Mycorrhiza fungus and plant root: description of symbiosis
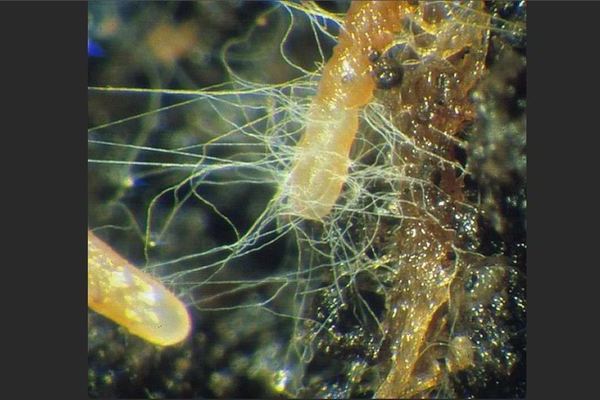

Mycorrhiza fungus
What is mycorrhiza? This is the interaction of a tree and a fungus, the so-called symbiosis in biology. Over the years, the symbiosis between the tree and the fungus has greatly intensified, therefore it has become mandatory, that is, without each other, they cannot fully exist. The root system of a higher plant, that is, a tree, saturates the mushroom with various amino acids, hormones, and also simple carbohydrates. Mushrooms, in turn, release a certain amount of phosphorus, water and trace elements. The root system of both representatives is much smaller than the mycorrhiza itself, thanks to which they are in contact. Hence, symbiosis allows both to develop and feel much better than without it.
Mycorrhiza becomes very important when there is insufficient nutrient soil that cannot saturate the plants. Such interaction can occur with higher and lower mushrooms, since almost all mushrooms (except honey agarics, champignons, umbrellas and dung beetles) can secrete a special protein element that strongly affects the soil, more precisely, its fertility.
What is the benefit
Mushrooms, with the help of the finest interweaving of mycelium filaments, are able to very well absorb nutrients and water from the soil. Thanks to the presence of antibiotic enzymes, they can defend against harmful organisms and they develop mechanisms that help them survive even in toxic soil.
Trees and other plants are the purest water energy converters - with the help of sunlight, they convert carbon dioxide into sugars and other "building materials" that mushrooms also need for their life.
Mycorrhiza of the fungus and plant root: how is the formation of mycorrhiza

Mycorrhiza fungus
Mycorrhiza is a natural process in nature, but experienced gardeners stimulate the process of mycorrhiza formation on their own, as it improves the soil and makes it more fertile.
The interaction begins immediately when the spores of the fungus enter the soil next to the tree. You can wait for this, or you can make the introduction of the dispute yourself. Just before that, it is necessary to distinguish several types of mycorrhiza.
1. The first is called ectotrophic, such mycorrhiza is the root system of a tree, which is entwined with the mycelium of the fungus. Most often the tree is birch, spruce, linden, larch, hazelnuts, cranberries, lingonberries, blueberries, rhododendron, beech.
2. The second type is called endotrophic, in this type the mycelium of the fungus begins to penetrate into the root system of the plant. This type is found quite often, since there are a lot of plant options: grapes, apricots, peanuts, artichoke, banana, bamboo, eggplant, begonia, cherry, peas, pear, apple, blackberry, raspberry, strawberry, clover, strawberry, lily, onion , pepper, tomato, pumpkin, plum, currant, gooseberry. About 85 percent of all plants can participate in this type.
3. The third type is called ectoendotrophic, it includes a mixture of the previous two types.
Two types of mycorrhiza
There are two types of mycorrhiza:
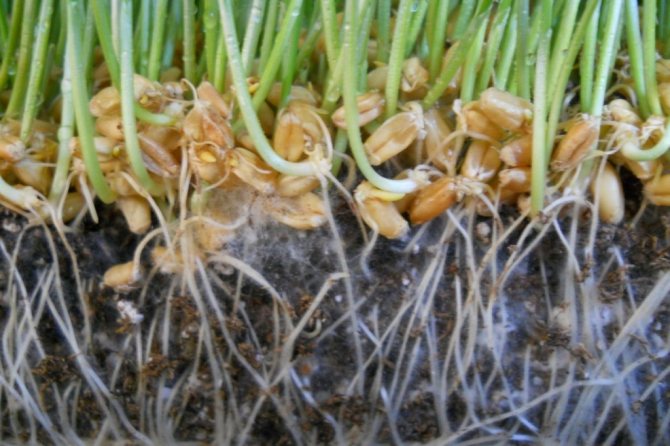
- Ectotrophic (lat ektos - outside) mycorrhiza, for example Abies, Carpinus, Fagus, Larix, covers the tips of the root hairs like a shell, forming a loose, reticular weave between the cells of the root cortex, and with the help of hyphae creates an optimal connection with the soil, which ensures better water absorption and nutrients (especially phosphorus, manganese, zinc, copper).


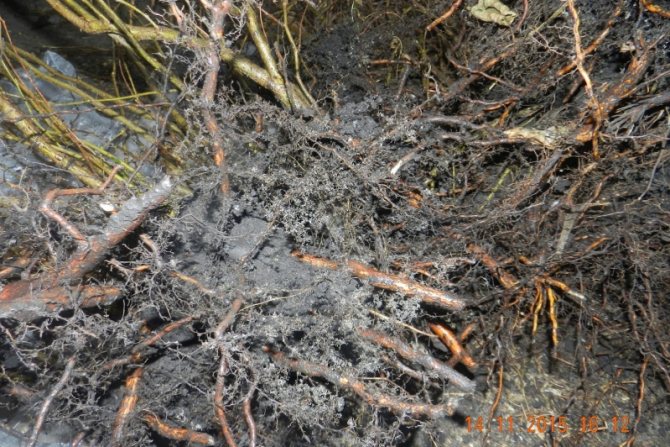
Mushrooms on root tissues
- Endotrophic (lat.endon - inside) mycorrhiza - Celtis., Fraxinus, Сleditsia - penetrates with hyphae into the cells of the root cortex and branches there. The absorption of water and nutrients is carried out mainly by the root hairs.


Mushrooms inside the root tissue
The types of mycorrhiza depend on the type of tree. There are trees with the necessary (obligate) mycorrhiza and there are with the optional (optional). On some tree species, both types can exist, which can form a range of mycorrhizal forms (for example, maple (Acer), chestnut (Castanea), hazel (Corylus), walnut (Juglans), pine (Pinus) and linden (Tilla)).
It is important
Ectotrophic mycorrhiza are viable only with a sufficient supply of oxygen. Soil compaction and stagnant waterlogging destroy them. Trees should be planted with or without a lump, taking into account the dependence of the roots on mycorrhiza. With an increased quality of seedlings, it is important that when planting clods on them, they provide an opportunity for growth.
Mycorrhiza root: enrichment
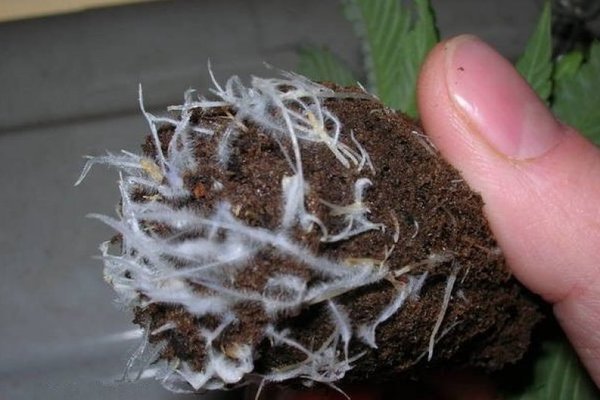


Root mycorrhiza
To enrich a plant with mycorrhiza, 4 methods of such enrichment should be studied. This process can be carried out regardless of the age, culture and development of the plant.
Note: Mycorrhiza is not formed when interacting with the Cruciferous, Amaranth family: cabbage, mustard, radish.
Some facts about symbionts
Some interesting facts are known to the science of symbionts. So,
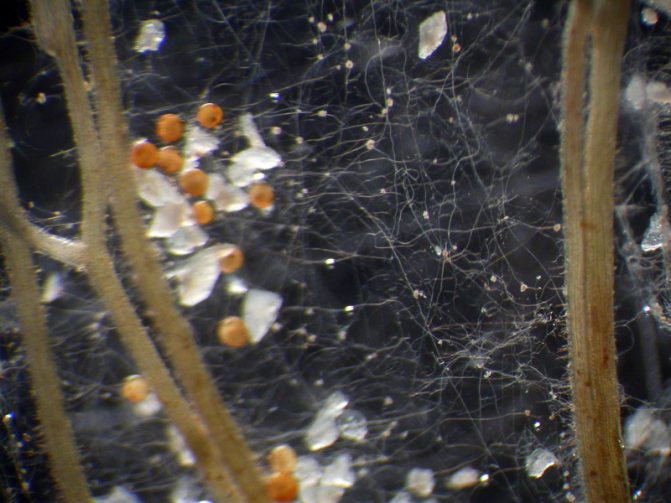
- in 1 cm³ of mycorrhiza, you can count mushroom filaments with a total length of up to 40 m.
- thanks to mycorrhizal fungi, a special substance accumulates in the soil layers - glomalin, which is impossible for the existence of the plant world;
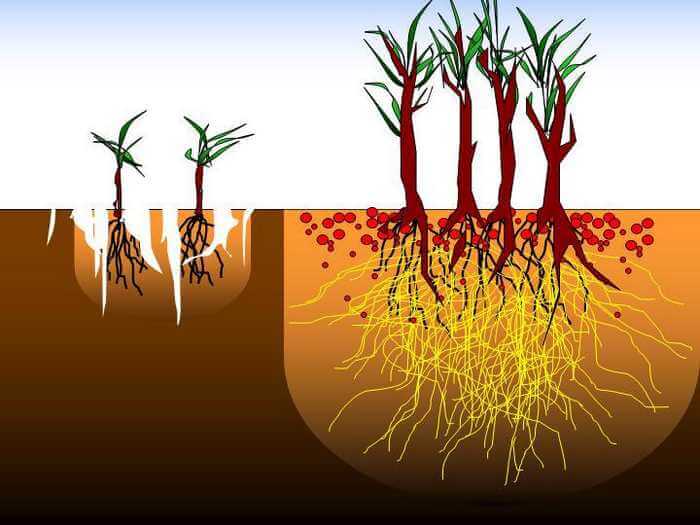
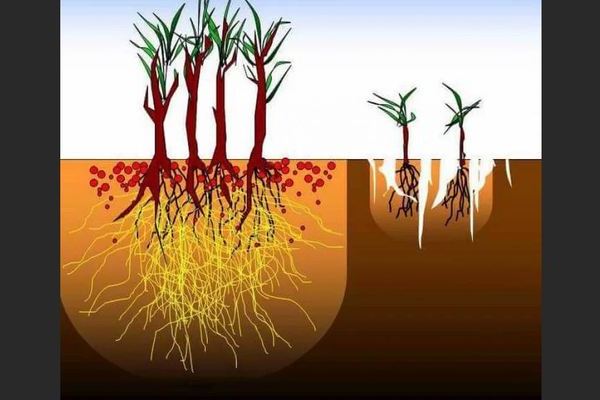
- about 90% of all plant organisms have mycorrhiza on the roots, which significantly increases the intensity of their growth and ensures full development;
- symbionts are able to save moisture up to 50%.
- some varieties of symbiotic fungi are capable of suppressing up to 60 types of pathogenic microorganisms that cause plant diseases, incl. fusarium wilting, rot, phytophthora, scab, etc.
- A large number of mycorrhizal fungi can coexist not with one tree species, but with many. For example, the boletus is capable of forming mycorrhiza with both aspen and birch, and the porcini mushroom - with representatives of almost 50 tree species.
Mycorrhiza: application, seed treatment methods
To start the life of a plant with a lot of strength and capabilities, it is necessary to process its seeds when they are preparing for planting. Processing takes place using mycorrhiza. Before the treatment itself, the gardener must think about whether the plant needs this treatment or development can take place without treatment. There are two processing methods.
1. The first way.
It will need paper or material and a nutritious talker. Nutritious talker consists of 120 milliliters of water, 2 grams of clay (white), 2 grams of mycorrhiza (powder). All components are mixed and material or paper is put into this mixture so that it is thoroughly saturated with it. Plant seeds are wrapped in this cloth or paper, this treatment will help spread the spores over a fairly large distance, about 1000 square meters.
2. The second way.
For the second method, you will need a talker and seeds. Seeds are poured into the pre-prepared liquid, left for 5 minutes and immediately start planting. But before pouring the seeds into the chatterbox, they must be processed using hydrogen peroxide 2% or vodka, after rinsing with clean water.
Note: If you treated the seeds using fungicides, although they were protected from diseases, then you do not need to treat them with mycorrhiza with mycorrhiza. When interacting with fungicides, it dies.
The benefits of agriculture grown with mycorrhiza:
– plants contain their own vitamins and minerals,
– higher nutritional value of products,
– growing food the way nature does,
- longer shelf life, less waste,
- healthier plants - healthier people,
- anyone can participate, having received the necessary education,
- we know for sure that what goes into the products goes into us.
Seedling processing
Using mycorrhiza as seedlings for various trees and plants is a very correct decision, since it is simply a source of nutrients that will saturate the plant or tree with strength. The root system that was cultivated using mycorrhiza developed much better than the rest of the plants. She became covered with fibers, which provided her with many trace elements.
The mycorrhizal chatterbox can be used not only for seeds, but also for a seedling, only with such a treatment the amount of water should increase. After the seedling has been processed, its root system can be planted in soil.
Mycorrhiza is bought in specialized stores, or ordered on the Internet. Each sachet contains either 20, 40, or 60 grams of mycorrhiza powder, there are also large versions, in which there are 300 grams. This amount will be enough for a long time, since very little is used in the recipe, but if you have an average site, and not a whole company, 40 grams will be enough for you.
Distinctive features of mushrooms
What are these features? It's all about the similarity of representatives with both plants and animals. For a long time, this puzzled scientists. After all, creatures turn out to be unique and incomprehensible, since they combine the characteristics of completely opposite organisms.
So, the common features that unite mushrooms with plants include:
- the ability to synthesize phytohormones and vitamins inside the body;
- unlimited apical growth throughout life;
- attached lifestyle (lack of ability to move);
- the presence of a strong cell wall;
- food by absorption of substances.
However, there are signs that are related to the organisms in question with animals:
- a heterotrophic way of nutrition (that is, the consumption of ready-made organic compounds, the impossibility of their independent synthesis within the body);
- the presence in the composition of the cell wall of a complex carbohydrate chitin, of which the integuments of crustaceans, insects and other animals are composed.
The combination of such traits allows us to consider mushrooms as unique creatures worthy of uniting into a separate kingdom of living nature.
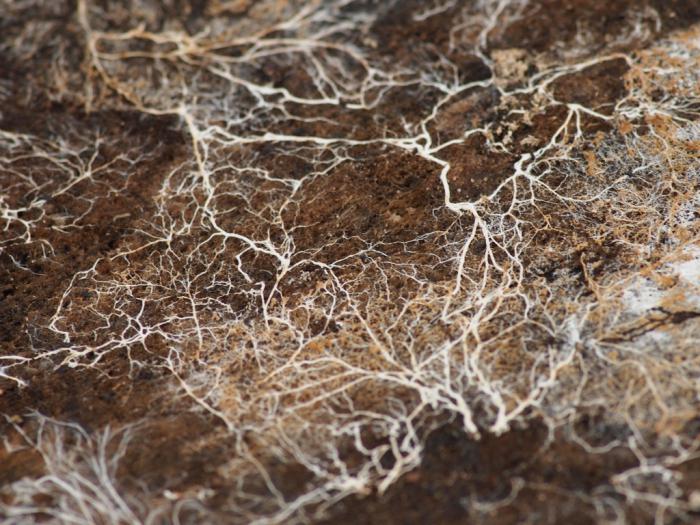


Mycorrhiza fungus: how to apply to the soil
To introduce mycorrhiza into the soil and to an adult plant, there is no need to be afraid that symbiosis will not form. This process does not depend on the age of the tree, therefore, it is suitable for the oldest trees, which, after the introduction of mycorrhiza, will thank you for such a decision. There is a small drawback to such an introduction. Young plants react very quickly to mycorrhiza, at the moment when adult plants react rather weakly to it, since the root system is deeper than that of young individuals.
The recipe for nutritious talkers remains the same, but the method of application changes. It should be applied in rainy weather, or after thorough watering. It is introduced into the soil, in small pits, the depth of which should be about 15 centimeters. The pits should be around the plant, close to the trunk. A young plant will need three pits, and an old one will need about seven pits. A chatterbox should be poured into these holes and then sprinkled with a small amount of earth. Such an introduction is made only once, while the plant lives. A shrub or tree that is already developing must be processed only in the autumn, this will allow the mushrooms to stretch out in the soil during the winter. After processing, when spring comes, the gardener will certainly notice all the changes. When processing in spring, the changes will be delayed for a longer period.
Note: The Nutrient Mouthwash should be cooked in a place where there is no sunlight, as you cannot open mycorrhiza in the sun. Also, the room should be cool. This is only done to protect the mycorrhiza.It consists of spores, and they, reacting with the sun's rays, are damaged and may die.
Noticeable effect of mycorrhiza action
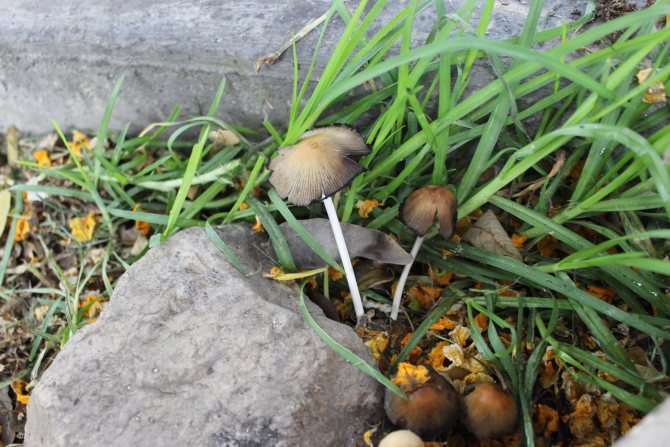
The most popular and most noticeable result of mycorrhiza is Forest mushrooms... These are the fruiting bodies of ectomycorrhizal fungi. Even a beginner in mushroom picking, after the first mushroom picking, will notice that specific mushrooms grow only in the immediate vicinity of specific trees.
Chanterelles grow under deciduous and coniferous trees, mushrooms under pines, spruces and firs. Porcini mushrooms can be found in not too dense forests, mainly under oaks, beeches, as well as pines and spruces. It is better to look for flywheels under spruce and pine trees, as well as in deciduous forests, under oak and beech trees. In birch groves and under spruce trees grow stumps, and boletus grows under birches, hornbeams and oaks.
Fertilizers containing mycorrhiza
After getting acquainted with mycorrhiza, many enthusiastic gardeners begin to think. Why didn't you watch at your dacha? Or just didn't notice? Various drugs for diseases and pests that you used on your site could not provide an opportunity for such a symbiosis.


And construction work does not contribute to this:
- One of the new products. The last squeak. Fertilizer sticks for orchids. With mycorrhiza. And also from pests: Place 1-2 sticks near the wall of the vase - and you don't have to worry about feeding;
- Deepen by 1-2 cm;
- And be sure to sprinkle with water. 3-4 months can not be fed.


- Mixes easily with water in required quantities;
- Flowers take on a more luxurious look;
Mycorrhizal preparations - vaccines
Mycorrhizal vaccines contain live fungal hyphae or fungal spores. For various plants, specific, adapted mixtures of mycorrhiza are intended (they also include edible varieties, however, they rarely form fruit bodies on personal plots).
You can buy mycorrhizal preparations for indoor plants (the most popular is mycorrhiza for orchids) and balcony plants. A much larger selection of vaccines for garden plants - for flower beds, conifers and deciduous plants, vegetables, heather, rhododendrons, hydrangeas, roses, and even lawn.
The roots of old trees go very deep, and by the tree itself there are only skeletal roots that are not suitable for mycorrhization. It should be remembered that in plants, both young and adult, the youngest roots are relatively shallow underground, within 10-40 cm. In the case of planting trees dug directly from the ground, with an open root system, the vaccine should be added to several of the youngest, living roots before planting.
Differences between mycorrhiza formers and saprotrophs
Both mycorrhiza formers and saprotrophs use dead organic matter for their nutrition, and therefore, within the framework of mycology, there is a problem of distinguishing between these groups.
The mycorrhiza-forming agent receives carbohydrates from the plant, which is used by the fungus as an energy source, and the plant receives from the fungus the elements of mineral nutrition, which the mycelium transforms into the form assimilable by the plant. At the same time, mycorrhiza formers are similar to saprotrophs in the absence of a plant with which symbiosis is formed or in the stage of free-living mycelium.
L. A. Garibova in the book "The Mysterious World of Fungi" distinguishes the following differences, which indicate a difference in the biochemistry of these ecological groups of fungi:
- only mycorrhiza formers form indole compounds (some saprotrophs also form them, but in a significantly smaller amount);
- mycorrhiza formers form growth substances of the auxin type;
- mycorrhiza formers have almost no antibiotic properties;
- mycorrhiza formers do not participate in the destruction of cellulose and are not able to develop on it without carbon sources available to them;
- most mycorrhiza formers do not have hydrolytic enzymes, in particular, they do not synthesize laccase, which is needed for the oxidation of lignin;
- mycorrhiza formers have a more complete amino acid composition.
Types of fungus root
Depending on the options for symbiosis conditions, there are types of mycorrhiza:
- Ectotrophic or external. It is characterized by braiding of the surface bark of plants.
- Endotrophic (internal). It is the penetration of the mycelium of the fungus into the inner tissues of the roots.
- Phycomycete type. It is characterized by complete penetration of rhizomes by fungi.
- With the euectotrophic type, symbiosis can cause the death of the hairs of the rhizomes.
- The ectoendotrophic type indicates the introduction of the fungus into the cells of the cortex.
- The ericoid type implies the subsequent digestion of the tangles formed by the fungus by the plant.
Each of the types is characteristic of certain types of plants. Trees and shrubs are predominantly susceptible to one type of mycorrhiza. But they can also be carriers of several types of mushrooms at the same time.
Since all mushrooms adapt to life in different ways, they all have their own type of existence. Their habitat is due to the need to eat. That is why you will never see a single mushroom on bare soil without vegetation.
Not all mycorrhizal fungi grow on the roots of trees, although they can often be found under the trees.
Mycorrhiza forms many of the familiar mushrooms. This is everyone's favorite and tasty - porcini mushrooms, chanterelles, aspen mushrooms, boletus mushrooms, honey agarics and others. Poisonous fungi are also mycorrhizal and nourish plants.
Almost all conifers are mycorrhizal plants. Root mycorrhiza is also inherent in birch, which at the same time enters into an alliance with boletus. A similar coexistence can be observed between pine and butterdish, aspen and aspen, beech and chanterelles, hornbeam and porcini mushroom. Amanita prefers birch and spruce. Poddubovik can grow both under trees and, like oyster mushrooms, on their trunks. Garden entholoma can be found not only under fruit trees, such as plum, apricot, but also under the forest bushes of dog-rose and hawthorn. Birches and conifers are preferred for most fungi. Therefore, near these trees, you can find various inhabitants of the named family.
Mycorrhizal fungi cannot exist without the roots of trees, shrubs or herbaceous plants. When the mycelium acts on the roots of higher plants, the transformation of the rhizome occurs, but such deformations are completely harmless to the plant. This symbiosis has existed for more than one thousand years, as evidenced by the fossilized rocks of ancient plants. Based on these findings, it becomes obvious that this is another of nature's perfect ideas. And everything is calculated in such a way that the coexistence of the fungus and plants is only beneficial to both representatives.
Indications for use
Even the relatively scant information on mycorrhiza and its properties did the trick. They ask her. Brought from abroad. It is not always easy to purchase, even in specialized flower shops.
The main motive is the desire of the plant owner to see him even better. I want to have large and beautiful fruits. Flowering is long-lasting and lush.
And for this, caring for him needs to be improved. And mycorrhiza not only allows it, but also provides it. If only the useful surface for the consumption of necessary substances increases hundreds of times:
- It is more advisable to vaccinate plants with a vaccine in the fall. And already in the spring the first positive results will be noticeable;
- The fungus does not hibernate. Its activity is not suspended. Manages to form mycorrhiza on plant roots. Plants have enough time to interact;
- It can also be applied in the spring. If you have time and don't want to wait until autumn. Application results - only from the spring of next year.
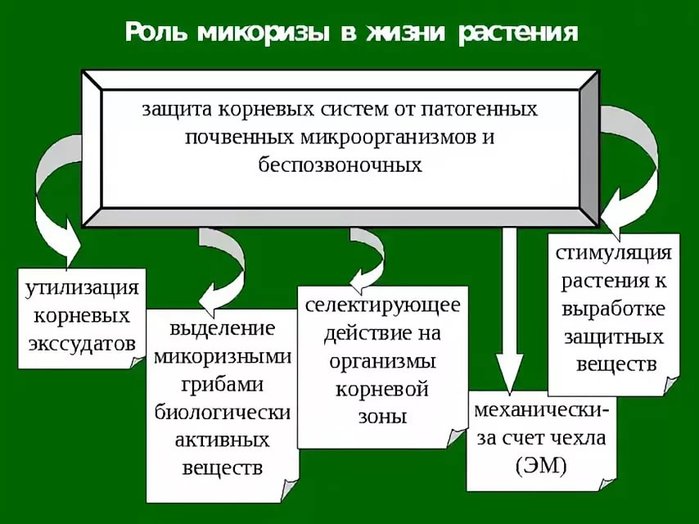
The role of mycorrhizal organisms in the biocenosis
The functions of mycorrhizal organisms in the biocenosis, as indicated in the book by L. G. Garibova "The Mysterious World of Fungi", are as follows:
- Mycorrhizal formers convert nitrogen-containing compounds of the upper soil layer into a form that can be assimilated by plants.
- Mycorrhizal fungi contribute to the supply of phosphorus, calcium and potassium to plants.
- The mycorrhizal fungus increases the area of nutrition and water supply to plants. In arid conditions of deserts and semi-deserts, woody plants receive soil nutrition due to mycorrhiza formers.
- Protection of plants from pathogenic microorganisms.
Varieties
The following fungi form mycorrhiza with roots:
- Myccorisa ectotrophyca - spreads only in the upper layers;
- Myccorisa endotrophyca - mycelium develops in the thickness of the root, sometimes piercing the body almost through;
- Еctotrophyca, endotrophyca myccorisa (mixed type) - characterized by the peculiarity of each of the upper species, spreading its mycelium both on the surface and in the root;
- Peritrophyca myccorisa is a simplified form of symbiosis and at the same time a new stage in development. Represents placement close to the root without the penetration of processes.