!
Top dressing of summer plantings is carried out in the fall. It is necessary to increase the vitality of plants in the winter. This time, they do without nitrogen fertilizers, since the plants must retire, stop vegetating. The introduction of phosphorus-potassium compounds and ash will help increase the chances of survival. Grapes respond well to foliar feeding with complex mineral fertilizers. And mulch from organic matter (compost, humus) will strengthen the stems and increase the level of shoot growth.
When planting in autumn, spraying with insecticides is carried out in the spring. This is necessary in order to destroy pests that have wintered in the soil and, with the arrival of heat, begin to climb onto young grape stems. For protection, when neither disease nor insects have managed to penetrate into the vegetation cover, it is enough to treat the bushes with insecticides and contact fungicides.
Note!
In the first year, the grapes are not allowed to bear fruit, since at this time he must use all his strength to build up a strong root system and vines. For this, all inflorescences are removed in a timely manner. In the second year, part of the fruit brushes is removed from the bush.
Care after transplanting to a permanent place
In order for a newly transplanted bush to quickly adapt to new conditions, it needs attention and care:
- periodic watering;
- timely fertilization;
- protection against diseases and pests;
- reliable shelter in the winter.
The above activities will help the grapes not only recover quickly, but also contribute to the development of strong shoots.
Watering
After transplanting, an adult plant needs abundant watering. In the first three weeks, the condition of the soil is closely monitored: it should always be slightly moistened.
Fertilizer
All necessary fertilizers are applied when preparing the soil for planting. They usually last for several years. When transplanting, you can only mulch the root zone with rotted manure in order to additionally saturate the soil with organic fertilizers.
Treatment against diseases and pests
Even with a careful transplant, an adult bush is stressed and becomes susceptible to any disease. He needs special protection and attention.
Various pests are very fond of young grapes. An annual two-time insecticide treatment will protect the plant from almost all common pests. Spraying grapes with complex fungicides will prevent the development of most fungal and viral diseases.
Frost protection
Newly transplanted grapes require reliable shelter for the winter. For this, covering materials or coniferous spruce branches are used. When the air temperature drops to zero, the grapes are laid on the ground and the covering material is pulled from above.
With a spring transplant in regions with a mild climate and warm winters, shelter of the grapes is not required.
Common mistakes when transplanting grapes
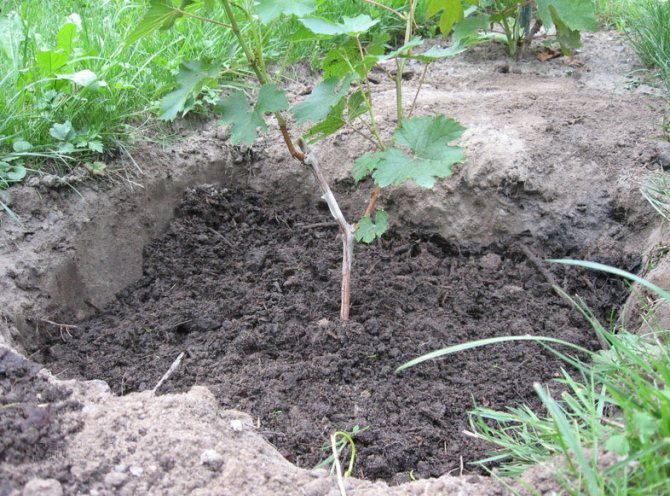


Many summer residents fail to transplant. Even successfully grown cuttings and seedlings, after transplantation, abruptly lose their healthy appearance, stop growing, dry out and die. This is mainly due to improper preparation of the planting material, a shift in planting dates.
Major mistakes:
- Strong pruning. When transplanting, it is recommended to trim the roots. But if only young, green roots are left at the base of the roots, while removing the middle and heel roots, then they will not be able to endure "such a burden." A weak root system cannot feed the ground part well, from which it stops developing, the grapes do not take root. Remember, the roots only need to be trimmed a little so that they grab onto the ground faster.
- Transplanting old grapes. Grapes take root well during the first three years of life. Every year its regenerative abilities are getting worse. Grapes older than five years in 99% of cases do not take root at all. Therefore, for transplanting, you need to choose only young and healthy grapes.
- Transplants are not on time. If you do not guess the timing and transplant much earlier or later than the period when the plant goes into hibernation or, on the contrary, wakes up, then the chances of engraftment drop sharply. It is important to determine the time for moving: grape transplanting in the fall should be carried out 2-3 weeks before the onset of cold weather, and in the spring - no later than the beginning of sap flow.
- Inappropriate place to transfer. If the grapes are planted on a site where this crop has already grown, then the land in this place is very depleted. In addition, pathogens of grape diseases or pests may be in the soil, which will gladly begin to eat a new victim. Experts recommend planting grape seedlings on a new site, where this culture has never grown before.
Transplant methods


The younger the bush, the smaller the diameter of the earth needs to be dug in.
It is recommended to replant grape bushes without clearing the roots from the ground at all - they should remain in a large coma, which is subsequently placed in a wide depression. This method - transshipment is suitable for bushes up to 3 years old.
If the bush is older (5–7 years old), some of its roots must be cut off, leaving the youngest. After that, the roots are lightly dipped in a mixture of clay and potassium permanganate.
, and the extra vines are cut off.
.
For older bushes, a transplant method such as layering is suitable: one vine must be taken to the side and buried in the ground. After some time, it will give its roots, and you can get rid of the old bush.
When to replant grape cuttings. Grape transplantation methods
Depending on the age of the shrub and the needs of the grower, it is possible to use several methods of grape transplantation. This is planting cuttings, layering or transplanting a whole bush.
Cuttings
Cutting grapes can rather be attributed to a propagation method, however, when moving a bush to a new place, this method can also be used.
- In autumn, after the foliage has completely fallen off, cuttings should be cut off from the main bush. It is advisable to cut off a straight section of a fruit shoot 0.3–0.4 m long.
- The cuttings are stored in a plastic bag in cool conditions (refrigerator or cellar) throughout the winter or buried in the ground for this period.
- At the onset of spring, the cuttings are soaked for 48 hours in water.
- Next, they should be rooted in a container filled with soil. The substrate must be watered daily.
- When the cutting takes root, it can be planted in a planting hole. At the same time, the roots should germinate well and take up almost all the space in the container.


Layers
By planting the layering, you can move the grapes a short distance from the main shrub. For this kind of transplant, you need one vine with a growing point and 3 leaves. The rest of the greens on the shoot must be removed.
- At a distance of at least 0.2–0.25 m from the main bush, a small trench should be dug about 0.5 m deep.
- The bottom of the trench must be filled with black soil mixed with dried humus in equal proportions.
- The prepared vine is laid out in the recess and sprinkled with soil.
- The planting should be watered abundantly, wait until the moisture is absorbed and sprinkle with soil again.
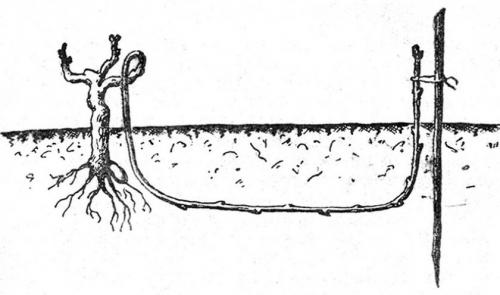

Before rooting, the layer of soil at its base must be regularly moistened. Further, before the final entry into growth, the plant needs to be pinned, leaving only the growth stems. When the cuttings take root, they are cut off from the main bush.
Whole vine
The whole bush method is suitable for young plants up to 5 years of age.
- The shrub is dug in at a distance of 0.5 m from the stem and deepened by at least 0.8 m.
- The grapes must be extracted with the rhizome.
- It is advisable to clean up the root system from old and damaged parts.
- Before being placed in a new place, the rhizome is treated with a clay mash.
- Next, you need to prune, as a result of which no more than two stems should remain. The tops must be removed.
- The planting material is placed in a hole at a slight angle, straightening the rhizome. The shoots must remain above the soil level.
- After planting, the shrub must be watered.


Important! When pruning vines, the cuts must be processed with a garden varnish.



















